ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) RLM.MD ICD-10-PCS
|
|
|
- Logan Palmer
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICD-10 Procedure Coding System () 1
2 Development Background CMS awarded a contract to 3M Health Information Systems to develop a new procedure coding system The new system is intended to replace ICD-9-CM Volume 3 for reporting inpatient procedures 2
3 Development History : First draft of completed : Training program developed Informal testing conducted revised : Independent formal testing conducted revised Final draft completed 1998-present updated annually 3
4 Major Development Goals Improve accuracy and efficiency of coding Reduce training effort Improve communication with physicians 4
5 Essential Attributes Completeness All substantially different procedures have a unique code Expandability The structure of the system allows incorporation of new procedures as unique codes 5
6 Essential Attributes Standardized terminology Includes definitions of the terminology used. While the meaning of specific words can vary in common usage, defines a single meaning for each term used in the system. 6
7 Essential Attributes Multiaxial The system has a multi-axial structure. Each character has the same meaning within a section and across sections to the extent possible 7
8 General Principles Diagnostic information is not included in the code description A not elsewhere classified option is allowed for new devices and substances All substantially different procedures are defined 8
9 General Principles Limited NOS Option A general body part, approach, or root operation can be used when the level of specificity required is not available in the record or cannot otherwise be obtained 9
10 General Principles Limited NOS Option Body Part: Example: Liver is used when the specific liver lobe is not identified Approach: Open, Percutaneous and Via Natural or Artificial Opening are used when a more specific type of approach is not documented and cannot otherwise be determined Root Operation: Repair is used when the procedure documentation does not support a specific root operation and the information cannot otherwise be obtained 10
11 Code Structure Codes are comprised of seven components. Each component is called a character All codes are seven characters long Individual units for each character are represented by a letter or number Each unit is called a value 34 possible values for each character Digits 0-9 Letters A-H, J-N, P-Z 11
12 System Structure 16 Sections Medical and Surgical Obstetrics Placement Administration Measurement and Monitoring Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Extracorporeal Therapies Osteopathic Other Procedures Chiropractic Imaging Nuclear Medicine Radiation Oncology Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Mental Health Substance Abuse Treatment 12
13 Tables Each table contains four columns and varying numbers of rows Column: Row: Specifies the allowable values for characters 4-7 Specifies the valid combinations of values 13
14 Example: Table 0DB Excerpt 14
15 Index Provides the first three or four values of the code The tables must always be used to obtain the complete code No eponyms are included 15
16 Index Conventions Main index term is a root operation, root procedure type, or common procedure name Examples: Resection (root operation) Fluoroscopy (root type) Prostatectomy (common procedure name) Secondary entries are underneath the main term PCS Table or code reference as specific as possible 16
17 Index Entry by Body Part Bypass Aorta, Thoracic 021W Aorta, Abdominal 0410 Artery, Axillary, Left Artery, Axillary, Right Artery, Brachial, Left Artery, Brachial, Right Artery, Common Carotid, Left 031J0 Artery, Common Carotid, Right 031H0 17
18 Medical and Surgical Section 18
19 Medical and Surgical Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Part 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Device 7 th Character = Qualifier 19
20 Medical and Surgical Section Principles The root operation is based on the objective of the procedure If multiple procedures as defined by distinct objectives are performed, then multiple codes are assigned 20
21 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Principles Value is consistent throughout the section Approach Value is consistent throughout the section Body part Value is consistent within a specific body system 21
22 Section Character Medical and Surgical Section 22
23 Section (Character 1) Defines the general type of procedure In the Medical and Surgical Section the first character is always the number 0 23
24 Body System Character Medical and Surgical Section 24
25 Body System (Character 2) Defines the general physiological system on which the procedure is performed, or anatomical region where the procedure is performed Uses generally accepted anatomical or physiological categories Some traditional categories are subdivided into several body systems. Cardiovascular is subdivided into five body systems: Heart and Great Vessels Upper Veins Upper Arteries Lower Veins Lower Arteries 25
26 Medical and Surgical Section Body Systems Central Nervous Peripheral Nervous Heart and Great Vessels Upper Arteries Lower Arteries Upper Veins Lower Veins Lymphatic and Hemic Eye Ear, Nose, Sinus Respiratory Mouth and Throat Gastrointestinal Hepatobiliary and Pancreas Endocrine Skin and Breast Subcutaneous Tissue and Fascia Muscles Tendons Bursae and Ligaments Head and Facial Bones Upper Bones Lower Bones Upper Joints Lower Joints Urinary Female Reproductive Male Reproductive Anatomical Regions, General Anatomical Regions, Upper Extremities Anatomical Regions, Lower Extremities 26
27 Root Operation Character Medical and Surgical Section 27
28 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation (Character 3) Defines the objective of the procedure 31 different root operation values Each root operation identifies a precise and distinct objective 28
29 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Alteration Bypass Change Control Creation Destruction Detachment Dilation Division Drainage Excision Extirpation Extraction Fragmentation Fusion Insertion Inspection Map Occlusion Reattachment Release Removal Repair Replacement Reposition Resection Restriction Revision Supplement Transfer Transplantation 29
30 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Principles The root operation is coded according to the objective of the procedure actually performed Discontinued or modified procedures coded to procedure actually performed Composite terms (e.g., colonoscopy, sigmoidectomy) are not root operations 30
31 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Principles Combination procedures are coded separately Each procedure with a distinct objective during an operative episode is coded separately The complete or partial redo of a procedure is coded to the root operation performed rather than Revision Revision is confined to correcting a malfunctioning or displaced device 31
32 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Groups Procedures that take out or eliminate all or a portion of a body part Procedures that involve putting in or on, putting back, or moving body parts Procedures that take out or eliminate solid matter, fluids, or gases from a body part Procedures that only involve examination of body parts and regions 32
33 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Groups Procedures that can be performed only on tubular body parts Procedures that always involve devices Procedures involving cutting or separation only Procedures involving other repairs Procedures with other objectives 33
34 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that take out or eliminate all or a portion of a body part»excision»resection»extraction»destruction»detachment 34
35 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Excision Definition Explanation Examples Cutting out or off, without replacement, a portion of a body part The qualifier Diagnostic is used to identify excision procedures that are biopsies Partial nephrectomy Liver biopsy 35
36 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Resection Definition Examples Cutting out or off, without replacement, all of a body part Total nephrectomy Total lobectomy of lung 36
37 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Extraction Definition Explanation Examples Pulling or stripping out or off all or a portion of a body part by the use of force The qualifier Diagnostic is used to identify extraction procedures that are biopsies Dilation and curettage Vein stripping 37
38 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Destruction Definition Explanation Examples Physical eradication of all or a portion of a body part by the direct use of energy, force or a destructive agent None of the body part is physically taken out Fulguration of rectal polyp Cautery of skin lesion 38
39 Definition Explanation Examples Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Detachment Cutting off all or part of the upper or lower extremities The body part value is the site of the detachment, with a qualifier if applicable to further specify the level where the extremity was detached Below knee amputation Disarticulation of shoulder 39
40 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that involve putting in or on, putting back, or moving living body parts» Transplantation» Reattachment» Reposition» Transfer 40
41 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Transplantation Definition Explanation Examples Putting in or on all or a portion of a living body part taken from another individual or animal to physically take the place and/or function of all or a portion of a similar body part The native body part may or may not be taken out, and the transplanted body part may take over all or a portion of its function Kidney transplant Heart transplant 41
