The new generation in ECG interpretation
|
|
|
- Walter Hubbard
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods for interpreting the resting ECG. While in the past ECG analysis programs were limited to 12 simultaneous leads, the DXL Algorithm analyzes up to 16 leads of simultaneously acquired ECG waveforms to provide an interpretation of rhythm and morphology for a wide variety of patient populations. The algorithm reflects new recommendations, such as the 2007 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations, Part II 1 and the 2009 AHA/ ACCF/HRS Recommendations, Part VI 2 for the Standardization and Interpretation of the ECG. Expanded diagnostic capabilities The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm goes beyond traditional 12-lead interpretation of the resting ECG. It also provides for incremental diagnostic capabilities not associated with analysis programs of the past: 16-lead integrated analysis to take advantage of optional right chest and back electrodes to provide extended interpretations for adult chest pain ST Maps to provide a visual representation of ST deviations in frontal and horizontal planes, responding to the 2009 Recommendations Updated criteria based upon the latest clinical research. Examples include the addition of acute global ischemia and incorporation of updated gender-specific STEMI criteria, as documented in the 2009 Recommendations STEMI-CA (Culprit Artery) criteria to suggest the probable site of the occlusion, consistent with the 2009 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations Critical Values to highlight conditions requiring immediate clinical attention Integrated 15-lead pediatric analysis LeadCheck program to identify 19 possible lead reversal and placement errors during ECG acquisition Updated statements to reflect new 2007 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations History In 2002, Philips acquired the former Hewlett- Packard Medical Products Group which pioneered the development of computerized ECG data analysis. Design of specialized algorithms began in the late 1960 s, and accelerated in the 1970 s as Philips enhanced the single lead programs that were the standard at the time. In 1978, Philips introduced its multilead, 12-lead analysis program, the first among the major electrocardiography companies. Philips has been a continuing leader in ECG analysis, with significant innovations and firsts in serial comparison, gender-specific analysis, pediatric analysis, pacemaker detection, sophisticated QT analysis, support of the XML data format, and other areas. In the past, a specialized ECG language ECG Criteria Language (ECL) was developed to encourage broader participation and speed development of sophisticated algorithms.
2 V1 V3R V4R V5R RA RL LL V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 LA Today, this experience and expertise is reflected in the Philips DXL ECG Algorithm with its industry leading integration of extended leads and expanded analysis capabilities. Analysis process The DXL Algorithm has multiple steps to produce precise and consistent ECG measurements that are used to generate interpretive statements. Rhythms with some paced complexes undergo morphologic analysis of the non-paced beats Individual lead and global measurements of representative beats are made. Innovative methods are used for difficult measurements, such as onset of P and end of T Specialized techniques, such as synthesized vectorcardiograms, are used for transverse plane measurements (specifically for pediatric ECGs) Acquisition and quality assessment Continuous signal quality feedback is provided to the user via color-coded waveforms and messages 12 to 16 user-selected leads are captured for 10 seconds and digitized at 8 KHz per lead Unique LeadCheck software identifies 19 possible swapped leads for correction Waveform recognition and measurement Pacemaker pulses are accurately identified Each complex in each lead is measured individually. Excessive variation in a lead can be used to determine if that lead is unreliable for global measurements Complexes are classified into families based upon rate and morphology parameters. Paced beats are classified independently Representative beats are created by averaging aligned beats from the dominant family Application of criteria The criteria can use any combination of lead and global measurements, enhancing the flexibility and power of interpretive capabilities Established traditional and modern interpretation criteria, including age- and gender-specific criteria and criteria based upon latest scientific findings and using current nomenclature, are applied If additional leads beyond the standard 12 are available, incremental criteria are applied to enhance specificity and sensitivity New measurements and criteria are applied for STEMI-CA (to suggest Culprit Artery occlusion sites), ST Maps (to show the spatial orientation of ST deviations), and Critical Values (to highlight ECGs requiring urgent clinical attention) Patient ECG and Patient Data Quality Assessment Feedback to Operator Smart Lead Quality LeadCheck I II. V9 Pace Pulse Detection Average Beat Formation Measurements ST Maps 16-Lead Criteria Morphology Rhythm Culprit Artery Critical Values Interpretive Report Overreader Overread Report From acquisition to report generation, the Philips DXL 16-Lead Algorithm uses multiple steps to ensure a high quality interpretation. 2
