WEP WPA WPS :: INDEX : Introduction :
|
|
|
- Isabella Dickerson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WEP WPA WPS With clients Without clients :: INDEX : Introduction > Overview > Terms & Definitions [ Step 1 ] : Configuring the network interface [ Step 2 ] : Collecting the network info [ Step 3 ] : Capturing data [ Step 4 ] : Faking Authentication [ Step 5 ] : Sniffing for packets [ Step 6 ] : Forging & Injecting an ARP-Reply package [ Step 7 ] : Decrypting the IVs Introduction : This guide was created to demonstrate the encryption vulnerabilities of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). Breaking into a protected wireless network is illegal! The content and instructions contained herein are for educational purposes, only. I did not break the law when creating this example. All information in the screenshots is that of my own networks that I compromised for this demonstration. You may attempt the steps outlined at your own risk - on your own network. If you wish to hack an other wireless network you must get permission from the network owner. Breaking a WEP key involves using network monitoring software to capture weak IVs (initialization vectors) and a cracking software to decrypt them. The software we will be using in this guide is the aircrack-ng suite that is included with Backtrack linux. There are several flavors of linux that come with this software including Auditor, Backtrack, and Kali linux. In this guide we will be using Backtrack 5 R3. Generally, the idea is to use your wireless adapter to capture any weak IVs being sent to/from the Access Point. We capture these IVs by intercepting and relaying ARP requests to the Access Point causing it to reply with more IVs. Once enough data (IVs) has been collected it can be decrypted using the Aircrack-ng software to display the wep key in plain text. This guide will explain how all of this takes place and outline the steps involved in a successful hack.
2 [Intro] - Overview : In this scenario we are targetting a WEP encrypted network with open authentication that has no active clients connected. Of the two possible scenarios - this one is the most challenging as some routers may have additional security or unusual configurations that may prevent this method from working (such as MAC address filtering, or if the Access Point is not broadcasting any packets). In this scenario we are making 3 assumptions : (1) You've got Backtrack running properly. (2) The target network is using WEP (open). (3) There are no clients connected to the Access point. The lesson to be learned from this demonstration is that WEP should be avoided whenever possible. Instead you should use WPA-PSK with a strong password consisting of both letters AND numbers. [Intro] - Terms & Definitions : There are a few terms used throughout this guide that are important to know when beginning the processes. Aircrack-ng MAC Address Access Point BSSID ESSID Channel Network Interface Client / Station Capture ARP Request IV A set of tools included with Backtrack. Includes aircrack, airodump, aireplay, airdecap, airolib. A unique combination of letters/numbers assigned as a "permanent" identifier to network hardware. The technical term for the "Router" or "Gateway". Also referred to as a "WAP". The MAC Address of the Access Point. The Broadcast name of the Access Point. The frequency at which data is being broadcast. The device used to send/receive data. Example : wlan0 or mon0. A computer/device connected/associated to an Access point. The process/data that is collected when monitoring an Access point with Airodump. Is a packet sent to/from the router/client in an to establish or maintain a connection. "Initialization Vectors" are packets that contain a small encrypted portion of the wep key. - Throughout this guide the terms Client and Station will be used interchangeably as they refer to the same thing. - The terms Password and Key will also be used interchangeably as they too mean the same thing.
3 [Step 1] - Configuring the network interface : - When executing commands in the terminal it is necessary to declare which network interface you would like to use. - You can retrieve a list of available interfaces by entering the iwconfig command with no parameters. The Interface names will be listed in the left column. - Your wireless interface will be identified as an "IEEE " device. possible examples : wlan0, wlan1 or rausb0. - In this scenario we will need to know the MAC address of our network interface to associate with the Access Point. - We can locate the MAC address using the ifconfig command. The MAC address will be listed in the top line. Make note of this MAC address. - To configure our network interface we must set it to "monitor mode" using the iwconfig command. iwconfig mode monitor mode monitor Sets the network interface to monitor mode. iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor
4 - If you receive an error stating that the device is busy then you will have to turn it off first using the ifconfig command. If so, you will also have to turn the device back on again after setting it to monitor mode. ifconfig down ifconfig up - If you are unable to put your device into monitor mode using the iwconfig command - you can also try using the airmon-ng command. - Using airmon-ng will usually create a new device / interface to monitor traffic with. It's often named mon0. - In most cases iwconfig works just fine and it doesn't create any additional interfaces but airmon-ng will usually work when iwconfig does not. airmon-ng start airmon-ng start wlan0 [Step 2] - Collecting the network info : - To perform the attack we must first gather a bit of information about the network. Everything we need can be collected using the airodump-ng command. - The required information includes: The BSSID (MAC Address of the target Access Point). The ESSID (Name of the Access Point). The Channel that the Access Point is broadcasting on. - After collecting the necessary information - you can terminate the airodump command by pressing Ctrl+C on the keyboard. - As you'll see in the see in the image below - Our selected target is using WEP which is vulnerable to our attack. airodump-ng airodump-ng wlan0
