Introduction to Nursing Informatics & Health Information Technology for Student Nurses
|
|
|
- Claribel Hancock
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course Overview In this 8 hour course, ADN nursing students will be introduced to health information systems and informatics concepts that they will most likely experience in a clinical setting. Course content will focus on general HIT concepts, terminology and key health information systems. Students will explore their own role as nurses in implementing patient-centered care in an environment of advancing technology. Students will critically evaluate health information systems and their role in patient safety, safe medication administration, maintenance of patient privacy, data security, and efficacy of health care processes. Students will also have hands on practice in a clinical information system and demonstrate an understanding of some common elements of HIT systems. Standards of practice and competencies will be based on a combination of industry standards, including the Office of National Coordinator for Health information Technology (ONC), the American Nurses Association (ANA), the National League of Nursing (NLN), Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN), Technology Informatics Guiding Education Reform (TIGER), Institutes of Medicine (IOM) and the JCAHO Patient Safety Goals. ONC Role Alignment: Clinical/Practitioner Consultant Course Objectives At the completion of the 8 hour course, the student nurse will be able to: 1. Describe the precipitating factors that have led to a need for health care information systems in the patient care setting 2. Provide examples of different types of health information systems technology used in the hospital setting 3. Demonstrate the effect health information technologies have on patient safety 4. Identify ways to maintain patient privacy and security of data in the hospital setting 5. Analyze current ethical issues that arise out of the use of health information technology 6. Compare and contrast different health IT systems and their role in patient-centered care 7. Demonstrate the use of electronic health record system Course Format The course is a mix of classroom lecture and discussion balanced by application-based activities. Prior to the classroom session, students will be expected to complete the Pretest for Attitudes Toward Computers in Healthcare (PATCH) self-assessment tool. Students will meet for a four hour classroom session where key concepts and material are presented. Following the lecture, students are to reflect on their experience with different documentation systems describing their observations in a brief two page paper. In addition, students will also access a cloud-based simulated Electronic Health Records system where they will experience firsthand software navigation and data input for a variety of demo patient scenarios. Additional critical thinking activities have also been identified depending on student level/ability.*
2 Activity 1: Write a 2 page paper discussing two documentation systems you have used while in nursing school. One system must be computer based. Compare and contrast each system and discuss how each system: o Supported patient safety o Incorporated EBP o Supported safe medication administration o Patient and Data security, privacy and confidentiality Activity 2: Complete identified tasks in ToolWire s cloud-based simulated Electronic Health Records System Activity 3*: Online discussion regarding NPSGs (National Patient Safety Goals) and/or a review/discussion of some of these case studies submitted to HIMSS and co-sponsor American Society for Quality (ASQ): Activity 4*: Online discussion of current news articles highlighting ethics/security issues involving EHRS oting_victims t_mom_s_medical_records Course Materials PowerPoint Slides Pretest for Attitudes Toward Computers in Healthcare (PATCH) self-assessment tool Supplemental readings (handouts and weblinks) Moodle course site ToolWire simulated Electronic Health Records system
3 ONC Curriculum Elements relevant to Nursing #4 Introduction to Information and Computer Science High level overview of computers and internet use in healthcare o Explain the development of computers and the Internet, including healthcare systems up until the present time Introduction to importance of security in health care o List and describe common security concerns (viruses, worms, etc.) o Describe safeguards against common security concerns, including firewalls, encryption, virus protection software and patterns, programming for security, etc. o Describe security concerns for wireless networks and how to address them. Describe latest advances in technology as applicable to healthcare Future of computing as related to health care #5 History of Health Information Technology in the US Evolution of Health IT o Introduce Meaningful Use Privacy and Security o List security concerns/regulations for health care applications. o Describe security safeguards used for health care applications. Patient-related issues and Role of HIT o Discuss implications for healthcare systems, including potential risks #6 Health Management Information Systems What is Health Informatics? o Summarize how the Institute of Medicine s Vision for 21st Century Health Care and Wellness may impact health management information systems. (*may read select portions of document) Hardware and Software Supporting Health Information Systems o Describe various types of technologies (e.g. medication administration systems/bar-coding, chart tracking, patient databases) that support health care information systems. o Examine the challenges presented by emerging trends in information technology (e.g., mobility, web services, the Internet, Intranet, and wireless computing), social media, and global communications. Electronic Health Records o Definitions of an electronic medical record (EMR) and electronic health record (EHR) o Identify attributes and functions of an HER o Impact of EHRs on patient care, safety, efficacy of care practices and outcomes
4 o Governmental efforts related to EHR systems including meaningful use of interoperable health information technology and a qualified EHR (define meaningful use and its implications for nurses) Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE) o Describe the purpose, attributes and functions of CPOE o Explain ways in which CPOE is currently being used in health care o Discuss the major values to CPOE adoption o Identify how CPOE can affect patient care safety, quality and efficiency, as well as patient outcomes (the role nurses play using CPOE- taking and transcribing orders, elements required to perform CPOE correctly) Clinical Decision Support Systems o Definition of a clinical decision support system o Discuss the importance of clinical practice guidelines and evidence-based practice and how these affect clinical decision support systems (potential for nurse exposure to these systems and how they affect nursing care of patients at the bedside, clinic, etc) Patient Monitoring Systems o Purpose, attributes and functions of patient monitoring systems (Types of systems nurses may use) o Applications of and ways in which automation can improve the quality of patient care advantages and disadvantages of using computers at the bedside Medical Imaging Systems o Briefly: Examine the purposes, processes, and management issues related to the use of imaging systems in health care. (how a nurse might interact with these kinds of systems) Consumer Health Informatics Briefly: Describe the emergence of Personal Health o Records and their implications for patients, health care providers, and health systems. (relating to how patients use these resources to improve their own health management) # 7 : Consumer Health Informatics Introduction & Overview: Components of HIT Systems o Define a system and relate systems concepts to HIT o Discuss specific examples of settings where Health IT is used (acute, rural, public health, clinic, office, patient home, etc.) o Identify common components of a clinical HIT system o Demonstrate beginning level competency in maneuvering the demonstration EHRS Facilitated Error Cause and Effect (relating to potential errors nurses may make) o Different classes of HIT errors (slips/mistakes, omission/commission) will be discussed and differentiated. Protecting Privacy, Security, and Confidentiality in HIT Systems
5 o Explain and illustrate privacy, security, and confidentiality in HIT settings. o Identify common threats encountered when using HIT. o Formulate strategies to minimize threats to privacy, security, and confidentiality in HIT systems. HIT and Aspects of Patient-Centered Care o Define patient-centered care. o Suggest HIT-enabled solutions/strategies to enhance patient involvement in health and healthcare o Assess the effectiveness of HIT systems in supporting patient-centered care. #10 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign o Define workflow o Describe how the workflow processes used by a healthcare facility might differ depending on facility type #12 Quality Improvement HIT design to support Teamwork and Communication ( o the role the nurse plays in using these tools) o The focus is on electronic tools to support communication and teamwork during hand-off, care planning, and care transitions. o Incorporation of automatic referral requests, data transfer to longitudinal records, and shared problem lists and daily goal forms into the EHR is discussed as well as the utility of electronic whiteboards and clipboard tools. HIT Design for Quality Reporting o the role the nurse plays in using HIT to provide accurate and useful quality reporting and data o Examine the importance of standardized and structured health information. (standardize language for example) o Discuss how HIT can facilitate data collection and reporting for improving quality and safety.