3 Waveform Storage Previous generation technologies down-sampled ECG waveforms for transmission and long-term data storage purposes. The DXL Algorithm uses lossless data compression, ensuring that the original, raw data is available for further review and analysis. This increases the value of collected data for the development of further enhancements and incorporation of new scientific findings. It also supports the needs of pharmaceutical clinical research. Use of additional right chest and posterior leads While the limb leads and chest leads comprise the standard 12-lead ECG, it has long been recognized that additional electrodes can provide information that is poorly or not at all seen on the traditional 12-lead ECG. In addition to the standard limb and chest leads, the DXL Algorithm can incorporate any four of six additional leads from the following: right chest leads: V3R, V4R, V5R posterior leads: V7, V8, V9 Some users may choose to add just one or two leads to the standard 12, while others may choose to record the maximum of 16 leads to provide the additional waveform information as well to gain the additional sensitivity and specificity that the DXL Algorithm can provide with the additional lead information. Among the areas that can benefit: Right heart analysis (V3R, V4R, V5R) Right ventricular infarcts may accompany inferior myocardial infarction and have strong prognostic implications. The signs are subtle in the right-sided leads and are generally invisible in the standard leads. in the posterior leads can aid in the interpretation, especially in the early stages of acute posterior myocardial infarction. The DXL Algorithm can take advantage of information in one or more of leads V7, V8, and V9 to provide greater specificity and sensitivity in detecting posterior infarcts. Pediatrics Many pediatric institutions add three leads to the 12 lead set. The most common sites are V3R, V4R, and V7. The selected incremental leads are integrated into the DXL Algorithm s pediatric analysis. ST Maps The 2009 AHA/ACCF/HRS document recommends the display of the spatial orientation of ST-segment deviations in both frontal and transverse planes. Philips cardiographs can display patented ST Maps in both planes to provide for rapid visual assessment of the degree of ST abnormalities. The maps are plotted in Cabrera sequence to reflect the anatomical orientation. This presentation, previously available only on Philips IntelliVue patient monitors, provides distinct patterns for different anatomic sites of infarcts, global ischemia, pericarditis, and other conditions that are readily seen using such maps. The DXL Algorithm is not limited to a single right lead and can take advantage of information that may be present in V3R, V4R, and/or V5R. Additional criteria use this information, plus criteria based upon the traditional 12 leads, to provide improved specificity and sensitivity. For example, consistent with the 2009 Recommendations, the algorithm supports the recording of both V3R and V4R for patients presenting with evidence of acute inferior wall ischemia or infarction. And the DXL Algorithm provides incremental analysis based upon those additional leads. Posterior wall analysis (V7, V8, V9) Posterior myocardial infarction has traditionally been diagnosed from reciprocal changes seen in leads V1 and V2. ST-segment depression may be very subtle in these leads and go unnoticed or misdiagnosed, especially if gender differences are ignored. ST-segment elevation recorded ST Maps provide for rapid visual assessment of ST abnormalities. 3
4 STEMI detection ST-segment elevations in ECG tracings provide highly effective risk stratification in early acute coronary syndromes. For patients with ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI), the most critical factor in improving survival rates is the earliest possible administration of reperfusion therapy and reduction of door-to-balloon and discovery-totreatment times. The DXL Algorithm provides advanced capabilities for fast, accurate detection of STEMI based on the newest recommendations. Unique to Philips, the DXL Algorithm can provide information in 16 ECG leads selected at the time of acquisition, allowing right heart (V3R, V4R, and/or V5R) and posterior (V7, V8, and/or V9) information to be included in the data presentation and subsequent analysis. Classical STEMI applies only to ST elevation in a group of leads. With obstructions in the left main coronary artery or multiple obstructions in several