5 [Step 3] - Capturing data : - Now that we have the required information - we can lock in on the Access Point and start capturing data. - This step also uses the airodump-ng command however we will add some parameters so that it saves traffic to a file. - The first parameter to specify is the channel. This is done with the -c [Channel] parameter. - The next parameter to specify is the output filename. This is done with the -w [Filename] parameter. - Another parameter we will use is the --ivs parameter. This tells airodump only to save the IVs in our capture. - This will display the same output as it did before but will be focused on a specified channel and will also save any traffic to our capture file. - The capture file automatically appends a number to the filename as well as a.ivs extension. mycapture-01.ivs - This command should be kept running in the background while you complete the next steps. Do not terminate it. airodump-ng -c [Channel] -w [Filename] --ivs -c The channel the Access Point is broadcasting on. -w The output filename to write to. --ivs Save IVs to file. airodump-ng -c 11 -w mycapture --ivs wlan0
6 [Step 4] - Faking Authentication : - To create our ARP request packet we must fake authentication & association to the Access Point. - We will do this using another aireplay-ng (-1) command in a new shell / tab. - Upon submitting the command - the shell should respond with a message stating that the authentication & association was successful. - If it is not successful it could possibly be due to the way the Access Point is configured (example: mac address filtering). aireplay-ng e [ESSID] -a [BSSID] -h [Your MAC] -1 "fake authentication" attack mode. 0 Just once. -e ESSID (name) of target network. -a BSSID (MAC Address) of target network. -h Your MAC Address. aireplay-ng e homenetwork -a 10:9F:A9:F4:F6:81 -h 00:22:75:3C:7E:26 wlan0
7 [Step 5] - Sniffing for packets : - Now that we are authenticated & associated - we must intercept any packets coming from the Access Point. - In this example we will be using a fragmentation attack (-5) with the aireplay-ng command to create our own ARP packet. We will do this by intercepting a packet from the Access Point and returning it in fragments in an attempt to retreive enough keystream to create our ARP packet. - This command should be started in a new shell / tab as we will need to leave it running. Do not terminate it. - Upon finding a usable packet - your listening aireplay-ng (-5) command will fragment and return the packets to gather keystream from the Access Point. - It will save the keystream as a.xor file and display the file name in your shell. - If you are unable to find any packets - you can try running the another fake authentication attack (-1) to re-associate with the Access Point. aireplay-ng -5 -b [BSSID] -h [Your MAC] -5 "Fragmentation" attack mode. -b BSSID (MAC Address) of target network. -h Your MAC Address. aireplay-ng -5 -b 10:9F:A9:F4:F6:81 -h 00:22:75:3C:7E:26 wlan0
8 [Step 6] - Forging & Injecting an ARP-Reply Package : - Using the.xor file we saved - we can create an ARP-Reply package and inject it to the network to stimulate the flow of IVs. - This is performed using 2 separate commands. We will use packetforge-ng to create our ARP request packet and aireplay-ng (-2) to inject it. packetforge-ng -0 -a [BSSID] -h [Your MAC] -w [ARP filename] -y [filename.xor] -k l a BSSID (MAC Address) of target network. -h Your MAC Address. -w Output file name for ARP package. Can be anything. -y Filename of generated.xor file. -k l packetforge-ng -0 -a 10:9F:A9:F4:F6:81 -h 00:22:75:3C:7E:26 -w arp-request -y fragment xor -k l Upon creating our ARP request packet we can inject it into the network using the aireplay-ng (-2) command : aireplay-ng -2 -r [ARP filename] -2 -r ARP Packet filename created with the packetforge-ng command. aireplay-ng -2 -r arp-request wlan0
9
10 [Step 7] - Decrypting the IVs : - After we have collected enough IVs we can begin decrypting the collected data. Usually about k is good for a 128 Bit wep key. 64 bit will work with much less. - We will crack the key using the aircrack-ng command. - Instead of specifying an exact number in the filename we will use a wildcard * (asterisk) to read all of our captured data. This is useful if you've ran airodump more than once resulting in multiple.ivs files. aircrack-ng -e [ESSID] [Filename] -e ESSID (name) of target network. [Filename] The output file name created with the airodump-ng command. aircrack-ng -e homenetwork mycapture*.ivs - In this example - my computer decrypted the 128-bit WEP key with just 50,000 IVs. - The recovered password / key is : FF7CBB65FFBF6596E5BAD7656A. Copyright 2014 QuickFix PEI
WEP WPA WPS :: INDEX : Introduction :
 WEP WPA WPS With clients Without clients :: INDEX : Introduction > Overview > Terms & Definitions [ Step 1 ] : Configuring the network interface [ Step 2 ] : Collecting the network info [ Step 3 ] : Capturing
WEP WPA WPS With clients Without clients :: INDEX : Introduction > Overview > Terms & Definitions [ Step 1 ] : Configuring the network interface [ Step 2 ] : Collecting the network info [ Step 3 ] : Capturing
MITM Man in the Middle
 MITM Man in the Middle Wifi Packet Capturing and Session Hijacking using Wireshark Introduction The main Objective of this Attack is to make a Fake Access point and send the fake ARP Packets on same Wi-Fi
MITM Man in the Middle Wifi Packet Capturing and Session Hijacking using Wireshark Introduction The main Objective of this Attack is to make a Fake Access point and send the fake ARP Packets on same Wi-Fi