6 Literature Review for Nursing Informatics and Health Information Technology Nursing informatics competencies: User level technical competencies include: 1. uses word processing applications 2. demonstrates keyboarding skills 3. uses spreadsheet applications 4. uses telecommunication devices to communicate with other systems 5. uses systems to communicate with other health care professionals 6. uses presentation applications to create slides, displays, overheads (PowerPoint, Corel Presentation, etc.) 7. uses multimedia presentations 8. uses internet resources to locate client support groups, online resources 9. uses sources of data that relate to nursing practice and care 10. accesses, enters and retrieves data related to client care via available hospital or nursing information systems 11. uses database management programs to develop and access databases and tables 12. uses database applications to enter and retrieve data and information 13. conducts online and database literature searches 14. uses decision support systems, expert systems and other aids for clinical decision making and care planning 15. uses computer applications to document client care 16. uses computer applications to plan client care, including discharge planning 17. uses computer applications to enter client data (demographic, vital signs, physiological data) 18. uses information management systems for client education 19. uses technology based client monitoring systems 20. operates peripheral devices (bedside and hand held) 21. uses operating systems 22. uses computer peripheral devices (CD ROMs, DVD, zip drives) 23. uses computer technology safely 24. navigates in Windows environment effectively 25. demonstrates basic technology skills (load paper, change toner, unjam printers, print) User level utility competencies include: 1. recognizes the relevance of nursing data for improving practice 2. recognizes limitations of computer applications
7 3. recognizes need for continual learning in informatics skills, applications and knowledge 4. recognizes the nature of computer - human interfaces and assesses impact on client care 5. understands the basic process of using networks for electronic communication 6. recognizes the basic components of computer systems User level leadership competencies include: 1. uses computerized management systems to record administrative data (billing data, quality assurance data, workload data, etc.) 2. uses applications for structured data entry (classification systems, acuity level, etc.) 3. understands client rights related to computerized information 4. recognizes the utility of nurse involvement in the planning, design, choice and implementation of information systems in the practice environment 5. incorporates a Code of Ethics in regards to client privacy and confidentiality QSEN (Quality and Safety Education for Nurses) Pre licensure: Informatics Definition: Use information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making. Knowledge Skills Attitudes Explain why information and technology skills are essential for safe patient care Identify essential information that must be available in a common database to support patient care Contrast benefits and limitations of different communication Seek education about how information is managed in care settings before providing care Apply technology and information management tools to support safe processes of care Navigate the electronic health record Document and plan patient care in an Appreciate the necessity for all health professionals to seek lifelong, continuous learning of information technology skills Value technologies that support clinical decision-making, error prevention, and care coordination Protect confidentiality of
8 technologies and their impact on safety and quality Describe examples of how technology and information management are related to the quality and safety of patient care Recognize the time, effort, and skill required for computers, databases and other technologies to become reliable and effective tools for patient care electronic health record Employ communication technologies to coordinate care for patients Respond appropriately to clinical decision-making supports and alerts Use information management tools to monitor outcomes of care processes Use high quality electronic sources of healthcare information protected health information in electronic health records Value nurses' involvement in design, selection, implementation, and evaluation of information technologies to support patient care The Technology Informatics Guiding Education Reform (TIGER) KEY ACTIONS: EDUCATION Vision Statement: Collaborative learning communities that maximize the possibilities of technology toward knowledge development and dissemination, driving rapid deployment and implementation of best practices. Reform the nursing curriculum through integration of IT, information literacy, and informatics and the infusion of technologies for learning. (65%) Seek funding to develop and implement learning innovations, foster faculty development, and ensure necessary infrastructure. (41%) Identify, model, and implement collaborative partnerships among public and private academic, service, and industry enterprises. (40%) Increase faculty acceptance of technology through education and training, incentives, and necessary supports. (38%) Convene a national group to develop strategies for the recruitment, retention, and training of current and future workforces in informatics education, practice and research. (37%)
9 Results of a Delphi Study to Determine Informatics Competencies for Nurses Beginning nurse Level 1: Computer Skills - Administration Uses administrative applications for practice management (e.g., searches for patient, retrieves demographics, billing data) Uses applications for structured data entry (e.g., patient acuity or classification applications) Computer Skills Communication ( , internet, telecommunications) Uses telecommunication devices (e.g., modems or other devices) to communicate with other systems (e.g., access data, upload, download) Use (e.g., create, send, respond, use attachments) Uses the Internet to locate, download items of interest (e.g., patient, nursing resources) Computer Skills Data access Uses sources of data that relate to practice and care Accesses, enters, and retrieves data used locally for patient care (e.g., uses HIS, CIS for plans of care, assessments, interventions, notes, discharge planning) Uses database applications to enter and retrieve information Conducts on-line literature searches Computer Skills - Documentation Uses an application to document patient care Uses an application to plan care for patients to include discharge planning Uses an application to enter patient data (e.g., vital signs Computer Skills Education Uses information management technologies for patient education (e.g., identifies areas for instruction, conducts education, evaluates outcomes, resources) Computer Skills-Monitoring Uses computerized patient monitoring systems Computer Skills Basic Desktop Software Uses multimedia presentations Uses word processing Demonstrates keyboarding (typing) skills Computer Skills - Systems Uses networks to navigate systems (e.g., file servers, www) Operates peripheral devices (e.g., bedside terminals, hand-helds) Uses operating systems (e.g., copy, delete, change directories) Uses existing external peripheral devices (e.g., CD-ROMs, zip drives) Uses computer technology safely
10 Is able to navigate Windows (e.g., manipulate files using file manager, determine active printer, access installed applications, create & delete directories) Identifies the appropriate technology to capture the required patient data (e.g., fetal monitoring device) Demonstrates basic technology skills (e.g., turn computer off & on, load paper, change toner, remove paper jams, print documents) Informatics Knowledge Data Recognizes the use and/or importance of nursing data for improving practice Informatics Knowledge - Impact Recognizes that a computer program has limitations due to its design and capacity of the computer Recognizes that it takes time, persistent effort, and skill for computers to become an effective tool Recognizes that health computing will become more common Recognizes that the computer is only a tool to provide better nursing care and that there are human functions that cannot be performed by computer Recognizes that one does not have to be a computer programmer to make effective use of the computer in nursing Informatics Knowledge Privacy/security Seeks available resources to help formulate ethical decisions in computing Describes patients' rights as they pertain to computerized information management Informatics Knowledge - Systems Recognizes the value of clinicians' involvement in the design, selection, implementation, and evaluation of applications, systems in health care Describes the computerized or manual paper system that is present Explains the use of networks for electronic communication (e.g., Internet) Identifies the basic components of the current computer system (e.g., features of a PC, workstation QSEN and TIGER are referenced by NLN here: NLN content areas recommended: Use of health information technology to augment/support the nursing care process - includes concepts such as safety, care improvement, decision assistance/support, outcome analysis and data analysis. Communication includes electronic health records, personal health records, standardized languages and terminology.
