Chapter 2 Wireless Networking Basics
|
|
|
- Rosamund Barber
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Wireless Networking Basics Wireless Networking Overview Some NETGEAR products conform to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) g standard for wireless LANs (WLANs). On an wireless link, data is encoded using direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology and is transmitted in the unlicensed radio spectrum at 2.5 GHz. The maximum data rate for the g wireless link is 54 Mbps, but it will automatically back down from 54 Mbps when the radio signal is weak or when interference is detected. The standard is also called Wireless Ethernet or Wi-Fi by the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA, see an industry standard group promoting interoperability among devices. The standard offers two methods for configuring a wireless network ad hoc and infrastructure. Infrastructure Mode With a wireless access point, the wireless LAN can operate in the infrastructure mode. This mode lets you connect wirelessly to wireless network devices within a fixed range or area of coverage. The access point has one or more antennas that allow you to interact with wireless nodes. In infrastructure mode, the wireless access point converts airwave data into wired Ethernet data, acting as a bridge between the wired LAN and wireless clients. Connecting multiple access points via a wired Ethernet backbone can further extend the wireless network coverage. As a mobile computing device moves out of the range of one access point, it moves into the range of another. As a result, wireless clients can freely roam from one access point domain to another and still maintain seamless network connection. Wireless Networking Basics 2-1
2 Ad Hoc Mode (Peer-to-Peer Workgroup) In an ad hoc network, computers are brought together as needed; thus, the network has no structure or fixed points each node can be set up to communicate with any other node. No access point is involved in this configuration. This mode enables you to quickly set up a small wireless workgroup and allows workgroup members to exchange data or share printers as supported by Microsoft networking in the various Windows operating systems. Some vendors also refer to ad hoc networking as peer-to-peer group networking. In this configuration, network packets are directly sent and received by the intended transmitting and receiving stations. As long as the stations are within range of one another, this is the easiest and least expensive way to set up a wireless network. Network Name: Extended Service Set Identification (ESSID) The Extended Service Set Identification (ESSID) is one of two types of Service Set Identification (SSID). In an ad hoc wireless network with no access points, the Basic Service Set Identification (BSSID) is used. In an infrastructure wireless network that includes an access point, the ESSID is used, but may still be referred to as SSID. An SSID is a 32-character (maximum) alphanumeric key identifying the name of the wireless local area network. Some vendors refer to the SSID as the network name. For the wireless devices in a network to communicate with each other, all devices must be configured with the same SSID. Wireless Channels IEEE g/b wireless nodes communicate with each other using radio frequency signals in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band between 2.4 GHz and 2.5 GHz. Neighboring channels are 5 MHz apart. However, due to the spread spectrum effect of the signals, a node sending signals using a particular channel will utilize frequency spectrum 12.5 MHz above and below the center channel frequency. As a result, two separate wireless networks using neighboring channels (for example, channel 1 and channel 2) in the same general vicinity will interfere with each other. Applying two channels that allow the maximum channel separation will decrease the amount of channel cross-talk and provide a noticeable performance increase over networks with minimal channel separation. 2-2 Wireless Networking Basics
3 The radio frequency channels used are listed in Table 2-1: Table g Radio Frequency Channels Channel Center Frequency Frequency Spread MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz Note: The available channels supported by wireless products in various countries are different. Regulations in the United States prohibit using channels greater than channel 11. For NETGEAR products sold outside the United States, the wireless region selection determines which channels are available for use in the product. The preferred channel separation between the channels in neighboring wireless networks is 25 MHz (five channels). This means that you can apply up to three different channels within your wireless network. In the United States, only 11 usable wireless channels are available, so we recommended that you start using channel 1, grow to use channel 6, and add channel 11 when necessary, because these three channels do not overlap. Wireless Networking Basics 2-3
4 WEP Wireless Security The absence of a physical connection between nodes makes the wireless links vulnerable to eavesdropping and information theft. To provide a certain level of security, the IEEE standard has defined two types of authentication methods, Open System and Shared Key. With Open System authentication, a wireless computer can join any network and receive any messages that are not encrypted. With Shared Key authentication, only those computers that possess the correct authentication key can join the network. By default, IEEE wireless devices operate in an Open System network. Recently, Wi-Fi, the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance ( developed the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), a new strongly enhanced Wi- Fi security. WPA will soon be incorporated into the IEEE standard. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is discussed below, and WPA is discussed on page 2-8. WEP Authentication The standard defines several services that govern how two devices communicate. The following events must occur before an station can communicate with an Ethernet network through an access point such as the one built in to the NETGEAR product: 1. Turn on the wireless station. 2. The station listens for messages from any access points that are in range. 3. The station finds a message from an access point that has a matching SSID. 4. The station sends an authentication request to the access point. 5. The access point authenticates the station. 6. The station sends an association request to the access point. 7. The access point associates with the station. 8. The station can now communicate with the Ethernet network through the access point. An access point must authenticate a station before the station can associate with the access point or communicate with the network. The IEEE standard defines two types of WEP authentication: Open System and Shared Key. Open System Authentication allows any device to join the network, assuming that the device SSID matches the access point SSID. Alternatively, the device can use the ANY SSID option to associate with any available access point within range, regardless of its SSID. Shared Key Authentication requires that the station and the access point have the same WEP key to authenticate. These two authentication procedures are described below. 2-4 Wireless Networking Basics
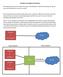
5 Cable/DSL ProSafeWirelessVPN Security Firewall PWR TEST IN TERN ET LNK ACT MODEL WLAN LOCAL FVM Enable LNK/ACT Wireless Networking Basics WEP Open System Authentication This process is illustrated below Authentication Open System Steps 1) Authentication request sent to AP Access Point (AP) 2) AP authenticates Client attempting to connect 3) Client connects to network Cable or DLS modem Figure 2-1 The following steps occur when two devices use Open System Authentication: 1. The station sends an authentication request to the access point. 2. The access point authenticates the station. 3. The station associates with the access point and joins the network. Wireless Networking Basics 2-5
