CHEST PAIN EVALUATION TOOL
|
|
|
- Robert Short
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEST PAIN EVALUATION TOOL Chest pain or discomfort is one of the commonest causes for presentation to the Emergency Room (ER) or physicians office. There are many causes for chest discomfort. The serious causes need to be excluded before less serious causes can be considered. Serious causes for chest pain include: Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS): New onset angina, accelerating or crescendo angina and prolonged angina or coronary insufficiency, non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). CHRONIC: stable angina. Aortic dissection (sudden, tearing chest or interscapular back pain with weakness, dizziness, diaphoresis, pallor, new aortic regurgitation, cerebral ischaemia or pulse deficits) Pulmonary embolism (sudden pleuritic chest discomfort with dyspnea, hypoxemia) Pericarditis (sharp, retrosternal chest discomfort. Worse with breathing or lying down) Pleurisy/pneumonia/pneumothorax (sharp thoracic discomfort associated with viral or pulmonary symptoms: fever, cough, sputum or spontaneously occurring in young people). Less serious causes include: Chest wall pain (costochondritis, pleurodynia) Referred pain from cervical disc disease, brachial plexus (neuritis, scalenus anticus syndrome, cervical rib) Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (reflux esophagitis or esophageal spasm) Referred abdominal pain (biliary colic, gastritis, perforated ulcer or other viscus) Zoster or shingles Causes of chest pain or discomfort are best identified by a careful medical history. First establish the acuity or chronicity of symptoms. Acute chest pain is best evaluated in the ER to rule out ACS, NSTEMI, STEMI or other serious causes. Less acute chest pain should be evaluated using three CARDINAL FEATURES to classify the chest discomfort and establish the likelihood of angiographically significant (>70% luminal stenosis) coronary artery disease. Ischaemic chest pain or discomfort may present with typical or atypical features. Typical features include: 1. Retrosternal location of discomfort (in whole or in part) 2. Provocation by activity or stress 3. Relief by rest or nitroglycerin If all three features are present the chest pain or discomfort is classified as TYPICAL ANGINA. If two of three features are present the chest discomfort is classified as ATYPICAL ANGINA. If only one of three features are present the chest discomfort is classified as NON ANGINAL CHEST PAIN. The angiographic likelihood of significant CAD can be derived from these three cardinal features as well as the AGE and GENDER of the patient as presented in the table at the top of the chest pain algorithm on the next page. In WOMEN, ischaemic symptoms may present atypically such as unusual fatigue, sleep disturbance and shortness of breath. Only 30% of women report chest discomfort prior to heart attack. The most frequent acute symptoms in women are shortness of breath (57.9%), weakness (54.8%), and fatigue (42.9%). Acute chest pain was absent in 43%. Evaluation of chest discomfort in women must be tempered by a lower pretest likelihood of CAD and the atypical symptom presentation.
2 CHEST PAIN ASSESSMENT ALGORITHM STABLE SYMPTOMS ASSESS PRE-TEST LIKELIHOOD CAD UNSTABLE SYMPTOMS New onset angina Accelerating angina Prolonged resting angina Low Likelihood CAD < 10% risk Consider no test Intermediate Likelihood CAD 10-90% risk High Risk CAD >90% risk Consider non-invasive assessment to determine severity and extent of CAD or cardiac catheterization based on severity of symptoms. Patient able to exercise Patient unable to exercise ECG Normal ECG Abnormal Exercise Stress Test Exercise Myocardial Perfusion Scan* Exercise Stress Echo Persantine** Myocardial Perfusion Scan* Dobutamine Stress Echo *Avoid in women of child-bearing years **Persantine may be contra-indicated in asthma Test Results: If suspected false + Exercise Stress Test (EST) consider Stress Echo or Stress Nuclear study. If inconclusive EST consider Persantine Nuclear study. Normal Equivocal or Mild Symptoms Abnormal Low/ Moderate Risk Abnormal High Risk ACS Protocol High Risk Indeterminate Risk Optimal Medical Therapy CT Angiogram Cardiac Catheterization Non-Invasive Risk Stratification