coronary arteries, an ECG pattern of widespread ST depression is seen along with ST elevation seen in avr and/or VI. This pattern, recognized by the DXL Algorithm, is called global ischemia and has prognostic significance. Gender-specific ECG interpretation As cardiac medicine continues to advance, there has been continued learning regarding the physiological differences between men and women. Gender-specific criteria are not new to Philips. They have been incorporated into the multi-lead algorithms since 1987 and have been enhanced continually based upon the latest research and guidelines. have prognostic significance as well as help to pinpoint the offending lesion when multiple obstructions are present and can thus be used to optimize the treatment approach in the cath lab. Specific anatomic sites can include the following coronary arteries: left anterior descending artery (LAD) right coronary artery (RCA) left circumflex artery (LCx) left main or multi-vessel disease (LM/MVD) Critical Values Critical Values are highly visible independent statements on the ECG report that highlight conditions requiring immediate clinical attention. Specific statements are made for: acute MI global ischemia complete heart block extreme tachycardia Use of the Critical Values feature is configurable, and can be used to support quality initiatives in multiple areas of the medical enterprise. For example, in the emergency department, Critical Values can support a hospital s focus on Door-to-Balloon and quality initiatives. For example, the DXL Algorithm applies gender, lead and age limits for improved detection of acute MI. Based upon the 2009 recommendations, STEMI criteria are subject to reduced ST thresholds in women. The algorithm also uses gender-specific axis deviation and MI criteria, Cornell gender-specific criteria for detection of left ventricular hypertrophies, and Rochester and Rautaharju criteria for the detection of prolonged QT. Application of these gender-specific criteria results in an ECG interpretation that helps clinicians more accurately assess the cardiac state of patients of either sex. STEMI-CA for identification of culprit artery If STEMI criteria are met, the DXL Algorithm s STEMI-CA criteria can identify the likely culprit artery or probable anatomical site causing the functional ischemia. This may The DXL Algorithm applies gender, age, and lead-specific criteria to provide for more accurate assessment of the cardiac status across diverse patient populations. 4
5 Integrated pediatric analysis Philips introduced the industry s first pediatric ECG analysis capabilities in 1982 and has built upon that experience to maintain an advanced, fully integrated pediatric interpretation. With the DXL Algorithm, the interpretation now can use the availability of additional leads typically 15 in the pediatric application. The pediatric criteria use 12 distinct age groups grouped progressively from hours through days, weeks, months, and years to ensure that the most agerelevant interpretation criteria are applied for analyzing the available waveform. The age is used throughout the criteria to define normal limits in heart rate, axis deviation, time intervals, voltage values for interpretation accuracy in tachycardia, bradycardia, prolongation or shortening of PR and QT intervals, hypertrophy, early repolarization, myocardial ischemia and infarct, and other cardiac conditions. Mild right ventricular hypertrophy and incomplete right bundle branch block differentiation is improved with a unique combination of transverse measurements from a derived vectorcardiogram with more traditional measurements from the standard 12 leads and the extra pediatric leads. Left ventricular hypertrophy criteria The widely accepted Cornell criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy are included with the traditional criteria. This increases the sensitivity and specificity of detection. Advanced pacemaker detection Between 2 and 5% of routine diagnostic ECGs are acquired from patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers, devices which have become increasingly capable, efficient, and complex. To keep pace with these pacemaker developments, the DXL Algorithm is designed to handle a variety of atrial, ventricular, and A-V sequential pacing modes. A sophisticated patented noise-adaptive pulse detector is run on all acquired leads with confirmation from multiple leads differentiating true pulses from noise. If the pacemaker is known to be present at the time of acquisition, the algorithm pulse detector sensitivity can be increased to improve detection of extremely small pulses. In addition, analysis of pacemaker pulse locations with respect to P-waves and QRS complexes permits classification of a variety of pacemaker rhythms and identification of nonpaced QRS complexes for further morphologic analysis in ECGs with paced and non-paced beats. Although the detector is quite sensitive, even to low amplitude pacer spikes