Guidelines for Best Practices in Data Management Roles and Responsibilities
|
|
|
- Hugh Page
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guidelines for Best Practices in Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Data Architecture Advisory Committee A subcommittee of Information Architecture & Standards Branch
2 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION Purpose Intended Audience Scope Owner Data Custodianship Principles Other Related References DATA Management ROLES and RESPONSIBILITIES Critical, Core, Additional and Existing Roles Data Management Roles and Interactions Critical Roles Core Roles Additional Roles Existing Related Roles Definitions ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Appendix A: Other BC Government Discipline Groups Role Definitions: Data, Security, and Records Management Definitions: Security and Records Disciplines Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 2 of 23
3 1 INTRODUCTION This document was created by the Data Architecture Advisory Committee (DAAC), as part of their expert advisor role to the Architecture and Standards Branch. The original version of these guidelines was published by the Data Administration Forum (DAAC forerunner) in April The roles and responsibilities described here reflect best practices for data management within the Province of British Columbia. From a business context, these concepts provide foundational support for improving information access and sharing both internally within government and to the public. 1.1 Purpose The Core Policy and Procedures Manual, Chapter 12 sets expectations for ministries and agencies to implement consistent data management practices. Beyond policy directives, the concept of accountability for a set of data is a critical building block for effective business operations and for fostering partner engagement to integrate information management activities across government. Where there is confusion around business accountability, operational risks are higher and there is little or no successful integration of information resources. Understanding and implementing the roles in these Guidelines will clarify business decision-making and encourage information sharing and integration. This data management model is based on the existence of Data Custodians: senior managers who are accountable and responsible for collecting and maintaining data of interest to government and in an appropriate manner making this data publicly available. The Guidelines provide a reference for building and improving this capability. 1.2 Intended Audience This document serves as a reference for resources involved in the management of government data or the development or maintenance of systems which act on government data. In particular, these guidelines can be used by ministries as part of the education and communication process for improving information management in their organization. 1.3 Scope The roles and responsibilities in this document pertain to data and information management roles pertinent to the governance, planning, definition, capture, usage and access to data and/or information. The defined roles cover a broad area some roles only data management, some roles both data management and information management depending on the context of the specific situation. Where data is used, it may also refer to information i.e. data that has been transformed into information. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 3 of 23
4 1.3.1 In Scope: Roles that deal with data stored in databases data wherever else it may reside and in whatever medium, including paper data with context (data translated into information) technical roles that have direct responsibilities for some aspect of data management, such as those related to database management information management leadership and guidance for appropriately planning for and turning data into useful business information Out of Scope: Roles that deal specifically with records management (e.g., role provided by the Ministry/Sector Records Officer position) information security (e.g., role provided by the Ministry Information Security Officer position) technical or enabling technology roles (e.g. application development or infrastructure delivery) 1.4 Owner Within British Columbia, the Crown is the owner of government information (i.e., the asset owner). For information that the Crown (e.g., a ministry) is holding on behalf of, or from another source (e.g., an individual s health information), the data management roles remain constant but the owner will be different. Information owners have accountability for information throughout its life cycle, including decision making authority for creating, classifying, restricting, regulating and administering its use or disclosure. The implementation of these decisions can be delegated. 1.5 Data Custodianship Principles There are many data-related roles, but the Data Custodian role is the single most important for decision-making and leadership. The Principles of Data Custodianship on the following page are defined in the Data Custodianship Guidelines for the Natural Resource Sector and are fundamental statements for the governance of government data. These Principles are aligned with industry best practices for data management as defined by The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF). Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 4 of 23
5 Custodian Principle Data Custodian is Corporate Trustee Data Custodian is Standards Bearer Data Custodian is the Authoritative Source for the Province Data Custodian is Accountable Data Custodian Ensures Availability One and Only One Data Custodian Description Data Custodians operate as a trustee on behalf of the Information Owner. Data Custodians ensure the development and enforcement of standards for data within their care. Data Custodians are the authoritative source for data within their care. Data Custodians are accountable for managing the data within their care Data Custodians will ensure that data is available to authorized users and, where possible, make this data accessible to the public Each set of data 1 has a single, designated Data Custodian, without exception 1.6 Other Related References The scope of this document includes the roles required for data management which may include some information management functions. Information management depends on data planning and management activities to optimize the use of information as a vital business resource Data Administration Standards The Data Administration Standards define minimum criteria for data management that apply to data within the BC government, and are for use by ministries when developing a data architecture function. The intent is to make a minimum set of data standards mandatory, while encouraging all ministries to follow best practices in all information management. 1 Set of data has a specific meaning in this document. It is defined as data holdings (collected data) for a discrete corporate information subject. The set of data must be of a lasting nature, collected, managed, and used to serve an essential defined business purpose for government. One may also use the term corporate data for similar meaning in the context of a ministry s business (i.e. ministry corporate data) or in the context of government-wide standards (i.e. government corporate data). It does not equate to a dataset, which is popularly used for anything from a single spreadsheet to massive multiple databases, and is therefore a term which is difficult to scope. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 5 of 23
6 2 DATA MANAGEMENT ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The responsibilities outlined here are meant to introduce basic concepts and roles, and are not intended to be used as the full set of functions for a specific staff position. To consistently manage data, and by extension, information, ministries should ensure they understand and use the three Critical Data Roles defined below. Core and Additional roles supplement the Critical Data Roles and will help support business operations and integration. Smaller ministries, or those with fewer data holdings, may be able to combine multiple roles into single jobs where this happens, the role descriptions will help Ministries understand and differentiate activities. The Data Custodian role needs to be positioned at a senior management level within ministries to be effective, e.g. Director in larger ministries or Executive Director in smaller ministries. Typically, ministries will already have staff performing some or all of the activities described in these role descriptions. The best practices described here will guide improvement. To effectively implement data management responsibilities they must be assigned to a specific set, or collection, of data (refer to Definitions). The word Manager describes the function of the role and does not necessarily imply it is at a management level. 2.1 Critical, Core, Additional and Existing Roles Critical Data Roles The following roles are critical for successful data management, and should be the first data management roles implemented or assigned within any ministry. Data Custodian Data Standards Manager Data Steward (where support to the Data Custodian is required) Core Data Roles The following core roles are important to help guide and implement successful data management. Larger ministries or those with larger data holdings will find these roles indispensible. Data Resource Manager Application Custodian Data Architect or Data Administrator Database Administrator Discipline Authority Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 6 of 23
7 2.1.3 Additional Roles for Best Practices Data Usage Contact Data Analyst Data User Data Product Provider Existing BC Government Roles The following three roles are defined within the normal government organizational structure and are included to provide context in supporting the data management roles. Government Chief Information Officer Ministry Executive Ministry Chief Information Officer Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 7 of 23
8 2.2 Data Management Roles and Interactions The following diagram depicts the three viewpoints of data management: Business, or business context for the data; Governance or overall planning for the data; and Operations, or the implementation and daily management of data. The interactions of the roles are depicted in the diagram below. The intersection of the circles depicts the areas of commonality and interaction between subject matter experts from different perspectives. Note: All roles may interact at times. Key interactions are depicted as specific roles (Data Standards Manager, Data Usage Contact). Data Management Roles (single organization / single ministry perspective) Data User (read only) Business ( owner view) Data Custodian Discipline Authority Data Analyst Ministry Executive Data Architect Data Standards Manager Ministry CIO Information Governance Council* e.g. Data Custodian Council Governance ( planner view) logical design & physical development Data Usage Contact * Information Governance Council - see Definitions RED text: business-focused role BLUE text: information management role Inside the circles = roles related to standards and decisions Outside the circles = data use and maintenance Database Administrator Data Resource Manager (updates) Data Steward Operations ( daily use view) Data Product Provider Data Management Roles The following sections include a description of each role and its responsibilities. In addition to the viewpoints above (Business, Governance, Operations), we included an Organizational (overseer) viewpoint. Thus, Ministry Executive and Ministry Chief Information Officer both have overall organizational responsibility for the effective management of data within the organization. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 8 of 23
