Pixel-based and object-oriented change detection analysis using high-resolution imagery
|
|
|
- Cathleen Turner
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pixel-based and object-oriented change detection analysis using high-resolution imagery Institute for Mine-Surveying and Geodesy TU Bergakademie Freiberg D Freiberg, Germany Programme Group Systems Analysis and Technology Evaluation (STE) Forschungszentrum Juelich D Juelich, Germany Abstract The high spatial resolution of state-of-the-art commercial satellite imagery provides a good basis for recognising and monitoring even small-scale structural changes within nuclear facilities and for planning of routine and/or challenge inspections of nuclear sites. Despite the advantages of the improved spatial resolution some problems exist that may make the interpretation of the changes more difficult: Firstly, the results of the change analysis can be very complex and unclear at a glance. Secondly, shadow formation and off-nadir images due to different sensor and solar conditions at the acquisition times can cause false signals or overlap real changes. In view to the fast-growing amount of data from different sensor types there are then some requirements of an effective change detection procedure for safeguards purposes: i. The techniques involved should possess a certain amount of robustness in terms of small misregistration errors, different atmospheric conditions at the acquiring dates, off-nadir angles. ii. Given large multisensor data sets it would be necessary that the procedure operates as automatically as possible. Iii. The procedure has to imply techniques to initially pinpoint out those parts of a scene in which significant changes have taken place. iv. All image areas indicating changes then should be subject to a detailed classification and interpretation procedure. We have already investigated some pixel-based change detection for the routine nuclear verification, based on recently published visualisation and change detection algorithms: canonical correlation analysis (MAD transformation) to enhance the change information in the difference images and bayesian techniques for the automatic determination of significant thresholds. Some steps have been taken by combining pixel- and objectoriented approaches, i.e. MAD transformation of the image data and object-oriented post-classification of the changes and object extraction for the image data or MAD transformation of the objects and post-classification of the change objects. Another approach implies a solely object-oriented change detection technique: Object extraction, semantic classification and post-classification comparison by means of a change matrix. The object-oriented change analysis procedures are carried out with a relatively new technology for image analysis, ecognition ( Keywords: change detection; pixel-based techniques; object-oriented approaches; high-resolution satellite imagery; safeguards purposes; 1. Introduction detection procedures intend to find and, where appropriate, to interpret the alterations of objects or phenomenon between the different acquiring times t 1, t 2... t n. When using multitemporal remote sensing image data, the value of an image pixel or object at time t 1 can be compared with the value of the corresponding image pixel or object at time t 2 in order to determine the degree of change. Many different procedures have been developed within the last 30 years, depending on the given spatial, spectral and temporal resolution of the available imagery and the computer capacities in regard to digital image processing. Reviews of change detection techniques are given in [1-4]. At the same time, the variety of change detection applications has increased. Whereas the first change detection studies particularly focused on large-scale and possibly long-term changes of land use and land cover, i.e. vegetation, forest, agriculture, water, urban areas, recent procedures
2 may also realise small-scale and short-term changes within urban areas or ecosystems. The improvements in spatial and spectral resolution bring with them new applications in new fields, for example the verification of international treaties on nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation. Now, the high spatial resolution satellite imagery from state-of-the-art commercial satellites IKONOS and QUICKBIRD provides a good basis for recognising and monitoring even small-scale structural changes within nuclear facilities and for planning of routine and/or challenge inspections of nuclear sites. 2. Methodology A comprehensive change detection system for nuclear verification purposes has to imply pixelbased techniques for geometric registration, radiometric normalisation, image fusion/sharpening and statistical change-/no-change-analysis of medium- or high-resolution imagery. Statistical change detection techniques may calculate the change of the spectral or texture pixel values (by arithmetic procedures, regression, change vector), may estimate the change of transformed pixel values (by principal component analysis, canonical correlation analysis) or may identify the change of class memberships of the pixels (by comparison of classifications, multitemporal classifications). For the specific application of nuclear monitoring the most satisfactory results were carried out by canonical correlation analysis [5] to enhance the change information in the difference images and bayesian techniques [6] for the automatic determination of significant thresholds [7-10]. Significant changes can then explicitly be analysed and interpreted by object-oriented approaches using high-resolution satellite imagery. Analysing satellite image data in an object-oriented way generally gives the possibility to involve specific knowledge