AN AUTOMATED PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR METRO OPERATIONS. A. Deloukas, E. Apostolopoulou Attiko Metro A.E.
|
|
|
- Sybil Riley
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AN AUTOMATED PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR METRO OPERATIONS A. Deloukas, E. Apostolopoulou Attiko Metro A.E. 1. INTRODUCTION Performance measurement has become an important concern for public transport operators in the last decade. With regard to metro operators, the need to measure their performance has become essential, as metro systems are capital-intensive and the expectations of key stakeholders (passengers, owners, employees, community) are raised to a high level. The paper handles the development of an automated system to measure the performance of the newly started metro lines 2&3 in Athens. Attiko Metro A.E. (AM) is responsible for the development of new metro lines in Athens operating since the year The main contributions of the paper pertain to the (a) development of a measurement system of metro performance based on the balanced scorecard framework, (b) evolution of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system implemented in a metro organization to a strategic application automating performance measurement, (c) novel integration of early warning signals and what-if capabilities (anticipating future metro performance) in the Performance Management and Controlling (PMC) module embedded within the ERP system. The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 depicts the adjustment of the balanced scorecard framework so as to evaluate strategic management processes of metro operations. Four balanced perspectives constituting a chain of causal relationships are contextualized. The objectives developed within the four perspectives are translated into a set of measures, termed Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). A detailed account of the KPI system is given. Measured performance is compared against benchmarks and, in case of low effectiveness, actions are proposed to improve metro performance and achieve the target benchmarks. In section 3, ERP systems, their risks and benefits are described in generic terms. A case study of an ongoing ERP implementation in the Athens metro organization is presented. Section 4 addresses the automated performance measurement system which facilitates the actual implementation of initiatives established within Attiko Metro s 20-year Business Plan. The respective PMC module enables the monitoring of metro performance in real time. The system tracks the KPI values against the target benchmarks. The use of key drivers of future performance advances PMC module reporting to an early warning system. The integration of a unit-cost allocation model of metro operations to the same
2 module allows the running of costing scenarios, thus facilitating strategic decision-making. 2. LINKING MANAGEMENT PROCESSES 2.1. A Framework for Performance Measurement Several conceptual frameworks have been proposed in the recent past years to evaluate the overall performance of organizations beyond pure economic considerations. Comprehensive approaches as the Baldridge model or the European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) standard focus on quality aspects, other like the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) concept maintain an equilibrium between financial objectives and key drivers of organizational performance (OLVE, ROY and WETTER 1999). Common to these evaluation frameworks is the linking of a wide range of management processes. Relevant processes refer to: (1) identifying business strategies, (2) translating strategic objectives into measures, (3) setting performance targets for the measures and developing action plans to achieve them, (4) enhancing feedback on controlling performance and corrective actions. Attiko Metro is the organization that has been established to manage the construction and to operate the new metro lines 2&3 in Athens. AM set up in stages during the year 2000 a metro system of 17kms in length. Extensions to the metro giving an additional 11kms are currently under construction, and scheduled to be in operation before the 2004 Olympic Games. An objective of this paper is to describe the system developed for strategic monitoring of metro performance. What is striven for is a balanced metro performance across multiple perspectives. The principles of the BSC framework have been substantiated to adjust to the particular organizational context. Starting from strategic initiatives assembled within the 20-year Attiko Metro Business Plan (B*A&H and PLANNING 1998), relevant business strategies are transformed into multiple objectives of critical importance, belonging to four perspectives shown in Diagram 1. The methodological framework provides a balance between financial outcomes of the operations (e.g. cost recovery ratio) and the drivers affecting the future performance of those outcomes. A cause-and-effect relationship between the four perspectives is set out in this Diagram. Employee satisfaction has been assessed as a very basic resource of efficient business processes (e.g. productivity growth). The latter processes determine quality of service satisfying the passengers (e.g. service reliability). The level of service along with the efficiency of business processes have, after all, a strong impact on the future financial effects of metro operation.
3 EMPLOYEE SATISFACTION BUSINESS PROCESS EFFICIENCY CUSTOMER SATISFACTION / SERVICE QUALITY FINANCIAL OUTCOMES Diagram 1: Cause-and-Effect Relationship of Metro Operator s Perspectives The rationale behind the choice of the four perspectives is that to focus on financial aspects only is inadequate for business decision-making. For instance, cost-cutting initiatives do not make sense if they seriously compromise the service standard set. On the other side of course, an underpricing of services may increase the customer satisfaction in the short term, while worsening the financial outcomes. The key drivers of performance depend on the organization type and the business scope (ATKINSON, WATERHOUSE and WELLS 1997). The key value driver of metro operations is the customer capital (passenger satisfaction), whereby a maximization of the cost recovery ratio is aimed. The critical driver of the metro construction management will be the human capital of the company, whereupon the focus is on project cost reduction. To explain non-financial perspectives further: human capital being an intangible asset, the employee satisfaction may be considered as a proxy of the organizational climate, which is important for the long-term development of the company. The efficiency of core processes refers mainly to labour productivity and capital (e.g. vehicle) utilization. The duty roster efficiency (train-kms/driver) becomes of critical importance for metro operations. Effective core processes create value for the customers. Customer-driven aspects of metro operations are the service quality and the safety, both being preconditions of customer satisfaction Selection of Key Performance Indicators The measurement system of the metro performance has been deductively evolved to match the proposed methodology. Broadly speaking, it combines aspects of cost, time and quality. The objectives developed within the four perspectives are translated into a set of measures, termed Key Performance Indicators. The KPIs relate input resources and factor costs (labour, energy, materials), service production (e.g. veh-kms, quality level), as well as service consumption variables (e.g. ridership, revenue), as shown in Diagram 2.
4 Input resources / factor costs Labour (staffing) Capital (e.g. # RS vehicles, materials) Energy (traction power) COST - EFFECTIVENESS Productivity measures COST - EFFICIENCY Service production Vehicle - kms Seat - kms Service availability Service reliability (regularity) SERVICE - EFFECTIVENESS Provided output Service consumption Diagram 2: Conceptual interrelationship of marker variables Passengers Passenger - kms Farebox revenue Safety (accidents) The decision sciences formulate desirable properties for the metrics to be selected, such as relevance, controllability throughout the organization, reliability and, of course, measurability. The selected KPIs measure more or less directly (as proxies) various aspects of the objectives to be evaluated. The selection of KPIs required structured discussions with senior managers of the company. The resulting KPI system (reviewed in a top management workshop) consists of 21 high-level KPIs. The KPIs have been defined as ratios to preserve scale independence. Multifaceted objectives, such as employee satisfaction, train availability and reliability, labour and vehicle efficiency are measured by more than a single KPI. However, it is not assumed the contributory KPIs to have the same importance for the particular goal achievement. The present KPI system is confined to objective measures based on metro usage data. Nevertheless, intersubjective measures resulting from repeatable surveys (e.g. customer satisfaction surveys) could be also incorporated. Financial objectives and corresponding KPIs pertain to cost efficiency (operating costs/veh-km), cost effectiveness (operating costs/passenger), degree of outsourcing (outsourced expenses/operating costs), revenue ratios (farebox revenue/ridership, ancillary revenues/operating revenue), and cost recovery ratio (operating revenue/operating costs). The customer-oriented objectives and related KPIs refer to train service availability (mileage operated as % of scheduled mileage, %-age of peak train cancellations), train service reliability (actual train runs with delay <2min as % of scheduled runs, failures causing delays/ veh-kms), in-vehicle peak
5 crowding level (standees/sq.m.), station service quality (escalators service time operated as % of planned service time), and safety (passenger injuries/ veh-kms). The business efficiency objectives and KPIs pertain to labour efficiency (employees/ veh-kms, employees/route-km, train-kms/driver, RS maintenance employees/vehicle), and vehicle efficiency (veh-kms/vehicle, peak vehicles/active vehicles). Finally, the employee satisfaction KPIs refer to the employee turnover rate and the non-attendance rate Setting of Benchmarks and Action Plans The AM Business Plan set out a normalized comparison with best practices of competitive European metro systems. The benchmarking technique has been used in order to set the desired target for each of the KPIs. Barcelona and Vienna have been selected as comparable metros to be benchmarked. Similar KPIs are the base for comparison. Apart from the high performing KPIs of both metros, the root causes of their business practices have been studied in detail to ensure that best practices are really represented (e.g. high degree of outsourcing distorts labour productivity indicators). The benchmarks were to stand for high but realistic (to-be) targets for the metro organization. A measurement system without given target values would be a weak concept. The derived target benchmarks represent a demand, such as a significant reduction in input factors utilized or a substantial increase in quality achieved. Action plans for the non-financial objectives are to be developed in order to attain the targets. The financial objectives are not considered but supposed to reflect plan outcomes of the non-financial objectives. An actual push on the performance drivers is assumed to enable sustainable financial results at a later stage. Compensation incentives counteract unplanned employee turn over, absenteeism and labour inefficiency. Standardization of operating procedures and adoption of new technologies may support higher process efficiency. Quality control initiatives lead to less accidents or failures causing train delays. 3. ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEM OF ATTIKO METRO 3.1. What is an ERP system? Prior to 1990 s, organizations used paper-based or stand-alone software applications to manage clusters of business processes such as maintenance, warehouse or finance. These applications were mostly not integrated. The growing needs for a better co-ordination as well as the advancement of distributed processing within integrated client/server architectures, resulted into business system solutions, called Enterprise Resource Planning Systems. An ERP-related project is accordingly more than a simple IT project, it is a business project linking most of the divisions and processes of an organization.
