Lecture 16: System-Level I/O
|
|
|
- Joan Gallagher
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSCI-UA Computer Systems Organization Lecture 16: System-Level I/O Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) Some slides adapted (and slightly modified) from: Clark Barrett Jinyang Li Randy Bryant Dave O Hallaron
2 CPU Memory
3 I/O Devices Very diverse devices behavior (i.e., input vs. output vs. storage) partner (who is at the other end?) data rate I/O Design affected by many factors (expandability, resilience) Performance: access latency throughput connection between devices and the system the memory hierarchy the operating system A variety of different users
4 Application programs If this is enough Language Run-time Systems high-level facility for I/O (e.g. ANSI C standard I/O) Kernel Level I/O system calls Why bother learning this?
5 Why Bother? Understanding kernel-level I/O will help you understand other systems concepts I/O plays a key role in process creation and execution Process creation plays a key role in how files are shared by different processes Sometimes language run-time is not enough to do what you want
6 Unix I/O A file is a sequence of m bytes. All I/O devices are modeled as files. All I/O is performed by reading and writing the appropriate files. Opening a file: an application wants to use and I/O device. Kernel gives the application a file descriptor (nonnegative integer) Changing the current file position: position is a byte offset from the beginning of the file (kept by kernel) Reading and writing files Closing files
7 Unix I/O UNIX abstracts many things into files E.g. regular files, devices (/dev/sda2), FIFO pipes, sockets Allow a common set of syscalls for handling I/O E.g. reading and writing to files/pipes/sockets: read and write
8 Overview of File System implementation in UNIX file data dir block root / inode 0 dir block inode 1 f1.txt 2 inode 2 home user Inode 3 f2.txt 2 Inodes contain meta-data about files/directories Last modification time, size, user id Hard links: multiple names for the same file (/home/f1.txt and /usr/f2.txt refer to the same file)
9 UNIX I/O (i.e. I/O related syscalls) Getting meta-data (info maintained in i- nodes) Stat Directory operations opendir, readdir, rmdir Open/close files Open,close Read/write files read/write
10 File Metadata Access file meta-data using stat syscall Example: rkmatch.c void read_file(const char *fname, char **doc, int *doc_len) { struct stat st; if (stat(fd, &st)!= 0) { perror("read_file: fstat "); exit(1); } } *doc = (char *)malloc(st.st_size);
11 File Metadata Access file meta-data using stat syscall struct stat { dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ blksize_t st_blksize; /* block size for file system I/O */ blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ };
12 Opening Files Open a file before access: Returns a small integer file descriptor (or -1 for error) int fd; /* file descriptor */ if ((fd = open( X", O_RDONLY)) < 0) { perror("open"); exit(1); } For more info, do man 2 open Why fd? Kernel maintains an array of info on currently opened files for a process fd indexes into this in-kernel array Each process starts out with three open files 0: standard input 1: standard output 2: standard error
13 Closing Files Closing a file informs kernel that you are finished accessing that file int fd; /* file descriptor */ if (close(fd) < 0) { perror("close"); exit(1); }
14 Simple read/write example Copying standard in to standard out, one byte at a time #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char c; Returns # of bytes read, -1 for error } while(read(stdin_fileno, &c, 1) == 1){ write(stdout_fileno, &c, 1); } exit(0); cpstdin.c Returns # of bytes written, -1 for error
15 Kernel Presentation of Open Files Kernel uses 3 related data structures to represent open files Descriptor table: per process Indexed by the process open file descriptor Each entry points to an entry in the file table File table: Shared by all processes Each entry contains info about file position, reference count,, and a pointer to an entry in the v-node table v-node table: Shared by all processes contains info that can be read by stat syscall
16 Kernel tracks user processes opened files kernel state Descriptor table [one table per process] Open file table [shared by all processes] v-node table [shared by all processes] stdin stdout stderr fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 File A (terminal) File pos refcnt=1 File access File size File type Info in stat struct File B (disk) File access File pos refcnt=1 File size File type
17 Kernel tracks user processes opened files Calling open twice with the same filename Descriptor table [one table per process] Open file table [shared by all processes] v-node table [shared by all processes] stdin stdout stderr fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 File A (disk) File pos refcnt=1 File access File size File type File B (disk) File pos refcnt=1
18 Child process inherits its parent s Before fork() call: open files Descriptor table [one table per process] Open file table [shared by all processes] v-node table [shared by all processes] stdin stdout stderr fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 File A (terminal) File pos refcnt=1 File access File size File type File B (disk) File access File pos refcnt=1 File size File type
19 Child process inherits its parent s open files After fork(): Child s descriptor table same as parent s, and +1 to each refcnt Descriptor table [one table per process] fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 Parent Open file table [shared by all processes] File A (terminal) File pos refcnt=2 v-node table [shared by all processes] File access File size File type fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 Child File B (disk) File pos refcnt=2 File access File size File type
20 Fun with File Descriptors (fork) #include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd1; char c1, c2; char *fname = argv[1]; fd1 = open(fname, O_RDONLY, 0); read(fd1, &c1, 1); if (fork()) { /* Parent */ read(fd1, &c2, 1); printf("parent: c1 = %c, c2 = %c\n", c1, c2); } else { /* Child */ sleep(5); read(fd1, &c2, 1); printf("child: c1 = %c, c2 = %c\n", c1, c2); } return 0; } Solution: Parent: c1 = a, c2 = b Child: c1 = a, c2 = c What would this program print for file containing abcde?
21 Fun with File Descriptors (dup2) #include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd1, fd2, fd3; char c1, c2, c3; char *fname = argv[1]; fd1 = open(fname, O_RDONLY, 0); fd2 = open(fname, O_RDONLY, 0); fd3 = open(fname, O_RDONLY, 0); dup2(fd2, fd3); read(fd1, &c1, 1); read(fd2, &c2, 1); read(fd3, &c3, 1); printf("c1 = %c, c2 = %c, c3 = %c\n", c1, c2, c3); return 0; } ffiles1.c Solution: c1 = a, c2= a, c3 = b What would this program print for file containing abcde?
