State of Minnesota. Enterprise Security Strategic Plan. Fiscal Years
|
|
|
- Ashlee Louise Reynolds
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 State of Minnesota Enterprise Security Strategic Plan Fiscal Years Jointly Prepared By: Office of Enterprise Technology - Enterprise Security Office Members of the Information Security Council
2 State of Minnesota Enterprise Security Strategic Plan Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 2 CHAPTER 1 - INTRODUCTION... 3 STAKEHOLDERS... 4 PLAN NAVIGATION... 5 GOVERNANCE... 6 CHAPTER 2 - MISSION AND UNDERLYING CORE VALUES... 7 CHAPTER 3 - STRATEGIC OUTCOMES... 8 CHAPTER 4 - KEY INITIATIVES Page 1
3 Executive Summary We are pleased to present the first Enterprise Security Strategic Plan for the State of Minnesota. This plan sets priorities for management, control, and protection of the state s information assets. The 5 year vision includes 19 high-level strategic objectives (see chapter 3), grouped into the following 3 categories: Improved situational awareness, which includes continuous system monitoring and continuous assessment of controls Proactive risk management, such as solidly articulated requirements and ongoing security training Robust crisis and security incident management, which allows critical services to continue uninterrupted in a crisis. This plan also outlines 8 key initiatives (see chapter 4) that have been prioritized for delivery during the ensuring 2 years: Security Information and Event Management: provide enterprise-wide security monitoring Enterprise Vulnerability and Threat Management: provide ongoing vulnerability assessments of all information technology assets Baseline Policies, Procedures, and Standards: complete enterprise security policy and standard framework Security Awareness for Employees: ongoing and comprehensive security awareness program for all state employees Security Awareness for Government Leaders: annual security awareness event for government leaders and policymakers Identity and Access Management: centralized and streamlined access control solution for state government Enterprise Business Continuity Program: ongoing continuity program to address unanticipated disruptions to government services Enterprise Security Incident Management: enterprise-wide approach to record, identify, and manage information security incidents Strong executive commitment and support are crucial to the implementation of this plan. We ask that you, as government leaders and policymakers, commit to partner with us in effective problem solving, and be our champions at the highest levels. Successful implementation will ensure information is both protected and available, and that critical government services are available when needed. Page 2
4 Chapter 1 - Introduction The State of Minnesota recognizes that information is a critical asset. How information is managed, controlled, and protected has a significant impact on the delivery of state services and on the trust instilled in the users of those services. Information assets, including those held in trust, must be protected from unauthorized disclosure, theft, loss, destruction, and alteration. Information assets must be available when needed, particularly during emergencies and times of crisis. The State of Minnesota s decentralized information technology environment is inherently difficult to secure. Most state agencies still operate their own data centers. Furthermore, the state has not defined or enforced standards limiting the diversity of hardware and software products. In testimony, the Legislative Auditor pointed to undue complexity as a primary factor for the large number of information security audit findings. Current data center consolidation initiatives will simplify the state s information technology environment, making it easier to secure. However, data center consolidation plans are complex and take many years to implement. The rapidly expanding use of the internet has increased the need for connectivity between government entities, third parties, and users of state services. This increase in connectivity has increased the state s risk posture and made it more difficult to protect information. Cyber crime has skyrocketed over the past few years, shifting from crimes of notoriety to far more serious crimes for financial gain. Attackers have become much more sophisticated in perpetrating and concealing cyber crimes, typically operating in stealth mode with a goal of avoiding detection altogether. This document is the first enterprise-wide information security strategic plan for the State of Minnesota. It sets priorities for how the enterprise can efficiently and effectively address the management, control, and protection of the state s information assets. It outlines the state s security community s five year vision, articulated as 19 high-level Strategic Objectives, grouped into three categories. There are significant gaps between where the state s security community is today and the five year vision. The importance of the strategic objectives was assessed, prioritizing the gaps. The results of this assessment are summarized as Key Initiatives; a two year strategic plan. A set of business and tactical plans detailing the deliverables necessary to achieve the key initiatives are maintained separately. Page 3
5 Figure 1 Security Strategy Alignment Security Strategies Information Technology Strategies As depicted in Figure 1, this plan attempts to align information security strategic objectives with broader government technology and business strategies. When developing this plan, the strategies outlined in the State of Minnesota Information Technology Master Plan and the 2005 Drive to Excellence Transformation Roadmap were incorporated. This plan incorporates core information Major Government Business Initiatives security requirements that must be in place to accomplish major government initiatives Global Trends efficiently and effectively. These initiatives include data center consolidation and the development of major government business applications, such as the new accounting and procurement system, and centralized electronic licensing. Finally, this plan incorporates global trends, such as: More stringent regulatory requirements pertaining to information security Increasing sophistication of criminals and politically motivated attackers New demands to access data and services through web applications and mobile devices (i.e., laptops, mobile-phones) New demands to share data across multiple organizations Intense pressure to reduce costs A shift from long-term employees to a more temporary and mobile workforce The expanding use of software as a service Stakeholders Government leaders and policymakers are the primary audience of this plan. From an information security perspective, they need to know the current state, the future vision, and the task necessary to bridge the gap. Achieving the strategic objectives will not be possible without strong executive Figure 2 Strategic Plan Primary Stakeholders Government Leaders Enterprise Security Strategic Plan Security Community Users of Services Page 4
6 commitment. Government leaders and policymakers must understand and have confidence in this plan. They must become problem-solving partners by committing resources and helping to remove barriers that impede progress. The security community itself is also a key audience of this plan. In the past, each government entity was forced to address information security issues on its own. This approach has fostered an environment where critical security duties are simply not done at many government entities. By joining forces to establish a common vision, the security community can ensure that all entities have appropriate information security controls, and can deploy those controls cost effectively. Finally, business partners and citizens the end users of government services have a vested interest in the success of this plan. End users of government services need to have complete confidence that government entities will protect their data from unauthorized disclosure. End users must be confident that critical government services will be available when needed, particularly during times of crisis. Developing this plan demonstrates due diligence to the people and businesses who rely on government services. Plan Navigation The plan is organized into three sections: Chapter 2 Mission and Underlying Core Values discusses the mission of the Enterprise Security Program, as defined by the security community. It also outlines the core values of a security program necessary to drive the strategic security outcomes in this document. Chapter 3 Strategic Outcomes lists the 19 high-level objectives for the State of Minnesota, segregated into three broad categories: Improved Situational Awareness, Robust Crisis and Security Incident Management, and Proactive Risk Management. Chapter 4 Key Initiatives discusses the highest-priority projects that the security community hopes to accomplish during the current biennium. Additional details concerning these projects can be seen in the separate Enterprise Security Tactical Plan. Page 5