6 An ERP system allows an organization to: - automate and integrate most of its business processes - share common data across the entire organization (unique identifier for each item) - maintain data integrity and consistency - produce and access information in real time. ERPs are typically semi-finished products with pre-determined tables and settings, in-built process chains based on good practices, functional procedures adapted to the local legal framework (e.g. tax law, social security requirements, accounting system), and many parameters to be configured by the adopting organization. The implementation of an ERP system is much more about modifying of existing business processes to adapt better practices embedded within the ERP, than about adapting the ERP-code to existing business processes (JOCHEM 1998). The former case necessitates change management processes to improve acceptance level within organization. The latter case makes sense only when effective unique processes need to be preserved. Ideally, ERP parameterization and (re-)engineering of business processes are to be done in parallel (TENG, GROVER and FIEDLER 1994) Risks and Benefits of ERP systems The use of ERP systems by transport organizations became widespread in the last decade due to their value generating features. Operational benefits refer mainly to the automation of routine tasks and removal of redundant timeconsuming transactions (information flow across business functions). Managerial benefits relate to better resource management (e.g. maintenance control, workforce allocation, stock replacement), informed decision-making and improved performance (e.g. business control and monitoring due to centralized information and data analysis capabilities). Organizational benefits refer largely to integrated business processes (e.g. less redundancies and conflicts), better business system co-ordination and increased accountability for decision-takers. For instance, Finance could know every time the status of a purchase order without having to ask the Warehouse or the Procurement. Prior separate suppliers files of Finance, Warehouse or Procurement are consolidated to one table without duplications and following a unique coding scheme. However, it is difficult to quantify the resulting cost savings of reengineered processes and changed workflows due to the ERP usage. The use of multiple ERP modules produces economies of scope and synergies, due to the higher degree of functional integration provided. Intangible benefits seem to dominate the overall ERP value generation (HITT, WU and ZHOU 2002). On the other hand, ERPs entail high-cost and high-risk projects. The immediate costs refer to substantial implementation costs, as well as license, training, maintenance and hardware costs. The associated implementation risks consist of critical business risks (e.g. resistance to change, loss of ERP
7 key users, schedule overruns) and less critical, technical uncertainty (e.g. no further s/w development by the vendor). The use of multiple ERP modules may generate diseconomies of scope (e.g. higher complexity, wider propagation of user errors). An important issue is the longer time-frame required for an ERP system evaluation. Whereas initial ERP expenditures are high, benefits begin to accrue 2-3 years after the full system goes live, in order for organizational learning to have occurred. During the ERP implementation itself there may even be performance reduction. The expected useful life span of an installed ERP system ranges from 8 to 15 years, depending mainly on s/w technology advancements and the change of the business needs The ERP system of Attiko Metro The 20-year Business Plan for Attiko Metro proposed the implementation of an ERP system for metro operations as a strategic initiative. A proprietary ERP system (BAAN) is currently implemented in AM, to cover important business processes of metro operations as well as metro construction management. The ERP standard software (BAAN IV) is based on the ORACLE 8 database platform and is licensed for about 200 concurrent end-users (WENZEL and POST 1998). The network consists of interconnected LANs at Attiko Metro head offices, Sepolia Depot, Operations Control Center, all connected together (see Diagram 3). During 2001 AM created an operating company (located at Sepolia Depot) to run L2&3. About 60% of the ERP end-users are currently placed at the Sepolia Depot. AM remains owner of the metro system and the operating company operates, maintains and manages the system. Therefore a financial link between both companies exists. Diagram 4: ERP Module Interrelationships A M H e a d O f f i c e s Finance Procurement Human Resources Performance Management Finance Duty Mgt AMEL Sepolia Depot Material Management Maintenance Mgt Procurement Timetable Scheduling Human Resources Finance Fare Collection Operations Control Center Timetable Mgt Duty Management Service Monitoring Incident Reports Duty Mgt Stations Fare Collection Incident Reports Material Mgt Duty Management Diagram 3: Functional Topology of the ERP System of ATTIKO METRO
8 The modular architecture of the ERP system integrates activities of Maintenance, Warehouse, Procurement, Finance and Human Resources based on a single database. The metro operation depends on maintenance of the track, rolling stock and fixed equipment. The scheduling and control of both preventative and corrective maintenance workflows is organized through ERP work orders. The Maintenance module uses repair materials (spares) provided by the Warehouse module. The latter module, sometimes called Logistics, takes over distribution of stock items and replenishment orders. Operations (automatic train supervision, fare collection, scheduling and rostering) are, however, covered by stand-alone applications. The Procurement module is used throughout the whole company for purchasing of goods and services. It depends heavily, as most of the modules, on order processes. Finance contains General Ledger, Analytical Ledger by cost center (sources of expenses), accounts payables/receivables, budget control, revenues and fixed asset depreciation submodules. The Human Resources module is less integrated than the other modules, it combines payroll and personnel management functions. The implementation of each module occurred in three distinct phases. In the first mapping phase, the existing business processes have been analyzed and the business requirements defined. In the next piloting phase, the to-be process chains and data structures have been designed in detail, and the ERP parameterization has been planned. The third migration phase contains parameterization, data transfer, testing, training and documentation activities. Finally, the cross-functionality and integration of all modules has to be checked. A sequential strategy for the implementation of the entire set of modules has been adopted (SCHWARTZ 2000). In a first stage, business processes have been engineered in parallel with the ERP customization for the core activities of Maintenance (a rarity for European metros) and Warehouse. Both core activities has been given high priority by the Business Plan, in view of the forthcoming opening of the metro operation. In a subsequent phase, the ERP modules for administrative functions have been parameterized. The existing operating procedures have been reengineered to fit with the ERP in-built processes. The interrelationships of the five base modules are shown in Diagram 4. Since the metro divisions can share information and communicate with each other, the introduction of ERP technology is expected to lead to improvements in the future metro performance. For instance, warehouse shortages are revealed in real time, so inventories may be reduced. Duplication of data entries for order processes is eradicated. Financial reporting becomes more transparent and detailed, so that accountability increases.
9 HUMAN RESOURCES PROCUREMENT FINANCE MAINTENANCE WAREHOUSE Diagram 4:ERP Module Inter-relationships 4. ERP-BASED PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL 4.1. Attiko Metro s Performance Management and Controlling Module The need for business intelligence to make strategic decisions has not been a focus of ERP implementations in the past. ERP systems were mainly transactional applications, not providing strong analysis and reporting capabilities suited to manage the overall organization. ERPs are still not optimized to perform complex data transformations that involve information from across business functions. Many organizations have recourse to dedicated data warehouse tools based on predefined queries and content reports. It is preferred, however, to develop the ERP system as a strategic application taking advantage of the transactional information lying within the data warehouse of the system itself. For that purpose a Performance Management and Controlling module has been developed as an application embedded within the ERP system of AM. The PMC module enables the automated monitoring of the overall performance of metro operations. It supports strategic management rather than operational processes (MARTINSONS, DAVISON and TSE 1999). Automated features of the PMC module are: (a) periodic calculation of KPIs, (b) comparison with external target benchmarks, (c) monitoring of internal performance variability over time, (d) prediction of performance through whatif scenarios calculation. The PMC module extracts and transforms consistent information from different sources. The sourcing scheme for calculating KPIs is shown in Diagram 5.
