VIRTUAL REALITY, AUGMENTED REALITY AND ROBOTICS IN SURGICAL PROCEDURES OF THE LIVER
|
|
|
- Deborah Lloyd
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VIRTUAL REALITY, AUGMENTED REALITY AND ROBOTICS IN SURGICAL PROCEDURES OF THE LIVER Luc SOLER 1, Nicholas AYACHE 2, Stéphane NICOLAU 1,2, Xavier PENNEC 2, Clément FOREST 1,2, Hervé DELINGETTE 2, Didier MUTTER 1, Jacques MARESCAUX 1 1 : IRCAD/EITS, 1 place de l hôpital, F Strasbourg 2 : EPIDAURE Project, INRIA, 2004 Route des Lucioles, F Sophia Antipolis Medical image processing led to a major improvement of patient care. The 3D modeling of patients from their CT-scan or MRI thus allows a better surgical planning. Simulation offers the opportunity to train the surgical gesture before carrying it out. And finally, augmented reality provides surgeons with a view in transparency of their patient which, in the future, will allow to obtain automation of the most complex gestures. We present our latest results in these different fields of research applied to surgical procedures of the liver. 1. Introduction During the 20 th century, medicine witnessed the appearance of a new tool, which revolutionized it : 3D medical MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computer Tomography) imaging. Though acquisition techniques keep on evolving, reading and understanding these images often remain highly complex skills. Progress achieved in computer technology allowed to solve part of these reading difficulties by translating the information contained in the image into a 3D or 4D (i.e. 3D + time) image of the patient anatomy and pathologies. Thanks to an improved preoperative knowledge of each patient's internal anatomy, practitioners can today establish an improved diagnosis and a better planning of the best suited therapy for a given case. Therefore, 3D modeling of a patient is generally used for diagnosis support or surgical planning tools. The other use is patient follow-up over time, easing visualization of therapy efficiency. However, surgical simulation still remains limited to virtual models, without really exploiting medical data of patients. Thus, to simulate an intervention on a virtual patient reconstructed from his/her medical image is nevertheless a major research which would allow to noticeably reduce medical mistakes thanks to an optimized preoperative training. Intraoperative use, which allows to improve the surgical gesture, has to be added to the preoperative use of 3D patient modeling. In this domain, augmented reality offers a more efficient steering of the surgical gesture, by superimposing preoperative information on the patient. Most applications have been developed in neurosurgery and in orthopedic surgery, since non-mobile bone landmarks are very reliable and allow an eased registration of the virtual
2 patient on the real patient. The few works that have been carried out on the abdominal region provide only little accurate information, because of possible organ movements due to breathing. In order to overcome limitations of 3D medical image analysis, preoperative simulation and augmented reality on organs and pathologies of the digestive system, we have been developing a set of tools over the last 8 years. Their objective is to provide support to surgeons of the digestive system, both before and during the surgical intervention. We are presenting those tools hereinafter. 2. 3D modeling of organs and surgical planning. The 3D reconstruction of patients from their CT-scan or MRI medical imaging is one of the main research topics in the field of medical image processing. Most systems allow to reconstruct anatomical and pathological structures from interactive systems, except for some of them, that propose automated systems allowing a real use in clinical routine, where processing time has to be kept at a minimum. The digestive system is one of the most complex regions to analyze, because of the great number of neighboring soft organs, that all have a very close density. In the case of the liver, main organ of the digestive system, radiologists use CT-scans, which are realized 60 seconds after the intravenous injection of a contrast medium. Theses images allow to visualize hepatic tumors, that are hypodense in the images, contrasted vessels are green as well as the liver, which has an intermediary grey level whereas it usually is higher than the one of surrounding organs. Despite these visible variations, liver delineation remains a highly complex procedure since its localization and its shape can vary considerably (its average density can vary between 70 to 150 HU). Several authors have proposed to delineate the liver with automatic [1-3], or semiautomatic methods [4-5]. These methods provide bad results in atypical-shaped liver or when the liver contains big capsular hepatic tumors, the only health parenchyma being detected. We have developed a novel method [6] which detects parenchyma and tumors from techniques developed in the works of Bae et al. [3]. In order to obtain reliable and automatic results, we have added the prior segmentation of neighboring organ. This way, we obtain a more efficient and still automatic method, which provides within 15 minutes from a CT-scan with a 2mm thickness and that has been taken 60 seconds after injection of a contrast medium : skin, bones, lungs, heart area, aorta, spleen, kidneys, gallbladder, liver, portal vein and hepatic tumors from 5 mm diameter [6]. In order to use this reconstruction, we have also developed a surgical planning system [7] working on a standard multimedia computer. Indeed, delineation of each organ allows us to deduce for each one of them a small
3 triangular meshing and to display it on any 3D card that is compatible with the OPEN GL standard. Besides 3D visualization of delineated and modeled structures, this system allows to put each structure in transparency, to interact on them, to navigate anywhere and thus to simulate any kind of cœlioscopy. It also allows to realize virtual resections defined by interactively positioned cutting plans and to provide the volume of all visualized structures (figure 1). Because of its compatibility with current standards, this system can be used on a laptop fitted with a 3D graphic card and can thus be used during the intervention so as to improve the control of the carried out gesture. Figure 1 : Virtual resection of a 3D reconstructed liver of a patient from his/her medical images and intra-operative clinical use of the planning software on a laptop. 3. Surgical simulation. Thanks to minimally invasive surgery, surgical simulation witnessed a very important expansion over the last years. This surgical technique consists in operating a patient with long instruments inserted into the patient s body, while looking at a screen linked to a camera for visualizing the interior of the operated cavity. Such a surgery offered thus a simulation favourable development field, since it is possible to replace the camera image by a virtual image of the patient. Furthermore, since the surgeon operates with instruments, it is also possible to link these instruments to motorized systems reproducing haptic sensations of force feedback. The first simulator of this type is the Minimally Invasive Surgery Trainer (MIST), developed in 1995 by the company Virtual Presence Ltd, which is today commercialized by Mentice ( Since then, a great number of companies took up surgical simulation. Some products propose deformable models, usually surfacic ones. The most used deformation model is the spring-mass model because of its easy implementation. If proposed, cutting only concerns surfacic organs. The most simulated surgery is the cholecystectomy, available on LapChole from Xitact ( LapSim