7 Governance The State Chief Information Security Officer will lead the effort to deliver the objectives in this plan. To be successful, the State Chief Information Security Officer must align and coordinate agency resources with those in Enterprise Security Office, a part of the Office of Enterprise Technology. Furthermore, these coordinated security efforts must be vetted by all impacted stakeholders through an agreed upon governance process. Though the governance process is still evolving, current stakeholders that participate in the decision-making process include: State Chief Information Officer. Under state law, the State Chief Information Officer is responsible for the overall management, direction, and security of the state s information assets. State Chief Information Security Officer. The State Chief Information Security Officer has delegated authority and is responsible for planning, developing, and deploying the Enterprise Security Program. Information Security Council. Agency security professionals who comprise the council serve as advisors to the State Chief Information Security Officer. These professionals are responsible for helping develop the enterprise-wide security strategies. They help craft the policies, standards, and systems to achieve the strategic objectives. Chief Information Officer Advisory Council. This council represents the government technology community as a whole. It is responsible for making sure that security efforts align with and support broader government technology and business initiatives. Commissioners Technology Advisory Board. This board represents leaders at the highest level in state government, ensuring buy-in and support for enterprise-wide projects and security efforts. Page 6
8 Chapter 2 Mission and Underlying Core Values The State of Minnesota s Enterprise Security Program began in June 2006 with the hiring of the first Chief Information Security Officer in the Office of Enterprise Technology. To advance enterprise security, the Chief Information Security Officer promptly established the Information Security Council, an advisory body to help plan, develop, and implement the new program. With help from the Information Security Council, the Chief Information Security Officer worked to create the following mission for the Enterprise Security Program: The Enterprise Security Program exists to support the efficient delivery of services to government entities and their customers; through a sustainable information security program. The program will accomplish its mission through enterprise information security policies, standards, guidelines, and services that protect the state s information assets and the security interests of the users of state services. The security community also agreed on eight core values as a foundation for the new Enterprise Security Program. The program must: have an increased focus on security planning activities. be comprehensive, clearly outlining the baseline requirements that all agencies must follow. ensure that important security decisions are made by people best suited to make those decisions. have broad-based support from people who will be expected to implement the provisions. be championed by government leaders at the highest levels. be supported by appropriate resources, including technical tools, training, and people. take advantage of the size of government to leverage financial and human resources to be cost effective. include methods to ensure compliance with baseline security requirements. With this foundation in place, the security community began the difficult task of defining, vetting, and prioritizing long-term security strategies for the State of Minnesota. The result of this effort can be seen in the following chapter. Page 7
9 Chapter 3 - Strategic Outcomes The high-level strategies outlined in this chapter collectively define where the State of Minnesota needs to be to appropriately manage cyber security risks. The security community believes that it will take at least five years to achieve these strategic outcomes, assuming that there will be sufficient resources for people, processes, and tools. Absent the necessary resources, the strategic outcomes will not change, however, the timeframe to achieve the outcomes will be extended. The strategic outcomes can be classified into three broad categories: Improved Situational Awareness (Table 1) Outcomes in this category will help the state obtain a better understanding of its risk posture. They also will give the state the ability to measure its risk posture with rigorous performance metrics. Proactive Risk Management (Table 2) Outcomes in this category will make employees and government leaders more aware of security threats. Also, they will garner the executive support needed for Enterprise Security Program to thrive long-term. Finally, they include various types of preventive controls. Robust Crisis and Security Incident Management (Table 3) Outcomes in this category will help the state manage security events more efficiently and effectively, thereby minimizing damage. Table 1 Improved Situational Awareness Strategic Outcome Description All state computer systems are continuously monitored for adverse information security events. Information security controls are continuously assessed for effectiveness. Key performance indicators are used to measure the information security program s effectiveness. The state has a consolidated and reportable information security risk profile. Current Biennium Priority Page 8
10 Table 2 Proactive Risk Management Strategic Outcome Description Government leaders at the highest levels understand and support the information security program. All state employees receive ongoing security training appropriate to their job duties. Information security program requirements are clearly articulated in a framework of policies, procedures, and standards. Established relationships between state, local, and federal government entities permit shared security solutions that span traditional parochial boundaries. Stakeholders participate in the design and implementation of information security solutions. The state attracts, develops, and retains professionals with the appropriate security skills. Exploitable technical vulnerabilities in state computer systems are promptly identified and remediated. Information security controls adapt rapidly to changing risk conditions. People and entities that conduct business with state government have appropriate and timely access to the necessary computer resources and data. State computer resources and data are protected from being used or accessed inappropriately. Government entities comply with the information security program and other externally mandated compliance requirements. Government entities, regardless of size, are supported by security professionals and engaged in the information security program. The Office of Enterprise Technology serves as a leader by setting high standards for excellence in information security. Current Biennium Priority Table 3 Robust Crisis and Security Incident Management Strategic Outcome Description When information security incidents occur, government entities promptly contain, remediate, and manage those incidents. Mission-critical services will continue in the event of a crisis. Current Biennium Priority Page 9
11 Chapter 4 - Key Initiatives The Enterprise Security Office and the Information Security Council identified certain security outcomes and specific projects as high priority. In general, these are areas where our current security controls are lax or have not been applied consistently across the enterprise, resulting in an unacceptable level of risk. In many cases, the security community has developed formal projects to address pressing concerns. In others, security projects are still in the planning stages. This chapter outlines security projects that the security community believes are high priority. It is not a complete inventory of the work being done by the security community. Rather, it is list of a key initiatives that are planned or are currently under way to address the most pressing risks. Additional details about each key initiative can be found in the Enterprise Security Tactical Plan. It is important to demonstrate the linkage between key initiatives, long-term strategic outcomes, and the broader strategic outcome categories. Therefore, included with each key initiative in this chapter is a graphic. Figure 3 illustrates the oneto-many relationship between broad strategic outcome categories, specific strategic outcomes, and key initiatives. Figure 3 Linking Key Initiatives to Outcomes Broad Outcome Category Specific Strategic Outcome Key Initiative Initiative #1 Security Information and Event Management Improved Situational Awareness Description: Central system to provide enterprisewide security monitoring All state computer systems are continuously monitored for adverse information security events Security Information and Event Management Project Improved ability to identify complex cyber attacks Reduced time and cost to investigate security incidents Consistent and robust monitoring of all agencies, including those with limited resources Page 10
12 Initiative #2 Enterprise Vulnerability and Threat Management Proactive Risk Management Exploitable technical vulnerabilities in state computer systems are promptly identified and remediated Enterprise Vulnerability and Threat Management Project Description: Central system to provide ongoing vulnerability assessments of all information technology assets State finds and remediates problems before they are exploited by hackers Inventory created of all technology assets Services offered to all agencies, including those with limited resources Initiative #3 Baseline Policies, Procedures, and Standards Proactive Risk Management Description: Complete enterprise security policy and standard framework Security program requirements are clearly articulated in a framework of policies, procedures, and standards Baseline Policies, Procedures, and Standards Clear security baselines for all government entities Policy-based foundation to measure results Consistent application of security controls across the enterprise Initiative #4 Security Awareness for Employees Proactive Risk Management Description: Ongoing and comprehensive security awareness program for all state employees All state employees receive ongoing security training that is commensurate with their job Employee Security Awareness Program Better awareness of security threats capable of impacting government operations Fewer security incidents caused by employee mistakes Common baseline of knowledge for all employees Page 11
