Disability identity predicts lower anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis
|
|
|
- Neal Brett Griffith
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disability identity predicts lower anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis Bogart, K. R. (2015). Disability Identity Predicts Lower Anxiety and Depression in Multiple Sclerosis. Rehabilitation Psychology, 60(1), doi: /rep /rep American Psychological Association Accepted Manuscript
2 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 1 Brief Report: Disability Identity Predicts Lower Anxiety and Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Kathleen R. Bogart, PhD Reference Bogart, K. R. (2015). Disability identity predicts lower depression and anxiety in Multiple Sclerosis. Rehabilitation Psychology, 60 (1), doi: /rep Acknowledgements I thank: Mariah Estill; the patient support groups and foundations for their help with recruitment; Amanda Hemmesch for her comments on an earlier draft of this article. Kathleen Bogart (corresponding author) Oregon State University School of Psychological Science 2950 SW Jefferson Way Corvallis, OR 97331, USA [email protected] Phone: (541)
3 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 2 Abstract Purpose/Objective: Disability identity involves affirming one s status as a person with a disability and incorporating this group membership into one s identity. It is associated with wellbeing in populations of people with disabilities, but its relationship with depression and anxiety in multiple sclerosis (MS) has yet to be examined. It was hypothesized that disability identity would predict lower depression and anxiety above and beyond the effects of demographic and disability variables. Research Method/Design: 106 participants with MS completed a crosssectional internet survey measuring disability identity, depression and anxiety, activities of daily living performance (ADL), MS duration, and demographic variables. Inclusion criteria were as follows: self-reported diagnosis of MS, self-reported impairment in walking, age 18 or older, living in the U.S., and English fluency. Results: Hierarchical regressions revealed that disability identity was a unique predictor of lower depression and anxiety. Older age and higher ADL performance also predicted lower depression and anxiety. Conclusions/Implications: Stronger disability identity predicts lower psychological distress in MS. Clinical implications include supporting patient disability identity by encouraging involvement in disability support and advocacy groups. Future research should examine psychosocial interventions to affirm identity. Keywords: Multiple Sclerosis; disability identity; depression; anxiety; social identity theory
4 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 3 Brief Report: Disability Identity Predicts Lower Anxiety and Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Impact This study is the first to examine disability identity in Multiple Sclerosis and to examine the relationship between disability identity and anxiety and depression. Findings confirm that affirmation of disability identity is associated with lower depression and anxiety in people with Multiple Sclerosis and mobility impairment. Clinicians should avoid attempts to normalize individuals with chronic disability and instead cultivate disability identity by encouraging involvement in disability support and advocacy groups. Introduction Negative aspects of disability, such as participation restrictions, are largely socially constructed (World Health Organization, 2001). Thus, disability studies scholars suggest that disability constitutes a marginalized identity, and it should be conceptualized as a minority group (Olkin, 2002). Social Identity Theory (Tajfel & Turner, 1979), a social psychological theory originally conceptualized for ethnic minorities, and recently applied to disability (Bogart, 2014; Dunn & Burcaw, 2013; Fernández, Branscombe, Gómez, & Morales, 2012), suggests that members of minority groups buffer their well-being despite having a stigmatized identity by taking one of two identity pathways. First, they may attempt to pass, adopting the values of the majority group, striving to be as normal as possible, and distancing themselves from others with disabilities. Second, they may affirm their identity as a person with a disability and align with their minority group, adopting its values and viewing themselves according to its norms. People who affirm their disability identity may seek support and advocacy groups, find meaning
5 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 4 in mentoring and advocating for disability rights, and develop a sense of pride about their group (Dunn & Burcaw, 2013). Although the protective effects of disability identity have been the subject of theorizing (Dunn & Burcaw, 2013), there has been little quantitative research on this construct. Bogart (2014) found that individuals with congenital mobility disabilities had higher satisfaction with life than those with acquired mobility disabilities. Disability identity and disability self-efficacy mediated this relationship, predicting greater satisfaction with life. Another study of people with a variety of disabilities found that stronger disability identity was associated with higher selfesteem (Nario-Redmond, Noel, & Fern, 2013). In a cross-cultural study, Fernández and colleagues (2012) found a more nuanced pattern, that following the social identity pathway endorsed by support organizations in one s country, whether it was affirmation or denial of disability, was associated with well-being. Because affirming disability identity in progressive or sporadic disabilities such as multiple sclerosis (MS) may be a particularly challenging and dynamic process, which has not been researched quantitatively, this study examined whether disability identity predicts lower levels of depression and anxiety in people with MS. MS is a chronic inflammatory disease which results in demyelination of the nerve fibers of the central nervous system. Onset is typically in early to middle adulthood. Common symptoms include muscle weakness in the extremities, ataxia, spasticity, significant fatigue, incontinence, vision problems, and speech dysarthria/dysphonia (Jonsson & Ravnborg, 1998). The two most common subtypes are relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive. Over the course of the disease, the majority of MS cases become progressive (Weinshenker, 1995). Thus, the course of MS is unpredictable, and affected individuals must contend with the high probability that they will become increasingly disabled over time.
