Endodontic Considerations in Traumatized Teeth รศ ป ทมา ช ยเล ศวณ ชก ล
|
|
|
- Britney Randall
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endodontic Considerations in Traumatized Teeth รศ ป ทมา ช ยเล ศวณ ชก ล
2
3
4 Prevalence of dental injuries Permanent dentition (50%<15 yr) Boys (12-33%) Girls (4-19%) Andreasen 1972
5 Incidence Most common 8-12 yr Bicycle, skateboard, playground or sport accident Maxillary central incisor is the most vulnerable (80%) Followed by maxillary lateral, mandibular central & lateral
6 Etiology Child physical abuse (Non-accidental injuries, NAI)
7 Falls & Collisions Sports Etiology
8 Automobile Injuries Assaults
9 Torture Mental retard Epilepsy Drug-related injuries Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
10 Mechanism of dental injuries Direct Trauma Indirect Trauma
11 Examination 1.Patient history How did the injury occur? Wheredidtheinjuryoccur? When did the injury occur? Has there been previous injury to the teeth? Is there any disturbance in the bite?
12 1.Patient history Examination Is there any reaction in the teeth to cold and/or heat? Has there been any treatment before? Time is essential because it affects prognosis Storage medium for avulsed tooth
13 2.Clinical examination Chief complaint Neurologic examination External examination Intraoralsofttissueexamination Examination of hard tissue Mobility testing Percussion testing Thermal & Electrometric testing
14 Cold test: The most effective CO 2 snow = F or 78 C Difluorodichlormethane =-85 F or -50 C
15 Laser doppler flowmetry (LDF)
16 3.Radiographic exam Soft tissue Periapical bisecting angle exposure of each tramatized tooth Occlusal radiographic exposure of the traumatized region Necessary to take x-ray from 3 different angles ( ) in root fracture
17 Radiographic examination
18 Classification Injuries to the hard dental tissue & the pulp Injuries to the periodontal tissue Injury to the supporting bone Injury to gingiva & oral mucosa
19 Classification of injuries to dental tissue & pulp Enamel infraction/ fracture Crown fracture without pulpal involvement Crown fracture with pulpal involvement FRACTURE Crown-root fracture Root fracture (rarely in immature teeth)
20 Classification of injuries to dental tissue & pulp Concussion Subluxation Extrusive luxation Lateral luxation Intrusive luxation Avulsion LUXATE Soft tissue injury & fracture of alveolar bone
21 Problems (Fracture) Calcification Pulp necrosis Color changed Apical periodontitis
22 Problems (Luxate) Calcification Pulp necrosis Color changed Apical periodontitis Loss of epithelial attachment Ankylosis
23
24 Luxation Apical neurovascular Cementum PDL Revascularize Necrosis Inflammation Obliteration Infected pulp Uninfected necrotic pulp Inflam root resorp Surface root resorp
25 Enamel infraction Incomplete fracture of enamel without enamel defect (crack) Polish or observe
26 Enamel fracture / Uncomplicated crown fracture Restore with CR
27 Prognosis Pulpal complications are extremely rare. Occur 0.1%
28 Complicated crown fracture Treatment plan dependd on Stage of development of the tooth Time between the accident & treatment Concomitant attachment damage Restoration treatment plan
29 Complicated crown fracture Complete root formation Pulpectomy Incomplete root formation Vital Apexogenesis Nonvital Apexification
30 Apexogenesis Small exposure Pulp capping Large exposure Partial pulpotomy
31 Pulp p capping Success relies on the ability of Ca(OH) 2 & enamel-boned CR. Prognosis: approximately 80%
32 Partial pulpotomy Cvek Pulpotomy Indication; zone of inflam pulp has extended >2 mm in the apical direction but has not reached the root pulp A traumatic exposure a few days post-injury in a large, young pulp
33 Partial pulpotomy Technique; A 1-2 mm deep cavity by sterile diamond bur with water cooling (high speed) If bleeding is excessive, the pulp is amputated deeper until only moderate is seen
34 Partial pulpotomy
35 Partial pulpotomy Follow up; maintenance of positive sensitivity test & x- ray check root development. Prognosis; 94-96%
36 Pulpectomy Indication; complicated crown fracture of mature teeth Prognosis; 90%
37 Crown fracture combined with luxation
38 Treatment plan Pulp WNL ; restoration Nonresponse to EPT after few months; close apex : RCT open apex : Apexification
39 Apexification A: Ca(OH) 2 B: Cotton pellet C: IRM D: Tissue barrier
40 Apexification Non-vital pulp therapy Immature tooth Prognosis; periapical healing & formation of a hard-tissue barrier can occur predictably 79-96%.