13 Initiative #5 Security Awareness for Government Leaders Proactive Risk Management Description: Annual security awareness event for government leaders and policymakers All state employees receive ongoing security training that is commensurate with their job duties Government leaders at the highest levels understand and support the information security program Annual Information Security Briefing for Government Executives Clear understanding of all enterprise security initiatives Overview of significant information security threats Support for the Enterprise Security Program Initiative #6 Identity and Access Management Proactive Risk Management Description: Centralized and streamlined access control solution for state government People and entities that conduct business with state government have appropriate and timely access to the necessary computer resources and data State computer resources and data are protected from being used or accessed inappropriately Identity and Access Management Project Better security through uniform and repeatable access control processes Better experience for users of state services by providing all access through a single user ID and password Reduced costs to develop new government systems by leveraging an external access control solution Page 12
14 Initiative #7 Enterprise Business Continuity Program Robust Crisis and Security Incident Management Mission critical services will continue in the event of a crisis Enterprise Continuity Program Description: Ongoing continuity program to address unanticipated disruptions to government services Faster recovery of critical government services during a crisis Reduced costs through leveraging shared recovery environment Better ability to share staff during times of crisis through adoption of a common plan format and tools Initiative #8 Enterprise Security Incident Management Robust Crisis and Security Incident Management When information security incidents occur, government entities promptly contain, remediate, and manage those incidents Enterprise Security Incident Management Description: Enterprise-wide approach to record, identify, and manage information security incidents Ability to limit damage through information sharing Fewer cross-agency infections Reduced costs through the sharing of staff and expensive forensic investigation tools Page 13
Enterprise Security Tactical Plan
 Enterprise Security Tactical Plan Fiscal Years 2011 2012 (July 1, 2010 to June 30, 2012) Prepared By: State Chief Information Security Officer The Information Security Council State of Minnesota Enterprise
Enterprise Security Tactical Plan Fiscal Years 2011 2012 (July 1, 2010 to June 30, 2012) Prepared By: State Chief Information Security Officer The Information Security Council State of Minnesota Enterprise
INFORMATION SECURITY STRATEGIC PLAN
 INFORMATION SECURITY STRATEGIC PLAN UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT INFORMATION SECURITY OFFICE 4/20/10 University of Connecticut / Jason Pufahl, CISSP, CISM 1 1 MISSION STATEMENT The mission of the Information
INFORMATION SECURITY STRATEGIC PLAN UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT INFORMATION SECURITY OFFICE 4/20/10 University of Connecticut / Jason Pufahl, CISSP, CISM 1 1 MISSION STATEMENT The mission of the Information
Cybersecurity and internal audit. August 15, 2014
 Cybersecurity and internal audit August 15, 2014 arket insights: what we are seeing so far? 60% of organizations see increased risk from using social networking, cloud computing and personal mobile devices
Cybersecurity and internal audit August 15, 2014 arket insights: what we are seeing so far? 60% of organizations see increased risk from using social networking, cloud computing and personal mobile devices
Leveraging innovative security solutions for government. Helping to protect government IT infrastructure, meet compliance demands and reduce costs
 IBM Global Technology Services Leveraging innovative security solutions for government. Helping to protect government IT infrastructure, meet compliance demands and reduce costs Achieving a secure government
IBM Global Technology Services Leveraging innovative security solutions for government. Helping to protect government IT infrastructure, meet compliance demands and reduce costs Achieving a secure government
State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework
 State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework June 2012 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 IT Governance Overview... 4 Process for Developing the New Framework... 4 Management of the
State of Minnesota IT Governance Framework June 2012 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 IT Governance Overview... 4 Process for Developing the New Framework... 4 Management of the
National Cyber Security Policy -2013
 National Cyber Security Policy -2013 Preamble 1. Cyberspace 1 is a complex environment consisting of interactions between people, software and services, supported by worldwide distribution of information
National Cyber Security Policy -2013 Preamble 1. Cyberspace 1 is a complex environment consisting of interactions between people, software and services, supported by worldwide distribution of information
State Agency Cyber Security Survey v 3.4 2 October 2014. State Agency Cybersecurity Survey v 3.4
 State Agency Cybersecurity Survey v 3.4 The purpose of this survey is to identify your agencies current capabilities with respect to information systems/cyber security and any challenges and/or successes
State Agency Cybersecurity Survey v 3.4 The purpose of this survey is to identify your agencies current capabilities with respect to information systems/cyber security and any challenges and/or successes
Experience the commitment WHITE PAPER. Information Security Continuous Monitoring. Charting the Right Course. cgi.com 2014 CGI GROUP INC.
 Experience the commitment WHITE PAPER Information Security Continuous Monitoring Charting the Right Course May 2014 cgi.com 2014 CGI GROUP INC. During the last few months of 2013, six federal agencies
Experience the commitment WHITE PAPER Information Security Continuous Monitoring Charting the Right Course May 2014 cgi.com 2014 CGI GROUP INC. During the last few months of 2013, six federal agencies
Cisco Security Optimization Service
 Cisco Security Optimization Service Proactively strengthen your network to better respond to evolving security threats and planned and unplanned events. Service Overview Optimize Your Network for Borderless
Cisco Security Optimization Service Proactively strengthen your network to better respond to evolving security threats and planned and unplanned events. Service Overview Optimize Your Network for Borderless
Agency Centralized IT Reference Model
 Agency Centralized IT Reference Model For State of Minnesota Agencies Planning and Version 2.0 March 8, 2012 658 Cedar Street Saint Paul, MN 55155 www.oet.state.mn.us PROVIDING THE LEADERSHIP AND SERVICES
Agency Centralized IT Reference Model For State of Minnesota Agencies Planning and Version 2.0 March 8, 2012 658 Cedar Street Saint Paul, MN 55155 www.oet.state.mn.us PROVIDING THE LEADERSHIP AND SERVICES
NATIONAL CREDIT UNION ADMINISTRATION OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL
 NATIONAL CREDIT UNION ADMINISTRATION OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL INDEPENDENT EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL CREDIT UNION ADMINISTRATION S COMPLIANCE WITH THE FEDERAL INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT ACT (FISMA)
NATIONAL CREDIT UNION ADMINISTRATION OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL INDEPENDENT EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL CREDIT UNION ADMINISTRATION S COMPLIANCE WITH THE FEDERAL INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT ACT (FISMA)
Audit Report. Management of Naval Reactors' Cyber Security Program
 U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections Audit Report Management of Naval Reactors' Cyber Security Program DOE/IG-0884 April 2013 Department of Energy Washington,
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections Audit Report Management of Naval Reactors' Cyber Security Program DOE/IG-0884 April 2013 Department of Energy Washington,
Vendor Risk Management Financial Organizations
 Webinar Series Vendor Risk Management Financial Organizations Bob Justus Chief Security Officer Allgress Randy Potts Managing Consultant FishNet Security Bob Justus Chief Security Officer, Allgress Current
Webinar Series Vendor Risk Management Financial Organizations Bob Justus Chief Security Officer Allgress Randy Potts Managing Consultant FishNet Security Bob Justus Chief Security Officer, Allgress Current
Legislative Language
 Legislative Language SEC. 1. COORDINATION OF FEDERAL INFORMATION SECURITY POLICY. (a) IN GENERAL. Chapter 35 of title 44, United States Code, is amended by striking subchapters II and III and inserting
Legislative Language SEC. 1. COORDINATION OF FEDERAL INFORMATION SECURITY POLICY. (a) IN GENERAL. Chapter 35 of title 44, United States Code, is amended by striking subchapters II and III and inserting
NASCIO 2014 State IT Recognition Awards
 NASCIO 2014 State IT Recognition Awards Project: California Cybersecurity Task Force Category: Cybersecurity Initiatives Project Initiation Date: September, 2012 Project Completion Date: May 2013 Carlos
NASCIO 2014 State IT Recognition Awards Project: California Cybersecurity Task Force Category: Cybersecurity Initiatives Project Initiation Date: September, 2012 Project Completion Date: May 2013 Carlos