9 2.3 Critical Roles Data Custodian Establishes province-wide standards, definitions, and rules for business information within their mandate, to enable the Province to gain maximum value from the information. Viewpoint: Business accountable for implementing operational policy, business value, scope, definitions, rules, standards, structure, content, use and disposal for data under their responsibility responsible for the collection, storage, protection, promotion and delivery of their data, ensuring it meets the business needs of the organization fulfilling the legislated responsibility or program mandate of ensuring data quality, completeness, and integrity through the management of its creation and maintenance allocating resources in order to meet data needs ensuring the value of data is maximized through sharing serving on an Information Governance Council or equivalent where the scope of their information resources is substantial within their Ministry. a major business need for data is identified issues arise concerning data policy, business value, scope, security Data Standards Manager Business expert with detailed knowledge of the data structure, content, and appropriate use of the business information for their program area(s), who develops and sets the data management standards approved by their Data Custodian. Responsible for the dayto-day management of the data and business issues, according to the defined data standards and data management plan. Viewpoint: Business & Operations acting as the primary contact for business data within the program area, on behalf of the Data Custodian authoring data management plan(s) (see Definitions), defining and managing the standards for acquisition, maintenance, and disposition of data to ensure data quality, resolving issues, and advising other roles ensuring designed data structures meet business needs ensuring the delivery of defined services at an operational level ensuring the protection of data is commensurate with its value and Information security classification Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 9 of 23
10 data access is required, within the scope of the program area operational, business, or data definition issues arise or cannot be resolved, or data errors are perceived further detailed information about their program area s data is required further data services are required to meet new business needs data management planning is required, or additional data may be encompassed within their business scope Data Steward An inclusive role that accepts one or more negotiated data stewardship activities on behalf of the Data Custodian. Data Stewards have the operational or technical ability to assist a Data Custodian in the collection, delivery, or maintenance of the set of data. Note that the Data Custodian cannot transfer accountability to the Data Steward although the Data Steward may be responsible for specific activities. Viewpoint: Operations supports the Data Custodian with expertise, or resources, to carry out one or more of their responsibilities as a peer of the Data Custodian, the Data Steward is bound by signed agreement which details the responsibilities with respect to both parties specific identified responsibility(s) are transferred from the Data Custodian to the Data Steward (accountability remains with the Data Custodian) Per the stewardship agreement, when operational needs arise Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 10 of 23
11 2.4 Core Roles Data Resource Manager Any employee who has responsibility for the collection and/or management of government data. The use or update of information must be consistent with standards set by the Data Custodian. Operational accountability resides with the most senior person in each office to verify that data collection and management is conducted to the defined standard. Viewpoint: Operations providing leadership for data collection, update, and management to the Data Custodian s defined standards providing operational input into the business design decision-making process assessing the quality of data collection efforts to ensure that the data is collected to the standards defined by the Data Custodian retaining a focus on overall program needs while collecting information, to optimize the use of that data and ensure business decisions are based on the best information available business-related queries are required Data Architect (a.k.a. Data Administrator) Senior technical data management expert with a corporate role (i.e. an overall organizational point of view), providing leadership on information systems theory and practice, data architecture and modeling expertise, and custodianship of the corporate data models. Provides and promotes the framework for consistency in scope, meaning, and handling of data across the entire organization (e.g. ministry). Viewpoint: Governance and Business Ministry-wide leadership role promoting data/information resource management: the concept that data/information is a major corporate resource and must be managed using the same basic principles used to manage other major assets promoting information management principles, practices, guidelines and standards within the organization, while adhering to published government standards and guidelines for data management Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 11 of 23
12 providing a framework for defining and interpreting the ministry s corporate data and its structure (information architecture, including metadata) to support the organization s data related goals and objectives, and ensuring the corporate value of data is maximized through sharing across diverse program areas creating or validating data models produced in the organization, and storing and maintaining the data models and definitions (e.g. a metadata repository) providing expertise to the ministry in improving data quality across all business areas defining compelling business arguments for senior management to elicit change on future or existing data issues cooperating with the Database Administrator in database design efforts liaise across-government (e.g., Data Architecture Advisory Committee (DAAC)) to develop and promote sound and consistent data management practices analysis of the organization s data inter-relationships is required access to data repositories is required standards for defining, storing, and delivering data are required responsibilities for data need to be determined data models require validating and quality assurance, prior to incorporating as corporate models and transposing them into physical models deviations from defined logical data structures are required Database Administrator Senior database management expert with a ministry-wide focus responsible for the analysis, design, and creation of new databases, the physical design and implementation of new database tables and applications on existing databases, and for database administration and backup. Typically, this role also plans, co-ordinates and implements security measures and improves the performance and efficiency of data storage. Viewpoint: Operations building databases to support developing, maintaining, and implementing of physical data structures defining ministry-wide standards for physical data management ensuring that efficient data structure design and disaster recovery/backup procedures are effectively tested and implemented developing (and reviewing) physical data structures in consultation with Data Administration and system development and maintenance staff Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 12 of 23
13 ensuring security administration through monitoring and administering DBMS security constraints, such as removing users, administering quotas, auditing, and checking for security problems. analyzing data stored in the database and making recommendations relating to performance and efficiency of that data storage. This includes the effective use of indexes, enabling "Parallel Query" execution, or other DBMS specific features logical data models are ready for implementation expertise is required to resolve issues related to: database management anomalies occurring in the operation of a database physical data security disaster recovery or database back-up system migration or database platform standards data performance degradation Application Custodian Sponsors projects to develop information systems, and provides ongoing support for those systems to meet business needs. Viewpoint: Business accountable for applications that enable information entry, retrieval, and updating, and derive the best possible business benefit from the use of the application ensuring that, within their application mandate, they provide local leadership in support of the Data Custodian(s) conducting impact analysis and coordinating application changes to avoid adverse impacts on other applications or data a need for a new business function(s) or new application(s) is identified there are major problems with existing applications Discipline Authority Business expert or specialist who understands the business relevance of the data standards within their scope of work. Interprets the meaning of detailed data standards to ensure the appropriate use of data and information needed to meet organizational needs. A primary resource for the Data Standards Manager. The Discipline Authority is usually at the senior scientific, analytical, or research level. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 13 of 23
14 Viewpoint: Business interpreting and defining data within the scope of their expertise and according to the business need providing expert understanding of the subject area and business definitions providing guidance and subject matter expertise on the business use of the data understanding of data is not clear from definitions and specifications interpretation of data, outside of existing specifications, is required Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 14 of 23
15 2.5 Additional Roles Data Usage Contact Business data expert that commonly provides technical services for decision making support for data managers, data custodians, business managers and operational users. A primary resource for the Data Resource Manager. Viewpoint: Business and Operations querying data content and using data effectively according to standards performing statistical analysis of business data analyzing business and system data business-related database queries are required data mining or data reporting is needed to solve system or business related questions Data Analyst Information management analysis and design role that focuses on providing business or IT system decision support through analysis, and problem solving data related topics including data design, integration, data relationships, data quality, data transformation, data replication and data modeling. This role varies widely across government. Viewpoint: Business and Operations Performing systems analysis and design, documenting the structure, relationships and types of business data through logical modeling, or validating logical models from other sources mapping the data dependencies from system to system to identify crossprogram impact issues or answer business-related technical questions Providing business intelligence support by performing business data analysis and reporting to enable better business decision-making analysis and problem solving of business or system data-related issues is required Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 15 of 23
16 2.5.3 Data User Anyone who uses data to conduct analyses, make decisions or otherwise carry out work. Viewpoint: Business obligated to abide by the Data Custodian s governing policies and standards understands the context in which the data can be used. business-related queries are required Data Product Provider Any party responsible for the creation or publication of a set of data that is derived from one or more sources of primary government data, i.e., data for which there is an assigned Data Custodian. (NOTE: must have written permission from the Data Custodian for proper acknowledgement of copyright. With future emphasis on government moving to open data, this may become less important.) A Data Product is created by combining or manipulating one or more sets of data in order to address a particular business need. Data Products may also be called resultants, derivative products, analytical products, value-added sets of data, integrated sets of data, etc. Viewpoint: Business and Operations recognizing that accountability for the original data remains with the originating Data Custodian ensuring that all aspects of the data lifecycle are followed for the Data Product ensuring that the Data Product is managed as a set of data, and that any interpretation, modification or aggregation with other sets of data is consistent with the original data; i.e., accountable for the data product standard ensuring acknowledgement of the primary data source(s), from which the Data Product is derived business-related queries into the Data Product are required Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 16 of 23
