A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ
|
|
|
- Myrtle Young
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I.J. Wireless and Microwave Technologies 2012, 4, Published Online August 2012 in MECS ( DOI: /ijwmt Available online at ijwmt A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ Huiting Liu a, b, Hua Zhang a, Weilin Xu a, b, Yigang Yang a, b a State Key Laboratory of Networking and Switching Technology, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications b School of Computer, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Beijing, , China Abstract As the main secret-key encryption techniques of the wireless local area network (WLAN) have been proven to be unsafe, wireless network security is faced with serious challenges. It is unpractical for home users and small companies to buy expansive network equipments to improve the network security. Therefore, the secure strategy of wireless network needs to be changed. In this paper, we first introduce secure issues of the main secret-key encryption techniques currently adopted by the most popular commercial wireless routers. Then we propose a new strategy for small-scale IEEE wireless local area network which can strengthen the network security. The new secure strategy is based on web authentication with unshared key and virtual local area network (VLAN) in wireless network. It can provide protection against practical attacks which are popular nowadays. Moreover, it is simple, wieldy and low-cost. Index Terms: WLAN; secure strategy; web authentication; identify theft; VLAN 2012 Published by MECS Publisher. Selection and/or peer review under responsibility of the Research Association of Modern Education and Computer Science 1. Introduction Wireless network brings great user experience to people for its flexibility, portability and low-cost. Commercial Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) products are widely available on the market and most of them setup easily and operate simply. WLAN is rapidly deployed around the world. More and more public places, offices and even homes set up their own WLANs. Thus, the demand for wireless network security rises sharply. Encryption techniques such as Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access-Enterprise (WPA-Enterprise) and WPA-Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK) are the main means to protect the security of WLAN at present. WPA-Enterprise requires a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server which is expensive and difficult for common user to setup. Because most small-scale wireless network will not select this strategy, we focus on WEP and WPA-PSK. Corresponding author: address: [email protected]
2 22 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ WEP is the most widely used security algorithm for IEEE wireless network. Several serious weaknesses in the protocol have been shown by cryptanalysts. In 2007, a research proposed a new attack which could recover a 104-bit WEP key with probability 50% less than one minute using only 40,000 captured packets [1]. WPA is defined in response to several serious weaknesses in WEP. WPA-PSK is designed for home and small office networks. Because the four-way handshake during the authentication is not protected in the WPA-PSK network, it is vulnerable to the password cracking attacks if users rely on a weak passphrase. In reality, most people use a simple password as a pre-shared passphrase. In November 2008 Erik Tews and Martin Beck researchers of two German technical universities (HTU DresdenH and HTU DarmstadtH) uncovered a WPA weakness which stems from a previously known flaw in WEP [2]. The flaw can decrypt short packets with mostly known contents, such as address resolution protocol (ARP) messages. In February 2010, a new attack was found by Martin Beck that allowed an attacker to decrypt all traffic towards the client [3]. Not only cryptanalysts and professional hackers can crack passwords of wireless network, but also ordinary computer users can do this by some decryption software such as Spoonwep and Spoonwpa in the famous hacker platform Back Track 4. Tutorials of these decryption software can be found easily from the Internet. As a matter of fact, because of the existence of the WLAN decryption software, there are a lot of people stealing other people s network resources without paying. In order to provide secure WLAN and resist existing attacks, a new secure strategy is needed. However, the new strategy must be able to be adopted by the existing wireless routers because millions of wireless routers have been released to market and are in use. Moreover, the new secure strategy should resist existing attacks and not introduce any new vulnerability. Finally, the new secure strategy should not increase users financial burden. Here, we propose a new strategy based on web authentication with unshared key and virtual local area network (VLAN) in wireless network. We choose Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer (HTTPS) and Message-Digest algorithm 5 (MD5) to provide protection for the user passwords in the web authentication. A random string is set to ensure that the login information is unique every time. Therefore, Wi-Fi-password decryption software will fail in the web authentication. In order to solve identify theft on the existing wireless routers. We divide the WLAN into two VLANs. Client devices which have not passed the authentication and those have passed the authentication are administered separately in the two VLANs. Thus the hacker can t send packets to get IP address and media access control (MAC) address from valid users. Our new secure strategy has the advantages of simplicity and compatibility with the existing wireless routers. It strengthens the security of wireless network and does not introduce new secure issues. Users can replace the old strategies with our new secure strategy or add it as a part in the network security framework according to the demands. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces some relevant knowledge occurred in this paper. Section 3 illustrates our new secure strategy. Section 4 evaluates the security of the new secure strategy. Finally, Section 5 gives our conclusions. 2. RELEVANT KNOWLEDGE 2.1. Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer (HTTPS) is a combination of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol with the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol to provide the encrypted communication and the secure identification of a network web server. HTTPS can provide sufficient protection against the eavesdropper attack and the man-in-the-middle attack Message-Digest Algorithm 5 This work is supported by the Research Innovation Fund for College Students of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Grant No ).
