KAPA Library Quantification Technical Guide
|
|
|
- Shanon Garrison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KAPA Library Quantification KAPA Library Quantification Kits for Illumina platforms v1.14 Contents Introduction...1 Product Description...2 Product Applications...2 Important Parameters...3 Product and sample handling...3 Consumables and equipment...3 Accurate liquid handling...3 Reaction volume...3 Library concentration and dilutions...4 Contamination and no-template controls...4 Internal, process or dilution controls...4 Replicates, data reliability, throughput and per-sample cost...6 Assay automation...6 Data Analysis and Interpretation...8 Standard 1 amplifies "too early"...8 Size-adjustment calculation...8 Melt curve analysis...8 Correlation between library concentration and cluster density...9 Library concentrations determined by qpcr vs other methods...10 Restrictions and Liabilities...12 Note to Purchaser: Limited Product Warranty...12 Note to Purchaser: Limited License...12 Effective date: August 2014 Introduction Accurate quantification of the number of adapterligated molecules in a library prepared for Illumina nextgeneration sequencing is desirable at various stages of sequencing workflows, including: After adapter ligation, to determine the amount of input material converted to adapter-ligated molecules (conversion rate) and/or the quantity of template used for library amplification. After library amplification, to determine whether a sufficient amount of each library has been generated and/or to ensure equal representation of indexed libraries pooled for target capture or cluster amplification. Prior to cluster amplification, to confirm that individual libraries or sample pools are diluted to the optimal concentration for flow cell loading. Overestimation of library concentration may result in a lower than desired cluster density. Underestimation of library concentration may result in higher than desired cluster density, which can lead to poor cluster resolution. Both scenarios result in suboptimal utilization of sequencing capacity. qpcr is widely regarded as the gold standard for NGS library quantification, as it accurately measures the number of molecules that can serve as templates during library and cluster amplification. Furthermore, the sensitivity and broad dynamic range of qpcr enables accurate quantification of very dilute libraries. Reliable qpcr-based library quantification depends on three factors: (i) the efficiency and reproducibility of the standard curve used for absolute quantification, (ii) the ability of the DNA polymerase to amplify all adapterligated molecules with similar efficiency, and (iii) accurate and reproducible liquid handling. KAPA Library Quantification Kits provide an industryleading solution for qpcr-based quantification of NGS libraries. The kit contains the novel KAPA SYBR FAST DNA Polymerase, engineered through a process of directed evolution for high-performance qpcr. The ability of the engineered polymerase to amplify diverse DNA fragments with similar efficiency renders it uniquely suitable for library quantification, and enables the use of a universal DNA standard for the accurate and reliable quantification of all Illumina libraries irrespective of library type, GC content or fragment length. The prediluted set of DNA Standards included in the kit are rigorously tested to ensure minimal lot-to-lot variation and consistent performance over time. 1
2 KAPA Library Quantification Product Description KAPA Library Quantification Kits for Illumina platforms provide all the reagents needed for absolute, qpcrbased quantification of Illumina libraries flanked by the P5 and P7 flow cell oligo sequences. Kits contain: Library Quantification DNA Standards 1 6 (a 10-fold dilution series of a linear, 452 bp template), Library Quantification Primer Premix (10X), containing the following primers: Primer 1: 5'-AAT GAT ACG GCG ACC ACC GA-3' Primer 2: 5'-CAA GCA GAA GAC GGC ATA CGA-3' KAPA SYBR FAST qpcr Master Mix (2X), available with various passive reference dyes. Library quantification is performed by amplifying the set of six pre-diluted DNA Standards and appropriately diluted library samples by qpcr, using the KAPA SYBR FAST qpcr Master Mix and primers based on the Illumina P5 and P7 flow cell oligo sequences. The average Cq value for each DNA Standard is plotted against log 10 (concentration in pm) to generate a standard curve, which is used to calculate library concentrations (Figure 1). Kits are subjected to stringent functional quality control to ensure consistent performance and minimal lot-to-lot variation. All components are free of detectable exo- and endonuclease activities, and meet strict requirements with respect to DNA contamination. Please contact support@ kapabiosystems.com for more information. Product Applications KAPA Library Quantification Kits for Illumina platforms are designed for the accurate and reproducible quantification of libraries prepared for Illumina sequencing. Any library with a concentration > pm that contains sequences complementary to the primers contained in the 10X Primer Premix can be quantified with the kit irrespective of the library type, how it was constructed, or on which Illumina instrument it will be sequenced. The kit supports quantification of libraries across a range of GC contents, and average fragment lengths up to 1 kb. In addition to NGS library quantification, the kit can also be used to detect library contamination in work spaces used during the preparation of Illumina libraries. KAPA Library Quantification Kits for libraries constructed for sequencing on other NGS platforms are also available. Please contact sales@kapabiosystems.com for details. The KAPA Library Quantification assay consists of repetitive pipetting steps, which can easily be automated. The use of an automated liquid handling system is highly recommended for high-throughput NGS pipelines. Please refer to Assay automation in the Important Parameters section for more information. Figure 1. Principle of the KAPA Library Quantification assay. A set of six pre-diluted DNA Standards (representing a 10-fold dilution series of a linear, 452 bp dsdna fragment), as well as appropriately diluted library samples, are amplified by qpcr, using the KAPA SYBR FAST qpcr Master Mix and primers based on the Illumina P5 and P7 flow cell oligo sequences. The average Cq value for each DNA Standard is plotted against log 10 (concentration in pm) to generate a standard curve. The standard curve is used to convert the average Cq values for diluted library samples to concentration. This is followed by a size-adjustment calculation, to compensate for differences between the length of the DNA Standard and the average fragment length of the libraries. Finally, the undiluted or working concentration of each library is calculated. Please refer to the KAPA Library Quantification Kit Technical Data Sheet for a detailed protocol and data analysis guidelines. 2