6 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 5 Soon after diagnosis, individuals with MS often respond with depression, anxiety, denial, and attempts to conceal their disability (Irvine, Davidson, Hoy, & Lowe-Strong, 2009; Janssens et al., 2003). Qualitative work reveals that diagnosis of MS is often experienced as a loss and reformation of one s identity (Irvine et al., 2009). At first, individuals attempt to pass as normal. In a qualitative account (Irvine et al., 2009), a participant noted that her son hid her disabled parking pass so others wouldn t see it. Initially, participants noted avoiding support groups because they did not want to be associated with others with MS. Over the course of several years, however, participants reported reduced psychological distress, increased acceptance of their new identities, and socializing primarily with the MS community (Irvine et al., 2009). Although disability identity has been found to be associated with higher self-esteem and satisfaction with life (Bogart, 2014; Nario-Redmond et al., 2013), its relationship with depression and anxiety has yet to be examined. MS is associated with increased risk of depression and anxiety compared to the general public, with a reported lifetime prevalence of 36-54% for depression (Beiske et al., 2008; Fruewald, Loeffler-Stastka, Eher, Saletu, & Baumhacki, 2001) and 19-36% for anxiety (Beiske et al., 2008; Korostil & Feinstein, 2007). Thus, if disability identity is found to be protective against anxiety and depression, this study can inform psychosocial treatment of individuals with MS and similar disabilities. It was hypothesized that higher disability identity would be associated with lower depression and anxiety above and beyond the effects of the following demographic variables which have been previously found to be associated with our variables of interest: ADL performance, age, MS duration, gender, and income (Beiske et al., 2008; Bogart, 2014; Janssens et al., 2003) Method
7 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 6 Participants Participants were a subsample of a larger internet-based study of people with mobility disabilities. 1 Data from these participants have not been previously published. Internet-based research allows for increased participation among populations that have historically had difficulty accessing research. For this reason, internet-based health research is becoming more common, and samples are becoming more diverse (Whitehead, 2007). Participants were recruited from organizations such as the Multiple Sclerosis Foundation, National Multiple Sclerosis Society and via newsletters, , discussion board posts, and social media. Inclusion criteria were as follows: self-reported diagnosis of MS, self-reported impairment in walking to any degree, age 18 or older, living in the U.S., and ability to read and write in English. Participants who met these criteria and had completed all measures of interest were selected for this study, resulting in 106 participants. See Table 1 for participant characteristics. TABLE 1 ABOUT HERE Measures The 8-item Disability Personal Identity Scale was used to measure disability identity (Hahn & Belt, 2004). It was designed to assess a sense of positive disability identity and belonging with the disability community. Early evidence suggests the scale has good reliability and validity (Hahn & Belt, 2004). Response options ranged on a 5 point scale from strongly disagree to strongly agree. Possible scores range from 8-40, with higher numbers indicating stronger disability identity. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), a 14-item scale for use as a brief instrument for detecting depression and anxiety in patient populations, was used (Zigmond & Snaith, 1983). HADS is unlikely to confound with physical symptoms such as pain and fatigue, 1 A different subsample from this dataset was published by Bogart (2014).
8 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 7 and it has been validated for use in the MS population (Honarmand & Feinstein, 2009). Possible scores for the depression subscale and the anxiety subscale range from 0-21, with higher numbers indicating greater anxiety and depression. Demographic information, including age, gender, duration of MS, and income was also collected. The 13-item Self-Report Functional Measure ADL scale was used to assess how much assistance is needed to complete daily tasks (Hoenig, Branch, McIntyre, Hoff, & Horner, 1999). This is a self-report measure based on the Functional Independence Measure (Guide for the use of the uniform data set for medical rehabilitation, 1996), has been validated in the MS population (Hoenig, Hoff, McIntyre, & Branch, 2001). Possible scores range from 13 (total assistance) to 52 (independent). Associated symptoms and use of mobility equipment were also assessed with the Self-Report Functional Measure. Procedures The Oregon State University Institutional Review Board provided oversight for this research. Participants gave informed consent and completed all measures on Qualtrics, an online survey presentation system, which took approximately 30 minutes. Data Analysis Descriptive statistics were calculated for all measures (see Table 1). The established cutoff of 8 for the two HADS subscales was used to describe likely cases of depression and anxiety. In order to test the hypothesis that disability identity would predict depression and anxiety above and beyond covariates, two separate hierarchical multiple regressions were conducted, one predicting depression and one predicting anxiety (see Table 2). ADL performance, age, MS duration, gender, and income were entered into the first step of each model. Disability identity was added in the second step.
9 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 8 Results Approximately half (53%) of participants used wheelchairs as their primary mode of mobility. Participants endorsed a variety of symptoms associated with MS; 73% had sexual or incontinence issues, 43% had vision symptoms, and 24% had speech symptoms. Based on HADS cutoff scores, 37% of participants had likely cases of depression, and 37% had likely cases of anxiety. TABLE 2 ABOUT HERE As predicted, stronger disability identity was significantly associated with less depression when added in the second step, contributing a significant 9% increase in variance predicting depression. The significant predictors of depression in the final model were age, disability identity, and ADL performance. The final model explained 27% of the variance in participants depression. In the regression predicting anxiety, as expected, stronger disability identity was associated with significantly lower anxiety and explained a significant 4% increase in variance. The significant predictors of anxiety in the final model were age, disability identity, and ADL. The final model explained 19% of the variance in participants anxiety. Discussion As hypothesized, stronger disability identity was a unique predictor of lower depression and anxiety in participants with MS. This was the first study to examine the benefits of disability identity among people with MS. Further, it provides the first evidence that disability identity is associated with lower psychological distress. Evidence for the benefits of disability identity are accumulating for a variety of disabilities and for a variety of outcomes: depression and anxiety, self-esteem (Nario-Redmond et al., 2013), and satisfaction with life (Bogart, 2014).
