Onabotulinumtoxin in the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Headaches
|
|
|
- Charleen Maxwell
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Onabotulinumtoxin in the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Headaches While BoNTA shows promise in the management of chronic migraine, optimal outcomes will be acheived when clinicians learn which patients are most likely to benefit. By Michael J Marmura, MD For the majority of patients presenting for neurological evaluation of headaches, effective headache prophylaxis is the key to improved outcomes. Preventative treatments, however, are generally underutilized. 1 Indications for headache prophylaxis include frequent or very severe headaches, excessive acute medication use, severe disability, or patient preference. 2 Many effective prophylactic medications are associated with significant adverse events (AEs) and often take a few months to notice clinical improvement. In addition, some patients prefer to avoid daily medication, and patient compliance can be an issue. Onabotulinumtoxin A (BoNTA) is an attractive alternative headache prophylactic treatment for patients with headache. Clinicians usually perform BoNTA injections every three months, and pain relief typically begins in less than two weeks. Recent clinical trials demonstrate that BoNTA is effective in the treatment of chronic migraine (CM), 3,4 leading to an approval by the US Food and Drug administration of BoNTA (Onabotulinum toxin A, Botox, Allergan) for CM prophylaxis. There are many other reports of BoNTA and its use in other headache disorders such as tensionheadache, episodic migraine, cluster headache, and nummular headache. Mechanism of Action BoNTA has traditionally been used for disorders such as dystonia, which relate to an increase in muscle tone. BoNTA binds to nerve terminals, is endocytosed, and cleaves SNAP-25 protein. This inhibits the release of acetylcholine from nerve terminals and blocks neuromuscular transmission. Similar phenomena occur in parasympathetic and sensory neurons. 5 There are several large randomized controlled trials demonstrating the effectiveness of BoNTA in cervical dystonia and a few smaller studies that support its use in the treatment of neck pain. 6 Interestingly, many patients from these trials reported pain relief well before November/December 2010 Practical Neurology 27
2 any decrease in muscle tension. 7 Starting a few days after injection, BoNTA produces partial chemical denervation of the muscle, resulting in a localized reduction in muscle activity for months. BoNTA may have other distinct properties that lead to effectiveness in headache treatment. BoNTA administration appears to inhibit the release of glutamate and neuropeptides, such as substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), from nociceptive neurons. 8 Glumate and CGRP appear to be especially important in migraine pathogenesis. By blocking peripheral sensitization of nocioceptive fibers, BoNTA may also inhibit central sensitization and allodynia. 9 Finally, BoNTA appears to prevent the development of central sensization in trigeminal nucleus caudalis in animal models of CM. 10 BoNTA in the Prophylaxis of Episodic Migraine Multiple studies have evaluated the effect of BoNTA for prophylaxis of episodic migraine with mixed results. In a placebo-controlled trial with 123 patients, Silberstein et al. reported that a dose of only 25 units (U) injected into fixed glabellar, frontal and temporal sites decreased the number and severity of migraine attacks compared to placebo. A 75 unit dose to the same areas resulted in improved global assessment of change compared to placebo but otherwise was not significantly more effective. 11 In a study of 60 patients, Evers et al. found no significant difference between BoNTA 16 U, 100 U and placebo in the prevention of migraine or acute medication use. 12 Other studies have reported decreases in migraine days and acute medication use. 13 In the largest study of BoNTA for the treatment of episodic migraine, 389 patients were treated with BoNTA or placebo. The dose used in this study was relatively larger with a mean of 190(5) U (range, 110 U to 260 U) injected into multiple sites including frontalis, temporalis, occipitalis, trapezius, semispinalis, and splenius capitis. Patients were allowed to remain on their current acute and preventative medications. Using a goal of 50 percent improvement in headache days from Table 1. Indications for Headache Prophylaxis Frequent or very severe headaches Excessive acute medication use Severe disability Patient preference baseline, both the BoNTA and the placebo groups had a response rate greater than 50 percent, with no significant differences in the two groups. In the group with more frequent headaches (12 or more per month) BoNTA patients experienced significantly fewer headache episodes (mean of four less) over 180 days compared with 1.9 fewer days in the placebo group (P=0.048). Interestingly the placebo response rate in this study was comparable to response rates for standard migraine medications, such as topiramate or gabapentin. 15 The rate of discontinuation was only 1.9 percent, again much lower than most migraine preventative trials. 14 BoNTA in the Prophylaxis of Chronic Daily Headache and Chronic Migraine CM is a highly disabling form of chronic daily headache and the most common disorder seen in tertiary headache centers. 16 Patients with CM have headache at least 15 headache days per month and have headaches that meet criteria for migraine on at least eight of those days. 17 Most preventive medications for migraine, such as many beta-adrenergic blockers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, have not been rigorously studied for the treatment of CM. Several preliminary studies have evaluated the efficacy of BoTNA in the prophylaxis of chronic daily headache, which includes CM. In a randomized, placebo-controlled study, Silberstein 18 studied the efficacy and tolerability of BoNT-A for the prevention of CDH in 702 patients using a "fixed-site" protocol using doses of 75 U, 150 U, or 225 U with three BoNTA treatments over a nine-month period. Patients receiving the higher doses (150 U and 225 U) had had significantly fewer headache 28 Practical Neurology November/December 2010