11 Issues including legal, ethical, social, security, advocacy, and public policy. Nursing involvement through teamwork/collaboration covering nurses s role in determining usability, workflow analysis, and systems selection/evaluation. Scope and Standards of Nursing Informatics Practice (ANA) Overall informatics competencies The following overall informatics competencies are required of beginning nurses, those individuals first learning about or entering into nursing practice. Overall informatics activities may include but are not limited to: Identifying, collecting, and recording data relevant to the nursing care of patients. Analyzing and interpreting patient and nursing information as part of the planning for the provision of nursing services. Using informatics applications designed for the practice of nursing. Implementing public and institutional policies related to privacy, confidentiality, and security of information. These include patient care information, confidential employer information, and other information gained in the nurses professional capacity. Health Professions Education: a bridge to quality IOM Core Competencies Include: Utilize informatics to reduce errors, manage knowledge and information, make decisions and communicate.
HIT Workflow & Redesign Specialist: Curriculum Overview
 HIT Workflow & Redesign Specialist: Curriculum Overview Component - Description Units - Description Appx. Time 1: Introduction to Health Care and Public Health in the U.S. Survey of how healthcare and
HIT Workflow & Redesign Specialist: Curriculum Overview Component - Description Units - Description Appx. Time 1: Introduction to Health Care and Public Health in the U.S. Survey of how healthcare and
Results of a Delphi Study to Determine Informatics Competencies for Nurses at Four Levels of Practice
 Results of a Delphi Study to Determine Informatics Competencies for Nurses at Four Levels of Practice ** Please see full length article in Nursing Research, Nov/Dec 2002** Initial panel work available
Results of a Delphi Study to Determine Informatics Competencies for Nurses at Four Levels of Practice ** Please see full length article in Nursing Research, Nov/Dec 2002** Initial panel work available
Integrating the Electronic Health Record in the Curriculum
 Integrating the Electronic Health Record in the Curriculum Judith J. Warren, PhD, RN, BC, FAAN, FACMI Christine A. Hartley Centennial Professor University of Kansas School of Nursing and Director of Nursing
Integrating the Electronic Health Record in the Curriculum Judith J. Warren, PhD, RN, BC, FAAN, FACMI Christine A. Hartley Centennial Professor University of Kansas School of Nursing and Director of Nursing
Nursing Informatics The Future is Here
 Nursing Informatics The Future is Here One (1) Contact Hour First Published: April 1, 2013 Course Expires: April 1, 2016 Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Nursing Informatics The Future is Here One (1) Contact Hour First Published: April 1, 2013 Course Expires: April 1, 2016 Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
6/10/2010 DISCLOSURES - NONE INTEGRATING QSEN COMPETENCIES INTO NURSING EDUCATION
 INTEGRATING QSEN COMPETENCIES INTO NURSING EDUCATION Brenda Zierler, PhD, RN, RVT University of Washington School of Nursing DISCLOSURES - NONE Brenda Zierler, PhD, RN, RVT University of Washington School
INTEGRATING QSEN COMPETENCIES INTO NURSING EDUCATION Brenda Zierler, PhD, RN, RVT University of Washington School of Nursing DISCLOSURES - NONE Brenda Zierler, PhD, RN, RVT University of Washington School
School of Nursing University of Minnesota Informatics Competencies across the Curriculum
 Informatics Competencies across the Curriculum Data - basic elements & related standards BSN DNP PhD Resources Course Assignment Describe the value of using standardized terminologies and messaging standards
Informatics Competencies across the Curriculum Data - basic elements & related standards BSN DNP PhD Resources Course Assignment Describe the value of using standardized terminologies and messaging standards
Developing Nurse Mangers Through Competency Based Informatics Education Session 39 Kathleen Guiney RN MN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed
 Developing Nurse Mangers Through Competency Based Informatics Education Session 39 Kathleen Guiney RN MN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do
Developing Nurse Mangers Through Competency Based Informatics Education Session 39 Kathleen Guiney RN MN DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do
Slide 10. On the following slides we have provided the KSAs that are specific to QSEN s Informatics competencies. Slide 11 Knowledge
 Slide 1 Informatics in the Simulation Lab Karen Fettig, MA, RN Lisa Robertson, MSN, RN Susan Priem, MS, RN Learn how faculty at Minnesota State College - Southeast Technical in Red Wing and Winona, MN
Slide 1 Informatics in the Simulation Lab Karen Fettig, MA, RN Lisa Robertson, MSN, RN Susan Priem, MS, RN Learn how faculty at Minnesota State College - Southeast Technical in Red Wing and Winona, MN
PREPARING THE NEXT GENERATION OF NURSES TO PRACTICE IN A TECHNOLOGY-RICH ENVIRONMENT: AN INFORMATICS AGENDA. Board of Governors May 9, 2008
 PREPARING THE NEXT GENERATION OF NURSES TO PRACTICE IN A TECHNOLOGY-RICH ENVIRONMENT: AN INFORMATICS AGENDA Board of Governors May 9, 2008 Since the 1970s, several authors and organizations recommended
PREPARING THE NEXT GENERATION OF NURSES TO PRACTICE IN A TECHNOLOGY-RICH ENVIRONMENT: AN INFORMATICS AGENDA Board of Governors May 9, 2008 Since the 1970s, several authors and organizations recommended
National Nursing Informatics Deep Dive Program
 National Nursing Informatics Deep Dive Program Integrating AACN Essentials, QSEN KSA s and TIGER Competencies for Nursing Informatics Thomas R. Clancy, PhD, MBA, RN, FAAN Clinical Professor and Assistant
National Nursing Informatics Deep Dive Program Integrating AACN Essentials, QSEN KSA s and TIGER Competencies for Nursing Informatics Thomas R. Clancy, PhD, MBA, RN, FAAN Clinical Professor and Assistant
The Future of Nursing and the. Role of Informatics
 The Future of Nursing and the Role of Informatics Willa Fields, RN, DNSc, FHIMSS Professor, San Diego State University Program Manager, Sharp Grossmont Hospital Outline Future of Nursing Report Health
The Future of Nursing and the Role of Informatics Willa Fields, RN, DNSc, FHIMSS Professor, San Diego State University Program Manager, Sharp Grossmont Hospital Outline Future of Nursing Report Health
ehealth Competencies for Undergraduate Medical Education
 ehealth Competencies for Undergraduate Medical Education Created by The Association of Faculties of Medicine of Canada in Partnership with Canada Health Infoway, May 2014 Contents Contents Acknowledgements...