22 I/O Redirection How does a shell redirect I/O? unix$ ls > foo.txt Use syscall dup2(oldfd, newfd) Copies descriptor table entry oldfd to entry newfd Descriptor table before dup2(4,1) Descriptor table after dup2(4,1) fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 a b fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 b b
23 I/O Redirection Example Step #1: open output file to which stdout should be redirected Descriptor table [one table per process] Open file table [shared by all processes] v-node table [shared by all processes] stdin stdout stderr fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 File A File pos refcnt=1 File access File size File type Opened file has fd=4 File B File pos refcnt=1 File access File size File type
24 I/O Redirection Example (cont.) Step #2: call dup2(4,1) cause fd=1 (stdout) to refer to disk file pointed at by fd=4 Descriptor table [one table per process] Open file table [shared by all processes] v-node table [shared by all processes] stdin stdout stderr fd 0 fd 1 fd 2 fd 3 fd 4 File A File pos refcnt=0 File access File size File type File B File access File pos refcnt=2 File size File type
25 Standard I/O Functions The C library (libc.so) contains a collection of higher-level standard I/O functions fopen fdopen fread fwrite fscanf fprintf sscanf sprintf fgets fputs fflush fseek fclose Internally invokes I/O syscalls open read write lseek stat close
26 Standard I/O Streams Standard I/O implements buffered streams Abstraction for a file descriptor and a buffer in memory. C programs begin life with three open streams stdin (standard input) stdout (standard output) stderr (standard error) #include <stdio.h> extern FILE *stdin; /* standard input (descriptor 0) */ extern FILE *stdout; /* standard output (descriptor 1) */ extern FILE *stderr; /* standard error (descriptor 2) */ int main() { fprintf(stdout, "Hello, world\n"); }
27 Unix I/O vs. standard I/O Unix I/O: Pros most general, lowest overhead. All other I/O packages are implemented using Unix I/O functions. Provides functions for accessing file metadata. async-signal-safe and can be used safely in signal handlers. Cons Efficient reading/writing may require some form of buffering
28 Unix I/O vs. Standard I/O: Standard I/O: Pros: Buffering increases efficiency by reducing # of read and write system calls Cons: Provides no function for accessing file metadata Not async-signal-safe, and not appropriate for signal handlers. Not appropriate for input and output on network sockets
29 Choosing I/O Functions General rule: use the highest-level I/O functions you can Many C programmers are able to do all of their work using the standard I/O functions When to use standard I/O When working with disk or terminal files When to use raw Unix I/O Inside signal handlers, because Unix I/O is async-signal-safe. When working with network sockets In rare cases when you want to tune for absolute highest performance.
30 Standard I/O Buffering in Action You can see this buffering in action for yourself use strace to monitor a program s syscall invocation: #include <stdio.h> void main() { char c; while ((c = getc(stdin))!='\n') { printf("%c",c); } printf("\n"); } linux% strace./a.out execve("./a.out", [./a.out"], [/* */]). read(0,"hello\n", 1024) = 6 write(1, "hello\n", 6) = 6 exit_group(0) =?
31 Conclusions UNIX/LINUX use files to abstract many I/O devices Accessing files can be done either by standard I/O or UNIX I/O
Giving credit where credit is due
 JDEP 284H Foundations of Computer Systems System-Level I/O Dr. Steve Goddard [email protected] Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based on slides created by Drs. Bryant
JDEP 284H Foundations of Computer Systems System-Level I/O Dr. Steve Goddard [email protected] Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based on slides created by Drs. Bryant
System Calls Related to File Manipulation
 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS Information and Computer Science Department ICS 431 Operating Systems Lab # 12 System Calls Related to File Manipulation Objective: In this lab we will be
KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS Information and Computer Science Department ICS 431 Operating Systems Lab # 12 System Calls Related to File Manipulation Objective: In this lab we will be
64 Bit File Access. 1.0 Introduction. 2.0 New Interfaces. 2.1 New User Visible Types. Adam Sweeney
 64 Bit File Access Adam Sweeney 1.0 Introduction In order to support the access of 64 bit files from 32 bit applications, new interfaces must be defined which take 64 bit parameters. These interfaces must
64 Bit File Access Adam Sweeney 1.0 Introduction In order to support the access of 64 bit files from 32 bit applications, new interfaces must be defined which take 64 bit parameters. These interfaces must
System Calls and Standard I/O
 System Calls and Standard I/O Professor Jennifer Rexford http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~jrex 1 Goals of Today s Class System calls o How a user process contacts the Operating System o For advanced services
System Calls and Standard I/O Professor Jennifer Rexford http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~jrex 1 Goals of Today s Class System calls o How a user process contacts the Operating System o For advanced services
Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C
 Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C A process is a currently executing instance of a program. All programs by default execute in the user mode. A C program can invoke UNIX system calls directly. A system
Lecture 24 Systems Programming in C A process is a currently executing instance of a program. All programs by default execute in the user mode. A C program can invoke UNIX system calls directly. A system
Linux Kernel Architecture
 Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Linux Kernel Architecture Amir Hossein Payberah [email protected] Contents What is Kernel? Kernel Architecture Overview User Space Kernel Space Kernel Functional Overview File System Process Management
Interlude: File and Directories
 39 Interlude: File and Directories Thus far we have seen the development of two key operating system abstractions: the process, which is a virtualization of the CPU, and the address space, which is a virtualization
39 Interlude: File and Directories Thus far we have seen the development of two key operating system abstractions: the process, which is a virtualization of the CPU, and the address space, which is a virtualization
As previously noted, a byte can contain a numeric value in the range 0-255. Computers don't understand Latin, Cyrillic, Hindi, Arabic character sets!