3 NON-INVASIVE CARDIAC INVESTIGATIONS AND PROCEDURES: PATIENT INFORMATION Treadmill Exercise Stress Testing Stress testing is also known as treadmill testing or graded exercise testing. During the test you will be asked to walk on a treadmill which gradually increases the speed and slope. Your electrocardiogram (ECG), blood pressure and symptoms will be continuously monitored. The test will be stopped when your symptoms warrant it or if a strongly positive result or arrhythmia occurs. Treadmill testing is useful to assess the presence and severity of coronary artery disease, and if present to indicate the prognosis and to guide therapy or intervention. Treadmill testing may show changes in the ECG which could the blood supply to your heart is reduced. Chest pain or shortness of breath may accompany these changes. Unfortunately treadmill testing is not perfect. About 30% of the time false positive results may be obtained. This may make further testing necessary to rule out coronary disease or assess its severity. Stress Echocardiography Stress echocardiography combines stress testing with an echocardiogram (cardiac ultrasound) obtained before and immediately after exercise. Exercise is usually carried out on a treadmill. Alternatively a bicycle (either upright or lying down) may be used to provide the exercise stress. This measures the pump function of the heart under stress and can be used to prove or disprove the presence of coronary artery disease. Stress echo may also be useful to evaluate the functional significance and severity of angiographically identified coronary narrowing. Sometimes a medication, dobutamine, is used to accelerate the heart rate in patients who are unable to exercise. Echocardiography is used to measure the pump function of the heart before and during this pharmacologic (medication induced) stress test and identify lack of blood supply to the heart muscle. Side effects of dobutamine include angina and cardiac arrhythmias. Sometimes if image quality is poor, echo contrast is given intravenously. This helps to better see the walls and pump function of the heart. Stress Nuclear Testing (Exercise Myocardial Perfusion Imaging) Stress nuclear testing is a form of stress test that may provide added useful information about your prognosis. A nuclear material is injected into your blood stream while you exercise on the treadmill. If unable to exercise, a medication called Persantne may be used as an alternative-see below. The material is safe and medically approved. Similar nuclear materials are used to obtain bone scans, brain scans, thyroid scans etc. The nuclear material is taken up by your heart and is distributed through the heart muscle according to blood flow. Areas of the heart that are supplied by narrowed arteries will have reduced blood flow that will show up on scanning as reduced areas of radioactivity. These techniques are more accurate than routine treadmill testing in finding coronary disease and determining its severity. Scanning agents include the isotopes thallium and Technetium 99m. Technetium 99m is bound to carrier molecules (MIBI or Myoview ; tetrafosmin or Cardiolyte ). Technetium 99m-based scanning has the added advantage of providing information on the pump function of the heart. Both stress and persantine nuclear stress tests are useful in excluding falsely abnormal treadmill stress tests and carry 90-95% accuracy. MPI is a widely used and safe non invasive test that has been well validated for more than 30 years. As with many non invasive tests, it results in a small radiation exposure. By appropriate selection of patients, the very small risk associated with the radiation exposure is far outweighed by the benefits of the test. In relative quantitative terms the exposure from a MPI test (8-10 msv) is roughly 3 times the naturally occurring annual background radiation (approximately 3 msv). Persantine Nuclear Stress Testing (Pharmacologic Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging) In patients who cannot exercise due to vascular or musculoskeletal problems (e.g. back pain, arthritis, etc.) an injection of intravenous persantine may be used to stress the heart. Persantine dilates blood vessels in the heart. If a vessel is narrowed or blocked it cannot dilate. That is why we can see a difference in blood flow across the heart when we inject the nuclear scanning agent. Nuclear isotopes are then administered and the heart scanned with a special camera to identify areas of reduced coronary artery blood flow. Persantine may not be given to patients with asthma or who are on asthma medications or to patients with unstable symptoms. Side effects of persantine include headaches, flushing, chest pain and shortness of breath. These effects are readily reversed with the antidote, aminophylline. Appropriate Use of Non-invasive Cardiac Testing Evaluate pre test likelihood of angiographically significant CAD with chest pain algorithm. Choose to test or not based on risk level. In low risk patients (<10 % risk of angiographically significant CAD) consider no testing. Choose the test with the lowest risk to the patient. Cost should be a consideration in choosing the appropriate test. Avoid repeated radiation exposure unless the value of the information derived exceeds the incremental radiation risk. Factor in lifetime radiation exposure from background radiation and other radiologic tests and procedures. In high risk patients (> 90% risk of angiographically significant CAD) consider imaging the coronary arteries directly.