10 BAAN - FINANCE General Ledger accounts and / or dimensions HUMAN RESOURCES Mgt System Staff - related data BAAN - FINANCE REAllocation accounts SOURCE 1 SOURCE 2 SOURCE 3 External Operational Data ( ATS, IVU, AFC etc. ) BAAN - PMC Key Performance Indicators Diagram 5: Sourcing Scheme for Calculating KPIs in the PMC Module Financial data of General Ledger accounts and dimensions are consolidated through the costing (named Reallocation ) submodule, staff-related data are drawn from the Human Resources module, and external operational data are entered through cold links from other applications (automatic train supervision system, train scheduling software system). Each of the five ERP base modules provides an integral but single-dimensional access to the database, while PMC provides a multi-dimensional access. Note that the detailed financial accounts and staff categories are regrouped in a manner that transcends the simple book-keeping function in order to support a strategic decision-making. The aggregations are fully compatible with the related categories used in the AM Business Plan. Using the Enterprise Performance Manager functionality of BAAN: (a) the calculation rules for KPIs are defined, (b) actual and target KPI values are linked, (c) the interrelationships between the KPI components have been fixed (see Diagram 6). KPI ALGORITHMS DEFINITION AND PARAMETERIZATION OF THE KPIs P M C LINKING OF KPIs AND FISHBONE DIAGRAMS KPI RELATIONSHIPS DEFINITION OF THE ENTERPRISE MODELS AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE FISHBONE DIAGRAMS KPI VALUES VS. BENCHMARKS RELATIONSHIP Diagram 6: Linking of Business Process Metrics
11 Cause-and-effect chains ( if-then statements) in the form of fishbone charts describe, within the PMC module, the multiple components ( causes ) of an activity measure ( potential problem or effect ). In fact, the achievement of hierarchically lower goals influence the achievement of higher-level goals. Only measures that are elements in a chain of cause-an-effect relationships are considered. An example pertaining to the cost recovery ratio and its components is demonstrated in Diagram 7. It enables a visual alert by underperformance ( what is happening ), so that an exception analysis ( why is happening ) and corrective actions are possible without delay. Especially, the use of non-financial indicators of future performance constitutes a novel early warning system, anticipating forthcoming problems.???5 : OPERATING COSTS KPI 1: SALARIES KPI 2: POWER COSTS KPI 3: MATERIAL COSTS KPI 4: MISCELLANNEOUS KPI 7: OPERATING COST RECOVERY RATIO KPI 6: OPERATING INCOME Diagram 7: Linking of KPIs with the Fishbone Diagrams (ISHIKAWA) 4.2. PMC Reporting and Exception Analysis The full set of measures refers to monthly reported KPIs and a subset of weekly KPIs. The generated KPI reports contain actual and cumulative (last 12-months average) values. An accompanying exception report is a strategic controlling tool providing insights about problem areas. It monitors the performance variance over the reference period and identifies the root causes in cases of underperformance. A typical excerpt of the KPI report containing customer-driven service quality indicators is displayed (Table 1). KPIs may be calculated at various level of detail (overall, business unit or metro line). In the presented table all moving average indicators of train service availability and train service reliability exceed targeted performance.
12 Month: May 2001 Target Actual Moving Average Related ID A. Quality KPIs Benchmark Monthly Performance Marker Notes Performance (01/06/00-31/05/01) Variables A1 Train service availability Kilometrage operated as % of scheduled >96% 91,2% 96,9% 1,2 Strike on 17/05/01 kilometrage (BP) A2* %- age of peak period train cancelations <2% L2: 0,3% L2: 0,1% 5,6 per line L3: 0,8% L3: 0,4% A3** In-vehicle peak crowding level <5 standees / sq. m. standing area L2: 2,5 L3: 1,1 4 L2 survey on 24/04/01(OMO PAN) L3 survey on 24/04/01(SYN EVA) A4* Train service reliability # of actual train runs per line with delay < 2 min from scheduled headway as % of scheduled runs L2: 99,9% L3: 99,9% L2: 99,8 % L3: 99,5% 7,8 Regularity indicator A5 # of failures per veh-kms operated <0,33 (BARCELONA) 0,26 0,28 1,9 Failures inducing cancellations or delays >2 min from scheduled headway A6 # of peak period train stops with dwel time 10 > 60 sec A7 Station service quality Escalators/ lifts service time operated as % of planned service time >98% Escal: 99,9% Lifts: 99,9% Escal: 99,9% Lifts: 99,9% 11 Planned annual service and time to alert OCC reduce further the planned service time A8 Peak period passengers waiting > 2min at < 1% 2,2% 12 Survey conducted in Omonia ticket outlets as % of tickets sold on 31/03/00 * : KPIs A2 and A4 have been calculated considering OCC ad-hoc modifications of timetable. ** : KPI A3 has been calculated considering the unevenness factor 0,85. Therefore, the effective standing area is 134 sq. m./train (=0,85*158 sq. m.) Note: Since October 2000, KPI A4 is based on regularity (time period between consecutive runs) instead of punctuality (time deviation from scheduled runs). The new measurement of reliability takes into account al delays more than 2 minutes from scheduled headway. Table 1: Monthly KPI Report 4.3. PMC and What-If Scenarios A value-adding functionality of the PMC module is, that it does not only monitors past performance, but also gives guidance about future performance through what-if scenarios calculation. Business scenarios may refer to altered train schedules, work rules or passenger demand, i.e. changing outputs such as veh-kms, train-hours, peak hour vehicles or ridership. The base algorithm is a unit-cost allocation model of metro operations, calibrated for a base year 1. Cost predictions are a function of input prices (labour, energy or material unit-costs) and fluctuating outputs. Costing scenarios are run by the Reallocation submodule. The PMC module capability thus goes beyond performance measurement and business reporting. Through what-if
13 scenarios it assists business planning and decision-making at the managerial level. 5. CONCLUSIONS The paper has considered the adjustment of the balanced scorecard framework to measure and evaluate strategic processes of metro operations. Four evaluation perspectives have been proposed for the new metro in Athens. Specific metrics have been considered for the more detailed strategic objectives. The resulting KPI system assesses performance against target benchmarks periodically. This controlling function in essential to identify business processes demanding quality improvements. In this respect, the high-level measures of metro performance place quality management within a strategic context. The automated strategic measurement system presents an innovative management tool to monitor and guide metro operations. Automation allows metro management to obtain strategic performance-related feedback without delay. The aim is to assist managerial decision-making based on solid information rather than intuition. Stored series of time-stamped KPI values enable a statistical estimation of the impacts of action plans on performance. PMC, as a decision support system (answering what-if questions) is equivalent to setting a hierarchy of multiple non-redundant objectives, leading to a set of measures quantifying future cost performance. The PMC module developed links performance measurement, benchmarking and business planning. It is therefore a comprehensive tool for strategy implementation. The automated performance monitoring of strategic processes in the case of the new Athens Metro may be prospectively considered, within an international context, as a good practice. However, further experience is needed in order to determine whether the proposed measures build up a sufficient set. Areas that need future investigation concern data reliability, benefits and satisfaction with PMC usage after implementation, adequacy to the managerial processes involved, and its long-term impact on metro performance. Notes 1 The unit-cost model has the following form: Total Operating Costs = = a*train-hours (TH) + b*veh-kms (VKM) + c*ridership (RIDER) + + d*peak Hour Vehicles (PHV) where: a*th = Passenger Service Costs (labour costs of train & station personnel) b*vkm = Maintenance of Equipment (rolling stock, fare collection etc.) + Maintenance of Ways&Sructures (track, stations, tunnel,
14 depot, systems) + Power Costs Maintenance costs contain labour and materials c*rider = Other costs (transit authority compensation, ticket sellers & inspectors) d*phv = Administration costs (general or indirect costs of administrative divisions and other overheads) dedicated to Operations as well as cleaning, security and other attributable costs The unit-cost rates {a, b, c, d} are inputs to be updated every year. REFERENCES Atkinson A., J. Waterhouse, R. Wells (1997), A Stakeholder Approach to Strategic Performance Measurement, Sloan Management Review, Vol. 38, pp B*A&H and Planning (1998) Attiko Metro 20-year Business Plan, Stages II and III, Final Report, Athens. Hitt L.M., D.J. Wu, X. Zhou (2002), Investment in Enterprise Resource Planning: Business Impact and Productivity Measures, Journal of Management Information Systems, Vol. 19, pp Jochem, M. (1998) Einführung Integrierter Standardsoftware: ein Ganzheitlicher Ansatz, Lang, Frankfurt. Martinsons M., R. Davison, D. Tse (1999), The Balanced Scorecard: A Foundation for the Strategic Management of Information Systems, Decision Support Systems, Vol. 25, pp Olve, N. G., Roy, J. and Wetter, M. (1999) Performance Drivers: A Practical Guide to Using the Balanced Scorecard, Wiley, Sussex. Schwartz, M. (2000) ERP-Standardsoftware und Organisatorischer Wandel, Gabler, Wiesbaden. Teng J., V. Grover, K. Fiedler (1994), Redesigning Business Processes with Information Technology, Long Range Planning, Vol. 27, pp Wenzel, P., Post H. (1998) (Hrsg.), Business Computing mit BAAN, Braunschweig, Vieweg.