17 2.6 Existing Related Roles Government Chief Information Officer (GCIO) Ensures government-wide policy for data creation, maintenance, and use is compliant with legislation, policy and standards. Operationalizes strategic directions for the management of IM/IT within government. The policy direction provided applies to all Ministries and sector groupings. Viewpoint: Governance leads the structure for IM/IT management and decision making, in concert with senior executives from all BC Government ministries manages the OCIO and for the Ministry Chief Information Officers (MCIOs), as described in detail in the Province's Core Policy and Procedures Manual is accountable for the creation of government-wide data management policy, frameworks, standards and infrastructures strengthens the IM/IT governance processes of the province through strategic planning and discussion with all ministries on priorities and possibilities to leverage best practices and industry standards Ministries are established or changed and this involves the definition of data management mandates or roles new/changed information management policy or standards are proposed that affect multiple ministries, or entire sectors IM/IT issues arise that require corporate consideration compliance issues arise between Ministries Ministry Executive Responsible for developing the policy framework within specific line(s) of business within a Ministry. Collectively define the strategic scope of the organization and overall business services. Viewpoint: Business and Governance identifying and communicating Custodianship responsibilities within their organization ensuring ministry Data Custodians liaise between their organizations and others establishing and resourcing the areas of data responsibility approving ministry policies ensuring compliance with legislation, policies and standards formally recognizing and communicating the importance of information to the business Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 17 of 23
18 lines of business are established or changed that require definition of data management roles new/changed policy or legislation is proposed compliance issues arise need resourcing for data responsibilities Ministry Chief Information Officer Ensures the organization uses information management and information technology (IM/IT) efficiently, in alignment with OCIO policy, standards and directions. Viewpoint: Governance ensuring compliance with the strategic direction of government ensuring strategic and operational plans for IM/IT are developed establishing and promoting the organization s information management policies, in alignment with OCIO policies and standards providing IM/IT leadership and facilitating data management within the organization advising the OCIO on information management and information technology issues and opportunities compliance issues arise strategic direction of the ministry changes information management policy amendments or new policy is required Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 18 of 23
19 3 DEFINITIONS Corporate information: information that is of a permanent or lasting nature, is essential to the Government s operation. Data Architecture: describes the structure of an organization s logical and physical data assets and data management resources (see TOGAF). Data Management Plan: describes the strategic use and future plans for a major set of data within a program area. The management of a set of data goes beyond where is it stored, what format and when was it last updated potential issues such as whether the data will meet future business and user needs, adequacy of data collection standards, level of data quality, adequacy of resourcing, etc. See the Natural Resource Sector s Data Management Plan Template. Information Governance Council: A strategy group made up of those Data Custodians responsible for the more substantial Ministry information resources. This core group concentrates on major issues, and chooses Ministry-wide options, thus influencing the choices that other Data Custodians will have available. The Council is also a forum for contemplating impacts of legislative or policy changes. Ministry Client (from a Data Custodian s perspective): any agency, company, office, or individual for whom services are rendered (e.g., a Ministry employee or Ministry office; another government Ministry or agency; an external private sector industry company or company employee; a member of the public). Set of Data: Set of data has a specific meaning in this document. It is defined as data holdings (collected data) for a discrete corporate information subject. The set of data must be of a lasting nature, collected, managed, and used to serve an essential defined business purpose for government. One may also use the term corporate data for similar meaning in the context of a ministry s business (i.e. ministry corporate data) or in the context of government-wide standards (i.e. government corporate data). It does not equate to a dataset, which is popularly used for anything from a single spreadsheet to massive multiple databases, and is therefore a term difficult to scope. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 19 of 23
20 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to acknowledge the work done by the following in establishing these roles and definitions: ANZLIC (Australia and New Zealand Land Information Council) Integrated Land Management Bureau, Province of British Columbia Ministry of Attorney General, Province of British Columbia Ministry of Education, Province of British Columbia Ministry of Environment, Province of British Columbia Ministry of Finance, Province of British Columbia Ministry of Forests and Range, Province of British Columbia Office of the Chief Information Officer, Province of British Columbia John Zachman s Framework for Enterprise Architecture Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 20 of 23
21 5 APPENDIX A: OTHER BC GOVERNMENT DISCIPLINE GROUPS The following diagram shows the relationship between the Data Management, Records Management, and Security Management disciplines major roles (in green roundcornered rectangles). Ownership flows from the Crown, and legislation, policy and standards define how the custodians can work with the information in their care. These custodians may be internal or external to government, but the Data Custodian is always within government, exercising the Crown s control over the information. Government can have full custody and control of the information in its care, or it may relinquish full or partial custody of the information to another party. Government always retains decision-making authority on how that information will be stored, managed and protected. For example, where data is in the custody of parties external to government (e.g. personal health information in Health Authorities), the Crown still sets the rules and requirements for how that information must be handled. The Crown retains control of the full information lifecycle for government information. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 21 of 23
22 5.1 Role Definitions: Data, Security, and Records Management Records Management and Security Management are two other discipline groups in the Province of British Columbia that have defined accountability for managing data and/or information. The following table shows some of the semantic differences between published roles from the three disciplines (Data Management, Records Management, and Security Management). Published Role (see definitions below) Information Owner 2 Information Custodian Data Custodian Office of Primary (OPR) Discipline Security Management Security Management Data Management Records Management Normally Assigned To: Deputy Minister, on behalf of the Crown; may be further delegated by the Deputy Minister Anyone who maintains or administers information resources on behalf of the Information Owner. Branch Director, on behalf of the Deputy Minister, who maintains or administers data resources on behalf of the Information Owner. Senior manager of any government office Information Owners (Information Security Policy, see Definitions) have the responsibility and decision making authority for information throughout its life cycle, including creating, classifying, restricting, regulating and administering its use or disclosure. Within the Government of British Columbia, information ownership flows from the Crown to government Ministers to Deputy Ministers (or equivalent). Information ownership may be further delegated by the Deputy Minister. Information Custodians (Information Security Policy, see Glossary) maintain or administer information resources on behalf of the Information Owner. Custodianship includes responsibility for accessing, managing, maintaining, preserving, disposing and providing security for the information resource. In contrast, information custody means having physical possession of information without necessarily having responsibility for the information. Data Custodian (this document) the branch director or senior manager who establishes province-wide policy, definitions, and rules for business information within their mandate, to enable government to gain maximum value from the information. 2 Information Security Policy (b) states: Within the Government of British Columbia, information ownership flows from the Crown to government Ministers to Deputy Ministers (or equivalent). Information ownership may be further delegated by the Deputy Minister. Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 22 of 23
23 Office of Primary (Recorded Information Management Manual and external Glossary) The office that has primary responsibility for a category of records or holds the master copy of any record series for that ministry or agency. The OPR maintains the official master copy of the records in order to satisfy operational, financial, legal, audit and other requirements. 5.2 Definitions: Security and Records Disciplines For the underlying policy framework and standards, see Core Policy chapter 12 ( including section Information Security roles are defined in policy and procedures (see gww.cio.gov.bc.ca). In scope of this document are responsibilities for granting access to data and the physical enabling of access to data in databases. Out of scope are other security responsibilities such as monitoring, handling incidents, security awareness and training. Records Management is the exercise of intellectual and physical control over records to ensure their integrity in support of an organization s accountabilities and actions. Ministries and agencies establish intellectual control over their records by ensuring they are classified, retained and disposed of in accordance with records schedules., and establish physical control by ensuring records are identified, documented, located, retrieved, and protected from loss, physical damage or inappropriate access. There are touch points and overlap with some aspects of data management, but the relationship to records management is not fully defined in this document. E N D Data Management Roles and Responsibilities September 2010 Page 23 of 23
BC Geographic Warehouse. A Guide for Data Custodians & Data Managers
 BC Geographic Warehouse A Guide for Data Custodians & Data Managers Last updated November, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Purpose... 1 Audience... 1 Contents... 1 It's All About Information...