4 MEDICAL RADIATION SAFETY What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the body, which allows a cardiologist or radiologist to produce pictures of internal structures. X-ray examinations provide valuable information about your health and play an important role in helping your doctor make an accurate diagnosis and prognosis. Measuring radiation dosage The scientific unit of measurement for radiation dose, commonly referred to as effective dose, is the millisievert (msv). Because different tissues and organs have varying sensitivity to radiation exposure, the actual radiation risk to different parts of the body from an x-ray procedure varies. The term effective dose is used when referring to the radiation risk averaged over the entire body. The effective dose accounts for the relative sensitivities of the different tissues exposed. More importantly, it allows for quantification of risk and comparison to more familiar sources of exposure that range from natural background radiation to radiographic medical procedures. Naturally-occurring background radiation exposure We are exposed to radiation from natural sources all the time. According to recent estimates, the average person in the U.S. receives an effective dose of about 3 msv per year from naturally occurring radioactive materials and cosmic radiation from outer space. These natural background doses vary throughout the country. People living at higher altitudes receive about 1.5 msv more per year than those living near sea level. The added dose from cosmic rays during a coast-to-coast round trip flight in a commercial airplane is about 0.03 msv. Altitude plays a big role, but the largest source of background radiation comes from radon gas in our homes (about 2 msv per year). Like other sources of background radiation, exposure to radon varies widely from one part of the country to another. To explain it in simple terms, we can compare the radiation exposure from one chest x-ray as equivalent to the amount of radiation exposure one experiences from our natural surroundings in 10 days. Safety in nuclear medicine procedures Nuclear medicine is a branch of medical imaging that uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and determine the severity of or treat a variety of diseases, including many types of cancers, heart disease and certain other abnormalities within the body. Depending on the type of nuclear medicine exam, the radioactive material, or radiotracer, may be injected into a vein, swallowed or inhaled as a gas. The radiotracer will accumulate in the organ or area of the body being examined, where it gives off energy in the form of gamma rays, allowing the radiologist or nuclear medicine physician to view structural and functional information about organs or tissues within the body. During nuclear medicine exams, patients are exposed to some radiation from the radiotracer and may be exposed to additional radiation, depending on the imaging method used during the procedure. Though the exact amount of radiation exposure can vary, based on the patient s physical dimensions and the part of the body being examined, radiologists and nuclear medicine physicians will use the lowest dose possible in order to obtain the highest quality images. Nuclear imaging exams can be performed safely on children and pregnant women as long as the benefits outweigh the small associated radiation risk. When performing such exams, careful evaluation should be done to ensure proper/optimal dosage is given. Women should always inform their physician or technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant or if they are breastfeeding.
5 Comparisons of effective radiation dose with background radiation exposure for cardiac radiology and nuclear procedures HEART For this Procedure *Your appropriate effective radiation dose is: Comparible to natural background radiation for: **Additional lifetime risk of fatal cancer from examination: Myocardial perfusion imaging with EF 16 msv 5 years Low Cardiac blood pool imaging (MUGA) 8 msv 32 months Low Cardiac CT for calcium scoring Coronary Computer Tomography Angiography (CTA) 3 msv 1 year Low 16 msv 5 years Low PET scan 4 msv 16 months Low Cardiac catheterization 7 msv 28 months Low Coronary angioplasty 15 msv 5 years Low CHEST Computed Tomography (CT)-Chest 7 msv 2 years Low Computed Tomography (CT)-Chest Low Dose 1.5 msv 6 months Very Low Radiography-Chest 0.1 msv 10 days Minimal CANCER RISK Risk Level Approximate additional risk of fatal cancer for an adult from examination: Negligible Less than 1 in 1,000,000 Minimal 1 in 1,000,000 to 1 in 100,000 Very Low 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 10,000 Low 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 1000 Moderate 1 in 1000 to 1 in 500 Note: These risk level represent very small additions to the 1 in 5 chance we all have of dying from cancer. Adapted from RadiologyInfo.org (
6 Stress Echocardiography versus Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (MPI) In general stress echocardiography is more specific in ruling out CAD. Stress nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging is more sensitive in identifying CAD. Stress echocardiography is also more operator and laboratory dependent and subject to technical limitations. The advent of contrast stress echo will help to overcome some of these limitations. CHOOSE STRESS ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IF: CHOOSE MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING IF: Younger < 50 Older > 50 Low Intermediate pre-test likelihood of CAD Female in childbearing years Good echo image quality Able to exercise Repeated tests expected Prior multiple radiologic/nuclear exposure LAD is primary vessel of interest Single vessel CAD likely Normal resting LV function Normal QRS on resting ECG Intermediate to hight pre-test likelihood of CAD Male > Female Poor image quality Unable to exercise (Persantine stress) Infrequent evaluation Low cumulative radiation exposure Need to evaluate significance of known coronary stenosis other than LAD Multi-vessel CAD likely; prior PCI/CABG