WiFi Security Assessments
 WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
WiFi Security Assessments Robert Dooling Dooling Information Security Defenders (DISD) December, 2009 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Table of Contents
Wireless LAN Pen-Testing. Part I
 Wireless LAN Pen-Testing Part I To know your Enemy, you must become your Enemy (Sun Tzu, 600 BC) Georg Penn 23.03.2012 Motivation Read manuals, documentation, standards Check sources for their reliability,
Wireless LAN Pen-Testing Part I To know your Enemy, you must become your Enemy (Sun Tzu, 600 BC) Georg Penn 23.03.2012 Motivation Read manuals, documentation, standards Check sources for their reliability,
Kali Linux Cookbook. Willie L. Pritchett David De Smet. Chapter No. 9 "Wireless Attacks"
 Kali Linux Cookbook Willie L. Pritchett David De Smet Chapter No. 9 "Wireless Attacks" In this package, you will find: A Biography of the authors of the book A preview chapter from the book, Chapter NO.9
Kali Linux Cookbook Willie L. Pritchett David De Smet Chapter No. 9 "Wireless Attacks" In this package, you will find: A Biography of the authors of the book A preview chapter from the book, Chapter NO.9
ALEXANDRE BORGES BLOG
 Cracking WEP Networks Author: Alexandre Borges Date: FEB/20/2014 Revision: 1.0 ALEXANDRE BORGES BLOG When I ve published the first document about Cracking Wireless Networks (http://alexandreborgesbrazil.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/cracking_wireless.pdf)
Cracking WEP Networks Author: Alexandre Borges Date: FEB/20/2014 Revision: 1.0 ALEXANDRE BORGES BLOG When I ve published the first document about Cracking Wireless Networks (http://alexandreborgesbrazil.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/cracking_wireless.pdf)
Wireless Network Security. Pat Wilbur Wireless Networks March 30, 2007
 Wireless Network Security Pat Wilbur Wireless Networks March 30, 2007 Types of Attacks Intrusion gain unauthorized access to a network in order to use the network or Internet connection Types of Attacks
Wireless Network Security Pat Wilbur Wireless Networks March 30, 2007 Types of Attacks Intrusion gain unauthorized access to a network in order to use the network or Internet connection Types of Attacks
WEP Overview 1/2. and encryption mechanisms Now deprecated. Shared key Open key (the client will authenticate always) Shared key authentication
 WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
WLAN Security WEP Overview 1/2 WEP, Wired Equivalent Privacy Introduced in 1999 to provide confidentiality, authentication and integrity Includes weak authentication Shared key Open key (the client will
S-38.2131/3133 Networking Technology, laboratory course A/B
 A! Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering Department of Communications and Networking S-38.2131/3133 Networking Technology, laboratory course A/B Student edition Anni Matinlauri, 3.1.2007 Tuomas
A! Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering Department of Communications and Networking S-38.2131/3133 Networking Technology, laboratory course A/B Student edition Anni Matinlauri, 3.1.2007 Tuomas
Wireless Encryption Protection
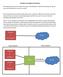 Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
Wireless Encryption Protection We re going to jump around a little here and go to something that I really find interesting, how do you secure yourself when you connect to a router. Now first and foremost
0) What is the wpa handhake?
 We have already seen how easy it is with time and the right tools to get the WEP key of any wireless network. We have already explained that these operations are not lawful but for pure interest and personal
We have already seen how easy it is with time and the right tools to get the WEP key of any wireless network. We have already explained that these operations are not lawful but for pure interest and personal
Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks. By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary
 Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary The evolution to wireless networks allows connections with the same quality of data transfer at a lower cost but
Methodology: Security plan for wireless networks By: Stephen Blair Mandeville A. Summary The evolution to wireless networks allows connections with the same quality of data transfer at a lower cost but
Vulnerabilities of Wireless Security protocols (WEP and WPA2)
 Vulnerabilities of Wireless Security protocols (WEP and WPA2) Vishal Kumkar, Akhil Tiwari, Pawan Tiwari, Ashish Gupta, Seema Shrawne Abstract - Wirelesses Local Area Networks (WLANs) have become more prevalent
Vulnerabilities of Wireless Security protocols (WEP and WPA2) Vishal Kumkar, Akhil Tiwari, Pawan Tiwari, Ashish Gupta, Seema Shrawne Abstract - Wirelesses Local Area Networks (WLANs) have become more prevalent
Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication and firewall captive portal
 EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 00029 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800029 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication
EPJ Web of Conferences 68, 00029 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20146800029 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 Building secure wireless access point based on certificate authentication
Wifi Penetration. Wireless Communication and Computer/Network Forensics
 Wifi Penetration Wireless Communication and Computer/Network Forensics Terms Skiddy(Derogatory): Variant of "Script Kiddy". Hacker(Derogatory):One who builds something. Cracker(Derogatory):One who breaks
Wifi Penetration Wireless Communication and Computer/Network Forensics Terms Skiddy(Derogatory): Variant of "Script Kiddy". Hacker(Derogatory):One who builds something. Cracker(Derogatory):One who breaks