in the classification or recognition process. Specific features can be defined by membership functions in a semantic model. Preliminary results [11] indicate that the analysis and interpretation of changes within nuclear plants can be more precisely and reliably if the change detection procedure makes use of the characteristic features of facility objects and changes (e.g. compared to other industrial sites). The change detection procedure then may analyse the changes the mean object features (spectral colour, form), may compare the relations between the objects (distance between objects, location of sub-objects within super-objects, existence of neighbouring objects) or the class memberships of the objects. The software solution for an object-oriented change analysis is given by a relatively new technology for image analysis, ecognition ( This system shows some fundamental differences compared to other more conventional (pixel-based) techniques for image analysis. A basic part of the system is a new patented technique for the knowledge free extraction of image object primitives at different resolutions, the so-called multiresolution segmentation. The segmentation operates as a heuristic optimization procedure which minimizes the average heterogeneity of image objects for a given resolution over the whole scene. The objective is to construct a hierarchical net of image objects, in which fine objects are sub-objects of coarser structures. Due to the hierarchical structure, the image data are simultaneously represented in different resolutions. Each object knows its context, its neighbourhood and its sub-objects. Thus, it is possible to define relations between the objects. The defined local object-oriented context information can then be used together with other (spectral, form, texture) features of the image objects for classification. 3. Investigations A change detection analysis procedure was carried out for two IKONOS-2 images acquired over the Pickering Nuclear Power Generating Station (Ontario, Canada) in July 2000 and July 2001 (Figure 1). The visual comparison of the images points out some of the problems related to highresolution satellite imagery: Due to different sensor and solar conditions at both acquisition times the objects are mismatched and form different shadows. Thus, a pixel-based change detection analysis may bring out a lot of false signals. The results of the pixel-based changed detection analysis by mutivariate alteration detection [5] are given in Figure 2. As expected, the results of the change analysis are very complex and unclear at a glance.
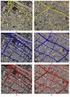
3 Problems due to different offnadir and sun angles Fig. 1: IKONOS-2 images over Pickering Nuclear Power Generating Station, Canada, July 2000 (left) and July 2001 (right). On the left image, major changes and problems due to different off-nadir and sun angels are indicated Problems due to different off-nadir and sun angles Fig. 2: Multivariate Alteration Detection (MAD): MAD component 1 in red, MAD component 2 in green, MAD component 3 in blue Assuming that an object-oriented approach could improve the results, we implemented a second procedure (see figure 3). As input data, we used the four change components carried out with the MAD transformation of the two IKONOS-2 images. In addition, we used the original panchromatic and multispectral IKONOS-2 data of July 2001 in order have the possibility to extract real objects. The segmentation was realised on the basis of the original IKONOS-2 data in different scales, so that the individual objects of the nuclear plant are extracted in a fine level In order to extract fine
4 objects we weight the panchromatic channel by a factor of 10. By increasing the scale parameter the objects become coarser, until the different parts of the site are included in one object (without figure). Four change classes were defined: changes DN- for objects with decreased grey values, changes DN+ in case of increased grey values, changes vegetation- for degraded vegetation and changes vegetation+ for accumulated vegetation. A class for water areas was added to the set of classes. The membership functions for the object description were defined in terms of standard deviations of the MAD components, some mean object values and object relations. Figure 4 shows the results of the change classification. This time, we received a very rough indication of changes Fig. 3: Object-oriented change detection using MAD components Fig. 4: Classification result for the object-oriented change detection using MAD components
5 4 Conclusions and Outlook Pixel-based techniques are suitable for change-/no change-analysis of medium-resolution imagery while object-oriented approaches (with ecognition) seem to expand the possibilities to detect and interpret changes using high-resolution satellite imagery. The next step should involve a solely objectoriented change detection scheme as shown in figure 5. Both images should be classified individually and then be compared by a change detection-matrix. At the moment, many unsolved problems in the remote sensing research community exist as to the object-oriented analysis of high-resolution image data in general, especially in terms of change detection procedures. Recent problems are connected to the question, how to compare segmentation levels with different object boundaries in (the usual) case of different offnadir angels. Parameters have to be found in order to quantify and qualify an object s change between two acquisitions times. An optimal set of input image (original, normalized, artificial) and GIS (topographic maps, site diagrams etc.) layer has to be defined. Relevant classes have to be defined by objects features and class relations and the change matrix has to be specified. For a comprehensive change detection and interpretation system signatures for different facility types in different geographical/ political areas are urgently needed. Thus, the features of the different elements of the nuclear fuel cycle - mining/milling, uranium enrichment, fuel fabrication, reactor (civil power plant), reprocessing plant, waste storage facility have to be analysed and utilised for image processing. Fig. 4: Object-oriented change detection using a change detection matrix References [1] Singh, A. (1989): Digital Detection Techniques Using Remotely Sensed Data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 10(6), [2] Jensen, J. R. (1996): Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective. 