CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: CASE STUDY OF PROFIT ZAMBIA
|
|
|
- Barry Oliver
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: IMPACT ASSESSMENT PRIMER SERIES PUBLICATION # 5 PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT IMPACT ASSESSMENT INITIATIVE OCTOBER 2007 This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development. It was prepared by Gary Woller, of Woller & Associates, and Jeanne Downing, of USAID.
2 CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: IMPACT ASSESSMENT PRIMER SERIES PUBLICATION # 5 PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT IMPACT ASSESSMENT INITIATIVE DISCLAIMER The authors views expressed in this publication do not necessarily reflect the views of the United States Agency for International Development or the United States Government.
3 CONTENTS IMPACT ASSESSMENT PRIMER SERIES... 1 IMPACT ASSESSMENT PRIMER SERIES PUBLICATION # PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT IMPACT ASSESSMENT INITIATIVE... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 CAUSAL MODEL DESIGN AND USE AT PROFIT... 1 PERFORMANCE MONITORING AT PROFIT... 4 CONCLUDING REMARKS... 6 ANNEX 1: MONTHLY FIELD REPORT... 8 CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: i
4 INTRODUCTION This paper is a follow-up to the earlier Primer Series paper on causal models. 1 The earlier paper demonstrated the usefulness of causal models in designing and implementing impact assessments of private sector development (PSD) programs and in reassessing and revising program design relative to its intended impacts. The paper drew on the case study of the PROFIT Zambia project to demonstrate what a causal model is, how it works, and what its benefits are. Another benefit of the causal model alluded to in the previous Primer Series paper is its usefulness in developing a program performance monitoring system. This Primer Series paper takes up this topic and expands on it. Specifically, it demonstrates how integrating the causal model into program design and operations can guide program implementation and increase the likelihood that the program achieves its intended impacts. As in the previous paper, it draws on the PROFIT case study for demonstration. By way of review, a casual model is a formal representation showing the causal (or logical) links between program activities and expected outputs, outcomes, and impacts. The concept of the causal model is not new. It has been around for as long as PSD programs, although at times under different names as a matter of practical necessity, all PSD programs are based on some kind of underlying causal logic. 2 Even though the concept of the causal model is well known, a surprising number of PSD programs do not articulate a formal causal model capturing all relevant program activities and associated outputs, outcomes, and impacts. Almost certainly, an even larger number of PSD programs do not integrate the causal model into their program management or operations. These omissions stem, to a large degree, from a lack of general lack of knowledge regarding the purpose and benefits of the causal model as a management tool. The purpose and benefits of the causal model in program design are generally much better understood. However, program design is dynamic rather than static; design flaws, unanticipated events, changing market conditions, external events, and the like often dictate that PSD programs adapt and change during the course of their operations. Program or project managers need management tools to help them monitor and navigate this process. As will be seen in below, the causal model is such a tool. This contribution to the Impact Assessment Primer Series describes how PROFIT has used the causal model and its related industry pathways as a practical management tool. Although the precise ways in which PROFIT has utilized the causal model are unique to it, the primary point that causal models are a useful program management tool applies to all PSD programs. It is expected that different PSD programs will find different uses for the causal model and do so at varying levels of complexity (PROFIT is an example of a fairly high level of complexity). Nonetheless, there is not a single PSD program that cannot benefit in one way or another from a careful and detailed delineation of its underlying causal model and an integration of this model into program management and operations. Along these lines, the paper concludes with some general observations and recommendations for all PSD programs. CAUSAL MODEL DESIGN AND USE AT PROFIT The Production, Finance, and Improved Technology (PROFIT) program seeks to increase the long-term competitiveness and growth of industry in Zambia while assuring that a growing number of micro and small 1 See Gary Woller and Jeanne Downing, (2007), Developing A Causal Model for Private Sector Development Programs, Impact Assessment Primer Series Paper #4. 2 The logical framework, for example, is essentially the causal model by another name. CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 1
5 enterprises (MSEs) contribute to and benefit from the growth process. It uses a value chain approach that seeks to create and strengthen the links between MSEs and other actors at different levels of the value chain. The application of PROFIT s value chain approach is dependent on its field staff s ability to read and react to market signals, make adjustments in tactics, and relay what they are learning to management. This approach presents a number of interesting management challenges; primary among them are: (1) empowering field staff to make decisions in line with program goals and approach, (2) fostering creativity in intervention design, and (3) structuring management mechanisms that capture and process knowledge quickly to inform PROFIT s dynamic decision making processes. The causal model is one of the primary tools PROFIT uses to address these management challenges. It has created two types of causal models in each of the five sectors where it works: cotton, beef cattle, retail input services, honey, and high value horticulture. The first type is the industry causal model, which lists program activities followed by outputs, outcomes, and impacts. Figure 1 shows the industry causal model for the beef sector. Specific activities defined in this causal model (or in other PROFIT causal models) are not set in stone: activities are merely the instruments that facilitate the industry s movement toward greater competitiveness. Whereas PROFIT rarely changes its desired impacts or the intermediate outcomes to get there, it continually changes its activities in response to how the industry is progressing. This point is central to the development of PROFIT s other type of causal model, the industry pathway. The industry pathway an innovative derivation of the industry causal model - depicts the cause and effect sequencing from activity to end result for each activity that PROFIT undertakes in targeted industries and key support markets. The industry causal model has proven useful in defining PROFIT s vision and monitoring key benchmarks along the path to increased industry competitiveness. It has proven less useful in helping staff understanding the dynamics of PROFIT s approach as applied to specific activities. PROFIT expects staff activities to change in response to changing sector conditions, the industry s reaction to program activities, and events outside the industry that affect industry performance. Consequently, program managers created the industry pathway to meet this need. The industry pathway matches program activities to the industry causal model so as to show the expected sequencing if the industry is to increase its competitiveness. Industry pathways are not static but are revised regularly in response to feedback from staff and management and industry performance. The value added of the industry pathway relative to the industry causal model is that it clearly shows the link between industry competitiveness and key support markets. When PROFIT identifies a support market as being critical to an industry s competitiveness, it treats that support market as a separate value chain. Examples of the industry pathways or the beef cattle industry are shown in Figures 2 and 3. Figure 2 shows the industry pathway for beef cattle support services in general, which includes vet services, feedlot services, abattoirs, and auction services. Figure 3 shows the industry pathway for vet services specifically. (PROFIT has also created industry pathways for feedlot services, abattoirs, and auction services.) CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 2