6 Cable/DSL ProSafeWirelessVPN Security Firewall PWR TEST IN TERN ET LNK ACT MODEL WLAN LOCAL FVM Enable LNK/ACT Wireless Networking Basics WEP Shared Key Authentication This process is illustrated below Authentication Shared Key Steps 1) Authentication request sent to AP Access Point (AP) Client attempting to connect 3) Client encrypts challenge text and sends it back to AP 2) AP sends challenge text Cable or DLS modem 4) AP decrypts, and if correct, authenticates client 5) Client connects to network Figure 2-2 The following steps occur when two devices use Shared Key Authentication: 1. The station sends an authentication request to the access point. 2. The access point sends challenge text to the station. 3. The station uses its configured 64-bit or 128-bit default key to encrypt the challenge text, and it sends the encrypted text to the access point. 4. The access point decrypts the encrypted text using its configured WEP key that corresponds to the station s default key. The access point compares the decrypted text with the original challenge text. If the decrypted text matches the original challenge text, then the access point and the station share the same WEP key, and the access point authenticates the station. 5. The station connects to the network. If the decrypted text does not match the original challenge text (that is, the access point and station do not share the same WEP key), then the access point will refuse to authenticate the station, and the station will be unable to communicate with either the network or Ethernet network. 2-6 Wireless Networking Basics
7 Key Size and Configuration The IEEE standard supports two types of WEP encryption: 40-bit and 128-bit. The 64-bit WEP data encryption method allows for a five-character (40-bit) input. Additionally, 24 factory-set bits are added to the forty-bit input to generate a 64-bit encryption key. (The 24 factoryset bits are not user-configurable). This encryption key will be used to encrypt/decrypt all data transmitted via the wireless interface. Some vendors refer to the 64-bit WEP data encryption as 40- bit WEP data encryption because the user-configurable portion of the encryption key is 40 bits wide. The 128-bit WEP data encryption method consists of 104 user-configurable bits. Similar to the 40- bit WEP data encryption method, the remaining 24 bits are factory-set and not user-configurable. Some vendors allow passphrases to be entered instead of the cryptic hexadecimal characters to ease encryption key entry. The 128-bit encryption is stronger than 40-bit encryption, but 128-bit encryption may not be available outside the United States due to U.S. export regulations. When configured for 40-bit encryption, products typically support up to four WEP keys. Each 40-bit WEP key is expressed as five sets of two hexadecimal digits (0 9 and A F). For example, is a 40-bit WEP key. When configured for 128-bit encryption, g products typically support four WEP keys, but some manufacturers support only one 128-bit key. The 128-bit WEP Key is expressed as 13 sets of two hexadecimal digits (0 9 and A F). For example, AB CD EF is a 128-bit WEP key. Typically, access points can store up to four 128-bit WEP keys, but some client adapters can only store one. Therefore, make sure that your access and client adapters configurations match. Whatever keys you enter for an access point, you must also enter the same keys for the client adapter in the same order. In other words, WEP key 1 on the AP must match WEP key 1 on the client adapter, WEP key 2 on the AP must match WEP key 2 on the client adapter, etc. Note: The access point and the client adapters can have different default WEP keys as long as the keys are in the same order. In other words, the AP can use WEP key 2 as its default key to transmit, while a client adapter can use WEP key 3 as its default key to transmit. The two devices will communicate as long as the access point s WEP key 2 is the same as the client s WEP key 2, and the AP s WEP key 3 is the same as the client s WEP key 3. Wireless Networking Basics 2-7
8 How to Use WEP Parameters WEP data encryption is used when the wireless devices are configured to operate in Shared Key authentication mode. There are two shared key methods implemented in most commercially available products, 64-bit and 128-bit WEP data encryption. Before enabling WEP on an network, you must first consider what type of encryption you require and the key size you want to use. Typically, there are three WEP Encryption options available for products: Do Not Use WEP: The network does not encrypt data. For authentication purposes, the network uses Open System Authentication. Use WEP for Encryption: A transmitting device encrypts the data portion of every packet it sends using a configured WEP key. The receiving g device decrypts the data using the same WEP key. For authentication purposes, the g network uses Open System Authentication. Use WEP for Authentication and Encryption: A transmitting device encrypts the data portion of every packet it sends using a configured WEP key. The receiving device decrypts the data using the same WEP key. For authentication purposes, the network uses Shared Key Authentication. Note: Some access points also support Use WEP for Authentication Only (Shared Key Authentication without data encryption). However, some NETGEAR products do not offer this option. WPA Wireless Security Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a specification of standards-based, interoperable security enhancements that increase the level of data protection and access control for existing and future wireless LAN systems. The IEEE introduced the WEP as an optional security measure to secure g (Wi-Fi) WLANs, but inherent weaknesses in the standard soon became obvious. In response to this situation, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced a new security architecture in October 2002 that remedies the shortcomings of WEP. This standard, formerly known as Safe Secure Network (SSN), is designed to work with existing products and offers forward compatibility with i, the new wireless security architecture being defined in the IEEE. WPA offers the following benefits: 2-8 Wireless Networking Basics
9 Enhanced data privacy Robust key management Data origin authentication Data integrity protection Starting in August of 2003, all new Wi-Fi certified products had to support WPA, and all existing Wi-Fi certified products had one year to comply with the new standard or lose their Wi-Fi certification. NETGEAR has implemented WPA on client and access point products. As of August 2004, all Wi-Fi certified products must support WPA. How Does WPA Compare to WEP? WEP is a data encryption method and is not intended as a user authentication mechanism. WPA user authentication is implemented using 802.1x and the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). Support for 802.1x authentication is required in WPA. In the standard, 802.1x authentication was optional. For details on EAP specifically, refer to IETF RFC With WEP, all access points and client wireless adapters on a particular wireless LAN must use the same encryption key. A major problem with the standard is that the keys are cumbersome to change. If you do not update the WEP keys often, an unauthorized person with a sniffing tool can monitor your network for less than a day and decode the encrypted messages. Products based on the standard alone offer system administrators no effective method to update the keys. For , WEP encryption is optional. For WPA, encryption using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is required. TKIP replaces WEP with a new encryption algorithm that is stronger than the WEP algorithm, but that uses the calculation facilities present on existing wireless devices to perform encryption operations. TKIP provides important data encryption enhancements including a per-packet key mixing function, a message integrity check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism. Through these enhancements, TKIP addresses all known WEP vulnerabilities. How Does WPA Compare to IEEE i? WPA is forward-compatible with the IEEE i security specification currently under development. WPA is a subset of the current i draft and uses certain pieces of the i draft that were ready to bring to market in 2003, such as 802.1x and TKIP. The main pieces of the i draft that are not included in WPA are secure IBSS (Ad-Hoc mode), secure fast handoff (for specialized VoIP phones), as well as enhanced encryption protocols such as AES- CCMP. These features are either not yet ready for market or will require hardware upgrades to implement. Wireless Networking Basics 2-9
