Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Botulinum Toxins
|
|
|
- Felicia Pearson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Effective: June 14, 2016 Prior Authorization Required Type of Review Care Management Not Covered Type of Review Clinical Review Pharmacy (RX) or Medical (MED) Benefit MED /RX Department to Review This Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guideline applies to the following: Tufts Health Plan Commercial Plans Tufts Health Plan Commercial Plans large group plans Tufts Health Plan Commercial Plans small group and individual plans Tufts Health Public Plans Tufts Health Direct Health Connector Tufts Health Together A MassHealth Plan Tufts Health Freedom Plan products Tufts Health Freedom Plan large group plans Tufts Health Freedom Plan small group plans PRECERT /MM /RXUM Fax Numbers: All plans except Tufts Health Public Plans: PRECERT: Tufts Health Direct Health Connector: MM: Tufts Health Together A MassHealth Plan: RxUM: Note: For Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred Members, please refer to the Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred Prior Authorization Criteria. Background, applicable product and disclaimer information can be found on the last page. OVERVIEW FDA-APPROVED INDICATIONS (NON-COSMETIC) Botox (onabotulinumtoxina) is indicated for Bladder Dysfunction The treatment of urinary incontinence due to detrusor overactivity associated with a neurologic condition (e.g., spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis) in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication. Injection of the bladder with Botox is performed using cystoscopy. The treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency, in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication. Blepharospasm and Strabismus The treatment of strabismus and blepharospasm associated with dystonia, including benign essential blepharospasm or VII nerve disorders in patients 12 years of age and above. Cervical Dystonia The treatment of adults with cervical dystonia, to reduce the severity of abnormal head position and neck pain associated with cervical dystonia. Chronic Migraine The prophylaxis of headaches in adult patients with chronic migraine ( 15 days per month with headache lasting 4 hours a day or longer). Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis The treatment of severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis that is inadequately managed with topical agents. Lower Limb Spasticity The treatment of lower limb spasticity in adult patients to decrease the severity of increased muscle tone in ankle and toe flexors (gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, and flexor digitorum longus). Upper Limb Spasticity The treatment of upper limb spasticity in adult patients, to decrease the severity of increased muscle tone in elbow flexors (biceps), wrist flexors (flexor carpi radialis and flexor carpi ulnaris), finger flexors (flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum sublimis), and thumb flexors (adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis longus) Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
2 Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) is indicated for Cervical Dystonia The treatment of adults with cervical dystonia to reduce the severity of abnormal head position and neck pain in both toxin-naïve and previously treated patients. Upper Limb Spasticity The treatment of upper limb spasticity in adult patients, to decrease the severity of increased muscle tone in elbow flexors, wrist flexors and finger flexors. Myobloc (rimabotulinumtoxinb) is indicated for The treatment of adults with cervical dystonia to reduce the severity of abnormal head position and neck pain associated with cervical dystonia. Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxina) is indicated for the treatment of adults with Cervical Dystonia Cervical dystonia to decrease the severity of abnormal head position and neck pain in both botulinum toxin-naïve and previously treated patients. Blepharospasm and Strabismus Blepharospasm who were previously treated with onabotulinumtoxina (Botox). Upper Limb Spasticity The treatment of upper limb spasticity in adult patients. COVERAGE GUIDELINES In addition to the coverage criteria listed for each diagnosis, the plan may authorize coverage of Botox, Dysport, Xeomin, or Myobloc when the presence of a dystonia/movement disorder contributes to a significant functional impairment and/or pain and other more conservative/less intensive levels/alternative treatments have been tried and failed. For OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox): 1. Blepharospasm (eyelid spasms / blinking) or Strabimus (cross-eyes, esotropia, exotropia) a) The Member is over the age of 12 years b) Documented diagnosis c) Dose of 100 units or less. 2. Spasmodic Torticollis / Cervical Dystonia (Neurologically based) b) Dose of 300 units or less. 3. Pediatric Limb Spasticity (e.g., Cerebral Palsy) a) The Member is over the age of 18 months b) Documented physical evidence of focal limb spasticity c) Dose of 400 units or less Note: Botox will not be covered for Pediatric Limb Spasticity when one of the following conditions is present: A joint immobilized by a fixed contracture Severe weakness of the opposing muscle in the limb for which the injection is intended Diffuse hypertonia (excessive muscle tone). 4. Anal fissures a) Dose is 100 units or less b) Documented diagnosis and response failure to prescription topical therapy (e.g., nitroglycerin ointment). 5. Jaw-closing oromandibular dystonia, and masseter spasticity b) Failure of conventional therapy such as physical therapy or local anesthetic injections. 6. Laryngeal or spasmodic dysphonia using videostroboscopy b) Dose of 100 units or less 7. Focal limb dystonia (Organic writer s cramp, foot dystonia) 2 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
