One School s Approach for Developing Critical Thinking Skills from Reception to Year 5
|
|
|
- Angelina Edwards
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 One School s Approach for Developing Critical Thinking Skills from Reception to Year 5 Presenter: Alison Thacker Co-ordinator of Teaching and Learning: Reception Year 5 Unity College Gifted Education Advisor L.S.A. Previously, Teaching and Learning Consultant, Curriculum Division, DECS Areas to be covered in this session are listed below. The presentation will include a resource pack for all participants, practical demonstrations of activities, interactive critical thinking exercises, and examples of whole campus initiatives and support plans developed by Unity College Junior Campus. Participants will be involved in a number of exercises that explore and support critical thinking skills for children. These will include Thinkers Keys and Visual/Auditory/Kinaesthetic teaching approaches to concepts. PRESENTATION OVERVIEW What is Critical Thinking? Definition Examples Why teach Critical Thinking? Rationale Examples How can we teach Critical Thinking? Whole School Scope and Sequence for the explicit teaching of Thinking Skills at Unity College R 5 campus. Implementation Plan for phasing in and supporting the practical application of the Scope and Sequence Plan. A range of Critical Thinking Tools will be discussed and utilised by participants. Examples of activities, units of work and tools at Year levels and classroom level will be included. What else supports and influences the development of Critical Thinking? Spark to a Flame igniting what may already be happening in the school. The Role of a Teaching and Learning Co-ordinator scope, sequence and possibilities. Other Major Teaching and Learning aspects that influence the development of Critical Thinking Skills in a Primary setting e.g. - Teaching and Learning styles - Professional Development structures, planning, access - Resources
2 What is Critical Thinking? Michael Pohl describes Critical Thinking as applying appropriate rules, criteria, standards, reasons and orders. Knight and Bailey define it as reasonable, reflective thinking that is focussed on what we believe or do. Its main characteristics are: - justification skills - analysis - conceptual development - formulating and investigating opinions - planning and decision making - analysing and evaluating data and information, including aspects such as bias, accuracy, truth versus perception, etc. - investigating a range of options - recommendations for change as a result of exploring options - making and justifying decisions - problem solving skills - metacognition / reflective thinking skills Why teach Critical Thinking? As educators and students of the 21 st century, we are teaching and learning in a world of rapid change and uncertainty. While it is difficult to predict the kinds of challenges, information loads, technologies, workplaces, types and longevity of careers we will face over the next fifty years, one thing is certain: namely that individuals who are equipped to think critically, creatively, caringly and reflectively will be better able to navigate the waters and challenges ahead of them. Within this context, I believe that we as educators have a moral, ethical and educational responsibility to provide our students with a rigorous and challenging Thinking and Learning Curriculum. Knowledge itself, access to it, and the respect that it (and the imparters of it) once held - have changed dramatically over the past twenty years, and it is likely that this transformation and rate of change will escalate. Lutheran schools and educators are guided by the Lutheran Curriculum Statement which clearly articulates the Qualities of Lifelong Learners as being: Self-directed, insightful investigators and learners Discerning resourceful problem solvers and implementers Adept, creative producers and contributors Open, responsive communicators and facilitators Principled, resilient leaders and collaborators Caring, steadfast supporters and advocates I believe that a Thinking and Learning Curriculum can only be effective if we focus on the explicit teaching of thinking skills and strategies as well as evaluate, cater for and teach students about their own learning styles. Without this 2-pronged approach, even the most comprehensive curriculum will become at least partially irrelevant to students whose learning styles preclude them from the learning program.
3 How can we teach Critical Thinking? Michael Pohl identifies the following 3 key components for the successful construction and support of a Thinking Culture: Adopting a Whole School Approach Utilising a wide range of thinking strategies Ensuring meaningful learning activities. Thinking communities and the skills necessary to participate meaningfully within them need to be developed rarely do they simply emerge. This requires a coordinated, whole school approach that is planned, negotiated, supported with professional development and resourced. Thinking skills need to become not only an integral part of teacher planning and programming, but also be explicitly taught to students such that at any given year level, teachers can be assured that all students in their class have a sound understanding, skill level and language for particular thinking skills. While several recommended outlines exist which schools can adopt, the process of developing a scope and sequence for your particular school is a powerful professional development exercise and ensures that its validity and relevance to your school setting is maximised *Note: A copy of the Unity College R Year 5 Scope and Sequence for Teaching Thinking Skills and an Implementation Plan is available from Alison Thacker at Unity College Junior Campus and is provided to all workshop participants. The following Tools may be useful in teaching and learning about Critical Thinking: Thinkers Keys (T. Ryan) e.g. - The What If Key - The Disadvantage Key - The Prediction Key - The Alternative Key - The Forced Relationship Key - The Brick Wall Key - The Variations Key Blooms Revised Taxonomy (Anderson s) - Analysis - Evaluating Philosophy for Children (moral and ethical dilemmas and conundrums) Future Problem Solving / Tournament of Minds Questioning techniques question Matrices, Fertile questioning, use of Wait Time, CAMPER (Consequences/consistency, Assumptions/accuracy, Meaning/main points, Prejudice/point of view, Evidence/examples, Relevance/reliability P.C.D. approach Possibilities, Consequences, Decision POOCH problem, options, outcomes, choices, how did it turn out? Creative problem solving Process Reflection / metacognition - thinking reflectively about how you have/are approached/ing the problem.