ehealth Competencies for Undergraduate Medical Education Created by The Association of Faculties of Medicine of Canada in Partnership with Canada Health Infoway, May 2014 Contents Contents Acknowledgements...
RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency
 RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency Evaluation of Nursing Students Informatics Competency Using an Adapted Self-Assessment of Nursing Informatics Competency Scale (SANICS)
RUNNING HEAD: Evaluation of nursing student s informatics competency Evaluation of Nursing Students Informatics Competency Using an Adapted Self-Assessment of Nursing Informatics Competency Scale (SANICS)
lclinical Informatics: Evaluation,
 1 Clinical Informatics: Evaluation, Selection, Implementation, and Management of Electronic Health Records lclinical Informatics: Evaluation, Marisa L Wilson DNSc MHSc RN-BC Selection, Implementation,
1 Clinical Informatics: Evaluation, Selection, Implementation, and Management of Electronic Health Records lclinical Informatics: Evaluation, Marisa L Wilson DNSc MHSc RN-BC Selection, Implementation,
Nursing Informatics 101
 Nursing Informatics 101 Nursing Informatics 101 Contributors Christel Anderson, MA Director, Clinical Informatics HIMSS Melissa F. Barthold, DNP, RN-BC,CPHIMS, FHIMSS Senior Clinical Solutions Strategist
Nursing Informatics 101 Nursing Informatics 101 Contributors Christel Anderson, MA Director, Clinical Informatics HIMSS Melissa F. Barthold, DNP, RN-BC,CPHIMS, FHIMSS Senior Clinical Solutions Strategist
Supporting the Advancement of Nursing Informatics throughout the Graduate Curriculum
 Supporting the Advancement of Nursing Informatics throughout the Graduate Curriculum Deb Poling, PhD and Tammy Toscos, PhD Indiana University - Purdue University, Fort Wayne IPFW was established in 1964
Supporting the Advancement of Nursing Informatics throughout the Graduate Curriculum Deb Poling, PhD and Tammy Toscos, PhD Indiana University - Purdue University, Fort Wayne IPFW was established in 1964
Role of the CNIO in Nursing Optimization of the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Mary Beth Mitchell, MSN, RN, BC CNIO, Texas Health Resources
 Role of the CNIO in Nursing Optimization of the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Mary Beth Mitchell, MSN, RN, BC CNIO, Texas Health Resources 1 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Mary Beth Mitchell, MSN, RN,
Role of the CNIO in Nursing Optimization of the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Mary Beth Mitchell, MSN, RN, BC CNIO, Texas Health Resources 1 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Mary Beth Mitchell, MSN, RN,
10/1/2015. National Library of Medicine definition of medical informatics:
 Heidi S. Daniels, PharmD Pharmacist Informaticist NEFSHP Fall Meeting: Pharmacy Practice Updates 2015 [email protected] Mayo Clinic Florida Campus Jacksonville, Florida I have nothing to disclose
Heidi S. Daniels, PharmD Pharmacist Informaticist NEFSHP Fall Meeting: Pharmacy Practice Updates 2015 [email protected] Mayo Clinic Florida Campus Jacksonville, Florida I have nothing to disclose
HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS
 SACRED HEART UNIVERSITY GRADUATE CATALOG 2013-2014 HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, CHAIR & PROGRAM DIRECTOR Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected]
SACRED HEART UNIVERSITY GRADUATE CATALOG 2013-2014 HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, CHAIR & PROGRAM DIRECTOR Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected]
Course Syllabus. Upon completion of all six modules, participants will have:
 Course Syllabus COURSE Health Informatics (101) Introduction to Health Informatics (101) COURSE DESCRIPTION Introduction to Health Informatics (101) offers an overview of the field of health informatics
Course Syllabus COURSE Health Informatics (101) Introduction to Health Informatics (101) COURSE DESCRIPTION Introduction to Health Informatics (101) offers an overview of the field of health informatics
HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS
 HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, CPHIT, CHAIR & PROGRAM DIRECTOR Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected] Overview/Rationale This interdisciplinary
HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, CPHIT, CHAIR & PROGRAM DIRECTOR Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected] Overview/Rationale This interdisciplinary
Increasing Nurse Leaders' Informatics Skills: Building from the TIGER Competencies
 Increasing Nurse Leaders' Informatics Skills: Building from the TIGER Competencies Melissa Barthold, MSN, RN-BC, CPHIMS, FHIMSS DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those
Increasing Nurse Leaders' Informatics Skills: Building from the TIGER Competencies Melissa Barthold, MSN, RN-BC, CPHIMS, FHIMSS DISCLAIMER: The views and opinions expressed in this presentation are those
Health Information Management Systems Technology and Analysis (HIMSTA) Domains, Competencies and Modules. The Curriculum.