Certified Identity and Access Manager (CIAM) Overview & Curriculum
 Identity and access management (IAM) is the most important discipline of the information security field. It is the foundation of any information security program and one of the information security management
Identity and access management (IAM) is the most important discipline of the information security field. It is the foundation of any information security program and one of the information security management
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits & Inspections
 U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits & Inspections Audit Report Follow-up Audit of the Department's Cyber Security Incident Management Program DOE/IG-0878 December 2012
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits & Inspections Audit Report Follow-up Audit of the Department's Cyber Security Incident Management Program DOE/IG-0878 December 2012
IMPROVING RISK VISIBILITY AND SECURITY POSTURE WITH IDENTITY INTELLIGENCE
 IMPROVING RISK VISIBILITY AND SECURITY POSTURE WITH IDENTITY INTELLIGENCE ABSTRACT Changing regulatory requirements, increased attack surfaces and a need to more efficiently deliver access to the business
IMPROVING RISK VISIBILITY AND SECURITY POSTURE WITH IDENTITY INTELLIGENCE ABSTRACT Changing regulatory requirements, increased attack surfaces and a need to more efficiently deliver access to the business
658 Cedar Street Saint Paul, MN 55155 www.oet.state.mn.us
 Legislative Report Consolidation of Information Technology Systems and Services January 19, 2012 658 Cedar Street Saint Paul, MN 55155 www.oet.state.mn.us PROVIDING THE LEADERSHIP AND SERVICES THAT IMPROVE
Legislative Report Consolidation of Information Technology Systems and Services January 19, 2012 658 Cedar Street Saint Paul, MN 55155 www.oet.state.mn.us PROVIDING THE LEADERSHIP AND SERVICES THAT IMPROVE
NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN SECURITY
 NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN SECURITY JANUARY 2012 Table of Contents Executive Summary 1 Introduction 2 Our Strategic Goals 2 Our Strategic Approach 3 The Path Forward 5 Conclusion 6 Executive
NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN SECURITY JANUARY 2012 Table of Contents Executive Summary 1 Introduction 2 Our Strategic Goals 2 Our Strategic Approach 3 The Path Forward 5 Conclusion 6 Executive
Vulnerability Management. Information Technology Audit. For the Period July 2010 to July 2011
 O L A OFFICE OF THE LEGISLATIVE AUDITOR STATE OF MINNESOTA FINANCIAL AUDIT DIVISION REPORT Vulnerability Management Information Technology Audit For the Period July 2010 to July 2011 May 22, 2012 Report
O L A OFFICE OF THE LEGISLATIVE AUDITOR STATE OF MINNESOTA FINANCIAL AUDIT DIVISION REPORT Vulnerability Management Information Technology Audit For the Period July 2010 to July 2011 May 22, 2012 Report
OPTIMUS SBR. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE.
 OPTIMUS SBR CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance This paper investigates the importance of establishing a robust Business Intelligence (BI)
OPTIMUS SBR CHOICE TOOLS. PRECISION AIM. BOLD ATTITUDE. Optimizing Results with Business Intelligence Governance This paper investigates the importance of establishing a robust Business Intelligence (BI)
Avoiding the Top 5 Vulnerability Management Mistakes
 WHITE PAPER Avoiding the Top 5 Vulnerability Management Mistakes The New Rules of Vulnerability Management Table of Contents Introduction 3 We ve entered an unprecedented era 3 Mistake 1: Disjointed Vulnerability
WHITE PAPER Avoiding the Top 5 Vulnerability Management Mistakes The New Rules of Vulnerability Management Table of Contents Introduction 3 We ve entered an unprecedented era 3 Mistake 1: Disjointed Vulnerability
SECURITY. Risk & Compliance Services
 SECURITY Risk & Compliance s V1 8/2010 Risk & Compliances s Risk & compliance services Summary Summary Trace3 offers a full and complete line of security assessment services designed to help you minimize
SECURITY Risk & Compliance s V1 8/2010 Risk & Compliances s Risk & compliance services Summary Summary Trace3 offers a full and complete line of security assessment services designed to help you minimize
Cybersecurity in the States 2012: Priorities, Issues and Trends
 Cybersecurity in the States 2012: Priorities, Issues and Trends Commission on Maryland Cyber Security and Innovation June 8, 2012 Pam Walker, Director of Government Affairs National Association of State
Cybersecurity in the States 2012: Priorities, Issues and Trends Commission on Maryland Cyber Security and Innovation June 8, 2012 Pam Walker, Director of Government Affairs National Association of State
State Governments at Risk: The Data Breach Reality
 State Governments at Risk: The Data Breach Reality NCSL Legislative Summit August 5, 2015 Doug Robinson, Executive Director National Association of State Chief Information Officers (NASCIO) About NASCIO
State Governments at Risk: The Data Breach Reality NCSL Legislative Summit August 5, 2015 Doug Robinson, Executive Director National Association of State Chief Information Officers (NASCIO) About NASCIO
Establishing A Multi-Factor Authentication Solution. Report to the Joint Legislative Oversight Committee on Information Technology
 Establishing A Multi-Factor Authentication Solution Report to the Joint Legislative Oversight Committee on Information Technology Keith Werner State Chief Information Officer Department of Information
Establishing A Multi-Factor Authentication Solution Report to the Joint Legislative Oversight Committee on Information Technology Keith Werner State Chief Information Officer Department of Information
Cybersecurity Enhancement Account. FY 2017 President s Budget
 Cybersecurity Enhancement Account FY 2017 President s Budget February 9, 2016 Table of Contents Section 1 Purpose... 3 1A Mission Statement... 3 1.1 Appropriations Detail Table... 3 1B Vision, Priorities
Cybersecurity Enhancement Account FY 2017 President s Budget February 9, 2016 Table of Contents Section 1 Purpose... 3 1A Mission Statement... 3 1.1 Appropriations Detail Table... 3 1B Vision, Priorities
Office of the Auditor General Performance Audit Report. Statewide UNIX Security Controls Department of Technology, Management, and Budget
 Office of the Auditor General Performance Audit Report Statewide UNIX Security Controls Department of Technology, Management, and Budget December 2015 State of Michigan Auditor General Doug A. Ringler,
Office of the Auditor General Performance Audit Report Statewide UNIX Security Controls Department of Technology, Management, and Budget December 2015 State of Michigan Auditor General Doug A. Ringler,
Utica College. Information Security Plan
 Utica College Information Security Plan Author: James Farr (Information Security Officer) Version: 1.0 November 1 2012 Contents Introduction... 3 Scope... 3 Information Security Organization... 4 Roles
Utica College Information Security Plan Author: James Farr (Information Security Officer) Version: 1.0 November 1 2012 Contents Introduction... 3 Scope... 3 Information Security Organization... 4 Roles
White Paper Achieving PCI Data Security Standard Compliance through Security Information Management. White Paper / PCI
 White Paper Achieving PCI Data Security Standard Compliance through Security Information Management White Paper / PCI Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction: Brief Overview of PCI...1 The PCI Challenge:
White Paper Achieving PCI Data Security Standard Compliance through Security Information Management White Paper / PCI Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction: Brief Overview of PCI...1 The PCI Challenge:
Unified Security Anywhere HIPAA COMPLIANCE ACHIEVING HIPAA COMPLIANCE WITH MASERGY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
 Unified Security Anywhere HIPAA COMPLIANCE ACHIEVING HIPAA COMPLIANCE WITH MASERGY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES HIPAA COMPLIANCE Achieving HIPAA Compliance with Security Professional Services The Health Insurance
Unified Security Anywhere HIPAA COMPLIANCE ACHIEVING HIPAA COMPLIANCE WITH MASERGY PROFESSIONAL SERVICES HIPAA COMPLIANCE Achieving HIPAA Compliance with Security Professional Services The Health Insurance
2009 HIMSS Analytics Report: Evaluating HITECH s Impact on Healthcare Privacy and Security
 2009 HIMSS Analytics Report: Evaluating HITECH s Impact on Healthcare Privacy and Security Commissioned by ID Experts November 2009 INTRODUCTION Healthcare breaches are on the rise; according to the 2009
2009 HIMSS Analytics Report: Evaluating HITECH s Impact on Healthcare Privacy and Security Commissioned by ID Experts November 2009 INTRODUCTION Healthcare breaches are on the rise; according to the 2009
FFIEC Cybersecurity Assessment Tool
 Overview In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed the Cybersecurity Tool (), on behalf of its members,
Overview In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed the Cybersecurity Tool (), on behalf of its members,
FINAL May 2005. Guideline on Security Systems for Safeguarding Customer Information
 FINAL May 2005 Guideline on Security Systems for Safeguarding Customer Information Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Purpose of Guideline 1 2 Definitions 2 3 Internal Controls and Procedures 2 3.1
FINAL May 2005 Guideline on Security Systems for Safeguarding Customer Information Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Purpose of Guideline 1 2 Definitions 2 3 Internal Controls and Procedures 2 3.1
Information Security Policy. Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services
 Information Security Policy Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services Contents 1 Purpose / Objective... 1 1.1 Information Security... 1 1.2 Purpose... 1 1.3 Objectives...