 Encoding of alphanumeric and special characters As previously noted, a byte can contain a numeric value in the range 0-255. Computers don't understand Latin, Cyrillic, Hindi, Arabic character sets! Alphanumeric
Encoding of alphanumeric and special characters As previously noted, a byte can contain a numeric value in the range 0-255. Computers don't understand Latin, Cyrillic, Hindi, Arabic character sets! Alphanumeric
File Handling. What is a file?
 File Handling 1 What is a file? A named collection of data, stored in secondary storage (typically). Typical operations on files: Open Read Write Close How is a file stored? Stored as sequence of bytes,
File Handling 1 What is a file? A named collection of data, stored in secondary storage (typically). Typical operations on files: Open Read Write Close How is a file stored? Stored as sequence of bytes,
Operating Systems. Privileged Instructions
 Operating Systems Operating systems manage processes and resources Processes are executing instances of programs may be the same or different programs process 1 code data process 2 code data process 3
Operating Systems Operating systems manage processes and resources Processes are executing instances of programs may be the same or different programs process 1 code data process 2 code data process 3
Linux/UNIX System Programming. POSIX Shared Memory. Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015. February 2015
 Linux/UNIX System Programming POSIX Shared Memory Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015 February 2015 Outline 22 POSIX Shared Memory 22-1 22.1 Overview 22-3 22.2 Creating and opening shared memory objects 22-10
Linux/UNIX System Programming POSIX Shared Memory Michael Kerrisk, man7.org c 2015 February 2015 Outline 22 POSIX Shared Memory 22-1 22.1 Overview 22-3 22.2 Creating and opening shared memory objects 22-10
Illustration 1: Diagram of program function and data flow
 The contract called for creation of a random access database of plumbing shops within the near perimeter of FIU Engineering school. The database features a rating number from 1-10 to offer a guideline
The contract called for creation of a random access database of plumbing shops within the near perimeter of FIU Engineering school. The database features a rating number from 1-10 to offer a guideline
Networks. Inter-process Communication. Pipes. Inter-process Communication
 Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
Networks Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Inter-process Communication process CS 217 process Network 1 2 Inter-process Communication Sockets o Processes can
CSI 402 Lecture 13 (Unix Process Related System Calls) 13 1 / 17
 CSI 402 Lecture 13 (Unix Process Related System Calls) 13 1 / 17 System Calls for Processes Ref: Process: Chapter 5 of [HGS]. A program in execution. Several processes are executed concurrently by the
CSI 402 Lecture 13 (Unix Process Related System Calls) 13 1 / 17 System Calls for Processes Ref: Process: Chapter 5 of [HGS]. A program in execution. Several processes are executed concurrently by the
OS: IPC I. Cooperating Processes. CIT 595 Spring 2010. Message Passing vs. Shared Memory. Message Passing: Unix Pipes
 Cooperating Processes Independent processes cannot affect or be affected by the execution of another process OS: IPC I CIT 595 Spring 2010 Cooperating process can affect or be affected by the execution
Cooperating Processes Independent processes cannot affect or be affected by the execution of another process OS: IPC I CIT 595 Spring 2010 Cooperating process can affect or be affected by the execution
1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision
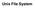 Unix File System 1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Operating System Concepts 7 th Edition, Feb 6, 2005 Logical structure in each FS (System V):
Unix File System 1. Introduction to the UNIX File System: logical vision Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Operating System Concepts 7 th Edition, Feb 6, 2005 Logical structure in each FS (System V):
Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part
 Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part Overview The goal of this lab is to familiarize yourself with application level programming with sockets, specifically stream or TCP sockets, by implementing a client/server
Lab 4: Socket Programming: netcat part Overview The goal of this lab is to familiarize yourself with application level programming with sockets, specifically stream or TCP sockets, by implementing a client/server
Operating System Structure
 Operating System Structure Lecture 3 Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission Recap Computer architecture CPU, memory, disk, I/O devices Memory hierarchy Architectural
Operating System Structure Lecture 3 Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission Recap Computer architecture CPU, memory, disk, I/O devices Memory hierarchy Architectural
UNIX File Management (continued)
 UNIX File Management (continued) OS storage stack (recap) Application FD table OF table VFS FS Buffer cache Disk scheduler Device driver 2 Virtual File System (VFS) Application FD table OF table VFS FS
UNIX File Management (continued) OS storage stack (recap) Application FD table OF table VFS FS Buffer cache Disk scheduler Device driver 2 Virtual File System (VFS) Application FD table OF table VFS FS
LOW LEVEL FILE PROCESSING
 LOW LEVEL FILE PROCESSING 1. Overview The learning objectives of this lab session are: To understand the functions provided for file processing by the lower level of the file management system, i.e. the
LOW LEVEL FILE PROCESSING 1. Overview The learning objectives of this lab session are: To understand the functions provided for file processing by the lower level of the file management system, i.e. the
Chapter 10 Case Study 1: LINUX
 MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Third Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM Chapter 10 Case Study 1: LINUX History of UNIX and Linux UNICS PDP-11 UNIX Portable UNIX Berkeley UNIX Standard UNIX MINIX Linux UNIX/Linux Goals
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Third Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM Chapter 10 Case Study 1: LINUX History of UNIX and Linux UNICS PDP-11 UNIX Portable UNIX Berkeley UNIX Standard UNIX MINIX Linux UNIX/Linux Goals
Unix System Calls. Dept. CSIE 2006.12.25
 Unix System Calls Gwan-Hwan Hwang Dept. CSIE National Taiwan Normal University 2006.12.25 UNIX System Overview UNIX Architecture Login Name Shells Files and Directories File System Filename Pathname Working
Unix System Calls Gwan-Hwan Hwang Dept. CSIE National Taiwan Normal University 2006.12.25 UNIX System Overview UNIX Architecture Login Name Shells Files and Directories File System Filename Pathname Working