 Health Information Management Systems Technology and Analysis (HIMSTA) Domains, Competencies and Modules Introduction: The Curriculum The outline below frames the 14 modules of this curriculum within their
Health Information Management Systems Technology and Analysis (HIMSTA) Domains, Competencies and Modules Introduction: The Curriculum The outline below frames the 14 modules of this curriculum within their
USING QSEN KSA'S TO BUILD AN UNDERGRADUATE ONLINE NURSING INFORMATICS COURSE. Beth Vottero PhD, RN, CNE
 USING QSEN KSA'S TO BUILD AN UNDERGRADUATE ONLINE NURSING INFORMATICS COURSE Beth Vottero PhD, RN, CNE Impetus for Change Addition of a new undergraduate course: Nursing Informatics Student feedback General
USING QSEN KSA'S TO BUILD AN UNDERGRADUATE ONLINE NURSING INFORMATICS COURSE Beth Vottero PhD, RN, CNE Impetus for Change Addition of a new undergraduate course: Nursing Informatics Student feedback General
HIMSS 2012. Nursing Informatics 101
 HIMSS 2012 Nursing Informatics 101 Nursing Informatics 101 Contributors: Christel Anderson Director, Clinical Informatics HIMSS Melissa F. Barthold, MSN, RN-BC, CPHIMS, FHIMSS Senior IT Clinical Informatics
HIMSS 2012 Nursing Informatics 101 Nursing Informatics 101 Contributors: Christel Anderson Director, Clinical Informatics HIMSS Melissa F. Barthold, MSN, RN-BC, CPHIMS, FHIMSS Senior IT Clinical Informatics
Electronic Medical Record Position Paper December 2014
 Electronic Medical Record Position Paper December 2014 Purpose: The purpose of this Electronic Medical Record (EMR) position paper is to present an overview of the electronic medical record along with
Electronic Medical Record Position Paper December 2014 Purpose: The purpose of this Electronic Medical Record (EMR) position paper is to present an overview of the electronic medical record along with
Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR)
 Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR) Agenda Definitions Attributes Differences Adoption Model Current State Challenges Implementation considerations What is it? EMR CMR EHR EPR PHR
Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR) Agenda Definitions Attributes Differences Adoption Model Current State Challenges Implementation considerations What is it? EMR CMR EHR EPR PHR
Nurse s Touch Nursing Informatics and Technology EDUCATOR IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE
 Nurse s Touch Nursing Informatics and Technology EDUCATOR IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE Nurse s Touch Educator Implementation Guide Nursing Informatics and Technology Table of Contents Description... 1 Features...
Nurse s Touch Nursing Informatics and Technology EDUCATOR IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE Nurse s Touch Educator Implementation Guide Nursing Informatics and Technology Table of Contents Description... 1 Features...
EHR IN THE NURSING CURRICULUM: IS IT NECESSARY? WHERE TO BEGIN? Laura Gonzalez PhD, ARNP, CNE Spring 2013
 1 EHR IN THE NURSING CURRICULUM: IS IT NECESSARY? WHERE TO BEGIN? Laura Gonzalez PhD, ARNP, CNE Spring 2013 2 Disclosure I am a Pearson Faculty Consultant and on the Speakers Bureau 3 Objectives Participant
1 EHR IN THE NURSING CURRICULUM: IS IT NECESSARY? WHERE TO BEGIN? Laura Gonzalez PhD, ARNP, CNE Spring 2013 2 Disclosure I am a Pearson Faculty Consultant and on the Speakers Bureau 3 Objectives Participant
Roles, Competencies, Skills, Organizations and Legislative Aspects Michelle R. Troseth, MSN, RN, DPNAP
 Objectives 1. Describe the history of nursing informatics as an emerging field in the nursing profession 2. Discuss evolving roles, competencies and skills impacting nursing informatics practice 3. Identify
Objectives 1. Describe the history of nursing informatics as an emerging field in the nursing profession 2. Discuss evolving roles, competencies and skills impacting nursing informatics practice 3. Identify
NETS for Students: Achievement Rubric
 NETS for Students: Achievement Rubric DRAFT (March 22, 2005) Purpose: This draft version of the NETS for Students: Achievement Rubric is available online for educational technology professionals to review
NETS for Students: Achievement Rubric DRAFT (March 22, 2005) Purpose: This draft version of the NETS for Students: Achievement Rubric is available online for educational technology professionals to review
Providence- OHSU Informatics Course
 Providence- OHSU Course Logistics, Detailed Curriculum, Learning Objectives, and Other Information William Hersh, M.D. Department of Medical & Clinical Epidemiology Oregon Health & Science University Course
Providence- OHSU Course Logistics, Detailed Curriculum, Learning Objectives, and Other Information William Hersh, M.D. Department of Medical & Clinical Epidemiology Oregon Health & Science University Course
Informatics Strategies & Tools to Link Nursing Care with Patient Outcomes in the Learning Health Care System
 Nursing Informatics Working Group Informatics Strategies & Tools to Link Nursing Care with Patient Outcomes in the Learning Health Care System Patricia C. Dykes PhD, RN, FAAN, FACMI Judy Murphy RN, FHIMSS,
Nursing Informatics Working Group Informatics Strategies & Tools to Link Nursing Care with Patient Outcomes in the Learning Health Care System Patricia C. Dykes PhD, RN, FAAN, FACMI Judy Murphy RN, FHIMSS,
Health Information Technology: Introduction to One Key Part - the EHR
 Health Information Technology: Introduction to One Key Part - the EHR Donald P. Connelly, MD, PhD Director, Health Informatics Division University of Minnesota Medical School February 21, 2006 Minnesota
Health Information Technology: Introduction to One Key Part - the EHR Donald P. Connelly, MD, PhD Director, Health Informatics Division University of Minnesota Medical School February 21, 2006 Minnesota
NETS for Teachers: Achievement Rubric
 NETS for Teachers: Achievement Rubric DRAFT (March 18, 2005) Purpose: This draft version of the NETS for Teachers: Achievement Rubric is available online for educational technology professionals to review
NETS for Teachers: Achievement Rubric DRAFT (March 18, 2005) Purpose: This draft version of the NETS for Teachers: Achievement Rubric is available online for educational technology professionals to review
Activities (see attached Appendix G) Page 71 of 100
 for I. TECHNOLOGY OPERATIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Demonstrate introductory knowledge, skills and understanding of concepts related to technology 1. Identify CPU, monitor, mouse, printer, projection device See
for I. TECHNOLOGY OPERATIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Demonstrate introductory knowledge, skills and understanding of concepts related to technology 1. Identify CPU, monitor, mouse, printer, projection device See
TECHNICAL COMPETENCIES FOR COUNSELOR EDUCATION: RECOMMENDED GUIDELINES FOR PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT
 TECHNICAL COMPETENCIES FOR COUNSELOR EDUCATION: RECOMMENDED GUIDELINES FOR PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT ACES Technology Interest Network (2007) Standards Committee: Marty Jencius, Tim Poynton, and Pamela Patrick
TECHNICAL COMPETENCIES FOR COUNSELOR EDUCATION: RECOMMENDED GUIDELINES FOR PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT ACES Technology Interest Network (2007) Standards Committee: Marty Jencius, Tim Poynton, and Pamela Patrick
Overview The AONE Nurse Executive Competencies
 Overview The AONE Nurse Executive Competencies The vision of the American Organization of Nurse Executives (AONE) is to shape the future of health care through innovative and expert nursing leadership.