Information Security Policy Document ID: 3809 Version: 1.0 Owner: Chief Security Officer, Security Services Contents 1 Purpose / Objective... 1 1.1 Information Security... 1 1.2 Purpose... 1 1.3 Objectives...
2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
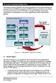 2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES This handout describes applicable roles and responsibilities for the Capital Planning and Investment Process (CPIC) as presented in the NIST Integrating IT Security into
2.0 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES This handout describes applicable roles and responsibilities for the Capital Planning and Investment Process (CPIC) as presented in the NIST Integrating IT Security into
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections. Evaluation Report
 U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections Evaluation Report The Department's Unclassified Cyber Security Program 2011 DOE/IG-0856 October 2011 Department of
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections Evaluation Report The Department's Unclassified Cyber Security Program 2011 DOE/IG-0856 October 2011 Department of
Independent Evaluation of NRC s Implementation of the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 for Fiscal Year 2015
 Independent Evaluation of NRC s Implementation of the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 for Fiscal Year 2015 OIG-16-A-03 November 12, 2015 All publicly available OIG reports (including
Independent Evaluation of NRC s Implementation of the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 for Fiscal Year 2015 OIG-16-A-03 November 12, 2015 All publicly available OIG reports (including
CA Vulnerability Manager r8.3
 PRODUCT BRIEF: CA VULNERABILITY MANAGER CA Vulnerability Manager r8.3 CA VULNERABILITY MANAGER PROTECTS ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS AND BUSINESS OPERATIONS BY IDENTIFYING VULNERABILITIES, LINKING THEM TO CRITICAL
PRODUCT BRIEF: CA VULNERABILITY MANAGER CA Vulnerability Manager r8.3 CA VULNERABILITY MANAGER PROTECTS ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS AND BUSINESS OPERATIONS BY IDENTIFYING VULNERABILITIES, LINKING THEM TO CRITICAL
CYBER SECURITY GUIDANCE
 CYBER SECURITY GUIDANCE With the pervasiveness of information technology (IT) and cyber networks systems in nearly every aspect of society, effectively securing the Nation s critical infrastructure requires
CYBER SECURITY GUIDANCE With the pervasiveness of information technology (IT) and cyber networks systems in nearly every aspect of society, effectively securing the Nation s critical infrastructure requires
Lessons from Defending Cyberspace
 Lessons from Defending Cyberspace The Challenge of Addressing National Cyber Risk Andy Purdy Workshop on Cyber Security Center for American Studies, Christopher Newport College 10 28-2009 Cyber Threat
Lessons from Defending Cyberspace The Challenge of Addressing National Cyber Risk Andy Purdy Workshop on Cyber Security Center for American Studies, Christopher Newport College 10 28-2009 Cyber Threat
7 Homeland. ty Grant Program HOMELAND SECURITY GRANT PROGRAM. Fiscal Year 2008
 U.S. D EPARTMENT OF H OMELAND S ECURITY 7 Homeland Fiscal Year 2008 HOMELAND SECURITY GRANT PROGRAM ty Grant Program SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCE: CYBER SECURITY GUIDANCE uidelines and Application Kit (October
U.S. D EPARTMENT OF H OMELAND S ECURITY 7 Homeland Fiscal Year 2008 HOMELAND SECURITY GRANT PROGRAM ty Grant Program SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCE: CYBER SECURITY GUIDANCE uidelines and Application Kit (October
Internal audit of cybersecurity. Presentation to the Atlanta IIA Chapter January 2015
 Internal audit of cybersecurity Presentation to the Atlanta IIA Chapter January 2015 Agenda Executive summary Why is this topic important? Cyber attacks: increasing complexity arket insights: What are
Internal audit of cybersecurity Presentation to the Atlanta IIA Chapter January 2015 Agenda Executive summary Why is this topic important? Cyber attacks: increasing complexity arket insights: What are
Bridging the HIPAA/HITECH Compliance Gap
 CyberSheath Healthcare Compliance Paper www.cybersheath.com -65 Bridging the HIPAA/HITECH Compliance Gap Security insights that help covered entities and business associates achieve compliance According
CyberSheath Healthcare Compliance Paper www.cybersheath.com -65 Bridging the HIPAA/HITECH Compliance Gap Security insights that help covered entities and business associates achieve compliance According
Middle Class Economics: Cybersecurity Updated August 7, 2015
 Middle Class Economics: Cybersecurity Updated August 7, 2015 The President's 2016 Budget is designed to bring middle class economics into the 21st Century. This Budget shows what we can do if we invest
Middle Class Economics: Cybersecurity Updated August 7, 2015 The President's 2016 Budget is designed to bring middle class economics into the 21st Century. This Budget shows what we can do if we invest
NASA OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL
 NASA OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL OFFICE OF AUDITS SUITE 8U71, 300 E ST SW WASHINGTON, D.C. 20546-0001 April 14, 2016 TO: SUBJECT: Renee P. Wynn Chief Information Officer Final Memorandum, Review of NASA
NASA OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL OFFICE OF AUDITS SUITE 8U71, 300 E ST SW WASHINGTON, D.C. 20546-0001 April 14, 2016 TO: SUBJECT: Renee P. Wynn Chief Information Officer Final Memorandum, Review of NASA
ISSUE BRIEF. Cloud Security for Federal Agencies. Achieving greater efficiency and better security through federally certified cloud services
 ISSUE BRIEF Cloud Security for Federal Agencies Achieving greater efficiency and better security through federally certified cloud services This paper is intended to help federal agency executives to better
ISSUE BRIEF Cloud Security for Federal Agencies Achieving greater efficiency and better security through federally certified cloud services This paper is intended to help federal agency executives to better
GAO. Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government. Internal Control. United States General Accounting Office.