10 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 9 Research has only begun to examine the correlates of disability identity. Affirmation of one s disability identity may involve acceptance of one s disability into the sense of self, social support through the disability community, stigma reduction through disability pride, and meaning-making through disability advocacy (Dunn & Burcaw, 2013). Redefining one s goals and values to fit those of the disability community, rather than the majority group, may be another beneficial aspect of disability identity. For example, one aspect of disability identity may involve valuing interdependence, whereas the majority Western culture values independence and physical competence; this value shift has been suggested to be protective of well-being among people with disabilities (Stensman, 1985). Age was the strongest predictor of depression and anxiety in this sample, indicating that younger individuals were more likely to experience depression and anxiety. Other research has suggested that younger individuals with acquired disabilities may experience more psychological distress because disability is less expected at their life stage, whereas when people age, disability becomes more common (Beiske et al., 2008; Horgan & MacLachlan, 2004). ADL performance also emerged as a predictor of depression and anxiety. The literature is mixed as to whether depression and anxiety are associated with functional independence, with some studies reporting significant associations (Beiske et al., 2008; Janssens et al., 2003) and some finding none (Figved et al., 2005; Fruewald et al., 2001). It is interesting to consider that disability identity was a stronger predictor of depression than ADL performance, suggesting that the way one s disability is appraised and incorporated into one s identity may be more important than one s functional independence in this case. Somewhat surprisingly, duration of MS was not associated with depression or anxiety. Depression and anxiety are often a reaction to diagnosis, and they tend to improve as individuals
11 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 10 adjust to their conditions (Janssens et al., 2003). Because participants in our sample had their conditions for an average of 20 years, it is possible that they had already employed coping strategies to reduce psychological distress. Other studies of people with long durations of MS have also failed to find a relationship between duration and depression and anxiety (Beiske et al., 2008). Limitations Participants were drawn from a larger internet-based study of mobility disability, so results relied on self-report, and detailed information about participants disease course was not available. Because the inclusion criteria for the larger study required some degree of difficulty walking, individuals who were younger, had earlier stages of MS, or more mild levels of disability were less likely to be enrolled. Additionally, our sample had similar levels of men and women, but MS occurs more frequently in women (Jonsson & Ravnborg, 1998), thus, women were somewhat underrepresented in the study. MS occurs most commonly in white individuals (Poser, 1994), and the lack of ethnic diversity in our sample reflected this. Future studies should examine the intersection of disability identity and other minority statuses. Results of this study would be best generalized to people with MS who have mobility disability. Clinical Implications Well-intentioned rehabilitation practitioners often attempt to normalize people with disabilities, implicitly serving to diminish disability identity (Olkin, 2009). Growing evidence of the benefits of disability identity suggests a shift away from this approach towards one that affirms disability identity. A natural first step toward improving disability identity is to encourage involvement in support and advocacy groups. Additionally, a few promising psychotherapeutic approaches may serve to improve disability identity. Disability Affirmative
12 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 11 Therapy emphasizes that living with a disability can be a source of value, meaning, and pride for an individual (Olkin, 2009). It encourages patients to develop a positive disability identity by finding mentors with disabilities and engaging in positive reframing of stigmatized traits. Additionally, a group-based cognitive behavior therapy program was developed for individuals with MS which focuses on helping individuals to redefine their identities and goals according to their disabilities, and promoting a sense of coherence and self-efficacy (Graziano, Calandri, Borghi, & Bonino, 2014). A randomized controlled trial of this therapeutic approach found that depression and quality of life improved at follow-up. Future research should examine the mediating role of disability identity in the effectiveness of such interventions.
13 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 12 References Beiske, A. G., Svensson, E., Sandanger, I., Czujko, B., Pedersen, E. D., Aarseth, J. H., & Myhr, K. M. (2008). Depression and anxiety amongst multiple sclerosis patients. European Journal of Neurology, 15(3), doi: /j x. Bogart, K. R. (2014). The role of disability self-concept in adaptation to congenital or acquired disability. Rehabilitation Psychology, 59(1), doi: /a Dunn, D. S., & Burcaw, S. (2013). Disability identity: Exploring narrative accounts of disability. Rehabilitation Psychology, 58(2), doi: /a Fernández, S., Branscombe, N. R., Gómez, Á., & Morales, J. (2012). Influence of the social context on use of surgical-lengthening and group-empowering coping strategies among people with dwarfism. Rehabilitation Psychology, 57(3), 224. doi: /a Figved, N., Klevan, G., Myhr, K. M., Glad, S., Nyland, H., Larsen, J. P., Aarsland, D. (2005). Neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 112(6), doi: /j x Fruewald, S., Loeffler-Stastka, H., Eher, R., Saletu, B., & Baumhacki, U. (2001). Depression and quality of life in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 104(5), doi: /j x Graziano, F., Calandri, E., Borghi, M., & Bonino, S. (2014). The effects of a group-based cognitive behavioral therapy on people with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation, 28(3), doi: / Guide for the use of the uniform data set for medical rehabilitation. (1996). Buffalo, NY: State University of New York at Buffalo.
14 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 13 Hahn, H. D., & Belt, T. L. (2004). Disability identity and attitudes toward cure in a sample of disabled activists. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 45(4), doi: / Hoenig, H., Branch, L. G., McIntyre, L., Hoff, J., & Horner, R. D. (1999). The validity in persons with spinal cord injury of a self-reported functional measure derived from the Functional Independence Measure. Spine, 24(6), doi: / Hoenig, H., Hoff, J., McIntyre, L., & Branch, L. G. (2001). The self-reported functional measure: Predictive validity for health care utilization in multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 82(5), doi: /apmr Honarmand, K., & Feinstein, A. (2009). Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale for use with multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis, 15(12), doi: / Horgan, O., & MacLachlan, M. (2004). Psychosocial adjustment to lower-limb amputation: a review. Disability & Rehabilitation, 26(14-15), doi: / Irvine, H., Davidson, C., Hoy, K., & Lowe-Strong, A. (2009). Psychosocial adjustment to multiple sclerosis: exploration of identity redefinition. Disability & Rehabilitation, 31(8), doi: / Janssens, A., Doorn, P. A., Boer, J. B., Meche, F. G. A., Passchier, J., & Hintzen, R. Q. (2003). Impact of recently diagnosed multiple sclerosis on quality of life, anxiety, depression and
15 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 14 distress of patients and partners. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 108(6), doi: /j x Jonsson, A., & Ravnborg, M. H. (1998). Rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis. Critical Reviews TM in Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 10(1), Korostil, M., & Feinstein, A. (2007). Anxiety disorders and their clinical correlates in multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis, 13(1), doi: / Nario-Redmond, M. R., Noel, J. G., & Fern, E. (2013). Redefining disability, re-imagining the self: Disability identification predicts self-esteem and strategic responses to stigma. Self and Identity, 12(5), doi: / Olkin, R. (2002). Could you hold the door for me? Including disability in diversity. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 8(2), doi: / Olkin, R. (2009). Disability-Affirmative Therapy. In The Professional Counselor s Desk Reference (pp ). New York, NY: Springer. Poser, C. M. (1994). The epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: a general overview. Annals of Neurology, 36(S2), S180 S193. Stensman, R. (1985). Severely mobility-disabled people assess the quality of their lives. Scandinavian Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 17, Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. C. (1979). An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In The social psychology of intergroup relations (pp ). Monterey: Brooks/Cole. Weinshenker, B. G. (1995). The natural history of multiple sclerosis. Neurologic Clinics, 13(1),
16 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 15 Whitehead, L. C. (2007). Methodological and ethical issues in Internet-mediated research in the field of health: an integrated review of the literature. Social Science & Medicine, 65(4), doi: /j.socscimed World Health Organization. (2001). International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Retrieved from Zigmond, A. S., & Snaith, R. (1983). The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 67(6), doi: /j tb09716.x
17 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 16 Table 1 Participant Characteristics Characteristic Statistic Range Female (%) 45 Black (%) 7 White (%) 90 Other or mixed ethnicity (%) 3 Income (median) $45,001-60,000 below 10,000-over 90,000 Age M(SD) (8.85) MS duration in years M(SD) (12.20) 2-54 ADL M(SD) (8.49) Disability Identity M(SD) (4.97) Depression M(SD) 6.33 (4.05) 0-20 Anxiety M(SD) 6.19 (4.21) 0-16 Note. MS is Multiple Sclerosis and ADL is performance of activities of daily living.
