Parental Request for Evaluation Flowchart. 1. Parental written request for evaluation. 22. Provide parents with a copy of the procedural safeguards.
|
|
|
- Madeleine Grant
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parental Request for Evaluation Flowchart 1. Parental written request for evaluation 22. Provide parents with a copy of the procedural safeguards. 3. School District explains the district s overall, general education referral or screening system to parents. 4. School District reviews student data from campus and parents. 5. Referral for Special Education is made. 6. Prior Written Notice proposing evaluation and consent for evaluation signed. Note: Parent must be provided an opportunity to sign consent no later than the 15th school day after the date the district receives the request for evaluation. Yes Is there evidence of a possible disability? 10. Parent may access dispute resolution options. No 9. Prior Written Notice to indicate refusal to evaluate no later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request for evaluation school days for completion of evaluation report. Student progress monitored in general education. 8. Upon completion of evaluation report, 30 calendar days to hold initial ARD to determine eligibility.
2 1. Parental Written Request for Evaluation Federal and state laws and regulations make clear that parents have the right to request an evaluation for special education services at any time. Public school districts and charter schools also have the right to request such an evaluation. However, a request does not automatically start the referral process. School districts who receive written requests for evaluations submitted to the special education director or other district administrative employee should reply to parent requests with data to support their decisions no later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request. Federal regulation states: 34 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Initial evaluations. (b) Request for initial evaluation. Consistent with the consent requirements in , either a parent of a child or a public agency may initiate a request for an initial evaluation to determine if the child is a child with a disability (b) State rule reads: 19 Texas Administrative Code (TAC) Referral for Full and Individual Initial Evaluation. This referral for a full and individual initial evaluation may be initiated by school personnel, the student's parents or legal guardian, or another person involved in the education or care of the student. State statute reads: Texas Education Code (TEC) Right to Information Concerning Special Education and Education of Students with Learning Difficulties.... (c) The agency shall produce and provide to school districts a written explanation of the options and requirements for providing assistance to students who have learning difficulties or who need or may need special education. The explanation must state that a parent is entitled at any time to request an evaluation of the parent's child for special education services under Section Each school year, each district shall provide the written explanation to a parent of each district student by including the explanation in the student handbook or by another means. Senate Bill 816 amends TEC as follows: Senate Bill 816 Section 1. Section , Education Code, is amended by amending Subsection (c) to read as follows (c) If a parent or legal guardian makes a written request to a school district s director of special education services or to a district administrative employee for a full individual and initial evaluation of a student, the district shall, not later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request: (1) provide an opportunity for the parent or legal guardian to give written consent for the evaluation; or (2) refuse to provide the evaluation and provide the parent or legal guardian with notice of procedural safeguards under 20 U.S.C. Section 1415(b).
3 2. Provide Parents with a Copy of the Procedural Safeguards Federal regulations require school districts and charter schools to provide parents a copy of their procedural safeguards when they request an evaluation for special education. The procedural safeguards must be given to parents in their native language or in their communication mode whenever possible. The federal regulation reads: 34 CFR Procedural safeguards notice. (a) General. A copy of the procedural safeguards available to the parents of a child with a disability must be given to the parents only one time a school year, except that a copy also must be given to the parents-- (1) Upon initial referral or parent request for evaluation; The comments to the Federal Regulations state the following: In addition to the prior written notice, (a)(1), consistent with section 615(d)(1)(A)(i) of the Act, requires that a copy of the procedural safeguards notice be given to parents upon an initial referral or parental request for an evaluation. Consistent with (c) and (d), the prior written notice and the procedural safeguards notice, respectively, must be written in language understandable to the general public and be provided in the native language of the parent or other mode of communication used by the parent, unless it is clearly not feasible to do so. (Federal Register, 2006, p )
4 3. The District s Overall, General Education Referral or Screening System School districts and charter schools are required by state statute to inform parents that they can request a referral for special education services at any time as a part of the district or charter school s overall general education referral or screening process. This should be communicated to parents in writing each school year. The required written statement is provided by the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and includes the following statement: Students having difficulty in the regular classroom should be considered for tutorial, compensatory, and other academic or behavior support services that are available to all students including a process based on Response to Intervention (RtI). Districts should clearly explain this process when parents ask for an evaluation in order to safeguard the parent s rights, provide for the well-being of the student, and clarify the roles and responsibilities of all parties involved during the process. Districts and charters may also want to inform parents that this process could include a systematic approach which seeks to determine the child s response to scientific, research-based intervention, commonly referred to as Response to Intervention (RtI). State rule states: 19 TAC Referral for Full and Individual Initial Evaluation. Referral of students for a full and individual initial evaluation for possible special education services shall be a part of the district's overall, general education referral or screening system. State statute reads: TEC Right to Information Concerning Special Education and Education of Students with Learning Difficulties.... (c) The agency shall produce and provide to school districts a written explanation of the options and requirements for providing assistance to students who have learning difficulties or who need or may need special education. The explanation must state that a parent is entitled at any time to request an evaluation of the parent's child for special education services under Section Each school year, each district shall provide the written explanation to a parent of each district student by including the explanation in the student handbook or by another means.
5 4. Review of Data Before any decision is made regarding whether to grant or refuse a request for a Full Individual Evaluation (FIE), district personnel should review data the school has at its disposal regarding the student including any data provided by the parent as part of the request for evaluation. Data could include, but is not limited to the following: Academic Standardized District Formal and Work samples Report Test Benchmarks informal cards Performance observations Language Language proficiency Language used at Formal and informal Behavioral Health Environmental, Cultural, Economic Factors Intervention History Formal and informal observations Vision screenings Cumulative folder review Interventions provided home Office referrals Hearing screenings At Risk status Duration of interventions observations Teacher comments Documentation of other health problems Data from classroom teachers, counselors, and other support personnel such as social workers Performance data collected during intervention Report cards Data from tutorials, compensatory, and other academic or behavior support services Parent input Data from a Response to Intervention (RtI) system in place* * RtI involves activities that typically occur in the general education setting as schools assist struggling students prior to and in lieu of a referral for a special education evaluation. Data collected should be used to inform a district s or charter school s decision as to whether to proceed with a referral. The comments to the federal regulations state the following: Comment: A few commenters recommended that the regulations clarify whether a public agency has the right to deny a parent s request for an initial evaluation. Discussion: The regulations are sufficiently clear on this point. Section (a), consistent with section 615(b)(3) of the Act, provides that a public agency may refuse to initiate or change the identification, evaluation, or educational placement of the child, or the provision of FAPE to the child, if the public agency provides written notice. This includes situations in which a public agency wishes to deny a parent s request for an initial evaluation. The written notice must meet the requirements in (b). Thus, for situations in which a public agency wishes to deny a
6 parent s request for an initial evaluation, the written notice would provide, among other things, an explanation of why the public agency refuses to conduct an initial evaluation and the information that was used to make that decision. A parent may challenge the public agency s refusal to conduct an initial evaluation by requesting a due process hearing. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) School districts should be aware that a simple review of grades is not sufficient and are cautioned not to deny an evaluation based solely on the fact that the student is passing. The comments to the federal regulations state the following: Comment: Some commenters expressed concern that children with disabilities have to fail or be retained in a grade or course in order to be considered eligible for special education and related services. Discussion: Section (c) provides that a child is eligible to receive special education and related services even though the child is advancing from grade to grade. Further, it is implicit from paragraph (c) of this section that a child should not have to fail a course or be retained in a grade in order to be considered for special education and related services. A public agency must provide a child with a disability special education and related services to enable him or her to progress in the general curriculum, thus making clear that a child is not ineligible to receive special education and related services just because the child is, with the support of those individually designed services, progressing in the general curriculum from grade-to-grade or failing a course or grade. The group determining the eligibility of a child for special education and related services must make an individual determination as to whether, notwithstanding the child s progress in a course or grade, he or she needs or continues to need special education and related services. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) We also believe it is important to clarify that a child suspected of having a disability but who has not failed, is making academic progress, and is passing from grade to grade must be considered in the child find process as any other child suspected of having a disability. As noted earlier in the discussion regarding , paragraph (c)(1) of has been revised to clarify that children do not have to fail or be retained in a course or grade in order to be considered for special education and related services. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) The referenced federal regulation reads: 34 CFR Free appropriate public education (FAPE). (c) Children advancing from grade to grade. (1) Each State must ensure that FAPE is available to any individual child with a disability who needs special education and related services, even though the child has not failed or been retained in a course or grade, and is advancing from grade to grade. (2) The determination that a child described in paragraph (a) of this section is eligible under this part, must be made on an individual basis by the group responsible within the child s LEA for making eligibility determinations.