15 Disclaimer The views expressed in this paper do not represent official views of Attiko Metro A.E., the authors being solely responsible for the views expressed herein.
Management Information Systems
 Faculty of Foundry Engineering Virtotechnology Management Information Systems Classification, elements, and evolution Agenda Information Systems (IS) IS introduction Classification Integrated IS 2 Information
Faculty of Foundry Engineering Virtotechnology Management Information Systems Classification, elements, and evolution Agenda Information Systems (IS) IS introduction Classification Integrated IS 2 Information
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects
 Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Data Analytics and Reporting in Toll Management and Supervision System Case study Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Data Analytics and Reporting in Toll Management and Supervision System Case study Bosnia and Herzegovina Gordana Radivojević 1, Gorana Šormaz 2, Pavle Kostić 3, Bratislav Lazić 4, Aleksandar Šenborn 5,
Data Analytics and Reporting in Toll Management and Supervision System Case study Bosnia and Herzegovina Gordana Radivojević 1, Gorana Šormaz 2, Pavle Kostić 3, Bratislav Lazić 4, Aleksandar Šenborn 5,
Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain. An Oracle White Paper December 2001
 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain An Oracle White Paper December 2001 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW This white paper illustrates why a fusion
Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain An Oracle White Paper December 2001 Building Relationships by Leveraging your Supply Chain EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW This white paper illustrates why a fusion
SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING BLUEPRINT BUSINESS VALUE GUIDE
 Business Value Guide SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING BLUEPRINT BUSINESS VALUE GUIDE INTRODUCTION What if it were possible to tightly link sales, marketing, supply chain, manufacturing and finance, so that
Business Value Guide SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING BLUEPRINT BUSINESS VALUE GUIDE INTRODUCTION What if it were possible to tightly link sales, marketing, supply chain, manufacturing and finance, so that
SUPPORTING LOGISTICS DECISIONS BY USING COST AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT TOOLS. Zoltán BOKOR. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 SUPPORTING LOGISTICS DECISIONS BY USING COST AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT TOOLS Zoltán BOKOR Department of Transport Economics Faculty of Transportation Engineering Budapest University of Technology and
SUPPORTING LOGISTICS DECISIONS BY USING COST AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT TOOLS Zoltán BOKOR Department of Transport Economics Faculty of Transportation Engineering Budapest University of Technology and
mysap ERP FINANCIALS SOLUTION OVERVIEW
 mysap ERP FINANCIALS SOLUTION OVERVIEW EFFECTIVE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT ... IS KEY TO BUSINESS SUCCESS mysap ERP FINANCIALS YOUR BUSINESS, YOUR FUTURE, YOUR SUCCESS mysap ERP is the world s most complete
mysap ERP FINANCIALS SOLUTION OVERVIEW EFFECTIVE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT ... IS KEY TO BUSINESS SUCCESS mysap ERP FINANCIALS YOUR BUSINESS, YOUR FUTURE, YOUR SUCCESS mysap ERP is the world s most complete
IAOP: Creating Sustainable value in Outsourcing Klaus Koefoed
 IAOP: Creating Sustainable value in Outsourcing Klaus Koefoed April 28 th 2010 Copyright 2009 Accenture All Rights Reserved. Accenture, its logo, and High Performance Delivered are trademarks of Accenture.
IAOP: Creating Sustainable value in Outsourcing Klaus Koefoed April 28 th 2010 Copyright 2009 Accenture All Rights Reserved. Accenture, its logo, and High Performance Delivered are trademarks of Accenture.
1 st RESOLUTE Workshop Florence 15.12.2015
 1 st RESOLUTE Workshop 15.12.2015 Dr. Alexandros Deloukas, Attiko Metro S.A. Evangelos Karagkounis, Metro Operations Expert Athens Metro System Overview System Description, Practices and Interdependencies
1 st RESOLUTE Workshop 15.12.2015 Dr. Alexandros Deloukas, Attiko Metro S.A. Evangelos Karagkounis, Metro Operations Expert Athens Metro System Overview System Description, Practices and Interdependencies
How To Improve Your Business
 ACHIEVING OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AND CUSTOMER INTIMACY: ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS Content How do enterprise systems help businesses achieve operational excellence? How do supply chain management systems
ACHIEVING OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AND CUSTOMER INTIMACY: ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS Content How do enterprise systems help businesses achieve operational excellence? How do supply chain management systems
Point of view* Shared Service Center - the 2nd Generation Taking the next step to reach a more efficient level of evolution.
 Point of view* Shared Service Center - the nd Generation Taking the next step to reach a more efficient level of evolution. Shared Service Center - the nd Generation Improving Shared Service business
Point of view* Shared Service Center - the nd Generation Taking the next step to reach a more efficient level of evolution. Shared Service Center - the nd Generation Improving Shared Service business
Do You Need ERP? The Magnum Group Technical Publications Division
 Do You Need ERP? A Cost-Benefit Analysis of ERP with Respect to Small and Medium Business Enterprises Compiled by the Database Services Division of The Magnum Group What is ERP? Today s business scenario
Do You Need ERP? A Cost-Benefit Analysis of ERP with Respect to Small and Medium Business Enterprises Compiled by the Database Services Division of The Magnum Group What is ERP? Today s business scenario
Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade
 Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade Summary Jamal Syed BI Practice Lead Emerging solutions 20 N. Wacker Drive Suite 1870 Chicago, IL 60606 Emerging Solutions, a professional services
Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade Summary Jamal Syed BI Practice Lead Emerging solutions 20 N. Wacker Drive Suite 1870 Chicago, IL 60606 Emerging Solutions, a professional services
Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade
 1 Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade Jamal Syed Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 Executive Summary... 3 Planning an ERP Upgrade?... 4 A Need for Speed... 6 Impact of data
1 Implementing Oracle BI Applications during an ERP Upgrade Jamal Syed Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 Executive Summary... 3 Planning an ERP Upgrade?... 4 A Need for Speed... 6 Impact of data
26/10/2015. Enterprise Information Systems. Learning Objectives. System Category Enterprise Systems. ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications
 Chapter 8 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications 8.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES How do enterprise systems help businesses
Chapter 8 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications 8.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES How do enterprise systems help businesses
Executive Summary...2. Introduction...3. Definitions...3. Why Operational Performance Optimization...4
 Optimizing Operational Performance from a Financial Management Perspective Executive Summary...2 Introduction...3 Definitions...3 Why Operational Performance Optimization....4 An Introduction to Optimizing
Optimizing Operational Performance from a Financial Management Perspective Executive Summary...2 Introduction...3 Definitions...3 Why Operational Performance Optimization....4 An Introduction to Optimizing
msd medical stores department Operations and Sales Planning (O&SP) Process Document
 msd medical stores department Operations and Sales Planning (O&SP) Process Document August 31, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Background... 3 1.1. Objectives... 3 1.2. Guiding Principles... 3 1.3. Leading Practice...
msd medical stores department Operations and Sales Planning (O&SP) Process Document August 31, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Background... 3 1.1. Objectives... 3 1.2. Guiding Principles... 3 1.3. Leading Practice...