4 from Surgical Science ( LapMentor from Simbionix ( or RLT from ReachIn ( Some of these companies have developed material platforms that can be used for simulating abdominal surgery, gynaecologic or arthroscopic procedures. Various scenarios are then available as separate modules. The increasing realism of visual rendering, due to the use of textures obtained from real images, and the progress in force feedback mechanisms enabled those products to acquire some maturity. All these simulators propose training exercises for learning basic gestures. Pedagogy follows a step by step training logic allowing in the end to realize a more complex gesture including a grading. Though they are attractive, these simulators are however limited to the simulation of restricted and determined virtual models in a set database. Thus, they do not exploit the 3D reconstruction of patients that can be realized from the medical image, and do not allow to prepare a surgical intervention on a copy of the patient. Furthermore, these simulators do not feature the opportunity to cut a voluminous organ like the liver and are in fact limited to learning basic gestures. From the 3D patient modeling, we propose to realize a realistic simulator allowing to prepare and simulate a surgical intervention before actually carrying it out [8]. Thus, our objective is to realize and validate a highly realistic simulator for the laparoscopic surgery of the liver, including realistic physical and visual modeling of organs, real-time force feedback and the opportunity to change patient topology thanks to broad resections realized on any region of the reconstructed patient. In order to realize such a simulator, it is important to reproduce sensations linked to carrying out surgical gestures. The first version described in [9] only allowed to simulate main prehension and resection gestures by applying an electric bistoury. In order to improve visual quality of the simulator, we worked on the realistic aspect of the cut region, by adding a local regeneration of the meshing that therefore provides a convincing simulation of ultrasound resection (figure 2 and [10]). We maintain meshing variety : this is the true novelty of this method [10]. This property is important since it allows us to compute the normal at each surface tip of the meshing, and thus to improve the stability of haptic interaction. Furthermore, this variety allows us to use a structure of simplified data for meshing, which is optimized for force computation. We also merged two different deformation algorithms in a same meshing : an explicit method called mass-tenser and a pre-computed method [9]. Thus, the virtual organ is separated into several volumetric regions in which the deformation method (mass-tenser or pre-computed) is chosen according to the interaction nature with the virtual tool (no interaction, deformation, cutting). This method is based on the domain decomposition theory and is optimized so as to minimize the amount of communication between two neighbouring
5 regions. Our current research works aim at parallelizing this method, what will allow to speed up computation time. Figure 2: Illustration of a resection showing the realistic aspect of cutting and vascular clamping. 4. Augmented Reality: the transparent patient. One of preoperative planning and simulation limitations is the difficulty of accurately reproducing the planed and simulated gesture on the real patient. This limitation can be overcome by superimposing preoperative data on the real patient during intervention. However, this superimposition is complex to achieve in practice since it requires the accurate correspondence of reference landmarks between the virtual and the real patient. We have developed a set of tools so as to obtain a reliable result that can be used in clinical routine. Therefore, we propose to offer a view in transparency of the patient by superimposing the 3D virtual patient reconstructed from MRI or CT medical images, on the video image realized during the intervention. In order to retrieve the constraint linked to deformation and movement of organs of the abdominal area due to patient breathing, the medical image and the video image can be realized under general anesthesia with a constant air volume inside lungs. Such a procedure is observed in practice for needle insertion interventions, such as radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors. Thanks to these restrictions, abdominal organs have the same position between both acquisitions with a movement observed in vivo of less than 1mm. Registration can thus be limited to a 2D (video) 3D (modeling) rigid registration of images. To perform an accurate registration it is essential to have reference landmarks that are visible in both images. In the case of neurosurgery or orthopedic surgery, fiducials (their number varies between 3 and 6) are usually fixed on bones in order to ensure their motionlessness. In the case of digestive surgery, we place a greater number of fiducials on the skin, what allows to ensure greater stability and thus a more reliable registration (a total of 25 fiducials). These fiducials will automatically be modeled during skin segmentation and will automatically be segmented in the video image. In order
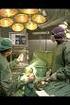
6 to carry out this registration, we orient two tri-cdd digital color cameras conjointly calibrated on the model under two different points of view with an angle between 40 and 90 for an accurate stereoscopic registration [11]. These cameras are connected to a personal computer thanks to a Matrox Meteor II acquisition card allowing the simultaneous acquisition of two video sources. In order to superimpose the 3D model in the video images, fiducials located on the 3D reconstruction have to be positioned on those visible in video images. To do so, we use a 3D/2D registration according to our method described in [11] : 3D points are spatial coordinates of fiducials reconstructed from data stemming from the scanner, and 2D points are pixel coordinates corresponding to fiducials in both camera views. The experimental study [11] we carried out with an abdominal model showed that superimposition accuracy for targets located inside the model reaches an average of 2mm after fiducial registration. Thus, we developed an efficient registration method, which allows to superimpose the 3D modeling of the patient on the real-time acquisition realized in the OR, thus providing a virtual view in transparency of the patient. For this transparency visualization to be useful, it has to be coupled with a visualization of tools that will be inserted inside the body, so as to make them visible during the whole intervention, and thus allowing to realize a precise targeting of the aimed tumor. Therefore, we developed a real-time tracking system of surgical tools allowing to superimpose a virtual instrument on the real instrument (figure 3). To do so, we have adapted the ARToolKit library [12] so that it works with the Meteor II acquisition card. Thus, tracking of the instrument is eased by adding a printed planar square, which is automatically recognized by the library, and permanent visualization of tool positioning is also possible. Figure 3 : Computer-assisted targeting thanks to the augmented reality vision.
7 In order to validate the interest of such a system, we have realized a targeting which is similar to the one carried out during a radiofrequency ablation intervention. We modeled targets with radio-opaque fiducials stuck on the synthetic liver inside a model (cf. figure 3). To reach targets, the augmented view provides the virtual position of target and needle on both video images. Needle orientation is guided by the color of the target, which changes when the needle points towards the right direction. Furthermore, the software indicates the distance (in mm) between virtual needle tip and virtual target in real-time. Two different users, software designer and expert surgeon, who did not participate in the software development, then carried out 50 targetings each. Targeting accuracy has been evaluated thanks to an endoscopic camera oriented towards target fiducials. Resulting mean distance and time to reach the target are indicated in Table 1. Table 1 :Targeting results (mean value ± standard deviation). Computer Total Surgeon Scientist Real mean distance (mm) 2.79 ± ± ± 1.27 Mean time (sec) ± ± ± These results clearly show an important targeting accuracy, since the expert has a targeting error of less than 2mm. Furthermore, comparison between targeting carried out by the software designer and the expert surgeon allows us to check that the system ensures a very high realism in usage, by favoring the expertise of gesture and not the expertise of the developed system. This is indeed a frequently encountered problem in computer-assisted surgical gesture systems, where knowledge of the system developed by the designer often enables him/her to carry out more accurate actions than the medical expert. The other advantage of this system is the time required for needle positioning. In clinical routine, such a positioning takes 5 to 10 minutes, due to the use of intraoperative imaging, such as ultrasonography or scanner, that prolongs intervention duration. Our experience shows that the gesture requires on average less than one minute to be carried out. 5. Conclusion The various works carried out by our research teams led us to develop a set of tools for diagnosis support and surgical intervention planning. They also allow to simulate a complex procedure on a 3D virtual copy of the patient and to use preoperative information during intervention, in particular by superimposing the virtual image of internal organs and pathologies on the abdomen of the patient.