3 b) Dose of 100 units or less 8. Lower Limb Spasticity a) Member is over the age of 18 years b) Documented diagnosis of lower limb spasticity to decrease the severity of increased muscle tone in ankle and toe flexors (gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, and flexor digitorum longus) c) Documented failure to control spasticity by conventional therapies, e.g., Physical Therapy Splinting / Bracing Systemic antispasticity medication d) The dose is 400 units or less e) Injections should occur no sooner than 12 weeks apart. 9. Neurologically-based Limb Spasticity other than lower limb of one of the following: Multiple Sclerosis Stroke Brain Injury Spinal Cord Injury b) Documented failure to control spasticity by conventional therapies, e.g., Physical Therapy Splinting / Bracing Systemic antispasticity medication c) Doses of 400 units or less 10. Hemifacial Spasms 11. Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis a) Treatment failure of the following prescription topical antiperspirant: Aluminum Chloride (hexahydrate) 20% (Drysol ) b) Dose of 100 units or less. 12. Palmar Hyperhidrosis b) Treatment failure of the following prescription topical antiperspirant: Aluminum Chloride (hexahydrate) 20% (Drysol ) c) Dose of 100 units or less per palm d) Injections should occur no sooner than 6 months apart. 13. Chronic Migraine Headaches of chronic migraine defined as History of migraine headaches lasting 4 hours a day or longer Migraine headaches occur on 15 days per month b) Previous treatment for at least three months each or contraindication to all of the following therapeutic categories/medications: Beta blockers (e.g., propranolol) Divalproex sodium Topiramate Tricyclic Antidepressants c) Concurrent treatment with at least 2 traditional migraine prophylaxis medications d) Must be ordered by a neurologist or ophthalmologist e) Dose of 155 units or less per treatment f) Injections should occur no sooner than 12 weeks apart. 14. Urinary Incontinence of urinary incontinence due to detrusor overactivity associated with a neurologic condition (e.g., spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis) b) Inadequate response to or failure of one or more anticholinergic medication(s) indicated for the treatment of urinary incontinence (e.g., flavoxate, oxybutynin, tolterodine, trospium, Detrol LA, Enablex, Toviaz, Vesicare ) c) Dose of 200 units or less per treatment d) Injections should occur no sooner than 6 months apart 3 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
4 e) Must be ordered by an urologist. 15. Overactive Bladder of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. b) Member has had at least 3 urinary urgency incontinence episodes at least 24 micturitions in a 3-day period. c) Inadequate response to or failure of one or more anticholinergic medication(s) indicated for the treatment of urinary incontinence (e.g., flavoxate, oxybutynin, tolterodine, tolterodine ER, trospium, Enablex, Toviaz, Vesicare ) d) Dose of 100 units or less per treatment e) Injections should occur no sooner than 3 months apart, to qualify for re-treatment, Member must have reported at least 2 urinary incontinence episodes in a 3-day period. f) Must be ordered by an urologist. For AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport) 1. Cervical Dystonia b) Documented diagnosis of cervical dystonia c) The dose is 1,000 units or less. 2. Upper Limb Spasticity b) Member is over the age of 18 years c) Documented diagnosis of upper limb spasticity to decrease the severity of increased muscle tone in elbow flexors, wrist flexors and finger flexors d) The dose is 1,000 units or less e) Injections should occur no sooner than 12 weeks apart. For RimabotulinumtoxinB (Myobloc) 1. Member has failed treatment with OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). OR 2. Physician documents a diagnosis of spasmodic torticollis as described under OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). 3. For spasmodic torticollis, the dose is 5000 units or less. Note: Injections should occur no sooner than 3 months apart. For IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin) 1. Blepharospasm (eyelid spasms/blinking) b) Member is over the age of 18 years c) Documented diagnosis d) Dose of 100 units or less 2. Cervical Dystonia b) Member is over the age of 18 years c) Documented diagnosis d) Dose of 120 units or less 4 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