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Internal Control November 1999 Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government GAO/AIMD-00-21.3.1 Foreword Federal policymakers and program managers
GAO United States General Accounting Office Internal Control November 1999 Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government GAO/AIMD-00-21.3.1 Foreword Federal policymakers and program managers
White Paper Achieving GLBA Compliance through Security Information Management. White Paper / GLBA
 White Paper Achieving GLBA Compliance through Security Information Management White Paper / GLBA Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction: Brief Overview of GLBA... 1 The GLBA Challenge: Securing Financial
White Paper Achieving GLBA Compliance through Security Information Management White Paper / GLBA Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction: Brief Overview of GLBA... 1 The GLBA Challenge: Securing Financial
Generally Accepted Recordkeeping Principles
 Generally Accepted Recordkeeping Principles Information Governance Maturity Model Information is one of the most vital strategic assets any organization possesses. Organizations depend on information to
Generally Accepted Recordkeeping Principles Information Governance Maturity Model Information is one of the most vital strategic assets any organization possesses. Organizations depend on information to
State of Oregon. State of Oregon 1
 State of Oregon State of Oregon 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Information Asset Management...2 3. Communication Operations...7 3.3 Workstation Management... 7 3.9 Log management... 11 4. Information
State of Oregon State of Oregon 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Information Asset Management...2 3. Communication Operations...7 3.3 Workstation Management... 7 3.9 Log management... 11 4. Information
Achieving Control: The Four Critical Success Factors of Change Management. Technology Concepts & Business Considerations
 Achieving Control: The Four Critical Success Factors of Change Management Technology Concepts & Business Considerations T e c h n i c a l W H I T E P A P E R Table of Contents Executive Summary...........................................................
Achieving Control: The Four Critical Success Factors of Change Management Technology Concepts & Business Considerations T e c h n i c a l W H I T E P A P E R Table of Contents Executive Summary...........................................................
Technology Services Strategic Plan
 Technology Services Strategic Plan 2014 Table of Contents A Changing Landscape... 3 Values... 4 Technology Services Goals... 5 Employee Engagement... 6 Operational Efficiency... 7 Agency Satisfaction...
Technology Services Strategic Plan 2014 Table of Contents A Changing Landscape... 3 Values... 4 Technology Services Goals... 5 Employee Engagement... 6 Operational Efficiency... 7 Agency Satisfaction...
Qatar Computer Emergency Team
 Cyber Security Division Qatar Computer Emergency Team An initiative Introduction Qatar aims to fully exploit information and communications technology to become one of the most successful knowledge-based
Cyber Security Division Qatar Computer Emergency Team An initiative Introduction Qatar aims to fully exploit information and communications technology to become one of the most successful knowledge-based
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY
 ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY TITLE OF POLICY POLICY OWNER POLICY CHAMPION DOCUMENT HISTORY: Policy Title Status Enterprise Risk Management Policy (current, revised, no change, redundant) Approving
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY TITLE OF POLICY POLICY OWNER POLICY CHAMPION DOCUMENT HISTORY: Policy Title Status Enterprise Risk Management Policy (current, revised, no change, redundant) Approving
Cyber Side-Effects: How Secure is the Personal Information Entered into the Flawed Healthcare.gov? Statement for the Record
 Cyber Side-Effects: How Secure is the Personal Information Entered into the Flawed Healthcare.gov? Statement for the Record Roberta Stempfley Acting Assistant Secretary for Cybersecurity and Communications
Cyber Side-Effects: How Secure is the Personal Information Entered into the Flawed Healthcare.gov? Statement for the Record Roberta Stempfley Acting Assistant Secretary for Cybersecurity and Communications
Value to the Mission. FEA Practice Guidance. Federal Enterprise Architecture Program Management Office, OMB
 Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
Value to the Mission FEA Practice Guidance Federal Enterprise Program Management Office, OMB November 2007 FEA Practice Guidance Table of Contents Section 1: Overview...1-1 About the FEA Practice Guidance...
Third Party Security Requirements Policy
 Overview This policy sets out the requirements expected of third parties to effectively protect BBC information. Audience Owner Contacts This policy applies to all third parties and staff, including contractors,
Overview This policy sets out the requirements expected of third parties to effectively protect BBC information. Audience Owner Contacts This policy applies to all third parties and staff, including contractors,
CYBERSECURITY IN FINANCIAL SERVICES POINT OF VIEW CHALLENGE 1 REGULATORY COMPLIANCE ACROSS GEOGRAPHIES
 POINT OF VIEW CYBERSECURITY IN FINANCIAL SERVICES Financial services institutions are globally challenged to keep pace with changing and covert cybersecurity threats while relying on traditional response
POINT OF VIEW CYBERSECURITY IN FINANCIAL SERVICES Financial services institutions are globally challenged to keep pace with changing and covert cybersecurity threats while relying on traditional response
From Information Management to Information Governance: The New Paradigm
 From Information Management to Information Governance: The New Paradigm By: Laurie Fischer Overview The explosive growth of information presents management challenges to every organization today. Retaining
From Information Management to Information Governance: The New Paradigm By: Laurie Fischer Overview The explosive growth of information presents management challenges to every organization today. Retaining
Information Security Program CHARTER
 State of Louisiana Information Security Program CHARTER Date Published: 12, 09, 2015 Contents Executive Sponsors... 3 Program Owner... 3 Introduction... 4 Statewide Information Security Strategy... 4 Information
State of Louisiana Information Security Program CHARTER Date Published: 12, 09, 2015 Contents Executive Sponsors... 3 Program Owner... 3 Introduction... 4 Statewide Information Security Strategy... 4 Information
The Cyber Security Leap: From Laggard to Leader. April 2015
 The Cyber Security Leap: From Laggard to Leader April 2015 How do some organizations achieve better security performance? We compared organizations that were able to leapfrog their security effectiveness
The Cyber Security Leap: From Laggard to Leader April 2015 How do some organizations achieve better security performance? We compared organizations that were able to leapfrog their security effectiveness
Introduction. Jason Lawrence, MSISA, CISSP, CISA Manager, EY Advanced Security Center Atlanta, Georgia jason.lawrence@ey.com Twitter: @ethical_infosec
 Introduction Jason Lawrence, MSISA, CISSP, CISA Manager, EY Advanced Security Center Atlanta, Georgia jason.lawrence@ey.com Twitter: @ethical_infosec More than 20 years of experience in cybersecurity specializing
Introduction Jason Lawrence, MSISA, CISSP, CISA Manager, EY Advanced Security Center Atlanta, Georgia jason.lawrence@ey.com Twitter: @ethical_infosec More than 20 years of experience in cybersecurity specializing
Commonwealth IT Threat Management: Keeping Out the Cyber Villains Category: Cyber Security Initiatives. Initiation date: January 2012
 Commonwealth IT Threat Management: Keeping Out the Cyber Villains Category: Cyber Security Initiatives Initiation date: January 2012 Completion date: June 2012 Nomination submitted by: Samuel A. Nixon
Commonwealth IT Threat Management: Keeping Out the Cyber Villains Category: Cyber Security Initiatives Initiation date: January 2012 Completion date: June 2012 Nomination submitted by: Samuel A. Nixon