3 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ 23 Message-Digest algorithm 5 (MD5) is a widely used cryptographic hash function which can produce a 128-bit hash value. It has been shown that MD5 is not collision resistant [4] [5] [6], but recovering the source value is still impossible. Therefore, MD5 is still employed in a wide variety of security applications Identity Theft In this paper, identity theft is narrowly defined as identity theft happened in Local Area Network. Network access system usually identifies client devices according to their IP addresses and MAC addresses. By thieving IP address and MAC address, the hacker can pretend to be a valid user to access the network and do whatever he wants Virtual Local Area Network Virtual Local Area Network, commonly known as VLAN is a data exchange technology which can divide local area network into separate segments thereby creating virtual workgroups. VLAN provides the flexibility to adapt to changes in network requirements and allow for simplified administration. By using VLAN, administrators can also control traffic between different segments to strengthen the network security. In recent year, VLAN has been applied in wireless network. Wireless routers with VLAN are widely available on the market Service Set Identifier Service Set Identifier (SSID) is used to identify a particular WLAN. A client device receives broadcast messages from all access points within range advertising their SSIDs. The client device can then either manually or automatically based on configuration select the network with which to associate. SSID broadcast can be forbidden, in this way, wireless network will not occur in the network selecting list on client devices The Man-In-The-Middle Attack The man-in-the-middle attack is a form of indirect intrusion. The attacker makes independent connections with the victims at both ends of a conversation and relays messages between them. The victims believe that they are talking directly to each other over a private connection while the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker. The attacker can obtain secrets and privacies which he is interested in by analyzing the messages going between the two victims. 3. A NEW SECURE STRATEGY BASED ON WEB AUTHENTICATION WITH UNSHARED KEY AND VLAN IN WIRELESS NETWORK 3. 1 Web Authentication with Unshared Key In reality, most wireless networks in homes or small offices are protected by Wi-Fi-password and almost all WLAN decryption software available in Internet aims at cracking the Wi-Fi-password. According to the actuality, in our new secure strategy, we set a mini web server in the wireless router. The mini web server provides a Web Authentication with unshared key, that is, every user has his own name and password. The user information is stored in a special file which can only be read and written by the root user. Before accessing network, all users must correctly input their names and passwords on an authentication web page. The Web Authentication is similar to WPA-Enterprise. However, it does not need additional equipments and based on different encryption. According to the actual security demand, users can replace the Wi-Fi-password Authentication with the Web Authentication or add the Web Authentication as a part in the network access authentication process.
4 24 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ We choose HTTPS and MD5 to ensure the security of the authentication process. The Web Authentication is based on Client/Server model and it is similar to the 802.1x authentication, but simpler. The authentication process is shown in the Fig.1. Step1: The Client sends a Login-Request to the Server to apply for the authentication. Step2: The Server sends a MD5-Challenge to the Client which contains a random 16-byte string. Step3: After receiving the MD5-Challenge, the Client adds the random string to the end of password and calls the MD5 function to deal with them. The MD5 function returns a 128-bit string and then the Client sends it with the username as a MD5-Response to the Server. Step4: After receiving the MD5-Response, the Server checks the user data and gets the corresponding password. The server does the same thing as the Client does in step3 to get a hash string. If the string in the MD5-Response matches the string produced by the Server, the corresponding IP address and MAC address will be recorded. Then a Success page will be sent to the Client and the Client is allowed to access the network. If the Client submits incorrect information, it will receive a Failure page. The logoff process needs two steps: Step1: The Client submits a Logoff-Request to the Server. Step2: The Server cancels the Client s network access qualification and sends a Logoff page to the Client. In the view of the security, the random string can be used only once and a life time is set to indicate the valid time of a random string to a specific client. If the Server doesn t receive the MD5-Response from the Client in the life time, the random string becomes invalid. If the Client wants to continue the authentication, it must send a new request to get a new random string. In addition, if the Client submits incorrect information ten times continuously, it will be refused to login in an hour A Solution to Identify Theft In the new security framework, whether a packet is from a valid user is determined by its IP address and MAC address. After cracking the Wi-Fi-password, the hacker can get IP addresses and MAC addresses of valid users easily. Therefore, the new security framework is vulnerable to identity theft. The most effective and widely used method to deal with the identity theft is IP-MAC-port-bind which means setting a binding of IP address, MAC address and port. The specific user s data stream can only get through the network from a corresponding port. The hackers cannot find out which port is the correct one, so identity theft is useless. However, IP-MAC-port- bind can only be done on advanced switches. Figure 1. Web authentication