5 3. Upper Limb Spasticity b) Member is over the age of 18 years c) Documented diagnosis of upper limb spasticity d) Dose of 200 units or less e) Injections should occur no sooner than 12 weeks apart. LIMITATIONS 1. The plan does not provide coverage for cosmetic procedures that involve the use of botulinum toxin injection. 2. The plan does not cover botulinum toxin therapy for the treatment of: Any condition not listed above in the Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines or Any patients with other types of muscle spasms not listed in the Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines including, but not limited to, smooth muscle spasms, myofascial pain, trigger points, and pyriformis syndrome. Plantar hyperhidrosis. Migraine headaches that occur 14 days or less per month (i.e., episodic migraine), or for other forms of headache. Other types of urinary incontinence not listed in the Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines. 3. For all botulinum toxins: For Members 18 years of age and older, initial authorization expires two months from the original authorization date for any diagnosis. For Members below the age of 18 years old and for subsequent authorizations for Members 18 years of age and older, authorization will be approved in 12-month intervals. Additional authorizations may be given based on clinical notes from the medical record documenting an objective measurable effect indicating clinical improvement of the condition and current status - For approvals beyond 12 months, clinical notes must indicate sustained clinical effectiveness. CODES The following HCPCS/CPT code(s) are: Code Description J0585 J0586 J0587 J0588 Injection, onabotulinumtoxina, 1 unit Injection, abobotulinumtoxina, 5 units Injection, rimabotulinumtoxinb,100 units Injection, incobotulinumtoxina, 1 unit Chemodenervation of internal anal sphincter Cystourethroscopy, with injection(s) for chemodenervation of the bladder Chemodenervation of muscle(s); muscle(s) innervated by facial nerve (e.g., for blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm) Chemodenervation of muscle(s); muscle(s) innervated by facial, trigeminal, cervical spinal and accessory nerves, bilateral (e.g., for chronic migraine) Chemodenervation of muscle(s); neck muscle(s), excluding muscles of the larynx, unilateral (e.g., for cervical dystonia, spasmodic torticollis) Chemodenervation of muscle(s); larynx, unilateral, percutaneous (e.g., for spasmodic dysphonia), includes guidance by needle electromyography, when performed Chemodenervation of one extremity; 1-4 muscle(s) Chemodenervation of one extremity; each additional extremity, 1-4 muscle(s) (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Chemodenervation of one extremity; 5 or more muscle(s) 5 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
6 Code Description Chemodenervation of one extremity; each additional extremity, 5 or more muscle(s) (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Chemodenervation of trunk muscle(s); 1-5 muscle(s) Chemodenervation of trunk muscle(s); 6 or more muscle(s) Chemodenervation of eccrine glands; both axillae Chemodenervation of eccrine glands; other area(s) (e.g., scalp, face, neck), per day Chemodenervation of extraocular muscle Note: This list of codes may not be all-inclusive. REFERENCES 1. An JS, Hyun Won C, Si Han J, Park HS, Seo KK. Comparison of onabotulinumtoxina and rimabotulinumtoxinb for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg Aug;41(8): Aurora SK, Winner P, Freeman MC et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: pooled analyses of the 56-week PREEMPT clinical program. Headache Oct;51(9): Botox (onabotulinumtoxina) [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc.; January Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Hyperhidrosis, Winifred S. Hayes, Inc. February Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Spasticity and Gastrointestinal Disorders, Winifred S. Hayes, Inc. January 28, Brashear, Allison. The in the Treatment of Cervical Dystonia [Sem Neurology 21(1): 85-90, Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.] 7. Cruz F, Herschorn S, Aliotta P et al. Efficacy and Safety of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Due to Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur Urol, 2011; 60(4): Brin MD, M. Botulinum Toxin, chemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and immunology, Muscle and Nerve, Supplement 6, 1997, p. S Denys P, Le Normand L, Ghout I et al. Efficacy and safety of low doses of onabotulinumtoxina for the treatment of refractory idiopathic overactive bladder: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. Eur Urol Mar;61(3): Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) [package insert]. Brisbane, CA: Tercica, Inc.; July Elovic EP, Munin MC, Kaňovský P, Hanschmann A, Hiersemenzel R, Marciniak C. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of incobotulinumtoxina for upper-limb post-stroke spasticity. Muscle Nerve Jul 22. [Epub ahead of print] 12. Fowler CJ, Auerbach S, Ginsberg D et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA improves health-related quality of life in patients with urinary incontinence due to idiopathic overactive bladder: a 36-week, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, randomized, dose-ranging trial. Eur Urol Jul;62(1): Ginsberg D, Gousse A, Keppenne V et al. Phase 3 efficacy and tolerability study of onabotulinumtoxina for urinary incontinence from neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J Urol Jun; 187(6): HCFA National Coverage Policy Botulinum Toxin A, NHIC September Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K et al. Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A Injection for Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity and Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. J Urol, 2011; 185(6): Kaji R, Osako Y, Suyama K, et al. Botulinum toxin type A in post-stroke lower limb spasticity: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Neurol Aug;257(8): Kennelly M, Dmochowski R, Ethans K et al. Long-term Efficacy and Safety of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Patients With Urinary Incontinence Due to Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity: An Interim Analysis. Urology Jan 3. pii: S (12) Khan S, Game X, Kalsi V et al. Long-Term Effect on Quality of Life of Repeat Detrusor Injections of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A for Detrusor Overactivity in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis. J Urol, 2011; 185(4): Myobloc (rimabotulinumtoxinb) [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Solstice Neurosciences, Inc.; May Naumann, M. et.al, Botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of autonomic disorders and pain (an evidence-based review). Neurology, 2008; 70; Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the Treatment of Patients with Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence: Results of a Phase 3 Randomized Placebo- Controlled Trial. J Urol Dec 13. pii: S (12) Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