41 Crown-root root fracture Margin above gum level Margin under gum level: Intra-alveolar transplantation Orthodontic extrusion
42 Margin above gum level Removal of loose tooth fragment Reattachment of the tooth fragment RCT with calcium hydroxide
43 Reattachment of fragment
44 Intra-alveolar alveolar transplantation Simple Extrusion & rotation Failure Limited to round-shaped roots
45 At least 4 mm of sound tooth structure should be preserved coronal to alveolar margin 2 mths
46 Orthodontic extrusion Gingiva & alveolar bone move: periodontal surgery is required
47 Root fracture Treatment plan depend on Position of the tooth Mobility of the tooth Status of the pulp Positionofthefractureline
48 Root fracture Deep fracture Repositioning & semirigid splint for 3-4 wk Clinical & radiographic exam Pulp necrosis & inflam of fracture sites RCT with Ca(OH) 2
49 Root fracture Shallow fracture & the remaining root is adequate to support a crown Extraction the crown Extrude the root RCT with Ca(OH) 2
50 Status of the pulp of root fracture Revascularization & reinnervation or not depend on Severity of trauma Healing capacity
51 Healing of root fractures Calcified tissue Reposition & splint to original position without irreversible pulpal injury Apposition of dentine inside the pulp & cementum outside the root
52 Healing of root fractures CNT Cannot reposition properly: blood clots in the fracture site Granulation tissue derived pulp or PDL invade to blood clot
53 Healing of root fractures CNT & bone Fracture occurs during eruption Wound heals by CNT Coronal continue to erupt Bone invades space between fragments
54 Healing of root fractures Granulation tissue without healing Result from pulp necrosis Clinical symptoms RCT Healing by CNT
55 Concussion/Subluxation Injury to periodontal tissue with (subluxation), without mobility (concussion) Chance vitality loss: 15% (pulp necrosis is rare in immature roots) Check occlusal interference, observe & check EPT
56 Subluxation Semi-rigid splint for 7-10 d Follow up Development of pulp necrosis: RCT with Ca(OH) 2
57 Prognosis of Subluxation Pulp necrosis 6-47 % Canal obliteration 10-26% Root resorption 4%
58 Extrusion Examination & diagnosis; it is important to know the stage of root formation because pulpal healing may occur in immature tooth
59 Extrusive luxation Semi-rigid splint for 3-4 wks
60 Extrusive luxation RCT with Ca(OH) 2
61 Prognosis of Extrusion Pulp necrosis 64 % External root resorption 7%
62 Lateral luxation Chance vitality loss: 75% (pulpal blood supply is usually completely severed) Semi-rigid splint for 3-4 wks
63 Lateral luxation RCT with Ca(OH) 2
64 Prognosis of Lateral luxation Pulp necrosis 77 % in mature tooth 58 % in immature tooth Pulp canal obliteration 33% External root resorption 36%
65 Intrusion The more extensive trauma involving multiple teeth & fracture of alveolar bone Extensivetraumato PDL & cementum
66 Treatment plan of Intrusion Administer anesthesia Surgical repositioning or transplantation of the intruded tooth
67 Intrusion Semi-rigid splint for 1-2 mths
68 Prognosis of Intrusion Pulp necrosis: mature tooth 100%: Ca(OH) 2 within 1-3 wks Highly occur in inflammatory external root resorption Recommend to prophylactic pulp extirpation in mature tooth
69 Patient Instructions Soft diet Brush teeth with a soft toothbrush after each meal Use of chlorhexidine mouthrinse (0.1%) twice a day for 2 wk Follow-up
70 Avulsion (Exarticulation) Incidence % in permanent dentition (fight & sport injuries) 7-13% in primary dentition (falls) Maxillary central incisors are the most frequently Occurs most often in 7-9 yr
71 Storage media Viaspan (tissue transplant media) HBSS (Hank s Balance salt sol.): Cell culture media; Save-A-Tooth TM (up to 12 h) Milk Normal Saline Tap water Saliva Dry (Not recommend)
72 Milk Practical Compatible osmolarlity Neutral ph Free of bacteria Essential nutrients
73 Milk Maintain vital PDL cells for 3 hr (Blomlof 1981) Sigalas et al.(2004) recommended iced low-fat milk Low-fat: maintain viability > higher fat content
74
75 Avulsion Closed apex Extra-oral dry time < 60 min Extra-oral dry time > 60 min Open apex Extra-oral dry time < 60 min Extra-oral dry time > 60 min
76 Closed apex < 60 min Gently cleansing of avulsed tooth & socket with NSS Replant immediately Semi-rigid splint for 1 wk
77 Preparation of the socket for gentle repositioning of the tooth Removed obstacles Light aspirate of blood clot is present Reposition
78 Management of soft tissues Suture Suture soft tissue lacerations, particularly in the cervical area
79 Closed apex > 60 min Replant is not indicated If replant is decided: Immerse the tooth in 2.4% NaF (ph 5.5) > 5 min Endo can be done extraorally Fill socket with Emdogain
80
81 Emdogain Enamel matrix proteins Compose of amelogenin & proteins (derived from porcine tooth buds) Important in development of acellular cementum, periodontal ligament & bone
82 Closed apex: Prescription Doxycycline 2x per d for 7 d Tetanus booster RCT after 7-10 d with Ca(OH) 2 Soft diet for 2 wk Chlorhexidine for 1 wk
83 Open apex < 60 mins Cleansing of avulsed tooth & socket with NaCl Place the tooth in doxycycline (1 mg/20 ml NaCl) Replant & Semi-rigid splint for 1 wk
84 Open apex < 60 mins No endodontic Rx initially If revascularization is a possibility avoid endodontic treatment unless obvious signs of failure are present.