3 KAPA Library Quantification Important Parameters KAPA Library Quantification Kits enable the accurate and reproducible qpcr-based quantification of libraries prepared for Illumina sequencing. Successful implementation of the assay in NGS workflows depends on a number of factors, which are discussed below. Product and sample handling Observe all product storage and handling guidelines, as outlined in the KAPA Library Quantification Kit Technical Data Sheet. Dilute DNA solutions (such as NGS libraries) are sensitive to degradation during freezing and thawing. This should be kept in mind when designing the most appropriate long-term storage strategy for your libraries and assay controls. Since dilute DNA quickly degrades in an unbuffered environment: Libraries and controls must always be stored and diluted in a weak buffer (10 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0 at 25 C). Tween 20 may be included in the dilution buffer at a final concentration of 0.05% to improve pipetting accuracy and reduce DNA adsorption to plastic tubes and pipette tips. Do not store diluted libraries and controls at room temperature, or for long periods of time prior to reaction setup. Dilutions must be prepared fresh for each assay and kept on ice or at 4 C while qpcrs are set up. Calculated library concentrations may be highly variable and/or inaccurate if diluted samples are stored at room temperature, or for long periods of time (even at 4 C) prior to reactoin setup. If a sample has to be re-assayed, fresh dilutions must be prepared for the repeat assay. Consumables and equipment Always use high-quality, low DNA-binding PCR tubes/ plates and pipette tips. Ensure that qpcr instruments and pipettes are properly maintained and regularly calibrated according to the manufacturers recommendations. Accurate liquid handling Since qpcr is a very sensitive technique, and the dynamic range of this assay extends to very low template copy numbers, the reliability of results is highly dependent on accurate liquid handling. Care must be taken to ensure the highest degree of accuracy when executing this protocol. This can be achieved as follows: Always ensure that reagents and samples are fully thawed and thoroughly mixed before use. After thawing and mixing, briefly centrifuge tubes to remove any droplets from tube walls. Concentrated solutions of DNA may be viscous, making it difficult to accurately dispense small volumes for analysis. Avoid making extremely large dilutions during sample preparation. If samples require very large dilutions to fall within the dynamic range of the assay, it is preferable to perform serial dilutions (e.g. make two consecutive 1/100 dilutions instead of a single 1/ dilution). If possible, avoid the use of multi-channel pipettes. Use a new pipette tip for each pipetting step, especially when dispensing the DNA Standards and when multiple dilutions of the same sample are prepared. Crosscontamination between standards and/or samples will affect the accuracy of quantification. Avoid placing the pipette tip too far under the reagent surface during aspiration, as this may result in liquid adhering to the outside of the tip. After aspirating the desired volume of any reaction component, examine the pipette tip before dispensing to ensure that the correct volume is being transferred. Always try to dispense reaction components as close as possible to the bottom of the tube or well. Flush/rinse pipette tips by pipetting up and down 2 3 times after dispensing. Ensure that no residual liquid remains in the tip after dispensing. Use an automated liquid handling system to dilute libraries and controls and set up reactions, especially when large numbers of samples are processed. Automated liquid handling provides the greatest consistency, both within assays, as well as among assays performed over extended periods of time. Reaction volume While the standard protocol for this assay specifies 20 µl reactions, the reaction volume can be scaled down to 10 µl, particularly if the assay is performed in 384-well format and/or for reasons of economy. Accurate liquid handling is particularly important when using 10 µl qpcr volumes. When scaling down to 10 µl reaction volumes, the volume of template (DNA Standard, diluted library or control) may also be halved (to 2 µl per reaction), or kept at the 4 µl used for 20 µl reactions. The latter is recommended, as it obviates the need to dispense very small template volumes (i.e. facilitates accuracy). If the template volume is not halved for 10 µl reactions, Cq values for all reactions are expected to be 1 cycle earlier (as compared to using the same volume of template in a 20 µl reaction). This has no impact on the assay, unless the Cq value for DNA Standard 1 is already very low (<3 cycles) on your particular instrument. Please refer to DNA Standard 1 amplifies "too early" in the Data Analysis and Interpretation section for a related discussion. Accurate and reproducible setup of 10 µl reactions in 96- well plates using multi-channel pipettes is challenging. When using 10 µl reaction volumes in 96-well plates, it is important to make sure that plates are properly sealed to prevent evaporation, particularly from those wells along the edges of the plate. 3
4 Reaction volume (continued) Manual setup of 10 μl reactions in 384-well plates is not recommended, unless only a small portion of the plate is used for an assay. When using 20 µl reaction volumes in 384-well plates, it is important to make sure that reaction mixes do not touch the sealing film, as this will lead to inaccuracies in the detection of the fluorescent signal. It is good practice to briefly centrifuge sealed plates prior to thermocycling, regardless of whether the assay is performed in 96- or 384-well plates. Libary concentration and dilutions Libraries and controls must be diluted to fall within the dynamic range of the assay ( pm, which equals pg/µl, or ~ dsdna molecules/µl). Although the standard curve is a straight line, data may not be extrapolated. Calculated concentrations for libraries derived from dilutions that were too concentrated or too dilute (i.e. that returned average Cq values lower than the average Cq value for DNA Standard 1, or higher than the average Cq value of DNA Standard 6) will not be accurate, as the relationship between template concentration and Cq is not linear during the very early and late stages of the assay. If only one dilution of a library was prepared and assayed in such cases, the library will have to be re-quantified using a more appropriate (larger or smaller) initial dilution. If more than one dilution of each library was prepared and assayed, the remaining dilution(s) that fell within the dynamic range of the assay may be used in concentration calculations. Initial library dilutions should be based on estimations from previous experience with libraries of the same typeor prepared using similar workflows and/or on concentration information obtained with other methods during library construction and quality control (e.g. those employing a NanoDrop, Qubit or Bioanalyzer). Since quantification by spectrophotometric and electrophoretic methods are based on different principles than qpcrbased quantification, the correlation between the concentration on which the initial dilution was based, and the concentration determined by qpcr may be poor, particularly for very concentrated or very dilute libraries, or libraries that were over-amplified. Please refer to the Data Analysis and Interpretation section at the end of this document for a more detailed discussion. Guidelines for the dilution of different types of libraries are given in Table 1 on the next page. Contamination and no-template controls The qpcrs carried out using this protocol are capable of amplifying very low amounts of DNA fragments flanked by adapters containing the Illumina P5 and P7 sequence motifs. Suitable templates will be ubiquitous in work areas where Illumina libraries are prepared and amplified. In addition, routine use of the KAPA Library Quantification Kit will generate extremely high numbers of amplicons. Significant contamination of reactions with exogenous template DNA (libraries, DNA