typical of modern pacemakers, it can still differentiate these spikes from the very narrow and sharp QRS complexes typical of neonatal ECGs, a problem that has plagued previous generation algorithms. QT analysis and clinical research Because of the relatively recent appreciation of the connection between many medications and the development of Torsade de Pointes, there has been renewed interest in the accurate measurement of the QT interval and the various QT corrections. The DXL Algorithm uses an innovative measurement technique to ensure an accurate and reproducible end of T measurement, even in the presence of large U waves and biphasic or notched T waves. Because high resolution ECG signals are maintained through analysis, transmission, and storage, the integrity of the end of T remains available for analysis and subsequent high resolution review typical in clinical research. The same QT algorithm has been further applied for use within Philips IntelliVue monitoring systems and ambulatory monitoring products. Nomenclature The DXL Algorithm conforms to the latest AHA/ACCF/ HRS statement recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the ECG 1. 1 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram, Part II: Electrocardiography Diagnostic Statement List. J Am Coll Cardiology, 2007; 49: AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram, Part VI: Acute Ischemia/Infarction. Circulation, 2009; 119:e262-e270. Note: A computer-interpreted ECG report is not intended to be a substitute for interpretation by a qualified physician. Physician overreading and confirmation of computer-based ECGs is required. This brochure describes features of the Philips DXL ECG Algorithm that may not be available on all Philips products incorporating ECG analysis. Please refer to the documentation supplied with your Philips product for specific versions and available features. 5
6 Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics How to reach us fax: Asia Europe, Middle East, Africa Latin America North America (toll free, US only) 2009 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. All rights are reserved. Philips Healthcare reserves the right to make changes in specifications and/or to discontinue any product at any time without notice or obligation and will not be liable for any consequences resulting from the use of this publication. Printed in The Netherlands. MAR 2009
Always in touch. Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph
 Always in touch Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph Intuitive and efficient You need to fit a lot into every day. That s why we ve fit a lot into the Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph. It s an affordable
Always in touch Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph Intuitive and efficient You need to fit a lot into every day. That s why we ve fit a lot into the Philips PageWriter TC50 cardiograph. It s an affordable
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks
 ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
The choice for quality ECG arrhythmia monitoring
 GE Healthcare EK-Pro The choice for quality ECG arrhythmia monitoring David A. Sitzman, MSEE. Mikko Kaski, MSAM. Ian Rowlandson, MSBE. Tarja Sivonen, RN. Olli Väisänen, MD, PhD. Clinical care environments
GE Healthcare EK-Pro The choice for quality ECG arrhythmia monitoring David A. Sitzman, MSEE. Mikko Kaski, MSAM. Ian Rowlandson, MSBE. Tarja Sivonen, RN. Olli Väisänen, MD, PhD. Clinical care environments
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed
 Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2
 12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2 McHenry Western Lake County EMS Localization: Left Coronary Artery Right Coronary Artery Right Ventricle Septal Wall Anterior Descending Artery Left Main
12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2 McHenry Western Lake County EMS Localization: Left Coronary Artery Right Coronary Artery Right Ventricle Septal Wall Anterior Descending Artery Left Main
Podcast with Dr. Kossick
 Podcast with Dr. Kossick Interviewed by Western Carolina University Graduate Anesthesia Student Kristin Andrejco From the Head of the Bed [email protected] December 5, 2014 (33 min) EKG Lead
Podcast with Dr. Kossick Interviewed by Western Carolina University Graduate Anesthesia Student Kristin Andrejco From the Head of the Bed [email protected] December 5, 2014 (33 min) EKG Lead
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
You ll love the Vue. Philips IntelliVue Information Center ix
 You ll love the Vue Philips IntelliVue Information Center ix IT Director It has to it into our IT infrastructure and integrate easily with our EMR and HIS. Clinical Engineering Make it easy to support.
You ll love the Vue Philips IntelliVue Information Center ix IT Director It has to it into our IT infrastructure and integrate easily with our EMR and HIS. Clinical Engineering Make it easy to support.