85 Open apex > 60 mins Replant is not indicated Pen V 1000 mg & 500 mg 4x per d for 7 d or doxycycline 100 mg 2x per d for 7 d Tetanus booster Soft diet for 2 wk Chlorhexidine for 1 wk
86 Delayed replantation Ankylosis During growth & development: resorb < 2 yr After growth & development: resorb > 10 yr
87 When to FRC? Ca(OH) 2 can be replaced by gutta-percha when intact lamina dura can be traced around the entire root surface
88 Healing Depends on area of damaging Cementum repair ผ วรากฟ นถ ก ท าลาย < 20% Ankylosis ผ วรากฟ นถ กท าลาย > 20%
89 Traumatized teeth Crown fracture Crown-root fracture Root fracture Luxation Avulsion
90 Crown fracture Enamel infraction Uncomplicated crown fracture Complicated crown fracture Enamel fracture Enamel - dentin fracture Vital Non vital Corrective grinding Restoration with CR Reattachment of fragment Restoration with CR Restoration with veneer Restoration with CR Pulp capping Pulpotomy Pulpectomy Endodontic treatment Apexification Radiographic & sensitivity test 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Radiographic & sensitivity test 3 weeks, 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Routine recall evaluation
91 Crown - root fracture Fracture does not involve pulp Fracture involves pulp Gingivectomy & osteotomy Orthodontic extrusion Y Proper treatment N Restoration Radiographic & pulpal sensitivity test 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Endodontic treatment Gingivectomy & esteotomy Restoration Orthodontic extrusion Extracion Routine recall evaluation
92 Root fracture Remove coronal fracture ( located very close to gingiva) Endodontic treatment Gingivectomy & osteotomy Restoration Orthodontic extrustion Routine recall evaluation Reposition & splinting for 4-8 weeks ( fracture contaminate to oral fluid) Radiographic & senstivity test 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Within normal limit Endodontic treatment through tooth length Keep apical part inside Pulpal degenerative Endodontic treatment only coronal part Surgically remove apical part Extraction ( fracture contaminate to oral fluid & not restorable) Endodontic treatment only apical part Gingivectomy & osteotomy Orthodontic extrution Restoration Routine recall evaluation
93 Luxation Concussion Subluxation Extrusion Lateral luxation Intrusion Relief occlusion if necessary Same as concussion Reposition & splinting for CR (3-4 weeks) Same as extrusion Reposition & splinting for 4-8 weeks Spontaneous extrusion Orthodontic extrusion Radiographic & pulpal sensitivity test 3 weeks 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Radiographic & pulpal sensitivity test 3 weeks 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Radiographic & pulpal sensitivity test 3 weeks 3, 6, 12 months & yearly Radiographic & pulpal sensitivity test 3 weeks, 3, months & yearly Same as spontaneous extrusion
94 Closed apex Gentle washing with NSS Replant Splint for 1 week Endodontic treatment in 7-10 days Obturation after short term Ca (OH) 2 medication Extra - oral dry time <20 mins Endodontic treatment delay after 7-10 days Obturation after Ca(OH) 2 medication 6-20 months Open apex Soak in 1 mg doxycycline in 20 cc NSS for 5 mins rinse with NSS Replant Splint for 1 week Recall 3-4 weeks /visit Follow up twice per year for 5 years yearly after Avulsion Prepare socket Prepare the root Extra - oral dry time mins Closed & open apex Gentle washing with NSS Replant Splint for 1 week Closed apex (same as dry time < 20 mins) Open apex (same as dry time < 20 mins) Extra - oral dry time >60 mins Closed & open apex Soak in citric acid 5 mins & 2% stannous fluoride 5 mins Replant Splint for 1 week Close apex (same as dry time < 20 mins) Open apex Apexification Routine recall evaluation
95 Cracked tooth Clinical examination Oral examination Laboratory examination Radiographic Cracked line Staining Translumination Biting finding N N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Observe Observe Observe Observe Observe Orthodontic band or adhesive restoration Reversible pulpitis Restoration Irreversible pulpitis Endodontic treatment Restoration
96 Follow up Time 1 wk 2-3 wk 3-4 wk 6-8 wk 6 mth Concus/Sublux 1 yr 5 yr Extrusion Luxation Intrusion Avulsion Crown fracture Root fracture
97 Recommend readings Textbook & Color Atlas of Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth Treatment Plan for Traumatized Teeth
98 Recommend readings ฟ นได ร บอ บ ต เหต : การตรวจ ว น จฉ ย และร กษา
99
Dental-based Injuries
 Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
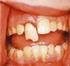 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy
 The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES
 International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY
 INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY CONSULTANT ENDODONTIST ROYAL CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MELBOURNE This article has been prepared on the basis that it may provide a useful aid for Dentists
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY CONSULTANT ENDODONTIST ROYAL CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MELBOURNE This article has been prepared on the basis that it may provide a useful aid for Dentists
Pediatric Dental Trauma. Acute Care Topics Mary Fox Braithwaite June 2008
 Pediatric Dental Trauma Acute Care Topics Mary Fox Braithwaite June 2008 Dental Injuries in Children Nearly 50% of children experience some type of dental injury during childhood, many of which are are
Pediatric Dental Trauma Acute Care Topics Mary Fox Braithwaite June 2008 Dental Injuries in Children Nearly 50% of children experience some type of dental injury during childhood, many of which are are
Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
 Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00592.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00592.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Replantation of Avulsed Permanent Anterior Teeth: A Case Report. Abu-Hussein Muhamad 1 *, Watted Nezar 2, and Abdulgani Azzaldeen 3. 1 Department of Pediatric
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth
 Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
Management of Avulsed Permanent Teeth Dr. Zuhair Al-Khatib Traumatic injuries to the teeth are so common among any community; trauma to the face especially to the oral region occurs frequently and comprises
Classification of dental trauma & management of dental avulsions
 Dr Tony Skapetis The University of Sydney Clinical Director Education WCOH Clinical Senior Lecturer University of Sydney [email protected] Classification of dental trauma & management of dental
Dr Tony Skapetis The University of Sydney Clinical Director Education WCOH Clinical Senior Lecturer University of Sydney [email protected] Classification of dental trauma & management of dental
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines
 Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
Treatment of traumatically intruded permanent incisor teeth in children. BSPD reviewed guidelines Albadri S, Zaitoun H, Kinirons MJ Introduction Traumatic intrusion is a luxation injury where the tooth
Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
 Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00592.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00592.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. I. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth
Dental traumatology: essential diagnosis and treatment planning
 Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 14 34 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Dental traumatology: essential diagnosis and treatment planning LEIF K.
Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 14 34 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Dental traumatology: essential diagnosis and treatment planning LEIF K.
Tooth avulsion-a Dental emergency in children: A Review
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Review Article Tooth avulsion-a Dental emergency in children: A Review Debapriya Pradhan 1, Prasant MC 2, Varsha H Tambe
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Review Article Tooth avulsion-a Dental emergency in children: A Review Debapriya Pradhan 1, Prasant MC 2, Varsha H Tambe
Apexogenesis after initial root canal treatment of an immature maxillary incisor a case report
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01645.x CASE REPORT Apexogenesis after initial root canal treatment of an immature maxillary incisor a case report S. R. Kvinnsland 1, A. Bårdsen 2 & I. Fristad 2 1 Clinic
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01645.x CASE REPORT Apexogenesis after initial root canal treatment of an immature maxillary incisor a case report S. R. Kvinnsland 1, A. Bårdsen 2 & I. Fristad 2 1 Clinic
Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth
 Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00605.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth Flores MT, Andersson
Dental Traumatology 2007; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2007.00605.x DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Guidelines Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries. II. Avulsion of permanent teeth Flores MT, Andersson
Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x QUALITY GUIDELINES Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology Abstract. Quality guidelines for endodontic
Multidisciplinary Approach to Delayed Treatment of Traumatic Teeth Injuries Involving Extrusive Luxation, Avulsion and Crown Fracture
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2014, 39-6, 566-571 Clinical Technique/Case Report Multidisciplinary Approach to Delayed Treatment of Traumatic Teeth Injuries Involving Extrusive Luxation, Avulsion and Crown Fracture
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2014, 39-6, 566-571 Clinical Technique/Case Report Multidisciplinary Approach to Delayed Treatment of Traumatic Teeth Injuries Involving Extrusive Luxation, Avulsion and Crown Fracture
ENDODONTICS. Colleagues for Excellence. The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Summer 2014 The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/colleagues
ENDODONTICS Colleagues for Excellence Summer 2014 The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries Published for the Dental Professional Community by the American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/colleagues
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE AVULSED TOOTH: PRESENT STRATEGIES and FUTURE DIRECTIONS
 Dental Traumatology 2002: 18: 1 11 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note After a year at the helm of Dental Traumatology I
Dental Traumatology 2002: 18: 1 11 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note After a year at the helm of Dental Traumatology I
Management of Dental Trauma in a Primary Care Setting
 Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care CLINICAL REPORT Management of Dental Trauma in a Primary Care Setting abstract The American Academy of Pediatrics and its Section on Oral Health have
Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care CLINICAL REPORT Management of Dental Trauma in a Primary Care Setting abstract The American Academy of Pediatrics and its Section on Oral Health have
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Chapter 15 ENDODONTIC CONSIDERATIONS IN DENTAL TRAUMA
 Chapter 15 ENDODONTIC CONSIDERTIONS IN DENTL TRUM Leif K. akland The outcome of traumatic events involving teeth depends on three factors: the extent of injury, the quality and timeliness of initial care,