Standard or amplicons) will 4 affect the accuracy of calculated library concentrations that are determined using the assay. Good laboratory practice should be observed at all times to avoid contamination of reagents, samples, consumables, pipettes and other equipment, and work areas with libraries, DNA Standards or amplicons. It is highly recommended that no-template controls (NTCs) are included in each assay to detect contamination introduced during reaction setup. NTC qpcrs should return Cq values that are at least 3 cycles later than the average Cq value for Standard 6. The six DNA Standards provided in the kit represent a 10-fold template dilution series. Average Cq values for consecutive Standards are expected to differ by ~3.3 cycles. A systematic decrease in the spacing of amplification curves for consecutive DNA Standards provides another indication of contamination with exogenous template, or contamination of dilute DNA Standards with more concentrated ones. The latter can be avoided by always dispensing the DNA Standards from the lowest to the highest concentration (i.e. from DNA Standard 6 to DNA Standard 1), and using a fresh tip for each Standard. Contamination with human or bacterial DNA from a biological source (i.e. non-library DNA) is not of much concern during library quantification, as the KAPA Library Quantification Primer Premix will only amplify DNA fragments flanked by adapters with binding sites for the quantification primers. Primer-dimer formation is not uncommon in this assay. This is a result of primer design, which is not optimal for qpcr, but dictated by the Illumina flow cell oligo sequences. The cycling times used for library quantification are also significantly longer than those used in typical qpcr applications performed with with KAPA SYBR FAST, thereby further increasing the probability of primer-dimer formation. As long as NTC's return average Cq values that are at least 3 cycles later then the average Cq value for DNA Standard 6, primer-dimer formation should have no impact on quantification. Internal, process or dilution controls Most Illumina libraries will have to be diluted to fall within the dynamic range of the KAPA Library Quantification assay ( pm). This step represents the biggest risk to accurate quantification, particularly if libraries are very concentrated and large initial dilutions are required. If more than one dilution of each library is assayed (and falls within the dynamic range of the standard curve), the delta Cq value for consecutive dilutions is usually a good indication of the reliability of calculated library concentrations (see Table 2 on p. 5). Delta Cq values for serial dilutions of a library, do however, not provide any indication of the accuracy of the initial dilution. To control for gross errors during sample dilution (or reaction setup) it is recommended that at least one appropriate internal process or dilution control be included in every assay.
5 Table 1. Factors to be considered when diluting Illumina libraries for the KAPA Library Quantification assay. Library type Amplified library, prepared for direct sequencing Target capture library, after post-capture amplification Target capture library, after pre-capture amplification Unamplified, adapter-ligated library Comments Examples: libraries prepared for WGS, ChIP-Seq, RNA-Seq or amplicon sequencing Optimally amplified libraries should have a concentration in the range of 2 20 nm. A 1/ dilution is recommended as a first approach (diluted library should fall between Standards 2 and 3 on the standard curve). Libraries with a higher concentration have to be diluted more to fall within the dynamic range of the assay. Library concentration after post-capture amplification will be dependent on the specific capture protocol. If you don't have an estimate of the library concentration (based on experience or data from a different quantification method), assay a 1/ dilution of libraries as a first approach. Use the results to adjust this dilution for future quantification of libraries produced using the same capture workflow and target library, Single capture workflows typically require ~1 µg of library per hybridization. For multiplexed capture, the requirement for each library is lower (total amount divided by number of libraries captured together). Library concentrations after pre-capture amplification are typically in the range of µl/µg ( µm), depending on the library volume and average fragment size. If you don't have an estimate of the library concentration (based on experience or a different quantification method), assay a 1/ dilution of libraries as a first approach (diluted libraries should fall between Standards 1 and 3 on the standard curve). Examples: libraries generated in PCR-free workflows, libraries quantified to determine optimal number of amplification cycles For libraries prepared from 100 ng 1 µg input DNA, try a 1/5 000 dilution as a first approach (diluted libraries should fall between Standards 1 and 3 on the standard curve). For unamplified libraries prepared from lower inputs ( ng), a 1/100 dilution is a good starting point (diluted libraries should fall between Standards 2 and 4 on the standard curve). Libraries prepared from 10 ng input DNA or less should not be diluted prior to library quantification. Internal, process or dilution controls (continued) One or more of the following may be used for this purpose: The KAPA Library Quantification Dilution Control (product code: KK4906). This internal control or "Standard 0" is a quality-controlled 200 pm solution of the same linear, 452 bp dsdna fragment comprising the DNA Standards. An Illumina library that has previously been quantified with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit, and that has been sequenced successfully. PhiX, a control library supplied by Illumina. To be most effective, the internal control should be processed in exactly the same way as the libraries to be assayed, i.e. the same initial dilution and serial dilutions (if applicable) should be prepared, and replicate reactions should be set up with each dilution of the internal control. Each of the different types of internal controls listed above has advantages and disadvantages: The KAPA Library Quantification Internal Control ("Standard 0") is subject to the same rigorous quality control as the set of DNA Standards supplied in the KAPA Library Quantification Kit. Absolute concentration and minimal lot-to-lot variation is guaranteed. At 200 pm, Standard 0 is, however, more dilute than most Illumina libraries. If Standard 0 is diluted to the same extent as the samples to be assayed, the Cq values for the dilutions are therefore likely to be a few cycles higher than for the libraries. This is acceptable, as long as at least one of the dilutions of Standard 0 falls within the dynamic range of the assay. Table 2: Expected Delta Cq values for consecutive library dilutions of different magnitudes Fold dilution Expected Delta Cq Acceptable Delta Cq* * If the average delta Cq for consecutive dilutions does not fall within this range, an error most likely occurred during the preparation of sample dilutions. Alternatively, it may point to contamination (smaller delta Cq) or inhibition (larger delta Cq) of the assay. 5