2. edition. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River [3] Mas, J.-F. (1999): Monitoring Land-Cover s - A Comparison of Detection Techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing 20(1), [4] Lunetta, R.S. and C.D. Elvidge (ed.) (1999): Remote Sensing Detection. Environmental Monitoring Methods and Applications. Taylor & Francis, London
6 [5] Nielsen, A.A., Conradsen, K. and J. J. Simpson (1998): Multivariate Alteration Detection (MAD) and MAF Postprocessing in Multispectral, Bitemporal Image Data: New Approaches to Detection Studies. Remote Sensing of Environment 64, 1 19 [6] Bruzzone, L. and D. F. Prieto (1999): A Bayesian Approach to Automatic Detection. Proc. IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 28 June-2 July 1999, Hamburg, Germany (CD-ROM) [7] Canty, M.J. (2001): Detection with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery in Support of Verification and Crisis Prevention: Nuclear Applications. Berichte des Forschungszentrum Jülich 3842, Jül-3842, Jülich [8] Canty, M.J., Niemeyer, I., Truong, B. and J. Schlittenhardt (2001): Detection with Multispectral Satellite Imagery: Application to Nuclear Verification. Proc. of the International Symposium on Spectral Sensing Research, ISSSR 2001, Quebec City, June 2001 (CD-Rom) [9] Canty, M.J., Niemeyer, I., Richter, B. and G. Stein (1999): Wide-area Detection: The Use of Multitemporal Landsat Images for Nuclear Safeguards. Journal of Nuclear Materials Management (JNMM), Vol. XXVII, No. 2, 1999, [10] Niemeyer, I. and M. J. Canty (1999): Multispectral Image Processing Techniques for Safeguards Purposes. Proc.21st Annual Meeting Symposium on Safeguards and Nuclear Material Management, 3-6 May 1999, Seville, Spain, [11] Niemeyer, I. and M.J. Canty (2001): Object-Oriented Post-Classification of Images. Proc. SPIE s International Symposium on Remote Sensing, Toulouse, September 2001, SPIE Vol. 4545, [12] Baatz, M. et al. (2002): ecognition. User Guide 3. ( )
An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance
 An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance Merve Yildiz 1, Taskin Kavzoglu 2, Ismail Colkesen 3, Emrehan K. Sahin Gebze Institute of Technology, Department
An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance Merve Yildiz 1, Taskin Kavzoglu 2, Ismail Colkesen 3, Emrehan K. Sahin Gebze Institute of Technology, Department
Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with Panchromatic Textural Features
 Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Lena Halounová, Editor not only for Scientific Cooperation EARSeL, 2011 Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with
Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Lena Halounová, Editor not only for Scientific Cooperation EARSeL, 2011 Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with
SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS
 Geography 309 Sample MidTerm Questions Page 1 SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Questions 4, 5, 6, Chapter 2 Questions 4, 7, 10 Chapter 4 Questions 8, 9 Chapter 10 Questions 1, 4, 7
Geography 309 Sample MidTerm Questions Page 1 SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Questions 4, 5, 6, Chapter 2 Questions 4, 7, 10 Chapter 4 Questions 8, 9 Chapter 10 Questions 1, 4, 7
Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule
 Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule Li Chaokui a,b, Fang Wen a,b, Dong Xiaojiao a,b a National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Geo-Spatial
Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule Li Chaokui a,b, Fang Wen a,b, Dong Xiaojiao a,b a National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Geo-Spatial
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK
 UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction from High Resolution Satellite Imagery
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May Jun. 2015), PP 47-52 www.iosrjournals.org Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May Jun. 2015), PP 47-52 www.iosrjournals.org Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction
DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION Y. Zhang* a, T. Maxwell, H. Tong, V. Dey a University of New Brunswick, Geodesy &
DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION Y. Zhang* a, T. Maxwell, H. Tong, V. Dey a University of New Brunswick, Geodesy &
DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION TO GIS
 Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 79, 2012 Rio de Janeiro Brazil. p.315 DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECTBASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION
Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 79, 2012 Rio de Janeiro Brazil. p.315 DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECTBASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION
VCS REDD Methodology Module. Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities
 1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021
 Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021 Lecture 4 Image classification 2 Purpose categorising data data abstraction / simplification data interpretation mapping for land cover mapping use land cover class
Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021 Lecture 4 Image classification 2 Purpose categorising data data abstraction / simplification data interpretation mapping for land cover mapping use land cover class
Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments
 Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments IKONOS The IKONOS satellite carries a high resolution panchromatic band covering most of the silicon response and four lower resolution spectral
Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments IKONOS The IKONOS satellite carries a high resolution panchromatic band covering most of the silicon response and four lower resolution spectral
Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks
 1 Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks Fabio Pacifici, Student Member, IEEE, and Fabio Del Frate, Member, IEEE Abstract A novel approach based on
1 Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks Fabio Pacifici, Student Member, IEEE, and Fabio Del Frate, Member, IEEE Abstract A novel approach based on
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS
 WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM
 PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM Rohan Ashok Mandhare 1, Pragati Upadhyay 2,Sudha Gupta 3 ME Student, K.J.SOMIYA College of Engineering, Vidyavihar, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM Rohan Ashok Mandhare 1, Pragati Upadhyay 2,Sudha Gupta 3 ME Student, K.J.SOMIYA College of Engineering, Vidyavihar, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images
 Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images H. Topan, G. Büyüksalih Zonguldak Karelmas University K. Jacobsen University of Hannover, Germany Keywords: satellite images, mapping, resolution,
Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images H. Topan, G. Büyüksalih Zonguldak Karelmas University K. Jacobsen University of Hannover, Germany Keywords: satellite images, mapping, resolution,
DETECTING LANDUSE/LANDCOVER CHANGES ALONG THE RING ROAD IN PESHAWAR CITY USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES
 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Full length Research Paper -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Full length Research Paper -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.3 Spatial Resolution, Pixel Size, and Scale
 Section 2.3 Spatial Resolution, Pixel Size, and Scale Page 39 2.3 Spatial Resolution, Pixel Size, and Scale For some remote sensing instruments, the distance between the target being imaged and the platform,
Section 2.3 Spatial Resolution, Pixel Size, and Scale Page 39 2.3 Spatial Resolution, Pixel Size, and Scale For some remote sensing instruments, the distance between the target being imaged and the platform,
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
 OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION 1 ALZIR FELIPPE B. ANTUNES 2 CHRISTEL LINGNAU 1 JORGE CENTENO DA SILVA 1 UFPR- Universidade Federal do Paraná Departamento
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION 1 ALZIR FELIPPE B. ANTUNES 2 CHRISTEL LINGNAU 1 JORGE CENTENO DA SILVA 1 UFPR- Universidade Federal do Paraná Departamento
Digital image processing
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 4 Digital image processing Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Digital Image Processing Most of the common
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 4 Digital image processing Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Digital Image Processing Most of the common
THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
 Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.678 THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.678 THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
- 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA)
 - 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA) Peter HOFMANN - DEFiNiENS AG Rindermarkt 7 D-80331
- 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA) Peter HOFMANN - DEFiNiENS AG Rindermarkt 7 D-80331
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches
 Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS
 COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery
 Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery WorldView-2 is the first commercial high-resolution satellite to provide eight spectral sensors in the visible to near-infrared
Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery WorldView-2 is the first commercial high-resolution satellite to provide eight spectral sensors in the visible to near-infrared
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED APPROACH FOR REDUCING CLOUD AND SHADOW ABSTRACT
 A KNOWLEDGE-BASED APPROACH FOR REDUCING CLOUD AND SHADOW Mingjun Song, Graduate Research Assistant Daniel L. Civco, Director Laboratory for Earth Resources Information Systems Department of Natural Resources
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED APPROACH FOR REDUCING CLOUD AND SHADOW Mingjun Song, Graduate Research Assistant Daniel L. Civco, Director Laboratory for Earth Resources Information Systems Department of Natural Resources
A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images
 A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images G.Gayathri PG student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Parisutham Institute of Technology and Science,
A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images G.Gayathri PG student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Parisutham Institute of Technology and Science,
Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information
 ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 239 258 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information Ursula
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 239 258 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information Ursula
APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED
 APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED S. J. GOETZ Woods Hole Research Center Woods Hole, Massachusetts 054-096 USA
APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED S. J. GOETZ Woods Hole Research Center Woods Hole, Massachusetts 054-096 USA
Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8
 Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8 Byeonghee Kim 1, Youkyung Han 2, Yonghyun Kim 3, Yongil Kim 4 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Seoul National University (SNU), Seoul,
Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8 Byeonghee Kim 1, Youkyung Han 2, Yonghyun Kim 3, Yongil Kim 4 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Seoul National University (SNU), Seoul,
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES
 THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES J. Chmiel, A. Fijałkowska Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Geodesy
THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES J. Chmiel, A. Fijałkowska Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Geodesy
Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques
 Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques Koen C. Mertens, Lieven P.C. Verbeke & Robert R. De Wulf Laboratory of Forest Management and Spatial Information Techniques, Ghent University, 9000 Gent, Belgium
Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques Koen C. Mertens, Lieven P.C. Verbeke & Robert R. De Wulf Laboratory of Forest Management and Spatial Information Techniques, Ghent University, 9000 Gent, Belgium
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping
 Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
Analysis of Landsat ETM+ Image Enhancement for Lithological Classification Improvement in Eagle Plain Area, Northern Yukon
 Analysis of Landsat ETM+ Image Enhancement for Lithological Classification Improvement in Eagle Plain Area, Northern Yukon Shihua Zhao, Department of Geology, University of Calgary, [email protected],
Analysis of Landsat ETM+ Image Enhancement for Lithological Classification Improvement in Eagle Plain Area, Northern Yukon Shihua Zhao, Department of Geology, University of Calgary, [email protected],
River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models
 River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models Steven M. de Jong & Raymond Sluiter Utrecht University Corné van der Sande Netherlands Earth Observation
River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models Steven M. de Jong & Raymond Sluiter Utrecht University Corné van der Sande Netherlands Earth Observation
A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS
 A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS Y. Gao a, *, J.F. Mas a a Centro de Investigaciones en Geografía Ambiental,
A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS Y. Gao a, *, J.F. Mas a a Centro de Investigaciones en Geografía Ambiental,
RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY
 RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY M. Erdogan, H.H. Maras, A. Yilmaz, Ö.T. Özerbil General Command of Mapping 06100 Dikimevi, Ankara, TURKEY - (mustafa.erdogan;
RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY M. Erdogan, H.H. Maras, A. Yilmaz, Ö.T. Özerbil General Command of Mapping 06100 Dikimevi, Ankara, TURKEY - (mustafa.erdogan;
KEYWORDS: image classification, multispectral data, panchromatic data, data accuracy, remote sensing, archival data
 Improving the Accuracy of Historic Satellite Image Classification by Combining Low-Resolution Multispectral Data with High-Resolution Panchromatic Data Daniel J. Getman 1, Jonathan M. Harbor 2, Chris J.
Improving the Accuracy of Historic Satellite Image Classification by Combining Low-Resolution Multispectral Data with High-Resolution Panchromatic Data Daniel J. Getman 1, Jonathan M. Harbor 2, Chris J.
Accuracy Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Classification using Google Earth
 American Journal of Environmental Protection 25; 4(4): 9-98 Published online July 2, 25 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajep) doi:.648/j.ajep.2544.4 ISSN: 228-568 (Print); ISSN: 228-5699 (Online)
American Journal of Environmental Protection 25; 4(4): 9-98 Published online July 2, 25 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajep) doi:.648/j.ajep.2544.4 ISSN: 228-568 (Print); ISSN: 228-5699 (Online)
Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology
 Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology Ann Johnson Associate Director [email protected] Funded by National Science Foundation Advanced Technological Education program [DUE
Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology Ann Johnson Associate Director [email protected] Funded by National Science Foundation Advanced Technological Education program [DUE
Resolutions of Remote Sensing
 Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands) 3. Temporal (time of day/season/year) 4. Radiometric (color depth) Spatial Resolution describes how
Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands) 3. Temporal (time of day/season/year) 4. Radiometric (color depth) Spatial Resolution describes how
OBJECT BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION AND WEB-MAPPING TECHNIQUES FOR FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT
 OBJECT BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION AND WEB-MAPPING TECHNIQUES FOR FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT Ejaz Hussain, KyoHyouk Kim, Jie Shan {ehussain, kim458, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil
OBJECT BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION AND WEB-MAPPING TECHNIQUES FOR FLOOD DAMAGE ASSESSMENT Ejaz Hussain, KyoHyouk Kim, Jie Shan {ehussain, kim458, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil
A remote sensing instrument collects information about an object or phenomenon within the
 Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch
 Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch Introduction In this time of large-scale planning and land management on public lands, managers are increasingly
Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch Introduction In this time of large-scale planning and land management on public lands, managers are increasingly
SEMI-AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN AREAS BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION RADAR DATA
 SEMI-AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN AREAS BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION RADAR DATA T. Esch, A. Roth German Aerospace Center DLR, German Remote Sensing Data Center DFD, 82234 Wessling, Germany- (Thomas.Esch,
SEMI-AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN AREAS BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION RADAR DATA T. Esch, A. Roth German Aerospace Center DLR, German Remote Sensing Data Center DFD, 82234 Wessling, Germany- (Thomas.Esch,
From Ideas to Innovation
 From Ideas to Innovation Selected Applications from the CRC Research Lab in Advanced Geomatics Image Processing Dr. Yun Zhang Canada Research Chair Laboratory in Advanced Geomatics Image Processing (CRC-AGIP
From Ideas to Innovation Selected Applications from the CRC Research Lab in Advanced Geomatics Image Processing Dr. Yun Zhang Canada Research Chair Laboratory in Advanced Geomatics Image Processing (CRC-AGIP
PROBLEMS IN THE FUSION OF COMMERCIAL HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE AS WELL AS LANDSAT 7 IMAGES AND INITIAL SOLUTIONS
 ISPRS SIPT IGU UCI CIG ACSG Table of contents Table des matières Authors index Index des auteurs Search Recherches Exit Sortir PROBLEMS IN THE FUSION OF COMMERCIAL HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE AS WELL AS
ISPRS SIPT IGU UCI CIG ACSG Table of contents Table des matières Authors index Index des auteurs Search Recherches Exit Sortir PROBLEMS IN THE FUSION OF COMMERCIAL HIGH-RESOLUTION SATELLITE AS WELL AS
Big data and Earth observation New challenges in remote sensing images interpretation
 Big data and Earth observation New challenges in remote sensing images interpretation Pierre Gançarski ICube CNRS - Université de Strasbourg 2014 Pierre Gançarski Big data and Earth observation 1/58 1
Big data and Earth observation New challenges in remote sensing images interpretation Pierre Gançarski ICube CNRS - Université de Strasbourg 2014 Pierre Gançarski Big data and Earth observation 1/58 1
Using Remote Sensing Imagery to Evaluate Post-Wildfire Damage in Southern California
 Graham Emde GEOG 3230 Advanced Remote Sensing February 22, 2013 Lab #1 Using Remote Sensing Imagery to Evaluate Post-Wildfire Damage in Southern California Introduction Wildfires are a common disturbance
Graham Emde GEOG 3230 Advanced Remote Sensing February 22, 2013 Lab #1 Using Remote Sensing Imagery to Evaluate Post-Wildfire Damage in Southern California Introduction Wildfires are a common disturbance
ANALYSIS OF FOREST CHANGE IN FIRE DAMAGE AREA USING SATELLITE IMAGES
 ANALYSIS OF FOREST CHANGE IN FIRE DAMAGE AREA USING SATELLITE IMAGES Joon Mook Kang, Professor Joon Kyu Park, Ph.D Min Gyu Kim, Ph.D._Candidate Dept of Civil Engineering, Chungnam National University 220
ANALYSIS OF FOREST CHANGE IN FIRE DAMAGE AREA USING SATELLITE IMAGES Joon Mook Kang, Professor Joon Kyu Park, Ph.D Min Gyu Kim, Ph.D._Candidate Dept of Civil Engineering, Chungnam National University 220
Very High Resolution Satellite Image Classification Using Fuzzy Rule-Based Systems
 Algorithms 2013, 6, 762-781; doi:10.3390/a6040762 Article OPEN ACCESS algorithms ISSN 1999-4893 www.mdpi.com/journal/algorithms Very High Resolution Satellite Image Classification Using Fuzzy Rule-Based
Algorithms 2013, 6, 762-781; doi:10.3390/a6040762 Article OPEN ACCESS algorithms ISSN 1999-4893 www.mdpi.com/journal/algorithms Very High Resolution Satellite Image Classification Using Fuzzy Rule-Based
ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY.
 ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI software uses proven scientific methods and automated processes to help you turn geospatial
ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI software uses proven scientific methods and automated processes to help you turn geospatial
Imagery. 1:50,000 Basemap Generation From Satellite. 1 Introduction. 2 Input Data
 1:50,000 Basemap Generation From Satellite Imagery Lisbeth Heuse, Product Engineer, Image Applications Dave Hawkins, Product Manager, Image Applications MacDonald Dettwiler, 3751 Shell Road, Richmond B.C.
1:50,000 Basemap Generation From Satellite Imagery Lisbeth Heuse, Product Engineer, Image Applications Dave Hawkins, Product Manager, Image Applications MacDonald Dettwiler, 3751 Shell Road, Richmond B.C.
The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories
 The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories Dr. Farrag Ali FARRAG Assistant Prof. at Civil Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Assiut University Assiut, Egypt.
The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories Dr. Farrag Ali FARRAG Assistant Prof. at Civil Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Assiut University Assiut, Egypt.