 If security were all that mattered, computers would never be turned on, let alone hooked into a network with literally millions of potential intruders. Dan Farmer, System Administrators Guide to Cracking
If security were all that mattered, computers would never be turned on, let alone hooked into a network with literally millions of potential intruders. Dan Farmer, System Administrators Guide to Cracking
Network Attacks. Common Network Attacks and Exploits
 Common and Exploits AGENDA A Few Observations Hacker Resources Attack Categories Some Common Attacks Wireless Specific Attacks Wireless Observations Because of Common Network Layers, Most of the Attacks
Common and Exploits AGENDA A Few Observations Hacker Resources Attack Categories Some Common Attacks Wireless Specific Attacks Wireless Observations Because of Common Network Layers, Most of the Attacks
WIRELESS SECURITY TOOLS
 WIRELESS SECURITY TOOLS Johanna Janse van Rensburg, Barry Irwin Rhodes University [email protected], [email protected] (083) 944 3924 Computer Science Department, Hamilton Building, Rhodes University
WIRELESS SECURITY TOOLS Johanna Janse van Rensburg, Barry Irwin Rhodes University [email protected], [email protected] (083) 944 3924 Computer Science Department, Hamilton Building, Rhodes University
SSI. Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2. Bertil Maria Pires Marques. E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009. Dez 2009 1
 SSI Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2 Bertil Maria Pires Marques E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009 Dez 2009 1 WEP -Wired Equivalent Privacy WEPisasecurityprotocol,specifiedintheIEEEWireless Fidelity
SSI Commons Wireless Protocols WEP and WPA2 Bertil Maria Pires Marques E-mail: [email protected] Dez 2009 Dez 2009 1 WEP -Wired Equivalent Privacy WEPisasecurityprotocol,specifiedintheIEEEWireless Fidelity
WIRELESS SECURITY. Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program. Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006
 WIRELESS SECURITY Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Wireless LAN Security Learning Objectives Students should be able
WIRELESS SECURITY Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Wireless LAN Security Learning Objectives Students should be able
Offensive Security. Wireless Attacks - WiFu
 Offensive Security Wireless Attacks - WiFu v. 3.0 Mati Aharoni Devon Kearns Thomas d Otreppe de Bouvette Course Overview The wireless industry continues to grow in leaps and bounds with more and more gadgets
Offensive Security Wireless Attacks - WiFu v. 3.0 Mati Aharoni Devon Kearns Thomas d Otreppe de Bouvette Course Overview The wireless industry continues to grow in leaps and bounds with more and more gadgets
ECE 4893: Internetwork Security Lab 10: Wireless 802.11 Security
 Group Number: Member Names: Date Assigned: March 23, 2004 Date Due: March 30, 2004 Last Revised: March 22, 2004 ECE 4893: Internetwork Security Lab 10: Wireless 802.11 Security Goal: The goal of this lab
Group Number: Member Names: Date Assigned: March 23, 2004 Date Due: March 30, 2004 Last Revised: March 22, 2004 ECE 4893: Internetwork Security Lab 10: Wireless 802.11 Security Goal: The goal of this lab
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009. Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected]
 802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
802.11 Security (WEP, WPA\WPA2) 19/05/2009 Giulio Rossetti Unipi [email protected] 802.11 Security Standard: WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy The packets are encrypted, before sent, with a Secret Key
Capture and analysis of 802.11 wireless traffic
 Capture and analysis of 802.11 wireless traffic October 2012 Ver. 1.00 Copyright Connect One Ltd., 2008-2012 The information in this document is subject to change without notice and shall not be construed
Capture and analysis of 802.11 wireless traffic October 2012 Ver. 1.00 Copyright Connect One Ltd., 2008-2012 The information in this document is subject to change without notice and shall not be construed
United States Trustee Program s Wireless LAN Security Checklist
 United States Trustee Program s Wireless LAN Security Checklist In support of a standing trustee s proposed implementation of Wireless Access Points (WAP) in ' 341 meeting rooms and courtrooms, the following
United States Trustee Program s Wireless LAN Security Checklist In support of a standing trustee s proposed implementation of Wireless Access Points (WAP) in ' 341 meeting rooms and courtrooms, the following
Introduction on Low level Network tools
 Georges Da Costa [email protected] http: //www.irit.fr/~georges.da-costa/cours/addis/ 1 Introduction 2 Aircrack-ng 3 Wireshark Low level tools Hacking tools Aircrack-ng (ex Aircrack, ex Airsnort) WEP/WPA
Georges Da Costa [email protected] http: //www.irit.fr/~georges.da-costa/cours/addis/ 1 Introduction 2 Aircrack-ng 3 Wireshark Low level tools Hacking tools Aircrack-ng (ex Aircrack, ex Airsnort) WEP/WPA
Introduction to WiFi Security. Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected]
 Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
Introduction to WiFi Security Frank Sweetser WPI Network Operations and Security [email protected] Why should I care? Or, more formally what are the risks? Unauthorized connections Stealing bandwidth Attacks
Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms
 Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms Jingan Xu, Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Technical University of Ilmenau, Integrated Hard- and Software Systems Group [email protected], [email protected] Abstract.
Wireless LAN Security Mechanisms Jingan Xu, Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Technical University of Ilmenau, Integrated Hard- and Software Systems Group [email protected], [email protected] Abstract.