University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter
 University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter 1 Table of Contents 1.0 SIGNATURE PAGE 2.0 REVISION HISTORY 3.0 PURPOSE OF DOCUMENT 4.0 DATA GOVERNANCE PROGRAM FOUNDATIONAL ELEMENTS
University of Michigan Medical School Data Governance Council Charter 1 Table of Contents 1.0 SIGNATURE PAGE 2.0 REVISION HISTORY 3.0 PURPOSE OF DOCUMENT 4.0 DATA GOVERNANCE PROGRAM FOUNDATIONAL ELEMENTS
Best Practices in ICS Security for Device Manufacturers. A Wurldtech White Paper
 Best Practices in ICS Security for Device Manufacturers A Wurldtech White Paper No part of this document may be distributed, reproduced or posted without the express written permission of Wurldtech Security
Best Practices in ICS Security for Device Manufacturers A Wurldtech White Paper No part of this document may be distributed, reproduced or posted without the express written permission of Wurldtech Security
DIVISION OF INFORMATION SECURITY (DIS) Information Security Policy Threat and Vulnerability Management V1.0 April 21, 2014
 DIVISION OF INFORMATION SECURITY (DIS) Information Security Policy Threat and Vulnerability Management V1.0 April 21, 2014 Revision History Update this table every time a new edition of the document is
DIVISION OF INFORMATION SECURITY (DIS) Information Security Policy Threat and Vulnerability Management V1.0 April 21, 2014 Revision History Update this table every time a new edition of the document is
Five keys to a more secure data environment
 Five keys to a more secure data environment A holistic approach to data infrastructure security Compliance professionals know better than anyone how compromised data can lead to financial and reputational
Five keys to a more secure data environment A holistic approach to data infrastructure security Compliance professionals know better than anyone how compromised data can lead to financial and reputational
How To Ensure Health Information Is Protected
 pic pic CIHI Submission: 2011 Prescribed Entity Review October 2011 Who We Are Established in 1994, CIHI is an independent, not-for-profit corporation that provides essential information on Canada s health
pic pic CIHI Submission: 2011 Prescribed Entity Review October 2011 Who We Are Established in 1994, CIHI is an independent, not-for-profit corporation that provides essential information on Canada s health
Proposed guidance for firms outsourcing to the cloud and other third-party IT services
 Guidance consultation 15/6 Proposed guidance for firms outsourcing to the cloud and other third-party IT services November 2015 1. Introduction and consultation 1.1 The purpose of this draft guidance is
Guidance consultation 15/6 Proposed guidance for firms outsourcing to the cloud and other third-party IT services November 2015 1. Introduction and consultation 1.1 The purpose of this draft guidance is
Preemptive security solutions for healthcare
 Helping to secure critical healthcare infrastructure from internal and external IT threats, ensuring business continuity and supporting compliance requirements. Preemptive security solutions for healthcare
Helping to secure critical healthcare infrastructure from internal and external IT threats, ensuring business continuity and supporting compliance requirements. Preemptive security solutions for healthcare
Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE. Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015
 Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015 This page has intentionally been left blank Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Background...
Office of the Auditor General AUDIT OF IT GOVERNANCE Tabled at Audit Committee March 12, 2015 This page has intentionally been left blank Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Background...
EVALUATION REPORT. The Department of Energy's Unclassified Cybersecurity Program 2014
 U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections EVALUATION REPORT The Department of Energy's Unclassified Cybersecurity Program 2014 DOE/IG-0925 October 2014 Department
U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inspector General Office of Audits and Inspections EVALUATION REPORT The Department of Energy's Unclassified Cybersecurity Program 2014 DOE/IG-0925 October 2014 Department
AN INFORMATION GOVERNANCE BEST
 SMALL BUSINESS ID THEFT AND FRAUD AN INFORMATION GOVERNANCE BEST PRACTICES GUIDE FOR SMALL BUSINESS IT IS NOT A MATTER OF IF BUT WHEN AN INTRUSION WILL BE ATTEMPTED ON YOUR BUSINESS COMPUTER SYSTEM IN
SMALL BUSINESS ID THEFT AND FRAUD AN INFORMATION GOVERNANCE BEST PRACTICES GUIDE FOR SMALL BUSINESS IT IS NOT A MATTER OF IF BUT WHEN AN INTRUSION WILL BE ATTEMPTED ON YOUR BUSINESS COMPUTER SYSTEM IN
Business resilience: The best defense is a good offense
 IBM Business Continuity and Resiliency Services January 2009 Business resilience: The best defense is a good offense Develop a best practices strategy using a tiered approach Page 2 Contents 2 Introduction
IBM Business Continuity and Resiliency Services January 2009 Business resilience: The best defense is a good offense Develop a best practices strategy using a tiered approach Page 2 Contents 2 Introduction
Water Critical Infrastructure and Key Resources Sector-Specific Plan as input to the National Infrastructure Protection Plan Executive Summary
 Water Critical Infrastructure and Key Resources Sector-Specific Plan as input to the National Infrastructure Protection Plan Executive Summary May 2007 Environmental Protection Agency Executive Summary
Water Critical Infrastructure and Key Resources Sector-Specific Plan as input to the National Infrastructure Protection Plan Executive Summary May 2007 Environmental Protection Agency Executive Summary
White Paper on Financial Institution Vendor Management
 White Paper on Financial Institution Vendor Management Virtually every organization in the modern economy relies to some extent on third-party vendors that facilitate business operations in a wide variety
White Paper on Financial Institution Vendor Management Virtually every organization in the modern economy relies to some extent on third-party vendors that facilitate business operations in a wide variety
THE DIGITAL AGE THE DEFINITIVE CYBERSECURITY GUIDE FOR DIRECTORS AND OFFICERS
 THE DIGITAL AGE THE DEFINITIVE CYBERSECURITY GUIDE FOR DIRECTORS AND OFFICERS Download the entire guide and follow the conversation at SecurityRoundtable.org Collaboration and communication between technical
THE DIGITAL AGE THE DEFINITIVE CYBERSECURITY GUIDE FOR DIRECTORS AND OFFICERS Download the entire guide and follow the conversation at SecurityRoundtable.org Collaboration and communication between technical
Developing a National Strategy for Cybersecurity FOUNDATIONS FOR SECURITY, GROWTH, AND INNOVATION. Cristin Flynn Goodwin J.
 Developing a National Strategy for Cybersecurity FOUNDATIONS FOR SECURITY, GROWTH, AND INNOVATION Cristin Flynn Goodwin J. Paul Nicholas October 2013 Contents Executive Summary... 3 What Is a National
Developing a National Strategy for Cybersecurity FOUNDATIONS FOR SECURITY, GROWTH, AND INNOVATION Cristin Flynn Goodwin J. Paul Nicholas October 2013 Contents Executive Summary... 3 What Is a National
Symantec Control Compliance Suite. Overview
 Symantec Control Compliance Suite Overview Addressing IT Risk and Compliance Challenges Only 1 in 8 best performing organizations feel their Information Security teams can effectively influence business
Symantec Control Compliance Suite Overview Addressing IT Risk and Compliance Challenges Only 1 in 8 best performing organizations feel their Information Security teams can effectively influence business
THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
 THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK ACCOUNTABLE SIGNATURE AUTHORISED for implementation SIGNATURE On behalf of Chief Executive Officer SAHRA Council Date Date
THE SOUTH AFRICAN HERITAGE RESOURCES AGENCY ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK ACCOUNTABLE SIGNATURE AUTHORISED for implementation SIGNATURE On behalf of Chief Executive Officer SAHRA Council Date Date
The CIPM certification is comprised of two domains: Privacy Program Governance (I) and Privacy Program Operational Life Cycle (II).