10 What are the Key Features of WPA Security? The following security features are included in the WPA standard: WPA Authentication WPA Encryption Key Management Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) Michael message integrity code (MIC) AES Support Support for a Mixture of WPA and WEP Wireless Clients These features are discussed below. WPA addresses most of the known WEP vulnerabilities and is primarily intended for wireless infrastructure networks as found in the enterprise. This infrastructure includes stations, access points, and authentication servers (typically Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service servers, called RADIUS servers). The RADIUS server holds (or has access to) user credentials (for example, user names and passwords) and authenticates wireless users before they gain access to the network. The strength of WPA comes from an integrated sequence of operations that encompass 802.1X/ EAP authentication and sophisticated key management and encryption techniques. Its major operations include: Network security capability determination. This occurs at the level and is communicated through WPA information elements in Beacon, Probe Response, and (Re) Association Requests. Information in these elements includes the authentication method (802.1X or Pre-shared key) and the preferred cipher suite (WEP, TKIP, or AES, which is Advanced Encryption Standard). The primary information conveyed in the Beacon frames is the authentication method and the cipher suite. Possible authentication methods include 802.1X and Pre-shared key. Pre-shared key is an authentication method that uses a statically configured passphrase on both the stations and the access point. This removes the need for an authentication server, which in many home and small office environments is neither available nor desirable. Possible cipher suites include: WEP, TKIP, and AES. We say more about TKIP and AES when addressing data privacy below. Authentication. EAP over 802.1X is used for authentication. Mutual authentication is gained by choosing an EAP type supporting this feature and is required by WPA. The 802.1X port access control prevents full access to the network until authentication completes. The 802.1X EAPOL-Key packets are used by WPA to distribute per-session keys to those stations successfully authenticated Wireless Networking Basics
11 The supplicant in the station uses the authentication and cipher suite information contained in the information elements to decide which authentication method and cipher suite to use. For example, if the access point is using the Pre-shared key method, then the supplicant need not authenticate using full-blown 802.1X. Rather, the supplicant must simply prove to the access point that it is in possession of the pre-shared key. If the supplicant detects that the service set does not contain a WPA information element, then it knows it must use pre-wpa 802.1X authentication and key management in order to access the network. Key management. WPA features a robust key generation/management system that integrates the authentication and data privacy functions. Keys are generated after successful authentication and through a subsequent four-way handshake between the station and access point. Data Privacy (Encryption). Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is used to wrap WEP in sophisticated cryptographic and security techniques to overcome most of its weaknesses. Data integrity. TKIP includes a message integrity code (MIC) at the end of each plain text message to ensure messages are not being spoofed. Wireless Networking Basics 2-11
12 WPA Authentication: Enterprise-level User Authentication via 802.1x/EAP and RADIUS Wireless LAN Login Authentication Wired Network with Optional 801.1x Port-based Network Access Control WPA enabled wireless client with supplicant WPA enabled Access Point using pre-shared key or 802.1x TCP/IP Ports Closed Until TCP/IP Ports Opened After Authentication RADIUS Server Login Authentication Certificate Authority (for example, Win Server, Verisign, etc.) Figure 2-3 IEEE 802.1x offers an effective framework for authenticating and controlling user traffic to a protected network, as well as providing a vehicle for dynamically varying data encryption keys via EAP from a RADIUS server, for example. This framework enables using a central authentication server, which employs mutual authentication, so that a rogue wireless user does not join the network. Note that 802.1x does not provide the actual authentication mechanisms. When using 802.1x, the EAP type, such as Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) or EAP Tunneled Transport Layer Security (EAP-TTLS), defines how the authentication takes place. Note: For environments with a RADIUS infrastructure, WPA supports Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). For environments without a RADIUS infrastructure, WPA supports the use of a pre-shared key. Together, these technologies provide a framework for strong user authentication Wireless Networking Basics
13 Windows XP implements 802.1x natively, and several NETGEAR switch and wireless access point products support 802.1x. Client with a WPAenabled wireless adapter and supplicant (Windows XP, Funk, Meetinghouse, etc.) For example, a WPA-enabled AP For example, a RADIUS server Figure 2-4 The access point (AP) sends Beacon Frames with WPA information elements to the stations in the service set. Information elements include the required authentication method (802.1x or Preshared key) and the preferred cipher suite (WEP, TKIP, or AES). Probe Responses (AP to station) and Association Requests (station to AP) also contain WPA information elements. 1. Initial 802.1x communications begin with an unauthenticated supplicant (that is, client device) attempting to connect with an authenticator (that is, access point). The client sends an EAP-start message. This begins a series of message exchanges to authenticate the client. 2. The access point replies with an EAP-request identity message. Wireless Networking Basics 2-13
14 3. The client sends an EAP-response packet containing the identity to the authentication server. The access point responds by enabling a port for passing only EAP packets from the client to an authentication server located on the wired side of the access point. The access point blocks all other traffic, such as HTTP, DHCP, and POP3 packets, until the access point can verify the client's identity using an authentication server (for example, RADIUS). 4. The authentication server uses a specific authentication algorithm to verify the client's identity. This could be through the use of digital certificates or some other EAP authentication type. 5. The authentication server will either send an accept or reject message to the access point. 6. The access point sends an EAP-success packet (or reject packet) to the client. 7. If the authentication server accepts the client, then the access point will transition the client's port to an authorized state and forward additional traffic. The important part to know at this point is that the software supporting the specific EAP type resides on the authentication server and within the operating system or application supplicant software on the client devices. The access point acts as a pass through for 802.1x messages, which means that you can specify any EAP type without needing to upgrade an 802.1x-compliant access point. As a result, you can update the EAP authentication type to such devices as token cards (Smart Cards), Kerberos, one-time passwords, certificates, and public key authentication or as newer types become available and your requirements for security change. WPA Data Encryption Key Management With 802.1x, the re-keying of unicast encryption keys is optional. Additionally, and 802.1x provide no mechanism to change the global encryption key used for multicast and broadcast traffic. With WPA, re-keying of both unicast and global encryption keys is required. For the unicast encryption key, the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) changes the key for every frame, and the change is synchronized between the wireless client and the wireless access point (AP). For the global encryption key, WPA includes a facility (the Information Element) for the wireless AP to advertise the changed key to the connected wireless clients. If configured to implement dynamic key exchange, the 802.1x authentication server can return session keys to the access point along with the accept message. The access point uses the session keys to build, sign and encrypt an EAP key message that is sent to the client immediately after sending the success message. The client can then use contents of the key message to define applicable encryption keys. In typical 802.1x implementations, the client can automatically change encryption keys as often as necessary to minimize the possibility of eavesdroppers having enough time to crack the key in current use Wireless Networking Basics