8 These systems, at an experimental stage, are progressively being tested clinically, with the objective of eventually being used in clinical routine. They represent the first essential phase for surgical gesture automation, that will allow to reduce surgical mistakes. Indeed, intervention simulation will allow to do without all superfluous or imperfect gestures, using it as a programming of the final gesture. This gesture will then be transmitted to a surgical robot which, thanks to augmented reality, will be able to precisely reproduce optimized gestures of the surgeon. Tomorrow s surgery is on its way. Acknowledgments We would like to thank all our medical partners, who have provided us medical images of patients, and in particular Pr. Afshin Gangi and Pr. Catherine Roy from the radiological department of the Civil Hospital in Strasbourg. We also thank the surgical team of Professor Marescaux for their help, medical analysis and validation of our works, especially Pr. Mutter, Pr. Leroy, Dr. Vix, Dr. Henry and Dr. Garcia. Finally, we are very grateful to the Virtual-Surg team of IRCAD and the Epidaure Team of INRIA for their great contribution to these works, and in particular S. Cotin, F. Doganis, C. Haessig, C. Koehl, J. Moreau, A.-B. Osswald, N. Papier, and G. Picinbono. References 1. J. Montagnat and H. Delingette : Volumetric Medical Images Segmentation using Shape Constrained Deformable Models. CVRMed- MRCAS 97, Springer Verlag Publisher, LNCS 1205, pp , (1997). 2. L. Gao, D.G. Heath, B.S. Kuszyk and E.K. Fishman : Automatic Liver Segmentation Techniques for Three-Dimensional Visualization of CT Data. Radiology, 2(201), pp , (1996). 3. K.T. Bae, M.L. Giger, C.-T. Chen and C.E. Kahn : Automatic segmentation of liver structure in CT images. Medical Physics, 1(20), pp , (1993). 4. A. Schenk, G. Prause and H.-O. Peitgen : Efficient SemiAutomatic Segmentation of 3D objects in Medical Images. MICCAI 2000, Springer Verlag Publisher, LNCS 1935, pp , (2000). 5. G. Glombitza, W. Lamadé, A. M. Demeris, M.-R. Göpfert, A. Mayer, M. L. Bahner, H.-P. Meinzer, G. Richter, T. Lehnert and C. Herfarth : Virtual planning of liver resections: image processing, visualisation and
9 volumetric evaluation. International Journal of Medical Informatics, Elsevier, vol. 53, pp , (1999). 6. L. Soler, H. Delingette, G. Malandain, J. Montagnat, N. Ayache, C. Koehl, O. Dourthe, B. Malassagne, M. Smith, D. Mutter, J. Marescaux : Fully automatic anatomical, pathological, and functional segmentation from CT scans for hepatic surgery. Computer Aided Surgery, Vol. 6, Num. 3, pp , (2001). 7. C. Koehl, L. Soler, J. Marescaux: A PACS Based Interface for 3D Anatomical Structures Visualization and Surgical Planning., SPIE proceeding Vol. 4681, pp , San diego USA, (2002). 8. N. Ayache : Epidaure: a Research Project in Medical Image Analysis, Simulation and Robotics at INRIA, IEEE Transaction on Medical Imaging, october 2003, 22(10), pp (2003). 9. S. Cotin, H. Delingette, and N. Ayache : A Hybrid Elastic Model allowing Real-Time Cutting, Deformations and Force-Feedback for Surgery Training and Simulation., The Visual Computer, 16(8), pp , (2000). 10. C. Forest, H. Delingette, N. Ayache : Cutting Simulation of Manifold Volumetric Meshes., in Medical Image Computing and Computer- Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 02), LNCS 2488, pp , (2002). 11. S. Nicolau, X. Pennec, L. Soler and N. Ayache : Evaluation of a new 3D/2D registration criterion for Liver Radio-frequencies Guided by Augmented reality., IS4TM 2003, LNCS 2673, pp (2003). 12. M. Billinghurst, H.Kato, M. Billinghurst, I. Poupyrev (2001) : The MagicBook: Moving Seamlessly between Reality and Virtuality., In IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, May/June, 2001, pp.2-4 (2001).
Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques
 Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques Alexander Bornik 1, Reinhard Beichel 1, Bernhard Reitinger 1, Georg Gotschuli 2, Erich Sorantin 2, Franz Leberl 1 and Milan Sonka
Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques Alexander Bornik 1, Reinhard Beichel 1, Bernhard Reitinger 1, Georg Gotschuli 2, Erich Sorantin 2, Franz Leberl 1 and Milan Sonka
Virtual Reality and Robotics in Digestive Surgery. Pr. Luc Soler, Pr. Jacques Marescaux
 Virtual Reality and Robotics in Digestive Surgery 1 Pr. Luc Soler, Pr. Jacques Marescaux 20 th century Surgical Evolution Open Laparoscopy Robotics 2 New vision of surgery WebSurg : Continuous education
Virtual Reality and Robotics in Digestive Surgery 1 Pr. Luc Soler, Pr. Jacques Marescaux 20 th century Surgical Evolution Open Laparoscopy Robotics 2 New vision of surgery WebSurg : Continuous education
Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye
 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye 8 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye Kazutoshi Kan Michio Oikawa Takashi Azuma Shio Miyamoto OVERVIEW: A surgery support
Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye 8 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye Kazutoshi Kan Michio Oikawa Takashi Azuma Shio Miyamoto OVERVIEW: A surgery support
Development of Simulation Tools Software
 Development of Simulation Tools Software Vincent Luboz Department of Biosurgery and Surgical Technology Imperial College London BSc VR Surgical Simulation Software Slide 1 Contents Virtual Reality VR Surgical
Development of Simulation Tools Software Vincent Luboz Department of Biosurgery and Surgical Technology Imperial College London BSc VR Surgical Simulation Software Slide 1 Contents Virtual Reality VR Surgical
Impact of Model-based Risk Analysis for Liver Surgery Planning
 Impact of Model-based Risk Analysis for Liver Surgery Planning C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz 1, B. Preim 2, G. Stavrou 3, K. J. Oldhafer 3, H. K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing,
Impact of Model-based Risk Analysis for Liver Surgery Planning C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz 1, B. Preim 2, G. Stavrou 3, K. J. Oldhafer 3, H. K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing,
Publication in link with the presentation
 Publication in link with the presentation 2007 1. Discrete Delaunay: Boundary extraction from voxel objects Boltcheva D, Bechmann D, Thery S. Sixth International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling
Publication in link with the presentation 2007 1. Discrete Delaunay: Boundary extraction from voxel objects Boltcheva D, Bechmann D, Thery S. Sixth International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling
MMVR: 10, January 2002. On Defining Metrics for Assessing Laparoscopic Surgical Skills in a Virtual Training Environment
 On Defining Metrics for Assessing Laparoscopic Surgical Skills in a Virtual Training Environment Shahram Payandeh, Alan J. Lomax, John Dill, Christine L. Mackenzie and Caroline G. L. Cao Schools of Engineering
On Defining Metrics for Assessing Laparoscopic Surgical Skills in a Virtual Training Environment Shahram Payandeh, Alan J. Lomax, John Dill, Christine L. Mackenzie and Caroline G. L. Cao Schools of Engineering
anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table
 anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table Anatomage offers a unique, life-size interactive anatomy visualization table for the medical community. Anatomage Table offers an unprecedented realistic
anatomage table Interactive anatomy study table Anatomage offers a unique, life-size interactive anatomy visualization table for the medical community. Anatomage Table offers an unprecedented realistic
Image Area. View Point. Medical Imaging. Advanced Imaging Solutions for Diagnosis, Localization, Treatment Planning and Monitoring. www.infosys.