OSBRiDGE 5XLi. Configuration Manual. Firmware 3.10R
 OSBRiDGE 5XLi Configuration Manual Firmware 3.10R 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 5XLi devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP Address:
OSBRiDGE 5XLi Configuration Manual Firmware 3.10R 1. Initial setup and configuration. OSBRiDGE 5XLi devices are configurable via WWW interface. Each device uses following default settings: IP Address:
An Experimental Study Analysis of Security Attacks at IEEE 802.11 Wireless Local Area Network
 , pp. 9-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2015.8.1.02 An Experimental Study Analysis of Security Attacks at IEEE 802.11 Wireless Local Area Network 1 Md Waliullah, 2 A B M Moniruzzaman and 3 Md. Sadekur
, pp. 9-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2015.8.1.02 An Experimental Study Analysis of Security Attacks at IEEE 802.11 Wireless Local Area Network 1 Md Waliullah, 2 A B M Moniruzzaman and 3 Md. Sadekur
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics
 The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
The next generation of knowledge and expertise Wireless Security Basics HTA Technology Security Consulting., 30 S. Wacker Dr, 22 nd Floor, Chicago, IL 60606, 708-862-6348 (voice), 708-868-2404 (fax), www.hta-inc.com
Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list)
 Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list) Hackers can easily trap information transmitted over wireless network, it has to be encrypted to avoid unauthorized users
Configuring Wireless Security on ProSafe wireless routers (WEP/WPA/Access list) Hackers can easily trap information transmitted over wireless network, it has to be encrypted to avoid unauthorized users
WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you...
 WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you... Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity / [email protected]) Diego Sor ([email protected] / [email protected]) July 2010 Abstract Cisco access points
WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you... Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity / [email protected]) Diego Sor ([email protected] / [email protected]) July 2010 Abstract Cisco access points
Wireless Security: Secure and Public Networks Kory Kirk
 Wireless Security: Secure and Public Networks Kory Kirk Villanova University Computer Science [email protected] www.korykirk.com/ Abstract Due to the increasing amount of wireless access points that
Wireless Security: Secure and Public Networks Kory Kirk Villanova University Computer Science [email protected] www.korykirk.com/ Abstract Due to the increasing amount of wireless access points that
CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK
 CLASSROOM CHALLENGE CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK In this lesson you will learn how to connect the Raspberry Pi computer to a network with both a wired and a wireless connection. To complete
CLASSROOM CHALLENGE CONNECTING THE RASPBERRY PI TO A NETWORK In this lesson you will learn how to connect the Raspberry Pi computer to a network with both a wired and a wireless connection. To complete
Overview. Summary of Key Findings. Tech Note PCI Wireless Guideline
 Overview The following note covers information published in the PCI-DSS Wireless Guideline in July of 2009 by the PCI Wireless Special Interest Group Implementation Team and addresses version 1.2 of the
Overview The following note covers information published in the PCI-DSS Wireless Guideline in July of 2009 by the PCI Wireless Special Interest Group Implementation Team and addresses version 1.2 of the
Topics in Network Security
 Topics in Network Security Jem Berkes MASc. ECE, University of Waterloo B.Sc. ECE, University of Manitoba www.berkes.ca February, 2009 Ver. 2 In this presentation Wi-Fi security (802.11) Protecting insecure
Topics in Network Security Jem Berkes MASc. ECE, University of Waterloo B.Sc. ECE, University of Manitoba www.berkes.ca February, 2009 Ver. 2 In this presentation Wi-Fi security (802.11) Protecting insecure
PENETRATION TESTING ON A WIRELESS NETWORK.
 Bachelor s Thesis (TUAS) Degree Program: Information Technology Specialization: Internet Technology 2013 Gbolahan Ola PENETRATION TESTING ON A WIRELESS NETWORK. USING BACKTRACK 5 BACHELOR S THESIS ABSTRACT
Bachelor s Thesis (TUAS) Degree Program: Information Technology Specialization: Internet Technology 2013 Gbolahan Ola PENETRATION TESTING ON A WIRELESS NETWORK. USING BACKTRACK 5 BACHELOR S THESIS ABSTRACT
Analysis of Security and Penetration Tests for Wireless Networks with Backtrack Linux
 Analysis of Security and Penetration Tests for Wireless Networks with Backtrack Linux Renata Lopes Rosa, Demóstenes Zegarra Rodríguez, Gabriel Pívaro, Jackson Sousa Faculdade de Arquitetura e Urbanismo
Analysis of Security and Penetration Tests for Wireless Networks with Backtrack Linux Renata Lopes Rosa, Demóstenes Zegarra Rodríguez, Gabriel Pívaro, Jackson Sousa Faculdade de Arquitetura e Urbanismo
DV230 Web Based Configuration Troubleshooting Guide
 DV230 Web Based Configuration Troubleshooting Guide 1. Login settings After getting a DHCP IP address from your P1 W1MAX Modem DV-230), open any Internet browser and type in the URL address: http://10.1.1.254