4 The support pack for all workshop participants will include the following: A whole school Thinking Skills Scope and Sequence which was developed by Unity College Junior Campus staff as a result of extensive P.D. sessions for all staff, trialling of a range of thinking tools, and identifying and sharing excellent practice already operating within the school. A three year Implementation Plan for phasing in, supporting and resourcing the above Scope and Sequence document. Lists of useful critical thinking resources. Examples of teacher programs that have been developed by staff at Unity College Junior Campus ranging from highly experienced staff to a unit designed by a final year student teacher. These will demonstrate a broad range of approaches and individual teacher preferences for how knowledge, concepts and skills are developed and integrated within their classes. A range of Spelling activities and resources that list a range of appropriate learning activities for Visual/Auditory / Kinaesthetic Learners. Examples of Thinkers Keys class resources. What else supports and influences the development of Critical Thinking? Spark to a Flame identifying pockets of excellent practice / willingness to trial new methodologies / enthusiasm for new directions, nurturing these with PD, resources and time, and providing a voice and platform for their efforts and accomplishments. Other Major Teaching and Learning aspects that influence the development of Critical Thinking Skills in a Primary setting - V.A.K. teaching and Learning styles identify them, utilise all of them, use dominant styles for key concept learning but extend and develop the weaker styles. The more broad based the learning styles, the greater the range of social and cognitive interactions available to individuals. Gardners s Multiple Intelligences support a broad range of learning styles. Grids that combine Gardners Multiple Intelligences and Bloom s Revised Taxonomy enable teachers and students to cater for a range of preferred learning styles and manage differing levels of complexity congruently. However, educators should be cautious of providing a range of activities that may be fun, interesting and developmental, but quite nebulous in terms of learning outcomes. Such grids should be carefully constructed for the needs of the students as opposed to the needs of the grid, and activities should accompany explicit teaching and be supported by teacher direction, suggestions, and guidance. - Global/Specific Learners - Visual/Spatial Learners - Professional Development Create structures and planning to support staff needs and Scope and Sequence Plans and Implementation Plans Enable access for all staff
5 - Resources Teaching and Learning Coordinator role, teams of teachers, printed, L.S.A. Thinking and Learning Curriculum Guidelines, other Schools experiences etc. The following is a summary of some of the major characteristics and teaching implications for learning styles. VISUAL LEARNERS: visual images are critical in their learning Characteristics Teaching Implications rely heavily on what they SEE in Use illustrations, flow charts, order to know or understand graphic organisers etc to organise tend to focus on PICTURES and and chunk information diagrams in preference to written Use colour coding, highlighters, or heard information coloured paper etc for grouping, have a strong sense of COLOUR classifying and making prefer to read rather than being associations between pieces of read to information. memorize by seeing the picture, Use VISUALISATION as a think using GRAPHIC images. powerful tool for spelling, setting tend to be good spellers and the scene in creative writing, recognise when a word doesn t poetry, imagining maths problems LOOK right. etc. Are less distracted by noise Provide written directions and May have trouble remembering outlines of work expectations, verbal instruction and their units of work, assessment criteria concentration will tend to wain if etc. too much verbal input. Allow and encourage students to Like to organise and order draw information from information and their illustrations, diagrams, graphs etc. surroundings Include videos, films, computer Tend to remember faces rather slideshows, theatre, performing than names arts and demonstrations within the Will tend to use phrases that have key learning areas. visual references i.e. I see what Develop Y Charts looks you mean it appears to be like sounds like feels like correct watch what happens Usually well organised
6 AUDITORY LEARNERS: Words and sounds are critical in their learning Characteristics Teaching Implications TALKS to self Provide verbal instruction and Learn best by LISTENING and ample opportunity for students to TALKING discuss their thoughts with SPOKEN LANGUAGE is easier partners, in small groups or whole than written language class discussion, especially prior Need to HEAR information to to written work. know it Read stories, novels to students. May find Maths and Writing more Use audio taped stories and group difficult than other areas of study. reading methodologies for Can repeat verbal instructions supporting reading. back to you but may find written Interviews, debates, open forums instructions difficult to follow. etc. Tend to memorise by steps, Guest speakers and lecturers. sequence etc. Practise spelling verbally, not just Tend to remember names but not in written form. faces. Allow opportunities for students Often unable to follow body to conference with teacher prior to language and facial expressions. and during written work to enable Tend to like music and other verbal feedback. performing arts presentations. Incorporate music, rhythm and Tend to use expressions such as rhyme in learning program. LISTEN to me, I HEAR what Develop Y Charts looks you are saying TELL me more like sounds like feels like please. KINAESTHETIC LEARNERS: Feeling and doing is critical in their learning Characteristics Teaching Implications Prefer HANDS ON learning Incorporate demonstrations, Learn by DEMONSTRATIONS, modelling and experimentation modelling and then having a go with a range of mediums and at the activity. textures. Learn best by DOING. Allow students to demonstrate Prefer ACTION and adventure their understandings beyond Can assemble models and traditional written products e.g. apparatus without needing models, sculptures, plays etc. directions. These need to be seen by students Strong use of GESTURES. May as being valued and assessed often respond with exaggerated equitably with other forms. PHYSICAL reactions to Use dance, drama, role playing, situations. movement etc. in explicit teaching Tend to be restless and find sitting of new concepts and activity still for long periods of time based learning. difficult. Use computers to reinforce Learn better with PHYSICAL learning through touch. ACTIVITY. Regular short bursts of active movement within lessons to assist
7 Tend to remember people by events they were associated with or by what they have done rather than by name or face. May have good co-ordination and their strengths are often in the sporting arena. May use phrases such as I FEEL for you, I can t GRASP this concept, I m trying to PLAY with the notion. with concentration and refocussing. Utilise a range of tactile materials for spelling and reading programs e.g. pipe cleaners, sandpaper, wool, chalk, paint, crayons etc. Incorporate movement and dance into areas such as spelling e.g. making up raps, dancing out their words, jumping out the number of syllables etc. Assist students to memorise by WALKING through learning recalling significant events, emotional responses, placing themselves in other s shoes, marching out sight words etc. Develop Y Charts looks like sounds like feels like *Note: While students will usually have a preferred 1 or 2 learning styles, different learning experiences will require students to utilise one style more than another due to the nature of the activity. It is also important that students weaker styles are given the opportunity to develop in order to increase their learning modalities and breadth of social interaction with others. GLOBAL / SPECIFIC LEARNING STYLES Global Learners have traditionally been referred to as Right Brain Dominant Learners, with Specific Learners referred to as Left Brain Dominant. The characteristics of each are outlined below and while we can t always accommodate the needs of one type of learner, we do need to ensure that our teaching and presentation style is not constantly alienating or irritating to one group or the other. Again, many of us will utilise both aspects at various times, however we tend to be dominant in one or the other over a period of time. GLOBAL LEARNERS Want to see the whole picture first and then work out its key components and details afterwards Tend to see the Big Picture with respect to problems, issues, events etc. Usually highly imaginative Pictorial Tend to demonstrate feelings quite freely Often intuitive SPECIFIC LEARNERS Want to see the details first and gradually build up to the Big Picture once all the pieces are in place Focus on all the details of issues, events, problems etc. Usually very linear, organised, logical and sequential learners Like to operate within systems, control and order Tend to control their feelings more than Global Learners