5 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ 25 We propose our strategy based on VLAN in wireless network. We divide the WLAN into two VLANs marked as VLAN0 and VLAN1 separately. VLAN0 associates with client devices before authentication and its SSID broadcast is permitted. VLAN1 associates with client devices after authentication and its SSID broadcast is forbidden (Fig.2). In this way, client devices can only receive broadcast messages from VLAN0. When a computer connects to the router, the IP it got is from VLAN0. After submitting correct username and password, it will receive SSID information of VLAN1 from VLAN0. Then the user can associate the computer with VLAN1 and gets a new IP. A rule is written in route table to forbid communications between the two VLANs. Thus the hacker can t send packets to valid users to get their IP addresses and MAC addresses, he even cannot get the fact that there is another VLAN in the network. In this way, we ensure the security of user identity. 4. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Now we evaluate the security of the new secure strategy Wi-Fi-Password Decryption Software Not all the people can handle complex and advanced decryption technique, so Wi-Fi-password decryption software is the most common and widely used method. We design the new secure strategy in response to weaknesses of Wi-Fi-password protection. A Web Authentication with unshared key is added as a part in the network access authentication process. We adopt MD5 and HTTPS to protect the user passwords. It is different from the encryption techniques of Wi-Fi-password. Therefore, Wi-Fi-password decryption software will fail in the new security framework Identity Theft In the new security framework, the WLAN is divided into two VLANs. Communications between the two VLANs are forbidden. The hacker cannot get users IP address and MAC address. So identity theft is useless. SSID broadcast VLAN0 VLAN1 Figure 2. Wireless network with two VLANs 4. 3 The Eavesdropper Attack After cracking Wi-Fi-password, the hacker listens in the authentication communication as an Eavesdropper (Fig.3). Based on the secure channel provided by HTTPS, most eavesdropping tools will be useless. However,
6 26 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ there are some infrequent attacks which are able to steal secure data from the connection. But what contain in the packet are a username and a 128-bit encrypted string. Besides, the string can be used only once, so the hacker will not succeed in accessing network by sending this message to the web server The Man-In-The-Middle Attack There are two authentication processes in the man-in-the-middle attack in fact (Fig.4). If the hacker chooses this attack, he needs to construct a wireless network with the same name and the same Wi-Fi-password to attract valid users. But it is not enough, because users can verify whether the server certificate is trusted or not. The worst situation is that the hacker succeeds in faking a server certificate. It has been proven practical by Arjen Lenstra[7]. But because of the life time which has been set to indicate the valid time of a random string to a specific client, the hacker needs to accomplish the whole attack in quite limited time. We suppose that an authentication process needs T seconds. The attack will fail if the life time is set to be a value between T and 2T. In addition, it is not worth to choose this high-cost attack for a small-scale wireless network The Brute Force Attack If the hacker gets a valid username and keeps on trying different passwords, he will not succeed. Failing ten times continuously, he will be refused to login in an hour by the system. Hacker User Router Figure 3. The eavesdropper attack Hacker Real Router User Fake Router Figure 4. The man-in-the-middle attack 5. CONCLUSIONS In this paper, we first introduce the secure issues of common secure strategies supported by most popular commercial wireless routers currently. Then we propose a new strategy for small-scale IEEE wireless
7 A New Secure Strategy for Small-Scale IEEE Wireless Local Area Networ 27 local area network based on web authentication with unshared key and VLAN in the wireless network. Finally we evaluate the new strategy s security against practical attacks. Based on known knowledge and techniques, the new strategy can ensure the security of the small-scale wireless network. Moreover, it is simple, wieldy and lowcost. References [1] E. Tews, R.-P. Weinmann, and A. Pyshki, Breaking 104 bit WEP in less than 60 seconds, WISA'07 Proceedings, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, pp , [2] E. Tews, M. Beck, Practical attacks against WEP and WPA, WiSec '09 Proceedings, ACM New York, pp [3] M. Beck, Enhanced TKIP michael attacks, unpublished. [4] Xiaoyun Wang, Dengguo Feng, Xuejia Lai, and Hongbo Yu, Collisions for hash functions MD4, MD5, HAVAL-128 and RIPEMD, Crypto 2004, August, 2004, retrieved July 27, 2008, in press. [5] Xiaoyun Wang and Hongbo Yu, How to break MD5 and other hash functions, EUROCRYPT 2005 Proceedings, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, pp.19-35, Retrieved December 21, [6] J. Black, M. Cochran, and T. Highland, A study of the MD5 attacks: insights and improvements, FSE 2006 Proceedings, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, pp , March, Retrieved July 27, [7] M. Stevens, A. Lenstra, and B. Weger, Chosen-Prefix collisions for MD5 and colliding X.509 certificates for different identities, EUROCRYPT '07 Proceedings, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, pp.1-22, 2007.
Authentication in WLAN
 Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network.