6 PROFIT BEEF CAUSAL MODEL S E M O C T U O OUTPUTS ACTIVITIES Objective 1 To Improve Inter-firm Cooperation in Selected Industries that Leads to Improved Productivity and Value Addition Industry productivity (Overall industry sales overtime) Employment created in beef industry SH gross margin Value of animals sold by SHs into commercial channels (feedlots, auctions, commercial abattoirs) % of beef sold as choice by SHs under vet contract Value of investment in the beef industry (ZMK) Vet income from SH contracts SH yield per animal # SH under formal contract with buyers # abattoirs with grading/pricing system in place Work with abattoirs to institute grades based pricing Work with tanneries to initiate grades based pricing for skins Facilitate beef outgrower model Objective 2 To Improve the Functioning and Responsiveness of Support Markets, Including Inputs, Finance, and ICT that Foster Innovation and Increased Industry Efficiency Value of SH investment (crawls, dip tanks) # Cattle loss among SH cattle in scheme Calving rates among SH cattle in scheme # New entrants providing feedlot and auction services to SHs # New entrants providing financial services to SHs Improved repayment rate # of CLW linked to vets # of private vets providing services # SH under vet contract # of animals on vet contract Value of Vet services sold to SH # of Vets. promoting and informing SH via SMS # of SH accessing auction services # of SH accessing feedlot services Value of auction services purchased by SHs Value of feedlot services purchased by SHs # of SHs animals going through feedlot services Value of Animals sold through auction Value of sales of animals from feedlot facilities (ZMK) # SH accessing finance (commercial) # SH accessing finance (value chain) Value of financial services accessed by SH (commercial) Value of financial services accessed by SH (value chain) # of SH accessing non-credit financial services (insurance, savings) Value of SH accessing non-credit financial services (insurance, savings) Facilitate development of private vet services market Facilitate links between CLW and private vets Facilitate dip tank investment in rural communities tied to vet contracts Facilitate capacity in rural communities to manage communal payment mechanism Facilitate market for auction and feed lot services Facilitate links between SHs and financial service providers Facilitate links between vets and SMS services providers Objective 3 To Improve the Non -Policy Enabling Environment that Leads to Increased Confidence of and Credibility of in Market Mechanisms % cost coverage from fees and membership dues for ZNFU SMS service. %CLW meetings skill standards audit # of private vets organized into network # CLW trained # of SH receiving broadbased market information # SH accessing alternative dispute mechanisms # transporters being certified by ZNFU Monitor and provide guidance to ZNFU in implementing grant Facilitate links between transporters and scale owners and ZNFU and certification/training programs Facilitate vets agreeing to standards for CLWs and adopting standard training and testing regimes Facilitate links between ZNFU SMS market information service and beef and vets firms BEEF Industry Overview Analysis The beef industry competes based on a combination of efficiency and differentiation. Delivering consistently high quality products that range from low margin high volume raw meat to high-value processed products is critical to the industry s overall competitive position. The industry must form efficient channels for high volume products that maintain a basic level of quality, but it is also important for the industry to develop specialized channels for differentiated products like certain processed meats. In this context, it is critical for firms and the industry to achieve effective and efficient linkages from inputs to production, transport, processing and retail distribution channels for the full range of products that are emerging. At present, the livestock industry is relatively disconnected with weak and ineffective linkages that are plaguing the industry s ability to respond to critical threats such as low productivity, drought, disease outbreak and competition from imports. Further, the disconnectedness in the industry has limited information flows and fostered a general lack of transparency that distorts commercial incentives, limits the adoption of better on-farm practices, and minimizes the demand for critical support products (e.g., veterinary services, financial products and services, and feed services and products). CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 3
7 To interpret Figures 2 and 3, it is helpful to note that that the industry pathway is sequential in structure. Moving from left to right implies that the industry is becoming more competitive, as defined by the key benchmark indicators. The narrative at the top of the figure provides a brief problem statement. The pathway itself is divided into three parts. The part with the diagonal text is the demonstration/buying down risk phase. 3 The part with the scattered activities is the scale up and exit phase. 4 Program activities are more likely to change during the demonstration phase based on the initial market response, but they can, and do, change in any phase. The last part of the industry pathway is a set of benchmark indicators that identify when an industry is becoming more competitive and the time for exit is approaching. PROFIT prefers to exit sooner rather than later, but the exact timing of exit depends on whether and how quickly value chain actors internalize a commitment to promote ongoing firm and industry upgrading. On reaching the exit phase on the pathway, PROFIT assesses its next steps based on responses from communities, lead firms, service providers, and other value chain actors. Causal modeling at PROFIT has yielded a number of operational benefits. 1. It provides a conceptual foundation underpinning PROFIT s approach, thereby setting a guideline for how the program will be managed. 2. It provides staff a solid vision of an industry s competitive potential, helps staff visualize why certain activities are relevant to program success, and highlights the links between industry competitiveness and key support markets. 3. It provides a conceptual structure for discussing complex issues surrounding industry competitiveness. Program staff regularly uses pathways as a means of determining whether program activities are moving an industry forward and/or are having an unintended effect. The causal models shift the focus of reporting away from outputs based on activities and towards qualitative/quantitative analysis based on whether an industry is moving in the right direction and at an acceptable pace. 4. It reinforces an operating culture that focuses on broader impact and information sharing as opposed to a focus on activity completion and reporting that highlights only successes. Absent a supportive organizational culture, the program risks getting bogged down in activities that produce basic outputs (e.g., number of people trained) but do not systematically build up the capacity of the industry to compete over time, as has been the case with other PSD programs. 5. It provides the foundation for creating an effective performance monitoring system. The role of causal modeling in PROFIT s performance monitoring system is the topic for the following section. PERFORMANCE MONITORING AT PROFIT PROFIT s approach is focused on sustainable industry competitiveness. Producing sustainable results requires behavioral change at multiple levels within an industry, including key supporting markets, and an effective system for keeping track of these behavioral changes. It requires, in other words, the ability to identify and monitor key 3 This phase follows a process from initial engagement with value chain participants (e.g., clients, lead firms, retailers, services providers, and communities) to establishment of new or improved commercial relationships that are mutually beneficial, more formal, longer-term, and supportive of industry level requirements. 4 As transactions or contract performance reach a sustainable level, PROFIT either exits completely or moves to the next stage of facilitating a scaling up or expanding process. Monitoring is critical during this phase as the exit decision is not clear cut and requires nuanced information. CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 4
8 benchmark indictors that show whether the program is on the right track and that capture critical learning used to adjust pathways and specific interventions. A good causal model shows the expected evolution of an industry and the key benchmarks indicators along the pathway to get there. If done well, therefore, a direct benefit of the causal modeling process is the identification of key benchmark indicators. This was the case with PROFIT, which used its industry causal models and industry pathways to pinpoint key benchmark indicators related to each of its program activities. PROFIT took these benchmark indicators and integrated them into the monthly field report completed by all field staff. The monthly field report is the primary data collection tool in PROFIT s performance monitoring system. (Annex 1 provides an example of the monthly field reports for the beef cattle sector.) The monthly field report is supplemented with qualitative information from the field drawn from field staff observations and interactions with market participants. Once a quarter, PROFIT aggregates the figures from the monthly field reports and analyzes them, along with the qualitative information, to obtain project-wide performance trends. In addition to the field reports and qualitative observations, PROFIT s performance monitoring system also includes twice yearly household evaluations and time-series impact assessment being carried out by the Private Sector Development Impact Assessment Initiative. 