3 days compared with those who received placebo. Despite the fact that 42 percent of patients met criteria for medication-overuse, these patients improved at a similar rate to the non-overusers. Mathew et al. 19 evaluated the effect of BoNT-A on 355 patients with chronic daily headache (CDH) in a randomized, placebo-controlled study using the "follow-the-pain" approach. Patients were injected three times at three-month intervals. Injections of BoNT-A were associated with a significant increase in headache-free days compared with placebo at day 180. Patients not taking other migraine preventatives actually had a greater decrease in headache frequency (7.8 vs 4.5 days/month) than those on preventatives. Injections of BoNTA non-significantly increased the number of headache-free days from baseline and decreased the use of acute pain medications more than placebo. The patients with chronic daily headache in these studies were often highly refractory to treatment as reflected by elevated disability scores and health-related quality of life indices. 20 Two recent, large, phase three multicenter studies, the PREEMPT 1 and 2 trials, have shown that BoNTA is an effective treatment for adults with CM. 21,22 These studies enrolled 1,384 subjects with CM in trials consisting of a 24-week, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase followed by a 32-week open-label phase. All subjects received at least a minimum dose of 155 units of BoNTA administered at 31 injection sites across seven head and neck muscles using a fixed-site, fixed-dose injection paradigm and up to extra 40 units into the temporalis, occipitalis, and/or trapezius using a modified follow-the-pain approach. (Table 2) The clinician performing the injections selected additional sites for injection based on pain location, muscle tenderness, and their personal judgment. Subjects receiving BoNTA in the doubleblind phase had statistically significant improvement from baseline after injection compared with placebo treatment in multiple clinical domains, including mean frequency of headache days and headache episodes. BoNTA-treated subjects also had fewer migraine episodes, fewer moderate or Table 2. Injection Sites for PREEMPT Study Muscle Injected Standard Dose Optional Sites Procerus 5 U (one site) Corrugator Frontalis Temporalis Cervical Paraspinals Occipitalis Trapezius Total 5 U each side (10 U) 15 U each side (30 U) 15 U each side (30 U) 155 U Up to 2 sites (10 U) Up to 2 sites (10 U) Up to 4 sites (20 U) Up to 40 U severe headache days than the placebo group. BoNTA subjects took similar amounts of acute medication but fewer triptans than controls. BoNTA treatment also significantly improved measures of disability and health-related quality of life. Based on the results of these two large randomized placebo-controls trials, the US Food and Drug Administration recently approved BoNTA for the treatment of CM. BoNTA in the Treatment of Other Headache Disorders BoNTA does not appear to be effective in the treatment of chronic tension-type headache (CTTH). Padeberg et al. injected 40 CTTH subjects demonstrating muscle tenderness using placebo or BoNTA with individualized sites and dosing in a double-masked design. 23 There were no significant differences between groups. A larger multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized study of BoNTA for the treatment of CTTH used doses of 50 U, 86 U, 100 U, or 150 U into multiple muscle groups including frontalis, sternocleidomastoid, upper trapezius, splenius capitis, and anterior temporalis. 24 BoNTA was not more effective in the primary outcome: number of tension-headache free days. November/December 2010 Practical Neurology 29
4 BoNTA may also be effective in less common headache disorders, but has not been established in controlled trials, mainly due to the fact that many of these disorders are rare. Nummular headache, a constant or remitting headache in a small circumscribed area such as an oval or elliptical shape, is often refractory to oral medications. A small case series of four patients with nummular headache reported significant improvement, lasting about 14 weeks, in all with a small dose of BoNTA (25 U). 25 Chronic cluster headache is another headache disorder that is often refractory to treatment. A recent open-label study of cluster headache used 50 units of BoNTA injected into the ipsilateral pericranial muscles of 12 patients. 26 Of the nine patients with chronic cluster headache, one had a cessation of attacks and two improved significantly. The other patients, including the three with episodic cluster headache, did not notice improvement. Other examples of using BoNTA for the treatment of headache include: occipital neuralgia improved with an injection of 50 units into the affected side at the site of the greater and lesser occipital nerves, 27 a case series of 24 patients with primary stabbing headache which improved with 5 U injections into each area of pain, 28 hemicrania continua, 29 and new daily persistent headache. Conclusions Injections using BoNTA appear to be a safe and effective treatment for the prophylaxis of chronic migraine and may be effective in other headache disorders as well. BoNTA offers a different approach to therapy for patients suffering from chronic migraine, including those in whom multiple oral preventative therapies have failed due to ineffectiveness or poor tolerability or in those with contraindications to other effective therapies. BoNTA also appears effective in CM patients with medication overuse. Despite achieving response rates equal to or greater than those of other migraine preventative agents, studies of BoNTA for the treatment of episodic migraine have been largely negative, probably due to a higher placebo response. Although the two recent CM trials used relatively higher doses, it is uncertain which dosing strategy and location of injections (fixed doses or follow-the-pain) is most effective. Based on earlier studies, it seems likely that smaller doses may be adequate for many patients. It is also worth noting that patients in clinical trials often remained on other preventative medications and continued to take acute medications. Finally, BoNTA is a fairly expensive treatment which requires special training to administer which may limit its use, so several studies have attempted to find factors that predict outcomes. Preliminary studies suggest women and those with unilateral headaches or allodynia are more likely to respond to BoNTA. In one sample of 63 patients, BoNTA responders were more likely to describe their headaches as pressure from the outside (imploding) or ocular pain, while non-responders were more likely to report exploding headache which builds up from the inside. 31 A relatively shorter duration of disease (less than 30 years) 32 and occasional headache free days before treatment 33 also appeared to predict improvement. Determining potential best responders before initiating treatment may lead to better outcomes. Michael J. Marmura, MD is Assistant Professor of Neurology at Thomas Jefferson University. 1. Lipton, R.B., Bigal, M.E., Diamond, M., Freitag, F., Reed, M.L., Stewart, W.F. Migraine prevalence, disease burden, and the need for preventive therapy. Neurology Jan 30;68(5): Dodick, D.W., Silberstein, S.D. Migraine prevention. Practical Neurology Nov;7(6): Aurora SK, Dodick DW, Turkel CC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial. Cephalalgia Jul;30(7): Diener HC, Dodick DW, Aurora SK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 2 trial. Cephalalgia Jul;30(7): Aoki KR, Guyer B. Botulinum toxin type A and other botulinum toxin serotypes; a comparative review of biochemical and pharmacological actions. Eur J Neurol 2001;8(suppl 5): Sycha T, Kranz G, Auff E, Schnider P. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of rare head and neck pain syndromes: a systematic review of the literature. J Neurol Feb;251 Suppl 1:I Brin MF. Botulinum toxin: chemistry, pharmacology, toxicity, and immunology. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1997;6:S146-S Aoki KR. Evidence for antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin Type A in pain management. Headache 2003;43(Suppl 3):S109-S Gazerani P, Staahl C, Drewes AM, Arendt-Nielsen L. The effects of Botulinum Toxin type A on 30 Practical Neurology November/December 2010