 9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
Wireless Networks. Welcome to Wireless
 Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
How To Secure A Wireless Network With A Wireless Device (Mb8000)
 MB8000 Network Security and Access Control Overview MB8000 employs almost all of the current popular WLAN security mechanisms. These include wireless-user isolation, closed system (by turning off SSID
MB8000 Network Security and Access Control Overview MB8000 employs almost all of the current popular WLAN security mechanisms. These include wireless-user isolation, closed system (by turning off SSID
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network
 Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3
 Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3 1. Abstract Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was the first encryption scheme used for protecting wireless traffic. It consisted of a private
Vulnerabilities in WEP Christopher Hoffman Cryptography 2 2011-3 1. Abstract Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) was the first encryption scheme used for protecting wireless traffic. It consisted of a private
Self Help Guide IMPORTANT! Securing Your Wireless Network. This Guide refers to the following Products: Please read the following carefully; Synopsis:
 IMPORTANT! This Guide refers to the following Products: Securing Your Wireless Network Please read the following carefully; Synopsis: This Guide is designed to help you if you have a Wireless Network that
IMPORTANT! This Guide refers to the following Products: Securing Your Wireless Network Please read the following carefully; Synopsis: This Guide is designed to help you if you have a Wireless Network that
 If security were all that mattered, computers would never be turned on, let alone hooked into a network with literally millions of potential intruders. Dan Farmer, System Administrators Guide to Cracking
If security were all that mattered, computers would never be turned on, let alone hooked into a network with literally millions of potential intruders. Dan Farmer, System Administrators Guide to Cracking
Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list)
 Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list) Hackers can easily trap information transmitted over wireless network, it has to be encrypted to avoid unauthorized users
Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list) Hackers can easily trap information transmitted over wireless network, it has to be encrypted to avoid unauthorized users
CSC574: Computer and Network Security
 CSC574: Computer and Network Security Lecture 21 Prof. William Enck Spring 2016 (Derived from slides by Micah Sherr) Wireless Security Wireless makes network security much more difficult Wired: If Alice
CSC574: Computer and Network Security Lecture 21 Prof. William Enck Spring 2016 (Derived from slides by Micah Sherr) Wireless Security Wireless makes network security much more difficult Wired: If Alice
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009. Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected]
 802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
Security. Contents. S-72.3240 Wireless Personal, Local, Metropolitan, and Wide Area Networks 1
 Contents Security requirements Public key cryptography Key agreement/transport schemes Man-in-the-middle attack vulnerability Encryption. digital signature, hash, certification Complete security solutions
Contents Security requirements Public key cryptography Key agreement/transport schemes Man-in-the-middle attack vulnerability Encryption. digital signature, hash, certification Complete security solutions
Nokia E90 Communicator Using WLAN
 Using WLAN Nokia E90 Communicator Using WLAN Nokia E90 Communicator Using WLAN Legal Notice Nokia, Nokia Connecting People, Eseries and E90 Communicator are trademarks or registered trademarks of Nokia
Using WLAN Nokia E90 Communicator Using WLAN Nokia E90 Communicator Using WLAN Legal Notice Nokia, Nokia Connecting People, Eseries and E90 Communicator are trademarks or registered trademarks of Nokia
Exam Questions SY0-401
 Exam Questions SY0-401 CompTIA Security+ Certification http://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/sy0-401/ 1. A company has implemented PPTP as a VPN solution. Which of the following ports would need to be opened
Exam Questions SY0-401 CompTIA Security+ Certification http://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/sy0-401/ 1. A company has implemented PPTP as a VPN solution. Which of the following ports would need to be opened
Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point
 Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003
 Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003 2003 Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance
Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003 2003 Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings
 Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
Security Awareness. Wireless Network Security
 Security Awareness Wireless Network Security Attacks on Wireless Networks Three-step process Discovering the wireless network Connecting to the network Launching assaults Security Awareness, 3 rd Edition
Security Awareness Wireless Network Security Attacks on Wireless Networks Three-step process Discovering the wireless network Connecting to the network Launching assaults Security Awareness, 3 rd Edition
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition. Chapter 6. Wireless Network Security
 Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
VPN. Date: 4/15/2004 By: Heena Patel Email:[email protected]
 VPN Date: 4/15/2004 By: Heena Patel Email:[email protected] What is VPN? A VPN (virtual private network) is a private data network that uses public telecommunicating infrastructure (Internet), maintaining
VPN Date: 4/15/2004 By: Heena Patel Email:[email protected] What is VPN? A VPN (virtual private network) is a private data network that uses public telecommunicating infrastructure (Internet), maintaining
SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer
 www.harmonysecurity.com [email protected] SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Encryption Techniques 3 3 Protocol Overview 3 3.1 The SSL Record
www.harmonysecurity.com [email protected] SSL A discussion of the Secure Socket Layer By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Encryption Techniques 3 3 Protocol Overview 3 3.1 The SSL Record
Table of Contents. Cisco Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example
 Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS
 Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS A Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: January 2009 Protecting Payment Card Information It is every retailer
Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS A Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: January 2009 Protecting Payment Card Information It is every retailer
Wireless Security Overview. Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected]
 Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
7 Network Security. 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Improving the Security 7.3 Internet Security Framework. 7.5 Absolute Security?