 Image Area View Point Medical Imaging Advanced Imaging Solutions for Diagnosis, Localization, Treatment Planning and Monitoring www.infosys.com Over the years, medical imaging has become vital in the early
Image Area View Point Medical Imaging Advanced Imaging Solutions for Diagnosis, Localization, Treatment Planning and Monitoring www.infosys.com Over the years, medical imaging has become vital in the early
Effectiveness of Haptic Feedback in Open Surgery Simulation and Training Systems
 Effectiveness of Haptic Feedback in Open Surgery Simulation and Training Systems John HU a 1, Chu-Yin CHANG a, Neil TARDELLA a, James ENGLISH b, Janey PRATT b a Energid Technologies Corporation b Massachusetts
Effectiveness of Haptic Feedback in Open Surgery Simulation and Training Systems John HU a 1, Chu-Yin CHANG a, Neil TARDELLA a, James ENGLISH b, Janey PRATT b a Energid Technologies Corporation b Massachusetts
Computer-Assisted Interventions on liver: Feasibility of the anchor needle technique for real-time targeting of lesions with respiratory motion.
 Computer-Assisted Interventions on liver: Feasibility of the anchor needle technique for real-time targeting of lesions with respiratory motion. Ivan Bricault 1,2, Simon DiMaio 2, Olivier Clatz 3, Sonia
Computer-Assisted Interventions on liver: Feasibility of the anchor needle technique for real-time targeting of lesions with respiratory motion. Ivan Bricault 1,2, Simon DiMaio 2, Olivier Clatz 3, Sonia
Ubiquitous Tracking. martin.bauer@in.tum.de. Ubiquitous Tracking. Martin Bauer Oberseminar Augmented Reality. 20. Mai 2003
 martin.bauer@in.tum.de What we have GPS, but only outside ART DTrack, but only in the Lab AR Toolkit, but only with Line-of-Sight Gyroscope, but only with some drift Compass, but only with distortions
martin.bauer@in.tum.de What we have GPS, but only outside ART DTrack, but only in the Lab AR Toolkit, but only with Line-of-Sight Gyroscope, but only with some drift Compass, but only with distortions
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
OPENNESS IN (TELE-) RADIOLOGY WORKSTATIONS: THE CHILI PLUGIN CONCEPT
 Reprint of :.Lemke HU, Vannier MW, Inamura K, Farman A (Eds). CAR 98 - Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Amsterdam: Elsevier (1998) 437-442. OPENNESS IN (TELE-) RADIOLOGY WORKSTATIONS: THE CHILI
Reprint of :.Lemke HU, Vannier MW, Inamura K, Farman A (Eds). CAR 98 - Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. Amsterdam: Elsevier (1998) 437-442. OPENNESS IN (TELE-) RADIOLOGY WORKSTATIONS: THE CHILI
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane
 Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane Olaf Konrad-Verse 1, Bernhard Preim 2, Arne Littmann 1 1 Center for Medical Diagnostic Systems and Visualization, Universitaetsallee 29, 28359 Bremen,
Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane Olaf Konrad-Verse 1, Bernhard Preim 2, Arne Littmann 1 1 Center for Medical Diagnostic Systems and Visualization, Universitaetsallee 29, 28359 Bremen,
Benefits of augmented reality function for laparoscopic and endoscopic surgical robot systems
 Benefits of augmented reality function for laparoscopic and endoscopic surgical robot systems Naoki Suzuki 1, Asaki Hattori 1, Makoto Hashizume 2 1 Institute for High Dimensional Medical Imaging, The Jikei
Benefits of augmented reality function for laparoscopic and endoscopic surgical robot systems Naoki Suzuki 1, Asaki Hattori 1, Makoto Hashizume 2 1 Institute for High Dimensional Medical Imaging, The Jikei
 Users Group Meeting 2011 Northeastern Society of Orthodontists 89th Annual Meeting November 11-14, 2010 Hilton Montréal Bonaventure Montréal, Quebec, Canada 14 Lecture Schedule Saturday continued w Doctor
Users Group Meeting 2011 Northeastern Society of Orthodontists 89th Annual Meeting November 11-14, 2010 Hilton Montréal Bonaventure Montréal, Quebec, Canada 14 Lecture Schedule Saturday continued w Doctor
Rapid Modeling für bildgestützte Interventionen Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Weber
 Rapid Modeling für bildgestützte Interventionen Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Weber ARTORG - Research Center ISTB - Institute for Surgical Technology and Biomechanics University of Bern Outline > Clinical Challenge:
Rapid Modeling für bildgestützte Interventionen Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Weber ARTORG - Research Center ISTB - Institute for Surgical Technology and Biomechanics University of Bern Outline > Clinical Challenge:
Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica
 Department of Innovation Engineering Salento University Lecce, Italy Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica Lucio Tommaso De Paolis, Giovanni
Department of Innovation Engineering Salento University Lecce, Italy Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica Lucio Tommaso De Paolis, Giovanni
Robotic Surgery 12 years of robotic assisted surgery vs. conventional laparoscopic surgery
 Robotic Surgery 12 years of robotic assisted surgery vs. conventional laparoscopic surgery A new chapter in medicine.from the first remote surgery by Prof. Dr. Senner to the today`s da Vinci technology
Robotic Surgery 12 years of robotic assisted surgery vs. conventional laparoscopic surgery A new chapter in medicine.from the first remote surgery by Prof. Dr. Senner to the today`s da Vinci technology
POLARIS OPTICAL TRACKING SYSTEMS
 POLARIS OPTICAL TRACKING SYSTEMS FROM A WORLD LEADER IN NAVIGATION TECHNOLOGY The Polaris Spectra and Polaris Vicra optical tracking systems from NDI are based on over 30 years of advanced 3D measurement
POLARIS OPTICAL TRACKING SYSTEMS FROM A WORLD LEADER IN NAVIGATION TECHNOLOGY The Polaris Spectra and Polaris Vicra optical tracking systems from NDI are based on over 30 years of advanced 3D measurement
Creation of an Unlimited Database of Virtual Bone. Validation and Exploitation for Orthopedic Devices
 Creation of an Unlimited Database of Virtual Bone Population using Mesh Morphing: Validation and Exploitation for Orthopedic Devices Najah Hraiech 1, Christelle Boichon 1, Michel Rochette 1, 2 Thierry
Creation of an Unlimited Database of Virtual Bone Population using Mesh Morphing: Validation and Exploitation for Orthopedic Devices Najah Hraiech 1, Christelle Boichon 1, Michel Rochette 1, 2 Thierry
SAMSUNG ULTRASOUND RS80A
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Computer Graphics in Medicine
 Computer Graphics in Medicine Loren Block For my presentation, I will discuss several different papers that are related to graphics and imaging in the medical field. The main areas that the papers cover