8 Make connections between pieces of information easily Can move relatively easily into Specific mode of Thinking and Operating Tend to focus on cause/effect aspects Find it difficult to move into Global mode of thinking and operating In Summary: Yoram Harpaz, lecturer at The School For Educational Leadership in Israel, defines the role of education as knowing how to engage and relate to knowledge, not knowledge itself. He lists critical thinking as a key component of this process. The nature and status of knowledge itself, and those who were the guardians of it, has changed markedly over the past twenty years. It is now easily accessed, available in massive chunks, and evolving at a rapid rate. In order for children to manage, manipulate, understand, synthesise and create with it, they need to be able to critically engage with it. The challenge for us as educators is to develop thinking communities within our schools in which individual students are explicitly taught and given opportunities to explore and refine a range of critical and creative thinking skills. A whole school approach, range of critical thinking tools and strategies and emphasis on relevant and meaningful content and activities will support a successful shift into a thinking skills based education. Within such an environment, students can then critically manage, understand, make connections with and generate new understandings and skills in order to participate morally, ethically, intellectually and spiritually within the rapidly changing world they are inheriting. References: Harpaz. Y. Conference: Developing Thinking Through Fertile Questioning Pedagogy Learning to Learn. Adelaide. August 2004 Knight and Bailey Parents As Lifelong Teachers of the Gifted Hawker Brownlow Education 1997 Pohl. M. Teaching Complex Thinking: Critical. Creative. Caring Hawker Brownlow Education 2000 Pohl. M. Teaching Thinking in the Primary Years. Hawker Brownlow Education 2000 Ryan. T. Thinkers Keys For Kids Woodridge, Qld Alison Thacker Unity College 10/29/2007
VAK Learning Styles. Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions:
 What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES
 New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES LEARNING AND TEACHING This student-centered perspective is a hallmark of the CSUDH approach to teaching. We strive to empower instructors
New Faculty Orientation 2012 CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT & LEARNING STYLES LEARNING AND TEACHING This student-centered perspective is a hallmark of the CSUDH approach to teaching. We strive to empower instructors
Meeting the Needs of Visual-Spatial Learners
 Meeting the Needs of Visual-Spatial Learners Component 13 of the Competencies Collaboration SEVA Council of Gifted Administrators Table of Contents 1. Characteristics and strengths of visual spatial learners
Meeting the Needs of Visual-Spatial Learners Component 13 of the Competencies Collaboration SEVA Council of Gifted Administrators Table of Contents 1. Characteristics and strengths of visual spatial learners
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire
 Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
Student Services Study Skills Student Development and Counselling VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to
Learning styles and writing in science
 Key Stage 3 National Strategy Guidance Curriculum & Standards Learning styles and writing in science Teachers at Key Stage 3 Status: Recommended Date of issue: 05/02 Ref: DfES 0384/2002 Standards and Effectiveness
Key Stage 3 National Strategy Guidance Curriculum & Standards Learning styles and writing in science Teachers at Key Stage 3 Status: Recommended Date of issue: 05/02 Ref: DfES 0384/2002 Standards and Effectiveness
English. Stage 6 Syllabus. English (Standard) English (Advanced) English as a Second Language (ESL) English (Extension) Fundamentals of English
 English Stage 6 Syllabus English (Standard) English (Advanced) English as a Second Language (ESL) English (Extension) Fundamentals of English Original published version updated: Nov/Dec 1999 Board Bulletin/Official
English Stage 6 Syllabus English (Standard) English (Advanced) English as a Second Language (ESL) English (Extension) Fundamentals of English Original published version updated: Nov/Dec 1999 Board Bulletin/Official
Responding to Arts Expressions
 Responding to Arts Expressions Supporting Arts Education September 2009 Introduction........................................................................2 Classroom Climate.................................................................2
Responding to Arts Expressions Supporting Arts Education September 2009 Introduction........................................................................2 Classroom Climate.................................................................2
Modifying Curriculum and Instruction
 Modifying Curriculum and Instruction Purpose of Modification: The purpose of modification is to enable an individual to compensate for intellectual, behavioral, or physical disabi1ities. Modifications
Modifying Curriculum and Instruction Purpose of Modification: The purpose of modification is to enable an individual to compensate for intellectual, behavioral, or physical disabi1ities. Modifications
Learning Styles and Aptitudes
 Learning Styles and Aptitudes Learning style is the ability to learn and to develop in some ways better than others. Each person has a natural way of learning. We all learn from listening, watching something
Learning Styles and Aptitudes Learning style is the ability to learn and to develop in some ways better than others. Each person has a natural way of learning. We all learn from listening, watching something
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss. A Guide to Services for Students with a
 Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
Office of Disability Support Service 0106 Shoemaker 301.314.7682 Fax: 301.405.0813 www.counseling.umd.edu/dss A Guide to Services for Students with a Learning Disability (Revised 4.28.14) Do I Have A Learning
Learning Style Inventory
 Learning Style Inventory To better understand how you prefer to learn and process information, place a check in the appropriate space after each statement below, then use the scoring directions at the
Learning Style Inventory To better understand how you prefer to learn and process information, place a check in the appropriate space after each statement below, then use the scoring directions at the
How To Write A Checkbook
 ThisPersonal checking account lesson is designed to be for grades 9-12 Financial Literacy classes. Financial Literacy is a state graduation requirement. 1 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES: The objective of this lesson
ThisPersonal checking account lesson is designed to be for grades 9-12 Financial Literacy classes. Financial Literacy is a state graduation requirement. 1 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES: The objective of this lesson
Modern foreign languages
 Modern foreign languages Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment targets (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007
Modern foreign languages Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment targets (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007
Every chance to learn
 Every chance to learn Curriculum framework for ACT schools Preschool to year 10 Contents Message from the Minister...4 Message from the Chair, Curriculum Renewal Taskforce...5 Introduction...6 Definition
Every chance to learn Curriculum framework for ACT schools Preschool to year 10 Contents Message from the Minister...4 Message from the Chair, Curriculum Renewal Taskforce...5 Introduction...6 Definition
School Management Plan 2012 2014. 2012 2014 School Management Plan Identifier: SPS PD/110712/D004
 School Management Plan 2012 2014 Policy: 2012 2014 School Management Plan Identifier: SPS PD/110712/D004 Author: Mr. Bernard Cheng Consultation: School Executive Endorsement: Kerri Brickley: School Education
School Management Plan 2012 2014 Policy: 2012 2014 School Management Plan Identifier: SPS PD/110712/D004 Author: Mr. Bernard Cheng Consultation: School Executive Endorsement: Kerri Brickley: School Education
PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS STEPHANIE, BUCK. Submitted to
 Animated Literacy 1 RUNNING HEAD: Years of Animated Literacy Letters PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS By STEPHANIE, BUCK Submitted to
Animated Literacy 1 RUNNING HEAD: Years of Animated Literacy Letters PRE AND POST TEST TO SEE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN YEARS OF ANIMATED LITERACY AND KNOWLEDGE OF LETTERS By STEPHANIE, BUCK Submitted to
Aesthetic of Lifelong Learning Betty K. Garner, Ed.D. [email protected] 2. How Cognitive Structures Process Information
 Aesthetic of Lifelong Learning Betty K. Garner, Ed.D. [email protected] 1 Getting to Got It! Helping Struggling Students Learn How to Learn Betty K. Garner, Ed.D. Email: [email protected], Web
Aesthetic of Lifelong Learning Betty K. Garner, Ed.D. [email protected] 1 Getting to Got It! Helping Struggling Students Learn How to Learn Betty K. Garner, Ed.D. Email: [email protected], Web
Beacon s Education Program:
 Beacon s Education Program: Why it works 2101 Livingston Street Oakland, CA 94606 510.436.4466 beaconday.org Part One: Curriculum Spirals Beacon s Education Program is based upon a system which we call
Beacon s Education Program: Why it works 2101 Livingston Street Oakland, CA 94606 510.436.4466 beaconday.org Part One: Curriculum Spirals Beacon s Education Program is based upon a system which we call
Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave.
 VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. (It s best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation.)
Questions to Consider in UDL Observations of Early Childhood Environments
 Questions to Consider in UDL Observations of Early Childhood Environments Universally Designed Learning (UDL) environments provide considerations for the widest diversity of learners possible so that all
Questions to Consider in UDL Observations of Early Childhood Environments Universally Designed Learning (UDL) environments provide considerations for the widest diversity of learners possible so that all
Illinois Professional Teaching Standards
 Illinois Professional Teaching Standards Preamble: We believe that all students have the potential to learn rigorous content and achieve high standards. A well-educated citizenry is essential for maintaining
Illinois Professional Teaching Standards Preamble: We believe that all students have the potential to learn rigorous content and achieve high standards. A well-educated citizenry is essential for maintaining
HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD?
 HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD? Results Learning Presented by Cyle A. Feingold Founder and Director Results Learning, LLC AGENDA Overview of Executive Function
HOW DOES EXECUTIVE FUNCTION IMPACT YOUR GIFTED AND/OR TWICE EXCEPTIONAL CHILD? Results Learning Presented by Cyle A. Feingold Founder and Director Results Learning, LLC AGENDA Overview of Executive Function
Standards for Excellence
 THE AUSTRALIAN ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS Standards for Excellence in Teaching Mathematics in Australian Schools 2006 edition These Standards were originally adopted by AAMT Council in 2002 as
THE AUSTRALIAN ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS Standards for Excellence in Teaching Mathematics in Australian Schools 2006 edition These Standards were originally adopted by AAMT Council in 2002 as
TOOL KIT for RESIDENT EDUCATOR and MENT OR MOVES
 Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
Get to Know My RE Observe Collect Evidence Mentor Moments Reflect Review Respond Tailor Support Provide Provide specific feedback specific Feedback What does my RE need? Practice Habits Of Mind Share Data
E-Learning and Personal Preferences. The aim of this article is to explore further the idea that E-learning should
 E-Learning and Personal Preferences Page 1 E-Learning and Personal Preferences Introduction The aim of this article is to explore further the idea that E-learning should cater to the learning needs of
E-Learning and Personal Preferences Page 1 E-Learning and Personal Preferences Introduction The aim of this article is to explore further the idea that E-learning should cater to the learning needs of
Approaches to learning (ATL) across the IB continuum
 Approaches to learning (ATL) across the IB continuum Through approaches to learning in IB programmes, students develop skills that have relevance across the curriculum that help them learn how to learn.
Approaches to learning (ATL) across the IB continuum Through approaches to learning in IB programmes, students develop skills that have relevance across the curriculum that help them learn how to learn.
Colorado Professional Teaching Standards
 Colorado Professional Teaching Standards Standard I: Teachers demonstrate knowledge of the content they teach a. Teachers provide instruction that is aligned with the Colorado Academic Standards and their
Colorado Professional Teaching Standards Standard I: Teachers demonstrate knowledge of the content they teach a. Teachers provide instruction that is aligned with the Colorado Academic Standards and their
Learning how you Learn.
 Learning how you Learn. A guide to learning styles and the benefits of understanding yours You are a unique learner. No one else learns in exactly the same way you do. There are many benefits to discovering
Learning how you Learn. A guide to learning styles and the benefits of understanding yours You are a unique learner. No one else learns in exactly the same way you do. There are many benefits to discovering
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment
 An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
An Investigation into Visualization and Verbalization Learning Preferences in the Online Environment Dr. David Seiler, Assistant Professor, Department of Adult and Career Education, Valdosta State University,
Inside: Overview of the eight intelligences, In the Montessori School, Harmonious Development
 International Montessori Schools and Child Development Centres Brussels, Belgium www.international-montessori.org Brussels Introduction to the Eight Intelligences Inside: Overview of the eight intelligences,
International Montessori Schools and Child Development Centres Brussels, Belgium www.international-montessori.org Brussels Introduction to the Eight Intelligences Inside: Overview of the eight intelligences,
Learning Styles. The VARK Categories. What is a Learning Style?