 7 Network Security 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Improving the Security 7.3 Internet Security Framework 7.4 Firewalls 7.5 Absolute Security? 7.1 Introduction Security of Communications data transport e.g. risk
7 Network Security 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Improving the Security 7.3 Internet Security Framework 7.4 Firewalls 7.5 Absolute Security? 7.1 Introduction Security of Communications data transport e.g. risk
Network Authentication - 802.1X Secure the Edge of the Network - Technical White Paper
 Bosch Security Systems Video Systems Network Authentication - 802.1X Secure the Edge of the Network - Technical White Paper 4 July 2016 Secure the edge of the network Security devices are mostly located
Bosch Security Systems Video Systems Network Authentication - 802.1X Secure the Edge of the Network - Technical White Paper 4 July 2016 Secure the edge of the network Security devices are mostly located
How To Protect A Wireless Lan From A Rogue Access Point
 : Understanding Security to Ensure Compliance with HIPAA Healthcare is a natural environment for wireless LAN solutions. With a large mobile population of doctors, nurses, physician s assistants and other
: Understanding Security to Ensure Compliance with HIPAA Healthcare is a natural environment for wireless LAN solutions. With a large mobile population of doctors, nurses, physician s assistants and other
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security
 Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
Wireless Encryption Protection
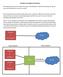 Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Wireless Technology Seminar
 Wireless Technology Seminar Introduction Adam Worthington Network Consultant [email protected] Wireless LAN Why? Flexible network access for your users? Guest internet access? VoWIP? RFID? Available
Wireless Technology Seminar Introduction Adam Worthington Network Consultant [email protected] Wireless LAN Why? Flexible network access for your users? Guest internet access? VoWIP? RFID? Available
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter with RangeBooster. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54GR. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Introduction to WiFi Security. Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected]
 Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
Question How do I access the router s web-based setup page? Answer
 http://linksys.custhelp.com/cgi-bin/linksys.cfg/php/enduser/std_adp.php?p_faqid=3676 Question How do I access the router s web-based setup page? Answer All Linksys routers have a built-in web-based setup
http://linksys.custhelp.com/cgi-bin/linksys.cfg/php/enduser/std_adp.php?p_faqid=3676 Question How do I access the router s web-based setup page? Answer All Linksys routers have a built-in web-based setup
WiFi Security Assessments
 WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
Overview. Summary of Key Findings. Tech Note PCI Wireless Guideline
 Overview The following note covers information published in the PCI-DSS Wireless Guideline in July of 2009 by the PCI Wireless Special Interest Group Implementation Team and addresses version 1.2 of the
Overview The following note covers information published in the PCI-DSS Wireless Guideline in July of 2009 by the PCI Wireless Special Interest Group Implementation Team and addresses version 1.2 of the
STEP III: Enable the Wireless Network Card. STEP IV: Print out the Printer Settings pages to determine the IP Address
 Title: How do I configure the wireless printer without a network cable and install the printer driver in Windows? NOTE: For successful wireless setup, you MUST know your network security settings. STEP
Title: How do I configure the wireless printer without a network cable and install the printer driver in Windows? NOTE: For successful wireless setup, you MUST know your network security settings. STEP
WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy
 WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy Digi Wi-Point 3G supports various Wi-Fi security options, including WEP-40/WEP-104 and WPA- PSK and WPA2-PSK. To configure WLAN security on DIGI WI-POINT 3G, you may
WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy Digi Wi-Point 3G supports various Wi-Fi security options, including WEP-40/WEP-104 and WPA- PSK and WPA2-PSK. To configure WLAN security on DIGI WI-POINT 3G, you may
CS5490/6490: Network Security- Lecture Notes - November 9 th 2015
 CS5490/6490: Network Security- Lecture Notes - November 9 th 2015 Wireless LAN security (Reference - Security & Cooperation in Wireless Networks by Buttyan & Hubaux, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2007, Chapter
CS5490/6490: Network Security- Lecture Notes - November 9 th 2015 Wireless LAN security (Reference - Security & Cooperation in Wireless Networks by Buttyan & Hubaux, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2007, Chapter
Network Security. Mobin Javed. October 5, 2011
 Network Security Mobin Javed October 5, 2011 In this class, we mainly had discussion on threat models w.r.t the class reading, BGP security and defenses against TCP connection hijacking attacks. 1 Takeaways
Network Security Mobin Javed October 5, 2011 In this class, we mainly had discussion on threat models w.r.t the class reading, BGP security and defenses against TCP connection hijacking attacks. 1 Takeaways
All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices
 Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
WI-FI SECURITY: A LITERATURE REVIEW OF SECURITY IN WIRELESS NETWORK
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 3, Issue 5, May 2015, 23-30 Impact Journals WI-FI SECURITY: A LITERATURE
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 3, Issue 5, May 2015, 23-30 Impact Journals WI-FI SECURITY: A LITERATURE
CTS2134 Introduction to Networking. Module 8.4 8.7 Network Security
 CTS2134 Introduction to Networking Module 8.4 8.7 Network Security Switch Security: VLANs A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical grouping of computers based on a switch port. VLAN membership is configured by
CTS2134 Introduction to Networking Module 8.4 8.7 Network Security Switch Security: VLANs A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical grouping of computers based on a switch port. VLAN membership is configured by
12/3/08. Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability. Mobility Makes it Difficult to Establish Trust
 Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY
 WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY Dec 2010 The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region The contents of this document remain the property of, and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY Dec 2010 The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region The contents of this document remain the property of, and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
Setting up a WiFi Network (WLAN)
 Setting up a WiFi Network (WLAN) How to set up Wi-Fi on your Huawei E960 InZone Step 1: In the address field on your internet browser, type http://192.168.1.1/ Step 2: Type admin into the Password box
Setting up a WiFi Network (WLAN) How to set up Wi-Fi on your Huawei E960 InZone Step 1: In the address field on your internet browser, type http://192.168.1.1/ Step 2: Type admin into the Password box