Computer Graphics in Medicine Loren Block For my presentation, I will discuss several different papers that are related to graphics and imaging in the medical field. The main areas that the papers cover
VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS FOR TRAINING CRITICAL SKILLS IN LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
 VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS FOR TRAINING CRITICAL SKILLS IN LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY MICHAEL DOWNES (1), M. Cenk Cavusoglu, MS (1), Walter Gantert, MD (2), Lawrence W. Way, MD (2), Frank Tendick, PhD (2) (1) Department
VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS FOR TRAINING CRITICAL SKILLS IN LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY MICHAEL DOWNES (1), M. Cenk Cavusoglu, MS (1), Walter Gantert, MD (2), Lawrence W. Way, MD (2), Frank Tendick, PhD (2) (1) Department
An Instructional Aid System for Driving Schools Based on Visual Simulation
 An Instructional Aid System for Driving Schools Based on Visual Simulation Salvador Bayarri, Rafael Garcia, Pedro Valero, Ignacio Pareja, Institute of Traffic and Road Safety (INTRAS), Marcos Fernandez
An Instructional Aid System for Driving Schools Based on Visual Simulation Salvador Bayarri, Rafael Garcia, Pedro Valero, Ignacio Pareja, Institute of Traffic and Road Safety (INTRAS), Marcos Fernandez
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Computer Animation and Visualisation. Lecture 1. Introduction
 Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 1 Introduction 1 Today s topics Overview of the lecture Introduction to Computer Animation Introduction to Visualisation 2 Introduction (PhD in Tokyo, 2000,
Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 1 Introduction 1 Today s topics Overview of the lecture Introduction to Computer Animation Introduction to Visualisation 2 Introduction (PhD in Tokyo, 2000,
Twelve. Figure 12.1: 3D Curved MPR Viewer Window
 Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
ASSESSMENT OF VISUALIZATION SOFTWARE FOR SUPPORT OF CONSTRUCTION SITE INSPECTION TASKS USING DATA COLLECTED FROM REALITY CAPTURE TECHNOLOGIES
 ASSESSMENT OF VISUALIZATION SOFTWARE FOR SUPPORT OF CONSTRUCTION SITE INSPECTION TASKS USING DATA COLLECTED FROM REALITY CAPTURE TECHNOLOGIES ABSTRACT Chris Gordon 1, Burcu Akinci 2, Frank Boukamp 3, and
ASSESSMENT OF VISUALIZATION SOFTWARE FOR SUPPORT OF CONSTRUCTION SITE INSPECTION TASKS USING DATA COLLECTED FROM REALITY CAPTURE TECHNOLOGIES ABSTRACT Chris Gordon 1, Burcu Akinci 2, Frank Boukamp 3, and
NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
High speed 3D capture for Configuration Management DOE SBIR Phase II Paul Banks Paul.banks@tetravue.com
 High speed 3D capture for Configuration Management DOE SBIR Phase II Paul Banks Paul.banks@tetravue.com Advanced Methods for Manufacturing Workshop September 29, 2015 1 TetraVue does high resolution 3D
High speed 3D capture for Configuration Management DOE SBIR Phase II Paul Banks Paul.banks@tetravue.com Advanced Methods for Manufacturing Workshop September 29, 2015 1 TetraVue does high resolution 3D
Applications of graphics in medicine training
 Applications of graphics in medicine training Clara Bayarri Table of contents The area... 2 Examples... 2 How are these applications used?... 3 Visual and interaction requirements... 4 Research groups
Applications of graphics in medicine training Clara Bayarri Table of contents The area... 2 Examples... 2 How are these applications used?... 3 Visual and interaction requirements... 4 Research groups
Training systems for endoscopic soft-tissue surgery
 Training systems for endoscopic soft-tissue surgery Review report GR/L80577/01 Researchers: Professor B.L. Davies, Principal Investigator Dr. M.P.S.F. Gomes-Bharath, Research Associate Mr. A.R.W. Barrett,
Training systems for endoscopic soft-tissue surgery Review report GR/L80577/01 Researchers: Professor B.L. Davies, Principal Investigator Dr. M.P.S.F. Gomes-Bharath, Research Associate Mr. A.R.W. Barrett,
Embedded Systems in Healthcare. Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008
 Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Making Machines Understand Facial Motion & Expressions Like Humans Do
 Making Machines Understand Facial Motion & Expressions Like Humans Do Ana C. Andrés del Valle & Jean-Luc Dugelay Multimedia Communications Dpt. Institut Eurécom 2229 route des Crêtes. BP 193. Sophia Antipolis.
Making Machines Understand Facial Motion & Expressions Like Humans Do Ana C. Andrés del Valle & Jean-Luc Dugelay Multimedia Communications Dpt. Institut Eurécom 2229 route des Crêtes. BP 193. Sophia Antipolis.
School of Computer Science Virtual Reality in Medicine How Close are we to Star Trek?
 Virtual Reality in Medicine How Close are we to Star Trek? Prof. Nigel John School of Computer Sciene University of Wales, Bangor Overview of Talk What is Virtual Reality? Into the Hospital Using medical
Virtual Reality in Medicine How Close are we to Star Trek? Prof. Nigel John School of Computer Sciene University of Wales, Bangor Overview of Talk What is Virtual Reality? Into the Hospital Using medical
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
TELEDIAGNOSTICS OF FRACTURE HEALING PROGRESS
 W.Glinkowski 1,2,6, J.Żyłkowski 4,6, A.Wojciechowski 3,6, P. Picewicz 5, A.Górecki 1 TELEDIAGNOSTICS OF FRACTURE HEALING PROGRESS 1 Chair and Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Locomotor System,
W.Glinkowski 1,2,6, J.Żyłkowski 4,6, A.Wojciechowski 3,6, P. Picewicz 5, A.Górecki 1 TELEDIAGNOSTICS OF FRACTURE HEALING PROGRESS 1 Chair and Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Locomotor System,
Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery
 Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery Duncan Gillies Department of Computing, Imperial College London Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery Lecture 1 Slide 1 A Brief History of Virtual Reality Techniques
Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery Duncan Gillies Department of Computing, Imperial College London Virtual Reality in Medicine and Surgery Lecture 1 Slide 1 A Brief History of Virtual Reality Techniques
Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing
 Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing Jürgen Rurainsky and Peter Eisert Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications - Heinrich-Hertz-Institute, Image Processing Department, Einsteinufer
Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing Jürgen Rurainsky and Peter Eisert Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications - Heinrich-Hertz-Institute, Image Processing Department, Einsteinufer
Virtual Training. Proven Results.