 Learning Styles What is a Learning Style? Learning styles focus on how your brain receives information. No one else learns or processes information exactly the way you do! If you discover how you process
Learning Styles What is a Learning Style? Learning styles focus on how your brain receives information. No one else learns or processes information exactly the way you do! If you discover how you process
Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
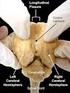 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE)
 CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
CALIFORNIA S TEACHING PERFORMANCE EXPECTATIONS (TPE) The Teaching Performance Expectations describe the set of knowledge, skills, and abilities that California expects of each candidate for a Multiple
Helping your child with Non-verbal Learning Disability
 Helping your child with Non-verbal Learning Disability What is non-verbal learning disability? Non-verbal learning disability (NVLD) is a term used to describe a pattern of strengths and weaknesses in
Helping your child with Non-verbal Learning Disability What is non-verbal learning disability? Non-verbal learning disability (NVLD) is a term used to describe a pattern of strengths and weaknesses in
How To Improve A Child'S Learning Experience
 Effective teaching and classroom management is about whole child - and whole school development for knowledge, skills and human values During the past years as an outcome of the UN Study on Violence against
Effective teaching and classroom management is about whole child - and whole school development for knowledge, skills and human values During the past years as an outcome of the UN Study on Violence against
A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS. Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA
 A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA This paper will describe a content-pedagogy course designed to prepare elementary
A STATISTICS COURSE FOR ELEMENTARY AND MIDDLE SCHOOL TEACHERS Gary Kader and Mike Perry Appalachian State University USA This paper will describe a content-pedagogy course designed to prepare elementary
Name Date Period Brain Orientation Unit 3 Self-Awareness Left/Right/Whole-Brain Assessment
 Left/Right/Whole-Brain Assessment In our search for a career that is best suited for us we must have a good understanding of our capabilities. A look at brain orientation should help us to better understand
Left/Right/Whole-Brain Assessment In our search for a career that is best suited for us we must have a good understanding of our capabilities. A look at brain orientation should help us to better understand
Professional Standards for Teachers
 Professional Standards for Teachers Guidelines for Professional Practice July 2005 Queensland the Smart State The State of Queensland (Department of Education) 2005 Copyright protects this publication.
Professional Standards for Teachers Guidelines for Professional Practice July 2005 Queensland the Smart State The State of Queensland (Department of Education) 2005 Copyright protects this publication.
Arkansas Teaching Standards
 Arkansas Teaching Standards The Arkansas Department of Education has adopted the 2011 Model Core Teaching Standards developed by Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium (InTASC) to replace
Arkansas Teaching Standards The Arkansas Department of Education has adopted the 2011 Model Core Teaching Standards developed by Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium (InTASC) to replace
Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program
 Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program Students are assessed to the prescribed learning outcomes Students receive letter grades Adapted Program Instructional practices: Options for: Giving instructions
Models for an Adapted and for a Modified Program Students are assessed to the prescribed learning outcomes Students receive letter grades Adapted Program Instructional practices: Options for: Giving instructions
Program of Studies. Preschool 2015-16
 Program of Studies Preschool 2015-16 PRESCHOOL BCD s preschool program provides a nurturing and stimulating educational environment for young children. Self-confidence and the ability to work with others
Program of Studies Preschool 2015-16 PRESCHOOL BCD s preschool program provides a nurturing and stimulating educational environment for young children. Self-confidence and the ability to work with others
Concept-Mapping Software: How effective is the learning tool in an online learning environment?
 Concept-Mapping Software: How effective is the learning tool in an online learning environment? Online learning environments address the educational objectives by putting the learner at the center of the
Concept-Mapping Software: How effective is the learning tool in an online learning environment? Online learning environments address the educational objectives by putting the learner at the center of the
Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire. Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos
 Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos To view Closed Captioning, click on the Notes tab to the left. For screen reader accessible
Developing Critical Thinking Skills Saundra Yancy McGuire Slide 1 TutorLingo On Demand Tutor Training Videos To view Closed Captioning, click on the Notes tab to the left. For screen reader accessible
Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]
![Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270]](/thumbs/24/3436110.jpg) I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
I.B. SPECIFIC TEACHING FIELDS Standards for Certification in Early Childhood Education [26.110-26.270] STANDARD 1 Curriculum The competent early childhood teacher understands and demonstrates the central
Home Economics Education
 Subject Area Syllabus and Guidelines Home Economics Education (Part 2 of 4) Level 4 to Beyond Level 6 Note: The PDF version of this document has been split into sections for easier download. This file
Subject Area Syllabus and Guidelines Home Economics Education (Part 2 of 4) Level 4 to Beyond Level 6 Note: The PDF version of this document has been split into sections for easier download. This file
BIMM Course Specification
 Full title of the course & award BA (Hons) in Music Production Mode of attendance Full-time Length of course This course is taught as a three-year course at levels four, five and six. Start date Initial
Full title of the course & award BA (Hons) in Music Production Mode of attendance Full-time Length of course This course is taught as a three-year course at levels four, five and six. Start date Initial
Universal Design for Learning An Approach to Maximise Learning for All Students
 Universal Design for Learning An Approach to Maximise Learning for All Students Jeff Souter Coordinator Learning Development Centre-ICTs-Students With Disabilities [email protected] Ph: 3240
Universal Design for Learning An Approach to Maximise Learning for All Students Jeff Souter Coordinator Learning Development Centre-ICTs-Students With Disabilities [email protected] Ph: 3240
Learning Disabilities Checklist
 Learning Disabilities Checklist Learning Disability is the term currently used to describe a handicap that interferes with someone s ability to store, process or produce information. Learning disabilities
Learning Disabilities Checklist Learning Disability is the term currently used to describe a handicap that interferes with someone s ability to store, process or produce information. Learning disabilities
Australian Professional Standard for Principals
 AITSL is funded by the Australian Government Australian Professional Standard for Principals July 2011 Formerly the National Professional Standard for Principals 2011 Education Services Australia as the
AITSL is funded by the Australian Government Australian Professional Standard for Principals July 2011 Formerly the National Professional Standard for Principals 2011 Education Services Australia as the
How To Write A Curriculum Paper On Arts Education In Nsw
 NSW Response to the Draft Shape of the Australian Curriculum: The Arts Background The Office of the Board of Studies has conducted consultation on the draft Arts Shape paper in order to provide feedback
NSW Response to the Draft Shape of the Australian Curriculum: The Arts Background The Office of the Board of Studies has conducted consultation on the draft Arts Shape paper in order to provide feedback
Chapter 117. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Fine Arts. Subchapter C. High School, Adopted 2013
 High School, Adopted 2013 117.C. Chapter 117. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Fine Arts Subchapter C. High School, Adopted 2013 Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter C issued
High School, Adopted 2013 117.C. Chapter 117. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Fine Arts Subchapter C. High School, Adopted 2013 Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter C issued
What s Your Learning Style?