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Agenda. References
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics
 The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
Wireless Security for Mobile Computers
 A Datalogic Mobile and Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: March 2009 Protecting Confidential and Sensitive Information It is every retailer s nightmare: An attacker
A Datalogic Mobile and Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: March 2009 Protecting Confidential and Sensitive Information It is every retailer s nightmare: An attacker
CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK
 CLASSROOM CHALLENGE CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK In this lesson you will learn how to connect the Raspberry Pi computer to a network with both a wired and a wireless connection. To complete
CLASSROOM CHALLENGE CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK In this lesson you will learn how to connect the Raspberry Pi computer to a network with both a wired and a wireless connection. To complete
The Wireless LAN (Local Area Network) USB adapter can be operated in one of the two following networking configurations :
 SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER Quick Start Guide About this guide This Quick Start Guide describes how to install and operate your SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER. Please read this manual before you install the
SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER Quick Start Guide About this guide This Quick Start Guide describes how to install and operate your SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER. Please read this manual before you install the
WEP Overview 1/2. and encryption mechanisms Now deprecated. Shared key Open key (the client will authenticate always) Shared key authentication
 WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication and firewall captive portal
 EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 00029 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800029 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication
EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 00029 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800029 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication
Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones
 Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones Polycom s SpectraLink 8400 Series wireless phones meet the highest security requirements. By the time you deploy
Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones Polycom s SpectraLink 8400 Series wireless phones meet the highest security requirements. By the time you deploy
Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance
 Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance Originally Published: September 2010 Updated: October 2012 A White Paper from Laird Technologies Connecting medical devices to a hospital s Wi-Fi network
Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance Originally Published: September 2010 Updated: October 2012 A White Paper from Laird Technologies Connecting medical devices to a hospital s Wi-Fi network
Developing Network Security Strategies
 NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Developing Network Security Strategies NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Security Design The 12 Step Program 1. Identify network
NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Developing Network Security Strategies NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Security Design The 12 Step Program 1. Identify network
Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks. By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary
 Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary The evolution to wireless networks allows connections with the same quality of data transfer at a lower cost but
Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary The evolution to wireless networks allows connections with the same quality of data transfer at a lower cost but
Advanced Security Issues in Wireless Networks
 Advanced Security Issues in Wireless Networks Seminar aus Netzwerke und Sicherheit Security Considerations in Interconnected Networks Alexander Krenhuber Andreas Niederschick 9. Januar 2009 Advanced Security
Advanced Security Issues in Wireless Networks Seminar aus Netzwerke und Sicherheit Security Considerations in Interconnected Networks Alexander Krenhuber Andreas Niederschick 9. Januar 2009 Advanced Security
A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS
 A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS Jose Perez Texas A&M University Corpus Christi Email: [email protected] Fax Number: (361) 825-2795 Faculty Advisor: Dr. Ahmed Mahdy, Texas A&M University
A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS Jose Perez Texas A&M University Corpus Christi Email: [email protected] Fax Number: (361) 825-2795 Faculty Advisor: Dr. Ahmed Mahdy, Texas A&M University
Ebonyi State University Abakaliki 2 Department of Computer Science. Our Saviour Institute of Science and Technology 3 Department of Computer Science
 Security Measures taken in Securing Data Transmission on Wireless LAN 1 AGWU C. O., 2 ACHI I. I., AND 3 OKECHUKWU O. 1 Department of Computer Science Ebonyi State University Abakaliki 2 Department of Computer
Security Measures taken in Securing Data Transmission on Wireless LAN 1 AGWU C. O., 2 ACHI I. I., AND 3 OKECHUKWU O. 1 Department of Computer Science Ebonyi State University Abakaliki 2 Department of Computer
WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document
 WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document Produced by FUNET led working group on wireless systems and mobility (MobileFunet) (WLAN security) Author: Wenche Backman Contributors: Ville Mattila/CSC
WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document Produced by FUNET led working group on wireless systems and mobility (MobileFunet) (WLAN security) Author: Wenche Backman Contributors: Ville Mattila/CSC
Wireless VPN White Paper. WIALAN Technologies, Inc. http://www.wialan.com
 Wireless VPN White Paper WIALAN Technologies, Inc. http://www.wialan.com 2014 WIALAN Technologies, Inc. all rights reserved. All company and product names are registered trademarks of their owners. Abstract
Wireless VPN White Paper WIALAN Technologies, Inc. http://www.wialan.com 2014 WIALAN Technologies, Inc. all rights reserved. All company and product names are registered trademarks of their owners. Abstract
The following chart provides the breakdown of exam as to the weight of each section of the exam.
 Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54GR. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WUSB54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WUSB54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without
Network Access Security. Lesson 10
 Network Access Security Lesson 10 Objectives Exam Objective Matrix Technology Skill Covered Exam Objective Exam Objective Number Firewalls Given a scenario, install and configure routers and switches.
Network Access Security Lesson 10 Objectives Exam Objective Matrix Technology Skill Covered Exam Objective Exam Objective Number Firewalls Given a scenario, install and configure routers and switches.