5 capsaicin-evoked pain, flare, and secondary hyperalgesia in an experimental human model of trigeminal sensitization. Pain Jun;122(3): Oshinsky ML. Botulinum toxins and migraine: how does it work. Pract Neurol. 2004(suppl): Silberstein SD, Mathew N, Saper J, Jenkins S. Botulinum toxin type A as a migraine preventive treatment: for the Botox Migraine Clinical Research Group. Headache. 2000;40(6): Evers S, Vollmer-Haase J, Schwaag S, Rahmann A, Husstedt IW, Frese A. Botulinum toxin A in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(10): Relja MA, Klepac N. Botulinum toxin type A reduces acute medication (triptans) use in migraine patients. Neurology. 2003;60(suppl):A Aurora SK, Gawel M, Brandes JL, Pokta S, Vandenburgh AM; BOTOX North American Episodic Migraine Study Group. Botulinum toxin type a prophylactic treatment of episodic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled exploratory study. Headache Apr;47(4): Silberstein SD, Neto W, Schmitt J, Jacobs D, for the MIGR-001 Study Group. Topiramate in migraine prevention: Results of a large controlled trial. Arch Neurol. 2004;61: Bigal ME, Serrano D, Reed M, Lipton RB. Chronic migraine in the population: burden, diagnosis, and satisfaction with treatment. Neurology Aug 19;71(8): Headache Classification Subcommitee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004; 24 (Suppl.1): Silberstein SD, Stark SR, Lucas SM; et al. Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylactic treatment of chronic daily headache: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80(9): Mathew NT, Frishberg BM, Gawel M, Dimitrova R, Gibson J, Turkel C, Botox CDH Study Group. Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) for the prophylactic treatment of chronic daily headache: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Headache. 2005;45(4): Silberstein SD, Marmura MJ, Shaw J, Yu S. Headache prophylaxis with BoNTA: patient characteristics. Headache prophylaxis with BoNTA: patient characteristics. 21. Aurora SK, Dodick DW, Turkel CC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial. Cephalalgia Jul;30(7): Diener HC, Dodick DW, Aurora SK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 2 trial. Cephalalgia Jul;30(7): Padberg M, de Bruijn SF, de Haan RJ, Tavy DL. Treatment of chronic tension-type headache with botulinum toxin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Cephalalgia.2004;24(8): Silberstein SD, Gobel H, Jensen R; et al. Botulinum toxin type A in the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Cephalalgia. 2006;26(7): Mathew NT, Kailasam J, Meadors L. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of nummular headache: four case studies. Headache Mar;48(3): Sostak P, Krause P, Förderreuther S, Reinisch V, Straube A. Botulinum toxin type-a therapy in cluster headache: an open study. J Headache Pain Sep;8(4): Kapural L, Stillman M, Kapural M, McIntyre P, Guirgius M, Mekhail N. Botulinum toxin occipital nerve block for the treatment of severe occipital neuralgia: a case series. Pain Pract Dec;7(4): Piovesan EJ, Teive HG, Kowacs PA, Silva LL, Werneck LC. Botulinum neurotoxin type-a for primary stabbing headache: an open study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr Apr;68(2): Garza I, Cutrer FM. Pain relief and persistence of dysautonomic features in a patient with hemicrania continua responsive to botulinum toxin type A. Cephalalgia Apr;30(4): Spears RC. Efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in new daily persistent headache. J Headache Pain Dec;9(6): Eross EJ, Gladstone JP, Lewis S; et al. Duration of migraine is a predictor for response to botulinum toxin type A. Headache. 2005;45(4): Conway S, Delplanche C, Crowder J, Rothrock J. Botox therapy for refractory chronic migraine. Headache. 2005;45(4): Jakubowski M, McAllister PJ, Bajwa ZH, Ward TN, Smith P, Burstein R. Exploding vs imploding headache in migraine prophylaxis with botulinum toxin A. Pain. 2006;125(3): Advertising Index Practical Neurology Vol. 9, No. 6 November/December 2010 Advertiser Page Avanir Pharmaceuticals Awareness Cadwell Laboratories Easy III Glaxosmithkline Lamictal Novartis Pharmaceuticals Gilenya For advertising inquiries please contact : Alan Guralnick Group Publisher aguralnick@bmctoday.com November/December 2010 Practical Neurology 31
WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel
 WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel Stovner, IHC 2009 New daily persistent headache Primair = dagelijkse and continue
WAT ALS HOOFDPIJN CHRONISCH WORDT? Prof Jan Versijpt, MD PhD Kliniek voor Hoofd- en Aangezichtspijn Neurologie, UZ Brussel Stovner, IHC 2009 New daily persistent headache Primair = dagelijkse and continue
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence. Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina
 Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
Neurotoxins and headache: A review of the evidence Alan G Finkel MD FAHS FAAN Carolina Headache Institute University of North Carolina Disclosures Allergan: Trainer 2010 present Glaxo Smith Kline: Speaker
PROCEEDINGS BOTULINUM TOXIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT * Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT
 BOTULINUM TOIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT Botulinum toxin type A has been studied for the treatment of headache disorders since the early 1990s when its usefulness for
BOTULINUM TOIN: PARADIGMS FOR TREATMENT Benjamin M. Frishberg, MD ABSTRACT Botulinum toxin type A has been studied for the treatment of headache disorders since the early 1990s when its usefulness for
Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia
 Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia David W. Dodick Professor Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic Phoenix Arizona, USA Onabotulinumtoxin A is the only botulinum toxin serotype
Botulinum Neurotoxin for Chronic Migraine and Trigeminal Neuralgia David W. Dodick Professor Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic Phoenix Arizona, USA Onabotulinumtoxin A is the only botulinum toxin serotype
Address all correspondence to A. Blumenfeld, Headache Center, The Headache Center of Southern CA, 320 Santa Fe Drive, Encinitas, CA 92024, USA.
 Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01766.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions Method of Injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA for Chronic
Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01766.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions Method of Injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA for Chronic
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine. Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15
 Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
Botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic migraine Gregory P. Hanes, MD Neuroscience Summit 5/14/15 Primary Headache Disorders: Frequency Classification After Secondary Causes Are Ruled Out Short-Duration
Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road?
 Acta Neurol. Belg., 2010, 110, 221-229 Review article Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road? Stephanie DELSTANCHE and Jean SCHOENEN Headache Research Unit.
Acta Neurol. Belg., 2010, 110, 221-229 Review article Botulinum toxin for the treatment of headache: a promising path on a dead end road? Stephanie DELSTANCHE and Jean SCHOENEN Headache Research Unit.
Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache?