 Virtual Training. Proven Results. NEW BASIC SKILLS TASK TRAINING CAMERA ANATOMY TRAINING CHOLECYSTECTOMY VATS LOBECTOMY BARIATRICS SUTURING & ANASTOMOSIS APPENDECTOMY GYNECOLOGY NEPHRECTOMY The Advantage.
Virtual Training. Proven Results. NEW BASIC SKILLS TASK TRAINING CAMERA ANATOMY TRAINING CHOLECYSTECTOMY VATS LOBECTOMY BARIATRICS SUTURING & ANASTOMOSIS APPENDECTOMY GYNECOLOGY NEPHRECTOMY The Advantage.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
A Three-Dimensional Correlation Method for Registration of Medical Images in Radiology
 A Three-Dimensional Correlation Method for Registration of Medical Images in Radiology Michalakis F. Georgiou 1, Joachim H. Nagel 2, George N. Sfakianakis 3 1,3 Department of Radiology, University of Miami
A Three-Dimensional Correlation Method for Registration of Medical Images in Radiology Michalakis F. Georgiou 1, Joachim H. Nagel 2, George N. Sfakianakis 3 1,3 Department of Radiology, University of Miami
How To Learn To Perform An Ultrasound
 CAE ICCU E-Learning CAE VIMEDIX Ultrasound Simulator Master Ultrasonography of the Thoracic, Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities An Engaging Learning Solution for Ultrasound Hands-on Simulation, Multimedia Content,
CAE ICCU E-Learning CAE VIMEDIX Ultrasound Simulator Master Ultrasonography of the Thoracic, Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities An Engaging Learning Solution for Ultrasound Hands-on Simulation, Multimedia Content,
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging
 Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging Courses: All RT-BMSc students must complete all of the program s core courses and the courses specific to their selected minor
Emory University RT to Bachelor of Medical Science Degree Medical Imaging Courses: All RT-BMSc students must complete all of the program s core courses and the courses specific to their selected minor
AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical Information
 In Proc. First International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 98), Cambridge, MA, 1998, pp. 720-731. AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical
In Proc. First International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 98), Cambridge, MA, 1998, pp. 720-731. AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical
Scooter, 3 wheeled cobot North Western University. PERCRO Exoskeleton
 Scooter, 3 wheeled cobot North Western University A cobot is a robot for direct physical interaction with a human operator, within a shared workspace PERCRO Exoskeleton Unicycle cobot the simplest possible
Scooter, 3 wheeled cobot North Western University A cobot is a robot for direct physical interaction with a human operator, within a shared workspace PERCRO Exoskeleton Unicycle cobot the simplest possible
Validation in medical image processing.
 Validation in medical image processing. Pierre Jannin, Elizabeth Krupinski, Simon K. Warfield To cite this version: Pierre Jannin, Elizabeth Krupinski, Simon K. Warfield. Validation in medical image processing..
Validation in medical image processing. Pierre Jannin, Elizabeth Krupinski, Simon K. Warfield To cite this version: Pierre Jannin, Elizabeth Krupinski, Simon K. Warfield. Validation in medical image processing..
A Cognitive Approach to Vision for a Mobile Robot
 A Cognitive Approach to Vision for a Mobile Robot D. Paul Benjamin Christopher Funk Pace University, 1 Pace Plaza, New York, New York 10038, 212-346-1012 benjamin@pace.edu Damian Lyons Fordham University,
A Cognitive Approach to Vision for a Mobile Robot D. Paul Benjamin Christopher Funk Pace University, 1 Pace Plaza, New York, New York 10038, 212-346-1012 benjamin@pace.edu Damian Lyons Fordham University,
Pipeline External Corrosion Analysis Using a 3D Laser Scanner
 Pipeline Technology Conference 2013 Pipeline External Corrosion Analysis Using a 3D Laser Scanner Pierre-Hugues ALLARD, Charles MONY Creaform, www.creaform3d.com 5825 rue St-Georges, Lévis (QC), Canada,
Pipeline Technology Conference 2013 Pipeline External Corrosion Analysis Using a 3D Laser Scanner Pierre-Hugues ALLARD, Charles MONY Creaform, www.creaform3d.com 5825 rue St-Georges, Lévis (QC), Canada,
-Increases the safety, accuracy and efficiency of certain spine procedures
 Chapter 13: Spinal Navigation Ben J Garrido, MD, Rick C Sasso, MD I. Key Points -Allows intraoperative real time navigation of instruments relative to the spinal anatomy -Provides 3-D real time anatomical
Chapter 13: Spinal Navigation Ben J Garrido, MD, Rick C Sasso, MD I. Key Points -Allows intraoperative real time navigation of instruments relative to the spinal anatomy -Provides 3-D real time anatomical
Changing The World One Hospital At a Time
 Changing The World One Hospital At a Time miplatform Integrated Medical Image and Information Management Platform PACS/RIS System Mobile Imaging System Image-based Conferencing System TeleMed/TeleRad System
Changing The World One Hospital At a Time miplatform Integrated Medical Image and Information Management Platform PACS/RIS System Mobile Imaging System Image-based Conferencing System TeleMed/TeleRad System
Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality
 Virtual and Augmented Reality Supported Simulators Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality Bernhard Reitinger, Alexander Bornik, Reinhard Beichel, and Dieter Schmalstieg Graz University of Technology
Virtual and Augmented Reality Supported Simulators Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality Bernhard Reitinger, Alexander Bornik, Reinhard Beichel, and Dieter Schmalstieg Graz University of Technology
REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART
 To appear in: Proceedings of the Interface to Real & Virtual Worlds (Montpellier, France, May 28-30, 1997) REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART Stefan Pieper, Michael Weidenbach*,
To appear in: Proceedings of the Interface to Real & Virtual Worlds (Montpellier, France, May 28-30, 1997) REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART Stefan Pieper, Michael Weidenbach*,
A Remote Maintenance System with the use of Virtual Reality.