RO-Why: The business value of a modern intranet
 RO-Why: The business value of a modern intranet 1 Introduction In the simplest terms, companies don t build products, do deals, or make service calls people do. But most companies struggle with isolated
RO-Why: The business value of a modern intranet 1 Introduction In the simplest terms, companies don t build products, do deals, or make service calls people do. But most companies struggle with isolated
Trapeze Rail System Simulation and Planning
 trapeze Rail System English Software for Rail Modelling and Planning Trapeze Rail System Simulation and Planning www.trapezegroup.com Enabling future railway plans Cost reductions through integrated planning
trapeze Rail System English Software for Rail Modelling and Planning Trapeze Rail System Simulation and Planning www.trapezegroup.com Enabling future railway plans Cost reductions through integrated planning
The fact is that 90% of business strategies are not implemented through operations as intended. Overview
 Overview It is important to recognize that a company s network determines its supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Designing an optimal supply chain network means the network must be able
Overview It is important to recognize that a company s network determines its supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Designing an optimal supply chain network means the network must be able
E Distribution: GENERAL RESOURCE, FINANCIAL AND BUDGETARY MATTERS. Agenda item 6 FINAL UPDATE ON THE WINGS II PROJECT.
 Executive Board First Regular Session Rome, 8 11 February 2010 RESOURCE, FINANCIAL AND BUDGETARY MATTERS Agenda item 6 For information* FINAL UPDATE ON THE WINGS II PROJECT E Distribution: GENERAL WFP/EB.1/2010/6
Executive Board First Regular Session Rome, 8 11 February 2010 RESOURCE, FINANCIAL AND BUDGETARY MATTERS Agenda item 6 For information* FINAL UPDATE ON THE WINGS II PROJECT E Distribution: GENERAL WFP/EB.1/2010/6
SUPPLY CHAIN MODELING USING SIMULATION
 SUPPLY CHAIN MODELING USING SIMULATION 1 YOON CHANG AND 2 HARRIS MAKATSORIS 1 Institute for Manufacturing, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, CB2 1RX, UK 1 To whom correspondence should be addressed.
SUPPLY CHAIN MODELING USING SIMULATION 1 YOON CHANG AND 2 HARRIS MAKATSORIS 1 Institute for Manufacturing, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, CB2 1RX, UK 1 To whom correspondence should be addressed.
THE NEXT GENERATION OF HR SHARED SERVICES SUBHEADLINE RUNS HERE AND HERE AND HERE AND HERE
 THE NEXT GENERATION OF HR SHARED SERVICES SUBHEADLINE RUNS HERE AND HERE AND HERE AND HERE SAP Executive Insight It s no secret that implementing HR shared services can help organizations generate significant
THE NEXT GENERATION OF HR SHARED SERVICES SUBHEADLINE RUNS HERE AND HERE AND HERE AND HERE SAP Executive Insight It s no secret that implementing HR shared services can help organizations generate significant
Developing and Implementing a Balanced Scorecard: A Practical Approach
 RL Consulting Developing and Implementing a Balanced Scorecard: A Practical Approach White Paper Prepared by: Rick Leopoldi March 31, 2004 Copyright 2004. All rights reserved. Duplication of this document
RL Consulting Developing and Implementing a Balanced Scorecard: A Practical Approach White Paper Prepared by: Rick Leopoldi March 31, 2004 Copyright 2004. All rights reserved. Duplication of this document
Finance Effectiveness Efficiency
 Business Unit Finance Effectiveness Efficiency An overview Agenda Page 1 Efficiency - An overview 1 2 Our services 7 3 Case study 14 Section 1 Efficiency - An overview 1 Section 1 Efficiency - An overview
Business Unit Finance Effectiveness Efficiency An overview Agenda Page 1 Efficiency - An overview 1 2 Our services 7 3 Case study 14 Section 1 Efficiency - An overview 1 Section 1 Efficiency - An overview
building and sustaining productive working relationships p u b l i c r e l a t i o n s a n d p r o c u r e m e n t
 building and sustaining productive working relationships p u b l i c r e l a t i o n s a n d p r o c u r e m e n t INTRODUCTION 1 1 THE GROWING INFLUENCE OF PROCUREMENT PROFESSIONALS 2 2 GUIDELINES FOR
building and sustaining productive working relationships p u b l i c r e l a t i o n s a n d p r o c u r e m e n t INTRODUCTION 1 1 THE GROWING INFLUENCE OF PROCUREMENT PROFESSIONALS 2 2 GUIDELINES FOR
PPM Maturity Value Assessment for Your Company
 PPM Maturity Value Assessment for Your Company Date Sponsored by: Prepared For: Valued Customer Name Third party model, methodology and data provided by: Disclaimer: NOTICE - THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED
PPM Maturity Value Assessment for Your Company Date Sponsored by: Prepared For: Valued Customer Name Third party model, methodology and data provided by: Disclaimer: NOTICE - THIS INFORMATION IS PROVIDED
MSD Supply Chain Programme Strategy Workshop
 MSD Supply Chain Programme Strategy Workshop Day 2 APPENDIX Accenture Development Partnerships Benchmarking MSD s Current Operating Supply Chain Capability 1.0 Planning 2.0 Procurement 3.0 Delivery 4.0
MSD Supply Chain Programme Strategy Workshop Day 2 APPENDIX Accenture Development Partnerships Benchmarking MSD s Current Operating Supply Chain Capability 1.0 Planning 2.0 Procurement 3.0 Delivery 4.0
ORACLE PROJECT PLANNING AND CONTROL
 ORACLE PROJECT PLANNING AND CONTROL (Formerly Oracle Project Management) KEY FEATURES COLLABORATIVE PROJECT PLANNING Define a project work breakdown structure to align plans to execution Coordinate financial
ORACLE PROJECT PLANNING AND CONTROL (Formerly Oracle Project Management) KEY FEATURES COLLABORATIVE PROJECT PLANNING Define a project work breakdown structure to align plans to execution Coordinate financial
14 TRUTHS: How To Prepare For, Select, Implement And Optimize Your ERP Solution
 2015 ERP GUIDE 14 TRUTHS: How To Prepare For, Select, Implement And Optimize Your ERP Solution Some ERP implementations can be described as transformational, company-changing events. Others are big disappointments
2015 ERP GUIDE 14 TRUTHS: How To Prepare For, Select, Implement And Optimize Your ERP Solution Some ERP implementations can be described as transformational, company-changing events. Others are big disappointments
THE BALANCED SCORECARD IN A STRATEGY-FOCUSED ORGANIZATION
 THE BALANCED SCORECARD IN A STRATEGY-FOCUSED ORGANIZATION Engineer (economist) Bogza (Cozma) Rodica Maria, PhD The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies ABSTRACT The power to focus means the power to succeed.
THE BALANCED SCORECARD IN A STRATEGY-FOCUSED ORGANIZATION Engineer (economist) Bogza (Cozma) Rodica Maria, PhD The Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies ABSTRACT The power to focus means the power to succeed.
Intelligent Process Management & Process Visualization. TAProViz 2014 workshop. Presenter: Dafna Levy
 Intelligent Process Management & Process Visualization TAProViz 2014 workshop Presenter: Dafna Levy The Topics Process Visualization in Priority ERP Planning Execution BI analysis (Built-in) Discovering
Intelligent Process Management & Process Visualization TAProViz 2014 workshop Presenter: Dafna Levy The Topics Process Visualization in Priority ERP Planning Execution BI analysis (Built-in) Discovering
Course 103402 MIS. Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 103402 MIS Topic 7 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy CS/MIS Department Enterprise Systems Management Information Systems Enterprise
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 103402 MIS Topic 7 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy CS/MIS Department Enterprise Systems Management Information Systems Enterprise
Strategic Solutions that Make Your Work Easier. Projects Made Easier Decisions Made Easier Business Made Easier
 Strategic Solutions that Make Your Work Easier Projects Made Easier Decisions Made Easier Business Made Easier Have You Outgrown Your Systems? Buyers Say the Partner and the Product are More Important
Strategic Solutions that Make Your Work Easier Projects Made Easier Decisions Made Easier Business Made Easier Have You Outgrown Your Systems? Buyers Say the Partner and the Product are More Important
Business Intelligence Meets Business Process Management. Powerful technologies can work in tandem to drive successful operations
 Business Intelligence Meets Business Process Management Powerful technologies can work in tandem to drive successful operations Content The Corporate Challenge.3 Separation Inhibits Decision-Making..3
Business Intelligence Meets Business Process Management Powerful technologies can work in tandem to drive successful operations Content The Corporate Challenge.3 Separation Inhibits Decision-Making..3
Management Excellence Framework: Record to Report
 An Oracle Thought Leadership White Paper August 2009 Management Excellence Framework: Record to Report Introduction Management Excellence Framework... 3 Record to Report... 5 Step by Step... 6 Key Metrics...