BC Geographic Warehouse A Guide for Data Custodians & Data Managers Last updated November, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Purpose... 1 Audience... 1 Contents... 1 It's All About Information...
Guideline for Roles & Responsibilities in Information Asset Management
 ISO 27001 Implementer s Forum Guideline for Roles & Responsibilities in Information Asset Management Document ID ISMS/GL/ 003 Classification Internal Use Only Version Number Initial Owner Issue Date 07-08-2009
ISO 27001 Implementer s Forum Guideline for Roles & Responsibilities in Information Asset Management Document ID ISMS/GL/ 003 Classification Internal Use Only Version Number Initial Owner Issue Date 07-08-2009
5 FAM 630 DATA MANAGEMENT POLICY
 5 FAM 630 DATA MANAGEMENT POLICY (Office of Origin: IRM/BMP/OCA/GPC) 5 FAM 631 GENERAL POLICIES a. Data management incorporates the full spectrum of activities involved in handling data, including its
5 FAM 630 DATA MANAGEMENT POLICY (Office of Origin: IRM/BMP/OCA/GPC) 5 FAM 631 GENERAL POLICIES a. Data management incorporates the full spectrum of activities involved in handling data, including its
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT MANUAL TRANSMITTAL SHEET. 1283 Data Administration and Management (Public)
 Form 1221-2 (June 1969) Subject UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT MANUAL TRANSMITTAL SHEET 1283 Data Administration and Management (Public) Release 1-1742 Date 7/10/2012
Form 1221-2 (June 1969) Subject UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT MANUAL TRANSMITTAL SHEET 1283 Data Administration and Management (Public) Release 1-1742 Date 7/10/2012
Rowan University Data Governance Policy
 Rowan University Data Governance Policy Effective: January 2014 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Regulations, Statutes, and Policies... 4 3. Policy Scope... 4 4. Governance Roles... 6 4.1. Data
Rowan University Data Governance Policy Effective: January 2014 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Regulations, Statutes, and Policies... 4 3. Policy Scope... 4 4. Governance Roles... 6 4.1. Data
NSW Data & Information Custodianship Policy. June 2013 v1.0
 NSW Data & Information Custodianship Policy June 2013 v1.0 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE... 4 2. INTRODUCTION... 4 2.1 Information Management Framework... 4 2.2 Data and information custodianship... 4 2.3 Terms...
NSW Data & Information Custodianship Policy June 2013 v1.0 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE... 4 2. INTRODUCTION... 4 2.1 Information Management Framework... 4 2.2 Data and information custodianship... 4 2.3 Terms...
PROCEDURE. The permission rights assigned to allow data custodians to view, copy, enter, download, update or query data.
 Section: Subject: Administration (AD) Data Governance AD.3.3.1 DATA GOVERNANCE PROCEDURE Legislation: Alberta Evidence Act, RSA 2000, c.a-18; Electronic Transactions Act, SA 2001, c.e- 5.5; Freedom of
Section: Subject: Administration (AD) Data Governance AD.3.3.1 DATA GOVERNANCE PROCEDURE Legislation: Alberta Evidence Act, RSA 2000, c.a-18; Electronic Transactions Act, SA 2001, c.e- 5.5; Freedom of
RECORDS MANAGEMENT POLICY
 RECORDS MANAGEMENT POLICY POLICY STATEMENT The records of Legal Aid NSW are a major component of its corporate memory and risk management strategies. They are a vital asset that support ongoing operations
RECORDS MANAGEMENT POLICY POLICY STATEMENT The records of Legal Aid NSW are a major component of its corporate memory and risk management strategies. They are a vital asset that support ongoing operations
Institutional Data Governance Policy
 Institutional Data Governance Policy Policy Statement Institutional Data is a strategic asset of the University. As such, it is important that it be managed according to sound data governance procedures.
Institutional Data Governance Policy Policy Statement Institutional Data is a strategic asset of the University. As such, it is important that it be managed according to sound data governance procedures.
Data Governance Policy. Staff Only Students Only Staff and Students. Vice-Chancellor
 Name of Policy Description of Policy Policy applies to Data Governance Policy To establish proper standards to assure the quality and integrity of University data. This policy also defines the roles and
Name of Policy Description of Policy Policy applies to Data Governance Policy To establish proper standards to assure the quality and integrity of University data. This policy also defines the roles and
Interagency Science Working Group. National Archives and Records Administration
 Interagency Science Working Group 1 National Archives and Records Administration Establishing Trustworthy Digital Repositories: A Discussion Guide Based on the ISO Open Archival Information System (OAIS)
Interagency Science Working Group 1 National Archives and Records Administration Establishing Trustworthy Digital Repositories: A Discussion Guide Based on the ISO Open Archival Information System (OAIS)
Technical Competency Framework for Information Management (IM)
 Technical Competency Framework for Information Management (IM) Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) June 15, 2009 Table of contents IM Competency Framework...1 Competency 1: Information Management
Technical Competency Framework for Information Management (IM) Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) June 15, 2009 Table of contents IM Competency Framework...1 Competency 1: Information Management
Information and records management. Purpose. Scope. Policy
 Information and records management NZQA Quality Management System Policy Purpose The purpose of this policy is to establish a framework for the management of corporate information and records within NZQA.
Information and records management NZQA Quality Management System Policy Purpose The purpose of this policy is to establish a framework for the management of corporate information and records within NZQA.