15 Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). WPA uses TKIP to provide important data encryption enhancements including a per-packet key mixing function, a message integrity check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a rekeying mechanism. TKIP also provides for the following: The verification of the security configuration after the encryption keys are determined. The synchronized changing of the unicast encryption key for each frame. The determination of a unique starting unicast encryption key for each pre-shared key authentication. Michael. With and WEP, data integrity is provided by a 32-bit integrity check value (ICV) that is appended to the payload and encrypted with WEP. Although the ICV is encrypted, you can use cryptanalysis to change bits in the encrypted payload and update the encrypted ICV without being detected by the receiver. With WPA, a method known as Michael specifies a new algorithm that calculates an 8-byte message integrity code (MIC) using the calculation facilities available on existing wireless devices. The MIC is placed between the data portion of the IEEE frame and the 4-byte ICV. The MIC field is encrypted together with the frame data and the ICV. Michael also provides replay protection. A new frame counter in the IEEE frame is used to prevent replay attacks. AES Support. One of the encryption methods supported by WPA, besides TKIP, is the advanced encryption standard (AES), although AES support will not be required initially for Wi-Fi certification. This is viewed as the optimal choice for security-conscious organizations, but the problem with AES is that it requires a fundamental redesign of the NIC s hardware in both the station and the access point. TKIP was a pragmatic compromise that allows organizations to deploy better security while AES-capable equipment is being designed, manufactured, and incrementally deployed. Is WPA Perfect? WPA is not without its vulnerabilities. Specifically, it is susceptible to denial of service (DoS) attacks. If the access point receives two data packets that fail the Message Integrity Code (MIC) check within 60 seconds of each other, then the network is under an active attack, and as a result the access point employs counter measures, which include disassociating each station using the access point. This prevents an attacker from gleaning information about the encryption key and alerts administrators, but it also causes users to lose network connectivity for 60 seconds. More than anything else, this may just prove that no single security tactic is completely invulnerable. WPA is a definite step forward in WLAN security over WEP and has to be thought of as a single part of an end-to-end network security strategy. Wireless Networking Basics 2-15
16 Product Support for WPA Some NETGEAR wireless Wi-Fi certified products support the WPA standard. WPA requires software changes to the following: Wireless access points Wireless network adapters Wireless client programs Supporting a Mixture of WPA and WEP Wireless Clients To support the gradual transition of WEP-based wireless networks to WPA, a wireless AP can support both WEP and WPA clients at the same time. During the association, the wireless AP determines which clients use WEP and which clients use WPA. The disadvantage to supporting a mixture of WEP and WPA clients is that the global encryption key is not dynamic. This is because WEP-based clients cannot support it. All other benefits to the WPA clients, such as integrity, are maintained. However, a mixed mode supporting WPA and non-wpa clients offers network security that is no better than that obtained with a non-wpa network, and thus this mode of operation is discouraged. Changes to Wireless Access Points Wireless access points must have their firmware updated to support the following: The new WPA information element To advertise their support of WPA, wireless APs send the Beacon frame with a new WPA information element that contains the wireless AP's security configuration (encryption algorithms and wireless security configuration information). The WPA two-phase authentication Open system, then 802.1x (EAP with RADIUS or Pre-shared key). TKIP Michael AES (optional) To upgrade your wireless access points to support WPA, obtain a WPA firmware update from your wireless AP vendor and upload it to your wireless AP Wireless Networking Basics
17 Changes to Wireless Network Adapters Wireless network adapters must have their firmware updated to support the following: The new WPA information element Wireless clients must be able to process the WPA information element and respond with a specific security configuration. The WPA two-phase authentication Open system, then 802.1x (EAP or Pre-shared key). TKIP Michael AES (optional) To upgrade your wireless network adapters to support WPA, obtain a WPA update from your wireless network adapter vendor, and update the wireless network adapter driver. For Windows wireless clients, you must obtain an updated network adapter driver that supports WPA. For wireless network adapter drivers that are compatible with Windows XP (Service Pack 1) and Windows Server 2003, the updated network adapter driver must be able to pass the adapter's WPA capabilities and security configuration to the Wireless Zero Configuration service. Microsoft has worked with many wireless vendors to embed the WPA firmware update in the wireless adapter driver. So, to update you Windows wireless client, all you have to do is obtain the new WPA-compatible driver and install the driver. The firmware is automatically updated when the wireless network adapter driver is loaded in Windows. Changes to Wireless Client Programs Wireless client programs must be updated to permit the configuration of WPA authentication (and Pre-shared key) and the new WPA encryption algorithms (TKIP and the optional AES component). To obtain the Microsoft WPA client program, visit the Microsoft Web site. Wireless Networking Basics 2-17
18 2-18 Wireless Networking Basics
Wireless Networking Basics. NETGEAR, Inc. 4500 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
 Wireless Networking Basics NETGEAR, Inc. 4500 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA n/a October 2005 2005 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks NETGEAR and Auto Uplink are trademarks
Wireless Networking Basics NETGEAR, Inc. 4500 Great America Parkway Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA n/a October 2005 2005 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks NETGEAR and Auto Uplink are trademarks
White paper. Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points. http://www.veryxtech.com
 White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition. Chapter 6. Wireless Network Security
 Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
12/3/08. Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability. Mobility Makes it Difficult to Establish Trust
 Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003
 Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003 2003 Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance
Wi-Fi Protected Access: Strong, standards-based, interoperable security for today s Wi-Fi networks Wi-Fi Alliance April 29, 2003 2003 Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance
Wireless security. Any station within range of the RF receives data Two security mechanism
 802.11 Security Wireless security Any station within range of the RF receives data Two security mechanism A means to decide who or what can use a WLAN authentication A means to provide privacy for the
802.11 Security Wireless security Any station within range of the RF receives data Two security mechanism A means to decide who or what can use a WLAN authentication A means to provide privacy for the
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009. Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected]
 802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
CS 356 Lecture 29 Wireless Security. Spring 2013
 CS 356 Lecture 29 Wireless Security Spring 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists Chapter
CS 356 Lecture 29 Wireless Security Spring 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists Chapter
WIRELESS SECURITY IN 802.11 (WI-FI ) NETWORKS
 January 2003 January WHITE 2003 PAPER WIRELESS SECURITY IN 802.11 (WI-FI ) NETWORKS With the increasing deployment of 802.11 (or Wi-Fi) wireless networks in business environments, IT organizations are
January 2003 January WHITE 2003 PAPER WIRELESS SECURITY IN 802.11 (WI-FI ) NETWORKS With the increasing deployment of 802.11 (or Wi-Fi) wireless networks in business environments, IT organizations are
Wireless Security. New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication. Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.