18 DISABILITY IDENTITY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 17 Table 2 Hierarchical Regressions Predicting Depression and Anxiety Predictor Variable Outcome Variable Depression Anxiety b (SE) β b (SE) β Step 1 Duration (.04) 0.13 Gender (.80) ADL (.05) -0.30** (.05) -0.25* Income (.19) -0.20* (.20) Age (.05) -0.33** (.05) -0.37** Step 2 Duration (.04) 0.12 Gender (.80) ADL (.04) -0.26** (.05) -0.22* Income (.19) (.20) Age (.05) -0.34** (.05) -0.38** Disability Identity (.07) -0.31** (.08) -0.21* ΔR ** 0.04* Total R ** 0.19** Note. ADL = performance of activities of daily living. ** p <.01. * p <.05
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information
 What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
Deirdre Dlugonski East Carolina University 160 Minges Coliseum 252.328.5266 [email protected]
 Deirdre Dlugonski East Carolina University 160 Minges Coliseum 252.328.5266 [email protected] Education PhD University of Illinois, Kinesiology, 2013 BS Pennsylvania State University, Kinesiology, 2005
Deirdre Dlugonski East Carolina University 160 Minges Coliseum 252.328.5266 [email protected] Education PhD University of Illinois, Kinesiology, 2013 BS Pennsylvania State University, Kinesiology, 2005
indicates that the relationship between psychosocial distress and disability in patients with CLBP is not uniform.
 Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is one of the most prevalent health problems in western societies. The prognosis of CLBP is poor, as indicated by very low rate of resolution, even with treatment. In CLBP,
Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is one of the most prevalent health problems in western societies. The prognosis of CLBP is poor, as indicated by very low rate of resolution, even with treatment. In CLBP,
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014
 International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING IN PATIENTS WITH
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. II, Issue 2, 2014 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING IN PATIENTS WITH
Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis
 Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Marie Namey, RN, MSN, MSCN Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Home of. Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Mellen Center Mission The Mellen Center remains committed
Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Marie Namey, RN, MSN, MSCN Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Home of. Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Mellen Center Mission The Mellen Center remains committed
Diagnosis communication and patients coping strategies. Dawn Langdon PhD
 Diagnosis communication and patients coping strategies Dawn Langdon PhD Patient focused quality interventions To improve health literacy To improve clinical decision making To improve self-care To improve
Diagnosis communication and patients coping strategies Dawn Langdon PhD Patient focused quality interventions To improve health literacy To improve clinical decision making To improve self-care To improve
Executive Summary. 1. What is the temporal relationship between problem gambling and other co-occurring disorders?
 Executive Summary The issue of ascertaining the temporal relationship between problem gambling and cooccurring disorders is an important one. By understanding the connection between problem gambling and
Executive Summary The issue of ascertaining the temporal relationship between problem gambling and cooccurring disorders is an important one. By understanding the connection between problem gambling and
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet
 Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
How To Cover Occupational Therapy
 Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know. For Professionals
 Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know For Professionals What will I learn today? The Basics: What is MS? Living with MS: A Family Affair We Can Help: The National MS Society What MS Is: MS is thought
Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know For Professionals What will I learn today? The Basics: What is MS? Living with MS: A Family Affair We Can Help: The National MS Society What MS Is: MS is thought
October 2013 Family Choice: Best Practices in Care for Nursing Home Residents
 SNP Alliance Best Practices October 2013 Family Choice: Best Practices in Care for Nursing Home Residents Overview of Family Choice of New York I-SNP Independent Health s Medicare Advantage Family Choice
SNP Alliance Best Practices October 2013 Family Choice: Best Practices in Care for Nursing Home Residents Overview of Family Choice of New York I-SNP Independent Health s Medicare Advantage Family Choice
GLOBAL SURVEY FACT SHEET
 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, often disabling, disease that attacks the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Symptoms may be mild or severe, ranging
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, often disabling, disease that attacks the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Symptoms may be mild or severe, ranging
The Inventory of Male Friendliness in Nursing Programs (IMFNP)
 The Inventory of Male Friendliness in Nursing Programs (IMFNP) Background At the 2001 annual conference of the American Assembly for Men in Nursing (AAMN), a nursing student discussed his educational experiences
The Inventory of Male Friendliness in Nursing Programs (IMFNP) Background At the 2001 annual conference of the American Assembly for Men in Nursing (AAMN), a nursing student discussed his educational experiences
Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Psychology
 Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Psychology 0731111 Psychology And Life {3}[3-3] Defining humans behavior; Essential life skills: problem solving,
Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Psychology 0731111 Psychology And Life {3}[3-3] Defining humans behavior; Essential life skills: problem solving,
New perception of disability including cognition, fatigue, pain and other impairments related to MS
 New perception of disability including cognition, fatigue, pain and other impairments related to MS Diego Cadavid, MD Director, MS Clinical Development Biogen Idec 1 Need for clarity on terminology for
New perception of disability including cognition, fatigue, pain and other impairments related to MS Diego Cadavid, MD Director, MS Clinical Development Biogen Idec 1 Need for clarity on terminology for
Psychology. Kansas Course Code # 04254
 High School Psychology Kansas Course Code # 04254 The American Psychological Association defines Psychology as the study of the mind and behavior. The discipline embraces all aspects of the human experience
High School Psychology Kansas Course Code # 04254 The American Psychological Association defines Psychology as the study of the mind and behavior. The discipline embraces all aspects of the human experience
Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults. Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City
 Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City What is Depression? Everyday use of the word Clinically significant depressive symptoms : more severe,
Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City What is Depression? Everyday use of the word Clinically significant depressive symptoms : more severe,
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015
 Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Evidence-Informed Recommendations in Rehabilitation for Older Adults Aging with HIV: A Knowledge Synthesis
 Evidence-Informed Recommendations in Rehabilitation for Older Adults Aging with HIV: A Knowledge Synthesis Work to Date November 2012 Kelly O Brien, Patty Solomon, Joy MacDermid, Barry Trentham, Larry
Evidence-Informed Recommendations in Rehabilitation for Older Adults Aging with HIV: A Knowledge Synthesis Work to Date November 2012 Kelly O Brien, Patty Solomon, Joy MacDermid, Barry Trentham, Larry
Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures. Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM
 Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM Objectives 1. Understand the Changing Medical System and the Changing Focus of Assessments
Importance, Selection and Use of Outcome Measures Carolyn Baum, PhD, OTR, FAOTA Allen Heinemann, PhD, ABPP (RP), FACRM Objectives 1. Understand the Changing Medical System and the Changing Focus of Assessments
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Predictors of Physical Therapy Use in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Maura Iversen,, PT, DPT, SD, MPH 1,2,3 Ritu Chhabriya,, MSPT 4 Nancy Shadick, MD 2,3 1 Department of Physical Therapy, Northeastern
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON
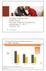 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON First-line DMTs Reduce Relapse Frequency by ~30% vs. Placebo Frequency of relapse with various DMTs, based
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON First-line DMTs Reduce Relapse Frequency by ~30% vs. Placebo Frequency of relapse with various DMTs, based
INVESTIGATING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY TRAINING ON INCREASED HARDINESS AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING
 INVESTIGATING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY TRAINING ON INCREASED HARDINESS AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING *Zahra Gholami Ghareh Shiran 1, Ghodsi Ahghar 2, Afshin Ahramiyan 3, Afsaneh Boostan
INVESTIGATING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POSITIVE PSYCHOLOGY TRAINING ON INCREASED HARDINESS AND PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING *Zahra Gholami Ghareh Shiran 1, Ghodsi Ahghar 2, Afshin Ahramiyan 3, Afsaneh Boostan
Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised. Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association
 Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association The Hobart Clinic Association Not-for-profit private Mental Health Service
Alcohol Disorders in Older Adults: Common but Unrecognised Amanda Quealy Chief Executive Officer The Hobart Clinic Association The Hobart Clinic Association Not-for-profit private Mental Health Service
Overview of evidence: Prognostic factors following whiplash injury
 Overview of evidence: Prognostic factors following whiplash injury Confidence in conclusions (that an association exists) are presented in both text and graphical format, using the following legend: =
Overview of evidence: Prognostic factors following whiplash injury Confidence in conclusions (that an association exists) are presented in both text and graphical format, using the following legend: =
The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample
 Addictive Behaviors 29 (2004) 843 848 The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample Irene Markman Geisner*, Mary
Addictive Behaviors 29 (2004) 843 848 The relationship among alcohol use, related problems, and symptoms of psychological distress: Gender as a moderator in a college sample Irene Markman Geisner*, Mary
Applied Psychology. Course Descriptions
 Applied Psychology s AP 6001 PRACTICUM SEMINAR I 1 CREDIT AP 6002 PRACTICUM SEMINAR II 3 CREDITS Prerequisites: AP 6001: Successful completion of core courses. Approval of practicum site by program coordinator.
Applied Psychology s AP 6001 PRACTICUM SEMINAR I 1 CREDIT AP 6002 PRACTICUM SEMINAR II 3 CREDITS Prerequisites: AP 6001: Successful completion of core courses. Approval of practicum site by program coordinator.