42 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Reattachment Definition Explanation Examples Putting back in or on all or a portion of a separated body part to its normal location or other suitable location Vascular circulation and nervous pathways may or may not be reestablished Reattachment of hand Reattachment of avulsed kidney 42
43 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Reposition Definition Explanation Examples Moving to its normal location or other suitable location all or a portion of a body part The body part is moved to a new location from an abnormal location, or from a normal location where it is not functioning correctly. The body part may or may not be cut out or off to be moved to the new location Reposition of undescended testicle Fracture reduction 43
44 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Transfer Definition Explanation Examples Moving, without taking out, all or a portion of a body part to another location to take over the function of all or a portion of a body part The body part transferred remains connected to its vascular and nervous supply Tendon transfer Skin pedicle flap transfer 44
45 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that take out or eliminate solid matter, fluids or gases from a body part» Drainage» Extirpation» Fragmentation 45
46 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Drainage Definition Explanation Examples Taking or letting out fluids and/or gases from a body part The qualifier Diagnostic is used to identify drainage procedures that are biopsies Thoracentesis Incision and drainage 46
47 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Extirpation Definition Explanation Examples Taking or cutting out solid matter from a body part The solid matter may be an abnormal byproduct of a biological function or a foreign body; it may be imbedded in a body part or in the lumen of a tubular body part. The solid matter may or may not have been previously broken into pieces Thrombectomy Choledocholithotomy 47
48 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Fragmentation Definition Explanation Examples Breaking solid matter in a body part into pieces Physical force (e.g., manual, ultrasonic) applied directly or indirectly is used to break the solid matter into pieces. The solid matter may be an abnormal byproduct of a biological function or a foreign body. The pieces of solid matter are not taken out Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy Transurethral lithotripsy 48
49 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that only involve examination of body parts and regions»inspection»map 49
50 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Inspection Definition Explanation Examples Visually and/or manually exploring a body part Visual exploration may be performed with or without optical instrumentation. Manual exploration may be performed directly or through intervening body layers Diagnostic arthroscopy Exploratory laparotomy 50
51 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Map Definition Explanation Examples Locating the route of passage of electrical impulses and/or locating functional areas in a body part Applicable only to the cardiac conduction mechanism and the central nervous system Cardiac mapping Cortical mapping 51
52 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that can be performed only on tubular body parts»bypass»dilation»occlusion»restriction 52
53 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Bypass Definition Explanation Examples Altering the route of passage of the contents of a tubular body part Rerouting contents of a body part to a downstream area of the normal route, to a similar route and body part, or to an abnormal route and dissimilar body part. Includes one or more anastomoses, with or without the use of a device Coronary artery bypass Colostomy formation 53
54 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Dilation Definition Explanation Examples Expanding an orifice or the lumen of a tubular body part The orifice can be a natural orifice or an artificially created orifice. Accomplished by stretching a tubular body part using intraluminal pressure or by cutting part of the orifice or wall of the tubular body part Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty Pyloromyotomy 54
55 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Occlusion Definition Explanation Example Completely closing the orifice or lumen of a tubular body part The orifice can be a natural orifice or an artificially created orifice Fallopian tube ligation Ligation of inferior vena cava 55
56 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Restriction Definition Explanation Examples Partially closing the orifice or lumen of a tubular body part The orifice can be a natural orifice or an artificially created orifice Esophagogastric fundoplication Cervical cerclage 56
57 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures that always involve devices» Insertion» Replacement» Supplement» Removal» Change» Revision 57
58 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Insertion Definition Examples Putting in a nonbiological appliance that monitors, assists, performs or prevents a physiological function but does not physically take the place of a body part Insertion of radioactive implant Insertion of central venous catheter 58
59 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Replacement Definition Explanation Examples Putting in or on biological or synthetic material that physically takes the place and/or function of all or a portion of a body part The body part may have been taken out or replaced, or may be taken out, physically eradicated, or rendered nonfunctional during the Replacement procedure. A Removal procedure is coded for taking out the device used in a previous replacement procedure Total hip replacement, bone graft Free skin graft 59
60 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Supplement Definition Explanation Examples Putting in or on biological or synthetic material that physically reinforces or augments the function of a body part The biological material is non-living, or the biological material is living and from the same individual. The body part may have been previously replaced. If the body part has been previously replaced, the Supplement procedure is performed to physically reinforce and/or augment the function of the replaced body part Herniorrhaphy using mesh, free nerve mitral valve ring annuloplasty, put a new acetabular liner in a previous hip replacement 60
61 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Removal Definition Explanation Examples Taking out or off a device from a body part If a device is taken out and a similar device put in without cutting or puncturing the skin or mucous membrane, the procedure is coded to the root operation Change. Otherwise, the procedure for taking out a device is coded to the root operation Removal Drainage tube removal Cardiac pacemaker removal 61
62 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Change Definition Explanation Examples Taking out or off a device from a body part and putting back an identical or similar device in or on the same body part without cutting or puncturing the skin or a mucous membrane All Change procedures are coded using the approach External Urinary catheter change Gastrostomy tube change 62
63 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Revision Definition Explanation Examples Correcting, to the extent possible, a malfunctioning or displaced device Revision can include correcting a malfunctioning or displaced device by taking out or putting in components of the device such as a screw Adjustment of position of pacemaker lead Recementing of hip prosthesis 63
64 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures involving cutting or separation only»division»release 64
65 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Division Definition Explanation Cutting into a body part without draining fluids and/or gasses from the body part in order to separate or transect a body part All or a portion of the body part is separated into two or more portions Examples Spinal cordotomy, osteotomy 65
66 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Release Definition Explanation Examples Freeing a body part from an abnormal physical constraint by cutting or by use of force Some of the restraining tissue may be taken out but none of the body part is taken out Adhesiolysis Carpal tunnel release 66
67 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures involving other repairs»control»repair 67
68 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Control Definition Explanation Examples Stopping, or attempting to stop, post-procedure bleeding The site of the bleeding is coded as an anatomical region and not to a specific body part Control of post-prostatectomy hemorrhage Control of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage 68
69 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Repair Definition Explanation Examples Restoring, to the extent possible, a body part to its normal anatomic structure and function Used only when the method to accomplish the repair is not one of the other root operations Colostomy takedown Suture of laceration 69
70 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Procedures with other objectives»alteration»creation»fusion 70
71 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Alteration Definition Modifying the anatomical structure of a body part without affecting the function of the body part Explanation Principal purpose is to improve appearance Examples Face lift Breast augmentation 71
72 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Creation Definition Explanation Examples Making a new genital structure that does not take over the function of a body part Used only for sex change operations Creation of vagina in a male Creation of penis in a female 72