An Oracle Thought Leadership White Paper August 2009 Management Excellence Framework: Record to Report Introduction Management Excellence Framework... 3 Record to Report... 5 Step by Step... 6 Key Metrics...
Sage ERP I White Paper. An ERP Guide to Driving Efficiency
 I White Paper An ERP Guide to Driving Efficiency Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Best-in-Class Organizations Look to Enhance Efficiency... 3 How ERP Improves Efficiency... 3 Results... 6 Conclusion...
I White Paper An ERP Guide to Driving Efficiency Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Best-in-Class Organizations Look to Enhance Efficiency... 3 How ERP Improves Efficiency... 3 Results... 6 Conclusion...
A technical paper for Microsoft Dynamics AX users
 s c i t y l a n a g n i Implement. d e d e e N is h c a o r Why a New app A technical paper for Microsoft Dynamics AX users ABOUT THIS WHITEPAPER 03 06 A TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO BI A NEW APPROACH This
s c i t y l a n a g n i Implement. d e d e e N is h c a o r Why a New app A technical paper for Microsoft Dynamics AX users ABOUT THIS WHITEPAPER 03 06 A TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO BI A NEW APPROACH This
Customer requirements. Asset management planning Inspection and assessment Route asset planning Annual work plans Contracting strategy
 Section 8 Output monitoring Inputs Customer requirements Safety standards Outputs and funding SRA and Government Policy Network stewardship strategy Asset and operational policies Maintenance & renewal
Section 8 Output monitoring Inputs Customer requirements Safety standards Outputs and funding SRA and Government Policy Network stewardship strategy Asset and operational policies Maintenance & renewal
Business Process Management (BPM) Software
 FlowCentric Processware 2013 FlowCentric Business Process Management (BPM) Software and Services enable organisations of all proportions, in a multitude of industries, to satisfy and often exceed their
FlowCentric Processware 2013 FlowCentric Business Process Management (BPM) Software and Services enable organisations of all proportions, in a multitude of industries, to satisfy and often exceed their
Business ByDesign. The SAP Business ByDesign solution helps you optimize project management
 SAP Functions in Detail SAP Solutions for Small Businesses and Midsize Companies Efficient Project Management Drive Project Success with SAP Business ByDesign The SAP Business ByDesign solution helps you
SAP Functions in Detail SAP Solutions for Small Businesses and Midsize Companies Efficient Project Management Drive Project Success with SAP Business ByDesign The SAP Business ByDesign solution helps you
Business Intelligence Enabling Transparency across the Enterprise
 White Paper Business Intelligence Enabling Transparency across the Enterprise Business solutions through information technology Entire contents 2004 by CGI Group Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction
White Paper Business Intelligence Enabling Transparency across the Enterprise Business solutions through information technology Entire contents 2004 by CGI Group Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction
Corporate Performance Management (CPM) - An Introduction
 CPM Overview Corporate Performance Management (CPM) - An Introduction The Business Drivers Common challenges corporations face today... Increasing demand for corporate accountability from stockholders
CPM Overview Corporate Performance Management (CPM) - An Introduction The Business Drivers Common challenges corporations face today... Increasing demand for corporate accountability from stockholders
An Introduction to. Metrics. used during. Software Development
 An Introduction to Metrics used during Software Development Life Cycle www.softwaretestinggenius.com Page 1 of 10 Define the Metric Objectives You can t control what you can t measure. This is a quote
An Introduction to Metrics used during Software Development Life Cycle www.softwaretestinggenius.com Page 1 of 10 Define the Metric Objectives You can t control what you can t measure. This is a quote
Government Business Intelligence (BI): Solving Your Top 5 Reporting Challenges
 Government Business Intelligence (BI): Solving Your Top 5 Reporting Challenges Creating One Version of the Truth Enabling Information Self-Service Creating Meaningful Data Rollups for Users Effortlessly
Government Business Intelligence (BI): Solving Your Top 5 Reporting Challenges Creating One Version of the Truth Enabling Information Self-Service Creating Meaningful Data Rollups for Users Effortlessly
BI4Dynamics provides rich business intelligence capabilities to companies of all sizes and industries. From the first day on you can analyse your
 BI4Dynamics provides rich business intelligence capabilities to companies of all sizes and industries. From the first day on you can analyse your data quickly, accurately and make informed decisions. Spending
BI4Dynamics provides rich business intelligence capabilities to companies of all sizes and industries. From the first day on you can analyse your data quickly, accurately and make informed decisions. Spending
PTC SERVICE PARTS MANAGEMENT SOLUTION
 PTC SERVICE PARTS MANAGEMENT SOLUTION PTC Service Parts Management Solution Increase Parts Availability and Reduce Inventory Costs In order to meet and exceed the stringent requirements of delivering world
PTC SERVICE PARTS MANAGEMENT SOLUTION PTC Service Parts Management Solution Increase Parts Availability and Reduce Inventory Costs In order to meet and exceed the stringent requirements of delivering world
Evaluation Framework for an ERP System using Balanced Scorecard Approach
 Evaluation Framework for an ERP System using Balanced Scorecard Approach SUDHANSHU JOSHI Faculty Member- Applied Finance & IS +91-9997410336,[email protected] Gurukul Kangri University, Haridwar
Evaluation Framework for an ERP System using Balanced Scorecard Approach SUDHANSHU JOSHI Faculty Member- Applied Finance & IS +91-9997410336,[email protected] Gurukul Kangri University, Haridwar
Chapter 9. Video Cases. 6.1 Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
 Chapter 9 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications Video Cases Video Case 1a: What Is Workday: Enterprise Software as a Service (Saas) Video Case 1b: Workday: Mobile
Chapter 9 Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise Applications Video Cases Video Case 1a: What Is Workday: Enterprise Software as a Service (Saas) Video Case 1b: Workday: Mobile
Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail
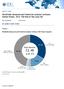 MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
The top ten reasons your organization needs Snow Optimizer for SAP Software. Snow optimizer for SAP software
 Snow optimizer for SAP software The top ten reasons your organization needs Snow Optimizer for SAP Software Manage your entire SAP deployment and SAP vendor relationship in a single integrated console
Snow optimizer for SAP software The top ten reasons your organization needs Snow Optimizer for SAP Software Manage your entire SAP deployment and SAP vendor relationship in a single integrated console
MODELING THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN ERP SOFTWARE
 MODELING THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN ERP SOFTWARE Paweł Kużdowicz 1, Dorota Kużdowicz 2, Anna Saniuk 3 1 University of Zielona Góra, Faculty of Economy and Management, Zielona Góra, Poland, EU 2 University
MODELING THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN ERP SOFTWARE Paweł Kużdowicz 1, Dorota Kużdowicz 2, Anna Saniuk 3 1 University of Zielona Góra, Faculty of Economy and Management, Zielona Góra, Poland, EU 2 University
Data Management Practices for Intelligent Asset Management in a Public Water Utility
 Data Management Practices for Intelligent Asset Management in a Public Water Utility Author: Rod van Buskirk, Ph.D. Introduction Concerned about potential failure of aging infrastructure, water and wastewater
Data Management Practices for Intelligent Asset Management in a Public Water Utility Author: Rod van Buskirk, Ph.D. Introduction Concerned about potential failure of aging infrastructure, water and wastewater
Evaluation Guide. Sales and Operations Planning Performance Blueprint
 Evaluation Guide Sales and Operations Planning Performance Blueprint Introduction What if it were possible to tightly link sales, marketing, supply chain, manufacturing and finance, so that executives
Evaluation Guide Sales and Operations Planning Performance Blueprint Introduction What if it were possible to tightly link sales, marketing, supply chain, manufacturing and finance, so that executives
Chapter 5 Information Technology and Changing Business Processes
 Chapter 5 Information Technology and Changing Business Processes Managing and Using Information Systems: A Strategic Approach by Keri Pearlson & Carol Saunders Introduction How can IT enable business change?