6 Internal, process or dilution controls (continued) An existing library that has been sequenced previously is a valuable internal control, as both qpcr-based concentration and cluster density data will be available for such a control. The absolute concentration of a control comprised of an existing library will, however, not have been validated, and the biggest risk is degradation of DNA quality over time particularly if the same library is used repeatedly as an internal control. The best approach is to select one or more internal controls from a pool of recently prepared and sequenced libraries, which have been stored in a buffered solution at -20 o C, and have not been subjected to too many freeze/thaw cycles. Single-use aliquots of such libraries can be prepared and stored at -20 o C for use as controls. The use of PhiX as an internal library quantification control has similar advantages as using a previously sequenced library. However, PhiX is not recommended if only one internal control is included in a library quantification assay, due to reported batch-to-batch variation in the given concentration and average fragment length of different lots. Kindly note that the KAPA Library Quantification Internal Control (Standard 0) is not suitable as a sequencing control, as it comprises a PCR amplicon, i.e. is a homogenous solution of a single species of dsdna. Replicates, data reliability, throughput and persample cost qpcr is an extremely sensitive measurement technique that is vulnerable to variation arising from a number of sources. Even if the greatest attention is paid to liquid handling, inherent sources of variability such as instrument performance and sampling error lead to unavoidable scatter among replicate data points. Technical replicates are necessary and valuable because they mitigate the effects of variability in the following ways: They provide insurance against gross errors or failures with respect to individual reactions, which may be identified as outliers and excluded from the analysis. They enable the calculation of replicate averages, thereby discounting the impact of individual data points that are scattered around the population mean. They provide an indication of the variability in the data, and a means to gauge the reliability of the assay. They may assist with troubleshooting, optimization and process control, for example by providing some indication of the frequency, nature and/or scale of liquid handling errors. Triplicate qpcrs are recommended for DNA Standards, library samples and controls. A set of triplicate qpcrs can be generated in several ways: By preparing a bulk reaction (volume = 3 x reaction volume) for each DNA Standard, library or control, and splitting this across three PCR tubes or wells of a qpcr plate. This is not recommended, as it only controls for variation associated with qpcr instrumentation and plasticware. By preparing three individual reactions (each with volume = reaction volume) for each DNA Standard, library or control. This controls for some of the variation associated with liquid handling, as well as qpcr instrumentation and plasticware. It is the most common form of replication, and the one most compatible with high-throughput workflows. By performing three independent dilutions of each library to be assayed, then preparing three separate reactions, each using a replicate dilution as template. This form of replication also controls for liquid handling associated with sample dilution, but is impractical when large numbers of libraries are assayed. The number of replicates must always be the same for DNA Standards and libraries/controls, and may be reduced to two in order to increase throughput, and reduce persample cost. When selecting the best strategy for your workflow and throughput requirements, it is important to keep in mind that the reliability of data is inversely proportional to the number of replicates. Reducing the number of replicates also increases the risk of having to re-assay libraries for which reliable data was not obtained. The risk of reducing the number of replicate qpcrs can be mitigated by designing workflows in such a way that at least two serial dilutions of each library are always assayed. Because of the quantitative nature of real-time PCR, such dilutions constitute technical replicates, provided that both/all dilutions fall within the dynamic range of the assay. The relationship between replicates, data reliability, throughput and per-sample costs is summarized in Table 3 on the next page. An assay configuration based on three replicates of a single dilution of each library, with at least one internal and one no template control represents the best compromise between these factors. Assay automation The repetitive nature of the KAPA Library Quantification assay makes it amenable to automation, and the use of automated liquid handling platforms is highly recommended for high-throughput library quantification workflows. Automated methods for the KAPA Library Quantification assay typically consist of two parts, namely sample dilution and qpcr setup. To ensure the highest degree of accuracy and lowest consumption of precious library material, libraries are diluted in a serial fashion, starting with 1 2 µl of library in a total volume <200 µl. Subsequent dilutions in the series may have fixed or variable intervals, depending on the nature of the libraries to be quantified. Covering a range of dilutions from 1/50 to 1/ across six columns of a 96-well plate provides a versatile dilution series that should provide for any type of library to be quantified (ref. Table 1), whilst keeping dilution intervals small. For larger sample numbers (>32), the number of dilutions may be reduced, and dilution intervals increased 6
7 Table 3. Relationship between replicates, reliability of data, throughput and per-sample cost. Number of replicates Dilutions per library 1 Reliability of data Throughput Persample cost Number of libraries that can be assayed per plate 3 96-well format 384-well format Number of libraries that can be assayed with a complete kit 4 96-well format 384-well format 3 3 Very high Lowest Highest High Low High Acceptable 2 Medium Medium High Low High Acceptable 2, with increased risk of repeats Acceptable 2, with high risk of repeats Acceptable 2, with increased risk of repeats Low, with high risk of repeats Very low. This configuration is not recommended. Medium Medium High Low Medium Medium High Low Highest Lowest Library dilutions that fall within the dynamic range of the assay, i.e. yield useable data. 2 Especially if sample throughput is low or automated liquid handling is used for high-throughput library dilutions and reaction setup, internal controls are included, and variation related to instrumentation and consumables has been minimized. 3 Calculations are based on the following assumptions: reaction volume is 20 µl for for 96-well format and 10 µl for 384-well format; number of replicates for DNA Standards are the same as for samples; 384-well plates are fully utilized. Where a range is given, the lower number of libraries is based on an assay configuration that includes at least one no template control (NTC) and one internal control, whereas the upper number is based on an assay configuration that excludes all types of controls to maximize the number of libraries that can be assayed. Assay configurations that include controls are always recommended. 