 Wireless Security New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.com National Conference on m-health and EOE Minneapolis, MN Sept 9, 2003 Key
Wireless Security New Standards for 802.11 Encryption and Authentication Ann Geyer 209-754-9130 [email protected] www.tunitas.com National Conference on m-health and EOE Minneapolis, MN Sept 9, 2003 Key
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Agenda. References
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 8 Mobile Networks: Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Introduce security vulnerabilities and defenses Describe security functions
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings
 Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
The Importance of Wireless Security
 The Importance of Wireless Security Because of the increasing popularity of wireless networks, there is an increasing need for security. This is because unlike wired networks, wireless networks can be
The Importance of Wireless Security Because of the increasing popularity of wireless networks, there is an increasing need for security. This is because unlike wired networks, wireless networks can be
WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY
 WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY Much attention has been focused recently on the security aspects of existing Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) wireless LAN systems. The rapid growth and deployment of these systems into a
WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY Much attention has been focused recently on the security aspects of existing Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) wireless LAN systems. The rapid growth and deployment of these systems into a
Table of Contents. Cisco Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example
 Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms
 Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms Jingan Xu, Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Technical University of Ilmenau, Integrated Hard- and Software Systems Group [email protected], [email protected] Abstract.
Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms Jingan Xu, Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Technical University of Ilmenau, Integrated Hard- and Software Systems Group [email protected], [email protected] Abstract.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54GR. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WUSB54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WUSB54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without
Wireless Security for Mobile Computers
 A Datalogic Mobile and Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: March 2009 Protecting Confidential and Sensitive Information It is every retailer s nightmare: An attacker
A Datalogic Mobile and Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: March 2009 Protecting Confidential and Sensitive Information It is every retailer s nightmare: An attacker
Wireless LAN Access Point. IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps. User s Manual
 Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents...2 1.2 Features...2 1.3 Specifications...2 1.4 Physical Description...3 Chapter
Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents...2 1.2 Features...2 1.3 Specifications...2 1.4 Physical Description...3 Chapter
Security in IEEE 802.11 WLANs
 Security in IEEE 802.11 WLANs 1 IEEE 802.11 Architecture Extended Service Set (ESS) Distribution System LAN Segment AP 3 AP 1 AP 2 MS MS Basic Service Set (BSS) Courtesy: Prashant Krishnamurthy, Univ Pittsburgh
Security in IEEE 802.11 WLANs 1 IEEE 802.11 Architecture Extended Service Set (ESS) Distribution System LAN Segment AP 3 AP 1 AP 2 MS MS Basic Service Set (BSS) Courtesy: Prashant Krishnamurthy, Univ Pittsburgh
Analysis of Security Issues and Their Solutions in Wireless LAN 1 Shenam Chugh, 2 Dr.Kamal
 Analysis of Security Issues and Their Solutions in Wireless LAN 1 Shenam Chugh, 2 Dr.Kamal 1,2 Department of CSE 1,2,3 BRCM Bahal, Bhiwani 1 [email protected], 2 [email protected] Abstract This paper
Analysis of Security Issues and Their Solutions in Wireless LAN 1 Shenam Chugh, 2 Dr.Kamal 1,2 Department of CSE 1,2,3 BRCM Bahal, Bhiwani 1 [email protected], 2 [email protected] Abstract This paper
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics
 The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
How To Secure Your Network With 802.1X (Ipo) On A Pc Or Mac Or Macbook Or Ipo On A Microsoft Mac Or Ipow On A Network With A Password Protected By A Keyed Key (Ipow)
 Wireless LAN Security with 802.1x, EAP-TLS, and PEAP Steve Riley Senior Consultant MCS Trustworthy Computing Services So what s the problem? WEP is a euphemism Wired Equivalent Privacy Actually, it s a
Wireless LAN Security with 802.1x, EAP-TLS, and PEAP Steve Riley Senior Consultant MCS Trustworthy Computing Services So what s the problem? WEP is a euphemism Wired Equivalent Privacy Actually, it s a
WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy
 WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy Digi Wi-Point 3G supports various Wi-Fi security options, including WEP-40/WEP-104 and WPA- PSK and WPA2-PSK. To configure WLAN security on DIGI WI-POINT 3G, you may
WLAN Authentication and Data Privacy Digi Wi-Point 3G supports various Wi-Fi security options, including WEP-40/WEP-104 and WPA- PSK and WPA2-PSK. To configure WLAN security on DIGI WI-POINT 3G, you may
How To Protect A Wireless Lan From A Rogue Access Point
 : Understanding Security to Ensure Compliance with HIPAA Healthcare is a natural environment for wireless LAN solutions. With a large mobile population of doctors, nurses, physician s assistants and other
: Understanding Security to Ensure Compliance with HIPAA Healthcare is a natural environment for wireless LAN solutions. With a large mobile population of doctors, nurses, physician s assistants and other
How To Secure Wireless Networks
 Lecture 24 Wireless Network Security modified from slides of Lawrie Brown Wireless Security Overview concerns for wireless security are similar to those found in a wired environment security requirements
Lecture 24 Wireless Network Security modified from slides of Lawrie Brown Wireless Security Overview concerns for wireless security are similar to those found in a wired environment security requirements
chap18.wireless Network Security
 SeoulTech UCS Lab 2015-1 st chap18.wireless Network Security JeongKyu Lee Email: [email protected] Table of Contents 18.1 Wireless Security 18.2 Mobile Device Security 18.3 IEEE 802.11 Wireless
SeoulTech UCS Lab 2015-1 st chap18.wireless Network Security JeongKyu Lee Email: [email protected] Table of Contents 18.1 Wireless Security 18.2 Mobile Device Security 18.3 IEEE 802.11 Wireless
Preparing the Computers for TCP/IP Networking
 Configuration Preparing the Computers for TCP/IP Networking Configuring Windows 98, and ME for TCP/IP Networking Verifying TCP/IP Properties Configuring Windows 2000 or XP for IP Networking Install or
Configuration Preparing the Computers for TCP/IP Networking Configuring Windows 98, and ME for TCP/IP Networking Verifying TCP/IP Properties Configuring Windows 2000 or XP for IP Networking Install or
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Wireless A/G. USB Network Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54AG. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. WIRELESS Wireless A/G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. WIRELESS Wireless A/G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered
WiFi Security: Deploying WPA/WPA2/802.1X and EAP in the Enterprise
 Michael Disabato Service Director Network & Telecom Strategies [email protected] Diana Kelley Senior Analyst Security & Risk Management Strategies [email protected] www.burtongroup.com WiFi
Michael Disabato Service Director Network & Telecom Strategies [email protected] Diana Kelley Senior Analyst Security & Risk Management Strategies [email protected] www.burtongroup.com WiFi
WEP Overview 1/2. and encryption mechanisms Now deprecated. Shared key Open key (the client will authenticate always) Shared key authentication
 WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security
 Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
Introduction to WiFi Security. Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected]
 Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. Access Point with SRX. User Guide WIRELESS WAP54GX. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point with SRX User Guide Model No. WAP54GX Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point with SRX User Guide Model No. WAP54GX Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
NXC5500/2500. Application Note. 802.11w Management Frame Protection. ZyXEL NXC Application Notes. Version 4.20 Edition 2, 02/2015
 NXC5500/2500 Version 4.20 Edition 2, 02/2015 Application Note 802.11w Management Frame Protection Copyright 2015 ZyXEL Communications Corporation 802.11w Management Frame Protection Introduction IEEE 802.11w
NXC5500/2500 Version 4.20 Edition 2, 02/2015 Application Note 802.11w Management Frame Protection Copyright 2015 ZyXEL Communications Corporation 802.11w Management Frame Protection Introduction IEEE 802.11w
Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview
 Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview This course will teach students about Legacy Security, encryption ciphers and methods, 802.11 authentication methods, dynamic encryption
Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Course Overview This course will teach students about Legacy Security, encryption ciphers and methods, 802.11 authentication methods, dynamic encryption
Security in Wireless Local Area Network
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
TL-WN310G 54M Wireless CardBus Adapter
 54M Wireless CardBus Adapter Rev: 1.0.1 1910010042 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands and
54M Wireless CardBus Adapter Rev: 1.0.1 1910010042 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands and
Link Layer and Network Layer Security for Wireless Networks
 Link Layer and Network Layer Security for Wireless Networks Interlink Networks, Inc. May 15, 2003 1 LINK LAYER AND NETWORK LAYER SECURITY FOR WIRELESS NETWORKS... 3 Abstract... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2.
Link Layer and Network Layer Security for Wireless Networks Interlink Networks, Inc. May 15, 2003 1 LINK LAYER AND NETWORK LAYER SECURITY FOR WIRELESS NETWORKS... 3 Abstract... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2.
ALL1682511. 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point. User s Manual
 ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
Wireless Robust Security Networks: Keeping the Bad Guys Out with 802.11i (WPA2)
 Wireless Robust Security Networks: Keeping the Bad Guys Out with 802.11i (WPA2) SUNY Technology Conference June 21, 2011 Bill Kramp FLCC Network Administrator Copyright 2011 William D. Kramp All Rights
Wireless Robust Security Networks: Keeping the Bad Guys Out with 802.11i (WPA2) SUNY Technology Conference June 21, 2011 Bill Kramp FLCC Network Administrator Copyright 2011 William D. Kramp All Rights
Self Help Guide IMPORTANT! Securing Your Wireless Network. This Guide refers to the following Products: Please read the following carefully; Synopsis:
 IMPORTANT! This Guide refers to the following Products: Securing Your Wireless Network Please read the following carefully; Synopsis: This Guide is designed to help you if you have a Wireless Network that
IMPORTANT! This Guide refers to the following Products: Securing Your Wireless Network Please read the following carefully; Synopsis: This Guide is designed to help you if you have a Wireless Network that
A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS
 A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS Jose Perez Texas A&M University Corpus Christi Email: [email protected] Fax Number: (361) 825-2795 Faculty Advisor: Dr. Ahmed Mahdy, Texas A&M University
A SURVEY OF WIRELESS NETWORK SECURITY PROTOCOLS Jose Perez Texas A&M University Corpus Christi Email: [email protected] Fax Number: (361) 825-2795 Faculty Advisor: Dr. Ahmed Mahdy, Texas A&M University
UNIK4250 Security in Distributed Systems University of Oslo Spring 2012. Part 7 Wireless Network Security
 UNIK4250 Security in Distributed Systems University of Oslo Spring 2012 Part 7 Wireless Network Security IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s charter to develop
UNIK4250 Security in Distributed Systems University of Oslo Spring 2012 Part 7 Wireless Network Security IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s charter to develop
CS 336/536 Computer Network Security. Summer Term 2010. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) compiled by Anthony Barnard
 CS 336/536 Computer Network Security Summer Term 2010 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) compiled by Anthony Barnard 2 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) These notes, intended to follow the previous handout IEEE802.11
CS 336/536 Computer Network Security Summer Term 2010 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) compiled by Anthony Barnard 2 Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) These notes, intended to follow the previous handout IEEE802.11
THE IMPORTANCE OF CRYPTOGRAPHY STANDARD IN WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORKING
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) Volume 6, Issue 9, Sep 2015, pp. 65-74, Article ID: IJECET_06_09_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijecetissues.asp?jtype=ijecet&vtype=6&itype=9
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) Volume 6, Issue 9, Sep 2015, pp. 65-74, Article ID: IJECET_06_09_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijecetissues.asp?jtype=ijecet&vtype=6&itype=9
Wireless Ethernet LAN (WLAN) General 802.11a/802.11b/802.11g FAQ
 Wireless Ethernet LAN (WLAN) General 802.11a/802.11b/802.11g FAQ Q: What is a Wireless LAN (WLAN)? Q: What are the benefits of using a WLAN instead of a wired network connection? Q: Are Intel WLAN products
Wireless Ethernet LAN (WLAN) General 802.11a/802.11b/802.11g FAQ Q: What is a Wireless LAN (WLAN)? Q: What are the benefits of using a WLAN instead of a wired network connection? Q: Are Intel WLAN products
Wireless Network Standard and Guidelines
 Wireless Network Standard and Guidelines Purpose The standard and guidelines listed in this document will ensure the uniformity of wireless network access points and provide guidance for monitoring, maintaining
Wireless Network Standard and Guidelines Purpose The standard and guidelines listed in this document will ensure the uniformity of wireless network access points and provide guidance for monitoring, maintaining
Journal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems, vol. I, no. 1, 2009 ISSN 2067 4074
 Issues in WiFi Networks Nicolae TOMAI Faculty of Economic Informatics Department of IT&C Technologies Babes Bolyai Cluj-Napoca University, Romania [email protected] Abstract: The paper has four sections.