Traffic Prediction and Analysis using a Big Data and Visualisation Approach
 Traffic Prediction and Analysis using a Big Data and Visualisation Approach Declan McHugh 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Institute of Technology Blanchardstown March 10, 2015 Summary This abstract
Traffic Prediction and Analysis using a Big Data and Visualisation Approach Declan McHugh 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Institute of Technology Blanchardstown March 10, 2015 Summary This abstract
LEOworks - a freeware to teach Remote Sensing in Schools
 LEOworks - a freeware to teach Remote Sensing in Schools Wolfgang Sulzer Institute for Geography and Regional Science University of Graz Heinrichstrasse 36, A-8010 Graz/Austria [email protected]
LEOworks - a freeware to teach Remote Sensing in Schools Wolfgang Sulzer Institute for Geography and Regional Science University of Graz Heinrichstrasse 36, A-8010 Graz/Austria [email protected]
RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING INTRODUCTION
 RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING Ejaz Hussain, Jie Shan {ehussain, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu} Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University
RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING Ejaz Hussain, Jie Shan {ehussain, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu} Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University
Training Manual. Land cover mapping using satellite data. Draft
 Training Manual Land cover mapping using satellite data Draft Contents 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Legend development and classification scheme... 3 1.2 Available satellite images and their spatial and spectral
Training Manual Land cover mapping using satellite data Draft Contents 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Legend development and classification scheme... 3 1.2 Available satellite images and their spatial and spectral
Chapter Contents Page No
 Chapter Contents Page No Preface Acknowledgement 1 Basics of Remote Sensing 1 1.1. Introduction 1 1.2. Definition of Remote Sensing 1 1.3. Principles of Remote Sensing 1 1.4. Various Stages in Remote Sensing
Chapter Contents Page No Preface Acknowledgement 1 Basics of Remote Sensing 1 1.1. Introduction 1 1.2. Definition of Remote Sensing 1 1.3. Principles of Remote Sensing 1 1.4. Various Stages in Remote Sensing
How Landsat Images are Made
 How Landsat Images are Made Presentation by: NASA s Landsat Education and Public Outreach team June 2006 1 More than just a pretty picture Landsat makes pretty weird looking maps, and it isn t always easy
How Landsat Images are Made Presentation by: NASA s Landsat Education and Public Outreach team June 2006 1 More than just a pretty picture Landsat makes pretty weird looking maps, and it isn t always easy
CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES
 Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES Sebastian Mader
Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES Sebastian Mader
TerraColor White Paper
 TerraColor White Paper TerraColor is a simulated true color digital earth imagery product developed by Earthstar Geographics LLC. This product was built from imagery captured by the US Landsat 7 (ETM+)
TerraColor White Paper TerraColor is a simulated true color digital earth imagery product developed by Earthstar Geographics LLC. This product was built from imagery captured by the US Landsat 7 (ETM+)
MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA
 MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA Li-Yu Chang and Chi-Farn Chen Center for Space and Remote Sensing Research, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Rd., Zhongli
MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA Li-Yu Chang and Chi-Farn Chen Center for Space and Remote Sensing Research, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Rd., Zhongli
Digital Classification and Mapping of Urban Tree Cover: City of Minneapolis
 Digital Classification and Mapping of Urban Tree Cover: City of Minneapolis FINAL REPORT April 12, 2011 Marvin Bauer, Donald Kilberg, Molly Martin and Zecharya Tagar Remote Sensing and Geospatial Analysis
Digital Classification and Mapping of Urban Tree Cover: City of Minneapolis FINAL REPORT April 12, 2011 Marvin Bauer, Donald Kilberg, Molly Martin and Zecharya Tagar Remote Sensing and Geospatial Analysis
High Productivity Data Processing Analytics Methods with Applications
 High Productivity Data Processing Analytics Methods with Applications Dr. Ing. Morris Riedel et al. Adjunct Associate Professor School of Engineering and Natural Sciences, University of Iceland Research
High Productivity Data Processing Analytics Methods with Applications Dr. Ing. Morris Riedel et al. Adjunct Associate Professor School of Engineering and Natural Sciences, University of Iceland Research
Map World Forum Hyderabad, India Introduction: High and very high resolution space images: GIS Development
 Very high resolution satellite images - competition to aerial images Dr. Karsten Jacobsen Leibniz University Hannover, Germany [email protected] Introduction: Very high resolution images taken
Very high resolution satellite images - competition to aerial images Dr. Karsten Jacobsen Leibniz University Hannover, Germany [email protected] Introduction: Very high resolution images taken
Classification of High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Image by Combining Spectral, Structural and Semantic Features Using SVM Approach
 Classification of High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Image by Combining Spectral, Structural and Semantic Features Using SVM Approach I Saranya.K, II [email protected] I PG Student, II Assistant Professor
Classification of High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Image by Combining Spectral, Structural and Semantic Features Using SVM Approach I Saranya.K, II [email protected] I PG Student, II Assistant Professor
DETECTION OF RING SHAPED STRUCTURES IN AGRICULTURAL LAND USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES
 DETECTION OF RING SHAPED STRUCTURES IN AGRICULTURAL LAND USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES S. Ø. Larsen a, *, Ø. D. Trier a, R. Solberg a a Norwegian Computing Center, P.O. Box 114 Blindern, NO-0314
DETECTION OF RING SHAPED STRUCTURES IN AGRICULTURAL LAND USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES S. Ø. Larsen a, *, Ø. D. Trier a, R. Solberg a a Norwegian Computing Center, P.O. Box 114 Blindern, NO-0314
Visualization of large data sets using MDS combined with LVQ.