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Position Statement: National Disability Insurance Scheme
 1 Position Statement: National Disability Insurance Scheme Multiple Sclerosis Australia (MSA) Position: People affected by MS, including their families and carers should have access to the type and level
1 Position Statement: National Disability Insurance Scheme Multiple Sclerosis Australia (MSA) Position: People affected by MS, including their families and carers should have access to the type and level
College of Education. Rehabilitation Counseling
 * 515 MEDICAL AND PSYCHOSOCIAL ASPECTS OF DISABILITIES I. (3) This course is designed to prepare rehabilitation and mental health counselors, social works and students in related fields with a working
* 515 MEDICAL AND PSYCHOSOCIAL ASPECTS OF DISABILITIES I. (3) This course is designed to prepare rehabilitation and mental health counselors, social works and students in related fields with a working
Q: Rehabilitation Nursing
 Q: Rehabilitation Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 163 Priority: One Competency: Q-1 Apply the Rehabilitation Process Q-1-1 Q-1-2 Q-1-3 Q-1-4 Q-1-5 Q-1-6 Demonstrate knowledge
Q: Rehabilitation Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 163 Priority: One Competency: Q-1 Apply the Rehabilitation Process Q-1-1 Q-1-2 Q-1-3 Q-1-4 Q-1-5 Q-1-6 Demonstrate knowledge
Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Special Education
 Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Special Education 0731111 Psychology and life {3} [3-3] Defining humans behavior; Essential life skills: problem
Al Ahliyya Amman University Faculty of Arts Department of Psychology Course Description Special Education 0731111 Psychology and life {3} [3-3] Defining humans behavior; Essential life skills: problem
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of life review through writing on depressive symptoms in older adults residing in senior residences? Chippendale, T., & Bear-Lehman,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of life review through writing on depressive symptoms in older adults residing in senior residences? Chippendale, T., & Bear-Lehman,
Learning Assurance Report. for the. WellStar Primary Care Nurse Practitioner Program. in the. Wellstar College of Health and Human Services
 Learning Assurance Report for the WellStar Primary Care Nurse Practitioner Program in the Wellstar College of Health and Human Services Spring 2004 Prepared by WellStar School of Nursing Curriculum Committee
Learning Assurance Report for the WellStar Primary Care Nurse Practitioner Program in the Wellstar College of Health and Human Services Spring 2004 Prepared by WellStar School of Nursing Curriculum Committee
A Definition of Multiple Sclerosis
 English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
CBT IN THE CITY. adjusted to the news of being with MS? April 2013. Experts at your fingertips call now. Check out our new services in you local area
 April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
Canines and Childhood Cancer
 Canines and Childhood Cancer Examining the Effects of Therapy Dogs with Childhood Cancer Patients and their Families Updated Executive Summary I n 2010, American Humane Association and Zoetis (formerly
Canines and Childhood Cancer Examining the Effects of Therapy Dogs with Childhood Cancer Patients and their Families Updated Executive Summary I n 2010, American Humane Association and Zoetis (formerly
Master of Arts, Counseling Psychology Course Descriptions
 Master of Arts, Counseling Psychology Course Descriptions Advanced Theories of Counseling & Intervention (3 credits) This course addresses the theoretical approaches used in counseling, therapy and intervention.
Master of Arts, Counseling Psychology Course Descriptions Advanced Theories of Counseling & Intervention (3 credits) This course addresses the theoretical approaches used in counseling, therapy and intervention.
Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery Clinical and Clinical Research Fellowship Application Form
 Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery Clinical and Clinical Research Fellowship Application Form Fellowship in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroinflammatory Disorders Type of Fellowship: Clinical Research
Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery Clinical and Clinical Research Fellowship Application Form Fellowship in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroinflammatory Disorders Type of Fellowship: Clinical Research
PRINCIPLES OF MULTICULTURAL PSYCHIATRIC REHABILITATION SERVICES Executive Summary
 PRINCIPLES OF MULTICULTURAL PSYCHIATRIC REHABILITATION SERVICES Executive Summary PRA recognizes the striking disparities in mental health care found for cultural, racial and ethnic minorities in the USA,
PRINCIPLES OF MULTICULTURAL PSYCHIATRIC REHABILITATION SERVICES Executive Summary PRA recognizes the striking disparities in mental health care found for cultural, racial and ethnic minorities in the USA,
Effectiveness of positive psychology training in the increase of hardiness of female headed households
 Effectiveness of positive psychology training in the increase of hardiness of female headed households 1,2, Ghodsi Ahghar* 3 1.Department of counseling, Khozestan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad
Effectiveness of positive psychology training in the increase of hardiness of female headed households 1,2, Ghodsi Ahghar* 3 1.Department of counseling, Khozestan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad
Pragmatic Evidence Based Review Substance Abuse in moderate to severe TBI
 Pragmatic Evidence Based Review Substance Abuse in moderate to severe TBI Reviewer Emma Scheib Date Report Completed November 2011 Important Note: This report is not intended to replace clinical judgement,
Pragmatic Evidence Based Review Substance Abuse in moderate to severe TBI Reviewer Emma Scheib Date Report Completed November 2011 Important Note: This report is not intended to replace clinical judgement,
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015 Course Definitions, Designators and Format Courses approved at the time of publication are listed in this bulletin. Not all courses are offered every term. Refer to the online
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 2014-2015 Course Definitions, Designators and Format Courses approved at the time of publication are listed in this bulletin. Not all courses are offered every term. Refer to the online
Psychological Self Care in Multiple Sclerosis: A Stepped Care Model
 Psychological Self Care in Multiple Sclerosis: A Stepped Care Model Dr Dawn Reeve Consultant Clinical Neuropsychologist Mrs Dawn Anderson Self Care Development Manager Background to service evaluation
Psychological Self Care in Multiple Sclerosis: A Stepped Care Model Dr Dawn Reeve Consultant Clinical Neuropsychologist Mrs Dawn Anderson Self Care Development Manager Background to service evaluation
Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013. Contents Summary 2 Commentary 3 Recommendations 5 Information on MS 6 Personal testimonies 9
 Submission to the Department of Health Consultation on Draft Misuse of Drugs (Amendment) Regulations 2013 which will amend the Misuse of Drugs Regulations, 1988 Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013
Submission to the Department of Health Consultation on Draft Misuse of Drugs (Amendment) Regulations 2013 which will amend the Misuse of Drugs Regulations, 1988 Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013
How To Become A Physio And Rehabilitation Medicine Specialist
 EUROPEAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE LOGBOOK EUROPEAN UNION OF MEDICAL SPECIALISTS UEMS IDENTIFICATION... 2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 3 THE TRAINING COURSE... 3 TRAINING PROGRAMME... 4
EUROPEAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE LOGBOOK EUROPEAN UNION OF MEDICAL SPECIALISTS UEMS IDENTIFICATION... 2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 3 THE TRAINING COURSE... 3 TRAINING PROGRAMME... 4
Under the Start Your Search Now box, you may search by author, title and key words.