Chapter 5 Information Technology and Changing Business Processes Managing and Using Information Systems: A Strategic Approach by Keri Pearlson & Carol Saunders Introduction How can IT enable business change?
Are you looking at procurement as an end-to-end process?
 Are you looking at procurement as an end-to-end process? Need for Source to pay transformation Digitization / Automation is the need of the hour. Many companies in pursuit of improving their purchasing
Are you looking at procurement as an end-to-end process? Need for Source to pay transformation Digitization / Automation is the need of the hour. Many companies in pursuit of improving their purchasing
The Balanced Scorecard
 The Balanced Scorecard Traditional financial performance metrics provide information about a firm's past results, but are not well-suited for predicting future performance or for implementing and controlling
The Balanced Scorecard Traditional financial performance metrics provide information about a firm's past results, but are not well-suited for predicting future performance or for implementing and controlling
English. Trapeze Rail System. www.trapezegroup.com
 English Trapeze Rail System www.trapezegroup.com Trapeze Rail System Enabling future railway, tram and metro transport The worldwide growth in demand for travel and increasing competition between all modes
English Trapeze Rail System www.trapezegroup.com Trapeze Rail System Enabling future railway, tram and metro transport The worldwide growth in demand for travel and increasing competition between all modes
Agile Manufacturing for ALUMINIUM SMELTERS
 Agile Manufacturing for ALUMINIUM SMELTERS White Paper This White Paper describes how Advanced Information Management and Planning & Scheduling solutions for Aluminium Smelters can transform production
Agile Manufacturing for ALUMINIUM SMELTERS White Paper This White Paper describes how Advanced Information Management and Planning & Scheduling solutions for Aluminium Smelters can transform production
PEOPLESOFT MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
 PEOPLESOFT MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT KEY BENEFITS Streamline Maintenance Operations Manage Full Asset Lifecycle Lower Total Cost of Ownership Oracle s PeopleSoft Maintenance Management completes the Enterprise
PEOPLESOFT MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT KEY BENEFITS Streamline Maintenance Operations Manage Full Asset Lifecycle Lower Total Cost of Ownership Oracle s PeopleSoft Maintenance Management completes the Enterprise
Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU. Enterprise Systems
 Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU Enterprise Systems Aka enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems Suite of integrated software modules and a common central database Collects data from
Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU Enterprise Systems Aka enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems Suite of integrated software modules and a common central database Collects data from
MODERNIZING IT PLATFORMS SUCCESSFULLY HOW PLATFORM RENEWAL PROJECTS CREATE VALUE
 MODERNIZING IT PLATFORMS SUCCESSFULLY HOW PLATFORM RENEWAL PROJECTS CREATE VALUE INTRODUCTION The machinery and plant engineering industry is under pressure to transform. Globalization, new competitors,
MODERNIZING IT PLATFORMS SUCCESSFULLY HOW PLATFORM RENEWAL PROJECTS CREATE VALUE INTRODUCTION The machinery and plant engineering industry is under pressure to transform. Globalization, new competitors,
SAP ERP FINANCIALS ENABLING FINANCIAL EXCELLENCE. SAP Solution Overview SAP Business Suite
 SAP Solution Overview SAP Business Suite SAP ERP FINANCIALS ENABLING FINANCIAL EXCELLENCE ESSENTIAL ENTERPRISE BUSINESS STRATEGY PROVIDING A SOLID FOUNDATION FOR ENTERPRISE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT 2 Even
SAP Solution Overview SAP Business Suite SAP ERP FINANCIALS ENABLING FINANCIAL EXCELLENCE ESSENTIAL ENTERPRISE BUSINESS STRATEGY PROVIDING A SOLID FOUNDATION FOR ENTERPRISE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT 2 Even
ATTACHMENT II - WRITTEN PROPOSAL RESPONSE AND GUIDELINES
 ATTACHMENT II - WRITTEN PROPOSAL RESPONSE AND GUIDELINES RFP#CON2014-18 Attachments I through VI from the Response Teams will be evaluated and scored (1000 points total) in accordance with the criteria
ATTACHMENT II - WRITTEN PROPOSAL RESPONSE AND GUIDELINES RFP#CON2014-18 Attachments I through VI from the Response Teams will be evaluated and scored (1000 points total) in accordance with the criteria
Best Practices for Planning and Budgeting. A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006
 A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
A white paper prepared by PROPHIX Software October 2006 Executive Summary The continual changes in the business climate constantly challenge companies to find more effective business practices. However,
TERMS OF REFERENCE (ToR)
 TERMS OF REFERENCE (ToR) Consultancy services for Monitoring the Implementation of Computerized Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) of BREB & PBSs for Institutional Strengthening
TERMS OF REFERENCE (ToR) Consultancy services for Monitoring the Implementation of Computerized Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) of BREB & PBSs for Institutional Strengthening
ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS This chapter introduces an approach to information system development that represents the next step on a continuum that began with stand-alone applications,
CHAPTER ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS This chapter introduces an approach to information system development that represents the next step on a continuum that began with stand-alone applications,
IBM Cognos Financial Performance Analytics Faster Insight: Smarter Financial Decisions
 IBM Cognos Financial Performance Analytics Faster Insight: Smarter Financial Decisions Business Analytics Smarter planet: Thinking and acting in new ways to make our systems more efficient, productive
IBM Cognos Financial Performance Analytics Faster Insight: Smarter Financial Decisions Business Analytics Smarter planet: Thinking and acting in new ways to make our systems more efficient, productive
Business Process Management & Workflow Solutions
 Business Process Management & Workflow Solutions Connecting People to Process, Data & Activities TouchstoneBPM enables organisations of all proportions, in a multitude of disciplines, the capability to
Business Process Management & Workflow Solutions Connecting People to Process, Data & Activities TouchstoneBPM enables organisations of all proportions, in a multitude of disciplines, the capability to
SAP Sales and Operations Planning Compare & Contrast with SAP APO. Phil Gwynne SAP UKI 2013
 SAP Sales and Operations Planning Compare & Contrast with SAP APO Phil Gwynne SAP UKI 2013 But the King is still reported alive regularly Disclaimer The information in this document is confidential and
SAP Sales and Operations Planning Compare & Contrast with SAP APO Phil Gwynne SAP UKI 2013 But the King is still reported alive regularly Disclaimer The information in this document is confidential and
Agenda. Copyright 2012 2013 Acuity Business Solutions, LLC All Rights Reserved
 Agenda Understand the reasons your firm purchased Vision analyzing your company s pain points What is an ERP and how is it different? Project Lifecycle Reasons why firms fail at implementation or user
Agenda Understand the reasons your firm purchased Vision analyzing your company s pain points What is an ERP and how is it different? Project Lifecycle Reasons why firms fail at implementation or user
White Paper March 2009. Government performance management Set goals, drive accountability and improve outcomes
 White Paper March 2009 Government performance management Set goals, drive accountability and improve outcomes 2 Contents 3 Business problems Why performance management? 4 Business drivers 6 The solution
White Paper March 2009 Government performance management Set goals, drive accountability and improve outcomes 2 Contents 3 Business problems Why performance management? 4 Business drivers 6 The solution
Exhibit F. VA-130620-CAI - Staff Aug Job Titles and Descriptions Effective 2015
 Applications... 3 1. Programmer Analyst... 3 2. Programmer... 5 3. Software Test Analyst... 6 4. Technical Writer... 9 5. Business Analyst... 10 6. System Analyst... 12 7. Software Solutions Architect...
Applications... 3 1. Programmer Analyst... 3 2. Programmer... 5 3. Software Test Analyst... 6 4. Technical Writer... 9 5. Business Analyst... 10 6. System Analyst... 12 7. Software Solutions Architect...
Making the right decisions with SCOR
 Making the right decisions with SCOR Bengt Jensfelt, Product Manager Business Intelligence, IBS AB 16 January 2007 In the relentless search for ever improving returns on investment and market competitiveness,
Making the right decisions with SCOR Bengt Jensfelt, Product Manager Business Intelligence, IBS AB 16 January 2007 In the relentless search for ever improving returns on investment and market competitiveness,
Feasibility study for the introduction of a Smart Ticketing System in Thessaloniki
 The Feasibility Study as a powerful tool in our hands Training Course, AUTh, 11 th September 2012 Feasibility study for the introduction of a Smart Ticketing System in Thessaloniki A. Deloukas ATTIKO METRO
The Feasibility Study as a powerful tool in our hands Training Course, AUTh, 11 th September 2012 Feasibility study for the introduction of a Smart Ticketing System in Thessaloniki A. Deloukas ATTIKO METRO
When to Leverage Video as a Platform A Guide to Optimizing the Retail Environment
 When to Leverage Video as a Platform A Guide to Optimizing the Retail Environment Contents S1 An Industry in Transition Over the past few years, retail has seen seismic changes in how the customer shops.