 ICAT 2001 December 5-7, Tokyo, JAPAN A Remote Maintenance System with the use of Virtual Reality. Moez BELLAMINE 1), Norihiro ABE 1), Kazuaki TANAKA 1), Hirokazu TAKI 2) 1) Kyushu Institute of Technology,
ICAT 2001 December 5-7, Tokyo, JAPAN A Remote Maintenance System with the use of Virtual Reality. Moez BELLAMINE 1), Norihiro ABE 1), Kazuaki TANAKA 1), Hirokazu TAKI 2) 1) Kyushu Institute of Technology,
Integration and Visualization of Multimodality Brain Data for Language Mapping
 Integration and Visualization of Multimodality Brain Data for Language Mapping Andrew V. Poliakov, PhD, Kevin P. Hinshaw, MS, Cornelius Rosse, MD, DSc and James F. Brinkley, MD, PhD Structural Informatics
Integration and Visualization of Multimodality Brain Data for Language Mapping Andrew V. Poliakov, PhD, Kevin P. Hinshaw, MS, Cornelius Rosse, MD, DSc and James F. Brinkley, MD, PhD Structural Informatics
The Exploration of Cross-Sectional Data with a Virtual Endoscope
 The Exploration of Cross-Sectional Data with a Virtual Endoscope William E. Lorensen, MS GE Corporate Research and Development, Schenectady, NY 1. Introduction Ferenc A. Jolesz, MD Ron Kikinis, MD Brigham
The Exploration of Cross-Sectional Data with a Virtual Endoscope William E. Lorensen, MS GE Corporate Research and Development, Schenectady, NY 1. Introduction Ferenc A. Jolesz, MD Ron Kikinis, MD Brigham
When is Hip Arthroscopy recommended?
 HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
High-accuracy ultrasound target localization for hand-eye calibration between optical tracking systems and three-dimensional ultrasound
 High-accuracy ultrasound target localization for hand-eye calibration between optical tracking systems and three-dimensional ultrasound Ralf Bruder 1, Florian Griese 2, Floris Ernst 1, Achim Schweikard
High-accuracy ultrasound target localization for hand-eye calibration between optical tracking systems and three-dimensional ultrasound Ralf Bruder 1, Florian Griese 2, Floris Ernst 1, Achim Schweikard
University Children s Hospital Basel
 Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Deformation-based Augmented Reality for Hepatic Surgery
 Deformation-based Augmented Reality for Hepatic Surgery Nazim Haouchine, Jérémie Dequidt, Marie-Odile Berger, Stéphane Cotin To cite this version: Nazim Haouchine, Jérémie Dequidt, Marie-Odile Berger,
Deformation-based Augmented Reality for Hepatic Surgery Nazim Haouchine, Jérémie Dequidt, Marie-Odile Berger, Stéphane Cotin To cite this version: Nazim Haouchine, Jérémie Dequidt, Marie-Odile Berger,
Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors. A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate
 Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate rose ella burkhardt brain tumor and neuro-oncology center Pioneering a Promising Surgical Treatment A brain tumor diagnosis is overwhelming
Novel Surgery for Inoperable Brain Tumors A Patient Guide to NeuroBlate rose ella burkhardt brain tumor and neuro-oncology center Pioneering a Promising Surgical Treatment A brain tumor diagnosis is overwhelming
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.
 DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
ExmoR A Testing Tool for Control Algorithms on Mobile Robots
 ExmoR A Testing Tool for Control Algorithms on Mobile Robots F. Lehmann, M. Ritzschke and B. Meffert Institute of Informatics, Humboldt University, Unter den Linden 6, 10099 Berlin, Germany E-mail: falk.lehmann@gmx.de,
ExmoR A Testing Tool for Control Algorithms on Mobile Robots F. Lehmann, M. Ritzschke and B. Meffert Institute of Informatics, Humboldt University, Unter den Linden 6, 10099 Berlin, Germany E-mail: falk.lehmann@gmx.de,
Organising multimedia technology for realtime transmission of image-guided surgery
 Organising multimedia technology for realtime transmission of image-guided surgery Margunn Aanestad *), Jan Sigurd Røtnes *), Trond Buanes **) *) Interventional Centre, The National Hospital, Oslo, Norway.
Organising multimedia technology for realtime transmission of image-guided surgery Margunn Aanestad *), Jan Sigurd Røtnes *), Trond Buanes **) *) Interventional Centre, The National Hospital, Oslo, Norway.
GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E. GynTrainer. the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy
 GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E GynTrainer the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy Virtual Reality (VR) in Medical Training and Further Education at KARL STORZ
GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E GynTrainer the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy Virtual Reality (VR) in Medical Training and Further Education at KARL STORZ
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications
 Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications Verbesserte Darstellungsmethoden für Volumendaten in medizinischen Anwendungen J. Georgii 1, J. Schneider 1, J. Krüger 1, R. Westermann 1,
Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications Verbesserte Darstellungsmethoden für Volumendaten in medizinischen Anwendungen J. Georgii 1, J. Schneider 1, J. Krüger 1, R. Westermann 1,
Introduction. C 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
 1 Introduction The purpose of this text on stereo-based imaging is twofold: it is to give students of computer vision a thorough grounding in the image analysis and projective geometry techniques relevant
1 Introduction The purpose of this text on stereo-based imaging is twofold: it is to give students of computer vision a thorough grounding in the image analysis and projective geometry techniques relevant
restricted to certain centers and certain patients, preferably in some sort of experimental trial format.
 Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
What is the CyberKnife System?
 CYBERKNIFE Robotic Radiosurgery System PATIENT BROChURE 1 What is the CyberKnife System? have stabilizing frames bolted to their head or limit their breathing during treatment to minimize movement of the
CYBERKNIFE Robotic Radiosurgery System PATIENT BROChURE 1 What is the CyberKnife System? have stabilizing frames bolted to their head or limit their breathing during treatment to minimize movement of the
Fast mobile reading on the go November 2013. syngo.via WebViewer. Unrestricted Siemens AG 2013 All rights reserved.