Scotland s Commissioner for Children and Young People Records Management Policy
 Scotland s Commissioner for Children and Young People Records Management Policy 1 RECORDS MANAGEMENT POLICY OVERVIEW 2 Policy Statement 2 Scope 2 Relevant Legislation and Regulations 2 Policy Objectives
Scotland s Commissioner for Children and Young People Records Management Policy 1 RECORDS MANAGEMENT POLICY OVERVIEW 2 Policy Statement 2 Scope 2 Relevant Legislation and Regulations 2 Policy Objectives
OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE. Data Stewardship and Custodianship Policy. Superseded By:
 OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE Enquiries to: Ruth Alberts OD number: OD0321/11 Performance Directorate Phone number: 9222 4218 Date: February 2011 Supersedes: OD 0107/08 File No: F-AA-00673 Subject: Data Stewardship
OPERATIONAL DIRECTIVE Enquiries to: Ruth Alberts OD number: OD0321/11 Performance Directorate Phone number: 9222 4218 Date: February 2011 Supersedes: OD 0107/08 File No: F-AA-00673 Subject: Data Stewardship
Information Management and Protection Policy
 Document Title: Information Management and Protection Policy Document Type: Policy No. Of Pages (11) Scope: Government of Newfoundland and Labrador and Public Bodies supported by the Office of the Chief
Document Title: Information Management and Protection Policy Document Type: Policy No. Of Pages (11) Scope: Government of Newfoundland and Labrador and Public Bodies supported by the Office of the Chief
U.S. Department of Education. Office of the Chief Information Officer
 U.S. Department of Education Office of the Chief Information Officer Investment Review Board (IRB) CHARTER January 23, 2013 I. ESTABLISHMENT The Investment Review Board (IRB) is the highest level IT investment
U.S. Department of Education Office of the Chief Information Officer Investment Review Board (IRB) CHARTER January 23, 2013 I. ESTABLISHMENT The Investment Review Board (IRB) is the highest level IT investment
Information Management Advice 39 Developing an Information Asset Register
 Information Management Advice 39 Developing an Information Asset Register Introduction The amount of information agencies create is continually increasing, and whether your agency is large or small, if
Information Management Advice 39 Developing an Information Asset Register Introduction The amount of information agencies create is continually increasing, and whether your agency is large or small, if
City of Minneapolis Policy for Enterprise Information Management
 City of Minneapolis Policy for Enterprise Information Management Origin: Developed by the City Clerk s Office and Business Information Services. Based on requirements set forth in Federal and State regulations
City of Minneapolis Policy for Enterprise Information Management Origin: Developed by the City Clerk s Office and Business Information Services. Based on requirements set forth in Federal and State regulations
Data Governance Policy. Version 2.0 19 October 2015
 Version 2.0 19 October 2015 Document Title: Summary: Date of Issue: Status: Contact Officer: Applies To: References: This policy provides the Cancer Institute NSW with an instrument to formally manage
Version 2.0 19 October 2015 Document Title: Summary: Date of Issue: Status: Contact Officer: Applies To: References: This policy provides the Cancer Institute NSW with an instrument to formally manage
Institutional Data Governance Policy
 Scope This document sets out the policy and framework to be followed to manage Institutional Data and applies to data in all its forms. Status and Effective date Approved, April 2015 Validity: under annual
Scope This document sets out the policy and framework to be followed to manage Institutional Data and applies to data in all its forms. Status and Effective date Approved, April 2015 Validity: under annual
Information Security Policy. Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services
 Information Security Policy Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services Contents 1 Purpose / Objective... 1 1.1 Information Security... 1 1.2 Purpose... 1 1.3 Objectives...
Information Security Policy Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services Contents 1 Purpose / Objective... 1 1.1 Information Security... 1 1.2 Purpose... 1 1.3 Objectives...
3. Provide the capacity to analyse and report on priority business questions within the scope of the master datasets;
 Business Intelligence Policy Version Information A. Introduction Purpose Business Intelligence refers to the practice of connecting facts, objects, people and processes of interest to an organisation in
Business Intelligence Policy Version Information A. Introduction Purpose Business Intelligence refers to the practice of connecting facts, objects, people and processes of interest to an organisation in
Management and Use of Information & Information Technology (I&IT) Directive. Management Board of Cabinet
 Management and Use of Information & Information Technology (I&IT) Directive Management Board of Cabinet February 28, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS PURPOSE... 1 APPLICATION AND SCOPE... 1 PRINCIPLES... 1 ENABLE
Management and Use of Information & Information Technology (I&IT) Directive Management Board of Cabinet February 28, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS PURPOSE... 1 APPLICATION AND SCOPE... 1 PRINCIPLES... 1 ENABLE
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS)
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS) Revised: October 2012 i Table of contents Attribute Standards... 3 1000 Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility...
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS) Revised: October 2012 i Table of contents Attribute Standards... 3 1000 Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility...
How To Develop An Enterprise Architecture
 OSI Solution Architecture Framework Enterprise Service Center April 2008 California Health and Human Services Agency Revision History REVISION HISTORY REVISION/WORKSITE # DATE OF RELEASE OWNER SUMMARY
OSI Solution Architecture Framework Enterprise Service Center April 2008 California Health and Human Services Agency Revision History REVISION HISTORY REVISION/WORKSITE # DATE OF RELEASE OWNER SUMMARY
COMDTINST 5200.7 11 JUL 2013 COAST GUARD C4I DATA MANAGEMENT (DM) POLICY
 Commandant 2100 2 nd St SW Stop 7101 United States Coast Guard Washington, DC 20593-7101 Staff Symbol: CG-6 Phone: (202) 475-3469 Fax: (202)475-3930 Email: [email protected] COMMANDANT INSTRUCTION 5200.7 COMDTINST
Commandant 2100 2 nd St SW Stop 7101 United States Coast Guard Washington, DC 20593-7101 Staff Symbol: CG-6 Phone: (202) 475-3469 Fax: (202)475-3930 Email: [email protected] COMMANDANT INSTRUCTION 5200.7 COMDTINST
NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture. Version 3.0
 NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture Version 3.0 October 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SOLUTION ARCHITECTURE...1 Introduction...1 Benefits...3 Link to Implementation Planning...4 Definitions...5
NASCIO EA Development Tool-Kit Solution Architecture Version 3.0 October 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SOLUTION ARCHITECTURE...1 Introduction...1 Benefits...3 Link to Implementation Planning...4 Definitions...5
October 8, 2014. User Conference. Ronald Layne Manager, Data Quality and Data Governance [email protected]
 Ensuring the highest quality data is delivered throughout the university providing valuable information serving individual and organizational need October 8, 2014 Ronald Layne Manager, Data Quality and
Ensuring the highest quality data is delivered throughout the university providing valuable information serving individual and organizational need October 8, 2014 Ronald Layne Manager, Data Quality and
4.10 Information Management Policy
 Policy Statement Information is a strategic business resource that the must manage as a public trust on behalf of Nova Scotians. Effective information management makes program and service delivery more
Policy Statement Information is a strategic business resource that the must manage as a public trust on behalf of Nova Scotians. Effective information management makes program and service delivery more
INFORMATION MANAGEMENT STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK GENERAL NAT 11852-08.2004 OVERVIEW
 GENERAL OVERVIEW NAT 11852-08.2004 SEGMENT FORMAT PRODUCT ID INFORMATION MANAGEMENT STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK In the context of the Information Management Strategic Framework, information is defined as: information
GENERAL OVERVIEW NAT 11852-08.2004 SEGMENT FORMAT PRODUCT ID INFORMATION MANAGEMENT STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK In the context of the Information Management Strategic Framework, information is defined as: information
RECORD AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK FOR ONTARIO SCHOOL BOARDS/AUTHORITIES
 PURPOSE Records and information are important strategic assets of an organization and, like other organizational assets (people, capital and technology), must be managed to maximize their value. Information
PURPOSE Records and information are important strategic assets of an organization and, like other organizational assets (people, capital and technology), must be managed to maximize their value. Information
Outline of a Research Data Management Policy for Australian Universities / Institutions
 Outline of a Research Data Management Policy for Australian Universities / Institutions This documents purpose: This document is intended as a basic starting point for institutions that are intending to