7 22. Russman MD, B, Tilton MD, A., and Gormley MD, Mark, Cerebral Palsy: A rational approach to a treatment protocol and the role of Botulinum toxin in treatment, Muscle and Nerve, Supplement 6, 1997, p. S Santamato A1, Panza F, Ranieri M, et al. Efficacy and safety of higher doses of botulinum toxin type A NT 201 free from complexing proteins in the upper and lower limb spasticity after stroke. J Neural Transm (Vienna) Mar;120(3): Tao W, Yan D, Li JH, Shi ZH. Gait improvement by low-dose botulinum toxin A injection treatment of the lower limbs in subacute stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci Mar;27(3): Visco AG, Brubaker L, Richter HE et al. Anticholinergic therapy vs. onabotulinumtoxina for urgency urinary incontinence. N Engl J Med Nov 8;367(19): Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxina) [package insert]. Greensboro, NC: Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC; December APPROVAL HISTORY October 2001: Reviewed by Pharmacy & Therapeutics Committee. Subsequent endorsement date(s) and changes made: December 14, 2004: Add when the presence of a dystonia/movement disorder contribute to a significant functional impairment and/or pain and other more conservative/less intensive levels/alternative treatments have been tried and failed as an general qualifier to Clinical Coverage Criteria. Add treatment of Hemificial Spasms to the Clinical Coverage Criteria. Add treatment of Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis to the Clinical Coverage Criteria. Add ACE Inhibitors to Exhibit B in the Coverage Limitations. December 13, 2005: For Botulinum Toxin A, delete the dose limit for Blepharospasm or Strabimus, Anal fissures, and Laryngeal or spasmodic dysphonia. For Botulinum Toxin A, add the dose limit of 100 units or less for Blepharospasm or Strabimus, Anal fissures, Laryngeal or spasmodic dysphonia, and Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis. November 14, 2006: Add clinical coverage criteria for Palmar Hyperhidrosis. Remove age limitation Over the age of 18 years from criteria for Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis. Add Aluminum Chloride (Hexahydrate) 20% to criteria for Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis. November 13, 2007: No changes September 9, 2008: Removed criteria for treatment of Migraine Headaches Removed corresponding Exhibits A and B in reference to remittive and prophylactic migraine therapies January 13, 2009: Added limitation that Plantar Hyperhidrosis is not a covered indication. September 8, 2009: Changed established drug names from Botulinum Toxin A to OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) and Botulinum Toxin B to RimabotulinumtoxinB (Myobloc). January 1, 2010: Removal of Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred language (separate criteria have been created specifically for Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred). January 12, 2010: Added Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) to Medical Necessity Guidelines. May 11, 2010: Updated HCPCS code descriptions for Botox and Myobloc. Updated diagnosis of neurologically-based limb spasticity to differentiate dosing limitations for upper and lower limb spasticity. Removed age limitation from diagnosis of spasmodic torticollis (neurologically based) and anal fissures. Removed age limitation from AbobotulinumtoxinA and RimabotulinumtoxinB. Updated initial authorization (2 months for Members 18 years of age and older, 12 months for Members below the age of 18 years old) and subsequent authorization intervals (12 months). Removed limitation language requiring a response following two sequential treatments/sets of injections in a 4-6 month period, using maximum dose for the size of the muscle for authorization of coverage of additional botulinum toxin injections. July 13, 2010: Removed requirement of starch iodine test and iontophoresis from coverage criteria for palmar hyperhidrosis. November 9, 2010: Changed policy title from OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox), abobotulinumtoxina (Dysport) and rimabotulinumtoxinb (Myobloc) to. Added requirement of documented diagnosis of cervical dystonia to Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) criteria. Added Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxina) to pharmacy medical necessity guidelines. Added coverage criteria for the diagnosis of chronic migraine headaches for OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). Added limitation that the plan does not cover botulinum toxin therapy for the treatment of migraine headaches that occur 14 days or less per month (i.e., episodic migraine), or for other forms of headache. January 1, 2011: Administrative Update: Added reimbursement code C9278 May 10, 2011: Clarified note regarding length of authorization. For subsequent authorizations beyond 2 months, provider needs to submit documentation of an objective measurable effect 7 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