73 Medical and Surgical Section Root Operations Fusion Definition Joining together portions of an articular body part rendering the articular body part immobile Explanation The body part is joined together by fixation device, bone graft, or other means Examples Spinal fusion Ankle arthrodesis 73
74 Body Part Character Medical and Surgical Section 74
75 Medical and Surgical Section Body Part Character (Character 4) Defines the specific anatomical site where the procedure is performed 34 possible body part values in each body system 75
76 Medical and Surgical Section Body Part Values Hepatobiliary and Pancreas Liver Liver, Right Lobe Liver, Left Lobe Gallbladder Hepatic Duct, Right Hepatic Duct, Left Cystic Duct Common Bile Duct Ampulla of Vater Pancreatic Duct Pancreatic Duct, Accessory Pancreas 76
77 Approach Character Medical and Surgical Section 77
78 Medical and Surgical Section Approach (Character 5) Defines the technique used to reach the site of the procedure 7 different approach values 78
79 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Approaches through the skin or mucous membrane Open Percutaneous Percutaneous Endoscopic 79
80 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions OPEN Cutting through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to expose the site of the procedure Example: Abdominal hysterectomy 80
81 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions PERCUTANEOUS Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure Example: Needle biopsy of liver 81
82 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions PERCUTANEOUS ENDOSCOPIC Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach and visualize the site of the procedure Example: Arthroscopy 82
83 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Approaches through an orifice Via Natural or Artificial Opening Via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic Via Natural or Artificial Opening with Percutaneous Endoscopic Assistance 83
84 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions VIA NATURAL OR ARTIFICIAL OPENING Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening to reach the site of the procedure Example: Endotracheal intubation 84
85 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions VIA NATURAL OR ARTIFICIAL OPENING ENDOSCOPIC Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening to reach and visualize the site of the procedure Example: Sigmoidoscopy 85
86 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions VIA NATURAL OR ARTIFICIAL OPENING WITH PERCUTANEOUS ENDOSCOPIC ASSISTANCE Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening and entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to aid in the performance of the procedure Example: Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy 86
87 Medical and Surgical Section Approach Definitions EXTERNAL Procedures performed directly on the skin or mucous membrane and procedures performed indirectly by the application of external force through the skin or mucous membrane Example: Closed fracture reduction 87
88 Device Character Medical and Surgical Section 88
89 Medical and Surgical Section Device Character (Character 6) The term device includes only devices that remain after the procedure is completed Instruments that describe how a procedure is performed are not specified in the device character Instruments for visualization are specified in the approach character Materials incidental to a procedure such as clips and sutures are not considered devices 89
90 Medical and Surgical Section Device Categories Biological or synthetic material that takes the place of all or a portion of a body part (e.g., skin graft, joint prosthesis) Biological or synthetic material that assists or prevents a physiological function (e.g., urinary catheter, IUD) 90
91 Medical and Surgical Section Device Categories Therapeutic material that is not absorbed by, eliminated by, or incorporated into a body part (e.g., radioactive implant, orthopedic pins). Therapeutic materials that are considered devices can be removed Mechanical or electronic appliances used to assist, monitor, take the place of, or prevent a physiological function (e.g., diaphragmatic pacemaker, hearing device) 91
92 Medical and Surgical Section Examples of Device Values Drainage Device Radioactive Element Autologous Tissue Substitute Extraluminal Device Intraluminal Device Synthetic Substitute Nonautologous Tissue Substitute 92
93 Qualifier Medical and Surgical Section 93
94 Medical and Surgical Section Qualifier (Character 7) Defines an additional attribute of the procedure performed, if applicable May have a narrow application, to a specific root operation, body system, or body part 94
95 Medical and Surgical Section Examples of Qualifiers Type of transplant Second site for a bypass Diagnostic excision (biopsy) 95
96 Obstetrics Section 96
97 Obstetrics Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Part 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Device 7 th Character = Qualifier 97
98 Obstetrics Section Includes only procedures performed on the products of conception Operations on the pregnant female are coded in the Medical and Surgical section (e.g., episiotomy) Two root operations unique to this section Other root operations same as Medical and Surgical section (e.g., Drainage, Inspection) 98
99 Obstetrics Section Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system: Pregnancy 99
100 Obstetrics Section Root Operation (Character 3) Abortion: Delivery: Artificially terminating a pregnancy Assisting the passage of the products of conception from the genital canal 100
101 Obstetrics Section Body Part (Character 4) Contains three different values for body part Products of Conception Products of Conception, Retained Products of Conception, Ectopic 101
102 Obstetrics Section Body Part Products of conception refers to all components of a pregnancy, including the fetus, embryo, amnion, umbilical cord and placenta There is no differentiation of the products of conception based on gestational age 102
103 Obstetrics Section Device (Character 6) Some device values unique to this section Examples: Laminaria Abortifacient Monitoring Electrode 103
104 Obstetrics Section Qualifier (Character 7) Values are dependent on the root operation, approach, or body part Examples (root operation dependent): Method of extraction (e.g., low forceps, vacuum) Substance drained (e.g., amniotic fluid, fetal blood) 104
105 Obstetrics Section Table 10D 105
106 Placement Section 106
107 Placement Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Region/ Orifice 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Device 7 th Character = Qualifier 107
108 Placement Section Body System (Character 2) Contains two body system values: Anatomical Regions Anatomical Orifices 108
109 Placement Section Root Operation (Character 3) Five root operations unique to this section Compression Dressing Immobilization Packing Traction Two root operations common to other sections Change Removal 109
110 Placement Section Root Operation (Character 3) Compression: Dressing: Immobilization: Packing: Traction: Putting pressure on a body region Putting material on a body region for protection Limiting or preventing motion of a body region Putting material in a body region or orifice Exerting a pulling force on a body region in a distal direction 110
111 Placement Section Body Regions/Orifices (Character 4) Two types of values: External body regions (e.g., chest wall) Natural orifices (e.g., mouth and pharynx) 111
112 Placement Section Device (Character 6) Specifies the material or device in the placement procedure (e.g., splint, bandage) Includes casts for fractures and dislocations Devices in the placement section are off the shelf and do not require any extensive design, fabrication or fitting The placement of devices that require extensive design, fabrication or fitting are coded in the Rehabilitation section 112
113 Placement Section Table 2Y4 113
114 Administration Section 114
115 Administration Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Physiological System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body System/ Region 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Substance 7 th Character = Qualifier 115
116 Administration Section Body System (Character 2) Contains three body system values: Physiological Systems and Anatomical Regions Circulatory Indwelling Device 116
117 Administration Section Root Operation (Character 3) Physiological Systems and Anatomical Regions Introduction: Irrigation: Putting in a therapeutic, diagnostic, nutritional, physiological or prophylactic substance except blood or blood products Putting in or on a cleansing substance 117
118 Administration Section Root Operation (Character 3) Circulatory System Transfusion: Putting in blood or blood products 118
119 Administration Section Root Operation (Character 3) Indwelling Device Irrigation: Putting in or on a cleansing substance 119
120 Administration Section Body Part (Character 4) For Introduction, the body part specifies where the procedure occurs and not necessarily the site where the substance introduced has an effect For Irrigation, the body part specifies the site of the irrigation 120
121 Administration Section Approach (Character 5) Approach uses values defined in the Medical and Surgical section The approach value for intradermal, subcutaneous and intramuscular introductions (i.e., injections) is percutaneous If a catheter is used to introduce a substance into a site within the circulatory system, the approach value is also percutaneous 121
122 Administration Section Substance (Character 6) Substances are specified in broad categories Substance values depend on body part 122
123 Administration Section Substance Physiological System & Anatomical Regions Antineoplastic Thrombolytic Anti-infective Anti-inflammatory Radioactive Substance Nutritional Substance Electrolytic and Water Balance Substance Irrigating Substance Dialysate Examples: Local Anesthetic Regional Anesthetic Inhalation Anesthetic Gas Contrast Agent Fertilized Ovum Sperm Pigment Platelet Inhibitor Destructive Agent 123