7 5. Referral Referrals are part of a school s overall, general education referral or screening system and should follow a process outlined in board policy, special education procedures (see the Legal Frameworks), and local operational guidelines. Students being referred for special education services should have been considered, not necessarily provided, for all support services available to all students prior to the referral. The state rule reads: 19 TAC Referral for Full and Individual Initial Evaluation. Referral of students for a full and individual initial evaluation for possible special education services shall be a part of the district's overall, general education referral or screening system. Prior to referral, students experiencing difficulty in the general classroom should be considered for all support services available to all students, such as tutorial; remedial; compensatory; response to scientific, research-based intervention; and other academic or behavior support services. If the student continues to experience difficulty in the general classroom after the provision of interventions, district personnel must refer the student for a full and individual initial evaluation. This referral for a full and individual initial evaluation may be initiated by school personnel, the student's parents or legal guardian, or another person involved in the education or care of the student.
8 6. Consent for Evaluation Receipt of signed parental consent for initial evaluation sets formal timelines in motion for completion of the evaluation. Consent is required for school districts to proceed with an evaluation for special education services. School districts and charter schools should provide parents with prior written notice of the proposal to evaluate that includes a description of any evaluation procedure it proposes to conduct, including information regarding the names and types of tests that will be used in the evaluation and for what purpose they will be used. The parent must be provided an opportunity to give written consent not later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request for evaluation. The federal regulations state the following: 34 CFR Parental consent. (a) Parental consent for initial evaluation. (1)(i) The public agency proposing to conduct an initial evaluation to determine if a child qualifies as a child with a disability under must, after providing notice consistent with and , obtain informed consent, consistent with 300.9, from the parent of the child before conducting the evaluation. (ii) Parental consent for initial evaluation must not be construed as consent for initial provision of special education and related services. (iii) The public agency must make reasonable efforts to obtain the informed consent from the parent for an initial evaluation to determine whether the child is a child with a disability. The state statute reads: TEC Information and consent for certain psychological examinations or tests. (a) On request of a child's parent, before obtaining the parent's consent under 20 U.S.C. Section 1414 for the administration of any psychological examination or test to the child that is included as part of the evaluation of the child's need for special education, a school district shall provide to the child's parent: (1) the name and type of the examination or test; and (2) an explanation of how the examination or test will be used to develop an appropriate individualized education program for the child. (b) If the district determines that an additional examination or test is required for the evaluation of a child's need for special education after obtaining consent from the child's parent under Subsection (a), the district shall provide the information described by Subsections (a)(1) and (2) to the child's parent regarding the additional examination or test and shall obtain additional consent for the examination or test. (c) The time required for the district to provide information and seek consent under Subsection (b) may not be counted toward the 60 calendar days for completion of an evaluation under Section If a parent does not give consent under Subsection (b) within 20 calendar days after the date the district provided to the parent the information required by that subsection, the parent's consent is considered denied. **Note: Senate Bill 816 changes Section from 60 calendar days to not later than the 45 th school day following the date on which the school district receives written consent from the parent.
9 Senate Bill 816 amends TEC as follows: Senate Bill 816 Section 1. Section , Education Code, is amended by amending Subsection (c) to read as follows (c) If a parent or legal guardian makes a written request to a school district s director of special education services or to a district administrative employee for a full individual and initial evaluation of a student, the district shall, not later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request: (1) provide an opportunity for the parent or legal guardian to give written consent for the evaluation; or (2) refuse to provide the evaluation and provide the parent or legal guardian with notice of procedural safeguards under 20 U.S.C. Section 1415(b).
10 7. 45 School Day Timeline Upon receipt of parental consent, school districts and charter schools have 45 school days in which to complete the initial evaluation. If a student is absent three or more days during the evaluation timeline, then the evaluation timeline is extended by the number of school days the student has been absent. If the district receives consent for the evaluation at least 35 school days but less than 45 school days before the last instructional day of the school year, then the evaluation report must be provided to the parent no later than June 30 of that year. In this case, if the student is absent three or more days during the evaluation period, then the timeline is extended to 45 school days, which will extend into the next school year, and is extended for the number of school days the student has been absent. If consent is received by the district less than 35 school days before the last instructional day of the school year, then the evaluation timeline is 45 school days, which will extend into the next school year. If a student is absent three or more days during the evaluation timeline, then the evaluation timeline is extended by the number of school days the student has been absent. The federal regulations state the following: 34 CFR Initial evaluations. (c) Procedures for initial evaluation. The initial evaluation (1) (i) Must be conducted within 60 days of receiving parental consent for the evaluation; or (ii) If the State establishes a timeframe within which the evaluation must be conducted, within that timeframe; and (2) Must consist of procedures-- (i) To determine if the child is a child with a disability under 300.8; and (ii) To determine the educational needs of the child (c) Senate Bill 816 amends TEC Full Individual and Initial Evaluation as follows: Senate Bill 816 (a)a written report of a full individual and initial evaluation of a student for purposes of special education services shall be completed as follows, except as otherwise provided by this section: (1) not later than the 45th school [60th calendar] day following the date on which the school district, in accordance with 20 U.S.C. Section 1414(a), as amended, receives written consent for the evaluation, signed by the student s parent or legal guardian, except that if a student has been absent from school during that period on three or more days, that period must be extended by a number of school days equal to the number of school days during that period on which the student has been absent; or (2) for students under five years of age by September 1 of the school year and not enrolled in public school and for students enrolled in a private or home school setting, not later than the 45th school day following the date on which the school district receives written consent for the evaluation, signed by a student s parent or legal guardian. (a-1) If a school district receives written consent signed by a student s parent or legal guardian for a full individual and initial evaluation of a student at least 35 but less than 45 school days before the
11 last instructional day of the school year, the evaluation must be completed and the written report of the evaluation must be provided to the parent or legal guardian not later than June 30 of that year. The student s admission, review, and dismissal committee shall meet not later than the 15th school day of the following school year to consider the evaluation. If a district receives written consent signed by a student s parent or legal guardian less than 35 school days before the last instructional day of the school year or if the district receives the written consent at least 35 but less than 45 school days before the last instructional day of the school year but the student is absent from school during that period on three or more days, Subsection (a)(1) applies to the date the written report of the full individual and initial evaluation is required. (a-2) For purposes of this section, "school day" does not include a day that falls after the last instructional day of the spring school term and before the first instructional day of the subsequent fall school term. The commissioner by rule may determine days during which year-round schools are recessed that, consistent with this subsection, are not considered to be school days for purposes of this section. (a-3) Subsection (a) does not impair any rights of an infant or toddler with a disability who is receiving early intervention services in accordance with 20 U.S.C. Section 1431.
12 8. Thirty Day Timeline In Texas, completion of the Full Individual Evaluation (FIE) begins a second timeline. From the completion of the report, the school district or charter school must convene an Admission, Review, or Dismissal (ARD) meeting within 30 calendar days. The ARD committee determines eligibility, the Individual Education Program (IEP), and placement for the student at this meeting. If the district receives consent for the evaluation at least 35 school days but less than 45 school days before the last instructional day of the school year and the student was not absent 3 or more days during this period, then the evaluation report must be provided to the parent no later than June 30 of that year. For this situation, the ARD meeting must be held no later than the 15th school day of the following school year to consider the evaluation. For the student who is evaluated during the school year but the 30 calendar days for the ARD meeting falls during the summer and school is not in session, then the ARD committee has until the first day of fall classes to convene to consider the evaluation unless the evaluation indicates the student may need extended school year services during that summer. Federal regulations read: 34 CFR When IEPs must be in effect. (c) Initial IEPs; provision of services. Each public agency must ensure that (1) A meeting to develop an IEP for a child is conducted within 30 days of a determination that the child needs special education and related services; State rule provides: 19 TAC (d) The ARD committee shall make its decisions regarding students referred for a full and individual initial evaluation within 30 calendar days from the date of the completion of the written full and individual initial evaluation report. If the 30th day falls during the summer and school is not in session, the ARD committee shall have until the first day of classes in the fall to finalize decisions concerning the initial eligibility determination, the IEP, and placement, unless the full and individual initial evaluation indicates that the student will need extended school year (ESY) services during that summer. Senate Bill 816 amends TEC as follows: Senate Bill 816 (a-1) If a school district receives written consent signed by a student s parent or legal guardian for a full individual and initial evaluation of a student at least 35 but less than 45 school days before the last instructional day of the school year, the evaluation must be completed and the written report of the evaluation must be provided to the parent or legal guardian not later than June 30 of that year. The student s admission, review, and dismissal committee shall meet not later than the 15th school day of the following school year to consider the evaluation. If a district receives written consent signed by a student s parent or legal guardian less than 35 school days before the last instructional day of the school year or if the district receives the written consent at least 35 but less than 45 school days before the last instructional day of the school year but the student is absent from school during that period on three or more days, Subsection (a)(1) applies to the date the written report of the full individual and initial evaluation is required.