 Fast mobile reading on the go November 2013 syngo.via WebViewer Answers for life. syngo.via WebViewer The mobile extension of syngo.via syngo.via WebViewer 1, enables mobile reading of images with brilliant
Fast mobile reading on the go November 2013 syngo.via WebViewer Answers for life. syngo.via WebViewer The mobile extension of syngo.via syngo.via WebViewer 1, enables mobile reading of images with brilliant
ISSN 1340-8763 Vol.14, No.2 December 2003
 ISSN 1340-8763 Vol.14, No.2 December 2003 mm m Continued on page Continued on page Continued on page Continued on page Extracorporeal Focused Ultrasound Lithotripsy Cavitation Control Lithotripsy Yoichiro
ISSN 1340-8763 Vol.14, No.2 December 2003 mm m Continued on page Continued on page Continued on page Continued on page Extracorporeal Focused Ultrasound Lithotripsy Cavitation Control Lithotripsy Yoichiro
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning
 Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning Konrad Muehler, Ragnar Bade, and Bernhard Preim Department of Simulation and Graphics, Department of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University
Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning Konrad Muehler, Ragnar Bade, and Bernhard Preim Department of Simulation and Graphics, Department of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University
Treatment of Hepatic Neoplasm
 I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
Training Environment for Inferior Vena Caval Filter Placement
 Training Environment for Inferior Vena Caval Filter Placement James K. Hahn, Ph.D. 1,2, Roger Kaufman, Ph.D. 1,4, Adam B. Winick, M.D. 3, Thurston Carleton 1, Youngser Park 1, Rob Lindeman 1, Kwang-Man
Training Environment for Inferior Vena Caval Filter Placement James K. Hahn, Ph.D. 1,2, Roger Kaufman, Ph.D. 1,4, Adam B. Winick, M.D. 3, Thurston Carleton 1, Youngser Park 1, Rob Lindeman 1, Kwang-Man
The Medical Imaging Detective
 Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
Solving Medical Mysteries with Imaging Richard S. Breiman, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging (Medical Imaging Detective) UCSF The Medical Imaging Detective Peering into the Patient to
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
ViewPoint 6. Clarify your View
 ViewPoint 6 Clarify your View Clear information helps you see the bigger picture Using over 20 years of experience and feedback from customers across the globe, we ve simplified ultrasound reporting and
ViewPoint 6 Clarify your View Clear information helps you see the bigger picture Using over 20 years of experience and feedback from customers across the globe, we ve simplified ultrasound reporting and
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC Medical image analysis the goal Automatic, semantic analysis and quantification of what observed in medical scans Brain
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC Medical image analysis the goal Automatic, semantic analysis and quantification of what observed in medical scans Brain
Simulation and training of lumbar punctures using haptic volume rendering and a 6DOF haptic device
 Simulation and training of lumbar punctures using haptic volume rendering and a 6DOF haptic device Matthias Färber, Julika Heller, and Heinz Handels Department of Medical Informatics, University Medical
Simulation and training of lumbar punctures using haptic volume rendering and a 6DOF haptic device Matthias Färber, Julika Heller, and Heinz Handels Department of Medical Informatics, University Medical
Integration of a Robotic Arm with the Surgical Assistant Workstation Software Framework
 Integration of a Robotic Arm with the Surgical Assistant Workstation Software Framework Release 1.7 Jessie Young 1, Haytham Elhawary 2 and Aleksandra Popovic 2 July 21, 2011 1 Center for Computer-Integrated
Integration of a Robotic Arm with the Surgical Assistant Workstation Software Framework Release 1.7 Jessie Young 1, Haytham Elhawary 2 and Aleksandra Popovic 2 July 21, 2011 1 Center for Computer-Integrated
Modelling 3D Avatar for Virtual Try on
 Modelling 3D Avatar for Virtual Try on NADIA MAGNENAT THALMANN DIRECTOR MIRALAB UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR MEDIA INNOVATION, NTU, SINGAPORE WWW.MIRALAB.CH/ Creating Digital Humans Vertex
Modelling 3D Avatar for Virtual Try on NADIA MAGNENAT THALMANN DIRECTOR MIRALAB UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR MEDIA INNOVATION, NTU, SINGAPORE WWW.MIRALAB.CH/ Creating Digital Humans Vertex
SOFA an Open Source Framework for Medical Simulation
 SOFA an Open Source Framework for Medical Simulation J. ALLARD a P.-J. BENSOUSSAN b S. COTIN a H. DELINGETTE b C. DURIEZ b F. FAURE b L. GRISONI b and F. POYER b a CIMIT Sim Group - Harvard Medical School
SOFA an Open Source Framework for Medical Simulation J. ALLARD a P.-J. BENSOUSSAN b S. COTIN a H. DELINGETTE b C. DURIEZ b F. FAURE b L. GRISONI b and F. POYER b a CIMIT Sim Group - Harvard Medical School
Cancer Care Delivered Locally by Physicians You Know and Trust
 West Florida Physician Office Building Johnson Ave. University Pkwy. Olive Road N. Davis Hwy. For more information on West Florida Cancer Center: 850-494-5404 2130 East Johnson Avenue Pensacola, Florida
West Florida Physician Office Building Johnson Ave. University Pkwy. Olive Road N. Davis Hwy. For more information on West Florida Cancer Center: 850-494-5404 2130 East Johnson Avenue Pensacola, Florida
Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT
 Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT Sep.10, 2014 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS Forward-looking statements, such as those relating to earnings forecasts and other projections contained in this material, are
Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT Sep.10, 2014 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS Forward-looking statements, such as those relating to earnings forecasts and other projections contained in this material, are
Development of Infrared-Based Positioning Simulator for Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
 Draft to be submitted to Journal of American College of Surgeons Development of Infrared-Based Positioning Simulator for Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Mason R. Jellings, Sarah R. Switalski,
Draft to be submitted to Journal of American College of Surgeons Development of Infrared-Based Positioning Simulator for Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Mason R. Jellings, Sarah R. Switalski,
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
Proposed Database System to Integrate Patient Information and Research Data for Maxillofacial and Craniofacial Domain
 Proposed Database System to Integrate Patient Information and Research Data for Maxillofacial and Craniofacial Domain FARIZA HANUM NASARUDDIN, MAIZATUL AKMAR ISMAIL, & EHAB NABIEL MOHAMMED * Faculty of
Proposed Database System to Integrate Patient Information and Research Data for Maxillofacial and Craniofacial Domain FARIZA HANUM NASARUDDIN, MAIZATUL AKMAR ISMAIL, & EHAB NABIEL MOHAMMED * Faculty of
Medical Image Processing on the GPU. Past, Present and Future. Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute andek@vtc.vt.
 Medical Image Processing on the GPU Past, Present and Future Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute andek@vtc.vt.edu Outline Motivation why do we need GPUs? Past - how was GPU programming
Medical Image Processing on the GPU Past, Present and Future Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute andek@vtc.vt.edu Outline Motivation why do we need GPUs? Past - how was GPU programming
Real-Time Stereo Reconstruction in Robotically Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Real-Time Stereo Reconstruction in Robotically Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery Abstract. The recovery of tissue structure and morphology during robotic assisted surgery is an important step towards
Real-Time Stereo Reconstruction in Robotically Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery Abstract. The recovery of tissue structure and morphology during robotic assisted surgery is an important step towards
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
A method of generating free-route walk-through animation using vehicle-borne video image
 A method of generating free-route walk-through animation using vehicle-borne video image Jun KUMAGAI* Ryosuke SHIBASAKI* *Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, Shibasaki lab. University of Tokyo 4-6-1
A method of generating free-route walk-through animation using vehicle-borne video image Jun KUMAGAI* Ryosuke SHIBASAKI* *Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, Shibasaki lab. University of Tokyo 4-6-1
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