Outline of a Research Data Management Policy for Australian Universities / Institutions This documents purpose: This document is intended as a basic starting point for institutions that are intending to
Digital Records Preservation Procedure No.: 6701 PR2
 Digital Records Preservation Procedure No.: 6701 PR2 Policy Reference: Category: Department Responsible: Current Approved Date: 6700 Records Management Information Management Records Management and Privacy
Digital Records Preservation Procedure No.: 6701 PR2 Policy Reference: Category: Department Responsible: Current Approved Date: 6700 Records Management Information Management Records Management and Privacy
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS)
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS) Introduction to the International Standards Internal auditing is conducted in diverse legal and cultural environments;
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR THE PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE OF INTERNAL AUDITING (STANDARDS) Introduction to the International Standards Internal auditing is conducted in diverse legal and cultural environments;
ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY # 32 8 2 (2014) Information Security Roles and Responsibilities
 Policy Title: Information Security Roles Policy Type: Administrative Policy Number: ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY # 32 8 2 (2014) Information Security Roles Approval Date: 05/28/2014 Revised Responsible Office:
Policy Title: Information Security Roles Policy Type: Administrative Policy Number: ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY # 32 8 2 (2014) Information Security Roles Approval Date: 05/28/2014 Revised Responsible Office:
A Holistic Framework for Enterprise Data Management DAMA NCR
 A Holistic Framework for Enterprise Data Management DAMA NCR Deborah L. Brooks March 13, 2007 Agenda What is Enterprise Data Management? Why an EDM Framework? EDM High-Level Framework EDM Framework Components
A Holistic Framework for Enterprise Data Management DAMA NCR Deborah L. Brooks March 13, 2007 Agenda What is Enterprise Data Management? Why an EDM Framework? EDM High-Level Framework EDM Framework Components
INFORMATION ACCESS OPERATIONS LIST OF CORE SERVICES TO MINISTRY CLIENTS
 INFORMATION ACCESS OPERATIONS LIST OF CORE SERVICES TO MINISTRY CLIENTS NOTE: Reflects core services derived from Target IAO Business Operations Design, May 2009 FREEDOM OF INFORMATION BUSINESS PROCESS
INFORMATION ACCESS OPERATIONS LIST OF CORE SERVICES TO MINISTRY CLIENTS NOTE: Reflects core services derived from Target IAO Business Operations Design, May 2009 FREEDOM OF INFORMATION BUSINESS PROCESS
US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor June 1, 2007
 US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor June 1, 2007 Draft Enterprise Data Management Data Policies Final i Executive Summary This document defines data
US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor June 1, 2007 Draft Enterprise Data Management Data Policies Final i Executive Summary This document defines data
EXPLORING THE CAVERN OF DATA GOVERNANCE
 EXPLORING THE CAVERN OF DATA GOVERNANCE AUGUST 2013 Darren Dadley Business Intelligence, Program Director Planning and Information Office SIBI Overview SIBI Program Methodology 2 Definitions: & Governance
EXPLORING THE CAVERN OF DATA GOVERNANCE AUGUST 2013 Darren Dadley Business Intelligence, Program Director Planning and Information Office SIBI Overview SIBI Program Methodology 2 Definitions: & Governance
Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing
 Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing THE INSTITUTE OF INTERNAL AUDITORS 247 Maitland Avenue Altamonte Springs, Florida 32701-4201 Copyright c 2001 by The Institute of Internal Auditors,
Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing THE INSTITUTE OF INTERNAL AUDITORS 247 Maitland Avenue Altamonte Springs, Florida 32701-4201 Copyright c 2001 by The Institute of Internal Auditors,
Creating a Corporate Integrated Data Environment through Stewardship
 The Open Group Creating a Corporate Integrated Data Environment through Stewardship Enterprise Architecture Practitioners Conference Given January 2007 San Diego Presented by: Robert (Bob) Weisman CGI
The Open Group Creating a Corporate Integrated Data Environment through Stewardship Enterprise Architecture Practitioners Conference Given January 2007 San Diego Presented by: Robert (Bob) Weisman CGI
University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter
 University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter 1 Table of Contents 1.0 SIGNATURE PAGE 2.0 REVISION HISTORY 3.0 PURPOSE OF DOCUMENT 4.0 DATA GOVERNANCE PROGRAM FOUNDATIONAL ELEMENTS
University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter 1 Table of Contents 1.0 SIGNATURE PAGE 2.0 REVISION HISTORY 3.0 PURPOSE OF DOCUMENT 4.0 DATA GOVERNANCE PROGRAM FOUNDATIONAL ELEMENTS
Final Report. 2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures. September 18, 2014. Office of Audit and Evaluation
 2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures September 18, 2014 Office of Audit and Evaluation TABLE OF CONTENTS MAIN POINTS... i INTRODUCTION... 1 FOCUS OF THE AUDIT... 7 STATEMENT OF
2013-709 Audit of Vendor Performance and Corrective Measures September 18, 2014 Office of Audit and Evaluation TABLE OF CONTENTS MAIN POINTS... i INTRODUCTION... 1 FOCUS OF THE AUDIT... 7 STATEMENT OF
DGD14-006. ACT Health Data Quality Framework
 ACT Health Data Quality Framework Version: 1.0 Date : 18 December 2013 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Acknowledgements... 3 Document Control... 3 Document Endorsement... 3 Glossary... 4 1 Introduction...
ACT Health Data Quality Framework Version: 1.0 Date : 18 December 2013 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Acknowledgements... 3 Document Control... 3 Document Endorsement... 3 Glossary... 4 1 Introduction...
Department of Information and Technology Management
 INFOTEC Overview Department of Information and Technology Management Introduction The Information and Technology Management Department (INFOTEC) is responsible for providing modern, secure, fit for purpose
INFOTEC Overview Department of Information and Technology Management Introduction The Information and Technology Management Department (INFOTEC) is responsible for providing modern, secure, fit for purpose
State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework
 State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework June 2012 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 IT Governance Overview... 4 Process for Developing the New Framework... 4 Management of the
State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework June 2012 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 IT Governance Overview... 4 Process for Developing the New Framework... 4 Management of the
ClOP CHAPTER 1351.39. Departmental Information Technology Governance Policy TABLE OF CONTENTS. Section 39.1
 ClOP CHAPTER 1351.39 Departmental Information Technology Governance Policy TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 39.1 Purpose... 1 Section 39.2 Section 39.3 Section 39.4 Section 39.5 Section 39.6 Section 39.7 Section
ClOP CHAPTER 1351.39 Departmental Information Technology Governance Policy TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 39.1 Purpose... 1 Section 39.2 Section 39.3 Section 39.4 Section 39.5 Section 39.6 Section 39.7 Section
Master Data Management Architecture
 Master Data Management Architecture Version Draft 1.0 TRIM file number - Short description Relevant to Authority Responsible officer Responsible office Date introduced April 2012 Date(s) modified Describes
Master Data Management Architecture Version Draft 1.0 TRIM file number - Short description Relevant to Authority Responsible officer Responsible office Date introduced April 2012 Date(s) modified Describes
NATO UNCLASSIFIED. 27 February 2012 DOCUMENT C-M(2012)0014 Silence Procedure ends: 16 Mar 2012 16:00
 27 February 2012 DOCUMENT Silence Procedure ends: 16 Mar 2012 16:00 Directive on the Management of Records Generated on Operational Deployment Note by the Secretary General 1. In June 2011 the NATO Records
27 February 2012 DOCUMENT Silence Procedure ends: 16 Mar 2012 16:00 Directive on the Management of Records Generated on Operational Deployment Note by the Secretary General 1. In June 2011 the NATO Records
FSDF SPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT POLICIES - CUSTODIANSHIP
 FSDF SPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT POLICIES - CUSTODIANSHIP Objective: To provide consistent custodial arrangements so that spatial information is managed to appropriate standards and made available in
FSDF SPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT POLICIES - CUSTODIANSHIP Objective: To provide consistent custodial arrangements so that spatial information is managed to appropriate standards and made available in
Managing Contracts under the FOIP Act. A Guide for Government of Alberta Contract Managers and FOIP Coordinators
 Managing Contracts under the FOIP Act A Guide for Government of Alberta Contract Managers and FOIP Coordinators ISBN 978-0-7785-6102-6 Produced by Access and Privacy Service Alberta 3rd Floor, 10155 102
Managing Contracts under the FOIP Act A Guide for Government of Alberta Contract Managers and FOIP Coordinators ISBN 978-0-7785-6102-6 Produced by Access and Privacy Service Alberta 3rd Floor, 10155 102
How To Ensure Health Information Is Protected
 pic pic CIHI Submission: 2011 Prescribed Entity Review October 2011 Who We Are Established in 1994, CIHI is an independent, not-for-profit corporation that provides essential information on Canada s health