When to Leverage Video as a Platform A Guide to Optimizing the Retail Environment Contents S1 An Industry in Transition Over the past few years, retail has seen seismic changes in how the customer shops.
How To Use Stratum Fpm
 Financial Performance Management CORPORATE AP / AR PRODUCT & CUSTOMER PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT PROFITABILITY Today, corporate finance executives are being tasked with far more strategic responsibilities
Financial Performance Management CORPORATE AP / AR PRODUCT & CUSTOMER PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT PROFITABILITY Today, corporate finance executives are being tasked with far more strategic responsibilities
ORACLE FINANCIAL SERVICES BALANCE SHEET PLANNING
 ORACLE FINANCIAL SERVICES BALANCE SHEET PLANNING KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS FEATURES Packaged application with prebuilt industry leading practices Net Interest Margin and balance sheet forecasts using cash
ORACLE FINANCIAL SERVICES BALANCE SHEET PLANNING KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS FEATURES Packaged application with prebuilt industry leading practices Net Interest Margin and balance sheet forecasts using cash
ENTERPRISE ASSET MANAGEMENT (EAM) The Devil is in the Details CASE STUDY
 ENTERPRISE ASSET MANAGEMENT (EAM) The Devil is in the Details CASE STUDY 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) is a strategy to provide an optimal approach for the management of the physical
ENTERPRISE ASSET MANAGEMENT (EAM) The Devil is in the Details CASE STUDY 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) is a strategy to provide an optimal approach for the management of the physical
Oracle ERP Cloud Period Close Procedures O R A C L E W H I T E P A P E R J U N E 2 0 1 5
 Oracle ERP Cloud Period Close Procedures O R A C L E W H I T E P A P E R J U N E 2 0 1 5 Table of Contents Introduction 7 Chapter 1 Period Close Dependencies 8 Chapter 2 Subledger Accounting Overview 9
Oracle ERP Cloud Period Close Procedures O R A C L E W H I T E P A P E R J U N E 2 0 1 5 Table of Contents Introduction 7 Chapter 1 Period Close Dependencies 8 Chapter 2 Subledger Accounting Overview 9
ACCA Certified Accounting Technician Examination Paper T7. Section A. 2 C ($200,000 ($200,000 0 2 x 0 15)) = $50,000
 Answers ACCA Certified Accounting Technician Examination Paper T7 Planning, Control and Financial Management December 2009 Answers Section A 1 A 2 C ($200,000 ($200,000 0 2 x 0 15)) = $50,000 3 D 4 B $3,600
Answers ACCA Certified Accounting Technician Examination Paper T7 Planning, Control and Financial Management December 2009 Answers Section A 1 A 2 C ($200,000 ($200,000 0 2 x 0 15)) = $50,000 3 D 4 B $3,600
TURNING LOGISTICS NETWORKS INTO STRATEGIC ASSETS
 Logistics TURNING LOGISTICS NETWORKS INTO STRATEGIC ASSETS AN INTEGRATED APPROACH BETWEEN STRATEGY & OPERATIONS TO EFFICIENTLY REDESIGN LOGISTICS NETWORKS TURNING LOGISTICS NETWORKS INTO STRATEGIC ASSETS
Logistics TURNING LOGISTICS NETWORKS INTO STRATEGIC ASSETS AN INTEGRATED APPROACH BETWEEN STRATEGY & OPERATIONS TO EFFICIENTLY REDESIGN LOGISTICS NETWORKS TURNING LOGISTICS NETWORKS INTO STRATEGIC ASSETS
POLAR IT SERVICES. Business Intelligence Project Methodology
 POLAR IT SERVICES Business Intelligence Project Methodology Table of Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Visualize... 3 3. Planning and Architecture... 4 3.1 Define Requirements... 4 3.1.1 Define Attributes...
POLAR IT SERVICES Business Intelligence Project Methodology Table of Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Visualize... 3 3. Planning and Architecture... 4 3.1 Define Requirements... 4 3.1.1 Define Attributes...
IFS-8000 V2.0 INFORMATION FUSION SYSTEM
 IFS-8000 V2.0 INFORMATION FUSION SYSTEM IFS-8000 V2.0 Overview IFS-8000 v2.0 is a flexible, scalable and modular IT system to support the processes of aggregation of information from intercepts to intelligence
IFS-8000 V2.0 INFORMATION FUSION SYSTEM IFS-8000 V2.0 Overview IFS-8000 v2.0 is a flexible, scalable and modular IT system to support the processes of aggregation of information from intercepts to intelligence
Introduction to Business Intelligence
 IBM Software Group Introduction to Business Intelligence Vince Leat ASEAN SW Group 2007 IBM Corporation Discussion IBM Software Group What is Business Intelligence BI Vision Evolution Business Intelligence
IBM Software Group Introduction to Business Intelligence Vince Leat ASEAN SW Group 2007 IBM Corporation Discussion IBM Software Group What is Business Intelligence BI Vision Evolution Business Intelligence
SC21 Manufacturing Excellence. Process Overview
 SC21 Manufacturing Excellence Process Overview Prepared by:- The SC21 Performance, Development and Quality (PDQ) Special Interest Group (SIG) Acknowledgement The scoring methodology used in the Management
SC21 Manufacturing Excellence Process Overview Prepared by:- The SC21 Performance, Development and Quality (PDQ) Special Interest Group (SIG) Acknowledgement The scoring methodology used in the Management
U.S. Department of the Treasury. Treasury IT Performance Measures Guide
 U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury IT Performance Measures Guide Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) Enterprise Architecture Program June 2007 Revision History June 13, 2007 (Version 1.1)
U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury IT Performance Measures Guide Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) Enterprise Architecture Program June 2007 Revision History June 13, 2007 (Version 1.1)
Return on Investment in Business Intelligence in Small and Mid-Sized Businesses
 Return on Investment in Business Intelligence in Small and Mid-Sized Businesses ZELJKO PANIAN The Graduate School for Economics and Business University of Zagreb J.F. Kennedy Sq. 6 CROATIA [email protected]
Return on Investment in Business Intelligence in Small and Mid-Sized Businesses ZELJKO PANIAN The Graduate School for Economics and Business University of Zagreb J.F. Kennedy Sq. 6 CROATIA [email protected]
DRAFT V5. PFSC 16/05/2014 Appendix 1. Outline Plan to deliver the County Council s investment property Strategy
 PFSC 16/05/2014 Appendix 1 Outline Plan to deliver the County Council s investment property Strategy 1. Strategic Drivers 1.1 The County Council s property investment strategy sets out how its property
PFSC 16/05/2014 Appendix 1 Outline Plan to deliver the County Council s investment property Strategy 1. Strategic Drivers 1.1 The County Council s property investment strategy sets out how its property
Contact Center Performance Management Software
 Markets, W. Close Research Note 7 March 2003 Contact Center Performance Software Enterprises face critical challenges in contact center management. Capitalizing on people, performance and analytics will
Markets, W. Close Research Note 7 March 2003 Contact Center Performance Software Enterprises face critical challenges in contact center management. Capitalizing on people, performance and analytics will
Workday Big Data Analytics
 Workday Big Data Analytics Today s fast-paced business climate demands that decision-makers stay informed. Having access to key information gives them the best insight into their business. However, many
Workday Big Data Analytics Today s fast-paced business climate demands that decision-makers stay informed. Having access to key information gives them the best insight into their business. However, many
Intelligent Government From Data to Decision. Robert Lindsley [email protected] Oracle, Public Sector Technology Group
 Intelligent Government From Data to Decision Robert Lindsley [email protected] Oracle, Public Sector Technology Group Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our general product
Intelligent Government From Data to Decision Robert Lindsley [email protected] Oracle, Public Sector Technology Group Safe Harbor Statement The following is intended to outline our general product