Operating Systems and Networks
 recap Operating Systems and Networks How OS manages multiple tasks Virtual memory Brief Linux demo Lecture 04: Introduction to OS-part 3 Behzad Bordbar 47 48 Contents Dual mode API to wrap system calls
recap Operating Systems and Networks How OS manages multiple tasks Virtual memory Brief Linux demo Lecture 04: Introduction to OS-part 3 Behzad Bordbar 47 48 Contents Dual mode API to wrap system calls
The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level
 TECHNOLOGIES The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level Course description The course fully covers the basics of programming in the C programming language and demonstrates fundamental programming
TECHNOLOGIES The C Programming Language course syllabus associate level Course description The course fully covers the basics of programming in the C programming language and demonstrates fundamental programming
System calls. Problem: How to access resources other than CPU
 System calls Problem: How to access resources other than CPU - Disk, network, terminal, other processes - CPU prohibits instructions that would access devices - Only privileged OS kernel can access devices
System calls Problem: How to access resources other than CPU - Disk, network, terminal, other processes - CPU prohibits instructions that would access devices - Only privileged OS kernel can access devices
File Systems Management and Examples
 File Systems Management and Examples Today! Efficiency, performance, recovery! Examples Next! Distributed systems Disk space management! Once decided to store a file as sequence of blocks What s the size
File Systems Management and Examples Today! Efficiency, performance, recovery! Examples Next! Distributed systems Disk space management! Once decided to store a file as sequence of blocks What s the size
Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO
 Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO Stefano Zacchiroli [email protected] Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot - Paris 7 15 novembre 2011 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1112/progsyst/ Copyright
Programmation Systèmes Cours 7 IPC: FIFO Stefano Zacchiroli [email protected] Laboratoire PPS, Université Paris Diderot - Paris 7 15 novembre 2011 URL http://upsilon.cc/zack/teaching/1112/progsyst/ Copyright
/* File: blkcopy.c. size_t n
 13.1. BLOCK INPUT/OUTPUT 505 /* File: blkcopy.c The program uses block I/O to copy a file. */ #include main() { signed char buf[100] const void *ptr = (void *) buf FILE *input, *output size_t
13.1. BLOCK INPUT/OUTPUT 505 /* File: blkcopy.c The program uses block I/O to copy a file. */ #include main() { signed char buf[100] const void *ptr = (void *) buf FILE *input, *output size_t
Lab 2 : Basic File Server. Introduction
 Lab 2 : Basic File Server Introduction In this lab, you will start your file system implementation by getting the following FUSE operations to work: CREATE/MKNOD, LOOKUP, and READDIR SETATTR, WRITE and
Lab 2 : Basic File Server Introduction In this lab, you will start your file system implementation by getting the following FUSE operations to work: CREATE/MKNOD, LOOKUP, and READDIR SETATTR, WRITE and
Outline. Review. Inter process communication Signals Fork Pipes FIFO. Spotlights
 Outline Review Inter process communication Signals Fork Pipes FIFO Spotlights 1 6.087 Lecture 14 January 29, 2010 Review Inter process communication Signals Fork Pipes FIFO Spotlights 2 Review: multithreading
Outline Review Inter process communication Signals Fork Pipes FIFO Spotlights 1 6.087 Lecture 14 January 29, 2010 Review Inter process communication Signals Fork Pipes FIFO Spotlights 2 Review: multithreading
Intro to GPU computing. Spring 2015 Mark Silberstein, 048661, Technion 1
 Intro to GPU computing Spring 2015 Mark Silberstein, 048661, Technion 1 Serial vs. parallel program One instruction at a time Multiple instructions in parallel Spring 2015 Mark Silberstein, 048661, Technion
Intro to GPU computing Spring 2015 Mark Silberstein, 048661, Technion 1 Serial vs. parallel program One instruction at a time Multiple instructions in parallel Spring 2015 Mark Silberstein, 048661, Technion
Transparent Monitoring of a Process Self in a Virtual Environment
 Transparent Monitoring of a Process Self in a Virtual Environment PhD Lunchtime Seminar Università di Pisa 24 Giugno 2008 Outline Background Process Self Attacks Against the Self Dynamic and Static Analysis
Transparent Monitoring of a Process Self in a Virtual Environment PhD Lunchtime Seminar Università di Pisa 24 Giugno 2008 Outline Background Process Self Attacks Against the Self Dynamic and Static Analysis
Chapter 6, The Operating System Machine Level
 Chapter 6, The Operating System Machine Level 6.1 Virtual Memory 6.2 Virtual I/O Instructions 6.3 Virtual Instructions For Parallel Processing 6.4 Example Operating Systems 6.5 Summary Virtual Memory General
Chapter 6, The Operating System Machine Level 6.1 Virtual Memory 6.2 Virtual I/O Instructions 6.3 Virtual Instructions For Parallel Processing 6.4 Example Operating Systems 6.5 Summary Virtual Memory General
Computer Systems II. Unix system calls. fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) How To Create New Processes? Creating and Executing Processes
 Computer Systems II Creating and Executing Processes 1 Unix system calls fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) 2 How To Create New Processes? Underlying mechanism - A process runs fork to create a child process - Parent
Computer Systems II Creating and Executing Processes 1 Unix system calls fork( ) wait( ) exit( ) 2 How To Create New Processes? Underlying mechanism - A process runs fork to create a child process - Parent
Shared Memory Introduction
 12 Shared Memory Introduction 12.1 Introduction Shared memory is the fastest form of IPC available. Once the memory is mapped into the address space of the processes that are sharing the memory region,
12 Shared Memory Introduction 12.1 Introduction Shared memory is the fastest form of IPC available. Once the memory is mapped into the address space of the processes that are sharing the memory region,
Lecture 7: Machine-Level Programming I: Basics Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com
 CSCI-UA.0201-003 Computer Systems Organization Lecture 7: Machine-Level Programming I: Basics Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com Some slides adapted (and slightly modified)
CSCI-UA.0201-003 Computer Systems Organization Lecture 7: Machine-Level Programming I: Basics Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com Some slides adapted (and slightly modified)
Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM
 Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM User s Guide Including Leak Analyzer For x86 Servers Document Number DLC20-L-021-1 Copyright 2003-2009 Dynamic Memory Solutions LLC www.dynamic-memory.com Notices Information