 Page 1 of 7 The CIPM certification is comprised of two domains: Privacy Program Governance (I) and Privacy Program Operational Life Cycle (II). Domain I provides a solid foundation for the governance of
Page 1 of 7 The CIPM certification is comprised of two domains: Privacy Program Governance (I) and Privacy Program Operational Life Cycle (II). Domain I provides a solid foundation for the governance of
OVERVIEW. In all, this report makes recommendations in 14 areas, such as. Page iii
 The Office of the Auditor General has conducted a procedural review of the State Data Center (Data Center), a part of the Arizona Strategic Enterprise Technology (ASET) Division within the Arizona Department
The Office of the Auditor General has conducted a procedural review of the State Data Center (Data Center), a part of the Arizona Strategic Enterprise Technology (ASET) Division within the Arizona Department
State of South Carolina Initial Security Assessment
 State of South Carolina Initial Security Assessment Deloitte & Touche LLP Date: May 1, 2013 Our services were performed in accordance with the Statement on Standards for Consulting Services that is issued
State of South Carolina Initial Security Assessment Deloitte & Touche LLP Date: May 1, 2013 Our services were performed in accordance with the Statement on Standards for Consulting Services that is issued
NICE and Framework Overview
 NICE and Framework Overview Bill Newhouse NIST NICE Leadership Team Computer Security Division Information Technology Lab National Institute of Standards and Technology TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to
NICE and Framework Overview Bill Newhouse NIST NICE Leadership Team Computer Security Division Information Technology Lab National Institute of Standards and Technology TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to
Cyber Security and Privacy Services. Working in partnership with you to protect your organisation from cyber security threats and data theft
 Cyber Security and Privacy Services Working in partnership with you to protect your organisation from cyber security threats and data theft 2 Cyber Security and Privacy Services What drives your security
Cyber Security and Privacy Services Working in partnership with you to protect your organisation from cyber security threats and data theft 2 Cyber Security and Privacy Services What drives your security
NASA Financial Management Requirements Volume 9, Chapter 4 April 2005 CHAPTER 4 RISK ASSESSMENTS
 CHAPTER 4 RISK ASSESSMENTS 0401 GENERAL 040101. Purpose. This chapter provides detailed guidance on National Aeronautics and Space Administration s (NASA) financial management internal control program
CHAPTER 4 RISK ASSESSMENTS 0401 GENERAL 040101. Purpose. This chapter provides detailed guidance on National Aeronautics and Space Administration s (NASA) financial management internal control program
Blending Corporate Governance with. Information Security
 Blending Corporate Governance with Information Security WHAT IS CORPORATE GOVERNANCE? Governance has proved an issue since people began to organise themselves for a common purpose. How to ensure the power
Blending Corporate Governance with Information Security WHAT IS CORPORATE GOVERNANCE? Governance has proved an issue since people began to organise themselves for a common purpose. How to ensure the power
Missouri Student Information System Data Governance
 Nicole R. Galloway, CPA Missouri State Auditor ELEMENTARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION Missouri Student Information System Data Governance October 2015 http://auditor.mo.gov Report No. 2015-093 Nicole R. Galloway,
Nicole R. Galloway, CPA Missouri State Auditor ELEMENTARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION Missouri Student Information System Data Governance October 2015 http://auditor.mo.gov Report No. 2015-093 Nicole R. Galloway,
Continuous Network Monitoring
 Continuous Network Monitoring Eliminate periodic assessment processes that expose security and compliance programs to failure Continuous Network Monitoring Continuous network monitoring and assessment
Continuous Network Monitoring Eliminate periodic assessment processes that expose security and compliance programs to failure Continuous Network Monitoring Continuous network monitoring and assessment
PROPOSED INTERPRETIVE NOTICE
 August 28, 2015 Via Federal Express Mr. Christopher J. Kirkpatrick Secretary Office of the Secretariat Commodity Futures Trading Commission Three Lafayette Centre 1155 21st Street, N.W. Washington, DC
August 28, 2015 Via Federal Express Mr. Christopher J. Kirkpatrick Secretary Office of the Secretariat Commodity Futures Trading Commission Three Lafayette Centre 1155 21st Street, N.W. Washington, DC
California Enterprise Architecture Framework
 Version 2.0 August 01, 2013 This Page is Intentionally Left Blank Version 2.0 ii August 01, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Executive Summary... 1 1.1 What is Enterprise Architecture?... 1 1.2 Why do we need
Version 2.0 August 01, 2013 This Page is Intentionally Left Blank Version 2.0 ii August 01, 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Executive Summary... 1 1.1 What is Enterprise Architecture?... 1 1.2 Why do we need
The Value of Vulnerability Management*
 The Value of Vulnerability Management* *ISACA/IIA Dallas Presented by: Robert Buchheit, Director Advisory Practice, Dallas Ricky Allen, Manager Advisory Practice, Houston *connectedthinking PwC Agenda
The Value of Vulnerability Management* *ISACA/IIA Dallas Presented by: Robert Buchheit, Director Advisory Practice, Dallas Ricky Allen, Manager Advisory Practice, Houston *connectedthinking PwC Agenda
Corporate Incident Response. Why You Can t Afford to Ignore It
 Corporate Incident Response Why You Can t Afford to Ignore It Whether your company needs to comply with new legislation, defend against financial loss, protect its corporate reputation or a combination
Corporate Incident Response Why You Can t Afford to Ignore It Whether your company needs to comply with new legislation, defend against financial loss, protect its corporate reputation or a combination
Microsoft Services Premier Support. Security Services Catalogue
 Microsoft Services Premier Support Security Services Catalogue 2014 Microsoft Services Microsoft Services helps you get the most out of your Microsoft Information Technology (IT) investment with integrated
Microsoft Services Premier Support Security Services Catalogue 2014 Microsoft Services Microsoft Services helps you get the most out of your Microsoft Information Technology (IT) investment with integrated
FFIEC Cybersecurity Assessment Tool Overview for Chief Executive Officers and Boards of Directors
 Overview for Chief Executive Officers and Boards of Directors In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed
Overview for Chief Executive Officers and Boards of Directors In light of the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council 1 (FFIEC) developed
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) White Paper
 Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) White Paper Table of Contents: Purpose page 2 Introduction _ page 3 What is GRC _ page 3 GRC Concepts _ page 4 Integrated Approach and Methodology page 4 Diagram:
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) White Paper Table of Contents: Purpose page 2 Introduction _ page 3 What is GRC _ page 3 GRC Concepts _ page 4 Integrated Approach and Methodology page 4 Diagram:
Information Technology Risk Management
 Find What Matters Information Technology Risk Management Control What Counts The Cyber-Security Discussion Series for Federal Government security experts... by Carson Associates your bridge to better IT
Find What Matters Information Technology Risk Management Control What Counts The Cyber-Security Discussion Series for Federal Government security experts... by Carson Associates your bridge to better IT
Lawson Healthcare Solutions Optimization of Key Resources Forms a Foundation for Excellent Patient Care
 Lawson Healthcare Solutions Optimization of Key Resources Forms a Foundation for Excellent Patient Care Healthcare organizations continue to experience an alarming erosion of their operational foundation,
Lawson Healthcare Solutions Optimization of Key Resources Forms a Foundation for Excellent Patient Care Healthcare organizations continue to experience an alarming erosion of their operational foundation,