Issues in WiFi Networks Nicolae TOMAI Faculty of Economic Informatics Department of IT&C Technologies Babes Bolyai Cluj-Napoca University, Romania [email protected] Abstract: The paper has four sections.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter with RangeBooster. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54GR. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with RangeBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GR Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS
 Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS A Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: January 2009 Protecting Payment Card Information It is every retailer
Wi-Fi Client Device Security and Compliance with PCI DSS A Summit Data Communications White Paper Original Version: June 2008 Update: January 2009 Protecting Payment Card Information It is every retailer
WiFi Security Assessments
 WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
Wireless Network Policy
 Wireless Network Policy Purpose Guide the deployment and integrity of wireless networking on the Kettering University campus to ensure reliable, compatible, and secure operation Protect the security of
Wireless Network Policy Purpose Guide the deployment and integrity of wireless networking on the Kettering University campus to ensure reliable, compatible, and secure operation Protect the security of
EPI-3601S Wireless LAN PCI adapter Version 1.2 EPI-3601S. Wireless LAN PCI Adapter. (802.11g & 802.11b up to 108 Mbps) User Manual. Version: 1.
 EPI-3601S Wireless LAN PCI Adapter (802.11g & 802.11b up to 108 Mbps) User Manual Version: 1.2 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...3 2 FEATURES...3 3 PACKAGE CONTENTS...4 4 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...5 5 INSTALLATION...5
EPI-3601S Wireless LAN PCI Adapter (802.11g & 802.11b up to 108 Mbps) User Manual Version: 1.2 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...3 2 FEATURES...3 3 PACKAGE CONTENTS...4 4 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...5 5 INSTALLATION...5
Huawei WLAN Authentication and Encryption
 Huawei WLAN Authentication and Encryption The Huawei integrated Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) solution can provide all-round services for municipalities at various levels and enterprises and institutions
Huawei WLAN Authentication and Encryption The Huawei integrated Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) solution can provide all-round services for municipalities at various levels and enterprises and institutions
LP-348. LP-Yagy2415. LP-510G/550G 54M Wireless Adapter PCMCIA/PCI. User Guide Ver:2.0 LP-5420G WWW.LANPRO.COM
 LP-348 LP-Yagy2415 LP-1518 LP-5P LP-510G/550G 54M Wireless Adapter PCMCIA/PCI User Guide Ver:2.0 LP-5420G WWW.LANPRO.COM COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a
LP-348 LP-Yagy2415 LP-1518 LP-5P LP-510G/550G 54M Wireless Adapter PCMCIA/PCI User Guide Ver:2.0 LP-5420G WWW.LANPRO.COM COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i
 Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices
 Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
Wireless-G Business PCI Adapter with RangeBooster
 Wireless-G Business PCI Adapter with RangeBooster USER GUIDE BUSINESS SERIES Model No. WMP200 Wireless Model Model No. No. Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Wireless-G Business PCI Adapter with RangeBooster USER GUIDE BUSINESS SERIES Model No. WMP200 Wireless Model Model No. No. Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network
 Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
Agenda. Wireless LAN Security. TCP/IP Protocol Suite (Internet Model) Security for TCP/IP. Agenda. Car Security Story
 Wireless s June September 00 Agenda Wireless Security ผศ. ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Asst. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. [email protected] http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~anan Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University,
Wireless s June September 00 Agenda Wireless Security ผศ. ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Asst. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. [email protected] http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~anan Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University,
802.11b and associated network security risks for the home user
 802.11b and associated network security risks for the home user by Michael Osten [email protected] Background ================= Approved in 1997 by the IEEE 802 committee, 802.11 details the framework
802.11b and associated network security risks for the home user by Michael Osten [email protected] Background ================= Approved in 1997 by the IEEE 802 committee, 802.11 details the framework
Lecture 3. WPA and 802.11i
 Lecture 3 WPA and 802.11i Lecture 3 WPA and 802.11i 1. Basic principles of 802.11i and WPA 2. IEEE 802.1X 3. Extensible Authentication Protocol 4. RADIUS 5. Efficient Handover Authentication 1 Lecture
Lecture 3 WPA and 802.11i Lecture 3 WPA and 802.11i 1. Basic principles of 802.11i and WPA 2. IEEE 802.1X 3. Extensible Authentication Protocol 4. RADIUS 5. Efficient Handover Authentication 1 Lecture
Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance
 Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance Originally Published: September 2010 Updated: October 2012 A White Paper from Laird Technologies Connecting medical devices to a hospital s Wi-Fi network
Wi-Fi Client Device Security & HIPAA Compliance Originally Published: September 2010 Updated: October 2012 A White Paper from Laird Technologies Connecting medical devices to a hospital s Wi-Fi network
WLAN Access Security Technical White Paper. Issue 02. Date 2012-09-24 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
 WLAN Access Security Technical White Paper Issue 02 Date 2012-09-24 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. . 2012. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
WLAN Access Security Technical White Paper Issue 02 Date 2012-09-24 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. . 2012. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
Symm ym e m t e r t ic i c cr c yptogr ypt aphy a Ex: RC4, AES 2
 Wi-Fi Security FEUP>MIEIC>Mobile Communications Jaime Dias Symmetric cryptography Ex: RC4, AES 2 Digest (hash) Cryptography Input: variable length message Output: a fixed-length bit
Wi-Fi Security FEUP>MIEIC>Mobile Communications Jaime Dias Symmetric cryptography Ex: RC4, AES 2 Digest (hash) Cryptography Input: variable length message Output: a fixed-length bit
Wireless-N. User Guide. PCI Adapter WMP300N (EU) WIRELESS. Model No.