124 Administration Section Substance Circulatory System Examples: Serum Albumin Frozen Plasma Fresh Plasma Plasma Cryoprecipitate Red Blood Cells Stem Cells, Hematopoietic White Cells Platelets Globulin Fibrinogen Factor IX Bone Marrow 124
125 Administration Section Qualifier (Character 7) May further specify a substance Examples: High-dose Interleukin-2 Liquid Brachytherapy Isotope Insulin 125
126 Administration Section Table 302 Excerpt 126
127 Measurement and Monitoring Section 127
128 Measurement and Monitoring Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Physiological System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body System 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Function 7 th Character = Qualifier 128
129 Measurement and Monitoring Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system value: Physiological Systems 129
130 Measurement and Monitoring Root Operation (Character 3) Measurement: Determining the level of a physiological or physical function at a point in time Monitoring: Determining the level of a physiological or physical function repetitively over a period of time 130
131 Measurement and Monitoring Approach (Character 5) Approach contains values also in the Medical and Surgical section Examples: Percutaneous Via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic 131
132 Measurement and Monitoring Function (Character 6) Specifies physiological or physical functions (e.g., nerve conductivity, cardiac electrical activity, respiratory capacity) 132
133 Measurement and Monitoring Table 4A1 Excerpt 133
134 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Section 134
135 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Physiological System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body System 5 th Character = Duration 6 th Character = Function 7 th Character = Qualifier 135
136 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system value: Physiological Systems 136
137 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Root Operation Assistance: Performance: Restoration: (Character 3) Taking over a portion of a physiological function by extracorporeal means Completely taking over a physiological function by extracorporeal means Returning, or attempting to return, a physiological function to its normal state by extracorporeal means 137
138 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Duration (Character 5) Specifies whether the procedure was a single occurrence, multiple occurrence, intermittent, or continuous For respiratory ventilation assistance or performance, the range of hours is specified (<24 hours, hours or >96 hours) 138
139 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Function (Character 6) Specifies the physiological function assisted or performed (e.g., oxygenation, ventilation) 139
140 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Qualifier (Character 7) May specify equipment used in the procedure (e.g., balloon pump) 140
141 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance Table 5A2 141
142 Extracorporeal Therapies Section 142
143 Extracorporeal Therapies Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Physiological System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body System 5 th Character = Duration 6 th Character = Qualifier 7 th Character = Qualifier 143
144 Extracorporeal Therapies Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system value: Physiological Systems 144
145 Extracorporeal Therapies Root Operation (Character 3) Contains ten root operation values: Atmospheric Control Pheresis Decompression Phototherapy Electromagnetic Therapy Ultrasound Therapy Hyperthermia Ultraviolet Light Hypothermia Therapy Shock Wave Therapy 145
146 Extracorporeal Therapies Duration (Character 5) Specifies whether the procedure was a single occurrence, multiple occurrence, or intermittent 146
147 Osteopathic Section 147
148 1 st Character = Section Osteopathic Section Character Specification 2 nd Character = Anatomical Regions 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Region 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Method 7 th Character = Qualifier 148
149 Osteopathic Section Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system value: Anatomical Regions 149
150 Osteopathic Section Root Operation (Character 3) Contains a single root operation value Treatment: Manual treatment to eliminate or alleviate somatic dysfunction and related disorders 150
151 Osteopathic Section Method (Character 6) Articulatory - Raising Fascial Release General Mobilization High Velocity - Low Amplitude Indirect Low Velocity- High Amplitude Lymphatic Pump Muscle Energy - Isometric Muscle Energy - Isotonic Other Method 151
152 Other Procedures Section 152
153 Other Procedures Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Physiological Systems/ Anatomical Regions 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Region 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Method 7 th Character = Qualifier 153
154 Other Procedures Section Root Operation (Character 3) Contains a single root operation value Other Procedures: Methodologies which attempt to remediate or cure a disorder or disease 154
155 Other Procedures Section Body Region (Character 4) Contains physiological system and anatomical region values: Nervous System Circulatory System Head and Neck Region Integumentary System and Breast Musculoskeletal System Female Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Trunk Region Upper Extremity Lower Extremity None 155
156 Miscellaneous Section Method (Character 6) Acupuncture Therapeutic Massage Collection Computer Assisted Procedure Robotic Assisted Procedure Near Infrared Spectroscopy Other Method 156
157 Chiropractic Section 157
158 Chiropractic Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Anatomical Regions 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Region 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Method 7 th Character = Qualifier 158
159 Chiropractic Section Body System (Character 2) Contains a single body system value: Anatomical Regions 159
160 Chiropractic Section Root Operation (Character 3) Contains a single root operation value Manipulation: Manual procedure that involves a directed thrust to move a joint past the physiological range of motion, without exceeding the anatomical limit 160
161 Chiropractic Section Method (Character 6) Non-Manual Indirect Visceral Extra-Articular Direct Visceral Long Lever Specific Contact Long and Short Lever Specific Contact Mechanically Assisted Other Method 161
162 Imaging Section 162
163 Imaging Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Body Part 5 th Character = Contrast 6 th Character = Qualifier 7 th Character = Qualifier 163
164 Imaging Section Contains diagnostic radiology procedures Nuclear medicine is a separate section Radiation Oncology is a separate section Interventional Radiology The intervention procedure is coded in the Medical and Surgical section 164
165 Imaging Section Root Type (Character 3) Plain Radiography Fluoroscopy CT Scan MRI Ultrasound 165
166 Imaging Section Root Type Definitions (Character 3) 166
167 Imaging Section Root Type Plain Radiography Planar display of an image developed from the capture of external ionizing radiation on photographic or photoconductive plate 167
168 Imaging Section Root Type Fluoroscopy Single plane or bi-plane real time display of an image developed from the capture of external ionizing radiation on a fluorescent screen. The image may also be stored by either digital or analog means 168
169 Imaging Section Root Type Computerized Tomography (CT Scan) Computer-reformatted digital display of multiplanar images developed from the capture of multiple exposures of external ionizing radiation 169
170 Imaging Section Root Type Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Computer-reformatted digital display of multiplanar images developed from the capture of radio-frequency signals emitted by nuclei in a body site excited within a magnetic field 170
171 Imaging Section Root Type Ultrasonography Real time display of images of anatomy or flow information developed from the capture of reflected and attenuated high frequency sound waves 171
172 Imaging Section Contrast Material (Character 5) Contrast is differentiated by the concentration of the contrast material (e.g., high or low osmolar) 172
173 Imaging Section Qualifier (Character 6) Specifies an imaging procedure without contrast followed by contrast 173
174 Nuclear Medicine Section 174
175 Nuclear Medicine Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Body Part 5 th Character = Radionuclide 6 th Character = Qualifier 7 th Character = Qualifier 175
176 Nuclear Medicine Section Type Definitions (Character 3) 176
177 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Planar Imaging Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for a single plane display of images developed from the capture of radioactive emissions 177
178 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Tomographic (Tomo) Imaging Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for three dimensional display of images developed from the capture of radioactive emissions 178
179 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Positron Emission Tomographic (PET) Imaging Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for three dimensional display of images developed from the simultaneous capture, 180 degrees apart, of radioactive emissions 179
180 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Nonimaging Uptake Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for measurements of organ function, from the detection of radioactive emissions 180