DV230 Web Based Configuration Troubleshooting Guide 1. Login settings After getting a DHCP IP address from your P1 W1MAX Modem DV-230), open any Internet browser and type in the URL address: http://10.1.1.254
How To Secure A Wireless Network With A Wireless Device (Mb8000)
 MB8000 Network Security and Access Control Overview MB8000 employs almost all of the current popular WLAN security mechanisms. These include wireless-user isolation, closed system (by turning off SSID
MB8000 Network Security and Access Control Overview MB8000 employs almost all of the current popular WLAN security mechanisms. These include wireless-user isolation, closed system (by turning off SSID
Developing Network Security Strategies
 NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Developing Network Security Strategies NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Security Design The 12 Step Program 1. Identify network
NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Developing Network Security Strategies NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Security Design The 12 Step Program 1. Identify network
Penetration Testing Report. Client: xxxxxx Date: 19 th April 2014
 1. Executive Summary Penetration Testing Report Client: xxxxxx Date: 19 th April 2014 On the 19th of April, a security assessment was carried out on the internal networks of xxxxxx, with the permission
1. Executive Summary Penetration Testing Report Client: xxxxxx Date: 19 th April 2014 On the 19th of April, a security assessment was carried out on the internal networks of xxxxxx, with the permission
Wireless Security Overview. Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected]
 Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
Wireless Security Overview Ann Geyer Partner, Tunitas Group Chair, Mobile Healthcare Alliance 209-754-9130 [email protected] Ground Setting Three Basics Availability Authenticity Confidentiality Challenge
FinIntrusion Kit / Release Notes FINUSB SUITE SPECIFICATIONS. FINFISHER: FinIntrusion Kit 2.2 Release Notes
 1 FINFISHER: FinIntrusion Kit 2.2 Release Notes 2 Copyright 2011 by Gamma Group International, UK Date 2011-09-23 Release information Version Date Author Remarks 1.0 2010-06-29 ht Initial version 2.0 2011-05-26
1 FINFISHER: FinIntrusion Kit 2.2 Release Notes 2 Copyright 2011 by Gamma Group International, UK Date 2011-09-23 Release information Version Date Author Remarks 1.0 2010-06-29 ht Initial version 2.0 2011-05-26
LOHU 4951L Outdoor Wireless Access Point / Bridge
 LOHU 4951L Outdoor Wireless Access Point / Bridge Version 2.3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -1- Software setup and configuration
LOHU 4951L Outdoor Wireless Access Point / Bridge Version 2.3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -1- Software setup and configuration
THE 123 OF WIRELESS SECURITY AT HOME 家 居 WIFI 保 安 123
 THE 123 OF WIRELESS SECURITY AT HOME 家 居 WIFI 保 安 123 CONFIGURING YOUR HOME WIRELESS NETWORK Presented by: Mr. Eric Fan, Chairman, PISA Knowledge 123 Firmware 軟 韌 體 Knowledge 123 Home Network Functions
THE 123 OF WIRELESS SECURITY AT HOME 家 居 WIFI 保 安 123 CONFIGURING YOUR HOME WIRELESS NETWORK Presented by: Mr. Eric Fan, Chairman, PISA Knowledge 123 Firmware 軟 韌 體 Knowledge 123 Home Network Functions
WLAN Attacks. Wireless LAN Attacks and Protection Tools. (Section 3 contd.) Traffic Analysis. Passive Attacks. War Driving. War Driving contd.
 Wireless LAN Attacks and Protection Tools (Section 3 contd.) WLAN Attacks Passive Attack unauthorised party gains access to a network and does not modify any resources on the network Active Attack unauthorised
Wireless LAN Attacks and Protection Tools (Section 3 contd.) WLAN Attacks Passive Attack unauthorised party gains access to a network and does not modify any resources on the network Active Attack unauthorised
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network.
 9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
9 Simple steps to secure your Wi-Fi Network. Step 1: Change the Default Password of Modem / Router After opening modem page click on management - access control password. Select username, confirm old password
Wireless Pre-Shared Key Cracking (WPA, WPA2)
 Wireless Pre-Shared Key Cracking (WPA, WPA2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 2 Mechanics Of PSKs And How They Work Demystified... 2 How PSKs Can Be Cracked!... 5 WPA2 PSK Cracking Demonstration.... 6
Wireless Pre-Shared Key Cracking (WPA, WPA2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 2 Mechanics Of PSKs And How They Work Demystified... 2 How PSKs Can Be Cracked!... 5 WPA2 PSK Cracking Demonstration.... 6
Hacking. Aims. Naming, Acronyms, etc. Sources
 Free Technology Workshop Hacking Hands on with wireless LAN routers, packet capture and wireless security Organised by Steven Gordon Bangkadi 3 rd floor IT Lab 10:30-13:30 Friday 18 July 2014 http://ict.siit.tu.ac.th/moodle/.-----.-----.-----..----.
Free Technology Workshop Hacking Hands on with wireless LAN routers, packet capture and wireless security Organised by Steven Gordon Bangkadi 3 rd floor IT Lab 10:30-13:30 Friday 18 July 2014 http://ict.siit.tu.ac.th/moodle/.-----.-----.-----..----.