13 9. Prior Written Notice of Refusal When a school district or charter school decides to refuse a parental request for evaluation, the school district must provide the parent with a written explanation of the refusal to take action and the reason why this decision was made including the data that supported that decision. This prior written notice must be provided to the parent no later than the 15 th school day after the request for evaluation was received. Districts should pay close attention to the required contents of the notice to be provided to parents as articulated in 34 CFR (b). (See below.) In the comments to the Federal Regulations, the Department of Education states the following: If, however, the public agency does not suspect that the child has a disability and denies the request for an initial evaluation, the public agency must provide written notice to the parents, consistent with (b) and section 615(c)(1) of the Act, which explains, among other things, why the public agency refuses to conduct an initial evaluation and the information that was used as the basis to make that decision. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) And: Section (a), consistent with section 615(b)(3) of the Act, provides that a public agency may refuse to initiate or change the identification, evaluation, or educational placement of the child, or the provision of FAPE to the child, if the public agency provides written notice. This includes situations in which a public agency wishes to deny a parent s request for an initial evaluation. The written notice must meet the requirements in (b). Thus, for situations in which a public agency wishes to deny a parent s request for an initial evaluation, the written notice would provide, among other things, an explanation of why the public agency refuses to conduct an initial evaluation and the information that was used to make that decision. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) The regulation reads: 34 CFR Prior notice by the public agency; content of notice. (a) Notice. Written notice that meets the requirements of paragraph (b) of this section must be given to the parents of a child with a disability a reasonable time before the public agency (1) Proposes to initiate or change the identification, evaluation, or educational placement of the child or the provision of FAPE to the child; or (2) Refuses to initiate or change the identification, evaluation, or educational placement of the child or the provision of FAPE to the child. (b) Content of notice. The notice required under paragraph (a) of this section must include (1) A description of the action proposed or refused by the agency; (2) An explanation of why the agency proposes or refuses to take the action; (3) A description of each evaluation procedure, assessment, record, or report the agency used as a basis for the proposed or refused action; (4) A statement that the parents of a child with a disability have protection under the procedural safeguards of this part and, if this notice is not an initial referral for evaluation, the means by which a copy of a description of the procedural safeguards can be obtained; (5) Sources for parents to contact to obtain assistance in understanding the provisions of this part; (6) A description of other options that the IEP Team considered and the reasons why those options were rejected; and (7) A description of other factors that are relevant to the agency s proposal or refusal.
14 (c) Notice in understandable language. (1) The notice required under paragraph (a) of this section must be (i) Written in language understandable to the general public; and (ii) Provided in the native language of the parent or other mode of communication used by the parent, unless it is clearly not feasible to do so. (2) If the native language or other mode of communication of the parent is not a written language, the public agency must take steps to ensure (i) That the notice is translated orally or by other means to the parent in his or her native language or other mode of communication; (ii) That the parent understands the content of the notice; and (iii) That there is written evidence that the requirements in paragraphs (c)(2)(i) and (ii) of this section have been met. State rules read: 19 TAC Notice to Parents for Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) Committee Meetings (a) A district shall invite the parents and adult student to participate as members of the admission, review, and dismissal (ARD) committee by providing written notice in accordance with 34 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), , , and (b) A parent may request an ARD committee meeting at any mutually agreeable time to address specific concerns about his or her child's special education services. The school district must respond to the parent's request either by holding the requested meeting or by requesting assistance through the Texas Education Agency's mediation process. The district should inform parents of the functions of the ARD committee and the circumstances or types of problems for which requesting an ARD committee meeting would be appropriate. Senate Bill 816 amends TEC as follows: Senate Bill 816 Section 1. Section , Education Code, is amended by amending Subsection (c) to read as follows (c) If a parent or legal guardian makes a written request to a school district s director of special education services or to a district administrative employee for a full individual and initial evaluation of a student, the district shall, not later than the 15 th school day after the date the district receives the request: (1) provide an opportunity for the parent or legal guardian to give written consent for the evaluation; or (2) refuse to provide the evaluation and provide the parent or legal guardian with notice of procedural safeguards under 20 U.S.C. Section 1415(b).
15 10. Parent Options Parents have a range of options if they disagree with the school s decision including mediation, the state complaint process, or filing for a due process hearing. Parents and local education agencies (school districts and charters) are encouraged to solve their disputes locally and may call upon assistance from their regional Education Service Center. The comments to the Federal Regulations state the following: The parent may challenge such a refusal by requesting a due process hearing, but the timeline for conducting the evaluation does not begin prior to parental consent for evaluation. (Federal Register, 2006, p ) The applicable federal regulation reads: 34 CFR Filing a due process complaint. (a) General. (1) A parent or a public agency may file a due process complaint on any of the matters described in (a)(1) and (2) (relating to the identification, evaluation or educational placement of a child with a disability, or the provision of FAPE to the child). State Rule says: 19 TAC General Provisions (a) From time to time, disputes may arise between a parent and a school district relating to the identification, evaluation, or educational placement of or the provision of a free appropriate public education (FAPE), to a student with a disability. (b) It is the policy and intent of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) to encourage and support the resolution of any dispute described in subsection (a) of this section at the lowest level possible and in a prompt, efficient, and effective manner. (c) The possible options for resolving disputes include, but are not limited to: (1) meetings of the student's admission, review, and dismissal committee; (2) meetings or conferences with the student's teachers; (3) meetings or conferences, subject to local school district policies, with campus administrator(s), the special education director of the district (or the shared services arrangement to which the district may be a party), the superintendent of the district, or the board of trustees of the district; (4) requesting mediation through the TEA in accordance with the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), 20 United States Code (USC), 1415(e), and 34 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), ; (5) filing a complaint with the TEA in accordance with 34 CFR, ; or (6) requesting a due process hearing through the TEA in accordance with IDEA, 20 USC, 1415(f), and 34 CFR, Upon the filing of a request for a due process hearing, the parent and the school district shall also be provided with an opportunity to resolve the dispute through the mediation process established by TEA.
How to Request an Initial Evaluation for Special Education Eligibility
 2222 West Braker Lane Austin, Texas 78758 MAIN OFFICE 512.454.4816 TOLL-FREE 800.315.3876 FAX 512.323.0902 How to Request an Initial Evaluation for Special Education Eligibility If you or someone you know
2222 West Braker Lane Austin, Texas 78758 MAIN OFFICE 512.454.4816 TOLL-FREE 800.315.3876 FAX 512.323.0902 How to Request an Initial Evaluation for Special Education Eligibility If you or someone you know
WHAT HAPPENS IF MY CHILD IS HAVING TROUBLE LEARNING IN SCHOOL?
 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 WHAT HAPPENS IF MY CHILD IS HAVING TROUBLE LEARNING IN SCHOOL?... 2 STEPS TO GETTING SERVICES... 3 ANSWERS TO FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS... 9 REQUEST FOR ASSISTANCE...
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 WHAT HAPPENS IF MY CHILD IS HAVING TROUBLE LEARNING IN SCHOOL?... 2 STEPS TO GETTING SERVICES... 3 ANSWERS TO FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS... 9 REQUEST FOR ASSISTANCE...