 VISTAS Online VISTAS Online is an innovative publication produced for the American Counseling Association by Dr. Garry R. Walz and Dr. Jeanne C. Bleuer of Counseling Outfitters, LLC. Its purpose is to
VISTAS Online VISTAS Online is an innovative publication produced for the American Counseling Association by Dr. Garry R. Walz and Dr. Jeanne C. Bleuer of Counseling Outfitters, LLC. Its purpose is to
University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program
 University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program Graduate Clinical Health Psychology Program Goals 1 Psychotherapy Skills Acquisition: To train students in the skills and knowledge
University of Michigan Dearborn Graduate Psychology Assessment Program Graduate Clinical Health Psychology Program Goals 1 Psychotherapy Skills Acquisition: To train students in the skills and knowledge
National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary
 National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary www.beyondblue.org.au 13 22 4636 October 213 Acknowledgements The National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students
National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students Executive summary www.beyondblue.org.au 13 22 4636 October 213 Acknowledgements The National Mental Health Survey of Doctors and Medical Students
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AUSTRALIA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS RESEARCH AUSTRALIA
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AUSTRALIA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS RESEARCH AUSTRALIA Submission to the ACT Legislative Assembly Health, Ageing, Community and Social Services Inquiry into the exposure draft of the Drugs
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS AUSTRALIA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS RESEARCH AUSTRALIA Submission to the ACT Legislative Assembly Health, Ageing, Community and Social Services Inquiry into the exposure draft of the Drugs
Profile: Kessler Patients
 Profile: Kessler Patients 65 Breakthrough Years Kessler Institute has pioneered the course of medical rehabilitation since 1948. Today, as the nation s largest single rehabilitation hospital, we continue
Profile: Kessler Patients 65 Breakthrough Years Kessler Institute has pioneered the course of medical rehabilitation since 1948. Today, as the nation s largest single rehabilitation hospital, we continue
Second Year Fall. Spring
 Occupational Therapy Program Curriculum (3+3 Students = OTFY courses; first year only.) Please note, course descriptions are updated periodically. First Year Fall Credits GMOT 6110/OTFY 4110 Functional
Occupational Therapy Program Curriculum (3+3 Students = OTFY courses; first year only.) Please note, course descriptions are updated periodically. First Year Fall Credits GMOT 6110/OTFY 4110 Functional
Life Stressors and Non-Cognitive Outcomes in Community Colleges for Mexican/Mexican American Men. Art Guaracha Jr. San Diego State University
 Life Stressors and Non-Cognitive Outcomes in Community Colleges for Mexican/Mexican American Men Art Guaracha Jr. San Diego State University JP 3 Journal of Progressive Policy & Practice Volume 2 Issue
Life Stressors and Non-Cognitive Outcomes in Community Colleges for Mexican/Mexican American Men Art Guaracha Jr. San Diego State University JP 3 Journal of Progressive Policy & Practice Volume 2 Issue
Global Economic Impact of Multiple Sclerosis
 Global Economic Impact of Multiple Sclerosis May 2010 Literature Review Executive Summary Prepared for Multiple Sclerosis International Federation London, United Kingdom Prepared by Michael Trisolini,
Global Economic Impact of Multiple Sclerosis May 2010 Literature Review Executive Summary Prepared for Multiple Sclerosis International Federation London, United Kingdom Prepared by Michael Trisolini,
Positive Psychology in the Israeli School System. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Maytiv Center s Intervention Programs in Schools Research Report
 Positive Psychology in the Israeli School System Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Maytiv Center s Intervention Programs in Schools Research Report Dr. Anat Shoshani, Dr. Sarit Steinmetz School of Psychology,
Positive Psychology in the Israeli School System Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Maytiv Center s Intervention Programs in Schools Research Report Dr. Anat Shoshani, Dr. Sarit Steinmetz School of Psychology,
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This file is posted on the Bayer HealthCare Clinical Trials Registry and Results website. It is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of
Clinical Study Synopsis This file is posted on the Bayer HealthCare Clinical Trials Registry and Results website. It is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
SOCIAL WORK RESEARCH ON INTERVENTIONS FOR ADOLESCENT SUBSTANCE MISUSE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 SOCIAL WORK RESEARCH ON INTERVENTIONS FOR ADOLESCENT SUBSTANCE MISUSE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE By: Christine Kim Cal State University, Long Beach May 2014 INTRODUCTION Substance use among
SOCIAL WORK RESEARCH ON INTERVENTIONS FOR ADOLESCENT SUBSTANCE MISUSE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE By: Christine Kim Cal State University, Long Beach May 2014 INTRODUCTION Substance use among
The Effect of Physical Exercise on Depression; Case study: Professional and Nonprofessional
 Available online athttp://www.ijashss.com International Journal of Advanced Studies in Humanities and Social Science Volume 1, Issue 8, 2013: 1161-1165 The Effect of Physical Exercise on Depression; Case
Available online athttp://www.ijashss.com International Journal of Advanced Studies in Humanities and Social Science Volume 1, Issue 8, 2013: 1161-1165 The Effect of Physical Exercise on Depression; Case
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
Engaging young people in mental health care: The role of youth workers
 Engaging young people in mental health care: The role of youth workers Debra Rickwood Professor of Psychology Faculty of Health University of Canberra Young people are reluctant to seek professional mental
Engaging young people in mental health care: The role of youth workers Debra Rickwood Professor of Psychology Faculty of Health University of Canberra Young people are reluctant to seek professional mental
Department of Psychology
 Department of Psychology Tanner Babb, Mary Ruthi The Psychology Department seeks to provide a curriculum that stimulates the necessary knowledge base and skills for participation in a variety of fields
Department of Psychology Tanner Babb, Mary Ruthi The Psychology Department seeks to provide a curriculum that stimulates the necessary knowledge base and skills for participation in a variety of fields
Occupational Therapy Entry-Level Degree Program M.S. Curriculum Guide
 Occupational Therapy Entry-Level Degree Program M.S. Curriculum Guide OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY ENTRY- LEVEL PROGRAM CURRICULUM (Residential) Enrollment in any course will not be permitted until prerequisites
Occupational Therapy Entry-Level Degree Program M.S. Curriculum Guide OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY ENTRY- LEVEL PROGRAM CURRICULUM (Residential) Enrollment in any course will not be permitted until prerequisites
Counselor Education Program Mission and Objectives
 Counselor Education Program Mission and Objectives Our Mission The LSU Counselor Education program prepares students to function as professional counselors in a variety of human service settings such as