 What s Your Learning Style? Different people have different learning styles. Style refers to a student s specific learning preferences and actions. One student may learn more effectively from listening
What s Your Learning Style? Different people have different learning styles. Style refers to a student s specific learning preferences and actions. One student may learn more effectively from listening
SAMPLE MIDAS PROFILE MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES DEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCALES MIDAS Version 2.0 Processed 09-23-1999 for Tara Student
 SAMPLE MIDAS PROFILE MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES DEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCALES MIDAS Version 2.0 Processed 09-23-1999 for Tara Student Sex: F Grade: 9 ID number: 407 Code: 1 Birth Date: 1984 The following
SAMPLE MIDAS PROFILE MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES DEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCALES MIDAS Version 2.0 Processed 09-23-1999 for Tara Student Sex: F Grade: 9 ID number: 407 Code: 1 Birth Date: 1984 The following
Principles of Adult Education
 Part Ⅳ-A Principles of Adult Education Brainstorming Compared to teaching child, why we should do differently for adults (what are special characteristics of adult learners)? 2 Adult Learners... Are autonomous
Part Ⅳ-A Principles of Adult Education Brainstorming Compared to teaching child, why we should do differently for adults (what are special characteristics of adult learners)? 2 Adult Learners... Are autonomous
A Study in Learning Styles of Construction Management Students. Amit Bandyopadhyay, Ph.D., PE, F.ASCE State University of New York -FSC
 A Study in Learning Styles of Construction Management Students Amit Bandyopadhyay, Ph.D., PE, F.ASCE State University of New York -FSC Abstract Students take in and process information in different ways.
A Study in Learning Styles of Construction Management Students Amit Bandyopadhyay, Ph.D., PE, F.ASCE State University of New York -FSC Abstract Students take in and process information in different ways.
It is vital that you understand the rationale behind the correct answer(s) as wel as the incorrect answer options.
 Getting the Most out of ATI www.atitesting.com What is ATI? ATI is an online resource that will be used throughout the nursing program to help you learn about nursing practice as well as help prepare you
Getting the Most out of ATI www.atitesting.com What is ATI? ATI is an online resource that will be used throughout the nursing program to help you learn about nursing practice as well as help prepare you
The benefits of using presentation software in the classroom include:
 NCTE ICT in the Classroom Presentation software - focus on literacy & numeracy (Primary) Ref: 12-11 Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide an overview of the benefits of using presentation
NCTE ICT in the Classroom Presentation software - focus on literacy & numeracy (Primary) Ref: 12-11 Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide an overview of the benefits of using presentation
2012 Music Standards GRADES K-1-2
 Students will: Personal Choice and Vision: Students construct and solve problems of personal relevance and interest when expressing themselves through A. Demonstrate how musical elements communicate meaning
Students will: Personal Choice and Vision: Students construct and solve problems of personal relevance and interest when expressing themselves through A. Demonstrate how musical elements communicate meaning
ART A. PROGRAM RATIONALE AND PHILOSOPHY
 ART A. PROGRAM RATIONALE AND PHILOSOPHY Art education is concerned with the organization of visual material. A primary reliance upon visual experience gives an emphasis that sets it apart from the performing
ART A. PROGRAM RATIONALE AND PHILOSOPHY Art education is concerned with the organization of visual material. A primary reliance upon visual experience gives an emphasis that sets it apart from the performing
4.4 Early Detection Guidelines
 4.4.2.2 Assessment for Identified Concerns 4.4.2.2.6 How Children Develop 9-10 Year Olds The following section outlines the major developmental milestones for nine to ten year old children. Six areas of
4.4.2.2 Assessment for Identified Concerns 4.4.2.2.6 How Children Develop 9-10 Year Olds The following section outlines the major developmental milestones for nine to ten year old children. Six areas of
ADEPT Performance Standards. for. Classroom-Based Teachers
 ADEPT Performance Standards for Classroom-Based Teachers Revised ADEPT Performance Standards for Classroom-Based Teachers Introduction Central to the ADEPT system is a set of expectations for what teaching
ADEPT Performance Standards for Classroom-Based Teachers Revised ADEPT Performance Standards for Classroom-Based Teachers Introduction Central to the ADEPT system is a set of expectations for what teaching
Visual and Performing Arts Subject Template (Required Information needed to prepare for course submission)
 Visual and Performing Arts Subject Template (Required Information needed to prepare for course submission) Course Purpose: What is the purpose of this course? Please provide a brief description of the
Visual and Performing Arts Subject Template (Required Information needed to prepare for course submission) Course Purpose: What is the purpose of this course? Please provide a brief description of the
Standards and progression point examples
 Personal Learning In Personal Learning, standards for assessing and reporting on student achievement are introduced at Level 3. The learning focus statements for Levels Foundation, 1 and 2 provide advice
Personal Learning In Personal Learning, standards for assessing and reporting on student achievement are introduced at Level 3. The learning focus statements for Levels Foundation, 1 and 2 provide advice
HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY. Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT. July 2014
 HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT July 2014 Mr. David C. Mango, Superintendent Ms. Nadia Inskeep, Director of Curriculum & Instruction Developed by:
HACKETTSTOWN, NEW JERSEY Computer Animation Grades 10-12 CURRICULUM GUIDE FINAL DRAFT July 2014 Mr. David C. Mango, Superintendent Ms. Nadia Inskeep, Director of Curriculum & Instruction Developed by:
COMMUNICATION COMMUNITIES CULTURES COMPARISONS CONNECTIONS. STANDARDS FOR FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING Preparing for the 21st Century
 COMMUNICATION COMMUNITIES CULTURES COMPARISONS CONNECTIONS STANDARDS FOR FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING Preparing for the 21st Century Language and communication are at the heart of the human experience. The
COMMUNICATION COMMUNITIES CULTURES COMPARISONS CONNECTIONS STANDARDS FOR FOREIGN LANGUAGE LEARNING Preparing for the 21st Century Language and communication are at the heart of the human experience. The
Appendix A: The Visual-Spatial Learner in School
 Appendix A: The Visual-Spatial Learner in School Betty Maxwell There are two main ways of organizing the world. These are spatial (using space) and sequential (using time). Spatial people tend to use space
Appendix A: The Visual-Spatial Learner in School Betty Maxwell There are two main ways of organizing the world. These are spatial (using space) and sequential (using time). Spatial people tend to use space
TYPES OF LEARNERS. Visual Learners. Auditory Learners
 utilize a variety of teaching modalities, such as small group process, lecture, and experiential activities be flexible and meet each learner s needs provide information that will overlap with information
utilize a variety of teaching modalities, such as small group process, lecture, and experiential activities be flexible and meet each learner s needs provide information that will overlap with information
How To Teach A Class
 Scientists Teaching Science Barbara Houtz January 13, 2014 Instructional Design The systematic design of materials, activities, and interactive environments for learning. Broadly informed by educational
Scientists Teaching Science Barbara Houtz January 13, 2014 Instructional Design The systematic design of materials, activities, and interactive environments for learning. Broadly informed by educational