Memorandum of Understanding
 Memorandum of Understanding The Department of Assistive and Rehabilitative Services and the Texas Education Agency I TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY I. PURPOSES The purposes of this Memorandum of Understanding
Memorandum of Understanding The Department of Assistive and Rehabilitative Services and the Texas Education Agency I TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY I. PURPOSES The purposes of this Memorandum of Understanding
Special Education Process: From Child-Find, Referral, Evaluation, and Eligibility To IEP Development, Annual Review and Reevaluation
 Special Education Process: From Child-Find, Referral, Evaluation, and Eligibility To IEP Development, Annual Review and Reevaluation Companion Document to NJOSEP Code Trainings October/November 2006 Updated
Special Education Process: From Child-Find, Referral, Evaluation, and Eligibility To IEP Development, Annual Review and Reevaluation Companion Document to NJOSEP Code Trainings October/November 2006 Updated
INDIVIDUALS WITH DISABILITIES EDUCATION ACT NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS
 INDIVIDUALS WITH DISABILITIES EDUCATION ACT NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS Tennessee Department of Education Division of Special Education Department of Education February 11, 2008; Publication Authorization
INDIVIDUALS WITH DISABILITIES EDUCATION ACT NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS Tennessee Department of Education Division of Special Education Department of Education February 11, 2008; Publication Authorization
Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE
 Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE New York State Education Department PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE Rights for Parents of Children with Disabilities, Ages 3-21 As a parent, you are a vital member of the
Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE New York State Education Department PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE Rights for Parents of Children with Disabilities, Ages 3-21 As a parent, you are a vital member of the
CHAPTER 16. SPECIAL EDUCATION FOR GIFTED STUDENTS
 CHAPTER 16. SPECIAL EDUCATION FOR GIFTED STUDENTS Sec. GENERAL PROVISIONS 16.1. Definitions. 16.2. Purpose. 16.3. Experimental programs. 16.4. Strategic plans. 16.5. Personnel. 16.6. General supervision.
CHAPTER 16. SPECIAL EDUCATION FOR GIFTED STUDENTS Sec. GENERAL PROVISIONS 16.1. Definitions. 16.2. Purpose. 16.3. Experimental programs. 16.4. Strategic plans. 16.5. Personnel. 16.6. General supervision.
Special Education Procedural Safeguards
 Special Education Procedural Safeguards Rights for Parents and Children School District of For more information or questions regarding your child s special education services contact: Director of Special
Special Education Procedural Safeguards Rights for Parents and Children School District of For more information or questions regarding your child s special education services contact: Director of Special
Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs for Students with Disabilities
 1 Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs for Students with Disabilities Mastery Charter School publishes the following Annual Notice in the school s Parent-Student Handbook and
1 Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs for Students with Disabilities Mastery Charter School publishes the following Annual Notice in the school s Parent-Student Handbook and
Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE
 Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE New York State Education Department PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE Rights for Parents of Children with Disabilities, Ages 3-21 As a parent, you are a vital member of the
Part B PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE New York State Education Department PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE Rights for Parents of Children with Disabilities, Ages 3-21 As a parent, you are a vital member of the
Role and Special Education in. A Principal s
 1 Role and Special Massachusetts Education in A Principal s Goal of This Presentation To provide information regarding general and special education laws and regulations to assist you in integrating the
1 Role and Special Massachusetts Education in A Principal s Goal of This Presentation To provide information regarding general and special education laws and regulations to assist you in integrating the
Q&A: Revocation of Parental Consent for the Provision of Special Education Services
 Q&A: Revocation of Parental Consent for the Provision of Special Education Services The (MDE) Division of Compliance and Monitoring has developed this document to address questions raised by parents and
Q&A: Revocation of Parental Consent for the Provision of Special Education Services The (MDE) Division of Compliance and Monitoring has developed this document to address questions raised by parents and
KANSAS STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PARENT RIGHTS IN SPECIAL EDUCATION (Procedural Safeguards)
 KANSAS STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PARENT RIGHTS IN SPECIAL EDUCATION (Procedural Safeguards) Both you and the school share in your child s education. If you or the school has issues or concerns about
KANSAS STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PARENT RIGHTS IN SPECIAL EDUCATION (Procedural Safeguards) Both you and the school share in your child s education. If you or the school has issues or concerns about
South Dakota Parental Rights and Procedural Safeguards
 South Dakota Parental Rights and Procedural Safeguards Special Education Programs Revised July 2011 Prior Written Notice... 1 Definition of Parental Consent... 3 Definition of a Parent... 3 Parental Consent...
South Dakota Parental Rights and Procedural Safeguards Special Education Programs Revised July 2011 Prior Written Notice... 1 Definition of Parental Consent... 3 Definition of a Parent... 3 Parental Consent...
CHILD FIND POLICY and ANNUAL PUBLIC NOTICE OF SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS AND PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES
 CHILD FIND POLICY and ANNUAL PUBLIC NOTICE OF SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS AND PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES It is the policy of YouthBuild Philadelphia Charter School that all students with disabilities,
CHILD FIND POLICY and ANNUAL PUBLIC NOTICE OF SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS AND PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES It is the policy of YouthBuild Philadelphia Charter School that all students with disabilities,
Regulation Special Education and Related Services for Eligible Students
 Regulation Special Education and Related Services for Eligible Students The purpose of the district s special education program regulations is to address program areas where state and federal regulations
Regulation Special Education and Related Services for Eligible Students The purpose of the district s special education program regulations is to address program areas where state and federal regulations
Notice of Special Education Procedural Safeguards for Students and Their Families
 Special Education A service, not a place. Notice of Special Education Procedural Safeguards for Students and Their Families Requirements under Part B of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act,
Special Education A service, not a place. Notice of Special Education Procedural Safeguards for Students and Their Families Requirements under Part B of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act,
SPECIAL EDUCATION RIGHTS OF PARENTS AND CHILDREN UNDER FEDERAL AND STATE REQUIREMENTS
 SPECIAL EDUCATION RIGHTS OF PARENTS AND CHILDREN UNDER FEDERAL AND STATE REQUIREMENTS The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act Amendments of 1997 (IDEA 97) is a federal special education law that
SPECIAL EDUCATION RIGHTS OF PARENTS AND CHILDREN UNDER FEDERAL AND STATE REQUIREMENTS The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act Amendments of 1997 (IDEA 97) is a federal special education law that
Q&A: Expanded Core Curriculum Instruction and Orientation and Mobility Evaluations Texas Updates Resulting From SB 39 and HB 590
 DRAFT GUIDANCE PENDING FINAL RULE ADOPTION Q&A: Expanded Core Curriculum Instruction and Orientation and Mobility Evaluations Texas Updates Resulting From SB 39 and HB 590 The 83rd session of the Texas
DRAFT GUIDANCE PENDING FINAL RULE ADOPTION Q&A: Expanded Core Curriculum Instruction and Orientation and Mobility Evaluations Texas Updates Resulting From SB 39 and HB 590 The 83rd session of the Texas
Traveling the Special Education Highway. A Parent s Guide to a Successful Journey. Arizona Department of Education Exceptional Student Services
 Traveling the Special Education Highway A Parent s Guide to a Successful Journey Arizona Department of Education Exceptional Student Services Revised 2015 TRAVELING THE SPECIAL EDUCATION HIGHWAY The Individuals
Traveling the Special Education Highway A Parent s Guide to a Successful Journey Arizona Department of Education Exceptional Student Services Revised 2015 TRAVELING THE SPECIAL EDUCATION HIGHWAY The Individuals
AUSTIN INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT INTERNAL AUDIT DEPARTMENT SPECIAL EDUCATION AUDIT PROGRAM
 SPECIAL EDUCATION GENERAL: Texas Administrative Code 89.1001 Special Education Services shall be provided to eligible students in accordance with all applicable federal law and regulations, state statutes,
SPECIAL EDUCATION GENERAL: Texas Administrative Code 89.1001 Special Education Services shall be provided to eligible students in accordance with all applicable federal law and regulations, state statutes,
SPECIAL EDUCATION IN MASSACHUSETTS
 SPECIAL EDUCATION IN MASSACHUSETTS Children's Law Center of Massachusetts 298 Union Street Lynn, MA 01901 (781) 581-1977 *updated February 2013 Introduction.1 When is a student eligible for special education
SPECIAL EDUCATION IN MASSACHUSETTS Children's Law Center of Massachusetts 298 Union Street Lynn, MA 01901 (781) 581-1977 *updated February 2013 Introduction.1 When is a student eligible for special education
89.1115. Memorandum of Understanding Concerning Interagency Coordination of Special Education Services to Students with Disabilities in Residential
 89.1115. Memorandum of Understanding Concerning Interagency Coordination of Special Education Services to Students with Disabilities in Residential Facilities. (a) (b) (c) Parties. The state agencies named
89.1115. Memorandum of Understanding Concerning Interagency Coordination of Special Education Services to Students with Disabilities in Residential Facilities. (a) (b) (c) Parties. The state agencies named
PART B NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS PARENTAL RIGHTS FOR PUBLIC SCHOOL SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS
 PART B NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS PARENTAL RIGHTS FOR PUBLIC SCHOOL SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS The material contained in this document is intended to provide general information and guidance regarding