Overview The AONE Nurse Executive Competencies The vision of the American Organization of Nurse Executives (AONE) is to shape the future of health care through innovative and expert nursing leadership.
Eligible Professionals please see the document: MEDITECH Prepares You for Stage 2 of Meaningful Use: Eligible Professionals.
 s Preparing for Meaningful Use in 2014 MEDITECH (Updated December 2013) Professionals please see the document: MEDITECH Prepares You for Stage 2 of Meaningful Use: Professionals. Congratulations to our
s Preparing for Meaningful Use in 2014 MEDITECH (Updated December 2013) Professionals please see the document: MEDITECH Prepares You for Stage 2 of Meaningful Use: Professionals. Congratulations to our
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS STANDARDS FOR ALL BEGINNING TEACHERS
 TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS STANDARDS FOR ALL BEGINNING TEACHERS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV. Standard V. Standard VI- Standard XI. All teachers use technology-related terms, concepts,
TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS STANDARDS FOR ALL BEGINNING TEACHERS Standard I. Standard II. Standard III. Standard IV. Standard V. Standard VI- Standard XI. All teachers use technology-related terms, concepts,
HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS
 HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, FHIMSS, CPHIT CHAIR, HEALTH SCIENCE & LEADERSHIP PROGRAM DIRECTOR, HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected]
HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS STEPHEN C. BURROWS, DPM, MBA, CPHIMS, FHIMSS, CPHIT CHAIR, HEALTH SCIENCE & LEADERSHIP PROGRAM DIRECTOR, HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS Phone: 203-416-3948 Fax: 203-416-3951 Email: [email protected]
Template 3: NLN and QSEN ADN Program Learner Outcomes
 Template 3: NLN and QSEN ADN Program Learner Outcomes National League for Nursing. (2010). Outcomes and competencies for graduates of practical/vocational, associate degree, baccalaureate, master s practice
Template 3: NLN and QSEN ADN Program Learner Outcomes National League for Nursing. (2010). Outcomes and competencies for graduates of practical/vocational, associate degree, baccalaureate, master s practice
Health Information Technology Professional (HIT Pro ) Examinations
 Health Information Technology Professional (HIT Pro ) Examinations Candidate Guide Health Information Technology Competency Exams for Tomorrow s Health IT Professionals Version 1.1 Note: It is your responsibility
Health Information Technology Professional (HIT Pro ) Examinations Candidate Guide Health Information Technology Competency Exams for Tomorrow s Health IT Professionals Version 1.1 Note: It is your responsibility
ehealth, HIS, etc ehealth All information about health HMIS mhealth HIS Statistical IS Credited: Karl Brown, Rockefeller Foundation
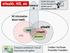 ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
2011-2016 Strategic Plan. Creating a healthier world through bold innovation
 2011-2016 Strategic Plan Creating a healthier world through bold innovation 2011-2016 STRATEGIC PLAN Table of contents I. Global direction 1 Mission and vision statements 2 Guiding principles 3 Organizational
2011-2016 Strategic Plan Creating a healthier world through bold innovation 2011-2016 STRATEGIC PLAN Table of contents I. Global direction 1 Mission and vision statements 2 Guiding principles 3 Organizational
Comparison of Tuning Competencies to U.S. National Accepted Competencies
 November, 2008 Comparison of Tuning Competencies to U.S. National Accepted Competencies How Tuning might benefit higher education in the U.S. We in the United States might learn a great deal from the Tuning
November, 2008 Comparison of Tuning Competencies to U.S. National Accepted Competencies How Tuning might benefit higher education in the U.S. We in the United States might learn a great deal from the Tuning
Master s Entry into Nursing. Academic Manual 2015-2016
 Master s Entry into Nursing Academic Manual 2015-2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview of the Master s Entry into Nursing (MEN) Program 2 Outcomes 2 Plan of Study 3-4 Course Descriptions 5-11 Overview of the
Master s Entry into Nursing Academic Manual 2015-2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview of the Master s Entry into Nursing (MEN) Program 2 Outcomes 2 Plan of Study 3-4 Course Descriptions 5-11 Overview of the
Health Information Technology (HIT) Guide for the Delta Rural Hospital Performance Improvement (RHPI) Program
 Health Information Technology (HIT) Guide for the Delta Rural Hospital Performance Improvement (RHPI) Program Health Information Technology Workforce: Current Issues and Recommended Solutions Prepared
Health Information Technology (HIT) Guide for the Delta Rural Hospital Performance Improvement (RHPI) Program Health Information Technology Workforce: Current Issues and Recommended Solutions Prepared
OKLAHOMA BOARD OF NURSING 2915 North Classen Blvd., Suite 524 Oklahoma City, OK 73106 (405) 962-1800
 OKLAHOMA BOARD OF NURSING 2915 North Classen Blvd., Suite 524 Oklahoma City, OK 73106 (405) 962-1800 NURSING COMPETENCIES BY EDUCATIONAL LEVEL: GUIDELINES FOR NURSING PRACTICE AND EDUCATION IN OKLAHOMA
OKLAHOMA BOARD OF NURSING 2915 North Classen Blvd., Suite 524 Oklahoma City, OK 73106 (405) 962-1800 NURSING COMPETENCIES BY EDUCATIONAL LEVEL: GUIDELINES FOR NURSING PRACTICE AND EDUCATION IN OKLAHOMA
Effectively Managing EHR Projects: Guidelines for Successful Implementation
 Phoenix Health Systems Effectively Managing EHR Projects: Guidelines for Successful Implementation Introduction Effectively managing any EHR (Electronic Health Record) implementation can be challenging.