Multiple wall motion abnormalities LBBB or Paced Rhythm (Persantine stress) Echocardiography Nuclear echo 100 nuclear angina ECG changes systolic dysfunction diastolic dysfunction (%) P=0.029 P=0.001 hypoperfusion 25 flow maldistribution Time from onset of ischemia 0 Sensitivity Specificity Fig. 1. The ischaemic cascade represents a sequence of pathophysiologic events caused by coronary artery disease. Nuclear imaging probes an earlier event hypo-perfusion) in the ischaemic cascade than stress echocardiography (systolic dysfunction). Fig. 2. Sensitivity and specificity of stress echocardiography and nuclear imaging for the detection of coronary artery disease (data based on Refs. 1-17). Noninvasive evaluation of ischaemic heart disease: myocardial perfusion imaging or stress echocardiography? Schinkel el al. European Heart Journal (2003) 24, Chest Pain Evaluation Tool April 2014 Prepared by Dr. J. Niznick Continuing Medical Implementation Inc.
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing. a maximal GXT?
 Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
6/5/2014. Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
123 Main St NY, New York 12345 ph: (202) 555 5555 fax: (202) 555 5555
 Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL
 Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
Marilyn Borkgren-Okonek, APN, CCNS, RN, MS Suburban Lung Associates, S.C. Elk Grove Village, IL www.goldcopd.com GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE GLOBAL STRATEGY FOR DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
38 year old female with mild obesity. She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD.
 Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
How To Know If You Should Get A Heart Test
 A SHARED DECISION-MAKING PROGRAM HEART TESTS This program content, including this booklet is copyright protected by Health Dialog Services Corporation (HDSC), a related entity of Bupa Health Dialog Pty
A SHARED DECISION-MAKING PROGRAM HEART TESTS This program content, including this booklet is copyright protected by Health Dialog Services Corporation (HDSC), a related entity of Bupa Health Dialog Pty
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Osama Jarkas. in Chest Pain Patients. STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015
 STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015 PROJECT TITLE: Analysis of ECG Exercise Stress Testing and Framingham Risk Score in Chest Pain Patients PRIMARY SUPERVISOR NAME: Dr. Edward Tan DEPARTMENT:
STUDENT NAME: Osama Jarkas DATE: August 10 th, 2015 PROJECT TITLE: Analysis of ECG Exercise Stress Testing and Framingham Risk Score in Chest Pain Patients PRIMARY SUPERVISOR NAME: Dr. Edward Tan DEPARTMENT:
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Chest Pain. Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management. Common complaint in ED. Wide range of etiologies
 Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Chest Pain
Acute Myocardial Infarction: Differential Diagnosis and Patient Management Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Chest Pain
RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department
 RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department Sohil Pothiawala FAMS (EM), MRCSEd (A&E), M.Med (EM), MBBS Consultant Dept. of Emergency Medicine Singapore General Hospital
RISK STRATIFICATION for Acute Coronary Syndrome in the Emergency Department Sohil Pothiawala FAMS (EM), MRCSEd (A&E), M.Med (EM), MBBS Consultant Dept. of Emergency Medicine Singapore General Hospital
Nuclear medicine. Answering your questions
 Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation
 Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
Perioperative Cardiac Evaluation Caroline McKillop Advisor: Dr. Tam Psenka 10-3-2007 Importance of Cardiac Guidelines -Used multiple times every day -Patient Safety -Part of Surgical Care Improvement Project
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging. Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469)
 Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Non Invasive Testing for CAD
 Non Invasive Testing for CAD Wael A. Jaber, MD Section of Cardiac Imaging Heart and Vascular Institute Cleveland Clinic 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose
Non Invasive Testing for CAD Wael A. Jaber, MD Section of Cardiac Imaging Heart and Vascular Institute Cleveland Clinic 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry
 National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
Acute Coronary Syndrome. What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know
 Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
Acute Coronary Syndrome What Every Healthcare Professional Needs To Know Background of ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to cover a spectrum of clinical conditions that are caused
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging. Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet
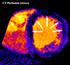 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Society of Nuclear Medicine 1850 Samuel Morse Drive Reston, VA 20190-5316 www.snm.org
 What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers
 CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego [email protected] 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego [email protected] 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics. Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
 Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Case Presentation 69 y.o. woman calls 911 with the complaint of
Is it really so? : Varying Presentations for ACS among Elderly, Women and Diabetics Yen Tibayan, M.D. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Case Presentation 69 y.o. woman calls 911 with the complaint of
Emory Healthcare Heart Disease Prevention Live Chat (2/21/2011) Transcript
 Emory Healthcare Heart Disease Prevention Live Chat (2/21/2011) Transcript [admin] We want to thank Dr. Sperling for joining us for an interactive online Q & A web chat on the topic of heart disease prevention.