Counselor Education Program Mission and Objectives Our Mission The LSU Counselor Education program prepares students to function as professional counselors in a variety of human service settings such as
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 2010 May 2010 Issue Background A review on the
OHTAC Recommendation Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 2010 May 2010 Issue Background A review on the
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population
 Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population Presented by: Renée El-Gabalawy, M.A., Ph.D Candidate Collaborators Dr. Corey Mackenzie Associate Professor
Health Anxiety and Hypochondriasis in Older Adults: Overlooked Conditions in a Susceptible Population Presented by: Renée El-Gabalawy, M.A., Ph.D Candidate Collaborators Dr. Corey Mackenzie Associate Professor
Department of Psychology
 The University of Texas at San Antonio 1 Department of Psychology The Department of Psychology offers the Master of Science Degree in Psychology and the Doctor of Philosophy Degree in Psychology. Master
The University of Texas at San Antonio 1 Department of Psychology The Department of Psychology offers the Master of Science Degree in Psychology and the Doctor of Philosophy Degree in Psychology. Master
The Relationship between Gender and Academic Success Online
 1 The Relationship between Gender and Academic Success Online Lori Kupczynski, Ed.D., Texas A&M University-Kingsville Michelle Brown, Ed.D., Walden University Glenda Holland, Ed.D, Texas A&M University
1 The Relationship between Gender and Academic Success Online Lori Kupczynski, Ed.D., Texas A&M University-Kingsville Michelle Brown, Ed.D., Walden University Glenda Holland, Ed.D, Texas A&M University
Psychology. Undergraduate programs. Graduate programs. Degree requirements. Admission requirements
 290 they are not prerequisites for law school admission: introductory economics (Ec 201, 202); ethics (Phl 202, 445, 446, 447); U.S. history (Hst 201, 202); legal history, constitutional history (Hst 410,
290 they are not prerequisites for law school admission: introductory economics (Ec 201, 202); ethics (Phl 202, 445, 446, 447); U.S. history (Hst 201, 202); legal history, constitutional history (Hst 410,
Purpose. Admission Requirements NURSING EDUCATION STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES RESIDENCY REQUIREMENTS. Clinical Requirements
 NURSING EDUCATION Purpose This program is designed for professional nurses who have earned a Master s or Doctoral Degree in Nursing and seek further education in advanced nursing practice. Concentrations
NURSING EDUCATION Purpose This program is designed for professional nurses who have earned a Master s or Doctoral Degree in Nursing and seek further education in advanced nursing practice. Concentrations
RN-MS Program. Purpose. Admission Requirements. State Requirements for Online/Distance Education. Degree Requirements
 RN-MS PROGRAM RN-MS Program Purpose This accelerated program is designed for the experienced, practicing registered nurse who plans to continue nursing studies through the master's level and does not hold
RN-MS PROGRAM RN-MS Program Purpose This accelerated program is designed for the experienced, practicing registered nurse who plans to continue nursing studies through the master's level and does not hold
Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review. The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and
 Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review Purpose The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and identify the most common causes of falls. Also included
Falls Risk Assessment: A Literature Review Purpose The purpose of this literature review is to determine falls risk among elderly individuals and identify the most common causes of falls. Also included
Outcome of in-patient Treatment for Severe Motor Conversion Disorder - does it work? A.S.David, R.McCormack and Lishman Unit MDT
 Outcome of in-patient Treatment for Severe Motor Conversion Disorder - does it work? A.S.David, R.McCormack and Lishman Unit MDT Evidence to date: inpatient rehab Inpatient multi-disciplinary intervention
Outcome of in-patient Treatment for Severe Motor Conversion Disorder - does it work? A.S.David, R.McCormack and Lishman Unit MDT Evidence to date: inpatient rehab Inpatient multi-disciplinary intervention
Pilot Study of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Trainee Clinical Psychologists
 Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 2011, 39, 235 241 First published online 13 December 2010 doi:10.1017/s1352465810000731 Pilot Study of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Trainee Clinical
Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 2011, 39, 235 241 First published online 13 December 2010 doi:10.1017/s1352465810000731 Pilot Study of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Trainee Clinical
PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis. Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15
 PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15 Group 1 - Comparison across DMTs, including differential effects in subgroups Consolidated straw man
PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15 Group 1 - Comparison across DMTs, including differential effects in subgroups Consolidated straw man
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
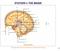 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Effect of Job Autonomy Upon Organizational Commitment of Employees at Different Hierarchical Level
 psyct.psychopen.eu 2193-7281 Research Articles Effect of Job Autonomy Upon Organizational Commitment of Employees at Different Hierarchical Level Shalini Sisodia* a, Ira Das a [a] Department of Psychology,
psyct.psychopen.eu 2193-7281 Research Articles Effect of Job Autonomy Upon Organizational Commitment of Employees at Different Hierarchical Level Shalini Sisodia* a, Ira Das a [a] Department of Psychology,
Objectives. Significant Costs Of Chronic Pain. Pain Catastrophizing. Pain Catastrophizing. Pain Catastrophizing
 Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Pain Rehabilitation Program in the Reduction of Pain Catastrophizing Michele Evans, MS, APRN-C, CNS, March 27, 2007 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER).
Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Pain Rehabilitation Program in the Reduction of Pain Catastrophizing Michele Evans, MS, APRN-C, CNS, March 27, 2007 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER).
Positive psychology in practice
 http://www.health.harvard.edu/newsweek/positive-psychology-in-practice.htm Positive psychology in practice (This article was first printed in the May 2008 issue of the Harvard Mental Health Letter.) Positive
http://www.health.harvard.edu/newsweek/positive-psychology-in-practice.htm Positive psychology in practice (This article was first printed in the May 2008 issue of the Harvard Mental Health Letter.) Positive
Nurse Practitioner Student Learning Outcomes
 ADULT-GERONTOLOGY PRIMARY CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER Nurse Practitioner Student Learning Outcomes Students in the Nurse Practitioner Program at Wilkes University will: 1. Synthesize theoretical, scientific,
ADULT-GERONTOLOGY PRIMARY CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER Nurse Practitioner Student Learning Outcomes Students in the Nurse Practitioner Program at Wilkes University will: 1. Synthesize theoretical, scientific,