5 PROFIT s performance monitoring system provides field staff with both the framework and the practical tools to spot and report trends in the target industry and support markets. Two examples taken from the cotton and beef cattle sectors illustrate this point. In the cotton sector, the primary scheme called for lead firms to offer credit to any interested farmer who were then to repay the credit using the proceeds from cotton sales. The scheme placed substantial risk on the lead firms, while at the same time providing limited incentives for the smallholders to respect the credit repayment process or to create a strong connection between farmers and cotton production. As a result the scheme was susceptible to external shocks, since large investments were required by lead firms, but without a corresponding increase in the assurances of consistent supply. While PROFIT initially proposed assistance in reforming the structure of this management scheme, cotton companies did not see the potential problem and refused assistance. PROFIT s performance monitoring system identified a serious threat resulting from a substantial shift in the local exchange rate forcing the value of exports down by 30%. As the lead firms realized the magnified affects of the shock due to their management structure, they asked for PROFIT assistance in initiating a restructuring process. The result has been substantial shifts in the use of third party service providers and increased investment in management systems to strengthen the links between smallholder cotton growers and the lead firms. In another example, the monitoring system uncovered demand for spraying services fostered by the lead firm. PROFIT subsequently assisted in the creation of thirty spraying business to meet this demand. In the beef cattle sector, the monitoring system picked up information that farmers were not honoring vet services contracts during the activity demonstration phase. The initial demonstration emphasized signing contracts for vet services with payment by farmers afterward. The market response, however, indicated a lack of respect for signed contracts; the fact that a farmer signs a contract has little to do with whether he actually pays for services. Early identification of this problem allowed PROFIT to switch its tactics before any significant damage had been done. Vets now require payment before signing a services contract. Meanwhile, PROFIT is working to increase awareness building activities with communities so as to foster a greater commitment to honoring contracts. 5 See CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 5
9 PROFIT s capacity to read and react to market signals is grounded in it performance monitoring system. While the system places heavy emphasis on qualitative tools to capture observations quickly and turn them into tactical knowledge, PROFIT also relies heavily on explicit data to assess broader industry wide progress. The combination of tools to capture, analyze and apply explicit and tactic knowledge is critical to the approach. However, the analysis and application of knowledge has to be conducted within a framework defined by PROFIT s causal model and industry pathways. By integrating fully its causal model, pathways, and its performance monitoring system, PROFIT has able to build in flexibility without loosing sight of its primary objectives. CONCLUDING REMARKS Causal models lay out a set of logical relationships that show how the activities to be undertaken in a PSD program can lead to a desired set of outputs, outcomes, and impacts of different kinds and at different levels. Defining such a logical framework is essential for designing both the PSD program itself and for program impact assessment. It also facilitates the monitoring and management of the program as implementation proceeds. While performance monitoring deals with the middle links of the causal chain by charting the degree to which planned outputs and outcomes are achieved, impact assessment is concerned with the later links in the causal chain program impacts. Both, however, come from the same causal chain. Performance monitoring and impact assessment complement each other. One is by no means a substitute for the other. One important issue with causal models, which is particularly pertinent to PSD programs, is that the nature of the causal model may change over time as learning results from implementation experience. Most PSD programs are market-driven and thus to a large extent dependent on the private sector s response, which may always be what was anticipated. The set of activities initially planned under the program may thus need to be modified as the market response suggests that an alternative approach may be more beneficial. Typically, the desired impacts of the program will remain the same, while changes in program activities lead to modifications in expected outputs and outcomes. PROFIT, for example, hopes to achieve sustainable improvements in the competitiveness of smallholder producers of cotton and beef and raising the incomes of their enterprises and households. The program began with certain analysisbased hypotheses about what program activities were most likely to contribute to these results. Over time, however, it may decide to abandon some of those activities and replace them with others. Performance monitoring based on the original causal model will be an invaluable means of identifying which program activities are succeeding and which are not. As the program evolves, the causal model will be modified to reflect the changes brought about in the activity mix. Performance monitoring will then continue, based on the new causal model. CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 6
10 PROFIT Beef Industry Pathway Smallholders are an critical part of the livestock industry, but do not have access to support services that can upgrade their herd management that would allow them to participate in more commercial and value added channels.... Profit s solution is to foster a range of support services markets on the input and output side of smallholder production. Demonstrate benefits of integrating smallholders into commercial channels Vet Service Market Growing SHs Under contract to Abattoirs SHs Accessing Auction Services Certified transport SHs utilizing finishing techniques Graded purchases at abattoirs Certified Disease Free Zone Smallholders accessing SMS services Links to byproduct markets Livestock Competitive National herd stabilized Beef sales growing in multiple market Increasing value from byproduct industries (leather, horns, etc ) Feedlot Services Targeting Smallholders Increasing SH wealth Demonstration/Buying Down Risk Phase Scale and Exit Phase Competitiveness Indicators PROFIT Vet Services Pathway Small holder need services to improve the health and value of their cattle.... Profit s solution is to foster private sector vet services.and based on this demonstration take follow up actions for sustainability and exit. Vet services not competitive services Improved Financial infrastructure Demonstrate benefits of integrating Services smallholders into commercial channels. Improved CLW Standards networking of Better managed vets vet businesses New AI and feed supplement services in HHP Vets & Communities identified Contract negotiated and signed Services and payment delivered Diagnostic Vet Services Competitive New vets enter market New communities under contract More Animals Under Contract More Services and Providers HHP Produced & presented to community Increasing smallholder productivity Demonstration/Buying Down Risk Phase Scale and Exit Phase Competitiveness Indicators CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 7
11 ANNEX 1: MONTHLY FIELD REPORT Value of vet sales to SHs PROFIT Field Report Region: Manager: Month: Year: Beef and Vets Indicators # of in community promotional events conducted # of SHs attending in community promotional events # of agreements between vets and SHs # of animals under vet contract # SHs under vet contract # of agreements between CLWs and vets # CLWs trained # SHs with agreement to sell beef Value of SH beef sold via agreements # SHs using improved technology # of animals using services Value of sales to SH from service providers Value of SH infrastructure (crawls, dip tanks, etc.) investments # of CLWs tested Value of vet contracts with trained CLWs # of private vets organized into network # vets promoting and informing SH via ICT # of transport providers trained # New entrants selling services to SHs # abattoirs with grading/pricing system in place Value of input sales to SHs Ag Inputs and Crops Indicators Value HHP Contract ZMK - Drugs and services ZMK - ZMK - Feedlot Auction Other Feedlot Auction Other Feedlot ZMK - Auction ZMK - Other ZMK - ZMK - Vets Feedlot Auction Other # new bulk buying mechanism in place # of in community promotional events conducted # of SHs attending in community promotional events # agents/retail managers/buyers club reps trained # agreements signed between retailers and agents # agreements signed between retailers and communities # of internal retail training events delivered without PROFIT assistance # new retail outlets (franchise, co-owned, wholly owned) Value of improved production technology services sold to SHs # SH buying improved technology services (tillage, spraying, weeding, IPM, etc.) # of agreements signed between retailers and service providers # service providers trained # SH trained in improved farming practices # of demo plots (tillage, IPM, herbicides, spraying, etc.) Hectares under improved technology # of SHs accessing market and production information via ITC ZMK - Value Agent ZMK - Buying Club ZMK - Store ZMK - Agent Buying Club In community event Demos Other Retailers Lead firm ZMK - CAUSAL MODELS AS A USEFUL PROGRAM MANAGEMENT TOOL: 8
12 U.S. Agency for International Development 1300 Pennsylvania Avenue, NW Washington, DC Tel: (202) Fax: (202)
M&E/Learning Guidelines for IPs. (To be used for preparation of Concept Notes and Proposals to LIFT)
 Published: 17 March 2015 Background M&E/Learning Guidelines for IPs (To be used for preparation of Concept Notes and Proposals to LIFT) LIFT's new strategy (2015-2018) envisions LIFT as a knowledge platform.
Published: 17 March 2015 Background M&E/Learning Guidelines for IPs (To be used for preparation of Concept Notes and Proposals to LIFT) LIFT's new strategy (2015-2018) envisions LIFT as a knowledge platform.