2012 VISUAL ART STANDARDS GRADES K-1-2
 COGNITIVE & K Critical and Creative Thinking: Students combine and apply artistic and reasoning skills to imagine, create, realize and refine artworks in conventional and innovative ways. The student will
COGNITIVE & K Critical and Creative Thinking: Students combine and apply artistic and reasoning skills to imagine, create, realize and refine artworks in conventional and innovative ways. The student will
Speaking and Listening Materials
 Speaking and Listening Materials The speaking and listening materials consist of a teacher s handbook, a book of teaching objectives and classroom activities, a pack of leaflets and posters and a video
Speaking and Listening Materials The speaking and listening materials consist of a teacher s handbook, a book of teaching objectives and classroom activities, a pack of leaflets and posters and a video
Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU
 Developing Your Course Outline Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU What Will We Be Doing Today? Use instructional design models and to decide on appropriate it approaches to:
Developing Your Course Outline Facilitator: Dr. Mervin E. Chisholm h Manager/Coordinator, IDU What Will We Be Doing Today? Use instructional design models and to decide on appropriate it approaches to:
Short Course. Physical Education. Specification for Junior Cycle
 Short Course Physical Education for June 2014 Contents Page 3 Introduction to junior cycle Page 4 Rationale Page 5 Aim Page 6 Links Page 8 Course overview Page 9 Expectations for students 10 Strand 1:
Short Course Physical Education for June 2014 Contents Page 3 Introduction to junior cycle Page 4 Rationale Page 5 Aim Page 6 Links Page 8 Course overview Page 9 Expectations for students 10 Strand 1:
Accessibility Strategies for Mathematics
 Accessibility Strategies for Mathematics "Equity does not mean that every student should receive identical instruction; instead, it demands that reasonable and appropriate accommodations be made as needed
Accessibility Strategies for Mathematics "Equity does not mean that every student should receive identical instruction; instead, it demands that reasonable and appropriate accommodations be made as needed
General Procedures for Developing an Online Course
 General Procedures for Developing an Online Course General Procedures for Developing an Online Course Questions to Ask before you Begin Analysis 1. What is your learner audience? Is the course for beginners
General Procedures for Developing an Online Course General Procedures for Developing an Online Course Questions to Ask before you Begin Analysis 1. What is your learner audience? Is the course for beginners
Ashton Community Science College Edexcel GCSE Drama Student guide. Is this the right subject for me?
 Ashton Community Science College Edexcel GCSE Drama Student guide Is this the right subject for me? Do you enjoy: Expressing yourself in an active and exciting way? Working in a group? Contributing your
Ashton Community Science College Edexcel GCSE Drama Student guide Is this the right subject for me? Do you enjoy: Expressing yourself in an active and exciting way? Working in a group? Contributing your
by Learning Area Achievement Objectives The New Zealand Curriculum Set of 8 charts
 The New Zealand Curriculum Achievement Objectives by Learning Area Set of 8 charts Published for the Ministry of Education by Learning Media Limited, Box 3293, Wellington, New Zealand. www.learningmedia.co.nz
The New Zealand Curriculum Achievement Objectives by Learning Area Set of 8 charts Published for the Ministry of Education by Learning Media Limited, Box 3293, Wellington, New Zealand. www.learningmedia.co.nz
Top Ten Tips for an Effective Fieldtrip! Effective Fieldtrip Guide. Introduction. Maximizing the impact of out-ofclassroom. learning: PREPARATION
 DC Arts & Humanities Education Collaborative Introduction Effective Fieldtrip Guide 1001 G Street, NW Suite 1000W Washington, DC 20001 (p) 202.879.9327 (f) 202.393.5705 www.dccollaborative.org [email protected]
DC Arts & Humanities Education Collaborative Introduction Effective Fieldtrip Guide 1001 G Street, NW Suite 1000W Washington, DC 20001 (p) 202.879.9327 (f) 202.393.5705 www.dccollaborative.org [email protected]
Filmmaking. How to... use a camera, lighting and audio (sound)
 Filmmaking How to... use a camera, lighting and audio (sound) 2 Lesson Objective For students to be able to use and fully understand the purpose of lighting, the importance of clear audio and the role
Filmmaking How to... use a camera, lighting and audio (sound) 2 Lesson Objective For students to be able to use and fully understand the purpose of lighting, the importance of clear audio and the role
What is Multiple Intelligence? Multiple Intelligences are 8 different ways to demonstrate intellectual ability. It is how you learn best.
 What is Multiple Intelligence? Multiple Intelligences are 8 different ways to demonstrate intellectual ability. It is how you learn best. The Multiple Intelligences How You Learn Best 1. Visual/Spatial
What is Multiple Intelligence? Multiple Intelligences are 8 different ways to demonstrate intellectual ability. It is how you learn best. The Multiple Intelligences How You Learn Best 1. Visual/Spatial
By Purnima Valiathan Head Instructional Design Team and Puja Anand CEO (Learning Solutions)
 AUDIO NARRATION: A FRAMEWORK By Purnima Valiathan Head Instructional Design Team and Puja Anand CEO (Learning Solutions) Knowledge Platform White Paper August 2008 Knowledge Platform 72a Tras Street Singapore
AUDIO NARRATION: A FRAMEWORK By Purnima Valiathan Head Instructional Design Team and Puja Anand CEO (Learning Solutions) Knowledge Platform White Paper August 2008 Knowledge Platform 72a Tras Street Singapore
Student Profile Template
 Step 1 Profile your student Student Teacher Year Level Date Student Profile Template Multiple Intelligence Strengths Tick top 2 identifiable Verbal Linguistic Interpersonal Logical/Mathematical Naturalist
Step 1 Profile your student Student Teacher Year Level Date Student Profile Template Multiple Intelligence Strengths Tick top 2 identifiable Verbal Linguistic Interpersonal Logical/Mathematical Naturalist
BOGOTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS Bogota, New Jersey. Forensic Science Curriculum. Grades 10-12
 BOGOTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS Bogota, New Jersey Forensic Science Curriculum Grades 10-12 Carol Fredericks, Ed.D. Interim Superintendent of Schools Letizia Pantoliano, Ed.D. Director of Curriculum Susan Johnson
BOGOTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS Bogota, New Jersey Forensic Science Curriculum Grades 10-12 Carol Fredericks, Ed.D. Interim Superintendent of Schools Letizia Pantoliano, Ed.D. Director of Curriculum Susan Johnson
The Creative Curriculum for Preschool: Objectives for Development & Learning
 Curriculum Alignment of The Creative Curriculum for Preschool: Objectives for Development & Learning with Alignment of The Creative Curriculum for Preschool: Objectives for Development & Learning With
Curriculum Alignment of The Creative Curriculum for Preschool: Objectives for Development & Learning with Alignment of The Creative Curriculum for Preschool: Objectives for Development & Learning With
Music in schools: promoting good practice
 Guidance from HMI for teachers, headteachers, and music hub leaders when observing musical teaching and learning Schools, all other funded providers of music education, and providers of Continuing Professional
Guidance from HMI for teachers, headteachers, and music hub leaders when observing musical teaching and learning Schools, all other funded providers of music education, and providers of Continuing Professional
Talking and Listening. Language and Literacy in the Foundation Stage
 Acknowledgements The Early Years Literacy Interboard Group wishes to record its thanks to the following schools for their willing co-operation in the production of this resource. Ballysillan Primary, Belfast;
Acknowledgements The Early Years Literacy Interboard Group wishes to record its thanks to the following schools for their willing co-operation in the production of this resource. Ballysillan Primary, Belfast;
Learning and Teaching Styles in Language, Science and Technology Education in Nigeria.