 Sherif M. Hamdy et al. Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache? Sherif M. Hamdy 1, Hatem Samir 1, M. El-Sayed 1, Nermin Adel 1, Rasha Hassan 2 Department of
Sherif M. Hamdy et al. Botulinum Toxin: Could It Be An Effective Treatment For Chronic Tension Type Headache? Sherif M. Hamdy 1, Hatem Samir 1, M. El-Sayed 1, Nermin Adel 1, Rasha Hassan 2 Department of
Efficacy, safety, and predictors of response to botulinum toxin type A in refractory chronic migraine: A retrospective study
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 77 (2014) 10e15 Original Article Efficacy, safety, and predictors of response to botulinum toxin type
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 77 (2014) 10e15 Original Article Efficacy, safety, and predictors of response to botulinum toxin type
Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders
 Dermatol Clin 22 (2004) 167 175 Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders Andrew M. Blumenfeld, MD a, *, David W. Dodick, MD, FRCP(C), FACP b,c, Stephen D.
Dermatol Clin 22 (2004) 167 175 Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders Andrew M. Blumenfeld, MD a, *, David W. Dodick, MD, FRCP(C), FACP b,c, Stephen D.
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]
![BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required]](/thumbs/29/13417512.jpg) BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Migraine Headaches [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-RX-01-11 Original Effective Date: March 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies to products
botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd
 Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
Resubmission botulinum toxin type A, 50 unit, 100 unit and 200 unit powder for solution for injection (Botox ) SMC No. (692/11) Allergan Ltd 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
TITLE: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches in Adults: A Review of Clinical-Effectiveness and Safety
 TITLE: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches in Adults: A Review of Clinical-Effectiveness and Safety DATE: 28 July 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that causes muscle paralysis
TITLE: Botulinum Toxin A for Headaches in Adults: A Review of Clinical-Effectiveness and Safety DATE: 28 July 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that causes muscle paralysis
Research Submissions. ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 Headache 21 American Headache Society ISSN 17-8748 doi: 1.1111/j.1526-461.21.1678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions OnabotulinumtoxinA for Treatment of Chronic Migraine: Pooled
Headache 21 American Headache Society ISSN 17-8748 doi: 1.1111/j.1526-461.21.1678.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submissions OnabotulinumtoxinA for Treatment of Chronic Migraine: Pooled
Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox:
 Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox: A Review of the Literature DIMA ROZEN, M.D. 1, AND JOYTI SHARMA, M.D. 2 Abstract Botulinum toxin has been shown to effectively treat several types of neurological
Treatment of Tension-Type Headache with Botox: A Review of the Literature DIMA ROZEN, M.D. 1, AND JOYTI SHARMA, M.D. 2 Abstract Botulinum toxin has been shown to effectively treat several types of neurological
OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1636-9 RESEARCH Open Access OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study Andrea Negro 1,2,6*, Martina Curto 2,3,4, Luana Lionetto 5, Dorotea
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1636-9 RESEARCH Open Access OnabotulinumtoxinA 155 U in medication overuse headache: a two years prospective study Andrea Negro 1,2,6*, Martina Curto 2,3,4, Luana Lionetto 5, Dorotea
Tension Type Headaches
 Tension Type Headaches Research Review by : Dr. Ian MacIntyre Physiotherapy for tension-type Headache: A Controlled Study P. Torelli, R. Jenson, J. Olsen: Cephalalgia, 2004, 24, 29-36 Tension-type headache
Tension Type Headaches Research Review by : Dr. Ian MacIntyre Physiotherapy for tension-type Headache: A Controlled Study P. Torelli, R. Jenson, J. Olsen: Cephalalgia, 2004, 24, 29-36 Tension-type headache
Onabotulinumtoxin A in the Treatment of Migraine Headache
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Jefferson Headache Center papers and presentations Jefferson Headache Center 1-1-2012 Onabotulinumtoxin A in the Treatment of Migraine
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Jefferson Headache Center papers and presentations Jefferson Headache Center 1-1-2012 Onabotulinumtoxin A in the Treatment of Migraine
Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches. William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P.
 Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P. Abstract Headaches are both a prevalent and disabling condition.
Natural Modality in the Treatment of Primary Headaches William S. Mihin, D.C. Catharine Helms, M.S. Michelle M. Anderson, M.S.N., F.N.P. Abstract Headaches are both a prevalent and disabling condition.
Will Botox help your migraines?
 Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
Will Botox help your migraines? In case you hadn t heard, Botox can now be used and potentially claimed on insurance for migraines. Surprising I know. You re probably wondering how will an injection of
Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 885 899 Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches Paul Winner, DO, FAAN a,b,* a Palm Beach Headache Center, Premiere Research Institute,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 885 899 Botulinum toxins in the treatment of migraine and tension-type headaches Paul Winner, DO, FAAN a,b,* a Palm Beach Headache Center, Premiere Research Institute,
Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network. Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine. Prepared by: Victoria Overland
 Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine Prepared by: Victoria Overland Date: To be considered at September 2012 PCN meeting 1. Purpose of the Review NICE
Review for NHS Surrey Prescribing Clinical Network Treatment: Botox for chronic migraine Prepared by: Victoria Overland Date: To be considered at September 2012 PCN meeting 1. Purpose of the Review NICE
Classification of Chronic Headache
 Chronic Headache Classification of Chronic Headache JMAJ 47(3): 112 117, 2004 Mitsunori MORIMATSU Professor, Department of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience, Yamaguchi University School of Medicine Abstract:
Chronic Headache Classification of Chronic Headache JMAJ 47(3): 112 117, 2004 Mitsunori MORIMATSU Professor, Department of Neurology and Clinical Neuroscience, Yamaguchi University School of Medicine Abstract:
New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine
 Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 20062006266742746Original ArticleA broader concept of chronic migrainej Olesen et al. BRIEF REPORT New appendix criteria open
Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 20062006266742746Original ArticleA broader concept of chronic migrainej Olesen et al. BRIEF REPORT New appendix criteria open
Views and Perspectives
 Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01764.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Views and Perspectives Defining the Pharmacologically Intractable Headache
Headache 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01764.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Views and Perspectives Defining the Pharmacologically Intractable Headache
Frequent headache is defined as headaches 15 days/month and daily. Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice
 DISEASE STATE REVIEW Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice Egilius L.H. Spierings, MD, PhD, Willem K.P. Mutsaerts, MSc Department of Neurology, Brigham and
DISEASE STATE REVIEW Course of Frequent/Daily Headache in the General Population and in Medical Practice Egilius L.H. Spierings, MD, PhD, Willem K.P. Mutsaerts, MSc Department of Neurology, Brigham and
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches
 BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
BOTOX Injection (Onabotulinumtoxin A) for Chronic Migraine Headaches [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores,
OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial
 Original Article OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial Cephalalgia 30(7) 793 803! International
Original Article OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial Cephalalgia 30(7) 793 803! International
Chronic daily headache
 Chronic daily headache Chronic daily headache (CDH) is defined as any headache syndrome affecting more than half of the month, i.e. a headache on more than 15 days per month. It is also known as daily
Chronic daily headache Chronic daily headache (CDH) is defined as any headache syndrome affecting more than half of the month, i.e. a headache on more than 15 days per month. It is also known as daily
Is Botox-A Effective For Headaches and Neck Pain?