 2,4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP300N (EU) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of
2,4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP300N (EU) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of
Top 10 Security Checklist for SOHO Wireless LANs
 Introduction Corporations, government agencies, the military, and enterprises in fact all medium to large scale wireless LANs have a different set of security requirements compared to the wireless LAN
Introduction Corporations, government agencies, the military, and enterprises in fact all medium to large scale wireless LANs have a different set of security requirements compared to the wireless LAN
Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones
 Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones Polycom s SpectraLink 8400 Series wireless phones meet the highest security requirements. By the time you deploy
Understanding Wireless Security on Your Polycom SpectraLink 8400 Series Wireless Phones Polycom s SpectraLink 8400 Series wireless phones meet the highest security requirements. By the time you deploy
Abstract. Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Enterasys Wireless Access Point 3000 (RBT3K-AG) to Support Avaya IP Office, Avaya IP Wireless Telephones and Avaya Phone Manager
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Enterasys Wireless Access Point 3000 (RBT3K-AG) to Support Avaya IP Office, Avaya IP Wireless Telephones and Avaya Phone Manager
Wireless Networks. Welcome to Wireless
 Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
WI-FI VS. BLUETOOTH TWO OUTSTANDING RADIO TECHNOLOGIES FOR DEDICATED PAYMENT APPLICATION
 WI-FI VS. BLUETOOTH TWO OUTSTANDING RADIO TECHNOLOGIES FOR DEDICATED PAYMENT APPLICATION Ingenico is often asked: what are the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies, which is the best one,
WI-FI VS. BLUETOOTH TWO OUTSTANDING RADIO TECHNOLOGIES FOR DEDICATED PAYMENT APPLICATION Ingenico is often asked: what are the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies, which is the best one,
Wireless Technology Seminar
 Wireless Technology Seminar Introduction Adam Worthington Network Consultant [email protected] Wireless LAN Why? Flexible network access for your users? Guest internet access? VoWIP? RFID? Available
Wireless Technology Seminar Introduction Adam Worthington Network Consultant [email protected] Wireless LAN Why? Flexible network access for your users? Guest internet access? VoWIP? RFID? Available
Authentication in WLAN
 Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Wireless Encryption Protection
 Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
How To Get A Power Station To Work With A Power Generator Without A Substation
 Wi-Fi Protected Access for Protection and Automation Key Material Authentication Key Presented to: 13 December 2006 Dennis K. Holstein on behalf of CIGRE B5.22 1 The good news and the bad news Who is CIGRE
Wi-Fi Protected Access for Protection and Automation Key Material Authentication Key Presented to: 13 December 2006 Dennis K. Holstein on behalf of CIGRE B5.22 1 The good news and the bad news Who is CIGRE
USER GUIDE Cisco Small Business
 USER GUIDE Cisco Small Business WBPN Wireless-N Bridge for Phone Adapters December 2011 Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries.
USER GUIDE Cisco Small Business WBPN Wireless-N Bridge for Phone Adapters December 2011 Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries.
Recommended 802.11 Wireless Local Area Network Architecture
 NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY Ft. George G. Meade, MD I332-008R-2005 Dated: 23 September 2005 Network Hardware Analysis and Evaluation Division Systems and Network Attack Center Recommended 802.11 Wireless
NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY Ft. George G. Meade, MD I332-008R-2005 Dated: 23 September 2005 Network Hardware Analysis and Evaluation Division Systems and Network Attack Center Recommended 802.11 Wireless
The following chart provides the breakdown of exam as to the weight of each section of the exam.
 Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
Apple AirPort Networks
 Apple AirPort Networks 1 Contents Chapter 1 3 Getting Started 5 Configuring an Apple Wireless Device for Internet Access Using AirPort Utility 6 Extending the Range of Your AirPort Network 6 Sharing a
Apple AirPort Networks 1 Contents Chapter 1 3 Getting Started 5 Configuring an Apple Wireless Device for Internet Access Using AirPort Utility 6 Extending the Range of Your AirPort Network 6 Sharing a
Implementing Security for Wireless Networks
 Implementing Security for Wireless Networks Action Items for this session Learn something! Take notes! Fill out that evaluation. I love to see your comments and we want to make these better! Most important:
Implementing Security for Wireless Networks Action Items for this session Learn something! Take notes! Fill out that evaluation. I love to see your comments and we want to make these better! Most important:
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network.
 9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
TL-WN422G High-Power Wireless USB Adapter
 High-Power Wireless USB Adapter Rev:1.0.0 1910010090 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands
High-Power Wireless USB Adapter Rev:1.0.0 1910010090 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands
User Guide. E-Series Routers
 User Guide E-Series Routers Table of Contents Table of Contents Product overview E900/E1200/E1500/E2500/E3200 1 Back view 1 Bottom view 1 E4200 2 Top view 2 Back view 2 Setting Up Your E-Series Router
User Guide E-Series Routers Table of Contents Table of Contents Product overview E900/E1200/E1500/E2500/E3200 1 Back view 1 Bottom view 1 E4200 2 Top view 2 Back view 2 Setting Up Your E-Series Router
Wireless Security Overview. Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected]
 Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
m-trilogix White Paper on Security in Wireless Networks
 m-trilogix White Paper on Security in Wireless Networks Executive Summary Wireless local area networks (WLANs) based on IEEE 802.11b (Wi-Fi) will ship, according to a Cahners- Instat study, 23.6 million
m-trilogix White Paper on Security in Wireless Networks Executive Summary Wireless local area networks (WLANs) based on IEEE 802.11b (Wi-Fi) will ship, according to a Cahners- Instat study, 23.6 million
IEEE 802.1X For Wireless LANs
 IEEE 802.1X For Wireless LANs John Roese, Ravi Nalmati, Cabletron Albert Young, 3Com Carl Temme, Bill McFarland, T-Span David Halasz, Aironet Paul Congdon, HP Andrew Smith, Extreme Networks Slide 1 Outline
IEEE 802.1X For Wireless LANs John Roese, Ravi Nalmati, Cabletron Albert Young, 3Com Carl Temme, Bill McFarland, T-Span David Halasz, Aironet Paul Congdon, HP Andrew Smith, Extreme Networks Slide 1 Outline
Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT)
 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Module 6: Implement Wireless Scalability Implementing WLAN QoS Objectives Describe why WLANs need to support QoS policies in enterprise networks. Explain the issues
Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Module 6: Implement Wireless Scalability Implementing WLAN QoS Objectives Describe why WLANs need to support QoS policies in enterprise networks. Explain the issues
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide
 MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54G. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter User Guide Model No. WMP54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a
HP M220 802.11n Access Point Configuration and Administration Guide
 HP M220 802.11n Access Point Configuration and Administration Guide HP Part Number: 5998-3140 Published: September 2012 Edition: 1 Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
HP M220 802.11n Access Point Configuration and Administration Guide HP Part Number: 5998-3140 Published: September 2012 Edition: 1 Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