181 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Nonimaging Probe Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for the study of distribution and fate of certain substances by the detection of radioactive emissions; or, alternatively, measurement of absorption of radioactive emissions from an external source 181
182 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Nonimaging Assay Introduction of radioactive materials into the body for the study of body fluids and blood elements, by the detection of radioactive emissions 182
183 Nuclear Medicine Root Type Systemic Therapy Introduction of unsealed radioactive materials into the body for treatment 183
184 Nuclear Medicine Section Body Part (Character 4) Indicates the body part or region to the degree of specificity that is usual and appropriate for the section Regional (e.g., lower extremity veins) and combination body parts (e.g., liver and spleen) are commonly used 184
185 Nuclear Medicine Section Radionuclide (Character 5) Character 5 is the source of the radiation An Other Radionuclide option is included for new FDA approved radiopharmaceuticals 185
186 Radiation Therapy Section 186
187 Radiation Therapy Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Treatment Site 5 th Character = Modality Qualifier 6 th Character = Isotope 7 th Character = Qualifier 187
188 Radiation Therapy Section Root Type (Character 3) Classified by the basic mode of radiation delivery used: Beam Radiation Brachytherapy Stereotactic Radiosurgery Other Radiation 188
189 Radiation Therapy Section Treatment Site (Character 4) Specifies the body part that is the target of the radiation therapy 189
190 Radiation Therapy Section Modality Qualifier (Character 5) Further specifies the type of radiation used: photons electrons heavy particles contact radiation 190
191 Radiation Therapy Section Isotope (Character 6) Specifies the isotope administered in oncology treatments 191
192 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Section 192
193 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Section Qualifier 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Body System and Region 5 th Character = Type Qualifier 6 th Character = Equipment 7 th Character = Qualifier 193
194 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Root Type (Character 3) Treatment: Use of specific activities or methods to develop, improve and/or restore the performance of necessary functions, compensate for dysfunction and /or minimize debilitation Assessment: Includes a determination of the patient s diagnosis when appropriate, need for treatment, planning for treatment, periodic assessment and documentation related to these activities 194
195 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Root Type (Character 3) Fitting(s): Design, fabrication, modification, selection and/or application of splint, orthosis, prosthesis, hearing aids and/or rehabilitation device Caregiver Training: Educating caregiver with the skills and knowledge used to interact with and assist the patient 195
196 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Body System and Region (Character 4) Body Systems Neurological System Circulatory System Respiratory System Integumentary System Musculoskeletal System Genitourinary System Body Regions - Head and Neck - Upper Back/Upper Extremity - Lower Back/Lower Extremity - Whole Body 196
197 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Type Qualifier (Character 5) Specifies the precise test or method employed Examples: Therapeutic exercise treatment Dressing or transfer assessment Prosthesis fitting Transfer caregiver training 197
198 Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology Equipment (Character 6) Specific types of equipment are not listed General categories of equipment are listed (e.g., physical agents, mechanical modalities, assistive/adaptive/supportive devices) 198
199 Mental Health Section 199
200 Mental Health Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Type Qualifier 5 th Character = Qualifier 6 th Character = Qualifier 7 th Character = Qualifier 200
201 Mental Health Section Psychological Tests Crisis Intervention Root Type (Character 3) Medication Management Individual Psychotherapy Counseling Family Psychotherapy Electroconvulsive Therapy Biofeedback Hypnosis Narcosynthesis Group Psychotherapy Light Therapy 201
202 Mental Health Section Type Qualifier (Character 4) Type qualifier provides additional specificity Not all types have type qualifier 202
203 Mental Health Section Type Qualifier (Character 4) Example: Psychological Tests Developmental Personality and Behavioral Intellectual and Psychoeducational Neuropsychological Neurobehavioral and Cognitive Status 203
204 Mental Health Section Qualifier (Character 5-7 ) Have a value of Z None 204
205 Substance Abuse Treatment Section 205
206 1 st Character = Section Substance Abuse Section Character Specification 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Type 4 th Character = Type Qualifier 5 th Character = Qualifier 6 th Character = Qualifier 7 th Character = Qualifier 206
207 Substance Abuse Treatment Root Type (Character 3) Detoxification Services Individual Counseling Group Counseling Individual Psychotherapy Family Counseling Medication Management Pharmacotherapy 207
208 Substance Abuse Treatment Type Qualifier (Character 4) Type qualifier provides additional specificity Not all types have type qualifier 208
209 Substance Abuse Treatment Type Qualifier (Character 4) Example: Pharmacotherapy Nicotine Replacement Therapy Methadone Maintenance LAAM Antabuse Naltrexone Naloxone Clonidine Bupropion Psychiatric Medications Other Replacement Medication 209
210 Substance Abuse Treatment Qualifier (Character 5-7 ) Have a value of Z None 210
211 New Technology Section 211
212 New Technology Section Character Specification 1 st Character = Section 2 nd Character = Body System 3 rd Character = Root Operation 4 th Character = Body Part 5 th Character = Approach 6 th Character = Device/Substance/Technology 7 th Character = Qualifier 212
213 New Technology Section Root Operation (Character 3) Uses the same root operation values as their counterparts in other sections of Example: The root operation Introduction has the same definition as its counterpart in Administration section of 213
214 New Technology Section Body Part (Character 4) Uses the same body part values that are used in other sections of. Example: Central Vein body part value has its counterpart in the Administration section of 214
215 New Technology Section Approach (Character 5) Uses the same approach values as their closest counterparts in other sections of. External Open Percutaneous Percutaneous Endoscopic Via Natural or Artificial Opening Via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic Via Natural or Artificial Opening With Percutaneous Endoscopic Assistance 215
216 New Technology Section Device/Substance/Technology (Character 6) Contains a general description of the key feature of the new technology Example: Ceftazidime-Avibactam Antiinfective is an example of a new technology substance 216
217 New Technology Section Qualifier (Character 7) Used exclusively to indicate the New Technology Group A number or letter that changes each year that new technology codes are added to the system Allows the to recycle the values in the third, fourth, and sixth characters as needed 217
218 Testing 218
219 Testing Tested by Clinical Data Abstraction Centers (CDACs) FMAS, Columbia, MD DynKePRO, York, PA Coded 5,000 records Offered feedback on issues found Suggested improvements Additional comparison test of 100 records Additional testing on ambulatory records 219
220 Major Modifications as a Result of Testing Limited Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) options added Number of approaches reduced Training manual revised Index entries added 220
221 Testing Findings More complete than ICD-9-CM, greater specificity Easy to expand the system Multi-axial structure makes it easier to analyze Standardized terminology makes it easier to use once the coder has initial training 221
222 Testing Findings Initial training time will be a factor since it differs significantly from ICD-9-CM Having all terms defined makes it easier to teach Once basic knowledge is acquired, the coder does not use the index 222
Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS)
 Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) Richard F. Averill, M.S., Robert L. Mullin, M.D., Barbara A. Steinbeck, ART, Norbert I. Goldfield, M.D, Thelma M. Grant, RRA The International
Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) Richard F. Averill, M.S., Robert L. Mullin, M.D., Barbara A. Steinbeck, ART, Norbert I. Goldfield, M.D, Thelma M. Grant, RRA The International
Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS)
 Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) Richard F. Averill, M.S., Robert L. Mullin, M.D., Barbara A. Steinbeck, RHIT, Norbert I. Goldfield, M.D, Thelma M. Grant, RHIA, Rhonda R.
Development of the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) Richard F. Averill, M.S., Robert L. Mullin, M.D., Barbara A. Steinbeck, RHIT, Norbert I. Goldfield, M.D, Thelma M. Grant, RHIA, Rhonda R.
Preparing for ICD-10: Understanding the Basics of ICD-10-PCS. Nelly Leon-Chisen, RHIA Director, Coding and Classification
 Preparing for ICD-10: Understanding the Basics of ICD-10-PCS Nelly Leon-Chisen, RHIA Director, Coding and Classification Learning Objectives Learn the basics of ICD-10-PCS code selection and how to navigate
Preparing for ICD-10: Understanding the Basics of ICD-10-PCS Nelly Leon-Chisen, RHIA Director, Coding and Classification Learning Objectives Learn the basics of ICD-10-PCS code selection and how to navigate
Long Island Health Information Management Association
 PREPARATION www.pwc.com IS THE KEY TO SUCCESS Long Island Health Information Management Association 2014 Annual Meeting-ICD-10-PCS Boot Camp April 2, 2014 John W. Ruth, MBA, RHIA Director, Health Industries