PART B NOTICE OF PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS PARENTAL RIGHTS FOR PUBLIC SCHOOL SPECIAL EDUCATION STUDENTS The material contained in this document is intended to provide general information and guidance regarding
Student Success Initiative Manual
 Student Success Initiative Manual Grade-Advancement Requirements Update for the 2014 2015 School Year Cover photography: From top, Pathathai Chungyam/fotolia.com; Glenda Powers/fotolia.com; moodboard/
Student Success Initiative Manual Grade-Advancement Requirements Update for the 2014 2015 School Year Cover photography: From top, Pathathai Chungyam/fotolia.com; Glenda Powers/fotolia.com; moodboard/
Accelerated Program of Instruction
 Accelerated Program of Instruction TEC 28.0211. SATISFACTORY PERFORMANCE ON ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED; ACCELERATED INSTRUCTION. (a) Except as provided by Subsection (b) or (e), a student may not
Accelerated Program of Instruction TEC 28.0211. SATISFACTORY PERFORMANCE ON ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED; ACCELERATED INSTRUCTION. (a) Except as provided by Subsection (b) or (e), a student may not
South Carolina Department of Education Office of Special Education Services Monitoring Overview and Rubric (MOR) for IEP Development
 South Carolina Department of Education Office of Special Education Services Monitoring Overview and Rubric (MOR) for IEP Development Item Inquiry Components and Corresponding IDEA Sections and Regulations
South Carolina Department of Education Office of Special Education Services Monitoring Overview and Rubric (MOR) for IEP Development Item Inquiry Components and Corresponding IDEA Sections and Regulations
Seven Generations Charter School 154 East Minor Street Emmaus, PA 18049. Board of Trustees Policy
 Seven Generations Charter School 154 East Minor Street Emmaus, PA 18049 Board of Trustees Policy Disciplinary Exclusions of Special Education Students Policy There are special rules in Pennsylvania for
Seven Generations Charter School 154 East Minor Street Emmaus, PA 18049 Board of Trustees Policy Disciplinary Exclusions of Special Education Students Policy There are special rules in Pennsylvania for
EAST QUOGUE UNION FREE SCHOOL DISTRICT PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES UNDER THE IDEA AND NEW YORK EDUCATION LAW ARTICLE 89 Policy 4321
 I. General The Board of Education shall make available a free appropriate public education to all students with disabilities who reside within the School District and are eligible for special education
I. General The Board of Education shall make available a free appropriate public education to all students with disabilities who reside within the School District and are eligible for special education
Your Family s Special Education Rights
 VIRGINIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DIVISION OF SPECIAL EDUCATION AND STUDENT SERVICES Your Family s Special Education Rights VIRGINIA PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS
VIRGINIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DIVISION OF SPECIAL EDUCATION AND STUDENT SERVICES Your Family s Special Education Rights VIRGINIA PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS NOTICE SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS
Kansas Special Education Services. Process Handbook
 Kansas Special Education Services Process Handbook ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Special Education Services wishes to thank all those that provided input for the 2011 Kansas Special Education Process Handbook, including
Kansas Special Education Services Process Handbook ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Special Education Services wishes to thank all those that provided input for the 2011 Kansas Special Education Process Handbook, including
1. Each LEA shall ensure that evaluation procedures are established and implemented that meet the requirements of this Rule.
 Code: IDDF (4) 160-4-7-.04 EVALUATIONS AND REEVALUATIONS. (1) INITIAL EVALUATIONS. (a) Each LEA must conduct a full and individual initial evaluation before the initial provision of special education and
Code: IDDF (4) 160-4-7-.04 EVALUATIONS AND REEVALUATIONS. (1) INITIAL EVALUATIONS. (a) Each LEA must conduct a full and individual initial evaluation before the initial provision of special education and
PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES UNDER IDEA AND NEW YORK S EDUCATION LAW ARTICLE 89
 PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES UNDER IDEA AND NEW YORK S EDUCATION LAW ARTICLE 89 The Board of Education shall make available a free appropriate public education to all students with disabilities
PROGRAMS FOR STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES UNDER IDEA AND NEW YORK S EDUCATION LAW ARTICLE 89 The Board of Education shall make available a free appropriate public education to all students with disabilities
Notice of Parental Rights for Gifted Students
 Notice of Parental Rights for Gifted Students Child s Name: ************************************************************************************* Date: Dear, This notice describes your rights and the procedures
Notice of Parental Rights for Gifted Students Child s Name: ************************************************************************************* Date: Dear, This notice describes your rights and the procedures
Side-by-side Comparison of Early Intervention and Preschool Special Education
 NM Part C Early Intervention Procedures - Appendix A. Side-by-side Comparison of Early Intervention and Preschool Special Education The following is a side-by-side comparison of: Early intervention services
NM Part C Early Intervention Procedures - Appendix A. Side-by-side Comparison of Early Intervention and Preschool Special Education The following is a side-by-side comparison of: Early intervention services
Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs
 Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs It is the responsibility of the Pennsylvania Department of Education to ensure that all children with disabilities residing in the Commonwealth,
Annual Public Notice of Special Education Services and Programs It is the responsibility of the Pennsylvania Department of Education to ensure that all children with disabilities residing in the Commonwealth,
Kansas Special Education Services. Process Handbook
 Kansas Special Education Services Process Handbook JUNE 2011 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Special Education Services wishes to thank the KASEA Organization and the Regional Representatives that participated in the
Kansas Special Education Services Process Handbook JUNE 2011 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Special Education Services wishes to thank the KASEA Organization and the Regional Representatives that participated in the
SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITY
 SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITY 24:05:24.01:18. Specific learning disability defined. Specific learning disability is a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding
SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITY 24:05:24.01:18. Specific learning disability defined. Specific learning disability is a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding
Child and Family Rights/Procedural Safeguards
 Child and Family Rights/Procedural Safeguards First Steps Early Intervention Program Mississippi State Department of Health Revised 03-06-15 Table of Contents Contents Page Number Introduction 3 Section
Child and Family Rights/Procedural Safeguards First Steps Early Intervention Program Mississippi State Department of Health Revised 03-06-15 Table of Contents Contents Page Number Introduction 3 Section
The Least Restrictive Environment (LRE): Question & Answer Document
 The Least Restrictive Environment (LRE): Question & Answer Document A collaborative project of the Texas Education Agency and the Statewide Access to the General Curriculum Network Copyright Notice These
The Least Restrictive Environment (LRE): Question & Answer Document A collaborative project of the Texas Education Agency and the Statewide Access to the General Curriculum Network Copyright Notice These
SUBCHAPTER 3. SPECIAL EDUCATION NEW JERSEY ADMINISTRATIVE CODE TITLE 6A EDUCATION
 CHAPTER 14 SPECIAL EDUCATION NEW JERSEY ADMINISTRATIVE CODE TITLE 6A EDUCATION CHAPTER 14. AUTHORITY: SPECIAL EDUCATION N.J.S.A. 18A:4-15, 18A:7A-1 et seq., 18A:7B-1 et seq., 18A:7C-1 et seq., 18A:40-4,
CHAPTER 14 SPECIAL EDUCATION NEW JERSEY ADMINISTRATIVE CODE TITLE 6A EDUCATION CHAPTER 14. AUTHORITY: SPECIAL EDUCATION N.J.S.A. 18A:4-15, 18A:7A-1 et seq., 18A:7B-1 et seq., 18A:7C-1 et seq., 18A:40-4,
Private Schools/Equitable Participation
 Private Schools/Equitable Participation Equitable Participation Q & A The revision to IDEA in 2004 and the subsequent 2006 IDEA regulations significantly changed the obligation of States and LEAs to children
Private Schools/Equitable Participation Equitable Participation Q & A The revision to IDEA in 2004 and the subsequent 2006 IDEA regulations significantly changed the obligation of States and LEAs to children
Reevaluation Procedures for Students with Disabilities
 Reevaluation Procedures for Students with Disabilities BACKGROUND This is one of a series of technical assistance materials related to the final regulations implementing the 1997 Amendments to Part B and
Reevaluation Procedures for Students with Disabilities BACKGROUND This is one of a series of technical assistance materials related to the final regulations implementing the 1997 Amendments to Part B and
Compliance Standards for Special Education
 s for Special Education Michigan Department of Education Office of Special Education October 2013 State Board of Education John C. Austin, President Casandra E. Ulbrich, Vice President Daniel Varner, Secretary
s for Special Education Michigan Department of Education Office of Special Education October 2013 State Board of Education John C. Austin, President Casandra E. Ulbrich, Vice President Daniel Varner, Secretary
CHAPTER 4 THE INDIVIDUALIZED EDUCATION PROGRAM (IEP) INTRODUCTION A. IEP TEAM
 C H A P T E R 4 : T H E I N D I V I D U A L I Z E D E D U C A T I O N P R O G R A M ( I E P ) INTRODUCTION The Individualized Education Program is defined as a written statement for each student with an
C H A P T E R 4 : T H E I N D I V I D U A L I Z E D E D U C A T I O N P R O G R A M ( I E P ) INTRODUCTION The Individualized Education Program is defined as a written statement for each student with an
OSPI Special Education Technical Assistance Paper No. 5 (TAP 5) REVISED
 OSPI Special Education Technical Assistance Paper No. 5 (TAP 5) REVISED The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA): Evaluation Procedures Under Part B Note: All TAPS are posted on OSPI s Web
OSPI Special Education Technical Assistance Paper No. 5 (TAP 5) REVISED The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA): Evaluation Procedures Under Part B Note: All TAPS are posted on OSPI s Web
504 or IEP: Which is Right for my Child?