pic pic CIHI Submission: 2011 Prescribed Entity Review October 2011 Who We Are Established in 1994, CIHI is an independent, not-for-profit corporation that provides essential information on Canada s health
The role of Information Governance in an Enterprise Architecture Framework
 The role of Information Governance in an Enterprise Architecture Framework Richard Jeffrey-Cook, MBCS, CITP, FIRMS Head of Information and Records Management In-Form Consult Ltd, Cardinal Point Park Road,
The role of Information Governance in an Enterprise Architecture Framework Richard Jeffrey-Cook, MBCS, CITP, FIRMS Head of Information and Records Management In-Form Consult Ltd, Cardinal Point Park Road,
FREEDOM OF INFORMATION (SCOTLAND) ACT 2002 CODE OF PRACTICE ON RECORDS MANAGEMENT
 FREEDOM OF INFORMATION (SCOTLAND) ACT 2002 CODE OF PRACTICE ON RECORDS MANAGEMENT November 2003 Laid before the Scottish Parliament on 10th November 2003 pursuant to section 61(6) of the Freedom of Information
FREEDOM OF INFORMATION (SCOTLAND) ACT 2002 CODE OF PRACTICE ON RECORDS MANAGEMENT November 2003 Laid before the Scottish Parliament on 10th November 2003 pursuant to section 61(6) of the Freedom of Information
Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline
 Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline June 2012 Version 1.1 Queensland State Archives Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security
Queensland recordkeeping metadata standard and guideline June 2012 Version 1.1 Queensland State Archives Department of Science, Information Technology, Innovation and the Arts Document details Security
Section 6. Governance & Investment Roadmap. Executive Governance
 Section 6 Governance & Investment Roadmap Executive Governance Strong governance is critical to the success of a long-term, complex transformative initiative. The following section provides a high-level
Section 6 Governance & Investment Roadmap Executive Governance Strong governance is critical to the success of a long-term, complex transformative initiative. The following section provides a high-level
Sample Career Development Roadmap
 Sample Career Development Roadmap Copyright TalentAlign IP (2006-2012) May not be copied or alienated without prior written permission Career Development Roadmap TM ABC Version: 1.0 ABC Career Development
Sample Career Development Roadmap Copyright TalentAlign IP (2006-2012) May not be copied or alienated without prior written permission Career Development Roadmap TM ABC Version: 1.0 ABC Career Development
GUIDELINE RECORDS AND INFORMATION INVENTORY
 Government of Newfoundland and Labrador Office of the Chief Information Officer Information Management Branch GUIDELINE RECORDS AND INFORMATION INVENTORY Guideline (Definition): OCIO Guidelines derive
Government of Newfoundland and Labrador Office of the Chief Information Officer Information Management Branch GUIDELINE RECORDS AND INFORMATION INVENTORY Guideline (Definition): OCIO Guidelines derive
OCIO Strategy 2014. Page 1 CTZ-2014-00129
 OCIO Strategy 2014 Page 1 Table of contents 03 Message from the GCIO & Strategy Steering Committee 05 Introduction and context 07 Our Vision and Mission 08 Our stakeholders 09 Our Roles 11 Our Values 12
OCIO Strategy 2014 Page 1 Table of contents 03 Message from the GCIO & Strategy Steering Committee 05 Introduction and context 07 Our Vision and Mission 08 Our stakeholders 09 Our Roles 11 Our Values 12
Information Management
 G i Information Management Information Management Planning March 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Open Government Service Alberta 3 rd Floor, Commerce Place 10155 102 Street Edmonton, Alberta,
G i Information Management Information Management Planning March 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Open Government Service Alberta 3 rd Floor, Commerce Place 10155 102 Street Edmonton, Alberta,
Governance Document Management Framework
 Governance Document Management Framework Relevant Definitions: In the context of this document: AB means Academic Board Contact Officer means the position responsible for the day to day implementation
Governance Document Management Framework Relevant Definitions: In the context of this document: AB means Academic Board Contact Officer means the position responsible for the day to day implementation
Value to the Mission. FEA Practice Guidance. Federal Enterprise Architecture Program Management Office, OMB
 Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
University of Hawai i Executive Policy on Data Governance (Draft 2/1/12)
 University of Hawai i Executive Policy on Data Governance (Draft 2/1/12) I. Definition Data governance is the exercise of authority and control (planning, monitoring, and enforcement) over the management
University of Hawai i Executive Policy on Data Governance (Draft 2/1/12) I. Definition Data governance is the exercise of authority and control (planning, monitoring, and enforcement) over the management
Copyright 2014 Carnegie Mellon University The Cyber Resilience Review is based on the Cyber Resilience Evaluation Method and the CERT Resilience
 Copyright 2014 Carnegie Mellon University The Cyber Resilience Review is based on the Cyber Resilience Evaluation Method and the CERT Resilience Management Model (CERT-RMM), both developed at Carnegie
Copyright 2014 Carnegie Mellon University The Cyber Resilience Review is based on the Cyber Resilience Evaluation Method and the CERT Resilience Management Model (CERT-RMM), both developed at Carnegie
Internal Audit Standards
 Internal Audit Standards Department of Public Expenditure & Reform November 2012 Copyright in material supplied by third parties remains with the authors. This includes: - the Definition of Internal Auditing
Internal Audit Standards Department of Public Expenditure & Reform November 2012 Copyright in material supplied by third parties remains with the authors. This includes: - the Definition of Internal Auditing
How To Manage Revenue Management In The Province Of Britain Colony
 MINISTRY OF FINANCE REVENUE SERVICES OF BRITISH COLUMBIA REPORT January - December 2008 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Background... 3 Status Update... 4 Contract Objectives... 5 Implementing a Revenue
MINISTRY OF FINANCE REVENUE SERVICES OF BRITISH COLUMBIA REPORT January - December 2008 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Background... 3 Status Update... 4 Contract Objectives... 5 Implementing a Revenue
Architecture Principles
 Architecture Principles Table of Contents 1 GENERAL INFORMATION...2 2 INTENT...2 3 OWNERSHIP...2 4 APPLYING THE PRINCIPLES...2 5 ARCHITECTURAL OBJECTIVES...2 6 ARCHITECTURE PRINCIPLES...3 6.1 General...
Architecture Principles Table of Contents 1 GENERAL INFORMATION...2 2 INTENT...2 3 OWNERSHIP...2 4 APPLYING THE PRINCIPLES...2 5 ARCHITECTURAL OBJECTIVES...2 6 ARCHITECTURE PRINCIPLES...3 6.1 General...
2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
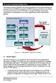 2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES This handout describes applicable roles and responsibilities for the Capital Planning and Investment Process (CPIC) as presented in the NIST Integrating IT Security into
2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES This handout describes applicable roles and responsibilities for the Capital Planning and Investment Process (CPIC) as presented in the NIST Integrating IT Security into
MedIT Strategic Plan. Mission: To support excellence in health education, research, and service with innovative and sustainable technology solutions.
 MedIT Strategic Plan 2010 2013 Mission: To support excellence in health education, research, and service with innovative and sustainable technology solutions. The UBC Faculty of Medicine and MedIT work
MedIT Strategic Plan 2010 2013 Mission: To support excellence in health education, research, and service with innovative and sustainable technology solutions. The UBC Faculty of Medicine and MedIT work
ASTRAZENECA GLOBAL POLICY SAFEGUARDING COMPANY ASSETS AND RESOURCES
 ASTRAZENECA GLOBAL POLICY SAFEGUARDING COMPANY ASSETS AND RESOURCES THIS POLICY SETS OUT THE REQUIREMENTS FOR SAFEGUARDING COMPANY ASSETS AND RESOURCES TO PROTECT PATIENTS, STAFF, PRODUCTS, PROPERTY AND
ASTRAZENECA GLOBAL POLICY SAFEGUARDING COMPANY ASSETS AND RESOURCES THIS POLICY SETS OUT THE REQUIREMENTS FOR SAFEGUARDING COMPANY ASSETS AND RESOURCES TO PROTECT PATIENTS, STAFF, PRODUCTS, PROPERTY AND
Information Management & Data Governance
 Data governance is a means to define the policies, standards, and data management services to be employed by the organization. Information Management & Data Governance OVERVIEW A thorough Data Governance
Data governance is a means to define the policies, standards, and data management services to be employed by the organization. Information Management & Data Governance OVERVIEW A thorough Data Governance
Office of the Auditor General of Canada. Internal Audit of Document Management Through PROxI Implementation. July 2014
 Office of the Auditor General of Canada Internal Audit of Document Management Through PROxI Implementation July 2014 Practice Review and Internal Audit Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented
Office of the Auditor General of Canada Internal Audit of Document Management Through PROxI Implementation July 2014 Practice Review and Internal Audit Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented
5 FAM 670 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) PERFORMANCE MEASURES FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 5 FAM 670 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) PERFORMANCE MEASURES FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT (CT:IM-92; 08-01-2007) (Office of Origin: IRM/BPC/PRG) 5 FAM 671 WHAT ARE IT PERFORMANCE MEASURES AND WHY ARE THEY REQUIRED?