PREPARATION www.pwc.com IS THE KEY TO SUCCESS Long Island Health Information Management Association 2014 Annual Meeting-ICD-10-PCS Boot Camp April 2, 2014 John W. Ruth, MBA, RHIA Director, Health Industries
Oregon CPT Preapproval Grid
 * The following grid only identifies items that require preapproval from. Breast Pumps Notes: No preapproval required for 1st month rental; beyond one month rental requires preapproval Genetic Testing
* The following grid only identifies items that require preapproval from. Breast Pumps Notes: No preapproval required for 1st month rental; beyond one month rental requires preapproval Genetic Testing
Preliminary 12/10/07. ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual
 Preliminary 12/10/07 ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual 12/10/07 Preliminary ii ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual Preliminary 12/10/07 THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DISEASES Tenth Revision Procedure Coding System
Preliminary 12/10/07 ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual 12/10/07 Preliminary ii ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual Preliminary 12/10/07 THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DISEASES Tenth Revision Procedure Coding System
Head Start to Implementation: Preparing Now for ICD-10 (Focus on PCS)
 Head Start to Implementation: Preparing Now for ICD-10 (Focus on PCS) 3M 2008. All rights reserved. Marc Berlinguet, MD, MPH, CSPQ- International Medical Manager, 3M HIS Spain, September 15 and 16, 2009
Head Start to Implementation: Preparing Now for ICD-10 (Focus on PCS) 3M 2008. All rights reserved. Marc Berlinguet, MD, MPH, CSPQ- International Medical Manager, 3M HIS Spain, September 15 and 16, 2009
CPT Code Changes for 2013
 CPT Code Changes for 2013 RADIOLOGY Cathy Woodall, CHC, CPC Nicholas Parish, CHC Compliance-Radiology McKesson Revenue Management Solutions This commentary is a summary prepared by McKesson s Revenue Management
CPT Code Changes for 2013 RADIOLOGY Cathy Woodall, CHC, CPC Nicholas Parish, CHC Compliance-Radiology McKesson Revenue Management Solutions This commentary is a summary prepared by McKesson s Revenue Management
The webinar will begin shortly
 Important Information for receiving your CE Certificate You will receive an email within 3-5 business days providing a LINK to the CE Certificate, the webinar recording and the presentation slides. This
Important Information for receiving your CE Certificate You will receive an email within 3-5 business days providing a LINK to the CE Certificate, the webinar recording and the presentation slides. This
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Exhibit 4 Effective January 1, 2009. Outpatient Surgery Facility Groupers and Fees 1/1/09 Group Description 1/1/09 1/1/09 Dollar Value
 Exhibit 4 Effective January 1, 2009 Outpatient Surgery Facility s and Fees 1 Level I Photochemotherapy 2 Level I Fine Needle Biopsy/Aspiration 3 Bone Marrow Biopsy/Aspiration $335.75 4 Level I Needle Biopsy/
Exhibit 4 Effective January 1, 2009 Outpatient Surgery Facility s and Fees 1 Level I Photochemotherapy 2 Level I Fine Needle Biopsy/Aspiration 3 Bone Marrow Biopsy/Aspiration $335.75 4 Level I Needle Biopsy/
DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY GENERAL SURGERY SECTION
 Privilege Request Form DIRECTIONS: This Privilege Request Form must accompany all initial applications for appointment to the General Surgery Section, Department of Surgery. Please indicate those privileges
Privilege Request Form DIRECTIONS: This Privilege Request Form must accompany all initial applications for appointment to the General Surgery Section, Department of Surgery. Please indicate those privileges
ICD-10-PCS Reference Manual
 Table of Contents Preface... xi Manual organization... xi Chapter 1 - Overview... xi Chapter 2 - Procedures in the Medical and Surgical section... xi Chapter 3 - Procedures in the Medical and Surgical-related
Table of Contents Preface... xi Manual organization... xi Chapter 1 - Overview... xi Chapter 2 - Procedures in the Medical and Surgical section... xi Chapter 3 - Procedures in the Medical and Surgical-related
Healthcare services requiring prior authorisation
 Annex 2 Healthcare requiring prior authorisation This list does not include organ transplants and does also not apply to long-term care and the primary purpose of which is to support people in need of
Annex 2 Healthcare requiring prior authorisation This list does not include organ transplants and does also not apply to long-term care and the primary purpose of which is to support people in need of
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Clinical Privileges Profile Physician Assistant. Indu & Raj Soin Medical Center
 Printed Name Clinical Privileges Profile Physician Assistant Indu & Raj Soin Medical Center Applicant: Check off the Requested box for each privilege requested. Applicants have the burden of producing
Printed Name Clinical Privileges Profile Physician Assistant Indu & Raj Soin Medical Center Applicant: Check off the Requested box for each privilege requested. Applicants have the burden of producing
Best of AHA Coding Clinic for ICD 10 PCS. Disclaimer
 Best of AHA Coding Clinic for ICD 10 PCS Wednesday, September 17, 2014 12:00 1:00pm CST 1 Disclaimer This audio conference is designed to provide accurate and authoritative information in regard to the
Best of AHA Coding Clinic for ICD 10 PCS Wednesday, September 17, 2014 12:00 1:00pm CST 1 Disclaimer This audio conference is designed to provide accurate and authoritative information in regard to the
2013 CPT Codes - Surgery
 Category Code Range New Deleted Revised Total Page SURGERY 10021-69990 47 11 22 80 Integumentary System 10021-19499 0 0 1 1 1 Musculoskeletal System 20000-29999 5 1 3 9 1 Respiratory Systen 30000-32999
Category Code Range New Deleted Revised Total Page SURGERY 10021-69990 47 11 22 80 Integumentary System 10021-19499 0 0 1 1 1 Musculoskeletal System 20000-29999 5 1 3 9 1 Respiratory Systen 30000-32999
CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (non-ivdd) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program
 CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (non-ivdd) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program Health Canada Regulations on Medical Devices Vancouver, B.C. October 29, 2007
CANADIAN RULE BASED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (non-ivdd) Life Sciences British Columbia NRC-Industry Research Assistance Program Health Canada Regulations on Medical Devices Vancouver, B.C. October 29, 2007
ICD-10. What Every Healthcare Professional Should Know. Shannon E. McCall RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, CPC, CPC-I, CCDS
 ICD-10 What Every Healthcare Professional Should Know Shannon E. McCall RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, CPC, CPC-I, CCDS ICD-10: What Every Healthcare Professional Should Know is published by HCPro, Inc. Copyright All
ICD-10 What Every Healthcare Professional Should Know Shannon E. McCall RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, CPC, CPC-I, CCDS ICD-10: What Every Healthcare Professional Should Know is published by HCPro, Inc. Copyright All
Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier)
 1 of 6 I. The Musculoskeletal System Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier) 1. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: The Comprehensive Health History 2. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: A Nursing Approach to
1 of 6 I. The Musculoskeletal System Medical Surgical Nursing (Elsevier) 1. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: The Comprehensive Health History 2. Med/Surg: Musculoskeletal System: A Nursing Approach to
53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology
 Learning Outcomes 53.1 Explain how x-rays are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. 53-2 CHAPTER 53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology 53.2 Compare invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures.
Learning Outcomes 53.1 Explain how x-rays are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. 53-2 CHAPTER 53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology 53.2 Compare invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures.
Radiologic Technology Training Program
 Radiologic Technology Training Program 438 Radiologic Technology Training Program Radiologic Technology Training Program Program Coordinator: Mansour, Zepure General Information The Radiologic Technology
Radiologic Technology Training Program 438 Radiologic Technology Training Program Radiologic Technology Training Program Program Coordinator: Mansour, Zepure General Information The Radiologic Technology
PHC4 35 Diseases, Procedures, and Medical Conditions for which Laboratory Data is Required Effective 10/1/2015
 PHC4 35 Diseases, Procedures, and Medical Conditions for which Laboratory Data is Required Effective 10/1/2015 Laboratory data is to be submitted for discharges in the following conditions: 1. Heart Attack
PHC4 35 Diseases, Procedures, and Medical Conditions for which Laboratory Data is Required Effective 10/1/2015 Laboratory data is to be submitted for discharges in the following conditions: 1. Heart Attack
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Procedure. 2 29827 $ 3,560 $ 1,476 Arthroscopy, shoulder, surgical; with rotator cuff repair 5.5% 241.1%
 Exhibit 1 Top 50% of Payments for Surgical s (Physician costs) On average, Workers' payments for Surgical s in are 256% the average allowed claim costs for Healthcare in. $6,000 $5,000 $4,000 Allowed Claim
Exhibit 1 Top 50% of Payments for Surgical s (Physician costs) On average, Workers' payments for Surgical s in are 256% the average allowed claim costs for Healthcare in. $6,000 $5,000 $4,000 Allowed Claim
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Cracking CPT Codes: An Interactive Discussion Presented by Tom Loughrey, CCS-P. Jumping Right In!