4 A complete kit contains 80 µl of each DNA Standard and qpcr mix and primers for 500 x 20 µl or x 20 µl reactions. The qpcr reagents are always the limiting component, irrespective of whether 2 or 4 µl DNA Standard is used per 10 µl reaction. Calculations are based on a 20 µl reaction volume for 96-well format and a 10 µl reaction volume for 384-well format, and assumes 10% of reagent wastage. Incomplete kits (containing qpcr mix and primers only) may be purchased to utilize leftover DNA Standards from complete kits. to limit the number of dilution plates. Assay automation (continued) To ensure accurate and reliable results, sample carry-over to less dilute library solutions must be prevented, and each column of dilutions must be mixed thoroughly before the next dilution is made. Use fresh tips for each serial dilution, or wash tips between dilutions. Keep transfer volumes between dilutions as large as possible, and well within the specifications for the pipetting device used for these transfers. qpcr setup consists of three simple steps, namely (i) broadcasting of qpcr Master Mix (including primers, passive reference dye and water, if needed) into replicate wells for each DNA Standard, library dilution or control to be assayed, (ii) transfer of template, and (iii) thorough mixing. For the standard curve, template consists of the appropriate volume (2 or 4 µl) of the appropriate, prediluted DNA Standard supplied in the kit. For libraries and controls, template is selected from the desired dilution(s) prepared during the first part of the assay. The capabilities of your liquid handling platform software will determine whether the same dilution(s) have to be assayed across all libraries, or whether dilutions can be "cherry-picked", i.e. whether very diverse libraries can be quantified in a single assay. A detailed protocol for qpcr setup may be found in the KAPA Library Quantification Kit Technical Data Sheet. Pre-validated KAPA Library Quantification methods are available from selected suppliers of automated liquid handling platforms. Please contact support@ kapabiosystems.com for more information. Since the assay is easy to automate, and plate layouts may already be integrated with other NGS sample preparation pipeline parameters, or determined by your LIMS system, inhouse development of a tailored, automated solution 7
8 may, however, be preferable. Data Analysis and Interpretation DNA Standard 1 amplifies "too early" Due to the design specifications and broad dynamic range of the KAPA Library Quantification assay, DNA Standard 1 has a higher copy number than samples that are typically analyzed by qpcr, particularly in relative quantification assays. As a result, Standard 1 (and any samples that were not sufficiently diluted) may return very early Cq values and/or an increasing fluorescent signal during the automatic baseline determination performed by the qpcr instrument. Most qpcr cyclers establish a signal baseline during the first 3 15 cycles of the qpcr, and any increase in fluorescence during those cycles is interpreted as background. This can impact the standard curve, as the Standard 1 signal may be regarded as "background". Alternatively, DNA Standard 1 may return a delayed Cq value. It is usually possible to tell whether this is an issue by examining the amplification plots. If the baseline-corrected amplification plot for Standard 1 or any diluted library or internal control with a very low Cq value has an unusual shape, or begins well below the baseline for samples with later Cq values, it is likely that baseline determination/ subtraction was not successful for that standard, library dilution or control. Another way to judge whether an early Cq value has created problems during data analysis is to confirm that the "Cq spacing" between consecutive DNA standards is ~3.32 cycles across the entire 10-fold dilution series (all six DNA Standards). Similarly, consecutive 10- fold dilutions of a library should have a delta Cq of ~3.32 cycles. The expected delta Cq for consecutive dilutions of different magnitudes are given in Table 2 on p. 5. The preferred course of action is to manually decrease the number of cycles over which baseline subtraction/ correction is performed (to cycles 1 3). Please consult your qpcr instrument manual for guidelines on how to manually adjust this setting. If this does not permanently resolve the problem, DNA Standard 1 may be omitted from future assays, i.e. the standard curve may be generated using Standards 2 6 only. Bear in mind though that library dilutions may have to be increased to ensure that all diluted samples fall within the dynamic range of Standards 2 6. Size-adjustment calculation Once the average Cq value for each library dilution has been converted to concentration (in pm) using the standard curve, a size-adjustment calculation has to be performed to compensate for any difference between the length of the DNA Standard (452 bp) and the average fragment length of libraries that were assayed. The size-adjustment calculation is a simple multiplication of the concentration derived from the standard curve with the ratio between the size of the DNA Standard (452 bp) and the average fragment size for that particular library. 8 Please refer to the Detailed Protocol and Working example in the KAPA Library Quantification Kit Technical Data Sheet for full details. The size-adjustment calculation is needed because the fluorescent signal generated in SYBR Green I-based qpcr quantification is dependent on the total mass (length) of DNA. A longer DNA fragment will carry more of the intercalating dye (reporter) molecules than a shorter fragment; hence, the relative fluorescence will be higher (and Cq value lower) for a population of long DNA fragments, compared to a population of shorter fragments with the same copy number or concentration. If the average fragment length of the Illumina libraries that are being quantified is significantly shorter or longer than 452 bp, the size-adjustment must be done to ensure that calculated library concentrations are accurate and reliable. Melt curve analysis A melt curve analysis is typically included at the end of SYBR Green I-based qpcr assays to provide information about the specificity of the reaction. In library quantification melt curve analysis is less relevant, as the template being amplified is not comprised of a single DNA fragment of defined length and GC content, but is a heterogenous population of molecules, with a range of lengths and GC contents. Unlike the melt curve for a single amplicon, the melt curve for an Illumina library is a "composite" analysis, representing an average across the entire population of library fragments. It is also important to keep in mind that library samples are expected to reach their quantification cycle (Cq) relatively early, whereas the melt curve analysis is only performed after 35 cycles, i.e. at a time when substrate depletion has occurred, and amplification artifacts that are no longer representative of the original template have been generated. This complicates the interpretation of melt curves generated in library quantification assays. Nevertheless, we have found melt curve analysis useful for the identification of carry-over adapter-dimer in Illumina libraries (Figure 2). Adapter-dimers, formed during library construction with full-length adapters, are very efficiently amplified in the KAPA Library Quantification assay, and will lead to an overestimation of library concentration if present in significant quantities. The melt curve analysis simply has diagnostic value, and does not offer a way to compensate for the contribution of adapter-dimer to the calculated library concentration. Please note that melt curves for the DNA Standard included in KAPA Library Quantification Kits for Illumina platforms display a very characteristic double peak. This is the result of differential local melting in the 452 bp linear template (which has been confirmed by in silico melt curve modelling), and is not indicative of non-specific amplification.