Leak Check Version 2.1 for Linux TM User s Guide Including Leak Analyzer For x86 Servers Document Number DLC20-L-021-1 Copyright 2003-2009 Dynamic Memory Solutions LLC www.dynamic-memory.com Notices Information
Intel P6 Systemprogrammering 2007 Föreläsning 5 P6/Linux Memory System
 Intel P6 Systemprogrammering 07 Föreläsning 5 P6/Linux ory System Topics P6 address translation Linux memory management Linux page fault handling memory mapping Internal Designation for Successor to Pentium
Intel P6 Systemprogrammering 07 Föreläsning 5 P6/Linux ory System Topics P6 address translation Linux memory management Linux page fault handling memory mapping Internal Designation for Successor to Pentium
NDK: NOVELL NSS AUDIT
 www.novell.com/documentation NDK: NOVELL NSS AUDIT Developer Kit August 2015 Legal Notices Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation,
www.novell.com/documentation NDK: NOVELL NSS AUDIT Developer Kit August 2015 Legal Notices Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation,
Introduction. dnotify
 Introduction In a multi-user, multi-process operating system, files are continually being created, modified and deleted, often by apparently unrelated processes. This means that any software that needs
Introduction In a multi-user, multi-process operating system, files are continually being created, modified and deleted, often by apparently unrelated processes. This means that any software that needs
CSC 2405: Computer Systems II
 CSC 2405: Computer Systems II Spring 2013 (TR 8:30-9:45 in G86) Mirela Damian http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~mdamian/csc2405/ Introductions Mirela Damian Room 167A in the Mendel Science Building [email protected]
CSC 2405: Computer Systems II Spring 2013 (TR 8:30-9:45 in G86) Mirela Damian http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~mdamian/csc2405/ Introductions Mirela Damian Room 167A in the Mendel Science Building [email protected]
Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user).
 Input/Output Devices Chapter 5 of Tanenbaum. Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user). Ideally have the same interface to all devices (device independence).
Input/Output Devices Chapter 5 of Tanenbaum. Have both hardware and software. Want to hide the details from the programmer (user). Ideally have the same interface to all devices (device independence).
Chapter 12 File Management
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Roadmap Overview File organisation and Access
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Roadmap Overview File organisation and Access
Chapter 12 File Management. Roadmap
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Overview Roadmap File organisation and Access
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/E William Stallings Chapter 12 File Management Dave Bremer Otago Polytechnic, N.Z. 2008, Prentice Hall Overview Roadmap File organisation and Access
Fortify on Demand Security Review. Fortify Open Review
 Fortify on Demand Security Review Company: Project: Version: Latest Analysis: Fortify Open Review GNU m4 1.4.17 4/17/2015 12:16:24 PM Executive Summary Company: Project: Version: Static Analysis Date:
Fortify on Demand Security Review Company: Project: Version: Latest Analysis: Fortify Open Review GNU m4 1.4.17 4/17/2015 12:16:24 PM Executive Summary Company: Project: Version: Static Analysis Date:
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove ([email protected]) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove ([email protected]) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
Device Management Functions
 REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEMS Lesson-6: Device Management Functions 1 1. Device manager functions 2 Device Driver ISRs Number of device driver ISRs in a system, Each device or device function having s a
REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEMS Lesson-6: Device Management Functions 1 1. Device manager functions 2 Device Driver ISRs Number of device driver ISRs in a system, Each device or device function having s a
Chapter I/O and File System
 Chapter 11 I/O and File System Tornado Training Workshop Copyright 11-1 ntroduction to VxWorks I/O System haracter I/O lock I/O I/O System 11.1 Introduction Character I/O Block I/O Tornado Training Workshop
Chapter 11 I/O and File System Tornado Training Workshop Copyright 11-1 ntroduction to VxWorks I/O System haracter I/O lock I/O I/O System 11.1 Introduction Character I/O Block I/O Tornado Training Workshop
Process definition Concurrency Process status Process attributes PROCESES 1.3
 Process Management Outline Main concepts Basic services for process management (Linux based) Inter process communications: Linux Signals and synchronization Internal process management Basic data structures:
Process Management Outline Main concepts Basic services for process management (Linux based) Inter process communications: Linux Signals and synchronization Internal process management Basic data structures:
ProTrack: A Simple Provenance-tracking Filesystem
 ProTrack: A Simple Provenance-tracking Filesystem Somak Das Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology [email protected] Abstract Provenance describes a file
ProTrack: A Simple Provenance-tracking Filesystem Somak Das Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology [email protected] Abstract Provenance describes a file
Operating System Structures
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Operating System Structures Zhi Wang Florida State University Content Operating system services User interface System calls System programs Operating
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Operating System Structures Zhi Wang Florida State University Content Operating system services User interface System calls System programs Operating
Laboratory Report. An Appendix to SELinux & grsecurity: A Side-by-Side Comparison of Mandatory Access Control & Access Control List Implementations
 Laboratory Report An Appendix to SELinux & grsecurity: A Side-by-Side Comparison of Mandatory Access Control & Access Control List Implementations 1. Hardware Configuration We configured our testbed on
Laboratory Report An Appendix to SELinux & grsecurity: A Side-by-Side Comparison of Mandatory Access Control & Access Control List Implementations 1. Hardware Configuration We configured our testbed on
Xillybus host application programming guide for Linux
 Xillybus host application programming guide for Linux Xillybus Ltd. Version 2.0 1 Introduction 3 2 Synchronous vs. asynchronous streams 5 2.1 Overview................................... 5 2.2 Motivation