Kvaser BlackBird Getting Started Guide
 Kvaser BlackBird Getting Started Guide Copyright 2007-2011 Kvaser AB, Mölndal, Sweden http://www.kvaser.com Last updated Wednesday, 18 September 2013 We believe that the information contained herein was
Kvaser BlackBird Getting Started Guide Copyright 2007-2011 Kvaser AB, Mölndal, Sweden http://www.kvaser.com Last updated Wednesday, 18 September 2013 We believe that the information contained herein was
Some Tools for Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT)
 Some Tools for Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) AfNOG 12 30 th May 2011 10 th June 2011 Tanzania By Marcus K. G. Adomey Overview Some Unix Commands Some Selected Tools Snort AirSnort hping
Some Tools for Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) AfNOG 12 30 th May 2011 10 th June 2011 Tanzania By Marcus K. G. Adomey Overview Some Unix Commands Some Selected Tools Snort AirSnort hping
N600 WiFi USB Adapter
 Model WNDA3100v3 User Manual December 2014 202-11470-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the serial
Model WNDA3100v3 User Manual December 2014 202-11470-01 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products. After installing your device, locate the serial
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network
 Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
Chapter 3 Safeguarding Your Network The RangeMax NEXT Wireless Router WNR834B provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this chapter. This chapter includes: Choosing Appropriate
CYBERTRON NETWORK SOLUTIONS
 CYBERTRON NETWORK SOLUTIONS CybertTron Certified Ethical Hacker (CT-CEH) CT-CEH a Certification offered by CyberTron @Copyright 2015 CyberTron Network Solutions All Rights Reserved CyberTron Certified
CYBERTRON NETWORK SOLUTIONS CybertTron Certified Ethical Hacker (CT-CEH) CT-CEH a Certification offered by CyberTron @Copyright 2015 CyberTron Network Solutions All Rights Reserved CyberTron Certified
WAP3205 v2. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Wireless N300 Access Point. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 Edition 2, 10/2015
 WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 10/2015 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup Password www.zyxel.com 1234 Copyright 2014 ZyXEL
WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 10/2015 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup Password www.zyxel.com 1234 Copyright 2014 ZyXEL
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition. Chapter 6. Wireless Network Security
 Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition Chapter 6 Wireless Network Security Objectives Overview of IEEE 802.11 wireless security Define vulnerabilities of Open System Authentication,
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings
 Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
Chapter 2 Configuring Your Wireless Network and Security Settings This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your DG834N RangeMax TM NEXT Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router. For a wireless
Wireless LAN Security: Securing Your Access Point
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.6 No.5B, May 2006 173 Wireless LAN Security: Securing Your Access Point Sia Sie Tung, Nurul Nadia Ahmad, Tan Kim Geok Faculty
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.6 No.5B, May 2006 173 Wireless LAN Security: Securing Your Access Point Sia Sie Tung, Nurul Nadia Ahmad, Tan Kim Geok Faculty
Configuring Your Network s Security
 Configuring Your Network s Security Security is an important issue when using a wireless home network. Because radio waves are used to transfer information between your networked computers, it's possible
Configuring Your Network s Security Security is an important issue when using a wireless home network. Because radio waves are used to transfer information between your networked computers, it's possible
Access Point Configuration
 Access Point Configuration Developed by IT +46 Based on the original work of: Onno Purbo and Sebastian Buettrich Goals Provide a general methodology to installation and configuration of access points Give
Access Point Configuration Developed by IT +46 Based on the original work of: Onno Purbo and Sebastian Buettrich Goals Provide a general methodology to installation and configuration of access points Give
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i
 Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Chapter 6 CDMA/802.11i IC322 Fall 2014 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Some material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
12/3/08. Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks. Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability. Mobility Makes it Difficult to Establish Trust
 Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Security in Wireless LANs and Mobile Networks Wireless Magnifies Exposure Vulnerability Information going across the wireless link is exposed to anyone within radio range RF may extend beyond a room or
Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards
 White Paper Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards By Dr. Wen-Ping Ying, Director of Software Development, February 2002 Introduction Wireless LAN networking allows the
White Paper Key Hopping A Security Enhancement Scheme for IEEE 802.11 WEP Standards By Dr. Wen-Ping Ying, Director of Software Development, February 2002 Introduction Wireless LAN networking allows the
All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices
 Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
Wireless Security All vulnerabilities that exist in conventional wired networks apply and likely easier Theft, tampering of devices Portability Tamper-proof devices? Intrusion and interception of poorly
Authentication in WLAN
 Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Authentication in WLAN Flaws in WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Based on draft 3 of the IEEE 802.11i. Provides stronger data encryption and user authentication (largely missing
Project 3: Network Security
 EECS 388 February 18, 2016 Intro to Computer Security Project 3: Network Security Project 3: Network Security This project is due on Friday, March 11 at 6 p.m. and counts for 8% of your course grade. Late
EECS 388 February 18, 2016 Intro to Computer Security Project 3: Network Security Project 3: Network Security This project is due on Friday, March 11 at 6 p.m. and counts for 8% of your course grade. Late
LEARNING COMPUTER SYSTEMS VULNERABILITIES EXPLOITATION THROUGH PENETRATION TEST EXPERIMENTS
 1 LEARNING COMPUTER SYSTEMS VULNERABILITIES EXPLOITATION THROUGH PENETRATION TEST EXPERIMENTS Te-Shun Chou and Tijjani Mohammed Department of Technology Systems East Carolina University [email protected] Abstract
1 LEARNING COMPUTER SYSTEMS VULNERABILITIES EXPLOITATION THROUGH PENETRATION TEST EXPERIMENTS Te-Shun Chou and Tijjani Mohammed Department of Technology Systems East Carolina University [email protected] Abstract
Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract
 Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms
Securing your Linksys Wireless Router BEFW11S4 Abstract Current implementations of the 802.11b wireless LAN standards have several potential pitfalls for security. However, built in security mechanisms
Wireless Networks. Welcome to Wireless
 Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Wireless Networks 11/1/2010 Wireless Networks 1 Welcome to Wireless Radio waves No need to be physically plugged into the network Remote access Coverage Personal Area Network (PAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
White paper. Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points. http://www.veryxtech.com