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
REFERRAL HOSPITAL. The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO
 REFERRAL HOSPITAL The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO Time to Treatment is critical for STEMI patients For patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), percutaneous coronary
REFERRAL HOSPITAL The Importance of Door In Door Out Time DIDO Time to Treatment is critical for STEMI patients For patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), percutaneous coronary
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal
 How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
Diagnostic ECG. ST80i stress-testing system. Workflow that works for you
 Diagnostic ECG ST80i stress-testing system Workflow that works for you The software features ST views including ST map and zoomed ST The next generation of stress testing Fueled by the workflow needs of
Diagnostic ECG ST80i stress-testing system Workflow that works for you The software features ST views including ST map and zoomed ST The next generation of stress testing Fueled by the workflow needs of
Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model
 Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model Daming Wei Graduate School of Information System The University of Aizu, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan A b s
Deriving the 12-lead Electrocardiogram From Four Standard Leads Based on the Frank Torso Model Daming Wei Graduate School of Information System The University of Aizu, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan A b s
GE Healthcare. Rest assured. MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system
 GE Healthcare Rest assured MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system Since 1965, GE has introduced on-going innovation, which has profoundly impacted healthcare delivery, clinical guidelines and ECG standards.
GE Healthcare Rest assured MAC 5500 resting ECG analysis system Since 1965, GE has introduced on-going innovation, which has profoundly impacted healthcare delivery, clinical guidelines and ECG standards.
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
Managing workflow your way
 Managing workflow your way Philips TraceMasterVue family of ECG Management Systems When is an ECG more When it s exactly where you need it, when you need it, increasing your diagnostic confidence. Philips
Managing workflow your way Philips TraceMasterVue family of ECG Management Systems When is an ECG more When it s exactly where you need it, when you need it, increasing your diagnostic confidence. Philips
Expand your view. IntelliVue MX600, MX700, and MX800 bedside patient monitors
 Expand your view IntelliVue MX600, MX700, and MX800 bedside patient monitors Trusted by more, for more Philips IntelliVue patient monitors are already the world s best selling, providing the accurate,
Expand your view IntelliVue MX600, MX700, and MX800 bedside patient monitors Trusted by more, for more Philips IntelliVue patient monitors are already the world s best selling, providing the accurate,
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
The heart walls and coronary circulation
 CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
Marquette 12SL Algorithm. Connected Clinical Excellence
 Marquette 12SL Algorithm Connected Clinical Excellence Clinical decision support for your ECG Since its introduction in 1980 the Marquette TM 12SL ECG analysis program has been consistently refined and
Marquette 12SL Algorithm Connected Clinical Excellence Clinical decision support for your ECG Since its introduction in 1980 the Marquette TM 12SL ECG analysis program has been consistently refined and
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
GE Healthcare. The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System
 GE Healthcare The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System Cardiac technology. Innovation to advance care. Success in today s healthcare environment requires your
GE Healthcare The heart of cardiology is connectivity The MUSE * v8 Cardiology Information System Cardiac technology. Innovation to advance care. Success in today s healthcare environment requires your
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Connected Care. Philips HeartStart connectivity and data management for EMS professionals
 Connected Care Philips HeartStart connectivity and data management for EMS professionals Flexible and reliable, like Connected Care is the Philips approach to open data management solutions that simplify
Connected Care Philips HeartStart connectivity and data management for EMS professionals Flexible and reliable, like Connected Care is the Philips approach to open data management solutions that simplify
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
GE Healthcare. Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system
 GE Healthcare Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system Each year, sudden cardiac death claims the lives of millions of people globally. Among the most compelling challenges facing clinicians today
GE Healthcare Predictive power. MARS ambulatory ECG system Each year, sudden cardiac death claims the lives of millions of people globally. Among the most compelling challenges facing clinicians today
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
ST Segment Monitoring. IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note
 ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
Signal-averaged electrocardiography late potentials
 SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Lead avr: The Neglected Lead
 Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Connect care for early intervention
 IntelliVue Information Center ix Central monitoring station Connect care for early intervention See more. Know more. Do more. Connecting your teams to each other and to the information they need supports