Step 1: Analyze Data. 1.1 Organize
 A private sector assessment combines quantitative and qualitative methods to increase knowledge about the private health sector. In the analytic phase, the team organizes and examines information amassed
A private sector assessment combines quantitative and qualitative methods to increase knowledge about the private health sector. In the analytic phase, the team organizes and examines information amassed
Guidelines for Animal Disease Control
 Guidelines for Animal Disease Control 1. Introduction and objectives The guidelines are intended to help countries identify priorities, objectives and the desired goal of disease control programmes. Disease
Guidelines for Animal Disease Control 1. Introduction and objectives The guidelines are intended to help countries identify priorities, objectives and the desired goal of disease control programmes. Disease
Monitoring and Evaluation Plan Primer for DRL Grantees
 Monitoring and Evaluation Plan Primer for DRL Grantees I. What is a monitoring and evaluation plan? A monitoring and evaluation plan (M&E plan), sometimes also referred to as a performance monitoring or
Monitoring and Evaluation Plan Primer for DRL Grantees I. What is a monitoring and evaluation plan? A monitoring and evaluation plan (M&E plan), sometimes also referred to as a performance monitoring or
FEED THE FUTURE LEARNING AGENDA
 FEED THE FUTURE LEARNING AGENDA OBJECTIVE OF THE LEARNING AGENDA USAID s Bureau of Food Security will develop Feed the Future s (FTF) Learning Agenda, which includes key evaluation questions related to
FEED THE FUTURE LEARNING AGENDA OBJECTIVE OF THE LEARNING AGENDA USAID s Bureau of Food Security will develop Feed the Future s (FTF) Learning Agenda, which includes key evaluation questions related to
Restructuring food markets in Zambia: Dynamics in the beef and chicken sub-sectors
 Regoverning Markets Policy Brief 9 Restructuring food markets in Zambia: Dynamics in the beef and chicken sub-sectors January 2008 REGOVERNING MARKETS Context This policy brief forms part of the Recovering
Regoverning Markets Policy Brief 9 Restructuring food markets in Zambia: Dynamics in the beef and chicken sub-sectors January 2008 REGOVERNING MARKETS Context This policy brief forms part of the Recovering
Value of Managing Beef Cattle Genetics
 Value of Managing Beef Cattle Genetics Lisa Rees University of Missouri Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics Contact Information: 803 E. Green Meadows, Apt. 102 Columbia, MO 65201 Profile-
Value of Managing Beef Cattle Genetics Lisa Rees University of Missouri Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics Contact Information: 803 E. Green Meadows, Apt. 102 Columbia, MO 65201 Profile-
The Feeders Meet the Eaters - Direct Marketing in Ontario s Organic Sector
 The Feeders Meet the Eaters - Direct Marketing in Ontario s Organic Sector There is a transparency revolution in our food system. Eaters want to know and connect with the faces behind their food and farmers
The Feeders Meet the Eaters - Direct Marketing in Ontario s Organic Sector There is a transparency revolution in our food system. Eaters want to know and connect with the faces behind their food and farmers
Research to improve the use and conservation of agricultural biodiversity for smallholder farmers
 Research to improve the use and conservation of agricultural biodiversity for smallholder farmers Agricultural biodiversity the variability of crops and their wild relatives, trees, animals, arthropods,
Research to improve the use and conservation of agricultural biodiversity for smallholder farmers Agricultural biodiversity the variability of crops and their wild relatives, trees, animals, arthropods,
TIPS BASELINES AND TARGETS ABOUT TIPS
 NUMBER 8 2 ND EDITION, 2010 PERFORMANCE MONITORING & EVALUATION TIPS BASELINES AND TARGETS ABOUT TIPS These TIPS provide practical advice and suggestions to USAID managers on issues related to performance
NUMBER 8 2 ND EDITION, 2010 PERFORMANCE MONITORING & EVALUATION TIPS BASELINES AND TARGETS ABOUT TIPS These TIPS provide practical advice and suggestions to USAID managers on issues related to performance
THE ROLE OF VET IN FACILITATING DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURAL SECTOR IN TANZANIA
 THE ROLE OF VET IN FACILITATING DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURAL SECTOR IN TANZANIA Abstract Agriculture industry is the foundation of Tanzanian economy. It accounts for about half of the national income, three
THE ROLE OF VET IN FACILITATING DEVELOPMENT OF AGRICULTURAL SECTOR IN TANZANIA Abstract Agriculture industry is the foundation of Tanzanian economy. It accounts for about half of the national income, three
Stop Reacting to Buyers Price Expectations; Manage Them
 Stop Reacting to Buyers Price Expectations; Manage Them BY THOMAS T. NAGLE AND JOSEPH ZALE Executive Takeways Pricing policies empower companies to manage customers price expectations, and avoid the cycle
Stop Reacting to Buyers Price Expectations; Manage Them BY THOMAS T. NAGLE AND JOSEPH ZALE Executive Takeways Pricing policies empower companies to manage customers price expectations, and avoid the cycle
Governance as Stewardship: Decentralization and Sustainable Human Development
 Governance as Stewardship: Decentralization and Sustainable Human Development by Jerry VanSant Research Triangle Institute USA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
Governance as Stewardship: Decentralization and Sustainable Human Development by Jerry VanSant Research Triangle Institute USA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
Food & Farming. Focus on Market Safety Nets. December 2015. Agriculture and Rural Development
 Food & Farming Focus on Market Safety Nets December 215 Agriculture and Rural Development 1 AGRICULTURAL MARKETS AS A DRIVER FOR EUROPEAN AGRICULTURE The agricultural markets and their prices have evolved
Food & Farming Focus on Market Safety Nets December 215 Agriculture and Rural Development 1 AGRICULTURAL MARKETS AS A DRIVER FOR EUROPEAN AGRICULTURE The agricultural markets and their prices have evolved
MONITORING AND EVALUATION WORKSHEETS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 MONITORING AND EVALUATION WORKSHEETS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION I. Introduction to Results Based Monitoring HED will use its results-based monitoring and evaluation system to effectively manage partnership
MONITORING AND EVALUATION WORKSHEETS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION I. Introduction to Results Based Monitoring HED will use its results-based monitoring and evaluation system to effectively manage partnership
BASELINE SURVEY: PRA TOOLS
 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF DECISION SUPPORT TOOLS TO CONSERVE AND SUSTAINABLY USE GENETIC DIVERSITY IN INDIGENOUS LIVESTOCK & WILD RELATIVES BASELINE SURVEY: PRA TOOLS Collaborating Institutions; FAnGR
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF DECISION SUPPORT TOOLS TO CONSERVE AND SUSTAINABLY USE GENETIC DIVERSITY IN INDIGENOUS LIVESTOCK & WILD RELATIVES BASELINE SURVEY: PRA TOOLS Collaborating Institutions; FAnGR
EU Milk Margin Estimate up to 2014
 Ref. Ares(215)2882499-9/7/215 EU Agricultural and Farm Economics Briefs No 7 June 215 EU Milk Margin Estimate up to 214 An overview of estimates of of production and gross margins of milk production in
Ref. Ares(215)2882499-9/7/215 EU Agricultural and Farm Economics Briefs No 7 June 215 EU Milk Margin Estimate up to 214 An overview of estimates of of production and gross margins of milk production in
THE MASTERCARD FOUNDATION: RURAL AND AGRICULTURAL FINANCE STRATEGY
 THE MASTERCARD FOUNDATION: RURAL AND AGRICULTURAL FINANCE STRATEGY SEPTEMBER 2015 The MasterCard Foundation works with visionary organizations to provide greater access to education, skills training and
THE MASTERCARD FOUNDATION: RURAL AND AGRICULTURAL FINANCE STRATEGY SEPTEMBER 2015 The MasterCard Foundation works with visionary organizations to provide greater access to education, skills training and
A SHORT GUIDE TO PRO-POOR VALUE CHAIN PROGRAM DESIGN
 Suite 304 4600 North Fairfax Drive Arlington, VA 22203 USA +1 703-243-9172 fax +1 703-243-9123 www.actionforenterprise.org A SHORT GUIDE TO PRO-POOR VALUE CHAIN PROGRAM DESIGN Prepared for the Australian
Suite 304 4600 North Fairfax Drive Arlington, VA 22203 USA +1 703-243-9172 fax +1 703-243-9123 www.actionforenterprise.org A SHORT GUIDE TO PRO-POOR VALUE CHAIN PROGRAM DESIGN Prepared for the Australian
CONSULTATION DELIVERING LIFETIME ASSURED BEEF
 CONSULTATION DELIVERING LIFETIME ASSURED BEEF January 2015 (Responses by Friday 27 th March 2015) 1 1 INTRODUCTION EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Cattle are currently considered assured under the Red Tractor scheme
CONSULTATION DELIVERING LIFETIME ASSURED BEEF January 2015 (Responses by Friday 27 th March 2015) 1 1 INTRODUCTION EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Cattle are currently considered assured under the Red Tractor scheme
September 2015. IFAC Member Compliance Program Strategy, 2016 2018
 September 2015 IFAC Member Compliance Program Strategy, 2016 2018 This Strategy is issued by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC ) with the advice and oversight of the Compliance Advisory
September 2015 IFAC Member Compliance Program Strategy, 2016 2018 This Strategy is issued by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC ) with the advice and oversight of the Compliance Advisory
Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions
 Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions November, 2003 This list of market assessment tools was prepared by Development Alternatives Inc. (DAI) as an internal working document to support
Existing Analytical Market Assessment Tools - Definitions November, 2003 This list of market assessment tools was prepared by Development Alternatives Inc. (DAI) as an internal working document to support
Business Model Cattle Sector
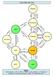 Business Model Sector Retailler Vet Clinic MAF APS GAHP s Processors Collectors Farmers Fin. Inst Kind Students Beef + info on quality demand Medicine + service Medicine + Capacity Building, vaccine, Quality
Business Model Sector Retailler Vet Clinic MAF APS GAHP s Processors Collectors Farmers Fin. Inst Kind Students Beef + info on quality demand Medicine + service Medicine + Capacity Building, vaccine, Quality
Part 1. MfDR Concepts, Tools and Principles
 Part 1. Concepts, Tools and Principles 3 Overview Part 1. MfDR Concepts, Tools and Principles M anaging for Development Results (MfDR) is multidimensional, relating back to concepts about how to make international
Part 1. Concepts, Tools and Principles 3 Overview Part 1. MfDR Concepts, Tools and Principles M anaging for Development Results (MfDR) is multidimensional, relating back to concepts about how to make international
TOC INDEX. Breakeven Analysis for Feeder Cattle. Alberta Agriculture Market Specialists. Introduction. Why Breakevens?