 504 or IEP: Which is Right for my Child? Students with disabilities can receive educational plans under one of two federal laws. One is Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, whose plan is commonly
504 or IEP: Which is Right for my Child? Students with disabilities can receive educational plans under one of two federal laws. One is Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, whose plan is commonly
Date: PARENT ASSISTANCE
 NOTICE OF PARENTAL RIGHTS FOR GIFTED STUDENTS Date: Dear This notice describes your rights and the procedures that safeguard your rights as found in Chapter 16 of the State Board of Education s Regulations
NOTICE OF PARENTAL RIGHTS FOR GIFTED STUDENTS Date: Dear This notice describes your rights and the procedures that safeguard your rights as found in Chapter 16 of the State Board of Education s Regulations
FAIRFAX COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS PROCEDURES REQUIRED FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF SPECIAL EDUCATION REGULATIONS IN VIRGINIA S PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 FAIRFAX COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS PROCEDURES REQUIRED FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF SPECIAL EDUCATION REGULATIONS IN VIRGINIA S PUBLIC SCHOOLS Table of Contents Child Find... 2 Screening... 3 General Screening Procedures...
FAIRFAX COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS PROCEDURES REQUIRED FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF SPECIAL EDUCATION REGULATIONS IN VIRGINIA S PUBLIC SCHOOLS Table of Contents Child Find... 2 Screening... 3 General Screening Procedures...
ARKANSAS DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES 5.00 FREE APPROPRIATE PUBLIC EDUCATION (FAPE) July 2008
 ARKANSAS DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES July 2008 5.01 PROVISION OF FAPE 5.01.1 Subject to 34 CFR 300.101 and this part, the State of Arkansas must ensure that all children
ARKANSAS DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SPECIAL EDUCATION AND RELATED SERVICES July 2008 5.01 PROVISION OF FAPE 5.01.1 Subject to 34 CFR 300.101 and this part, the State of Arkansas must ensure that all children
CFR 300.5 CFR 300.6 CFR 300.105 CFR 300.346(a)(2)(v) TEC 30.0015 19 TAC 89
 Assistive Technology Legal Reference Assistive Technology service means any service that directly assists a student with a disability in the selection, acquisition, or use of an assistive technology device.
Assistive Technology Legal Reference Assistive Technology service means any service that directly assists a student with a disability in the selection, acquisition, or use of an assistive technology device.
N.J.A.C. 6A:14, SPECIAL EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 N.J.A.C. 6A:14, SPECIAL EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS SUBCHAPTER 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS 6A:14-1.1 General requirements 6A:14-1.2 District eligibility for assistance under IDEA Part B 6A:14-1.3 Definitions
N.J.A.C. 6A:14, SPECIAL EDUCATION TABLE OF CONTENTS SUBCHAPTER 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS 6A:14-1.1 General requirements 6A:14-1.2 District eligibility for assistance under IDEA Part B 6A:14-1.3 Definitions
SCITUATE PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES MANUAL
 SCITUATE PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES MANUAL UPDATED: August 2014 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Identification/Referrals/Evaluation Process Page Scituate Public Schools Procedures for Pre-referral
SCITUATE PUBLIC SCHOOLS SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES MANUAL UPDATED: August 2014 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Identification/Referrals/Evaluation Process Page Scituate Public Schools Procedures for Pre-referral
Special Education Procedural Manual
 Houston Gateway Academy, Inc. Special Education Procedural Manual Developed by Special Education Department 1 Table of Contents MISSION STATEMENT... 3 Preface... 4 1. Definitions... 5 2. Full Educational
Houston Gateway Academy, Inc. Special Education Procedural Manual Developed by Special Education Department 1 Table of Contents MISSION STATEMENT... 3 Preface... 4 1. Definitions... 5 2. Full Educational
Eligibility, and Individualized Education Program (IEP) Process in Maryland
 A Guide For Parents of Students With Disabilities Understanding the Evaluation, Eligibility, and Individualized Education Program (IEP) Process in Maryland Maryland State Department of Education Division
A Guide For Parents of Students With Disabilities Understanding the Evaluation, Eligibility, and Individualized Education Program (IEP) Process in Maryland Maryland State Department of Education Division
Chapter 89. Adaptations for Special Populations. Subchapter D. Special Education Services and Settings
 Chapter 89. Adaptations for Special Populations Subchapter D. Special Education Services and Settings 89.61. Contracting for Residential Educational Placements for Students with Disabilities. Residential
Chapter 89. Adaptations for Special Populations Subchapter D. Special Education Services and Settings 89.61. Contracting for Residential Educational Placements for Students with Disabilities. Residential
Special Education For Preschoolers
 C A L I F O R N I A E A R L Y S T A R T Special Education For Preschoolers A G U I D E F O R P A R E N T S Early Intervention services system encouraging partnerships between families and professionals,
C A L I F O R N I A E A R L Y S T A R T Special Education For Preschoolers A G U I D E F O R P A R E N T S Early Intervention services system encouraging partnerships between families and professionals,
Special Education Services. Serving Children Supporting Families Encouraging Success
 Special Education Services Serving Children Supporting Families Encouraging Success 1 If you have this brochure in your hand, then you are most likely asking: 1. Does PA Distance Learning Charter School
Special Education Services Serving Children Supporting Families Encouraging Success 1 If you have this brochure in your hand, then you are most likely asking: 1. Does PA Distance Learning Charter School
20 U.S.C. 1415 PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS
 20 U.S.C. 1415 PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS Introduction On November 17, 2004, a House-Senate Conference Committee agreed on changes to reauthorize the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). On Friday,
20 U.S.C. 1415 PROCEDURAL SAFEGUARDS Introduction On November 17, 2004, a House-Senate Conference Committee agreed on changes to reauthorize the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). On Friday,
The IEP Process: Frequently Asked Questions
 The IEP Process: Frequently Asked Questions A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE IEP February 2010 Developed for Rhode Island Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Deborah A. Gist Commissioner Rhode Island
The IEP Process: Frequently Asked Questions A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE IEP February 2010 Developed for Rhode Island Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Deborah A. Gist Commissioner Rhode Island
Chapter 6: Individualized Education Programs (IEPs)
 33 Chapter 6: Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) In this chapter you will: learn the parts of an IEP learn who is on an IEP team discover tips and things to remember when working on the IEP understand
33 Chapter 6: Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) In this chapter you will: learn the parts of an IEP learn who is on an IEP team discover tips and things to remember when working on the IEP understand
290-8-9.04(3) 290-8-9.04(4)(e)
 290-8-9.04(3) 290-8-9.04(4)(e) (3) Age Requirements. The following age requirements apply to the provision of special education and related services: (a) Preschool children with disabilities by the child