Phoenix Health Systems Effectively Managing EHR Projects: Guidelines for Successful Implementation Introduction Effectively managing any EHR (Electronic Health Record) implementation can be challenging.
Assessment of Quality and Safety Education in Nursing: A New York State Perspective
 Assessment of Quality and Safety Education in Nursing: A New York State Perspective Presented by: Marilyn Stapleton, PhD, RN (PI); Mary Lee Pollard, PhD, RN (PI); Lisa Bagdan, MPS, MS,RN; Linda Millenbach,
Assessment of Quality and Safety Education in Nursing: A New York State Perspective Presented by: Marilyn Stapleton, PhD, RN (PI); Mary Lee Pollard, PhD, RN (PI); Lisa Bagdan, MPS, MS,RN; Linda Millenbach,
APPENDIX to http://dx.doi.org/10.4338/aci-2014-09-ra-0083 CAHIIM 2012 Curriculum Requirements Health Informatics Master s Degree
 APPENDIX to http://dx.doi.org/10.4338/aci-2014-09-ra-0083 CAHIIM 2012 Curriculum Requirements Health Informatics Master s Degree Column 1 - Health Informatics Facet I. Information Systems concerned with
APPENDIX to http://dx.doi.org/10.4338/aci-2014-09-ra-0083 CAHIIM 2012 Curriculum Requirements Health Informatics Master s Degree Column 1 - Health Informatics Facet I. Information Systems concerned with
Dear Colleagues, Best Regards, Pamela L. Quinones, RDH, BS
 A Letter from the 2011-2012 ADHA President Dear Colleagues, Partnering with ADEA to develop the Core Competencies for Graduate Dental Hygiene Education was a very positive and rewarding experience for
A Letter from the 2011-2012 ADHA President Dear Colleagues, Partnering with ADEA to develop the Core Competencies for Graduate Dental Hygiene Education was a very positive and rewarding experience for
M.S.N. Graduate Program
 M.S.N. Graduate Program Graduate Program Mission The Saint Luke s College of Health Sciences is an educational leader serving exceptional students pursuing a graduate nursing degree. An institution of
M.S.N. Graduate Program Graduate Program Mission The Saint Luke s College of Health Sciences is an educational leader serving exceptional students pursuing a graduate nursing degree. An institution of
FEATURE ARTICLE. Course Development: Nursing Informatics
 OJNI Online Journal of Nursing Informatics, 13 (2), Summer 2009 Page 1 of 20 Course Development: Nursing Informatics Patricia E. PerryMSN, RN-BC, CNS, OCN and Major King PhD, RN, CCNS Citation: Perry,
OJNI Online Journal of Nursing Informatics, 13 (2), Summer 2009 Page 1 of 20 Course Development: Nursing Informatics Patricia E. PerryMSN, RN-BC, CNS, OCN and Major King PhD, RN, CCNS Citation: Perry,
Integrating Quality and Safety (QSEN) Content into Skills and Simulation Curricula
 Integrating Quality and Safety (QSEN) Content into Skills and Simulation Curricula Carol F. Durham MSN RN Clinical Associate Professor Director, Clinical Education & Resource Center The University of North
Integrating Quality and Safety (QSEN) Content into Skills and Simulation Curricula Carol F. Durham MSN RN Clinical Associate Professor Director, Clinical Education & Resource Center The University of North
Massachusetts Department of Higher Education. Nursing Education Redesign Grant Program. Final Project Implementation Report
 Massachusetts Department of Higher Education Nursing Education Redesign Grant Program Final Project Implementation Report Submitted by: Berkshire Community College November 30, 2012 Executive Summary Overview
Massachusetts Department of Higher Education Nursing Education Redesign Grant Program Final Project Implementation Report Submitted by: Berkshire Community College November 30, 2012 Executive Summary Overview
Massachusetts Technology Literacy Standards
 Massachusetts Technology Literacy Standards The Massachusetts Technology Literacy Standards incorporate the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Literacy skills developed by the Partnership for
Massachusetts Technology Literacy Standards The Massachusetts Technology Literacy Standards incorporate the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Literacy skills developed by the Partnership for
Health Information Technology
 Health Information Technology (HIT) Certificate Programs Train Td Today for Jobs Tomorrow Fact Sheet Certificate Program Descriptions Course Descriptions September 2010 Enrollment Ongoing Certificate
Health Information Technology (HIT) Certificate Programs Train Td Today for Jobs Tomorrow Fact Sheet Certificate Program Descriptions Course Descriptions September 2010 Enrollment Ongoing Certificate
NURSING INFORMATICS CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW OF NURSING INFORMATICS
 NURSING INFORMATICS CHAPTER 1 1 OVERVIEW OF NURSING INFORMATICS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 2 1. Define nursing informatics (NI) and key terminology. 2. Explore NI Metastructures, concepts and tools 3. Reflect
NURSING INFORMATICS CHAPTER 1 1 OVERVIEW OF NURSING INFORMATICS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 2 1. Define nursing informatics (NI) and key terminology. 2. Explore NI Metastructures, concepts and tools 3. Reflect
No one was ever able to teach who was not able to learn. Florence Nightingale. The Preceptor Role. Beth Tamplet Ulrich, EdD, RN, FACHE, FAAN
 No one was ever able to teach who was not able to learn. Florence Nightingale 1 The Preceptor Role Beth Tamplet Ulrich, EdD, RN, FACHE, FAAN 1 Precepting is an organized, evidence-based, outcome-driven
No one was ever able to teach who was not able to learn. Florence Nightingale 1 The Preceptor Role Beth Tamplet Ulrich, EdD, RN, FACHE, FAAN 1 Precepting is an organized, evidence-based, outcome-driven
THE E-HEALTH JOURNEY. Ministry of Health Jamaica. Optimizing the use of ICT Applications in Health and Patient Care
 THE E-HEALTH JOURNEY Ministry of Health Jamaica Optimizing the use of ICT Applications in Health and Patient Care 8 th Caribbean Conference on Health Financing Initiatives Presenter: Mr. Arnold Cooper
THE E-HEALTH JOURNEY Ministry of Health Jamaica Optimizing the use of ICT Applications in Health and Patient Care 8 th Caribbean Conference on Health Financing Initiatives Presenter: Mr. Arnold Cooper
Certified Healthcare Technology Specialist (CHTS) Examinations. Candidate Guide