 0008-3194/2006/263 270/$2.00/ JCCA 2006 The use of botulinum neurotoxin type A (Botox) for headaches: a case review Mia Oliver, BA, DC* Joanna MacDonald, BHK, DC* Moez Rajwani, DC** Chiropractic care is
0008-3194/2006/263 270/$2.00/ JCCA 2006 The use of botulinum neurotoxin type A (Botox) for headaches: a case review Mia Oliver, BA, DC* Joanna MacDonald, BHK, DC* Moez Rajwani, DC** Chiropractic care is
Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders
 J Neural Transm (2007) DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0832-3 Printed in The Netherlands Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders W. J. Schulte-Mattler, E. Leinisch Department
J Neural Transm (2007) DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0832-3 Printed in The Netherlands Evidence based medicine on the use of botulinum toxin for headache disorders W. J. Schulte-Mattler, E. Leinisch Department
Treatment of Chronic Migraine with Focus on Botulinum Neurotoxins
 Toxins 2015, 7, 2615-2628; doi:10.3390/toxins7072615 Review OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins Treatment of Chronic Migraine with Focus on Botulinum Neurotoxins Sara M. Schaefer
Toxins 2015, 7, 2615-2628; doi:10.3390/toxins7072615 Review OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins Treatment of Chronic Migraine with Focus on Botulinum Neurotoxins Sara M. Schaefer
Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series
 Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series L. Di Lorenzo 1, F. Di Stani 2, D. Santopadre 3, C. Foti 4 1 Department of Rehabilitation, Hospital G. Rummo, Benevento, Italy
Ultrasound guided onabotulinum injection in chronic migraine: a case series L. Di Lorenzo 1, F. Di Stani 2, D. Santopadre 3, C. Foti 4 1 Department of Rehabilitation, Hospital G. Rummo, Benevento, Italy
An impressive arsenal of medications and
 COMMON PROPHYLACTIC PRACTICES FOR CHRONIC DAILY HEADACHE * John F. Rothrock, MD ABSTRACT A variety of medications and treatment interventions, including antiepileptic drugs, tricyclic antidepressants,
COMMON PROPHYLACTIC PRACTICES FOR CHRONIC DAILY HEADACHE * John F. Rothrock, MD ABSTRACT A variety of medications and treatment interventions, including antiepileptic drugs, tricyclic antidepressants,
Introduction. Jean-Christophe Cuvellier 1 Frédéric Couttenier 2 Stéphane Auvin 1 Louis Vallée 1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The classifi cation of chronic daily headache in French children and adolescents: A comparison between the second edition of the International Classifi cation of Headache Disorders and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH The classifi cation of chronic daily headache in French children and adolescents: A comparison between the second edition of the International Classifi cation of Headache Disorders and
Treatment of migraine headache with botulinum toxin type A
 Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 11 (2003) 465 475 Treatment of migraine headache with botulinum toxin type A William J. Binder, MD, FACS a,b, *, Andrew Blitzer, DDS, MD, FACS c a Department of Head and Neck
Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 11 (2003) 465 475 Treatment of migraine headache with botulinum toxin type A William J. Binder, MD, FACS a,b, *, Andrew Blitzer, DDS, MD, FACS c a Department of Head and Neck
Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment
 Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine
 Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine Produced by Warwick Evidence Authors: Dr Pamela Royle, senior research fellow Dr Ewen
Evidence review group report: Botulinum toxin type A for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine Produced by Warwick Evidence Authors: Dr Pamela Royle, senior research fellow Dr Ewen
Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria
 Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01753.x C Sun-Edelstein 1, ME Bigal 2 & AM Rapoport
Chronic migraine and medication overuse headache: clarifying the current International Headache Society classification criteria doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01753.x C Sun-Edelstein 1, ME Bigal 2 & AM Rapoport
The Prevalence of Neck Pain in Migrainehead_1608
 1..5 Headache 2010 the Authors Journal compilation 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01608.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submission The Prevalence
1..5 Headache 2010 the Authors Journal compilation 2010 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01608.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Research Submission The Prevalence
Disclosures & Shameless Plug
 Duren Michael Ready, MD FAHS Director, Headache Clinic Scott & White Healthcare DMReady@medicine.tamhsc.edu Disclosures & Shameless Plug Family Physician UCNS Certified in Headache Medicine Just one blind
Duren Michael Ready, MD FAHS Director, Headache Clinic Scott & White Healthcare DMReady@medicine.tamhsc.edu Disclosures & Shameless Plug Family Physician UCNS Certified in Headache Medicine Just one blind
New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01647.x New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population E Kung 1, SJ Tepper 2, AM Rapoport 3, FD Sheftell 4 & ME Bigal 1,5 1 Department of Neurology, Albert Einstein
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01647.x New daily persistent headache in the paediatric population E Kung 1, SJ Tepper 2, AM Rapoport 3, FD Sheftell 4 & ME Bigal 1,5 1 Department of Neurology, Albert Einstein
The Chronification of Migraine
 The Chronification of Migraine Jennifer Bickel, MD Medical Director, Comprehensive Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Division of Neurology Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Missouri-Kansas
The Chronification of Migraine Jennifer Bickel, MD Medical Director, Comprehensive Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Division of Neurology Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Missouri-Kansas
33 % of whiplash patients develop. headaches originating from the upper. cervical spine
 33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code
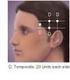 How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
How Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Reimbursed For Chronic Migraine? Impact Of FDA Approval And The New CPT Code Effective January 1, 2013, physicians will be able to report the new CPT code 64615 when performing
Chronic Headaches. David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015
 s David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015 Why is Headache Important? 36,000,000 people have migraine - more than asthma and diabetes combined 13,000,000 have chronic daily
s David R. Greeley, MD, FAAN Northwest Neurological, PLLC October 23, 2015 Why is Headache Important? 36,000,000 people have migraine - more than asthma and diabetes combined 13,000,000 have chronic daily
Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment
 Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Danish Headache Center Tension-type headache Non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment Lars Bendtsen Associate professor, MD, PhD, Dr Med Sci Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology Glostrup
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study
 Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study Background The training was based on the learning cycle of Kolb 1. According to this cycle effective
Appendix 1 (as supplied by the authors): Framework and content of the intervention of the LIMIT study Background The training was based on the learning cycle of Kolb 1. According to this cycle effective
HEADACHE. as. MUDr. Rudolf Černý, CSc. doc. MUDr. Petr Marusič, Ph.D.