9 Figure 2. Melt curves for libraries and DNA Standards generated with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit for Illumina platforms. Libraries in the top panel contain no or a negligible amount of carry-over adapter-dimer. Libraries in the bottom panel contain an unacceptable amount of adapterdimer, which have contributed to an inflated calculated library concentration. Note the characteristic double melt peak for the DNA Standard. Correlation between library concentration and cluster density The KAPA Library Quantification Kit has become an integral part of Illumina sequencing workflows, in both low- and high-throughput settings. The assay and reagents are capable of yielding reproducible, accurate and reliable results. The guidelines and instructions provided in this document and the KAPA Library Quantification Kit Technical Data Sheet should enable both new and experienced users to determine whether each data set generated with the assay is reliable. Since the metrics used to evaluate data cannot rule out gross errors in library dilutions, calculated library concentrations can only be accepted with confidence if an internal, process or dilution control was included in the assay. Even if data generated with the assay is determined to be reliable, there is no guarantee that libraries diluted for flow cell loading will yield optimal number of clusters. Reasons for a possible discrepancy between calculated library concentration and cluster density include the following: There are multiple liquid handling steps between library quantification and flow cell loading, all of which are error-prone. Cluster amplification is a complex process with many variables, some of which are instrument-related. qpcr-based quantification with the engineered KAPA SYBR FAST DNA Polymerase ensures that all the molecules in a complex DNA population are "counted" with high and similar efficiency, irrespective of fragment length or GC content. Cluster amplification (bridge PCR) is, however, performed with a different enzyme and is more challenging. Cluster generation may therefore not be equally efficient for all library fragments. Anecdotal evidence suggests that not all library types cluster similarly on a specific instrument, and that libraries of the same type do not yield the same number of clusters on different instruments of the same model when loaded at a specific concentration. Reasons for this fall outside the scope of this document. The reader is encouraged to explore the SeqAnswers blog for insightful NGS community forum discussions. Ultimately, the correlation between library concentration determined with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit and cluster density must be determined empirically for your libraries, instrumentation and workflow. To discover and define this correlation, it is important that the assay is performed meticulously, and that data is analyzed and interpreted correctly. If you are new to NGS and qpcrbased quantification, the following guidelines may be helpful: Assay different dilutions of a few selected (preferably previously sequenced) libraries on different days, to ensure that reproducible qpcr data is obtained. As indicated previously, fresh dilutions of test libraries used for this evaluation should be prepared for each assay. Variation of 10% in the concentration of a library calculated from different dilutions (within an assay) or in separate assays, is generally regarded as acceptable. Perform cluster amplification with the same set of test libraries, more than once, on the instrument(s) that will be used routinely. This is important to determine the variability of the cluster amplification process. Establish and maintain a database of library concentrations (determined with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit and any other quantification methods that are being used), as well as cluster density data, generated for different library types and/ or instruments. This data will enable you to define the correlation between calculated library concentration and cluster density for your specific situation, and will also be invaluable for process optimization, quality control and troubleshooting. 9
10 Library concentrations determined by qpcr vs other methods Most NGS workflows employ more than one library quantification method. Data generated with a spectrophotometer (e.g. NanoDrop ), a fluorometric (e.g. Qubit or PicoGreen ) assay, or an electrophoretic device (e.g. a Bioanalyzer, TapeStation or LabChip GX) is often used to determine the most appropriate initial dilutions for accurate, qpcr-based quantification using the KAPA Library Quantification Kit. The conventional wisdom is that library concentrations determined by qpcr should be lower than those determined with spectrophotometric, fluorimetric and electrophoretic methods, as qpcr only "counts" those molecules that have the correct adapter on each end, whereas other assays "count" total DNA. However, this is often not the case, and a weak correlation between library concentrations determined with different quantification method is fairly common. The primary reasons are the following: Different quantification methods "count different things". Different quantification methods are prone to inaccuracy for different reasons. Library amplification can have a profound impact on library quantification. When comparing library concentrations determined with different quantification methods, consider the following: Spectrophotometric methods for DNA quantification are sensitive to contaminants that absorb in the UV spectrum. These include organic solvents (e.g. ethanol) used during library purification/cleanup procedures. Electrophoretic assays are not primarily designed for quantification, and may have high inherent variation when it comes to quantification (as opposed to size determination). Quantification is typically dependent on the integrity of assay components such as DNA ladders and fluorescent dyes included in the gel matrix, which are often sensitive to light exposure and/or damage induced by repeated freezing and thawing. Library concentrations determined using an electrophoretic assay may or may not correlate well with concentrations determined with other methods, and the extent of the correlation (or lack thereof) could be highly variable. Amplified libraries that are ready for sequencing should be comprised of DNA fragments that are fully doublestranded and free of inhibitors/contaminants that affect fluorimetric and qpcr assays employing dsdnabinding dyes. Library amplification also enriches the library preparation for sequenceable molecules (e.g. fragments flanked by two adapters in the correct configuration for cluster amplification). Library concentrations determined by Qubit /PicoGreen and the KAPA Library Quantification Kit are therefore expected to correlate fairly well for optimally-amplified libraries. 10 In practice, many libraries are "over-amplified", and are not comprised of individual, fully double-stranded fragments. Accurate quantification is only achievable by qpcr-based quantification, and library concentrations determined with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit are typically higher than those obtained by Qubit / PicoGreen, for reasons outlined below: During the first few library amplification cycles, each successive round of denaturation, primer annealing and extension produces more or less double the number (mass) of full-length, double-stranded library fragments. However, as thermocycling continues, primers are depleted (in NGS library amplification, this happens before dntps become limiting, and fairly early in the reaction if the amount of library used as template exceeds ~100 ng). At this point, denatured, singlestranded library molecules are no longer converted to double-stranded DNA. Subsequent rounds of denaturation, annealing and extension doesn't produce additional DNA (library yields are "capped"), and simply results in the separation of complementary DNA strands. Because libraries are extremely heterogenous, denatured fragments are statistically unlikely to ever re-anneal to their complementary strands. Primer depletion is therefore followed by imperfect annealing of non-complementary partners, driven by common adapter sequences. This results in the formation of socalled "daisy-chains" or "tangled knots", comprising large assemblies of improperly annealed, partially double-stranded, heteroduplex DNA. These species migrate slower and are observed as secondary, higher molecular weight peaks during the electrophoretic analysis of amplified libraries. However, they are typically comprised of library molecules of the desired length, which are individualized during denaturation prior to probe hybridization (in target capture workflows) or cluster amplification. Since these heteroduplexes contain significant portions of single-stranded DNA, over-amplification leads to the under-quantification with assays employing dsdna-binding dyes. Over-amplification does not impact qpcr-based quantification, which involves initial denaturation of heteroduplexes, and real-time detection of perfectly complementary molecules that accumulate before substrate depletion occurs. Over-amplification should, however, it should be avoided in order to achieve optimal library quality. Please refer to the KAPA Library Preparation or contact support@kapabioystems.com for assistance with the optimization of library amplification parameters. Libraries may be quantified after adapter-ligation, prior to library amplification. The conversion of input DNA to adapter-ligated library is an important library construction metric, as this ultimately determines library diversity. Prior to library amplification, the forked portions of Illumina adapters are still single-stranded. Assays relying on dsdna-binding dyes are likely to underestimate the concentrations of unamplified