 TOC INDEX Feeder Associations of Alberta Ltd. Breakeven Analysis for Feeder Cattle Alberta Agriculture Market Specialists Introduction Breakevens are specialized partial budgets used to evaluate feeder
TOC INDEX Feeder Associations of Alberta Ltd. Breakeven Analysis for Feeder Cattle Alberta Agriculture Market Specialists Introduction Breakevens are specialized partial budgets used to evaluate feeder
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks
 Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
Guide for the Development of Results-based Management and Accountability Frameworks August, 2001 Treasury Board Secretariat TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1. Introduction to the Results-based Management and
White Paper from Global Process Innovation. Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program
 White Paper from Global Process Innovation by Jim Boots Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program This white paper presents 14 metrics which may be useful for monitoring progress on a BPM program or initiative.
White Paper from Global Process Innovation by Jim Boots Fourteen Metrics for a BPM Program This white paper presents 14 metrics which may be useful for monitoring progress on a BPM program or initiative.
Glossary Monitoring and Evaluation Terms
 Glossary Monitoring and Evaluation Terms This glossary includes terms typically used in the area of monitoring and evaluation (M&E) and provides the basis for facilitating a common understanding of M&E.
Glossary Monitoring and Evaluation Terms This glossary includes terms typically used in the area of monitoring and evaluation (M&E) and provides the basis for facilitating a common understanding of M&E.
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Introduction to Project Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Introduction to Project Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Introduction to Project Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage
Implementation of a Quality Management System for Aeronautical Information Services -1-
 Implementation of a Quality Management System for Aeronautical Information Services -1- Implementation of a Quality Management System for Aeronautical Information Services Chapter IV, Quality Management
Implementation of a Quality Management System for Aeronautical Information Services -1- Implementation of a Quality Management System for Aeronautical Information Services Chapter IV, Quality Management
TIPS. Performance Monitoring and Evaluation BUILDING A RESULTS FRAMEWORK. What Is a Results Framework? What Functions Does a Results Framework Serve?
 Performance Monitoring and Evaluation TIPS 2000, Number 13 USAID Center for Development Information and Evaluation BUILDING A RESULTS FRAMEWORK What Is a Results Framework? The strategic planning process
Performance Monitoring and Evaluation TIPS 2000, Number 13 USAID Center for Development Information and Evaluation BUILDING A RESULTS FRAMEWORK What Is a Results Framework? The strategic planning process
Fodder R&D Funding. A Subsequent Submission to the Productivity Commission s. Review into Rural Research and Development Corporations
 Suite 3.01 620 St Kilda Road Melbourne, Vic, 3004 t: 03 9530 2199 f: 03 9510 7558 Fodder R&D Funding A Subsequent Submission to the Productivity Commission s Review into Rural Research and Development
Suite 3.01 620 St Kilda Road Melbourne, Vic, 3004 t: 03 9530 2199 f: 03 9510 7558 Fodder R&D Funding A Subsequent Submission to the Productivity Commission s Review into Rural Research and Development
DG ENLARGEMENT SECTOR BUDGET SUPPORT GUIDELINES
 Ref. Ares(2014)571140-04/03/2014 DG ENLARGEMENT SECTOR BUDGET SUPPORT GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY January 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1. RATIONALE FOR BUDGET SUPPORT 1.1 What is Budget Support?
Ref. Ares(2014)571140-04/03/2014 DG ENLARGEMENT SECTOR BUDGET SUPPORT GUIDELINES EXECUTIVE SUMMARY January 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1. RATIONALE FOR BUDGET SUPPORT 1.1 What is Budget Support?
Key Issues and Actions Facing the Cotton Sector in India Report from the CottonConnect Organic Cotton Roundtable, 19-20 March 2014, Indore
 Time for Action Key Issues and Actions Facing the Cotton Sector in India Report from the Introduction The organic cotton sector is at a critical stage in its development. The sector faces a global shortfall
Time for Action Key Issues and Actions Facing the Cotton Sector in India Report from the Introduction The organic cotton sector is at a critical stage in its development. The sector faces a global shortfall
GOOD LAND TRUST Fundraising Plan
 GOOD LAND TRUST Fundraising Plan OVERVIEW OF THE FUNDRAISING PLAN Background The Good Land Trust is a land trust working in Ecotopia actively protecting natural resources and the open landscapes that define
GOOD LAND TRUST Fundraising Plan OVERVIEW OF THE FUNDRAISING PLAN Background The Good Land Trust is a land trust working in Ecotopia actively protecting natural resources and the open landscapes that define
The Communications Audit NEVER MORE RELEVANT, NEVER MORE VALUABLE:
 WHITE PAPER The Communications Audit NEVER MORE RELEVANT, NEVER MORE VALUABLE: VALUE PROPOSITION OBJECTIVES METHODOLOGY BY GARY DOLZALL CHIEF COMMUNICATIONS OFFICER I. INTRODUCTION: THE VALUE PROPOSITION
WHITE PAPER The Communications Audit NEVER MORE RELEVANT, NEVER MORE VALUABLE: VALUE PROPOSITION OBJECTIVES METHODOLOGY BY GARY DOLZALL CHIEF COMMUNICATIONS OFFICER I. INTRODUCTION: THE VALUE PROPOSITION
GAO PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. IRS s Systems for Frontline Employees and Managers Align with Strategic Goals but Improvements Can Be Made
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Report to Congressional Requesters July 2002 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IRS s Systems for Frontline Employees and Managers Align with Strategic Goals but
GAO United States General Accounting Office Report to Congressional Requesters July 2002 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IRS s Systems for Frontline Employees and Managers Align with Strategic Goals but
Exchanging Agricultural Market Information through SMS in Cambodia
 TECHNICAL BRIEF GCP/RAS/247/EC EC-FAO Food Security Programme Linking Information and Decision-Making to Improve Food Security Exchanging Agricultural Market Information through SMS in Cambodia Market
TECHNICAL BRIEF GCP/RAS/247/EC EC-FAO Food Security Programme Linking Information and Decision-Making to Improve Food Security Exchanging Agricultural Market Information through SMS in Cambodia Market
Leadership for Change Flying Squad Program Review and New Approach to Organizational Development
 Leadership for Change Flying Squad Program Review and New Approach to Organizational Development September 19, 2013 Bringing the arts to life Contents I. What is the purpose of this Context Document?...