 , Vol.5 No.2 (2012) BritishJournal Publishing, Inc. 2012 http://www.bjournal.co.uk/bjass.aspx Learning and Teaching Styles in Language, Science and Technology Education in Nigeria. Olasumbo S.Apanpa (Ph.D)
, Vol.5 No.2 (2012) BritishJournal Publishing, Inc. 2012 http://www.bjournal.co.uk/bjass.aspx Learning and Teaching Styles in Language, Science and Technology Education in Nigeria. Olasumbo S.Apanpa (Ph.D)
Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex
 Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex A White Paper by Dr. Gary Woodill, Ed.D. Chief Learning Officer, Operitel Corporation [email protected] Dr. Karen Anderson, PhD. Senior
Instructional Design Principles in the Development of LearnFlex A White Paper by Dr. Gary Woodill, Ed.D. Chief Learning Officer, Operitel Corporation [email protected] Dr. Karen Anderson, PhD. Senior
INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES *
 INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES * DIRECTIONS Enter your answers to every question on the ILS scoring sheet. Please choose only one answer for each question. If both a and b seem to apply to you, choose the one
INDEX OF LEARNING STYLES * DIRECTIONS Enter your answers to every question on the ILS scoring sheet. Please choose only one answer for each question. If both a and b seem to apply to you, choose the one
Form: Filled in table. Method: Peer assessment. Tool: Checklist. Form: Completed table. Method: Peer assessment. Tool: Checklist
 Lesson Plan English First Additional Language Grade 5 Content in context: Text from other Learning Area - Whether Los and ASs Learning Activities Details of Assessment Barriers to Learning LO 1 Listening
Lesson Plan English First Additional Language Grade 5 Content in context: Text from other Learning Area - Whether Los and ASs Learning Activities Details of Assessment Barriers to Learning LO 1 Listening
Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession
 12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
12 Section Two: Ohio Standards for the Teaching Profession 1 Teachers understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Teachers display knowledge of how
Language, Learning, and Content Instruction
 CHAPTER 2 Language, Learning, and Content Instruction WHAT DO YOU KNOW WHEN YOU KNOW A LANGUAGE? Have you ever thought about what you know when you know a language? Most people s first reaction is to say,
CHAPTER 2 Language, Learning, and Content Instruction WHAT DO YOU KNOW WHEN YOU KNOW A LANGUAGE? Have you ever thought about what you know when you know a language? Most people s first reaction is to say,
Growing Up With Epilepsy
 Teaching Students with Epilepsy: Children with epilepsy often experience learning issues as a result of their seizures. These may include ongoing problems with motor skills or cognitive functions, as well
Teaching Students with Epilepsy: Children with epilepsy often experience learning issues as a result of their seizures. These may include ongoing problems with motor skills or cognitive functions, as well
Foundations of the Montessori Method (3 credits)
 MO 634 Foundations of the Montessori Method This course offers an overview of human development through adulthood, with an in-depth focus on childhood development from birth to age six. Specific topics
MO 634 Foundations of the Montessori Method This course offers an overview of human development through adulthood, with an in-depth focus on childhood development from birth to age six. Specific topics
BRAIN-BASED LEARNING: UNDERSTANDING HOW YOUR BRAIN LEARNS. Demoine Adams
 BRAIN-BASED LEARNING: UNDERSTANDING HOW YOUR BRAIN LEARNS Demoine Adams First, some science: Our brain is made up of two halves Left brain and right brain They are connected to each other by a thick cable
BRAIN-BASED LEARNING: UNDERSTANDING HOW YOUR BRAIN LEARNS Demoine Adams First, some science: Our brain is made up of two halves Left brain and right brain They are connected to each other by a thick cable
Subject specific vocabulary (version 2.0)
 Subject specific vocabulary (version 2.0) The following subject specific vocabulary provides definitions of key terms used in our GCSE Dance specification (8236). Students should be familiar with and gain
Subject specific vocabulary (version 2.0) The following subject specific vocabulary provides definitions of key terms used in our GCSE Dance specification (8236). Students should be familiar with and gain
Bachelor of Graphic Design with nested Associate Degree of Graphic Design
 Bachelor of Graphic Design with nested Associate Degree of Graphic Design Transforming lives through excellence in Christian higher education Bachelor of Graphic Design with nested Associate Degree of
Bachelor of Graphic Design with nested Associate Degree of Graphic Design Transforming lives through excellence in Christian higher education Bachelor of Graphic Design with nested Associate Degree of
Elementary and Middle School Technology Curriculum Guidelines
 Elementary and Middle School Technology Curriculum Guidelines Catholic Schools Office Diocese of Erie March, 2007 PHILOSOPHY STATEMENT... 1 TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM FOUNDATION... 1 TECHNOLOGY FOUNDATION STANDARDS
Elementary and Middle School Technology Curriculum Guidelines Catholic Schools Office Diocese of Erie March, 2007 PHILOSOPHY STATEMENT... 1 TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM FOUNDATION... 1 TECHNOLOGY FOUNDATION STANDARDS