 Cracking CPT Codes: An Interactive Discussion Presented by Tom Loughrey, CCS-P Jumping Right In! Code the following: 38 year old female for right breast biopsy with percutaneous needle core using image
Cracking CPT Codes: An Interactive Discussion Presented by Tom Loughrey, CCS-P Jumping Right In! Code the following: 38 year old female for right breast biopsy with percutaneous needle core using image
V: Infusion Therapy. Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217
 V: Infusion Therapy Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217 Competency: V-1 Knowledge of Intravenous Therapy V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability to apply critical
V: Infusion Therapy Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217 Competency: V-1 Knowledge of Intravenous Therapy V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability to apply critical
The Medical Imaging Detective
 Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes
 RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes Radiology 2014 CPT Codes CMS has issued 36 new procedure codes (one is a radiation therapy code) for CY 2014 that directly pertain to radiology with 26 of those codes the result
RADIOLOGY 2014 CPT Codes Radiology 2014 CPT Codes CMS has issued 36 new procedure codes (one is a radiation therapy code) for CY 2014 that directly pertain to radiology with 26 of those codes the result
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P Director, HIM Solutions, AHIMA
 ICD-10-PCS: Let s Code, Part II Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P Director, HIM Solutions, AHIMA Agenda Coding questions answered ICD-10-PCS Coding Wrap-up of ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding ICD-10-PCS Coding Questions
ICD-10-PCS: Let s Code, Part II Kathryn DeVault, RHIA, CCS, CCS-P Director, HIM Solutions, AHIMA Agenda Coding questions answered ICD-10-PCS Coding Wrap-up of ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding ICD-10-PCS Coding Questions
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
APPLICATION FOR APPOINTMENT TO MEDICAL STAFF BAFFIN REGIONAL HOSPITAL IQALUIT, NU
 APPLICATION FOR APPOINTMENT TO MEDICAL STAFF BAFFIN REGIONAL HOSPITAL IQALUIT, NU Name: Your completed application MUST include COPIES of the following documents, otherwise it will not go forward to the
APPLICATION FOR APPOINTMENT TO MEDICAL STAFF BAFFIN REGIONAL HOSPITAL IQALUIT, NU Name: Your completed application MUST include COPIES of the following documents, otherwise it will not go forward to the
Your Map of the ICD-9 to ICD-10 PCS Conversion
 Your Map of the ICD-9 to ICD-10 PCS Conversion Table of Contents Disclaimer 3 Endoscopy 4 Interventional Cardiology 20 Neuromodulation 34 Peripheral Interventions 35 Rhythm Management and Electrophysiology
Your Map of the ICD-9 to ICD-10 PCS Conversion Table of Contents Disclaimer 3 Endoscopy 4 Interventional Cardiology 20 Neuromodulation 34 Peripheral Interventions 35 Rhythm Management and Electrophysiology
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Nurse Practitioner Privileges
 Boulder Community Health Medical Staff Department Nurse Practitioner Privileges Name: Please print To be eligible to request clinical privileges, the applicant must meet the following threshold criteria:
Boulder Community Health Medical Staff Department Nurse Practitioner Privileges Name: Please print To be eligible to request clinical privileges, the applicant must meet the following threshold criteria:
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Preparation iagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview"
 Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer Overview The Field - Preparation - Specialty Areas - Day in the Life - Earnings - Employment - Career Path Forecast - Professional Organizations The Field Diagnostic imaging
Pat Cox, CPC, CPC-H, CPMA, CPC-I, CEMC, CCS-P. Professional Medical Coding Education
 Pat Cox, CPC, CPC-H, CPMA, CPC-I, CEMC, CCS-P Professional Medical Coding Education Thank you for your interest in the upcoming Certified Professional Coder (CPC ) class. This session is a 16-week class
Pat Cox, CPC, CPC-H, CPMA, CPC-I, CEMC, CCS-P Professional Medical Coding Education Thank you for your interest in the upcoming Certified Professional Coder (CPC ) class. This session is a 16-week class
UPMC For Reference Only PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT 2014
 Summary of Services and Availability (by location) UPMC Each location has sufficient space, equipment, staffing and financial resources in place or available in sufficient time as required to support each
Summary of Services and Availability (by location) UPMC Each location has sufficient space, equipment, staffing and financial resources in place or available in sufficient time as required to support each
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner
 Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic
Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic
Treatment Category Inpatient Treatment Categories DRG (MS DRG) ICD9 [Hip & Knee Only]
![Treatment Category Inpatient Treatment Categories DRG (MS DRG) ICD9 [Hip & Knee Only] Treatment Category Inpatient Treatment Categories DRG (MS DRG) ICD9 [Hip & Knee Only]](/thumbs/27/9641615.jpg) NCCT List of Procedures Treatment Category Inpatient Treatment Categories DRG (MS DRG) ICD9 [Hip & Knee Only] Bariatric Surgery - Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass DRG - 288 MS DRG - 621 Cardiac Angioplasty
NCCT List of Procedures Treatment Category Inpatient Treatment Categories DRG (MS DRG) ICD9 [Hip & Knee Only] Bariatric Surgery - Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass DRG - 288 MS DRG - 621 Cardiac Angioplasty
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Patient Care Technician (Bridge Program)
 Patient Care Technician (Bridge Program) Introduction: At Prestige Medical Solutions we are fully vested in helping students succeed. Our vision is to be a great place to learn, where people are inspired
Patient Care Technician (Bridge Program) Introduction: At Prestige Medical Solutions we are fully vested in helping students succeed. Our vision is to be a great place to learn, where people are inspired
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Clinical Privileges Profile Diagnostic Radiology. Greene Memorial Hospital
 Printed Name Clinical Privileges Profile Diagnostic Radiology Greene Memorial Hospital Privileges are covered by an exclusive contract. Practitioners who are not a party to the contract are not eligible
Printed Name Clinical Privileges Profile Diagnostic Radiology Greene Memorial Hospital Privileges are covered by an exclusive contract. Practitioners who are not a party to the contract are not eligible
Coronary Arteries: Number of Vessels/Number of Stents
 Coronary Arteries: Number of Vessels/Number of Stents Issue Should code table 027 be revised to capture the number of coronary vessels treated and/or the number of coronary stents inserted? New Technology
Coronary Arteries: Number of Vessels/Number of Stents Issue Should code table 027 be revised to capture the number of coronary vessels treated and/or the number of coronary stents inserted? New Technology
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Surgical Technician (ORT) Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
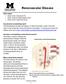 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Classification Rules for Medical Devices a
 Classification Rules for Medical Devices a The actual classification of each device depends on the precise claims made by the manufacturer and on its intended use. While the provision of examples in the
Classification Rules for Medical Devices a The actual classification of each device depends on the precise claims made by the manufacturer and on its intended use. While the provision of examples in the
V: Infusion Therapy. College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 181
 V: Infusion Therapy College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 181 Competency: V-1 Principles of V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
V: Infusion Therapy College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 181 Competency: V-1 Principles of V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes
 Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
Doctor of Physical Therapy Degree Curriculum:
 Doctor of Physical Therapy Degree Curriculum: SUMMER SEMESTER 1 st YEAR (BOTH SESSIONS) DPT 744 Gross Human Anatomy I 2 credits DPT 744L Gross Human Anatomy I Lab 1 credit DPT 745 Gross Human Anatomy II
Doctor of Physical Therapy Degree Curriculum: SUMMER SEMESTER 1 st YEAR (BOTH SESSIONS) DPT 744 Gross Human Anatomy I 2 credits DPT 744L Gross Human Anatomy I Lab 1 credit DPT 745 Gross Human Anatomy II
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
Medical Transcriptionist Online
 Education & Training Plan Medical Transcriptionist Online MyCAA Information Tuition: $3200 (RMT- AHDI exam included) MyCAA Course Code: LIT-MT2 Course Contact Hours: 185 Hours Program Duration: 3 Months
Education & Training Plan Medical Transcriptionist Online MyCAA Information Tuition: $3200 (RMT- AHDI exam included) MyCAA Course Code: LIT-MT2 Course Contact Hours: 185 Hours Program Duration: 3 Months
ICD-10-PCS Documentation and Coding for Spinal Procedures October 22, 2015