 HEADACHE as. MUDr. Rudolf Černý, CSc. doc. MUDr. Petr Marusič, Ph.D. Dpt. of Neurology Charles University in Prague, 2nd Faculty of Medicine Motol University Hospital History of headache 1200 years B.C.
HEADACHE as. MUDr. Rudolf Černý, CSc. doc. MUDr. Petr Marusič, Ph.D. Dpt. of Neurology Charles University in Prague, 2nd Faculty of Medicine Motol University Hospital History of headache 1200 years B.C.
Procedural Treatment of Migraine
 Procedural Treatment of Migraine Matthew S Robbins, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine Chief of Neurology, Jack D. Weiler Hospital, Montefiore Medical Center
Procedural Treatment of Migraine Matthew S Robbins, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine Chief of Neurology, Jack D. Weiler Hospital, Montefiore Medical Center
Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x REVIEW Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults S Silberstein 1 (Chairman, USA), P Tfelt-Hansen 2 (Co-Chairman, Denmark),
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x REVIEW Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults S Silberstein 1 (Chairman, USA), P Tfelt-Hansen 2 (Co-Chairman, Denmark),
Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
 Brief Report Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study Cephalalgia 33(3) 202 207! International
Brief Report Prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study Cephalalgia 33(3) 202 207! International
When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache
 When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache Arnolda Eloff, MB, ChB, Mmed Presented at the University of Calgary s Wednesday Evening Course Program, Calgary, Alberta. Copyright Chronic daily
When the Pain Won t Stop: Managing Chronic Daily Headache Arnolda Eloff, MB, ChB, Mmed Presented at the University of Calgary s Wednesday Evening Course Program, Calgary, Alberta. Copyright Chronic daily
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain
 P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
P a g e 1 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS Evaluation of long-term opioid efficacy for chronic pain Clinical Phase 4 Study Centers Study Period 25 U.S. sites identified and reviewed by the Steering Committee and Contract
Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache
 REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will recognize the risk of developing medication overuse headache with increasing use of medications to treat acute migraine Stewart J. Tepper, MD * Center
REVIEW CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will recognize the risk of developing medication overuse headache with increasing use of medications to treat acute migraine Stewart J. Tepper, MD * Center
Migraine is one of the most prevalent
 Migraine is a common, incapacitating disorder that is underdiagnosed in clinical practice. Early and correct diagnosis of migraine is essential and can lead to significant improvements in a patient s quality
Migraine is a common, incapacitating disorder that is underdiagnosed in clinical practice. Early and correct diagnosis of migraine is essential and can lead to significant improvements in a patient s quality
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the UBC Headache Clinic Rotation
 UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the UBC Headache Clinic Rotation Overview: The UBC Headache Clinic is located in located in rm. 267, on the 2nd floor of UBC Hospital.
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the UBC Headache Clinic Rotation Overview: The UBC Headache Clinic is located in located in rm. 267, on the 2nd floor of UBC Hospital.
Diagnosing and treating episodic migraine
 D A N I S H H E A D A C H E C E N T E R Danish Headache Center Disclosures Diagnosing and treating episodic migraine M.A. is a consultant or scientific adviser for Allergan, Alder, Amgen, ATI, Bayer and
D A N I S H H E A D A C H E C E N T E R Danish Headache Center Disclosures Diagnosing and treating episodic migraine M.A. is a consultant or scientific adviser for Allergan, Alder, Amgen, ATI, Bayer and
Chronic daily headache is defined
 : Diagnosis and Management JOSEPH R. YANCEY, MAJ, MC, USA, Fort Belvoir Community Hospital, Fort Belvoir, Virginia RICHARD SHERIDAN, CPT, MC, USA, 1/25 Stryker Brigade Combat Team, Fort Wainwright, Alaska
: Diagnosis and Management JOSEPH R. YANCEY, MAJ, MC, USA, Fort Belvoir Community Hospital, Fort Belvoir, Virginia RICHARD SHERIDAN, CPT, MC, USA, 1/25 Stryker Brigade Combat Team, Fort Wainwright, Alaska
Cervicogenic Headache: A Review of Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies
 Cervicogenic Headache: A Review of Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies 1 Journal of the American Osteopathic Association April 2005, Vol. 105, No. 4 supplement, pp. 16-22 David M. Biondi, DO FROM ABSTRACT:
Cervicogenic Headache: A Review of Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies 1 Journal of the American Osteopathic Association April 2005, Vol. 105, No. 4 supplement, pp. 16-22 David M. Biondi, DO FROM ABSTRACT:
Migraine, Tension-type Headache, and Transformed Migraine
 Migraine, Tension-type Headache, and Transformed Migraine Mario F. P. Peres, MD, PhD, Andre Leite Gonçalves, MD, and Abouch Krymchantowski, MD, MSc, PhD Corresponding author Mario F. P. Peres, MD, PhD
Migraine, Tension-type Headache, and Transformed Migraine Mario F. P. Peres, MD, PhD, Andre Leite Gonçalves, MD, and Abouch Krymchantowski, MD, MSc, PhD Corresponding author Mario F. P. Peres, MD, PhD
POSTER PRESENTATIONS
 POSTER PRESENTATIONS POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following are based on posters presented at the 44th Annual Meeting of the American Headache Society, held June 21-23, 2002, in Seattle, Washington. TOPIRAMATE
POSTER PRESENTATIONS POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following are based on posters presented at the 44th Annual Meeting of the American Headache Society, held June 21-23, 2002, in Seattle, Washington. TOPIRAMATE
Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse Epidemiology and impact on quality of life. NEUROLOGY April, 2004;62:1338 1342
 Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse Epidemiology and impact on quality of life 1 NEUROLOGY April, 2004;62:1338 1342 R. Colás, MD; P. Muñoz, MD; R. Temprano, MD; C. Gómez, SW; and J. Pascual,
Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse Epidemiology and impact on quality of life 1 NEUROLOGY April, 2004;62:1338 1342 R. Colás, MD; P. Muñoz, MD; R. Temprano, MD; C. Gómez, SW; and J. Pascual,
Migraine and the greater occipital nerve
 Migraine and the greater occipital nerve What is the greater occipital nerve? The nerves that travel from your spine (in the neck) to the back of the head and scalp are known as the occipital nerves. There
Migraine and the greater occipital nerve What is the greater occipital nerve? The nerves that travel from your spine (in the neck) to the back of the head and scalp are known as the occipital nerves. There
Anesthesiology Pain Medicine
 KOWSAR Anesth Pain. 2012;2(1):5-11. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.6286 Anesthesiology Pain Medicine www.anesthpain.com Beyond Beauty: Onobotulinumtoxin A (BOTOX ) and the Management of Migraine Headaches Devra Becker
KOWSAR Anesth Pain. 2012;2(1):5-11. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.6286 Anesthesiology Pain Medicine www.anesthpain.com Beyond Beauty: Onobotulinumtoxin A (BOTOX ) and the Management of Migraine Headaches Devra Becker