 Certified Healthcare Technology Specialist (CHTS) Examinations Candidate Guide Health Information Technology Competency Exams for Tomorrow s Health IT Professionals Version 1.1 Updated 7.18.13 Note: It
Certified Healthcare Technology Specialist (CHTS) Examinations Candidate Guide Health Information Technology Competency Exams for Tomorrow s Health IT Professionals Version 1.1 Updated 7.18.13 Note: It
Post-Master's Adult Nurse Practitioner (AGNP)
 : Post-Master's Adult Nurse Practitioner (AGNP) University of Florida College of Nursing M. Dee Williams, PhD, RN [email protected] 1 Table of Contents A. Rationale... 3 B. Mission... 3 C. Student Learning
: Post-Master's Adult Nurse Practitioner (AGNP) University of Florida College of Nursing M. Dee Williams, PhD, RN [email protected] 1 Table of Contents A. Rationale... 3 B. Mission... 3 C. Student Learning
COMPUTER SCIENCE High School Standards
 COMPUTER SCIENCE High School Standards CONTENT STANDARD 1 1. Components Of A Computer System 1.HS.1 1.HS.2 1.HS.3 1.HS.4 Demonstrate the ability to store data on a variety of storage media, i.e., floppy,
COMPUTER SCIENCE High School Standards CONTENT STANDARD 1 1. Components Of A Computer System 1.HS.1 1.HS.2 1.HS.3 1.HS.4 Demonstrate the ability to store data on a variety of storage media, i.e., floppy,
Version: January 2008 ASTM E-31: EHR and Informatics Standards Education For Health Professional Disciplines. Background
 Version: January 2008 ASTM E-31: EHR and Informatics Standards Education For Health Professional Disciplines Background Work on standards for the EHR in the context of all such standards for the Health
Version: January 2008 ASTM E-31: EHR and Informatics Standards Education For Health Professional Disciplines Background Work on standards for the EHR in the context of all such standards for the Health
HIMSS Electronic Health Record Definitional Model Version 1.0
 HIMSS Electronic Health Record Definitional Model Version 1.0 Prepared by HIMSS Electronic Health Record Committee Thomas Handler, MD. Research Director, Gartner Rick Holtmeier, President, Berdy Systems
HIMSS Electronic Health Record Definitional Model Version 1.0 Prepared by HIMSS Electronic Health Record Committee Thomas Handler, MD. Research Director, Gartner Rick Holtmeier, President, Berdy Systems
NATIONAL INFORMATICS STANDARDS for NURSES AND MIDWIVES
 NATIONAL INFORMATICS STANDARDS for NURSES AND MIDWIVES Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation Standards funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing NATIONAL INFORMATICS STANDARDS
NATIONAL INFORMATICS STANDARDS for NURSES AND MIDWIVES Australian Nursing and Midwifery Federation Standards funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing NATIONAL INFORMATICS STANDARDS
Nursing Informatics Integration in a 4 year BSN Program. June Kaminski, RN MSN PhD St CNIA President-Elect [email protected]
 Nursing Informatics Integration in a 4 year BSN Program June Kaminski, RN MSN PhD St CNIA President-Elect [email protected] Rationale Curriculum supported Nursing Informatics as a central thread Stressed
Nursing Informatics Integration in a 4 year BSN Program June Kaminski, RN MSN PhD St CNIA President-Elect [email protected] Rationale Curriculum supported Nursing Informatics as a central thread Stressed
Alliance for Nursing Informatics (ANI) Sponsored by AMIA & HIMSS
 Statement to the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Initiative Future of Nursing: Acute Care, focusing on the area of Technology October 19, 2009 Alliance for Nursing Informatics (ANI) Sponsored by AMIA &
Statement to the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Initiative Future of Nursing: Acute Care, focusing on the area of Technology October 19, 2009 Alliance for Nursing Informatics (ANI) Sponsored by AMIA &
VA Nursing Academic Partnership (VANAP) Strategic Plan
 1 VA Nursing Academic Partnership (VANAP) Strategic Plan VISION Ensure high quality Veteran nursing care now and in the future. MISSION Promote the safe and effective care of Veterans within and across
1 VA Nursing Academic Partnership (VANAP) Strategic Plan VISION Ensure high quality Veteran nursing care now and in the future. MISSION Promote the safe and effective care of Veterans within and across
How To Understand And Understand The Benefits Of A Health Insurance Risk Assessment
 4547 The Case For HIPAA Risk Assessment Leader s Guide IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR EDUCATION COORDINATORS & PROGRAM FACILITATORS PLEASE NOTE: In order for this program to meet Florida course requirements,
4547 The Case For HIPAA Risk Assessment Leader s Guide IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR EDUCATION COORDINATORS & PROGRAM FACILITATORS PLEASE NOTE: In order for this program to meet Florida course requirements,
ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK
 ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK The organizing framework of the associate degree in nursing program is derived from the Philosophy of the Division of Nursing. It supports the Values of the College, which include
ORGANIZATIONAL FRAMEWORK The organizing framework of the associate degree in nursing program is derived from the Philosophy of the Division of Nursing. It supports the Values of the College, which include
A Living Document from the National League for Nursing December 2015
 VISIONSERIES TRANSFORMING NURSING EDUCATION L E A D I N G T H E C A L L T O R E F O R M Interprofessional Collaboration in Education and Practice A Living Document from the National League for Nursing
VISIONSERIES TRANSFORMING NURSING EDUCATION L E A D I N G T H E C A L L T O R E F O R M Interprofessional Collaboration in Education and Practice A Living Document from the National League for Nursing
Health Informatics for Medical Librarians. Ana D. Cleveland and Donald B. Cleveland. Table of Contents
 Health Informatics for Medical Librarians Ana D. Cleveland and Donald B. Cleveland Table of Contents List of Tables List of Sidebars Preface Acknowledgments Part I: Understanding Health Informatics Chapter
Health Informatics for Medical Librarians Ana D. Cleveland and Donald B. Cleveland Table of Contents List of Tables List of Sidebars Preface Acknowledgments Part I: Understanding Health Informatics Chapter