 Questions and Answers 1. We have a question regarding a spinal surgical procedure. The diagnosis was bilateral lateral recess stenosis and central stenosis from L2-L5. The procedure was an open lumbar
Questions and Answers 1. We have a question regarding a spinal surgical procedure. The diagnosis was bilateral lateral recess stenosis and central stenosis from L2-L5. The procedure was an open lumbar
HCIM ICD-10 Training Online Course Catalog August 2015
 HCIM ICD-10 Training Online Course Catalog August 2015 Course/Content Duration Quiz Duration CME Credits Assessments: Assessment: Provider - Baseline - E/M Emergency Department 45 5/1/2015 Assessment:
HCIM ICD-10 Training Online Course Catalog August 2015 Course/Content Duration Quiz Duration CME Credits Assessments: Assessment: Provider - Baseline - E/M Emergency Department 45 5/1/2015 Assessment:
Evaluation methods. Competency domain. Teaching methods. Goals and Objectives Procedure Elective PC P SBP. Clinical encounters
 rocedure Elective lease note that the list of procedures is comprehensive. GOAL: Diagnostic Testing. Use and perform common diagnostic tests and imaging studies, and technical and therapeutic procedures
rocedure Elective lease note that the list of procedures is comprehensive. GOAL: Diagnostic Testing. Use and perform common diagnostic tests and imaging studies, and technical and therapeutic procedures
INSURANCE COMPANY OF SCOTT AND WHITE FIXED INDEMNITY BASIC MEDICAL-SURGICAL EXPENSE POLICY REQUIRED OUTLINE OF COVERAGE
 INSURANCE COMPANY OF SCOTT AND WHITE FIXED INDEMNITY BASIC MEDICAL-SURGICAL EXPENSE POLICY REQUIRED OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (1) READ YOUR POLICY CAREFULLY. This outline of coverage provides a very brief description
INSURANCE COMPANY OF SCOTT AND WHITE FIXED INDEMNITY BASIC MEDICAL-SURGICAL EXPENSE POLICY REQUIRED OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (1) READ YOUR POLICY CAREFULLY. This outline of coverage provides a very brief description
Plastic Surgery ICD-10 Analysis
 Plastic Surgery ICD-10 Analysis Plastics The Hard Way with ICD-10 Z42 Encounter for plastic and reconstructive surgery following medical procedure or healed injury Z41.1 Encounter for cosmetic surgery
Plastic Surgery ICD-10 Analysis Plastics The Hard Way with ICD-10 Z42 Encounter for plastic and reconstructive surgery following medical procedure or healed injury Z41.1 Encounter for cosmetic surgery
Administering Medications
 Administering Medications Pharmacology for Healthcare Professionals seventh edition Donna F. Gauwitz, R.N., Nursing Consultant Senior Teaching Specialist of Nursing University of Minnesota Minnesota and
Administering Medications Pharmacology for Healthcare Professionals seventh edition Donna F. Gauwitz, R.N., Nursing Consultant Senior Teaching Specialist of Nursing University of Minnesota Minnesota and
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics
 Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell Basics What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells are the starting point from which the rest of the body grows. The adult human body is made up of hundreds of millions of different
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
www.backandspinefl.com Back and Spine Center 509 Riverside Dr., Suite 203 Stuart, FL 34994 Phone: (772) 288-5862
 Non-Profit ORG. U.S. Postage PAID West Palm BCH. FL. PERMIT NO. 4709 www.backandspinefl.com Back and Spine Center 509 Riverside Dr., Suite 203 Stuart, FL 34994 Phone: (772) 288-5862 The evolution of neurosurgery
Non-Profit ORG. U.S. Postage PAID West Palm BCH. FL. PERMIT NO. 4709 www.backandspinefl.com Back and Spine Center 509 Riverside Dr., Suite 203 Stuart, FL 34994 Phone: (772) 288-5862 The evolution of neurosurgery
Workers Compensation Insurance
 Workers Compensation Insurance New Hampshire Insurance Department Detailed Medical Cost Comparison The following exhibits compare the cost of Workers Compensation Medical services in New Hampshire to our
Workers Compensation Insurance New Hampshire Insurance Department Detailed Medical Cost Comparison The following exhibits compare the cost of Workers Compensation Medical services in New Hampshire to our
MODIFIER 59 ARTICLE. The CPT Manual defines modifier 59 as follows:
 MODIFIER 59 ARTICLE The Medicare National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) includes Procedure-to-Procedure (PTP) edits that define when two Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)/ Current Procedural
MODIFIER 59 ARTICLE The Medicare National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) includes Procedure-to-Procedure (PTP) edits that define when two Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)/ Current Procedural
ICD-10 Transition Overview
 ICD-10 Transition Overview Donna Pickett, MPH, RHIA OSELS/National Center for Health Statistics Centers for Disease Control and Prevention U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease
ICD-10 Transition Overview Donna Pickett, MPH, RHIA OSELS/National Center for Health Statistics Centers for Disease Control and Prevention U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
Medical Recovery Insurance Company Guide. Let MyRecoveryCheque TM ease the financial pain of a hospital stay. www.myrecoverycheque.co.
 Medical Recovery Insurance Company Guide Let MyRecoveryCheque TM ease the financial pain of a hospital stay www.myrecoverycheque.co.uk Introducing MyRecoveryCheque TM Many employees today are concerned
Medical Recovery Insurance Company Guide Let MyRecoveryCheque TM ease the financial pain of a hospital stay www.myrecoverycheque.co.uk Introducing MyRecoveryCheque TM Many employees today are concerned
surg urin Surgery: Urinary System 1
 Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
ALBERTA HEALTH CARE INSURANCE PLAN
 ALBERTA HEALTH CARE INSURANCE PLAN Podiatry Procedure List As Of 01 October 2007 ALBERTA HEALTH CARE INSURANCE PLAN Page i Generated 2007/09/26 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2007/10/01 I. CERTAIN DIAGNOSTIC
ALBERTA HEALTH CARE INSURANCE PLAN Podiatry Procedure List As Of 01 October 2007 ALBERTA HEALTH CARE INSURANCE PLAN Page i Generated 2007/09/26 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2007/10/01 I. CERTAIN DIAGNOSTIC
Schedule of Benefits HARVARD PILGRIM LAHEY HEALTH VALUE HMO MASSACHUSETTS MEMBER COST SHARING
 Schedule of s HARVARD PILGRIM LAHEY HEALTH VALUE HMO MASSACHUSETTS ID: MD0000003378_ X Please Note: In this plan, Members have access to network benefits only from the providers in the Harvard Pilgrim-Lahey
Schedule of s HARVARD PILGRIM LAHEY HEALTH VALUE HMO MASSACHUSETTS ID: MD0000003378_ X Please Note: In this plan, Members have access to network benefits only from the providers in the Harvard Pilgrim-Lahey
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
CORE MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
SURGICAL SERVICES. Touching Lives
 SURGICAL SERVICES Touching Lives with MODERN TOOLS of EXPERT PHYSICIANS in the Hands and Staff FROM DISCOVERY TO RECOVERY St. Mary s Health System offers a full range of surgical services in almost every
SURGICAL SERVICES Touching Lives with MODERN TOOLS of EXPERT PHYSICIANS in the Hands and Staff FROM DISCOVERY TO RECOVERY St. Mary s Health System offers a full range of surgical services in almost every
Workers Compensation Medical Costs in NH Significantly Higher
 EMBARGOED: FOR RELEASE THURSDAY, MAY 22, 10 AM NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL: May 22, 2014 Contact: Danielle Barrick, director of communications, (603) 271-7973, ext. 336, [email protected]; Deb Stone,
EMBARGOED: FOR RELEASE THURSDAY, MAY 22, 10 AM NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL: May 22, 2014 Contact: Danielle Barrick, director of communications, (603) 271-7973, ext. 336, [email protected]; Deb Stone,
Kaiser Permanente 2015 Sample Fee List 1 Members in any deductible plan can use this list to help estimate their charges.
 Kaiser Permanente 2015 Sample Fee List 1 Members in any deductible plan can use this list to help estimate their charges. COLORADO As your partner in health, we want to help you manage your health care
Kaiser Permanente 2015 Sample Fee List 1 Members in any deductible plan can use this list to help estimate their charges. COLORADO As your partner in health, we want to help you manage your health care
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Procedure Codes. RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY
 Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Guideline on the Controlled Acts and Delegation
 Guideline on the Controlled Acts and Delegation C o l l e g e o f O c c u p a t i o n a l T h e r a p i s t s o f O n t a r i o June 2000 Introduction The College receives numerous practice calls seeking
Guideline on the Controlled Acts and Delegation C o l l e g e o f O c c u p a t i o n a l T h e r a p i s t s o f O n t a r i o June 2000 Introduction The College receives numerous practice calls seeking
Code submitted by: CPT code. Allowed Services. 2005 work RVU. Descriptor
 20600 20610 22520 27603 32020 33877 34001 43750 45020 46040 46600 46604 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection; small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes) 328,030 CMS 0.66 Arthrocentesis, aspiration
20600 20610 22520 27603 32020 33877 34001 43750 45020 46040 46600 46604 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection; small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes) 328,030 CMS 0.66 Arthrocentesis, aspiration