290-8-9.04(3) 290-8-9.04(4)(e) (3) Age Requirements. The following age requirements apply to the provision of special education and related services: (a) Preschool children with disabilities by the child
THE RIGHT TO SPECIAL EDUCATION IN PENNSYLVANIA: A GUIDE FOR PARENTS
 THE RIGHT TO SPECIAL EDUCATION IN PENNSYLVANIA: A GUIDE FOR PARENTS EDUCATION LAW CENTER 1315 Walnut Street, 4th Floor, Philadelphia, PA 19107 Phone: 215-238-6970 Fax: 215-772-3125 TTY: 215-789-2498 1901
THE RIGHT TO SPECIAL EDUCATION IN PENNSYLVANIA: A GUIDE FOR PARENTS EDUCATION LAW CENTER 1315 Walnut Street, 4th Floor, Philadelphia, PA 19107 Phone: 215-238-6970 Fax: 215-772-3125 TTY: 215-789-2498 1901
SPECIAL EDUCATION STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES MANUAL BRIDGEPORT PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 SPECIAL EDUCATION STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES MANUAL BRIDGEPORT PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2014 The District understands and acknowledges that the laws and interpretations of the laws may change over time. Readers
SPECIAL EDUCATION STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES MANUAL BRIDGEPORT PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2014 The District understands and acknowledges that the laws and interpretations of the laws may change over time. Readers
RULES FOR THE ADMINISTRATION, CERTIFICATION AND OVERSIGHT OF COLORADO ONLINE PROGRAMS
 DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION Colorado State Board of Education RULES FOR THE ADMINISTRATION, CERTIFICATION AND OVERSIGHT OF COLORADO ONLINE PROGRAMS 1 CCR 301-71 1.0 Statement of Basis and Purpose. These rules
DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION Colorado State Board of Education RULES FOR THE ADMINISTRATION, CERTIFICATION AND OVERSIGHT OF COLORADO ONLINE PROGRAMS 1 CCR 301-71 1.0 Statement of Basis and Purpose. These rules
Special Education Operating Guidelines
 Special Education Operating Guidelines Special Education Cooperative Cotulla ISD, Dilley ISD, Pearsall ISD Revised as of June 2011 Special Education Operating Guidelines The Special Education Cooperative
Special Education Operating Guidelines Special Education Cooperative Cotulla ISD, Dilley ISD, Pearsall ISD Revised as of June 2011 Special Education Operating Guidelines The Special Education Cooperative
FILING A COMPLAINT WITH THE TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY
 FILING A COMPLAINT WITH THE TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY Rev. May 2011 - ED11 Introduction Parents, and others, who have complaints about the special education services being provided by a school district may
FILING A COMPLAINT WITH THE TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY Rev. May 2011 - ED11 Introduction Parents, and others, who have complaints about the special education services being provided by a school district may
The Right to Special Education in New Jersey
 NJ The Right to Special Education in New Jersey A G U I D E F O R A D V O C A T E S Education Law Center Sponsored by New Jersey State Bar Foundation Acknowledgments This manual was written by Ellen Boylan,
NJ The Right to Special Education in New Jersey A G U I D E F O R A D V O C A T E S Education Law Center Sponsored by New Jersey State Bar Foundation Acknowledgments This manual was written by Ellen Boylan,
Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION
 Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION in MISSOURI Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Division of Special Education D. Kent King, Commissioner of Education Revised September 2008 This
Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION in MISSOURI Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Division of Special Education D. Kent King, Commissioner of Education Revised September 2008 This
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
 FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DPS: 2011-23 Date: May 11, 2011 Dr. Eric J. Smith Commissioner of Education Technical Assistance Paper Students with Disabilities Enrolled by Their Parents in Private Schools
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION DPS: 2011-23 Date: May 11, 2011 Dr. Eric J. Smith Commissioner of Education Technical Assistance Paper Students with Disabilities Enrolled by Their Parents in Private Schools
Special Education Operating Guidelines Overview
 Special Education Operating Guidelines Overview Local Education Agencies (LEA) are required to develop and implement policies, procedures and practices related to the provision of special education services
Special Education Operating Guidelines Overview Local Education Agencies (LEA) are required to develop and implement policies, procedures and practices related to the provision of special education services
Assistive Technology
 Tips from the Special Education Section: Reminders to the Field The following tips are compiled from the monthly updates. They are sorted by topical areas, and will be updated quarterly. Assistive Technology
Tips from the Special Education Section: Reminders to the Field The following tips are compiled from the monthly updates. They are sorted by topical areas, and will be updated quarterly. Assistive Technology
INITIAL REFERRAL FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY
 INITIAL REFERRAL FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY 1. Pre-Referral Student Support Team (SST) Referral for special education services typically culminates with the recommendation for referral from the
INITIAL REFERRAL FOR SPECIAL EDUCATION ELIGIBILITY 1. Pre-Referral Student Support Team (SST) Referral for special education services typically culminates with the recommendation for referral from the
Parent s Guide to Special Education
 Revised 2010 Parent s Guide to Special Education Virginia Department of Education Division of Special Education and Student Services Table of Contents Introduction....3 Understanding Special Education
Revised 2010 Parent s Guide to Special Education Virginia Department of Education Division of Special Education and Student Services Table of Contents Introduction....3 Understanding Special Education
BEFORE THE STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION ) ) ) ) I. BACKGROUND
 BEFORE THE STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION In the Matter of Salem-Keizer School District 24J ) ) ) ) FINDINGS OF FACT, CONCLUSIONS, AND FINAL ORDER Case No. 06-054-048 I. BACKGROUND On November
BEFORE THE STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION In the Matter of Salem-Keizer School District 24J ) ) ) ) FINDINGS OF FACT, CONCLUSIONS, AND FINAL ORDER Case No. 06-054-048 I. BACKGROUND On November
GRANDVIEW INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ENGLISH AS A SECOND LANGUAGE POLICY AND PROCEDURES
 GRANDVIEW INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ENGLISH AS A SECOND LANGUAGE POLICY AND PROCEDURES ESL PROGRAM GOAL and MISSION The goal of the English as a Second Language (ESL) program in Grandview ISD is to enable
GRANDVIEW INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ENGLISH AS A SECOND LANGUAGE POLICY AND PROCEDURES ESL PROGRAM GOAL and MISSION The goal of the English as a Second Language (ESL) program in Grandview ISD is to enable
NC General Statutes - Chapter 115C Article 9 1
 Article 9. Education of Children With Disabilities. Part 1. State Policy. 115C-106: Repealed by Session Laws 2006-69, s. 1, effective from and after July 1, 2006. Part 1A. General Provisions. 115C-106.1.
Article 9. Education of Children With Disabilities. Part 1. State Policy. 115C-106: Repealed by Session Laws 2006-69, s. 1, effective from and after July 1, 2006. Part 1A. General Provisions. 115C-106.1.
SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES
 SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES This Procedures Manual ensures the implementation of special education services in Salt Lake City School District. It is to be used in coordination
SALT LAKE CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT SPECIAL EDUCATION PROCEDURES This Procedures Manual ensures the implementation of special education services in Salt Lake City School District. It is to be used in coordination
Parental Rights in Special Education. New Jersey Department of Education. Christopher D. Cerf Commissioner of Education
 New Jersey Department of Education Christopher D. Cerf Commissioner of Education Barbara Gantwerk Assistant Commissioner Division of Student and Field Services Peggy McDonald Director Office of Special
New Jersey Department of Education Christopher D. Cerf Commissioner of Education Barbara Gantwerk Assistant Commissioner Division of Student and Field Services Peggy McDonald Director Office of Special
Parent Rights & Responsibilities in Nevada Early Intervention
 P a g e 1 Parent Rights & Responsibilities in Nevada Early Intervention What are my rights and why are they important? Rights protect your family and child. All families enrolled in early intervention
P a g e 1 Parent Rights & Responsibilities in Nevada Early Intervention What are my rights and why are they important? Rights protect your family and child. All families enrolled in early intervention
INDIVIDUALIZED FAMILY SERVICE PLAN
 INDIVIDUALIZED FAMILY SERVICE PLAN Introduction [34 CFR 303.20] The Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP) is the written agreement between the family and the local tiny-k program that documents a plan
INDIVIDUALIZED FAMILY SERVICE PLAN Introduction [34 CFR 303.20] The Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP) is the written agreement between the family and the local tiny-k program that documents a plan
Navigating the Course:
 Navigating the Course: Finding Your Way Through Indiana s Special Education Rules A companion guide to: ARTICLE 7 September 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents... 1 Section I: INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Navigating the Course: Finding Your Way Through Indiana s Special Education Rules A companion guide to: ARTICLE 7 September 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents... 1 Section I: INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
eci early childhood intervention Planning Transition conference or Meeting Next Steps Terms You may hear Resources Timelines Regulations
 beyond early childhood intervention eci Planning Moving on from the Texas Early Childhood Intervention (ECI) Program! This booklet will help your family make the transition from ECI. Transition conference
beyond early childhood intervention eci Planning Moving on from the Texas Early Childhood Intervention (ECI) Program! This booklet will help your family make the transition from ECI. Transition conference
PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION SUBPART A: GENERAL
 ISBE 23 ILLINOIS ADMINISTRATIVE CODE 226 TITLE 23: EDUCATION AND CULTURAL RESOURCES : EDUCATION CHAPTER I: STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION : INSTRUCTION FOR SPECIFIC STUDENT POPULATIONS PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION
ISBE 23 ILLINOIS ADMINISTRATIVE CODE 226 TITLE 23: EDUCATION AND CULTURAL RESOURCES : EDUCATION CHAPTER I: STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION : INSTRUCTION FOR SPECIFIC STUDENT POPULATIONS PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION
Communicating with Your Child s School Through Letter Writing
 Communicating with Your Child s School Through Letter Writing A publication of the National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities Throughout your child s school years, there is always a need
Communicating with Your Child s School Through Letter Writing A publication of the National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities Throughout your child s school years, there is always a need
DELAWARE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION EXCEPTIONAL CHILDREN RESOURCES FINAL REPORT ADMINISTRATIVE COMPLAINT RESOLUTION. DE AC 13-8 (March 15, 2013)
 DELAWARE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION EXCEPTIONAL CHILDREN RESOURCES FINAL REPORT ADMINISTRATIVE COMPLAINT RESOLUTION DE AC 13-8 (March 15, 2013) On February 11, 2013, Student s mother filed a complaint with
DELAWARE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION EXCEPTIONAL CHILDREN RESOURCES FINAL REPORT ADMINISTRATIVE COMPLAINT RESOLUTION DE AC 13-8 (March 15, 2013) On February 11, 2013, Student s mother filed a complaint with
A Sample of California Special Education Regulations Related to Students with Emotional Disturbances
 A Sample of California Special Education Regulations Related to Students with Emotional Disturbances 5 CCR 3030 - Eligibility Criteria Because of a serious emotional disturbance, a pupil exhibits one or
A Sample of California Special Education Regulations Related to Students with Emotional Disturbances 5 CCR 3030 - Eligibility Criteria Because of a serious emotional disturbance, a pupil exhibits one or
The Special Education Referral & Identification Process. Menlo Park City School District Source: US Department of Education and
 The Special Education Referral & Identification Process Olivia Mandilk, Director Menlo Park City School District Source: US Department of Education and Protection and Advocacy, Inc. 11/07 Step One Child
The Special Education Referral & Identification Process Olivia Mandilk, Director Menlo Park City School District Source: US Department of Education and Protection and Advocacy, Inc. 11/07 Step One Child
What is special education?
 P arents play an important role in their children s education. When a child has a disability and needs special education, parents are their most important advocates. If you believe that your child has
P arents play an important role in their children s education. When a child has a disability and needs special education, parents are their most important advocates. If you believe that your child has
Department of Education
 Monday, August 14, 2006 Part II Department of Education 34 CFR Parts 300 and 301 Assistance to States for the Education of Children With Disabilities and Preschool Grants for Children With Disabilities;
Monday, August 14, 2006 Part II Department of Education 34 CFR Parts 300 and 301 Assistance to States for the Education of Children With Disabilities and Preschool Grants for Children With Disabilities;
Advocating for Services: How a Parent Can Access a Special Education Program, Special Education Teacher Support Services and/or Related Services
 Advocating for Services: How a Parent Can Access a Special Education Program, Special Education Teacher Support Services and/or Related Services Applied Behavioral Counseling Applied ABC Presented by Joan
Advocating for Services: How a Parent Can Access a Special Education Program, Special Education Teacher Support Services and/or Related Services Applied Behavioral Counseling Applied ABC Presented by Joan
Oregon Administrative Rules Talented and Gifted
 Oregon Administrative Rules Talented and Gifted 581-022-1310 Identification of Academically Talented and Intellectually Gifted Students (1) Each school district shall have local district policies and procedures
Oregon Administrative Rules Talented and Gifted 581-022-1310 Identification of Academically Talented and Intellectually Gifted Students (1) Each school district shall have local district policies and procedures
The amended regulations set out below were approved by the Board of Elementary and Secondary Education on December 16, 2014, and
 The amended regulations set out below were approved by the Board of Elementary and Secondary Education on December 16, 2014, and take effect on January 1, 2016. (Until such date, a current version of 603
The amended regulations set out below were approved by the Board of Elementary and Secondary Education on December 16, 2014, and take effect on January 1, 2016. (Until such date, a current version of 603
Annual Public Notice of Special Education & Early Intervention Services and Programs
 Annual Public Notice of Special Education & Early Intervention Services and Programs It is the responsibility of the Pennsylvania Department of Education to ensure that all children with disabilities residing
Annual Public Notice of Special Education & Early Intervention Services and Programs It is the responsibility of the Pennsylvania Department of Education to ensure that all children with disabilities residing
The Transition Process: From Birth to Three to Special Education. Connecticut Parent Advocacy Center. Workshop Outcomes 11/9/2010
 The Transition Process: From Birth to Three to Special Education Connecticut Parent Advocacy Center, Inc. 338 Main Street, Niantic, CT 06357 1 800 445 2722 www.cpacinc.org Connecticut Parent Advocacy Center
The Transition Process: From Birth to Three to Special Education Connecticut Parent Advocacy Center, Inc. 338 Main Street, Niantic, CT 06357 1 800 445 2722 www.cpacinc.org Connecticut Parent Advocacy Center
PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION SUBPART A: GENERAL
 ISBE 23 ILLINOIS ADMINISTRATIVE CODE 226 TITLE 23: EDUCATION AND CULTURAL RESOURCES : EDUCATION CHAPTER I: STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION : INSTRUCTION FOR SPECIFIC STUDENT POPULATIONS PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION
ISBE 23 ILLINOIS ADMINISTRATIVE CODE 226 TITLE 23: EDUCATION AND CULTURAL RESOURCES : EDUCATION CHAPTER I: STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION : INSTRUCTION FOR SPECIFIC STUDENT POPULATIONS PART 226 SPECIAL EDUCATION
NEW MEXICO PRIMER ON SPECIAL EDUCATION IN CHARTER SCHOOLS: BACKGROUND SECTION
 NEW MEXICO PRIMER ON SPECIAL EDUCATION IN CHARTER SCHOOLS: BACKGROUND SECTION This section is divided into two parts: a discussion of the legal status of charter schools and their linkage to other local
NEW MEXICO PRIMER ON SPECIAL EDUCATION IN CHARTER SCHOOLS: BACKGROUND SECTION This section is divided into two parts: a discussion of the legal status of charter schools and their linkage to other local
LPAC/ARD Communication, Collaboration, and Compliance: Three Keys to Success
 Interactive Convention 2014 Learning Labs LPAC/ARD Communication, Collaboration, and Compliance: Three Keys to Success Anna Mondragon & Jose Velazquez, ESC Region 19 Documentation of the process for considering
Interactive Convention 2014 Learning Labs LPAC/ARD Communication, Collaboration, and Compliance: Three Keys to Success Anna Mondragon & Jose Velazquez, ESC Region 19 Documentation of the process for considering
Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION
 Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION in MISSOURI Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Division of Special Education D. Kent King, Commissioner of Education Revised September 2008 ADDENDUM
Parent s Guide to SPECIAL EDUCATION in MISSOURI Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Division of Special Education D. Kent King, Commissioner of Education Revised September 2008 ADDENDUM
Kindergarten. Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
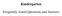 Kindergarten Frequently Asked Questions and Answers 1. Are school districts required to offer the kindergarten program? Yes. The board of trustees of each school district shall establish and maintain one
Kindergarten Frequently Asked Questions and Answers 1. Are school districts required to offer the kindergarten program? Yes. The board of trustees of each school district shall establish and maintain one