Emory Healthcare Heart Disease Prevention Live Chat (2/21/2011) Transcript [admin] We want to thank Dr. Sperling for joining us for an interactive online Q & A web chat on the topic of heart disease prevention.
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY
 INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
INTRODUCTION TO EECP THERAPY is an FDA cleared, Medicare approved, non-invasive medical therapy for the treatment of stable and unstable angina, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY
 BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions
 Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions Your Guide to EXPRESS Critical Illness Insurance Definitions This guide to critical illness definitions will help you understand the illnesses
Your Guide to Express Critical Illness Insurance Definitions Your Guide to EXPRESS Critical Illness Insurance Definitions This guide to critical illness definitions will help you understand the illnesses
Heart Center Packages
 Heart Center Packages For more information and appointments, Please contact The Heart Center of Excellence at the American Hospital Dubai Tel: +971-4-377-6571 Email: [email protected] www.ahdubai.com
Heart Center Packages For more information and appointments, Please contact The Heart Center of Excellence at the American Hospital Dubai Tel: +971-4-377-6571 Email: [email protected] www.ahdubai.com
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Imaging Technology. Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist
 Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Diagnostic Imaging Prior Review Code List 3 rd Quarter 2016
 Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Radiology Tech
 From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS)
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO SECONDARY PREVENTION IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99)
 CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
CHAPTER 9 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (I00-I99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 9 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Official Online ACLS Exam
 \ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
\ Official Online ACLS Exam Please fill out this form before you take the exam. Name : Email : Phone : 1. Hypovolemia initially produces which arrhythmia? A. PEA B. Sinus tachycardia C. Symptomatic bradyarrhythmia
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2010 STRESS ECHOCARDIOLOGY Page 1 of 15 CPT Codes: 93350, 93351, + 93352 Last Reviewed Date: June 2012 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_026
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: February 2010 STRESS ECHOCARDIOLOGY Page 1 of 15 CPT Codes: 93350, 93351, + 93352 Last Reviewed Date: June 2012 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_026
Renovascular Disease. Renal Artery and Arteriosclerosis
 Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
Other names: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) Renal Vascular Hypertension (RVH) Renal Artery Aneurysm (RAA) How does the normal kidney work? The blood passes through the kidneys to remove the body s waste.
CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet
 What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
CBT/OTEP 243 Aspirin Administration for ACS
 Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 243
Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 296-4693 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 243
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges
 CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA. a) pharmacy records reflecting the dispensing of Bextra and/or Celebrex to the Class Member; or
 EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA 1. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION DOCUMENTATION In order to be eligible for compensation under the Settlement Agreement, each Claimant must provide evidence of the Class
EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA 1. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION DOCUMENTATION In order to be eligible for compensation under the Settlement Agreement, each Claimant must provide evidence of the Class
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin
 Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Educational Goals & Objectives
 Educational Goals & Objectives The Cardiology rotation will provide the resident with an understanding of cardiovascular physiology and its broad systemic manifestations. The resident will have the opportunity
Educational Goals & Objectives The Cardiology rotation will provide the resident with an understanding of cardiovascular physiology and its broad systemic manifestations. The resident will have the opportunity
www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND
 www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND Cardiomyopathy Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have cardiomyopathy. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart
www.irishheart.ie CARDIOMYOPATHY SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND Cardiomyopathy Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have cardiomyopathy. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION. CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST
 CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
CARDIA 288 MONTH FOLLOW-UP SUPPLEMENTAL FORM (FORM B) HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: INTERVIEWER ID FY288BIVID2. Page 1 of 6 FY288BH4CN
 HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: 2 8 8 0 H FY288BH4CN Has the participant indicated any of the following reasons for being admitted overnight for this case? 1. Suspected or confirmed problems with the heart, circulation,
HOSPITALIZATION CASE #: 2 8 8 0 H FY288BH4CN Has the participant indicated any of the following reasons for being admitted overnight for this case? 1. Suspected or confirmed problems with the heart, circulation,
Imaging of Acute Stroke. Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group
 Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Imaging of Acute Stroke Noam Eshkar, M.D New Jersey Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Edison Radiology Group Modalities Non Contrast CT (NCCT) Contrast CT Angiography MRI MR Angiography Perfusion
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
CIGI Direct Insurance Services, Inc. QUICK QUOTE CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY/CORONARY BYPASS
 QUICK QUOTE CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY/CORONARY BYPASS Amount of Insurance $ Type of Insurance 1. Has patient had: Date of last symptom, list date (or dates if more than one ) Angina pectoris (heart pain)? r
QUICK QUOTE CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY/CORONARY BYPASS Amount of Insurance $ Type of Insurance 1. Has patient had: Date of last symptom, list date (or dates if more than one ) Angina pectoris (heart pain)? r
53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology
 Learning Outcomes 53.1 Explain how x-rays are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. 53-2 CHAPTER 53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology 53.2 Compare invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures.
Learning Outcomes 53.1 Explain how x-rays are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. 53-2 CHAPTER 53 X-rays and Diagnostic Radiology 53.2 Compare invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures.
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
PATIENT REGISTRATION
 Orthopedic & Sports Therapy Center PATIENT REGISTRATION NAME DATE OF BIRTH SSN# FIRST MI LAST PHONE INFO: HOME BEST WAY TO CONFIRM APPOINTMENTS WORK CALL TEXT EMAIL MOBILE (TEXT) MOBILE CARRIER EMAIL ADDRESS
Orthopedic & Sports Therapy Center PATIENT REGISTRATION NAME DATE OF BIRTH SSN# FIRST MI LAST PHONE INFO: HOME BEST WAY TO CONFIRM APPOINTMENTS WORK CALL TEXT EMAIL MOBILE (TEXT) MOBILE CARRIER EMAIL ADDRESS
FFR CT : Clinical studies
 FFR CT : Clinical studies Bjarne Nørgaard Department Cardiology B Aarhus University Hospital Skejby, Denmark Disclosures: Research grants: Edwards and Siemens Coronary CTA: High diagnostic sensitivity
FFR CT : Clinical studies Bjarne Nørgaard Department Cardiology B Aarhus University Hospital Skejby, Denmark Disclosures: Research grants: Edwards and Siemens Coronary CTA: High diagnostic sensitivity
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options. A Guide for Patients
 Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Redefining the NSTEACS pathway in London
 Redefining the NSTEACS pathway in London Sotiris Antoniou Consultant Pharmacist, Cardiovascular Medicine, Barts and The London NHS Trust and Project Lead, North East London Cardiovascular and Stroke Network
Redefining the NSTEACS pathway in London Sotiris Antoniou Consultant Pharmacist, Cardiovascular Medicine, Barts and The London NHS Trust and Project Lead, North East London Cardiovascular and Stroke Network
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of
 APPENDIX: Online Data Supplements Clinical Trial Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were screened
APPENDIX: Online Data Supplements Clinical Trial Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria All patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were screened
EVALUATION OF MEDICAL RECORDS COMPLETENESS IN THE ADULT CARDIOLOGY CLINIC AT NORK MARASH MEDICAL CENTER
 American University of Armenia Center for Health Services Research and Development Nork Marash Medical Center EVALUATION OF MEDICAL RECORDS COMPLETENESS IN THE ADULT CARDIOLOGY CLINIC AT NORK MARASH MEDICAL
American University of Armenia Center for Health Services Research and Development Nork Marash Medical Center EVALUATION OF MEDICAL RECORDS COMPLETENESS IN THE ADULT CARDIOLOGY CLINIC AT NORK MARASH MEDICAL