Xillybus host application programming guide for Linux Xillybus Ltd. Version 2.0 1 Introduction 3 2 Synchronous vs. asynchronous streams 5 2.1 Overview................................... 5 2.2 Motivation
Embedded Systems. Review of ANSI C Topics. A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming. Basic features of C
 Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
File Management. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 File Management File is the basic element of most of the applications, since the input to an application, as well as its output, is usually a file. They also typically outlive the execution
Chapter 12 File Management File is the basic element of most of the applications, since the input to an application, as well as its output, is usually a file. They also typically outlive the execution
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 4. Introduction to I/O (Continued), Sockets, Networking. Recall: Fork and Wait
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 4 Introduction to I/O (Continued), Sockets, Networking February 2 nd, 2015 Prof. John Kubiatowicz http://cs162.eecs.berkeley.edu Recall: Fork and
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 4 Introduction to I/O (Continued), Sockets, Networking February 2 nd, 2015 Prof. John Kubiatowicz http://cs162.eecs.berkeley.edu Recall: Fork and
Network File System (NFS)
 Network File System (NFS) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 10 th October 2011 NFS Is Relevant Original paper from 1985 Very successful, still widely used today Early result; much subsequent
Network File System (NFS) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 10 th October 2011 NFS Is Relevant Original paper from 1985 Very successful, still widely used today Early result; much subsequent
Module 816. File Management in C. M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University
 M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
M. Campbell 1993 Deakin University Aim Learning objectives Content After working through this module you should be able to create C programs that create an use both text and binary files. After working
Lecture 25 Systems Programming Process Control
 Lecture 25 Systems Programming Process Control A process is defined as an instance of a program that is currently running. A uni processor system or single core system can still execute multiple processes
Lecture 25 Systems Programming Process Control A process is defined as an instance of a program that is currently running. A uni processor system or single core system can still execute multiple processes
Operating System Components and Services
 Operating System Components and Services Tom Kelliher, CS 311 Feb. 6, 2012 Announcements: From last time: 1. System architecture issues. 2. I/O programming. 3. Memory hierarchy. 4. Hardware protection.
Operating System Components and Services Tom Kelliher, CS 311 Feb. 6, 2012 Announcements: From last time: 1. System architecture issues. 2. I/O programming. 3. Memory hierarchy. 4. Hardware protection.
Virtual Memory. How is it possible for each process to have contiguous addresses and so many of them? A System Using Virtual Addressing
 How is it possible for each process to have contiguous addresses and so many of them? Computer Systems Organization (Spring ) CSCI-UA, Section Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Teaching Assistants: Paige Connelly
How is it possible for each process to have contiguous addresses and so many of them? Computer Systems Organization (Spring ) CSCI-UA, Section Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Teaching Assistants: Paige Connelly
Distributed Systems [Fall 2012]
![Distributed Systems [Fall 2012] Distributed Systems [Fall 2012]](/thumbs/19/283009.jpg) Distributed Systems [Fall 2012] [W4995-2] Lec 6: YFS Lab Introduction and Local Synchronization Primitives Slide acks: Jinyang Li, Dave Andersen, Randy Bryant (http://www.news.cs.nyu.edu/~jinyang/fa10/notes/ds-lec2.ppt,
Distributed Systems [Fall 2012] [W4995-2] Lec 6: YFS Lab Introduction and Local Synchronization Primitives Slide acks: Jinyang Li, Dave Andersen, Randy Bryant (http://www.news.cs.nyu.edu/~jinyang/fa10/notes/ds-lec2.ppt,
Operating Systems Concepts: Chapter 7: Scheduling Strategies
 Operating Systems Concepts: Chapter 7: Scheduling Strategies Olav Beckmann Huxley 449 http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ob3 Acknowledgements: There are lots. See end of Chapter 1. Home Page for the course: http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ob3/teaching/operatingsystemsconcepts/
Operating Systems Concepts: Chapter 7: Scheduling Strategies Olav Beckmann Huxley 449 http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ob3 Acknowledgements: There are lots. See end of Chapter 1. Home Page for the course: http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ob3/teaching/operatingsystemsconcepts/
Building accurate intrusion detection systems. Diego Zamboni Global Security Analysis Lab IBM Zürich Research Laboratory
 Building accurate intrusion detection systems Diego Zamboni Global Security Analysis Lab IBM Zürich Research Laboratory Outline Brief introduction to intrusion detection The MAFTIA project Accurate intrusion
Building accurate intrusion detection systems Diego Zamboni Global Security Analysis Lab IBM Zürich Research Laboratory Outline Brief introduction to intrusion detection The MAFTIA project Accurate intrusion
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005 Quiz II Solutions Average 84, median 83, standard deviation
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Operating System Engineering: Fall 2005 Quiz II Solutions Average 84, median 83, standard deviation
Grundlagen der Betriebssystemprogrammierung
 Grundlagen der Betriebssystemprogrammierung Präsentation A3, A4, A5, A6 21. März 2013 IAIK Grundlagen der Betriebssystemprogrammierung 1 / 73 1 A3 - Function Pointers 2 A4 - C++: The good, the bad and
Grundlagen der Betriebssystemprogrammierung Präsentation A3, A4, A5, A6 21. März 2013 IAIK Grundlagen der Betriebssystemprogrammierung 1 / 73 1 A3 - Function Pointers 2 A4 - C++: The good, the bad and
COSC 6374 Parallel Computation. Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics. Concept of a clusters
 COSC 6374 Parallel Computation Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics Spring 2008 Concept of a clusters Processor 1 local disks Compute node message passing network administrative network Memory Processor 2 Network
COSC 6374 Parallel Computation Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics Spring 2008 Concept of a clusters Processor 1 local disks Compute node message passing network administrative network Memory Processor 2 Network
How To Understand How A Process Works In Unix (Shell) (Shell Shell) (Program) (Unix) (For A Non-Program) And (Shell).Orgode) (Powerpoint) (Permanent) (Processes