IntelliVue Information Center ix Central monitoring station Connect care for early intervention See more. Know more. Do more. Connecting your teams to each other and to the information they need supports
510(k) Summary May 7, 2012
 510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
510(k) Summary Medicalgorithmics 510(k) Premarket Notification 510(k) Summary May 7, 2012 1. Submitter Name and Address Medicalgorithmics LLC 245 West 107th St., Suite 11A New York, NY 10025, USA Contact
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
A passion for patients. Philips Patient Monitoring Services
 A passion for patients Philips Patient Monitoring Services Our goal is to make sure you re highly satisfied with every part of your Philips service experience from your conversations with our account managers
A passion for patients Philips Patient Monitoring Services Our goal is to make sure you re highly satisfied with every part of your Philips service experience from your conversations with our account managers
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Introduction. Planned surgical procedures
 Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
Guidelines for the perioperative management of patients with implantable pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators, where the use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is anticipated. Introduction
IntelliVue to go. IntelliVue MX40 wearable patient monitor
 IntelliVue to go IntelliVue MX40 wearable patient monitor Freedom of movement Real time, real mobility Get ready to go. You ve never seen anything like the Philips IntelliVue MX40, which combines the benefits
IntelliVue to go IntelliVue MX40 wearable patient monitor Freedom of movement Real time, real mobility Get ready to go. You ve never seen anything like the Philips IntelliVue MX40, which combines the benefits
Davis Medical Electronics
 Accelerate your workflow Holter Monitoring System, Release 2.9 DigiTrak XT Designed to meet your every need Philips Holter Monitoring System is designed to simplify life for you and your patients. It provides
Accelerate your workflow Holter Monitoring System, Release 2.9 DigiTrak XT Designed to meet your every need Philips Holter Monitoring System is designed to simplify life for you and your patients. It provides
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin 1. Definition The electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG) represents the graphic recording of electrical
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin 1. Definition The electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG) represents the graphic recording of electrical
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs
 ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
Networked versatility. IntelliVue MP60 and MP70 patient monitors
 Networked versatility IntelliVue MP60 and MP70 patient monitors Critical performance The IntelliVue family of networked patient monitors gives care teams throughout the hospital more of the information
Networked versatility IntelliVue MP60 and MP70 patient monitors Critical performance The IntelliVue family of networked patient monitors gives care teams throughout the hospital more of the information
ECG Findings. IV Access. 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI. ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia.
 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery
 Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
Management of Pacing Wires After Cardiac Surgery David E. Lizotte, Jr. PA C, MPAS, FAPACVS President, Association of Physician Assistants in Cardiovascular Surgery Conflicts: None Indications 2008 Journal
ECG Measurement and Interpretation
 ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
CardioSoft * Diagnostic System
 GE Healthcare CardioSoft * Diagnostic System Connecting Hearts and Minds Clinically connected. Simply smart. CardioSoft Diagnostic System from GE Healthcare is more than a software program it is a data
GE Healthcare CardioSoft * Diagnostic System Connecting Hearts and Minds Clinically connected. Simply smart. CardioSoft Diagnostic System from GE Healthcare is more than a software program it is a data
6/5/2014. Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
The Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
X Series Extensive Capabilities
 X Series Extensive Capabilities for Patient Transport Transporting Patients throughout the Hospital Requires the Right Equipment Full Featured yet Compact When transporting critically ill patients, you
X Series Extensive Capabilities for Patient Transport Transporting Patients throughout the Hospital Requires the Right Equipment Full Featured yet Compact When transporting critically ill patients, you
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
GE Healthcare. The new MAC * 800
 GE Healthcare The new MAC * 800 Fits your needs wherever you are. Advanced ECG technology can make a real difference in patient care. As long as it s working for you and not the other way around. The new
GE Healthcare The new MAC * 800 Fits your needs wherever you are. Advanced ECG technology can make a real difference in patient care. As long as it s working for you and not the other way around. The new
Policy & Procedures. I.D. Number: 1142
 Policy & Procedures Title: CARDIAC (ECG) MONITORING I.D. Number: 1142 Authorization: [X] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Date Revised: November 2012 Date Effective: October 2004 Scope: SHR - Acute
Policy & Procedures Title: CARDIAC (ECG) MONITORING I.D. Number: 1142 Authorization: [X] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Date Revised: November 2012 Date Effective: October 2004 Scope: SHR - Acute
Improve your image. ClearVue 350 ultrasound system. The print quality of this copy is not an accurate representation of the original.