11 libraries, and the degree of under-quantification depends on the adapter design and library fragment length (i.e. the proportion of each library molecule that is single-stranded). For reasons outlined above, qpcr is recommended for the accurate quantification of unamplified, adapter-ligated libraries. The 10X Primer Premix included in the KAPA Library Quantification Kit for Illumina platforms is suitable for the quantification of unamplified libraries prepared with "full-length" adapters. For libraries prepared with truncated or custom adapters, the DNA Standards and qpcr Master Mix can be used in combination with user-supplied primers. Please contact com for more information. 11
12 Restrictions and Liabilities This technical data sheet is provided "as is" and Kapa Biosystems assumes no responsibility for any typographical, technical, or other inaccuracies. The document is subject to being changed, without notice, in future editions. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Kapa Biosystems disclaims all warranties, either express or implied, with regard to this technical data sheet and any information contained herein, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Kapa Biosystems shall not be liable for errors or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, use, or performance of this document or of any information contained herein. This document might contain references to third party sources of information, hardware or software, products, or services and/or third party web sites (collectively the Third-Party Information ). Kapa Biosystems does not control, and is not responsible for, any Third-Party Information. The inclusion of Third-Party Information in this document does not imply endorsement by Kapa Biosystems of the Third-Party Information or the third party in any way. Kapa Biosystems does not in any way guarantee or represent that you will obtain satisfactory results from using Kapa Biosystems products as described herein. The only warranties provided to you are included in the Limited Warranty enclosed with this document. You assume all risk in connection with your use of Kapa Biosystems products. Kapa Biosystems is not responsible nor will be liable in any way for your use of any software or equipment that is not supplied by Kapa Biosystems in connection with your use of Kapa Biosystems products. Note to Purchaser: Limited Product Warranty Any product that does not meet the performance standards stated in the product specification sheet will be replaced at no charge. This warranty limits our liability to the replacement of the product. No other warranties of any kind, express or implied, including without limitation, implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, are provided by Kapa Biosystems. Kapa Biosystems shall have no liability for any direct, indirect, consequential or incidental damages arising out of the use, the results of use or the inability to use any product. Note to Purchaser: Limited License KAPA Library Quantification Kits are developed, designed and sold exclusively for research purposes and in vitro use. Neither the product, nor any individual component, has been tested for use in diagnostics or for drug development, nor is it suitable for administration to humans or animals. Please refer to the MSDS, which is available on request. Certain applications of this product are covered by patents issued to parties other than Kapa Biosystems and applicable in certain countries. Purchase of this product does not include a license to perform any such applications. Users of this product may therefore be required to obtain a patent license depending upon the particular application and country in which the product is used. Prism is a trademark of Applera Corporation. icycler is a trademark of Bio-Rad. TruSeq, HiSeq and Illumina are trademarks or registered trademarks of Illumina. SYBR, Qubit and PicoGreen are registered trademarks or trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation. LabChip is a registered trademark of PerkinElmer. LightCycler is a registered trademark of Roche. NanoDrop is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific. For support please contact: support@kapabiosystems.com Boston, Massachusetts, United States Int. Tel: Tel: KAPA BIO Fax: sales@kapabiosystems.com Cape Town, South Africa Tel: Fax: sales@kapabiosystems.com
Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide
 Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Quantification Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 Consumables and Equipment 6 Select Control Template 8 Dilute qpcr Control Template
Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Quantification Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 Consumables and Equipment 6 Select Control Template 8 Dilute qpcr Control Template
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide
 qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Topics 3 Introduction 5 User-Supplied Consumables and Equipment 7 Select Template 8 Dilute qpcr Template 9 Dilute Libraries 10 Prepare Reaction
qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Topics 3 Introduction 5 User-Supplied Consumables and Equipment 7 Select Template 8 Dilute qpcr Template 9 Dilute Libraries 10 Prepare Reaction
FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES
 BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Protocol. Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR
 Protocol Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR Copyright 2008, 2010 Applied Biosystems. All rights reserved. Ambion and Applied Biosystems products are for Research Use Only.
Protocol Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR Copyright 2008, 2010 Applied Biosystems. All rights reserved. Ambion and Applied Biosystems products are for Research Use Only.
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix
 Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix Optimized for 98C Denaturation Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 lucigen@lucigen.com
Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix Optimized for 98C Denaturation Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 lucigen@lucigen.com
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform
 QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA
 Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform
 Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform Introduction, 3 Sample Prep Workflow, 4 Best Practices, 5 DNA Input Recommendations,
Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform Introduction, 3 Sample Prep Workflow, 4 Best Practices, 5 DNA Input Recommendations,
Cluster Generation. Module 2: Overview
 Cluster Generation Module 2: Overview Sequencing Workflow Sample Preparation Cluster Generation Sequencing Data Analysis 2 Cluster Generation 3 5 DNA (0.1-5.0 μg) Library preparation Single Cluster molecule
Cluster Generation Module 2: Overview Sequencing Workflow Sample Preparation Cluster Generation Sequencing Data Analysis 2 Cluster Generation 3 5 DNA (0.1-5.0 μg) Library preparation Single Cluster molecule
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Whole genome Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform
 Whole genome Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform Introduction, 2 Sample Prep Workflow, 3 Best Practices, 4 DNA Input Recommendations, 6
Whole genome Bisulfite Sequencing for Methylation Analysis Preparing Samples for the Illumina Sequencing Platform Introduction, 2 Sample Prep Workflow, 3 Best Practices, 4 DNA Input Recommendations, 6
Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR
 APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012
 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit. Performance Characteristics
 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit Performance Characteristics Monolythix, Inc. 4720 Calle Carga Camarillo, CA 93012 Tel: (805) 484-8478 monolythix.com Page 2 of 9 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic
MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit Performance Characteristics Monolythix, Inc. 4720 Calle Carga Camarillo, CA 93012 Tel: (805) 484-8478 monolythix.com Page 2 of 9 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic
2.500 Threshold. 2.000 1000e - 001. Threshold. Exponential phase. Cycle Number
 application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 18/2004. Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data
 Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco Real-Time PCR System
 Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco System Introduction Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is converted into a functional product. This process
Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco System Introduction Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is converted into a functional product. This process