 White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
White paper Testing for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in WLAN Access Points http://www.veryxtech.com White Paper Abstract Background The vulnerabilities spotted in the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm
Table of Contents. Cisco Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example
 Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Table of Contents Wi Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA 2) Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 67134...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Conventions...2 Background Information...2
Practical Approach in Teaching Wireless LAN Security using Open Source Software
 Practical Approach in Teaching Wireless LAN Security using Open Source Software Mohd Azizi Sanwani & * Kamaruddin Mamat Centre for Diploma Programme, Multimedia University Cyberjaya, MALAYSIA * Faculty
Practical Approach in Teaching Wireless LAN Security using Open Source Software Mohd Azizi Sanwani & * Kamaruddin Mamat Centre for Diploma Programme, Multimedia University Cyberjaya, MALAYSIA * Faculty
Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point
 Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
Article ID: 5036 Configure WorkGroup Bridge on the WAP131 Access Point Objective The Workgroup Bridge feature enables the Wireless Access Point (WAP) to bridge traffic between a remote client and the wireless
P r o t o l ck w fi ma a n ger User s Guide
 Po rtl wifi oc manager k Portlock WiFi Manager Introduction New in version 5.08 of the Portlock Boot CD is Portlock WiFi Manager, a utility for connecting to wireless networks. It is located on the Portlock
Po rtl wifi oc manager k Portlock WiFi Manager Introduction New in version 5.08 of the Portlock Boot CD is Portlock WiFi Manager, a utility for connecting to wireless networks. It is located on the Portlock
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide
 MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
Wireless LAN Access Point. IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps. User s Manual
 Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents...2 1.2 Features...2 1.3 Specifications...2 1.4 Physical Description...3 Chapter
Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents...2 1.2 Features...2 1.3 Specifications...2 1.4 Physical Description...3 Chapter
Wireless Auditing on a Budget
 Wireless Auditing on a Budget Open Source on Low Cost Hardware James A. Edge Jr., CISSP, CISM, CISA, CPTE, MCSE Sr. Security Analyst Cincinnati Bell Technology Solutions Agenda & Presentation Goals Background
Wireless Auditing on a Budget Open Source on Low Cost Hardware James A. Edge Jr., CISSP, CISM, CISA, CPTE, MCSE Sr. Security Analyst Cincinnati Bell Technology Solutions Agenda & Presentation Goals Background
VIDEO Intypedia012en LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY. AUTHOR: Raúl Siles. Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong
 VIDEO Intypedia012en LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY AUTHOR: Raúl Siles Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Hello and welcome to Intypedia. Today we will talk about the exciting world of security
VIDEO Intypedia012en LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY AUTHOR: Raúl Siles Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Hello and welcome to Intypedia. Today we will talk about the exciting world of security
How To Classify A Dnet Attack
 Analysis of Computer Network Attacks Nenad Stojanovski 1, Marjan Gusev 2 1 Bul. AVNOJ 88-1/6, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia [email protected] 2 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, Ss. Cyril
Analysis of Computer Network Attacks Nenad Stojanovski 1, Marjan Gusev 2 1 Bul. AVNOJ 88-1/6, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia [email protected] 2 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, Ss. Cyril
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security
 Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings and Security This chapter describes how to set up the wireless features of your WGT624 v4 wireless router. In planning your wireless network, select a location for the wireless
AXIS 207W Network Camera Technical Information
 A few things that should help you get the AXIS 207W connected to your network. It s not always easy to install new products on your network and this document describes some of the things you may need to
A few things that should help you get the AXIS 207W connected to your network. It s not always easy to install new products on your network and this document describes some of the things you may need to
ALL1682511. 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point. User s Manual
 ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
ALL1682511 500Mbits Powerline WLAN N Access Point User s Manual Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. System Requirements...1 3. Configuration...1 4. WPS...9 5. Wireless AP Settings...9 6. FAQ... 15 7. Glossary...
WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY
 WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY Dec 2010 The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region The contents of this document remain the property of, and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
WIRELESS NETWORKING SECURITY Dec 2010 The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region The contents of this document remain the property of, and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without
WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document
 WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document Produced by FUNET led working group on wireless systems and mobility (MobileFunet) (WLAN security) Author: Wenche Backman Contributors: Ville Mattila/CSC
WLAN Information Security Best Practice Document Produced by FUNET led working group on wireless systems and mobility (MobileFunet) (WLAN security) Author: Wenche Backman Contributors: Ville Mattila/CSC
Security in Wireless Local Area Network
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Virtual Access Points
 Virtual Access Points Performance Impacts in an 802.11 environment and Alternative Solutions to overcome the problems By Thenu Kittappa Engineer Author: Thenu Kittappa Page 1 Virtual Access Points... 1
Virtual Access Points Performance Impacts in an 802.11 environment and Alternative Solutions to overcome the problems By Thenu Kittappa Engineer Author: Thenu Kittappa Page 1 Virtual Access Points... 1
WHITE PAPER. WEP Cloaking for Legacy Encryption Protection
 WHITE PAPER WEP Cloaking for Legacy TM Encryption Protection Introduction Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is the encryption protocol defined in the original IEEE 802.11 standard for Wireless Local Area
WHITE PAPER WEP Cloaking for Legacy TM Encryption Protection Introduction Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is the encryption protocol defined in the original IEEE 802.11 standard for Wireless Local Area
Network Security. Security of Wireless Local Area Networks. Chapter 15. Network Security (WS 2002): 15 Wireless LAN Security 1 Dr.-Ing G.
 Network Security Chapter 15 Security of Wireless Local Area Networks Network Security WS 2002: 15 Wireless LAN Security 1 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.11 standardizes medium access control MAC and physical characteristics
Network Security Chapter 15 Security of Wireless Local Area Networks Network Security WS 2002: 15 Wireless LAN Security 1 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.11 standardizes medium access control MAC and physical characteristics