 Visualization of large data sets using MDS combined with LVQ. Antoine Naud and Włodzisław Duch Department of Informatics, Nicholas Copernicus University, Grudziądzka 5, 87-100 Toruń, Poland. www.phys.uni.torun.pl/kmk
Visualization of large data sets using MDS combined with LVQ. Antoine Naud and Włodzisław Duch Department of Informatics, Nicholas Copernicus University, Grudziądzka 5, 87-100 Toruń, Poland. www.phys.uni.torun.pl/kmk
Object-based classification of remote sensing data for change detection
 ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 225 238 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Object-based classification of remote sensing data for change detection Volker Walter* Institute for
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 225 238 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Object-based classification of remote sensing data for change detection Volker Walter* Institute for
The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery.
 Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge Geospatial imagery is used more and more across industries because
Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge Geospatial imagery is used more and more across industries because
Understanding Raster Data
 Introduction The following document is intended to provide a basic understanding of raster data. Raster data layers (commonly referred to as grids) are the essential data layers used in all tools developed
Introduction The following document is intended to provide a basic understanding of raster data. Raster data layers (commonly referred to as grids) are the essential data layers used in all tools developed
Remotely sensed images and GIS data fusion for automatic change detection
 International Journal of Image and Data Fusion ISSN: 1947-9832 (Print) 1947-9824 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tidf20 Remotely sensed images and GIS data fusion for automatic
International Journal of Image and Data Fusion ISSN: 1947-9832 (Print) 1947-9824 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tidf20 Remotely sensed images and GIS data fusion for automatic
Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results
 ALOS 2008 Symposium, 3-7 November Rhodes, Greece Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results Thomas Esch*, Achim Roth*, Michael Thiel, Michael Schmidt*,
ALOS 2008 Symposium, 3-7 November Rhodes, Greece Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results Thomas Esch*, Achim Roth*, Michael Thiel, Michael Schmidt*,
The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing
 The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing 1. Picking the right imagery 1 2. Accessing imagery 1 3. Processing steps 1 a. Geocorrection 2 b. Processing Landsat images layerstacking 4 4. Landcover classification
The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing 1. Picking the right imagery 1 2. Accessing imagery 1 3. Processing steps 1 a. Geocorrection 2 b. Processing Landsat images layerstacking 4 4. Landcover classification
Automatic post-classification land cover change detection in Landsat images: Analysis of changes in agricultural areas during the Syrian crisis
 Automatic post-classification land cover change detection in Landsat images: Analysis of changes in agricultural areas during the Syrian crisis DIRK TIEDE 1, FRITJOF LÜTHJE 1, ANDREA BARALDI 2 Within the
Automatic post-classification land cover change detection in Landsat images: Analysis of changes in agricultural areas during the Syrian crisis DIRK TIEDE 1, FRITJOF LÜTHJE 1, ANDREA BARALDI 2 Within the
'Developments and benefits of hydrographic surveying using multispectral imagery in the coastal zone
 Abstract With the recent launch of enhanced high-resolution commercial satellites, available imagery has improved from four-bands to eight-band multispectral. Simultaneously developments in remote sensing
Abstract With the recent launch of enhanced high-resolution commercial satellites, available imagery has improved from four-bands to eight-band multispectral. Simultaneously developments in remote sensing
Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images
 Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images Petra PHILIPSON and Frida ANDERSSON, Sweden Key words: remote sensing, high resolution, hydrographic survey, depth estimation. SUMMARY The
Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images Petra PHILIPSON and Frida ANDERSSON, Sweden Key words: remote sensing, high resolution, hydrographic survey, depth estimation. SUMMARY The
Some elements of photo. interpretation
 Some elements of photo Shape Size Pattern Color (tone, hue) Texture Shadows Site Association interpretation Olson, C. E., Jr. 1960. Elements of photographic interpretation common to several sensors. Photogrammetric
Some elements of photo Shape Size Pattern Color (tone, hue) Texture Shadows Site Association interpretation Olson, C. E., Jr. 1960. Elements of photographic interpretation common to several sensors. Photogrammetric
SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA
 SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA A.M.Ramiya a, Rama Rao Nidamanuri a, R Krishnan a Dept. of Earth and Space Science, Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram,Kerala
SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA A.M.Ramiya a, Rama Rao Nidamanuri a, R Krishnan a Dept. of Earth and Space Science, Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram,Kerala
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field
 Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