5 FAM 670 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (IT) PERFORMANCE MEASURES FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT (CT:IM-92; 08-01-2007) (Office of Origin: IRM/BPC/PRG) 5 FAM 671 WHAT ARE IT PERFORMANCE MEASURES AND WHY ARE THEY REQUIRED?
Research Data Ownership, Retention, Access, and Security
 , Access, and Security Policy Type: Administrative Responsible Office: VCU Office of Research and Innovation Initial Policy Approved: 05/15/09 Current Revision Approved: 11/05/2015 Policy Statement and
, Access, and Security Policy Type: Administrative Responsible Office: VCU Office of Research and Innovation Initial Policy Approved: 05/15/09 Current Revision Approved: 11/05/2015 Policy Statement and
BPA Policy 236-1 Information Governance & Lifecycle Management
 B O N N E V I L L E P O W E R A D M I N I S T R A T I O N BPA Policy 236-1 Table of Contents 236-1.1 Purpose & Background... 2 236-1.2 Policy Owner... 2 236-1.3 Applicability... 2 236-1.4 Terms & Definitions...
B O N N E V I L L E P O W E R A D M I N I S T R A T I O N BPA Policy 236-1 Table of Contents 236-1.1 Purpose & Background... 2 236-1.2 Policy Owner... 2 236-1.3 Applicability... 2 236-1.4 Terms & Definitions...
US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor January 25, 2007
 US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor January 25, 2007 Task 18 - Enterprise Data Management 18.002 Enterprise Data Management Concept of Operations i
US Department of Education Federal Student Aid Integration Leadership Support Contractor January 25, 2007 Task 18 - Enterprise Data Management 18.002 Enterprise Data Management Concept of Operations i
Building a Strong Organization CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
 chapter III Building a Strong Organization To remain a strong organization that is able to fulfil its mandate, CMHC draws on sound corporate governance, financial and risk management practices, progressive
chapter III Building a Strong Organization To remain a strong organization that is able to fulfil its mandate, CMHC draws on sound corporate governance, financial and risk management practices, progressive
Information Security Classification
 i Information Management Information Security Classification February 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Government and Program Support Services Division Alberta Government Services 3 rd Floor,
i Information Management Information Security Classification February 2005 Produced by Information Management Branch Government and Program Support Services Division Alberta Government Services 3 rd Floor,
PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS COUNCIL HANDBOOK
 PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS COUNCIL HANDBOOK Adopted by the Public Accountants Council for the Province of Ontario: April 17, 2006 PART I: PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS FOR PUBLIC ACCOUNTING PART II: PRACTICAL
PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS COUNCIL HANDBOOK Adopted by the Public Accountants Council for the Province of Ontario: April 17, 2006 PART I: PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS FOR PUBLIC ACCOUNTING PART II: PRACTICAL
Enterprise Architecture Glossary by Set
 Set: Enterprise Architecture (EA) Glossary Term Source Enterprise architecture terms based on NASCIO,, and other industry best practices. Description Albers Equal Area Projection egsc.usgs.gov A projection
Set: Enterprise Architecture (EA) Glossary Term Source Enterprise architecture terms based on NASCIO,, and other industry best practices. Description Albers Equal Area Projection egsc.usgs.gov A projection
Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff
 Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff The Challenge IT Executives are challenged with issues around data, compliancy, regulation and making confident decisions on their business
Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff The Challenge IT Executives are challenged with issues around data, compliancy, regulation and making confident decisions on their business
Certified Information Professional 2016 Update Outline
 Certified Information Professional 2016 Update Outline Introduction The 2016 revision to the Certified Information Professional certification helps IT and information professionals demonstrate their ability
Certified Information Professional 2016 Update Outline Introduction The 2016 revision to the Certified Information Professional certification helps IT and information professionals demonstrate their ability
Scope The data management framework must support industry best practice processes and provide as a minimum the following functional capability:
 Data Management Policy Version Information A. Introduction Purpose 1. Outline and articulate the strategy for data management across Redland City Council (RCC). This document will provide direction and
Data Management Policy Version Information A. Introduction Purpose 1. Outline and articulate the strategy for data management across Redland City Council (RCC). This document will provide direction and
Bringing agility to Business Intelligence Metadata as key to Agile Data Warehousing. 1 P a g e. www.analytixds.com
 Bringing agility to Business Intelligence Metadata as key to Agile Data Warehousing 1 P a g e Table of Contents What is the key to agility in Data Warehousing?... 3 The need to address requirements completely....
Bringing agility to Business Intelligence Metadata as key to Agile Data Warehousing 1 P a g e Table of Contents What is the key to agility in Data Warehousing?... 3 The need to address requirements completely....
Solutions. Master Data Governance Model and the Mechanism
 Solutions Master Data Governance Model and the Mechanism Executive summary Organizations worldwide are rapidly adopting various Master Data Management (MDM) solutions to address and overcome business issues
Solutions Master Data Governance Model and the Mechanism Executive summary Organizations worldwide are rapidly adopting various Master Data Management (MDM) solutions to address and overcome business issues
Information Technology Project Oversight Framework
 i This Page Intentionally Left Blank i Table of Contents SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW...1 SECTION 2: PROJECT CLASSIFICATION FOR OVERSIGHT...7 SECTION 3: DEPARTMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT REQUIREMENTS...11
i This Page Intentionally Left Blank i Table of Contents SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW...1 SECTION 2: PROJECT CLASSIFICATION FOR OVERSIGHT...7 SECTION 3: DEPARTMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT REQUIREMENTS...11
INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALIST 8 1488
 INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALIST 8 1488 SERIES DESCRIPTION The INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALIST (ISS) classification series has eight levels that describe technical and professional non-supervisory positions
INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALIST 8 1488 SERIES DESCRIPTION The INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALIST (ISS) classification series has eight levels that describe technical and professional non-supervisory positions
Position Classification Flysheet for Grants Management Series, 1109
 Position Classification Flysheet for Grants Management Series, 1109 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...2 COVERAGE...2 ESTABLISHING THE OCCUPATIONAL SERIES AND STANDARD...2 GENERAL SERIES DETERMINATION GUIDELINES...3
Position Classification Flysheet for Grants Management Series, 1109 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...2 COVERAGE...2 ESTABLISHING THE OCCUPATIONAL SERIES AND STANDARD...2 GENERAL SERIES DETERMINATION GUIDELINES...3
Head of Information & Communications Technology Responsible work team: ICT Security. Key point summary... 2
 Policy Procedure Information security policy Policy number: 442 Old instruction number: MAN:F005:a1 Issue date: 24 August 2006 Reviewed as current: 11 July 2014 Owner: Head of Information & Communications
Policy Procedure Information security policy Policy number: 442 Old instruction number: MAN:F005:a1 Issue date: 24 August 2006 Reviewed as current: 11 July 2014 Owner: Head of Information & Communications
PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION AUDIT REPORTS 2012
 PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION AUDIT REPORTS 2012 All of the audit work in this publication was conducted in accordance with the legislative mandate and audit policies of the Public Service Commission of Canada.
PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION AUDIT REPORTS 2012 All of the audit work in this publication was conducted in accordance with the legislative mandate and audit policies of the Public Service Commission of Canada.