8 indicating clinical improvement of condition. For authorizations beyond one year, provider needs to submit documentation of sustained clinical effectiveness. September 13, 2011: Added coverage criteria for treatment of urinary incontinence due to detrusor overactivity associated with a neurologic condition in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication for OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). Added limitation that the plan does not cover botulinum toxin for other types of urinary incontinence not listed in the Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines. January 1, 2012: Administrative Update: Replaced reimbursement code C9278 with J0588 April 10, 2012: Changed maximum dose of Botox for chronic migraine headaches from 150 units to 155 units or less per treatment January 1, 2013: Administrative Update: Added CPT codes and February 12, 2013: Added coverage criteria for treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. January 1, 2014: Administrative Update. Removed CPT codes and Added CPT codes 64616, 64617, February 11, 2014: For the diagnosis of chronic migraine headaches, added neurologist or ophthalmologist prescriber requirement and prior treatment or contraindication with conventional pharmaceutical treatment measures. February 10, 2015: Removed NSAIDS and Serotonin 5-HT1 receptor from previous treatment requirement for the diagnosis of chronic migraine headaches. Moved initial approval time frames and reauthorization requirements to Limitations section. Clarified documentation with clinical notes from the medical record. May 12, 2015: Changed dosing limitation to 400 units for upper limb spasticity. September 16, 2015: Added pharmacy coverage guidelines for Dysport for the diagnosis of upper limb spasticity. January 1, 2016: Administrative change to rebranded template. February 9, 2016: Added pharmacy coverage guidelines for Botox for the diagnosis of lower limb spasticity and for Xeomin for the diagnosis of upper limb spasticity. June 14, 2016: Clarified that neurologically-based limb spasticity refers to other than lower limb. BACKGROUND, PRODUCT DISCLAIMER INFORMATION Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines have been developed for determining coverage for plan benefits and are published to provide a better understanding of the basis upon which coverage decisions are made. They are used in conjunction with a Member s benefit document and in coordination with the Member s physician(s). The plan makes coverage decisions on a case-by-case basis considering the individual Member s health care needs. Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines are developed for selected therapeutic classes or drugs found to be safe, but proven to be effective in a limited, defined population of patients or clinical circumstances. They include concise clinical coverage criteria based on current literature review, consultation with practicing physicians in the service area who are medical experts in the particular field, FDA and other government agency policies, and standards adopted by national accreditation organizations. The plan revises and updates Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines annually, or more frequently if new evidence becomes available that suggests needed revisions. This Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guideline does not apply to Uniformed Services Family Health Plan Members or to certain delegated service arrangements. Unless otherwise noted in the Member s benefit document or applicable Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guideline, Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines do not apply to CareLink SM Members. For self-insured plans, drug coverage may vary depending on the terms of the benefit document. If a discrepancy exists between a coverage guideline and a self-insured Member s benefit document, the provisions of the benefit document will govern. Applicable state or federal mandates will take precedence. For Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred, please refer to Tufts Health Plan Medicare Preferred Prior Authorization Criteria. Treating providers are solely responsible for the medical advice and treatment of Members. The use of this policy is not a guarantee of payment or a final prediction of how specific claim(s) will be adjudicated. Claims payment is subject to Member eligibility and benefits on the date of service, coordination of benefits, referral/authorization and utilization management guidelines when applicable, and adherence to plan policies and procedures and claims editing logic. Provider Services 8 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines:
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]
![BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]](/thumbs/29/13417512.jpg) BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
Anthem Central Region Clinical Claims Edit
 Please compare the claim's date of adjudication to the range of the edit in question. Prior versions, if any, can be found below. Subject: Chemodenervation of Muscles of Different Areas with Chemodenervation
Please compare the claim's date of adjudication to the range of the edit in question. Prior versions, if any, can be found below. Subject: Chemodenervation of Muscles of Different Areas with Chemodenervation