 Content Introduction and History File I/O The File System Shell Programming Standard Unix Files and Configuration Processes Programs are instruction sets stored on a permanent medium (e.g. harddisc). Processes
Content Introduction and History File I/O The File System Shell Programming Standard Unix Files and Configuration Processes Programs are instruction sets stored on a permanent medium (e.g. harddisc). Processes
COSC 6374 Parallel Computation. Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics. Concept of a clusters
 COSC 6374 Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics Fall 2012 Concept of a clusters Processor 1 local disks Compute node message passing network administrative network Memory Processor 2 Network card 1 Network card
COSC 6374 Parallel I/O (I) I/O basics Fall 2012 Concept of a clusters Processor 1 local disks Compute node message passing network administrative network Memory Processor 2 Network card 1 Network card
The Linux Virtual Filesystem
 Lecture Overview Linux filesystem Linux virtual filesystem (VFS) overview Common file model Superblock, inode, file, dentry Object-oriented Ext2 filesystem Disk data structures Superblock, block group,
Lecture Overview Linux filesystem Linux virtual filesystem (VFS) overview Common file model Superblock, inode, file, dentry Object-oriented Ext2 filesystem Disk data structures Superblock, block group,
Migration of Process Credentials
 C H A P T E R - 5 Migration of Process Credentials 5.1 Introduction 5.2 The Process Identifier 5.3 The Mechanism 5.4 Concluding Remarks 100 CHAPTER 5 Migration of Process Credentials 5.1 Introduction Every
C H A P T E R - 5 Migration of Process Credentials 5.1 Introduction 5.2 The Process Identifier 5.3 The Mechanism 5.4 Concluding Remarks 100 CHAPTER 5 Migration of Process Credentials 5.1 Introduction Every
Linux Syslog Messages in IBM Director
 Ever want those pesky little Linux syslog messages (/var/log/messages) to forward to IBM Director? Well, it s not built in, but it s pretty easy to setup. You can forward syslog messages from an IBM Director
Ever want those pesky little Linux syslog messages (/var/log/messages) to forward to IBM Director? Well, it s not built in, but it s pretty easy to setup. You can forward syslog messages from an IBM Director
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS 1) INTRODUCTION : Data base systems data models instances and schemes Database Models Relation,Hierarchical and Network Data independence DDL and DML Data base manager database
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS 1) INTRODUCTION : Data base systems data models instances and schemes Database Models Relation,Hierarchical and Network Data independence DDL and DML Data base manager database
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets
 Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski [email protected] 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
Operating Systems Design 16. Networking: Sockets Paul Krzyzanowski [email protected] 1 Sockets IP lets us send data between machines TCP & UDP are transport layer protocols Contain port number to identify
Lecture 16: Storage Devices
 CS 422/522 Design & Implementation of Operating Systems Lecture 16: Storage Devices Zhong Shao Dept. of Computer Science Yale University Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from previous versions of
CS 422/522 Design & Implementation of Operating Systems Lecture 16: Storage Devices Zhong Shao Dept. of Computer Science Yale University Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from previous versions of
Operating Systems. 05. Threads. Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Spring 2015
 Operating Systems 05. Threads Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 February 9, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Thread of execution Single sequence of instructions Pointed to by the program
Operating Systems 05. Threads Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 February 9, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Thread of execution Single sequence of instructions Pointed to by the program
Lecture 17. Process Management. Process Management. Process Management. Inter-Process Communication. Inter-Process Communication
 Process Management Lecture 17 Review February 25, 2005 Program? Process? Thread? Disadvantages, advantages of threads? How do you identify processes? How do you fork a child process, the child process
Process Management Lecture 17 Review February 25, 2005 Program? Process? Thread? Disadvantages, advantages of threads? How do you identify processes? How do you fork a child process, the child process
Undergraduate Course Syllabus
 College of Software Engineering Undergraduate Course Syllabus Course ID 311006040 Course Name Operating System Course Attribute Compulsory Selective Course Language English Chinese Credit Hour 4 Period
College of Software Engineering Undergraduate Course Syllabus Course ID 311006040 Course Name Operating System Course Attribute Compulsory Selective Course Language English Chinese Credit Hour 4 Period
Operating System Components
 Lecture Overview Operating system software introduction OS components OS services OS structure Operating Systems - April 24, 2001 Operating System Components Process management Memory management Secondary
Lecture Overview Operating system software introduction OS components OS services OS structure Operating Systems - April 24, 2001 Operating System Components Process management Memory management Secondary
How ToWrite a UNIX Daemon
 How ToWrite a UNIX Daemon Dave Lennert Hewlett-Packard Company ABSTRACT On UNIX systems users can easily write daemon programs that perform repetitive tasks in an unnoticed way. However, because daemon
How ToWrite a UNIX Daemon Dave Lennert Hewlett-Packard Company ABSTRACT On UNIX systems users can easily write daemon programs that perform repetitive tasks in an unnoticed way. However, because daemon
CHAPTER 17: File Management
 CHAPTER 17: File Management The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 17: File Management The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Processes and Non-Preemptive Scheduling. Otto J. Anshus
 Processes and Non-Preemptive Scheduling Otto J. Anshus 1 Concurrency and Process Challenge: Physical reality is Concurrent Smart to do concurrent software instead of sequential? At least we want to have
Processes and Non-Preemptive Scheduling Otto J. Anshus 1 Concurrency and Process Challenge: Physical reality is Concurrent Smart to do concurrent software instead of sequential? At least we want to have
Storage Management. in a Hybrid SSD/HDD File system
 Project 2 Storage Management Part 2 in a Hybrid SSD/HDD File system Part 1 746, Spring 2011, Greg Ganger and Garth Gibson 1 Project due on April 11 th (11.59 EST) Start early Milestone1: finish part 1