Review of BTX-A in Neuropathic Pain Syndromes -
 Review of BTX-A in Neuropathic Pain Syndromes - Allan Gordon MD, FRCP(C) Wasser Pain Management Centre John and Josie Watson Pain Research and Education Centre Function and Pain Clinic Mount Sinai Hospital
Review of BTX-A in Neuropathic Pain Syndromes - Allan Gordon MD, FRCP(C) Wasser Pain Management Centre John and Josie Watson Pain Research and Education Centre Function and Pain Clinic Mount Sinai Hospital
Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments 2011; 15: 1401-1420 A. NEGRO, M. ROCCHIETTI-MARCH, M. FIORILLO, P. MARTELLETTI Department
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments 2011; 15: 1401-1420 A. NEGRO, M. ROCCHIETTI-MARCH, M. FIORILLO, P. MARTELLETTI Department
XXXXX Petitioner v File No. 121439-001. Issued and entered this 27 TH day of October 2011 by R. Kevin Clinton Commissioner ORDER
 In the matter of STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation XXXXX Petitioner
In the matter of STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation XXXXX Petitioner
Neurovascular Orofacial Pain. Orofacial pain of potential neurovascular origin may mimic odontogenic pain to the extent that
 Neurovascular Orofacial Pain Introduction Orofacial pain of potential neurovascular origin may mimic odontogenic pain to the extent that a large population of patients with migraine and trigeminal autonomic
Neurovascular Orofacial Pain Introduction Orofacial pain of potential neurovascular origin may mimic odontogenic pain to the extent that a large population of patients with migraine and trigeminal autonomic
Pain Management. Practical Applications in Electrotherapy
 Pain Management Practical Applications in Electrotherapy The TENS Advantage Deliver Immediate Pain Relief using a unique waveform designed to help prevent nerve accommodation. Manage Dynamic Pain by adjusting
Pain Management Practical Applications in Electrotherapy The TENS Advantage Deliver Immediate Pain Relief using a unique waveform designed to help prevent nerve accommodation. Manage Dynamic Pain by adjusting
Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug fact box cannabis extract (Sativex) Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further
Version History. Previous Versions. Policy Title. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box Glatiramer Acetate Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields
SYNOPSIS. 2-Year (0.5 DB + 1.5 OL) Addendum to Clinical Study Report
 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Akuter Kopfschmerz. Till Sprenger, MD Neurologie USB
 Akuter Kopfschmerz Till Sprenger, MD Neurologie USB Disclosure I have consulted for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Mitsubishi Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Genzyme and Allergan. I have received compensation for
Akuter Kopfschmerz Till Sprenger, MD Neurologie USB Disclosure I have consulted for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Mitsubishi Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Genzyme and Allergan. I have received compensation for
Is All Headache Pain The Same? Diagnostic and Treatment Pearls
 Is All Headache Pain The Same? Diagnostic and Treatment Pearls Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic International Classification of Headache Disorders Second Edition Jan 2004 4 Primary Headache
Is All Headache Pain The Same? Diagnostic and Treatment Pearls Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic International Classification of Headache Disorders Second Edition Jan 2004 4 Primary Headache
The term chronic daily headache (CDH)
 Chronic daily headache represents a range of disorders characterized by the occurrence of long-duration headache 15 or more days per month. The classification of these disorders continues to undergo revision
Chronic daily headache represents a range of disorders characterized by the occurrence of long-duration headache 15 or more days per month. The classification of these disorders continues to undergo revision
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE
 HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
Lidocaine injection of pericranial myofascial trigger points in the treatment of frequent episodic tension-type headache
 Karadaş et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2013, 14:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lidocaine injection of pericranial myofascial trigger points in the treatment of frequent episodic tension-type
Karadaş et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2013, 14:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lidocaine injection of pericranial myofascial trigger points in the treatment of frequent episodic tension-type
Botulinum Toxins A and B
 DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
DRUG POLICY Botulinum Toxins A and B Policy Number: 2015D0017P Effective Date: 11/1/2015 Table of Contents Page Related Medical or Drug Policies: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders COVERAGE RATIONALE...
C 2 / C 3 N E RVE BLOCKS AND GREATER OCCIPITAL NERVE BLOCK IN CERV I C O G E N I C HEADACHE TREATMENT
 C 2 / C 3 N E RVE BLOCKS AND GREATER OCCIPITAL NERVE BLOCK IN CERV I C O G E N I C HEADACHE TREATMENT N u rten Inan, Aysegul Ceyhan, Levent Inan*, Ozlem Kavaklioglu, Alp Alptekin, Nurten Unal Ministry
C 2 / C 3 N E RVE BLOCKS AND GREATER OCCIPITAL NERVE BLOCK IN CERV I C O G E N I C HEADACHE TREATMENT N u rten Inan, Aysegul Ceyhan, Levent Inan*, Ozlem Kavaklioglu, Alp Alptekin, Nurten Unal Ministry
The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire (MIDAS)
 Continuing Medical Education 43 The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire () Pei-Hua Hung, Jong-Ling Fuh, and Shuu-Jiun Wang Abstract- Migraine is a recurring and disabling pain disorder
Continuing Medical Education 43 The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire () Pei-Hua Hung, Jong-Ling Fuh, and Shuu-Jiun Wang Abstract- Migraine is a recurring and disabling pain disorder
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment
 Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
One Day at a Time: When Headaches Become Chronic. Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD
 One Day at a Time: When Headaches Become Chronic Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD Disclosures Scientific/Medical Advisory Boards (since 10/12) Transcept Pharmaceuticals Chronic Headaches: Overview What is a chronic
One Day at a Time: When Headaches Become Chronic Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD Disclosures Scientific/Medical Advisory Boards (since 10/12) Transcept Pharmaceuticals Chronic Headaches: Overview What is a chronic
Headaches and Kids. Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital
 Headaches and Kids Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Overview Headache classifications and diagnosis Address common headache
Headaches and Kids Jennifer Bickel, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director of Headache Clinic Children s Mercy Hospital Overview Headache classifications and diagnosis Address common headache
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Histamine Desensitization Therapy NMP351 Effective Date*: June 2007 Updated: June 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Histamine Desensitization Therapy NMP351 Effective Date*: June 2007 Updated: June 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT
Headache - What is Your Migraine Size?