Leadership for Change Flying Squad Program Review and New Approach to Organizational Development September 19, 2013 Bringing the arts to life Contents I. What is the purpose of this Context Document?...
Market Definition Does Not Yield Evidence of Class-Wide Impact
 Market Definition Does Not Yield Evidence of Class-Wide Impact Dr. Michael D. Noel, Ph.D. & Parker Normann, Ph.D. Edgeworth Economics June 2012 (published version available in the Antitrust Practitioner)
Market Definition Does Not Yield Evidence of Class-Wide Impact Dr. Michael D. Noel, Ph.D. & Parker Normann, Ph.D. Edgeworth Economics June 2012 (published version available in the Antitrust Practitioner)
SUSTAINABLE CONTRACT FARMING FOR INCREASED COMPETITIVENESS: CASE STUDY ON POULTRY SECTOR IN SARAWAK, MALAYSIA
 SUSTAINABLE CONTRACT FARMING FOR INCREASED COMPETITIVENESS: CASE STUDY ON POULTRY SECTOR IN SARAWAK, MALAYSIA BY Sugumar Saminathan National Productivity Corporation The agriculture sector contributed
SUSTAINABLE CONTRACT FARMING FOR INCREASED COMPETITIVENESS: CASE STUDY ON POULTRY SECTOR IN SARAWAK, MALAYSIA BY Sugumar Saminathan National Productivity Corporation The agriculture sector contributed
Procuring Penetration Testing Services
 Procuring Penetration Testing Services Introduction Organisations like yours have the evolving task of securing complex IT environments whilst delivering their business and brand objectives. The threat
Procuring Penetration Testing Services Introduction Organisations like yours have the evolving task of securing complex IT environments whilst delivering their business and brand objectives. The threat
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES Vol. II - Crop Production Capacity In North America - G.K. Pompelli CROP PRODUCTION CAPACITY IN NORTH AMERICA
 CROP PRODUCTION CAPACITY IN NORTH AMERICA G.K. Pompelli Economic Research Service, U. S. Department of Agriculture, USA Keywords: Supply, policy, yields. Contents 1. Introduction 2. Past Trends in Demand
CROP PRODUCTION CAPACITY IN NORTH AMERICA G.K. Pompelli Economic Research Service, U. S. Department of Agriculture, USA Keywords: Supply, policy, yields. Contents 1. Introduction 2. Past Trends in Demand
Financing Smallholder Farmers. to Increase Incomes and Transform Lives in Rural Communities
 Financing Smallholder Farmers to Increase Incomes and Transform Lives in Rural Communities EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Africa is home to a quarter of the world s farmland, yet it generates only 10 percent of all
Financing Smallholder Farmers to Increase Incomes and Transform Lives in Rural Communities EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Africa is home to a quarter of the world s farmland, yet it generates only 10 percent of all
Standards for Engineering, Technology, and the Applications of Science
 Standards for Engineering, Technology, and the Applications of Science One of the most important messages of the Next Generation Science Standards for teachers, parents, and students is that science is
Standards for Engineering, Technology, and the Applications of Science One of the most important messages of the Next Generation Science Standards for teachers, parents, and students is that science is
Commercialization of Smallholder. Horticultural Farming in Kenya. Poverty, Gender, and Institutional Arrangements. Beatrice Wambui Muriithi
 Commercialization of Smallholder Horticultural Farming in Kenya Poverty, Gender, and Institutional Arrangements Beatrice Wambui Muriithi PL ACADEMIC RESEARCH Table of Contents ListofTables 11 List of Figures
Commercialization of Smallholder Horticultural Farming in Kenya Poverty, Gender, and Institutional Arrangements Beatrice Wambui Muriithi PL ACADEMIC RESEARCH Table of Contents ListofTables 11 List of Figures
TOR - Consultancy Announcement Final Evaluation of the Cash assistance and recovery support project (CARSP)
 TOR - Consultancy Announcement Final Evaluation of the Cash assistance and recovery support project (CARSP) Organization Project Position type Adeso African Development Solutions and ACTED - Agency for
TOR - Consultancy Announcement Final Evaluation of the Cash assistance and recovery support project (CARSP) Organization Project Position type Adeso African Development Solutions and ACTED - Agency for
Beef - Key performance indicators. Mary Vickers
 Beef - Key performance indicators Mary Vickers Today Suckler herd KPIs Update on new project Responses KPIs for finishing systems What is a KPI? a business metric used to evaluate factors that are crucial
Beef - Key performance indicators Mary Vickers Today Suckler herd KPIs Update on new project Responses KPIs for finishing systems What is a KPI? a business metric used to evaluate factors that are crucial
GLOSSARY OF EVALUATION TERMS
 Planning and Performance Management Unit Office of the Director of U.S. Foreign Assistance Final Version: March 25, 2009 INTRODUCTION This Glossary of Evaluation and Related Terms was jointly prepared
Planning and Performance Management Unit Office of the Director of U.S. Foreign Assistance Final Version: March 25, 2009 INTRODUCTION This Glossary of Evaluation and Related Terms was jointly prepared
Factors Impacting Dairy Profitability: An Analysis of Kansas Farm Management Association Dairy Enterprise Data
 www.agmanager.info Factors Impacting Dairy Profitability: An Analysis of Kansas Farm Management Association Dairy Enterprise Data August 2011 (available at www.agmanager.info) Kevin Dhuyvetter, (785) 532-3527,
www.agmanager.info Factors Impacting Dairy Profitability: An Analysis of Kansas Farm Management Association Dairy Enterprise Data August 2011 (available at www.agmanager.info) Kevin Dhuyvetter, (785) 532-3527,
Revenue Administration: Performance Measurement in Tax Administration
 T e c h n i c a l N o t e s a n d M a n u a l s Revenue Administration: Performance Measurement in Tax Administration William Crandall Fiscal Affairs Department I n t e r n a t i o n a l M o n e t a r
T e c h n i c a l N o t e s a n d M a n u a l s Revenue Administration: Performance Measurement in Tax Administration William Crandall Fiscal Affairs Department I n t e r n a t i o n a l M o n e t a r
Master Sustainability with a Better Approach to LTL Sourcing. Shipper and Carrier Success Stories Perspectives from Users of Freedom Logistics.
 Logistics Management Solutions Master Sustainability with a Better Approach to LTL Sourcing Shipper and Carrier Success Stories Perspectives from Users of Freedom Logistics. 1 Master Sustainability with
Logistics Management Solutions Master Sustainability with a Better Approach to LTL Sourcing Shipper and Carrier Success Stories Perspectives from Users of Freedom Logistics. 1 Master Sustainability with
Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM
 IGG-06252003-01 S. Nelson Article 25 June 2003 Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM Customer relationship management (CRM) represents the key business strategy that will determine successful
IGG-06252003-01 S. Nelson Article 25 June 2003 Management Update: The Eight Building Blocks of CRM Customer relationship management (CRM) represents the key business strategy that will determine successful
Chapter 6 Marketing services
 Egg marketing 81 Chapter 6 Marketing services Market information, marketing education and training, promotional campaigns to promote egg consumption, marketing research to aid in producer and trader decision
Egg marketing 81 Chapter 6 Marketing services Market information, marketing education and training, promotional campaigns to promote egg consumption, marketing research to aid in producer and trader decision
Analysis on future developments in the milk sector
 Analysis on future developments in the milk sector Prepared for the European Commission DG Agriculture and Rural Development Brussels, 24th September 2013 Introduction Purpose of the study : a prospective
Analysis on future developments in the milk sector Prepared for the European Commission DG Agriculture and Rural Development Brussels, 24th September 2013 Introduction Purpose of the study : a prospective
The Role of Public Policy in Sustainable Infrastructure
 The Role of Public Policy in Sustainable Infrastructure Zia Qureshi Nonresident Senior Fellow, Global Economy and Development, Brookings Institution Infrastructure development, economic growth, and climate
The Role of Public Policy in Sustainable Infrastructure Zia Qureshi Nonresident Senior Fellow, Global Economy and Development, Brookings Institution Infrastructure development, economic growth, and climate
USAID PROGRAM CYCLE OVERVIEW
 USAID PROGRAM CYCLE OVERVIEW USAID AUGUST 2012 CONTENTS Background... 3 Overview Summary... 3 Program Cycle Components:... 3 Agency Policies and Strategies:... 4 Country Development Cooperation Strategies:...