Chapter 15 ENDODONTIC CONSIDERTIONS IN DENTL TRUM Leif K. akland The outcome of traumatic events involving teeth depends on three factors: the extent of injury, the quality and timeliness of initial care,
Emergency management of dental trauma
 Australasian Emergency Nursing Journal (2010) 13, 30 34 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aenj CLINICAL PRACTICE UPDATE Emergency management of dental trauma
Australasian Emergency Nursing Journal (2010) 13, 30 34 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aenj CLINICAL PRACTICE UPDATE Emergency management of dental trauma
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting
 Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Pediatric Dental Emergencies
 Pediatric Dental Emergencies 36th Annual Common Childhood Problems Conference Sujatha S. Sivaraman BDS, DMD May 16 th 2014 Disclosures: None Objectives Identify Dental Emergencies Best methods to address
Pediatric Dental Emergencies 36th Annual Common Childhood Problems Conference Sujatha S. Sivaraman BDS, DMD May 16 th 2014 Disclosures: None Objectives Identify Dental Emergencies Best methods to address
DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES
 DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2011 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic injuries to primary teeth Disclaimer: These
DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2011 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic injuries to primary teeth Disclaimer: These
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
An overview of classification of dental trauma
 Review Article An overview of classification of dental trauma Sasikala Pagadala 1*, Deepti Chaitanya Tadikonda 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department t of Periodontics, Nanded Rural Dental College and Research
Review Article An overview of classification of dental trauma Sasikala Pagadala 1*, Deepti Chaitanya Tadikonda 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department t of Periodontics, Nanded Rural Dental College and Research
Page 1 of 11 BDS FINAL PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2007 OPERATIVE DENTISTRY (MCQs) Model Paper
 Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
Page 1 of 11 Marks 45 Time 45 minutes Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each 01. Hand cutting instruments are composed of: A. Handle and neck. B. Handle and blade only. C. Handle, shank and blade. D. Handle,
DENTAL INJURIES IN 0-15 YEAR OLDS AT THE KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL, NAIROBI. H. M. MURIITHI, M. A. MASIGA and M. L.
 592 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL November 2005 East African Medical Journal Vol. 82 No. 11 November 2005 DENTAL INJURIES IN 0-15 YEAR OLDS AT THE KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL, NAIROBI H. M. Muriithi, BDS,
592 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL November 2005 East African Medical Journal Vol. 82 No. 11 November 2005 DENTAL INJURIES IN 0-15 YEAR OLDS AT THE KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL, NAIROBI H. M. Muriithi, BDS,
OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees
 OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees IN NETWORK: Staying in network saves you money. 1 Participating dentists have agreed to MetLife s negotiated fees which are typically 15% to 45% below the
OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees IN NETWORK: Staying in network saves you money. 1 Participating dentists have agreed to MetLife s negotiated fees which are typically 15% to 45% below the
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME
 CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
CRACKED TOOTH SYNDROME Dr Vijay Salvi We all come across apparently healthy teeth eliciting complex and often bizarre symptoms. The patient will give a long history of undiagnosed but severe pain, and
An Overview of Your Dental Benefits
 An Overview of Your Dental Benefits Educators Health Alliance ii \ DENTAL BENEFITS PPO Dental Plan Options OPTION 1 Maintenance Dentistry OPTION 2 (STANDARD PLAN) IN-NETWORK OUT-OF-NETWORK Maintenance
An Overview of Your Dental Benefits Educators Health Alliance ii \ DENTAL BENEFITS PPO Dental Plan Options OPTION 1 Maintenance Dentistry OPTION 2 (STANDARD PLAN) IN-NETWORK OUT-OF-NETWORK Maintenance
Humana Health Plans of Florida. Important:
 Humana Health Plans of Florida Important: Dental discount membership in Florida is determined by viewing the member s ID card and verifying that the Humana Logo and Medicare name is listed with an effective
Humana Health Plans of Florida Important: Dental discount membership in Florida is determined by viewing the member s ID card and verifying that the Humana Logo and Medicare name is listed with an effective
The Obvious and the Obscure:Diagnostic Steps for Crack Confirmation
 Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
Management of Traumatic Tooth Injuries in the Dental Office
 Management of Traumatic Tooth Injuries in the Dental Office John M. Coulter, D.D.S., O. Lee Wilson, D.M.D., Murray K. Marks, Ph.D. T D A EXAM #61 Introduction Pediatric and adult traumatic dental injuries
Management of Traumatic Tooth Injuries in the Dental Office John M. Coulter, D.D.S., O. Lee Wilson, D.M.D., Murray K. Marks, Ph.D. T D A EXAM #61 Introduction Pediatric and adult traumatic dental injuries
Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction
 1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
1 Complications Associated with Tooth Extraction Mark M. Smith, VMD, DACVS, DAVDC Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery 9041 Gaither Road Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Introduction Tooth extraction
TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS.
 TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS. The attached is a list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under
TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS. The attached is a list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under
Schedule B Indemnity plan People First Plan Code #4084
 : Calendar year deductible Waived for Type I preventive dental services Calendar year maximum Type I, II, III Waiting period Type I, II, III $50 individual $150 family (3 per family) $1,000 per covered
: Calendar year deductible Waived for Type I preventive dental services Calendar year maximum Type I, II, III Waiting period Type I, II, III $50 individual $150 family (3 per family) $1,000 per covered
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function!
 Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
www.iadt-dentaltrauma.org
 Current Treatment Options Of Guidelines of the International Association of tology Asgeir Sigurdsson, cand odont, MS Chairman of the Department of Endodontics NYU College of Dentistry Past President of
Current Treatment Options Of Guidelines of the International Association of tology Asgeir Sigurdsson, cand odont, MS Chairman of the Department of Endodontics NYU College of Dentistry Past President of
Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma
 Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Review Council Council on Clinical Affairs Adopted 2001 Revised 2004, 2007, 2010, 2011 Purpose The American
Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Review Council Council on Clinical Affairs Adopted 2001 Revised 2004, 2007, 2010, 2011 Purpose The American
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS
 RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
RESIDENT TRAINING GOALS AND OBJECTIVES STATEMENTS Evaluation and treatment of dental emergencies Recognize, anticipate and manage emergency problems related to the oral cavity. Differentiate between those
Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical Periodontitis: New Treatment Protocol?
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 CLINICAL RESEARCH Revascularization of Immature Permanent Teeth With Apical
Trauma in Young Permanent Teeth: Factors Associated with Adverse Outcomes. Ahmed Hosamuddin Rozi. A thesis. Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
 Trauma in Young Permanent Teeth: Factors Associated with Adverse Outcomes Ahmed Hosamuddin Rozi A thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry
Trauma in Young Permanent Teeth: Factors Associated with Adverse Outcomes Ahmed Hosamuddin Rozi A thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry
Periodontal surgery report for crown lengthening of tooth number 24,25
 411 PDS Periodontal surgery report for crown lengthening of tooth number -Course director : Dr. Nahid Ashri - instructor: Dr.Fatin Awaratani - - Student Name: Hanadi Alyami Computer Number: K S U - D E
411 PDS Periodontal surgery report for crown lengthening of tooth number -Course director : Dr. Nahid Ashri - instructor: Dr.Fatin Awaratani - - Student Name: Hanadi Alyami Computer Number: K S U - D E
[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location
![[PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location](/thumbs/31/14971568.jpg) Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
Eddie Stephens//Copywriter Sample: Website copy/internal Dental Services Pages [PAGE HEADLINE] Improve your Health and Change Your Smile with Complete Dental Services in One [CITYNAME] Location [LEAD SENTENCE/PARAGRAPH]
A collection of pus. Usually forms because of infection. A tooth or tooth structure which is responsible for the anchorage of a bridge or a denture.
 Abscess A collection of pus. Usually forms because of infection. Abutment A tooth or tooth structure which is responsible for the anchorage of a bridge or a denture. Amalgam A silver filling material.
Abscess A collection of pus. Usually forms because of infection. Abutment A tooth or tooth structure which is responsible for the anchorage of a bridge or a denture. Amalgam A silver filling material.
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care. Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203
 Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
Preventive Pediatric Dental Care Lawrence A. Kotlow DDS Practice Limited to Pediatric Dental Care 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Patient comfort and safety 1. All children are treated using the
Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury: its prospects and limitations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.68 Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury:
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.68 Use of ultrasound Doppler to determine tooth vitality in a discolored tooth after traumatic injury:
Chapter 10--Endodontics
 Overview --Endodontics Introduction The following material is presented to help orient the clinician to sound endodontic principles recommended by the IHS Endodontic Consultants. The contents represent
Overview --Endodontics Introduction The following material is presented to help orient the clinician to sound endodontic principles recommended by the IHS Endodontic Consultants. The contents represent
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of. the procedure.
 Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Postendodontic Tooth Restoration - Part I: The Aim and the Plan of the Procedure Sanja egoviê 1 Nada GaliÊ 1 Ana Davanzo 2 Boæidar PaveliÊ 1 1 Department of Dental Pathology School of Dental Medicine University
Extrusive Luxation and Lateral Luxation
 NDR15 1/3/07 6:23 PM Page 411 15 Extrusive Luxation and Lateral Luxation F. M. Andreasen & J. O. Andreasen Definition Extrusive luxation (peripheral dislocation, partial avulsion) Partial displacement
NDR15 1/3/07 6:23 PM Page 411 15 Extrusive Luxation and Lateral Luxation F. M. Andreasen & J. O. Andreasen Definition Extrusive luxation (peripheral dislocation, partial avulsion) Partial displacement
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
ARTICLE 20-03 DENTAL ASSISTANTS CHAPTER 20-03-01 DUTIES
 ARTICLE 20-03 DENTAL ASSISTANTS Chapter 20-03-01 Duties CHAPTER 20-03-01 DUTIES Section 20-03-01-01 Duties 20-03-01-01.1 Expanded Duties of Registered Dental Assistants 20-03-01-02 Prohibited Services
ARTICLE 20-03 DENTAL ASSISTANTS Chapter 20-03-01 Duties CHAPTER 20-03-01 DUTIES Section 20-03-01-01 Duties 20-03-01-01.1 Expanded Duties of Registered Dental Assistants 20-03-01-02 Prohibited Services
Top Extras dental schedule as at 1 September 2014
 Top Extras dental schedule as at 1 September 2014 Item Description Benefit Service limit Category Waiting 011 Comprehensive oral examination $41.00 1 per Preventive 2 months 012 Periodic oral examination
Top Extras dental schedule as at 1 September 2014 Item Description Benefit Service limit Category Waiting 011 Comprehensive oral examination $41.00 1 per Preventive 2 months 012 Periodic oral examination
SECURITY LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF AMERICA Minnetonka, Minnesota
 SECURITY LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF AMERICA Minnetonka, Minnesota COVERAGE SCHEDULE PREFERRED (In-Network) PROVIDER: WE WILL PAY BASED ON THE CONTRACTED FEE FOR SERVICE WITH THE PREFERRED PROVIDER ORGANIZATION
SECURITY LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY OF AMERICA Minnetonka, Minnesota COVERAGE SCHEDULE PREFERRED (In-Network) PROVIDER: WE WILL PAY BASED ON THE CONTRACTED FEE FOR SERVICE WITH THE PREFERRED PROVIDER ORGANIZATION
LANAP. (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
 LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
LANAP (Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure) Marcus Hannah, DDS 970 N. Kalaheo Avenue, Suite A305 Kailua, HI 96734 Tel: 808.254.5454 Fax: 808.254.5427 Dental Laser ANAP Informed Consent and Authorization
A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN):
 A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN): AS EARLY AS THE SECOND MONTH OF FETAL LIFE, THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH MAY FIRST BECOME EVIDENT. 1. Dental lamina and Bud stage At about six
A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN): AS EARLY AS THE SECOND MONTH OF FETAL LIFE, THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH MAY FIRST BECOME EVIDENT. 1. Dental lamina and Bud stage At about six
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES
 DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
DENTAL ASSISTING CATEGORIES EFFECTIVE JANUARY 1, 2010 Starting January 1, 2010, the dental assisting scope of practice will include new duties and two new specialty permits in orthodontics and dental sedation
Libyan general dentists knowledge of dental trauma management
 International Dental & Medical Journal of Advanced Research (2015), 1, 1 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Libyan general dentists knowledge of dental trauma management Marwa Hatem, Elsanousi M. Taher Department of Oral
International Dental & Medical Journal of Advanced Research (2015), 1, 1 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Libyan general dentists knowledge of dental trauma management Marwa Hatem, Elsanousi M. Taher Department of Oral
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Informed Consent for the Orthodontic Patient As a general rule, positive orthodontic results can be achieved by informed and cooperative patients. Thus, the following information
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract.
 Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
Teeth and Dental Implants: When to save, and when to extract. One of the most difficult decisions a restorative dentist has to make is when to refer a patient for extraction and placement of dental implants.
Anatomic Anomalies. Anomalies. Anomalies. Anomalies. Supernumerary Teeth. Supernumerary Teeth. Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 srs2@columbia.
 Anatomic Anomalies Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 [email protected] Anomalies! Anomalies are variations in the:! Size! Morphology! Number! Eruption of the teeth Anomalies Anomalies There are two categories:!
Anatomic Anomalies Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 [email protected] Anomalies! Anomalies are variations in the:! Size! Morphology! Number! Eruption of the teeth Anomalies Anomalies There are two categories:!