Botulinum Toxins (BOTOX, DYSPORT, MYOBLOC and XEOMIN)
 Botulinum Toxins (BOTOX, DYSPORT, MYOBLOC and XEOMIN) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.004 03/14/2006 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 10/01/2012 Section: Prescription
Botulinum Toxins (BOTOX, DYSPORT, MYOBLOC and XEOMIN) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.004 03/14/2006 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 10/01/2012 Section: Prescription
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 03/19/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Botox (onabotulinumtoxina, injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Botox (onabotulinumtoxina, injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
Billing and Coding Guidelines
 Billing and Coding Guidelines Contractor Name Wisconsin Physicians Service Insurance Corporation Title INJ- 018 Botulinum Toxin Type A & Type B Revision Effective Date 10/01/2011 AMA CPT/ ADA CDT Copyright
Billing and Coding Guidelines Contractor Name Wisconsin Physicians Service Insurance Corporation Title INJ- 018 Botulinum Toxin Type A & Type B Revision Effective Date 10/01/2011 AMA CPT/ ADA CDT Copyright
The use of botulinum toxin is considered medically necessary for the FDA-labeled indications of:
 COVERAGE: The use of botulinum toxin is considered medically necessary for the FDA-labeled indications of: Strabismus, Blepharospasm, Facial nerve (VII) disorders, or Cervical dystonia. The use of botulinum
COVERAGE: The use of botulinum toxin is considered medically necessary for the FDA-labeled indications of: Strabismus, Blepharospasm, Facial nerve (VII) disorders, or Cervical dystonia. The use of botulinum
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition
 A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
A Guide to Urinary Incontinence (UI) in Adults With Overactive Bladder (OAB) Due to a Neurologic Condition Information and treatment options BOTOX is a prescription medicine that is injected into muscles
Ask your doctor about BOTOX and Chronic Migraine. Learn more at BOTOXChronicMigraine.com
 Track your headache days and see if you have Chronic Migraine Indication (onabotulinumtoxina) is a prescription medicine that is injected to prevent headaches in adults with chronic migraine who have 15
Track your headache days and see if you have Chronic Migraine Indication (onabotulinumtoxina) is a prescription medicine that is injected to prevent headaches in adults with chronic migraine who have 15
Botulinum Toxins A and B
 DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd
 botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
botulinum toxin type A 50, 100, 200 Allergan units/vial (Botox ) SMC No. (916/13) Allergan Ltd 06 September 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code
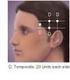 How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
Clinical & Quality Management BOTULINUM TOXIN. Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy:
 BOTULINUM TOXIN Policy Number: 2014D0070A Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available. COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
BOTULINUM TOXIN Policy Number: 2014D0070A Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available. COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Botulinum Toxin. Policy MEDICAL POLICY. Focal dystonias
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Botulinum Toxin Number 5.01.512 Effective Date July 14, 2015
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Botulinum Toxin Number 5.01.512 Effective Date July 14, 2015
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects?
 Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
Frustrated with your Overactive Bladder (OAB) medication not working? Can t handle the side effects? BOTOX treats adults with the OAB symptoms of leaking, going too often, and the strong sudden need to
Botulinum Toxin for an Overactive Bladder
 Botulinum Toxin for an Overactive Bladder Scientific Impact Paper No. 42 February 2014 Botulinum Toxin for an Overactive Bladder 1. Introduction Preparations of botulinum toxin (BoNT-A) have rapidly become
Botulinum Toxin for an Overactive Bladder Scientific Impact Paper No. 42 February 2014 Botulinum Toxin for an Overactive Bladder 1. Introduction Preparations of botulinum toxin (BoNT-A) have rapidly become
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches
 BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
BOTOX (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection, for intramuscular, intradetrusor, or intradermal use Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection,
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection,
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University
 Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON
 MEDIA RELEASE [Insert embargo time and date] March 2014 CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A) receives government subsidy for debilitating condition Sydney, Australia, [insert
MEDIA RELEASE [Insert embargo time and date] March 2014 CHRONIC MIGRAINE TACKLED HEAD-ON BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A) receives government subsidy for debilitating condition Sydney, Australia, [insert
BOTOX (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection, for intramuscular, intradetrusor, or intradermal use Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection,
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. (onabotulinumtoxina) for injection,
Will Botox help your migraines?
 Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
Guidelines for Insurance Approval and the Appeal Process in the Treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia with Botulinum Toxin Injections
 NATIONAL SPASMODIC DYSPHONIA ASSOCIATION Guidelines for Insurance Approval and the Appeal Process in the Treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia with Botulinum Toxin Injections Published by National Spasmodic
NATIONAL SPASMODIC DYSPHONIA ASSOCIATION Guidelines for Insurance Approval and the Appeal Process in the Treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia with Botulinum Toxin Injections Published by National Spasmodic
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy. Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015
 Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity
 Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Intrathecal Baclofen for CNS Spasticity Last Review Date: November 13, 2015 Number: MG.MM.ME.31bC5 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: MEDPD SPAP Inj - Botox Therapeutic Class: Musculoskeletal Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Musculoskeletal Relaxant Agents Client: PDP SPAP Inj Approval Date: 3/17/2000
Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: MEDPD SPAP Inj - Botox Therapeutic Class: Musculoskeletal Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Musculoskeletal Relaxant Agents Client: PDP SPAP Inj Approval Date: 3/17/2000
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for
 Fresno Laser Aesthetics 1105 E. Spruce Ph (559) 432-3492 Suite 203 Fax (559) 256-7711 Fresno, CA 93720 Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document
Fresno Laser Aesthetics 1105 E. Spruce Ph (559) 432-3492 Suite 203 Fax (559) 256-7711 Fresno, CA 93720 Informed Consent BOTOX / DYSPORT / XEOMIN Injection for INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed-consent document
Committee Approval Date: February 17, 2015 Next Review Date: February 2016
 Medication Policy Manual Topic: Botulinum toxin type A injection: - Botox (onabotulinumtoxina) - Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) - Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxina) Policy No: dru006 Date of Origin: January 1996
Medication Policy Manual Topic: Botulinum toxin type A injection: - Botox (onabotulinumtoxina) - Dysport (abobotulinumtoxina) - Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxina) Policy No: dru006 Date of Origin: January 1996
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Surgery: Trigger Point Injections (L30066)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Surgery: Trigger Point Injections (L30066) Contractor Information Contractor Name Cahaba Government Benefit Administrators, LLC LCD Information Document Information
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Surgery: Trigger Point Injections (L30066) Contractor Information Contractor Name Cahaba Government Benefit Administrators, LLC LCD Information Document Information
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities
 Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity
 Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
XXXXX Petitioner v File No. 121439-001. Issued and entered this 27 TH day of October 2011 by R. Kevin Clinton Commissioner ORDER
 In the matter of STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation XXXXX Petitioner
In the matter of STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation XXXXX Petitioner
Safety of High-Dose Botulinum Toxin Type A Therapy for the Treatment of Pediatric Spasticity
 Original Article Safety of High-Dose Botulinum Toxin Type A Therapy for the Treatment of Pediatric Spasticity Edward M. Goldstein, MD ABSTRACT This retrospective chart review examines the safety of high-dose
Original Article Safety of High-Dose Botulinum Toxin Type A Therapy for the Treatment of Pediatric Spasticity Edward M. Goldstein, MD ABSTRACT This retrospective chart review examines the safety of high-dose
OAB (Overactive Bladder)
 OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_cord_stimulation 3/1980 10/2015 10/2016 10/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal cord stimulation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_cord_stimulation 3/1980 10/2015 10/2016 10/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal cord stimulation
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.86 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013
MP 7.01.86 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013
botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd
 Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Insurance Reimbursement Assistance Guide
 Insurance Reimbursement Assistance Guide Contents: Overview Sample Letter of Medical Necessity (LMN) template Medical Insurance Claim Form Resources: List of State Insurance Departments Overview At this
Insurance Reimbursement Assistance Guide Contents: Overview Sample Letter of Medical Necessity (LMN) template Medical Insurance Claim Form Resources: List of State Insurance Departments Overview At this
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence. A Review of the Research for Women
 Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents
 THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents 1 Congress Street, Suite 100 Boston, Massachusetts 02114-2017 DEVAL L. PATRICK Governor PHILIP L. HILLMAN Director TIMOTHY P. MURRAY
THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Industrial Accidents 1 Congress Street, Suite 100 Boston, Massachusetts 02114-2017 DEVAL L. PATRICK Governor PHILIP L. HILLMAN Director TIMOTHY P. MURRAY
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY SERVICE: Botulinum Toxin Injection for Chemodenervation. SERVICE: Botulinum Toxin Injection for chemo-denervation
 Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply may be considered covered, this conclusion is not based upon the terms of your particular benefit plan. Each benefit
Botox treatment for chronic migraine
 University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology
 Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
Urodynamics in Neuro-Urology R Hamid MD (Res), FRCS (Urol) Consultant Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & University College London Hospitals Micturition Micturition can be visualized as
Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management
 Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management Dr. Corrie Graboski Definition by Quebec Task Force Pain Generators an acceleration-deceleration mechanism of energy transfer to the neck
Whiplash and Cervical Spine Disorders: Evaluation and Management Dr. Corrie Graboski Definition by Quebec Task Force Pain Generators an acceleration-deceleration mechanism of energy transfer to the neck
DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK
 DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK WHAT IS FOOT DROP Foot drop / Drop foot the inability to lift the front part of the foot not a disease a symptom of some other medical problems a sign of an underlying
DROP FOOT AND TREATMENTS YOUNGMEE PARK WHAT IS FOOT DROP Foot drop / Drop foot the inability to lift the front part of the foot not a disease a symptom of some other medical problems a sign of an underlying
Medical Necessity Guidelines: Transgender Surgical Procedures
 Medical Necessity Guidelines: Transgender Surgical Procedures Effective: July 20, 2016 Clinical Documentation and Prior Authorization Required Applies to: Coverage Guideline, No Prior Authorization Tufts
Medical Necessity Guidelines: Transgender Surgical Procedures Effective: July 20, 2016 Clinical Documentation and Prior Authorization Required Applies to: Coverage Guideline, No Prior Authorization Tufts
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR SPASTICITY
 The clinical impact of upper motor neuron (UMN) syndrome on patients is broad. UMN syndrome limits functional capacity by reducing mobility and limb usage and leads to, contractures, osteoporosis, neurogenic
The clinical impact of upper motor neuron (UMN) syndrome on patients is broad. UMN syndrome limits functional capacity by reducing mobility and limb usage and leads to, contractures, osteoporosis, neurogenic
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013
 London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013 Summary Mirabegron is first of a new class of drug, beta-3-adrenoceptor agonists, for the treatment
London New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing Document Mirabegron (Betmiga TM ) for overactive bladder March 2013 Summary Mirabegron is first of a new class of drug, beta-3-adrenoceptor agonists, for the treatment
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Chronic Headaches. David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015
 s David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015 Why is Headache Important? 36,000,000 people have migraine - more than asthma and diabetes combined 13,000,000 have chronic daily
s David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015 Why is Headache Important? 36,000,000 people have migraine - more than asthma and diabetes combined 13,000,000 have chronic daily
Clinical and Therapeutic Cannabis Information. Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved
 Clinical and Therapeutic Cannabis Information Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved Contents Introduction... 3 Chronic Pain... 6 Neuropathic Pain... 8 Movement Disorders...
Clinical and Therapeutic Cannabis Information Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved Contents Introduction... 3 Chronic Pain... 6 Neuropathic Pain... 8 Movement Disorders...
Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015
 Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence. Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina
 Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine
 Botulinum Toin in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine ERIC L. FRY, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF OPHTHALMOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS FRY EYE ASSOCIATES, GARDEN CITY, KS History of Botulinum Toin Justinus Kerner,
Botulinum Toin in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine ERIC L. FRY, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF OPHTHALMOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS FRY EYE ASSOCIATES, GARDEN CITY, KS History of Botulinum Toin Justinus Kerner,
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy
 Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP
 CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
CIRRICULUM VITAE KELLI DEWITT WHITEHEAD, RN, MS, ARNP Associated Urologist, PA 341 Wheatfield, Suite 180 Sunnyvale, TX 75182 972-270-8859 EDUCATION Master of Science, Family Nurse Practitioner University
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine. Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15
 Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS:
 2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