USAID PROGRAM CYCLE OVERVIEW USAID AUGUST 2012 CONTENTS Background... 3 Overview Summary... 3 Program Cycle Components:... 3 Agency Policies and Strategies:... 4 Country Development Cooperation Strategies:...
Best in Class Referral Programs
 Take your business to the next level Best in Class Referral Programs Lower cost per sale, Higher Retention, Increased Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Best in Class Customer Referral
Take your business to the next level Best in Class Referral Programs Lower cost per sale, Higher Retention, Increased Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Best in Class Customer Referral
Policy for Monitoring and Evaluation of Compacts and Threshold Programs
 Policy for Monitoring and Evaluation of Compacts and Threshold Programs May 1, 2012 Version: Final Submitted by: Department of Policy and Evaluation Millennium Challenge Corporation 875 15th Street N.W.
Policy for Monitoring and Evaluation of Compacts and Threshold Programs May 1, 2012 Version: Final Submitted by: Department of Policy and Evaluation Millennium Challenge Corporation 875 15th Street N.W.
Definitions of Marketing Terms
 E-472 RM2-32.0 11-08 Risk Management Definitions of Marketing Terms Dean McCorkle and Kevin Dhuyvetter* Cash Market Cash marketing basis the difference between a cash price and a futures price of a particular
E-472 RM2-32.0 11-08 Risk Management Definitions of Marketing Terms Dean McCorkle and Kevin Dhuyvetter* Cash Market Cash marketing basis the difference between a cash price and a futures price of a particular
Terms of Reference Project Title: Supporting Indian Trade and Investment for Africa (SITA)
 Terms of Reference Project Title: Supporting Indian Trade and Investment for Africa (SITA) Project Number: INT/71/21A Assignment title: International Consultant: Leather Tanning, Re-tanning and Finishing
Terms of Reference Project Title: Supporting Indian Trade and Investment for Africa (SITA) Project Number: INT/71/21A Assignment title: International Consultant: Leather Tanning, Re-tanning and Finishing
This work aimed to identify the underlying environmental and organizational
 5 Conclusion This work aimed to identify the underlying environmental and organizational factors that enable CRM alliances to flourish in certain countries. The contributions of this paper are two-fold.
5 Conclusion This work aimed to identify the underlying environmental and organizational factors that enable CRM alliances to flourish in certain countries. The contributions of this paper are two-fold.
Private Certification to Inform Regulatory Risk-Based Oversight: Discussion Document
 Private Certification to Inform Regulatory Risk-Based Oversight: Discussion Document 1 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 BACKGROUND... 3 PRIVATE CERTIFICATION SCHEMES VS. REGULATORY STANDARDS... 3 PRIVATE
Private Certification to Inform Regulatory Risk-Based Oversight: Discussion Document 1 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 BACKGROUND... 3 PRIVATE CERTIFICATION SCHEMES VS. REGULATORY STANDARDS... 3 PRIVATE
Sourcing Products From Suppliers Certified Under Other Fair Trade Schemes
 Sourcing Products From Suppliers Certified Under Other Fair Trade Schemes A Guide for Fair for Life certified Handlers Version April 2014 Table of Content Overview Fair for Life Product Sourcing... 1 Buying
Sourcing Products From Suppliers Certified Under Other Fair Trade Schemes A Guide for Fair for Life certified Handlers Version April 2014 Table of Content Overview Fair for Life Product Sourcing... 1 Buying
Driving Profits from Loyalty
 Driving Profits from Loyalty Overview 1 P a g e 5 Steps to Driving Profit from Loyalty 1. Customer Portfolio Analysis This is the first step on the road to customer profitability where we can begin to
Driving Profits from Loyalty Overview 1 P a g e 5 Steps to Driving Profit from Loyalty 1. Customer Portfolio Analysis This is the first step on the road to customer profitability where we can begin to
How To Finance A Value Chain
 Using the Value Chain in Financing Agriculture Rural and Agricultural Finance Conference Marrakech, Morocco Calvin Miller FAO Agribusiness and Finance Senior Officer Rome, Italy Presentation Applying Agri
Using the Value Chain in Financing Agriculture Rural and Agricultural Finance Conference Marrakech, Morocco Calvin Miller FAO Agribusiness and Finance Senior Officer Rome, Italy Presentation Applying Agri
PJ 22/12. 7 February 2012 English only. Projects Committee/ International Coffee Council 5 8 March 2012 London, United Kingdom
 PJ 22/12 7 February 2012 English only E Projects Committee/ International Coffee Council 5 8 March 2012 London, United Kingdom Sustainable input credit for financing the production end of the coffee value
PJ 22/12 7 February 2012 English only E Projects Committee/ International Coffee Council 5 8 March 2012 London, United Kingdom Sustainable input credit for financing the production end of the coffee value
Guidance for Industry. Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System
 Guidance for Industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos. Understanding Organizational Barriers
 Select Strategy www.selectstrategy.com 1 877 HR ASSET 1 877 472 7738 Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos Understanding Organizational Barriers Restructuring initiatives have become
Select Strategy www.selectstrategy.com 1 877 HR ASSET 1 877 472 7738 Improving Performance by Breaking Down Organizational Silos Understanding Organizational Barriers Restructuring initiatives have become
China s experiences in domestic agricultural support. Tian Weiming China Agricultural University
 China s experiences in domestic agricultural support Tian Weiming China Agricultural University Contents Background The policy system Major measures and their implementation Empirical assessment of the
China s experiences in domestic agricultural support Tian Weiming China Agricultural University Contents Background The policy system Major measures and their implementation Empirical assessment of the
Alberta Health. Primary Health Care Evaluation Framework. Primary Health Care Branch. November 2013
 Primary Health Care Evaluation Framewo Alberta Health Primary Health Care Evaluation Framework Primary Health Care Branch November 2013 Primary Health Care Evaluation Framework, Primary Health Care Branch,
Primary Health Care Evaluation Framewo Alberta Health Primary Health Care Evaluation Framework Primary Health Care Branch November 2013 Primary Health Care Evaluation Framework, Primary Health Care Branch,
How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies
 How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies Helen Westmoreland, Consultant M. Elena Lopez, Senior Consultant Heidi Rosenberg, Senior Research Analyst November, 2009 For questions
How to Develop a Logic Model for Districtwide Family Engagement Strategies Helen Westmoreland, Consultant M. Elena Lopez, Senior Consultant Heidi Rosenberg, Senior Research Analyst November, 2009 For questions
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma
 Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
A new electricity market for Northern Ireland and Ireland from 2016 - Integrated Single Electricity Market (I-SEM)
 A new electricity market for Northern Ireland and Ireland from 2016 - Integrated Single Electricity Market (I-SEM) Non-technical summary High level design Draft Decision Paper SEM -14-047 June 2014 1 INTRODUCTION
A new electricity market for Northern Ireland and Ireland from 2016 - Integrated Single Electricity Market (I-SEM) Non-technical summary High level design Draft Decision Paper SEM -14-047 June 2014 1 INTRODUCTION
A Better Approach to Target Date Strategies
 February 2011 A Better Approach to Target Date Strategies Executive Summary In 2007, Folio Investing undertook an analysis of Target Date Funds to determine how these investments might be improved. As
February 2011 A Better Approach to Target Date Strategies Executive Summary In 2007, Folio Investing undertook an analysis of Target Date Funds to determine how these investments might be improved. As
Lesson 2. Cash Flow Budgets
 A Project Funded by USDA BFRDP Grant #10506276 Development Partners Include: Lesson 2. Cash Flow Budgets Introduction Cash flow budgets provide detail about periods when cash outflows exceed cash inflows.