A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University
 Aetna Dental presents A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University CODE CODE Office Visit Copay $5 DIAGNOSTIC CROWNS/BRIDGES D0120 Exam-Periodic No Charge D2510 Inlay, Metallic, One surface $225 D0150
Aetna Dental presents A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University CODE CODE Office Visit Copay $5 DIAGNOSTIC CROWNS/BRIDGES D0120 Exam-Periodic No Charge D2510 Inlay, Metallic, One surface $225 D0150
Bone augmentation procedure without wound closure
 THE CREATION OF ATTACHED GINGIVA IMMEDIATELY AFTER EXTRACTION Bone augmentation procedure without wound closure One of the characteristics of wound healing after an extraction is that the alveolar process
THE CREATION OF ATTACHED GINGIVA IMMEDIATELY AFTER EXTRACTION Bone augmentation procedure without wound closure One of the characteristics of wound healing after an extraction is that the alveolar process
Communication Task - Scenario 1 CANDIDATE COPY
 Communication Task - Scenario 1 Your patient is 30 years old, and has presented today complaining of pain from the lower right posterior side. The tooth had been cold sensitive for several weeks, but the
Communication Task - Scenario 1 Your patient is 30 years old, and has presented today complaining of pain from the lower right posterior side. The tooth had been cold sensitive for several weeks, but the
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079)
 Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
A single visit, multidisciplinary approach to the management of traumatic tooth crown fracture C. P.K. Wadhwani, 1
 A single visit, multidisciplinary approach to the management of traumatic tooth crown fracture C. P.K. Wadhwani, 1 PRACTICE An immediate restorative technique resolving the acute problem of traumatic tooth
A single visit, multidisciplinary approach to the management of traumatic tooth crown fracture C. P.K. Wadhwani, 1 PRACTICE An immediate restorative technique resolving the acute problem of traumatic tooth
CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT. Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System. Patient Care Goals
 University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
J. O. Andreasen 1, F. M. Andreasen 1, I. Mejàre 2, M. Cvek 1 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University
 Dental Traumatology 2004; 20: 203 211 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Healing of 400 intra-alveolar root fractures. 2. Effect of treatment
Dental Traumatology 2004; 20: 203 211 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY Healing of 400 intra-alveolar root fractures. 2. Effect of treatment
Anthem Blue Dental PPO Plan
 Anthem Blue Dental PPO Plan For Individuals and Families Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield 700 Broadway Denver, Colorado 80273 anthem.com An independent licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association.
Anthem Blue Dental PPO Plan For Individuals and Families Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield 700 Broadway Denver, Colorado 80273 anthem.com An independent licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association.
Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team. Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia
 Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia The art of medicine Herodatus, a historian, described the medical art in Egypt: "The art of medicineis distributed thus:
Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia The art of medicine Herodatus, a historian, described the medical art in Egypt: "The art of medicineis distributed thus:
Secondary dentition permanent teeth - 32. Primary dentition deciduous teeth - 20
 Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
Dental Traumatology. Key words: consensus; fracture; luxation; review; trauma; tooth
 Delltal Traumatology 2012; 28: 2-12: do;: 10.11 I l/j.1600-9657.20 I 1.01 103.x Dental Traumatology International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries:
Delltal Traumatology 2012; 28: 2-12: do;: 10.11 I l/j.1600-9657.20 I 1.01 103.x Dental Traumatology International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries:
The extraction of teeth in Pets
 Ban0108_043-050 2/1/08 8:51 AM Page 43 Techniques for dental extractions Refined techniques allow practitioners to perform successful extractions and enhance a Pet s well-being. The extraction of teeth
Ban0108_043-050 2/1/08 8:51 AM Page 43 Techniques for dental extractions Refined techniques allow practitioners to perform successful extractions and enhance a Pet s well-being. The extraction of teeth
Rochester Regional Health. Dental Plan
 Rochester Regional Health Dental Plan TABLE OF CONTENTS EXPLANATION OF TERMS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 DENTAL BENEFITS... 5 DEDUCTIBLES AND COINSURANCE... 7 PRE-TREATMENT ESTIMATES... 8 LIMITATIONS... 8
Rochester Regional Health Dental Plan TABLE OF CONTENTS EXPLANATION OF TERMS... 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 DENTAL BENEFITS... 5 DEDUCTIBLES AND COINSURANCE... 7 PRE-TREATMENT ESTIMATES... 8 LIMITATIONS... 8
Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys 9 Miomir Cvek, DMS, PhD; Peter E. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, PhD; John C. Austin, 8VSc; and Jens
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Pulp reactions to exposure after experimental crown fractures or grinding in adult monkeys 9 Miomir Cvek, DMS, PhD; Peter E. Cleaton-Jones, BDS, PhD; John C. Austin, 8VSc; and Jens