 Improve your image ClearVue 350 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive The system looks sleek from the outside, but it s what s on the inside that you ll value most. ClearVue
Improve your image ClearVue 350 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive The system looks sleek from the outside, but it s what s on the inside that you ll value most. ClearVue
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99)
 CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005
 ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005 Introduction: The purpose of this document is to outline the equivalent biphasic protocols specific to
ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With the ZOLL Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform AHA/ERC Guidelines 2005 Introduction: The purpose of this document is to outline the equivalent biphasic protocols specific to
EKG Technician Program TST Tuition - $999; Total Hours 50
 EKG Technician Program TST Tuition - $999; Total Hours 50 January 25 January 27 February 1 February 3 February 8 February 10 February 15 February 17 February 22 February 24 February 29 March 2 March 7
EKG Technician Program TST Tuition - $999; Total Hours 50 January 25 January 27 February 1 February 3 February 8 February 10 February 15 February 17 February 22 February 24 February 29 March 2 March 7
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
High-intensity performance. IntelliVue MP90 patient monitor
 High-intensity performance IntelliVue MP90 patient monitor See a higher level The IntelliVue family of networked patient monitors gives care teams throughout the hospital more of the information they need
High-intensity performance IntelliVue MP90 patient monitor See a higher level The IntelliVue family of networked patient monitors gives care teams throughout the hospital more of the information they need
GE Healthcare. MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital
 GE Healthcare MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital smart. MAC 2000 Complex hospital environments demand simple solutions. Equipment that simply works, every time. Technology that
GE Healthcare MAC 2000 ECG Analysis System Streamlined for your hospital smart. MAC 2000 Complex hospital environments demand simple solutions. Equipment that simply works, every time. Technology that
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
 Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Improving ECG Quality
 Improving ECG Quality Application Note Introduction Good ECG signal quality it is something every clinician strives to secure every time they monitor a patient s heart. This application note will look
Improving ECG Quality Application Note Introduction Good ECG signal quality it is something every clinician strives to secure every time they monitor a patient s heart. This application note will look
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
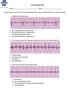 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
EMR Tutorial Acute Coronary Syndrome
 EMR Tutorial Acute Coronary Syndrome How to find the Acute Coronary Syndrome AAA Home Page 1 of 26 Master Tool Bar Icon When the Template button is clicked you will be presented with the preference list.
EMR Tutorial Acute Coronary Syndrome How to find the Acute Coronary Syndrome AAA Home Page 1 of 26 Master Tool Bar Icon When the Template button is clicked you will be presented with the preference list.
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias
 Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Medical Tourism - The Role of Intervals inCardiovascular Cancer
 Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Time Critical Interventions MO-51 / 1 Hour Faculty: Matthew Strehlow, MD, FACEP Monday, 10/26/2015 / 3:30 PM - 4:20 PM The treatment of congestive heart failure (CHF)
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Time Critical Interventions MO-51 / 1 Hour Faculty: Matthew Strehlow, MD, FACEP Monday, 10/26/2015 / 3:30 PM - 4:20 PM The treatment of congestive heart failure (CHF)
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
GE Healthcare. The ECG with more knowledge built in Introducing the MAC * 5500 HD
 GE Healthcare The ECG with more knowledge built in Introducing the MAC * 5500 HD If you can t see the pacemaker, you re not seeing the whole patient During a patient s cardiac event, physicians have moments
GE Healthcare The ECG with more knowledge built in Introducing the MAC * 5500 HD If you can t see the pacemaker, you re not seeing the whole patient During a patient s cardiac event, physicians have moments
EKG Abnormalities. I. Early repolarization abnormality:
 I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
Acute Coronary Syndrome. What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know
 Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls
 Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