A Project Funded by USDA BFRDP Grant #10506276 Development Partners Include: Lesson 2. Cash Flow Budgets Introduction Cash flow budgets provide detail about periods when cash outflows exceed cash inflows.
IRAS e-tax Guide. Transfer Pricing Guidelines (Third edition)
 IRAS e-tax Guide Transfer Pricing Guidelines (Third edition) Published by Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore Published on 04 Jan 2016 First edition on 23 Feb 2006 Disclaimers: IRAS shall not be responsible
IRAS e-tax Guide Transfer Pricing Guidelines (Third edition) Published by Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore Published on 04 Jan 2016 First edition on 23 Feb 2006 Disclaimers: IRAS shall not be responsible
ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORDS. Nonfederal Efforts to Help Achieve Health Information Interoperability
 United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters September 2015 ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORDS Nonfederal Efforts to Help Achieve Health Information Interoperability GAO-15-817
United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters September 2015 ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORDS Nonfederal Efforts to Help Achieve Health Information Interoperability GAO-15-817
APPENDIX X1 - FIFTH EDITION CHANGES
 APPENDIX X1 FIFTH EDITION CHANGES The purpose of this appendix is to give a detailed explanation of the changes made to A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Fourth Edition
APPENDIX X1 FIFTH EDITION CHANGES The purpose of this appendix is to give a detailed explanation of the changes made to A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Fourth Edition
Guidelines for Minimum Standards Property Management Planning. Financial Management Module
 Guidelines for Minimum Standards Property Management Planning Financial Management Module June 2011 June 2011 Acknowledgements All stakeholders who contributed to the development of the Financial Management
Guidelines for Minimum Standards Property Management Planning Financial Management Module June 2011 June 2011 Acknowledgements All stakeholders who contributed to the development of the Financial Management
Competitive analysis of the fruit processing industry in Nepal, Vietnam, India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh Using Porter s Five Forces Model
 Competitive analysis of the fruit processing industry in Nepal, Vietnam, India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh Using Porter s Five Forces Model For an ICUC (International Centre for Underutilised Crops) Project
Competitive analysis of the fruit processing industry in Nepal, Vietnam, India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh Using Porter s Five Forces Model For an ICUC (International Centre for Underutilised Crops) Project
5. SOCIAL PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT IN MICROFINANCE 1
 5. SOCIAL PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT IN MICROFINANCE 1 INTRODUCTION TO SOCIAL PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Achieving Social and Financial Performance In the microfinance arena, performance has long been associated
5. SOCIAL PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT IN MICROFINANCE 1 INTRODUCTION TO SOCIAL PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT Achieving Social and Financial Performance In the microfinance arena, performance has long been associated
Strategic Plan 2013-2018
 Strategic Plan 2013-2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LIST OF ACRONYMS 2. MESSAGE FROM THE AUDITOR GENERAL 3. OVERVIEW OF SAIB STRATEGIC PLAN 2013 2018 4. MISSION 5. VISION 6. VALUES 7. SAIB STRATEGIC THRUSTS
Strategic Plan 2013-2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LIST OF ACRONYMS 2. MESSAGE FROM THE AUDITOR GENERAL 3. OVERVIEW OF SAIB STRATEGIC PLAN 2013 2018 4. MISSION 5. VISION 6. VALUES 7. SAIB STRATEGIC THRUSTS
OPTIMIZING SALES EFFECTIVENESS THROUGH VALUE AND DIFFERENTIATION
 OPTIMIZING SALES EFFECTIVENESS THROUGH VALUE AND DIFFERENTIATION UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER NEEDS Most sales organizations strive to preserve their margins during the sales process; but even the savviest salesperson
OPTIMIZING SALES EFFECTIVENESS THROUGH VALUE AND DIFFERENTIATION UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER NEEDS Most sales organizations strive to preserve their margins during the sales process; but even the savviest salesperson
Review of Card Surcharging: A Consultation Document
 Review of Card Surcharging: A Consultation Document june 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Background 2 3. Concerns about Surcharging Practices 5 4. Policy Options and Discussion 7 5. Summary of Issues
Review of Card Surcharging: A Consultation Document june 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Background 2 3. Concerns about Surcharging Practices 5 4. Policy Options and Discussion 7 5. Summary of Issues
Re: Big Data: A Tool for Inclusion or Exclusion? Workshop Project No. P145406
 October 30, 2014 Federal Trade Commission Office of the Secretary Room H 113 (Annex X) 600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW Washington, DC 20580 Re: Big Data: A Tool for Inclusion or Exclusion? Workshop Project
October 30, 2014 Federal Trade Commission Office of the Secretary Room H 113 (Annex X) 600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW Washington, DC 20580 Re: Big Data: A Tool for Inclusion or Exclusion? Workshop Project
How To Understand Farm Financial Performance
 Understanding Key Financial Ratios and Benchmarks How does my business stack up compared to my neighbors? This question is becoming more and more common as the agricultural industry continues to change
Understanding Key Financial Ratios and Benchmarks How does my business stack up compared to my neighbors? This question is becoming more and more common as the agricultural industry continues to change
RISK MANAGEMENT IN AGRICULTURE: WHAT ROLE FOR GOVERNMENTS?
 RISK MANAGEMENT IN AGRICULTURE: WHAT ROLE FOR GOVERNMENTS? Recent years have been tumultuous in the agricultural sector. Price volatility has increased, with sharp swings in product and input prices. Markets
RISK MANAGEMENT IN AGRICULTURE: WHAT ROLE FOR GOVERNMENTS? Recent years have been tumultuous in the agricultural sector. Price volatility has increased, with sharp swings in product and input prices. Markets
U.S. Farm Policy: Overview and Farm Bill Update. Jason Hafemeister 12 June 2014. Office of the Chief Economist. Trade Bureau
 U.S. Farm Policy: Office of the Chief Economist Trade Bureau Overview and Farm Bill Update Jason Hafemeister 12 June 2014 Agenda Background on U.S. Agriculture area, output, inputs, income Key Elements
U.S. Farm Policy: Office of the Chief Economist Trade Bureau Overview and Farm Bill Update Jason Hafemeister 12 June 2014 Agenda Background on U.S. Agriculture area, output, inputs, income Key Elements
Building Agribusiness Risk Management System: Strategy and Stages of Development
 Building Agribusiness Risk Management System: Strategy and Stages of Development Roman Shynkarenko Agricultural Insurance and Risk Management Consultant Most Ukrainian experts in agricultural risks insurance
Building Agribusiness Risk Management System: Strategy and Stages of Development Roman Shynkarenko Agricultural Insurance and Risk Management Consultant Most Ukrainian experts in agricultural risks insurance
PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY SYSTEM Q10
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY SYSTEM Q10 Current Step
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE PHARMACEUTICAL QUALITY SYSTEM Q10 Current Step