 Headache The Pharmacist s Role in Assessment & Peter Loewen, B.Sc.(Pharm), Pharm.D. Vancouver Hospital & Health Sciences Centre University of British Columbia ETC, Headache. Nan Quintin www.vhpharmsci.com
Headache The Pharmacist s Role in Assessment & Peter Loewen, B.Sc.(Pharm), Pharm.D. Vancouver Hospital & Health Sciences Centre University of British Columbia ETC, Headache. Nan Quintin www.vhpharmsci.com
Refractory Migraine: Definition, Diagnosis, Management
 Refractory Migraine: Definition, Diagnosis, Management Morris Levin, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Associate Professor of Psychiatry Dartmouth Medical School Co director, Dartmouth Headache Center
Refractory Migraine: Definition, Diagnosis, Management Morris Levin, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Associate Professor of Psychiatry Dartmouth Medical School Co director, Dartmouth Headache Center
Double-Blind Trial of Fluoxetine: Chronic Daily Headache and Migraine
 Double-Blind Trial of Fluoxetine: Chronic Daily Headache and Migraine Joel R. Saper, M.D., 1 Stephen D. Silberstein, M.D., 2 Alvin E. Lake III, Ph.D., 1 Marjorie E. Winters, R.N., B.S.N. 1 1 Michigan Head-Pain
Double-Blind Trial of Fluoxetine: Chronic Daily Headache and Migraine Joel R. Saper, M.D., 1 Stephen D. Silberstein, M.D., 2 Alvin E. Lake III, Ph.D., 1 Marjorie E. Winters, R.N., B.S.N. 1 1 Michigan Head-Pain
Neck pain in episodic migraine: premonitory symptom or part of the attack?
 Lampl et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:80 DOI 10.1186/s10194-015-0566-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neck pain in episodic migraine: premonitory symptom or part of the attack? Christian Lampl 1*,
Lampl et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:80 DOI 10.1186/s10194-015-0566-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neck pain in episodic migraine: premonitory symptom or part of the attack? Christian Lampl 1*,
Chronic migraine. Todd J Schwedt STATE OF THE ART REVIEW
 Chronic migraine Todd J Schwedt Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ 85054, USA Correspondence to: T J Schwedt Schwedt.todd@mayo.edu Cite this as: BMJ 2014;348:g1416 doi: 10.1136/bmj.g1416 ABSTRACT Chronic migraine
Chronic migraine Todd J Schwedt Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ 85054, USA Correspondence to: T J Schwedt Schwedt.todd@mayo.edu Cite this as: BMJ 2014;348:g1416 doi: 10.1136/bmj.g1416 ABSTRACT Chronic migraine
Botox treatment for chronic migraine
 University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
University Teaching Trust Botox treatment for chronic migraine Humphrey Booth Building Neurosciences 0161 206 2563 0161 206 2427 All Rights Reserved 2016. Document for issue as handout.. This information
Headache. Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic headache and implications for practice. Cervicogenic Headache. Cervicogenic Headache
 Headache Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic and implications for practice Deborah Falla Headache is a common complaint which only 1% of the population escape in their lifetimes The most common are the
Headache Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic and implications for practice Deborah Falla Headache is a common complaint which only 1% of the population escape in their lifetimes The most common are the
Migraine headaches affect over 35 million RECONSTRUCTIVE
 RECONSTRUCTIVE A Comparison of Outcome of Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Using a Constellation of Symptoms versus Botulinum Toxin Type A to Identify the Trigger Sites Mengyuan T. Liu, B.S. Bryan
RECONSTRUCTIVE A Comparison of Outcome of Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Using a Constellation of Symptoms versus Botulinum Toxin Type A to Identify the Trigger Sites Mengyuan T. Liu, B.S. Bryan
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis?
 Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
9/2/2010. Debbie Zajac has no conflict of interest to disclose.
 Management of Chronic Headaches: An Interdisciplinary Approach September 25, 2010 Deborah C. Zajac RN-BC Clinical Coordinator / IMATCH Program Debbie Zajac has no conflict of interest to disclose. Identify
Management of Chronic Headaches: An Interdisciplinary Approach September 25, 2010 Deborah C. Zajac RN-BC Clinical Coordinator / IMATCH Program Debbie Zajac has no conflict of interest to disclose. Identify
Chronic Migraine - Medication Overuse and Its Effect on Headache Frequencies
 An Update on the Management of Chronic Migraine Randolph W. Evans, MD In 1672, Thomas Willis provided the first description of chronic migraine (CM) when he reported the case of the philosopher, Anne,
An Update on the Management of Chronic Migraine Randolph W. Evans, MD In 1672, Thomas Willis provided the first description of chronic migraine (CM) when he reported the case of the philosopher, Anne,
Sporadic attacks of severe tension-type headaches may respond to analgesics.
 MEDICATIONS While we are big advocates of non-drug treatments, many people do require the use of medications to control headaches. Headache medications are divided into two categories. Abortive drugs are
MEDICATIONS While we are big advocates of non-drug treatments, many people do require the use of medications to control headaches. Headache medications are divided into two categories. Abortive drugs are
Version History. Previous Versions. Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author
 Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Version History Policy Title Drugs for MS.Drug facts box fampridine Version 1.0 Author West Midlands Commissioning Support Unit Publication Date Jan 2013 Review Date Supersedes/New (Further fields as required
Headache Medicine Core Curriculum
 Headache Medicine Core Curriculum Adopted by the United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties (UCNS) Board of Directors December 2005 2005 Table of Contents 1. Traditional Curriculum Components 3 A. Definition
Headache Medicine Core Curriculum Adopted by the United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties (UCNS) Board of Directors December 2005 2005 Table of Contents 1. Traditional Curriculum Components 3 A. Definition