WLAN Security Networking with Confidence
 WLAN Security Networking with Confidence Introduction So you ve just installed a new wireless local area network (WLAN) in your small business or home. The access point is on and connected, the client
WLAN Security Networking with Confidence Introduction So you ve just installed a new wireless local area network (WLAN) in your small business or home. The access point is on and connected, the client
SSI. Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2. Bertil Maria Pires Marques. E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009. Dez 2009 1
 SSI Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2 Bertil Maria Pires Marques E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009 Dez 2009 1 WEP -Wired Equivalent Privacy WEPisasecurityprotocol,specifiedintheIEEEWireless Fidelity
SSI Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2 Bertil Maria Pires Marques E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009 Dez 2009 1 WEP -Wired Equivalent Privacy WEPisasecurityprotocol,specifiedintheIEEEWireless Fidelity
Design and Implementation Guide. Apple iphone Compatibility
 Design and Implementation Guide Apple iphone Compatibility Introduction Security in wireless LANs has long been a concern for network administrators. While securing laptop devices is well understood, new
Design and Implementation Guide Apple iphone Compatibility Introduction Security in wireless LANs has long been a concern for network administrators. While securing laptop devices is well understood, new
Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract
 Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms
Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms
WIRELESS SECURITY. Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program. Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006
 WIRELESS SECURITY Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Wireless LAN Security Learning Objectives Students should be able
WIRELESS SECURITY Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Wireless LAN Security Learning Objectives Students should be able
Portal Authentication Technology White Paper
 Portal Authentication Technology White Paper Keywords: Portal, CAMS, security, authentication Abstract: Portal authentication is also called Web authentication. It authenticates users by username and password
Portal Authentication Technology White Paper Keywords: Portal, CAMS, security, authentication Abstract: Portal authentication is also called Web authentication. It authenticates users by username and password
Securing your Linksys WRT54G
 Securing your Linksys WRT54G Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b and 802.11g wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms in these
Securing your Linksys WRT54G Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b and 802.11g wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms in these
A Dynamic Extensible Authentication Protocol for Device Authentication in Transport Layer Raghavendra.K 1, G. Raghu 2, Sumith N 2
 A Dynamic Extensible Authentication Protocol for Device Authentication in Transport Layer Raghavendra.K 1, G. Raghu 2, Sumith N 2 1 Dept of CSE, P.A.College of Engineering 2 Dept of CSE, Srnivas institute
A Dynamic Extensible Authentication Protocol for Device Authentication in Transport Layer Raghavendra.K 1, G. Raghu 2, Sumith N 2 1 Dept of CSE, P.A.College of Engineering 2 Dept of CSE, Srnivas institute
Security in Wireless Local Area Network
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
ALL1682511. 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point. User s Manual
 ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
Secure Sockets Layer
 SSL/TLS provides endpoint authentication and communications privacy over the Internet using cryptography. For web browsing, email, faxing, other data transmission. In typical use, only the server is authenticated
SSL/TLS provides endpoint authentication and communications privacy over the Internet using cryptography. For web browsing, email, faxing, other data transmission. In typical use, only the server is authenticated
New Avatars of Honeypot Attacks on WiFi Networks
 New Avatars of Honeypot Attacks on WiFi Networks Prabhash Dhyani Wireless Security Researcher,Airtight Networks,Pune Email: [email protected] Abstract WiFi has become mainstream technology
New Avatars of Honeypot Attacks on WiFi Networks Prabhash Dhyani Wireless Security Researcher,Airtight Networks,Pune Email: [email protected] Abstract WiFi has become mainstream technology
STEP III: Enable the Wireless Network Card
 How do I configure the wireless printer without a network cable and install the printer driver in Macintosh OS X? NOTE: For successful wireless setup, you MUST know your network security settings. STEP
How do I configure the wireless printer without a network cable and install the printer driver in Macintosh OS X? NOTE: For successful wireless setup, you MUST know your network security settings. STEP
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54G. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a
CS549: Cryptography and Network Security
 CS549: Cryptography and Network Security by Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, IIT Cryptography and Network Security 1 Notice This lecture note (Cryptography and Network Security) is prepared
CS549: Cryptography and Network Security by Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, IIT Cryptography and Network Security 1 Notice This lecture note (Cryptography and Network Security) is prepared
Top 10 Security Checklist for SOHO Wireless LANs
 Introduction Corporations, government agencies, the military, and enterprises in fact all medium to large scale wireless LANs have a different set of security requirements compared to the wireless LAN
Introduction Corporations, government agencies, the military, and enterprises in fact all medium to large scale wireless LANs have a different set of security requirements compared to the wireless LAN
White paper. Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points. http://www.veryxtech.com
 White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
Configuring Security Solutions
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains these sections: Cisco Wireless LAN Solution Security, page 3-2 Using WCS to Convert a Cisco Wireless LAN Solution from
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains these sections: Cisco Wireless LAN Solution Security, page 3-2 Using WCS to Convert a Cisco Wireless LAN Solution from
Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs
 Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs Why Network Security? Keep the bad guys out. (1) Closed networks
Overview of Network Security The need for network security Desirable security properties Common vulnerabilities Security policy designs Why Network Security? Keep the bad guys out. (1) Closed networks
Quick Start Guide. WRV210 Wireless-G VPN Router with RangeBooster. Cisco Small Business
 Quick Start Guide Cisco Small Business WRV210 Wireless-G VPN Router with RangeBooster Package Contents WRV210 Router Ethernet Cable Power Adapter Product CD-ROM Quick Start Guide Welcome Thank you for
Quick Start Guide Cisco Small Business WRV210 Wireless-G VPN Router with RangeBooster Package Contents WRV210 Router Ethernet Cable Power Adapter Product CD-ROM Quick Start Guide Welcome Thank you for
Security. TestOut Modules 12.6 12.10
 Security TestOut Modules 12.6 12.10 Authentication Authentication is the process of submitting and checking credentials to validate or prove user identity. 1. Username 2. Credentials Password Smart card
Security TestOut Modules 12.6 12.10 Authentication Authentication is the process of submitting and checking credentials to validate or prove user identity. 1. Username 2. Credentials Password Smart card
The Importance of Wireless Security
 The Importance of Wireless Security Because of the increasing popularity of wireless networks, there is an increasing need for security. This is because unlike wired networks, wireless networks can be
The Importance of Wireless Security Because of the increasing popularity of wireless networks, there is an increasing need for security. This is because unlike wired networks, wireless networks can be
WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you...
 WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you... Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity / [email protected]) Diego Sor ([email protected] / [email protected]) July 2010 Abstract Cisco access points
WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you... Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity / [email protected]) Diego Sor ([email protected] / [email protected]) July 2010 Abstract Cisco access points
Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview
 Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview This course will teach students about Legacy Security, encryption ciphers and methods, 802.11 authentication methods, dynamic encryption
Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview This course will teach students about Legacy Security, encryption ciphers and methods, 802.11 authentication methods, dynamic encryption
Differences Between SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS
 Differences Between SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS Loren Weith: 0600978 July 3, 2006 SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS (1.0) all provide for a secure channel between clients and servers: if looked at in terms of the OSI reference
Differences Between SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS Loren Weith: 0600978 July 3, 2006 SSLv2, SSLv3, and TLS (1.0) all provide for a secure channel between clients and servers: if looked at in terms of the OSI reference
Chapter 7 Transport-Level Security
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 7 Transport-Level Security Lectured by Nguyễn Đức Thái Outline Web Security Issues Security Socket Layer (SSL) Transport Layer Security (TLS) HTTPS Secure Shell
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 7 Transport-Level Security Lectured by Nguyễn Đức Thái Outline Web Security Issues Security Socket Layer (SSL) Transport Layer Security (TLS) HTTPS Secure Shell
Using etoken for SSL Web Authentication. SSL V3.0 Overview
 Using etoken for SSL Web Authentication Lesson 12 April 2004 etoken Certification Course SSL V3.0 Overview Secure Sockets Layer protocol, version 3.0 Provides communication privacy over the internet. Prevents
Using etoken for SSL Web Authentication Lesson 12 April 2004 etoken Certification Course SSL V3.0 Overview Secure Sockets Layer protocol, version 3.0 Provides communication privacy over the internet. Prevents
Wireless Security. New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication. Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.
 Wireless Security New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.com National Conference on m-health and EOE Minneapolis, MN Sept 9, 2003 Key
Wireless Security New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.com National Conference on m-health and EOE Minneapolis, MN Sept 9, 2003 Key
SY0-201. system so that an unauthorized individual can take over an authorized session, or to disrupt service to authorized users.
 system so that an unauthorized individual can take over an authorized session, or to disrupt service to authorized users. From a high-level standpoint, attacks on computer systems and networks can be grouped
system so that an unauthorized individual can take over an authorized session, or to disrupt service to authorized users. From a high-level standpoint, attacks on computer systems and networks can be grouped
Hole196 Vulnerability in WPA2
 Hole196 Vulnerability in WPA2 1 Hole196 Vulnerability in WPA2 Presenters: Anthony Paladino, Managing Director, Systems Engineering Dr. Kaustubh Phanse, Principal Wireless Architect Md. Sohail Ahmad, Senior
Hole196 Vulnerability in WPA2 1 Hole196 Vulnerability in WPA2 Presenters: Anthony Paladino, Managing Director, Systems Engineering Dr. Kaustubh Phanse, Principal Wireless Architect Md. Sohail Ahmad, Senior
Sinus 1054 data Installation Guide
 Sinus 1054 data Installation Guide Please also pay careful attention to the safety notices concerning the handling of this product as described in the operating instructions on the supplied CD-ROM. T-Com
Sinus 1054 data Installation Guide Please also pay careful attention to the safety notices concerning the handling of this product as described in the operating instructions on the supplied CD-ROM. T-Com
Chapter 2 Wireless Networking Basics
 Chapter 2 Wireless Networking Basics Wireless Networking Overview Some NETGEAR products conform to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11g standard for wireless LANs (WLANs).
Chapter 2 Wireless Networking Basics Wireless Networking Overview Some NETGEAR products conform to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11g standard for wireless LANs (WLANs).