Project 2 Storage Management Part 2 in a Hybrid SSD/HDD File system Part 1 746, Spring 2011, Greg Ganger and Garth Gibson 1 Project due on April 11 th (11.59 EST) Start early Milestone1: finish part 1
Introduction to Socket programming using C
 Introduction to Socket programming using C Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Vinay Narasimhamurthy [email protected] CLIENT SERVER MODEL Sockets are
Introduction to Socket programming using C Goal: learn how to build client/server application that communicate using sockets Vinay Narasimhamurthy [email protected] CLIENT SERVER MODEL Sockets are
CS161: Operating Systems
 CS161: Operating Systems Matt Welsh [email protected] Lecture 2: OS Structure and System Calls February 6, 2007 1 Lecture Overview Protection Boundaries and Privilege Levels What makes the kernel different
CS161: Operating Systems Matt Welsh [email protected] Lecture 2: OS Structure and System Calls February 6, 2007 1 Lecture Overview Protection Boundaries and Privilege Levels What makes the kernel different
COS 217: Introduction to Programming Systems
 COS 217: Introduction to Programming Systems 1 Goals for Todayʼs Class Course overview Introductions Course goals Resources Grading Policies Getting started with C C programming language overview 2 1 Introductions
COS 217: Introduction to Programming Systems 1 Goals for Todayʼs Class Course overview Introductions Course goals Resources Grading Policies Getting started with C C programming language overview 2 1 Introductions
CSC230 Getting Starting in C. Tyler Bletsch
 CSC230 Getting Starting in C Tyler Bletsch What is C? The language of UNIX Procedural language (no classes) Low-level access to memory Easy to map to machine language Not much run-time stuff needed Surprisingly
CSC230 Getting Starting in C Tyler Bletsch What is C? The language of UNIX Procedural language (no classes) Low-level access to memory Easy to map to machine language Not much run-time stuff needed Surprisingly
COS 318: Operating Systems. File Layout and Directories. Topics. File System Components. Steps to Open A File
 Topics COS 318: Operating Systems File Layout and Directories File system structure Disk allocation and i-nodes Directory and link implementations Physical layout for performance 2 File System Components
Topics COS 318: Operating Systems File Layout and Directories File system structure Disk allocation and i-nodes Directory and link implementations Physical layout for performance 2 File System Components
Runtime Monitoring & Issue Tracking
 Runtime Monitoring & Issue Tracking http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek [email protected] CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Runtime monitoring Nástroje pro vývoj software
Runtime Monitoring & Issue Tracking http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek [email protected] CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Runtime monitoring Nástroje pro vývoj software
As shown, the emulator instance connected to adb on port 5555 is the same as the instance whose console listens on port 5554.
 Tools > Android Debug Bridge Android Debug Bridge (adb) is a versatile tool lets you manage the state of an emulator instance or Android-powered device. It is a client-server program that includes three
Tools > Android Debug Bridge Android Debug Bridge (adb) is a versatile tool lets you manage the state of an emulator instance or Android-powered device. It is a client-server program that includes three
Software Vulnerabilities
 Software Vulnerabilities -- stack overflow Code based security Code based security discusses typical vulnerabilities made by programmers that can be exploited by miscreants Implementing safe software in
Software Vulnerabilities -- stack overflow Code based security Code based security discusses typical vulnerabilities made by programmers that can be exploited by miscreants Implementing safe software in
CS420: Operating Systems OS Services & System Calls
 NK YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVANIA HG OK 2 YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVAN OS Services & System Calls James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts,
NK YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVANIA HG OK 2 YORK COLLEGE OF PENNSYLVAN OS Services & System Calls James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts,
Objectives. Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures. Operating System Services (Cont.) Operating System Services. Operating System Services (Cont.
 Objectives To describe the services an operating system provides to users, processes, and other systems To discuss the various ways of structuring an operating system Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
Objectives To describe the services an operating system provides to users, processes, and other systems To discuss the various ways of structuring an operating system Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
1 Posix API vs Windows API
 1 Posix API vs Windows API 1.1 File I/O Using the Posix API, to open a file, you use open(filename, flags, more optional flags). If the O CREAT flag is passed, the file will be created if it doesnt exist.
1 Posix API vs Windows API 1.1 File I/O Using the Posix API, to open a file, you use open(filename, flags, more optional flags). If the O CREAT flag is passed, the file will be created if it doesnt exist.
Capability-Based Access Control
 Lecture Notes (Syracuse University) Capability: 1 Capability-Based Access Control 1 An Analogy: Bank Analogy We would like to use an example to illustrate the need for capabilities. In the following bank
Lecture Notes (Syracuse University) Capability: 1 Capability-Based Access Control 1 An Analogy: Bank Analogy We would like to use an example to illustrate the need for capabilities. In the following bank
ELEC 377. Operating Systems. Week 1 Class 3
 Operating Systems Week 1 Class 3 Last Class! Computer System Structure, Controllers! Interrupts & Traps! I/O structure and device queues.! Storage Structure & Caching! Hardware Protection! Dual Mode Operation
Operating Systems Week 1 Class 3 Last Class! Computer System Structure, Controllers! Interrupts & Traps! I/O structure and device queues.! Storage Structure & Caching! Hardware Protection! Dual Mode Operation
CS 377: Operating Systems. Outline. A review of what you ve learned, and how it applies to a real operating system. Lecture 25 - Linux Case Study
 CS 377: Operating Systems Lecture 25 - Linux Case Study Guest Lecturer: Tim Wood Outline Linux History Design Principles System Overview Process Scheduling Memory Management File Systems A review of what
CS 377: Operating Systems Lecture 25 - Linux Case Study Guest Lecturer: Tim Wood Outline Linux History Design Principles System Overview Process Scheduling Memory Management File Systems A review of what