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr
 DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
Sequencing Guidelines Adapted from ABI BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit and Roswell Park Cancer Institute Core Laboratory website
 Biomolecular Core Facility AI Dupont Hospital for Children, Rockland Center One, Room 214 Core: (302) 651-6712, Office: (302) 651-6707, mbcore@nemours.org Katia Sol-Church, Ph.D., Director Jennifer Frenck
Biomolecular Core Facility AI Dupont Hospital for Children, Rockland Center One, Room 214 Core: (302) 651-6712, Office: (302) 651-6707, mbcore@nemours.org Katia Sol-Church, Ph.D., Director Jennifer Frenck
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR. Results Interpretation Guide
 PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol. Stack Lab
 Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol Stack Lab Overview Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) differs from regular PCR by including in the reaction fluorescent reporter molecules that
Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol Stack Lab Overview Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) differs from regular PCR by including in the reaction fluorescent reporter molecules that
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR
 Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
Illumina GAIIx Sequencing Service
 Illumina GAIIx Sequencing Service As researchers continue to develop novel applications for next generation sequencers, the technology landscape of the industry continues to advance at an unprecedented
Illumina GAIIx Sequencing Service As researchers continue to develop novel applications for next generation sequencers, the technology landscape of the industry continues to advance at an unprecedented
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR. so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed
 Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit
 USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix. Protocol
 TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
Human Herpes Virus 1 (Herpes simplex type 1) genesig Standard Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Herpes Virus 1 (Herpes simplex type 1) Capsid assembly and DNA maturation gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Herpes Virus 1 (Herpes simplex type 1) Capsid assembly and DNA maturation gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) genesig Standard Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
PreciseTM Whitepaper
 Precise TM Whitepaper Introduction LIMITATIONS OF EXISTING RNA-SEQ METHODS Correctly designed gene expression studies require large numbers of samples, accurate results and low analysis costs. Analysis
Precise TM Whitepaper Introduction LIMITATIONS OF EXISTING RNA-SEQ METHODS Correctly designed gene expression studies require large numbers of samples, accurate results and low analysis costs. Analysis
Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit
 Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
NimbleGen SeqCap EZ Library SR User s Guide Version 3.0
 NimbleGen SeqCap EZ Library SR User s Guide Version 3.0 For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Copyright 2011 Roche NimbleGen, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Editions Version
NimbleGen SeqCap EZ Library SR User s Guide Version 3.0 For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Copyright 2011 Roche NimbleGen, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Editions Version
HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr)
 Techne qpcr test Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein
Techne qpcr test Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein Barr) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Herpes Virus 4 (Epstein
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System
 qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine
 Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine Kyle Dobbs and Peter Hansen Table of Contents Overview..3 Setup Reaction Guidelines 4 Starting up the Software 5 Setup Protocol on Software 6 Setup
Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine Kyle Dobbs and Peter Hansen Table of Contents Overview..3 Setup Reaction Guidelines 4 Starting up the Software 5 Setup Protocol on Software 6 Setup
Paired-End Sample Preparation Guide
 Paired-End Sample Preparation Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Sample Prep Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 DNA Input Recommendations 7 Kit Contents 9 Consumables and Equipment 11 Fragment DNA 13
Paired-End Sample Preparation Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Sample Prep Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 DNA Input Recommendations 7 Kit Contents 9 Consumables and Equipment 11 Fragment DNA 13
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
Intended Use: The kit is designed to detect the 5 different mutations found in Asian population using seven different primers.
 Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners
 Technical Note: Illumina Systems and Software Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners There are multiple Universal Array and scanner options for running Illumina DASL and GoldenGate
Technical Note: Illumina Systems and Software Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners There are multiple Universal Array and scanner options for running Illumina DASL and GoldenGate
TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5
 Data Sheet: Targeted Resequencing TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5 A new and improved amplicon sequencing solution for interrogating custom regions of interest. Highlights Figure 1: TruSeq Custom Amplicon Workflow
Data Sheet: Targeted Resequencing TruSeq Custom Amplicon v1.5 A new and improved amplicon sequencing solution for interrogating custom regions of interest. Highlights Figure 1: TruSeq Custom Amplicon Workflow
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results
 How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
Fluorescent dyes for use with the
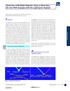 Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Welcome to Pacific Biosciences' Introduction to SMRTbell Template Preparation.
 Introduction to SMRTbell Template Preparation 100 338 500 01 1. SMRTbell Template Preparation 1.1 Introduction to SMRTbell Template Preparation Welcome to Pacific Biosciences' Introduction to SMRTbell
Introduction to SMRTbell Template Preparation 100 338 500 01 1. SMRTbell Template Preparation 1.1 Introduction to SMRTbell Template Preparation Welcome to Pacific Biosciences' Introduction to SMRTbell
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System
 PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
Oligonucleotide Stability Study
 Oligonucleotide Stability Study IDT is performing a long term study of oligo stability. The study has been ongoing for 2 years and has tested oligo stability under various conditions. An overview of the
Oligonucleotide Stability Study IDT is performing a long term study of oligo stability. The study has been ongoing for 2 years and has tested oligo stability under various conditions. An overview of the
AxyPrep TM Mag PCR Clean-up Protocol
 AxyPrep TM Mag PCR Clean-up Protocol Intro The AxyPrep Mag PCR Clean-up kit utilizes a unique paramagnetic bead technology for rapid, high-throughput purification of PCR amplicons. Using this kit, PCR
AxyPrep TM Mag PCR Clean-up Protocol Intro The AxyPrep Mag PCR Clean-up kit utilizes a unique paramagnetic bead technology for rapid, high-throughput purification of PCR amplicons. Using this kit, PCR
Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide
 5 cdna Reverse Primer Oligo d(t) or random hexamer Synthesis of 1st cdna strand 3 5 cdna Applied Biosystems 7300/7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide Introduction
5 cdna Reverse Primer Oligo d(t) or random hexamer Synthesis of 1st cdna strand 3 5 cdna Applied Biosystems 7300/7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide Introduction
Protocol 001298v001 Page 1 of 1 AGENCOURT RNACLEAN XP IN VITRO PRODUCED RNA AND CDNA PURIFICATION
 Page 1 of 1 AGENCOURT RNACLEAN XP IN VITRO PRODUCED RNA AND CDNA PURIFICATION Please refer to http://www.agencourt.com/technical for updated protocols and refer to MSDS instructions when handling or shipping
Page 1 of 1 AGENCOURT RNACLEAN XP IN VITRO PRODUCED RNA AND CDNA PURIFICATION Please refer to http://www.agencourt.com/technical for updated protocols and refer to MSDS instructions when handling or shipping
ncounter Gene Expression Assay Manual Total RNA and Cell Lysate Protocols
 ncounter Gene Expression Assay Manual Total RNA and Cell Lysate Protocols v.20090807 For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Limited License Subject to the terms and conditions of
ncounter Gene Expression Assay Manual Total RNA and Cell Lysate Protocols v.20090807 For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Limited License Subject to the terms and conditions of
The RNAi Consortium (TRC) Broad Institute
 TRC Laboratory Protocols Protocol Title: One Step PCR Preparation of Samples for Illumina Sequencing Current Revision Date: 11/10/2012 RNAi Platform,, trc_info@broadinstitute.org Brief Description: This
TRC Laboratory Protocols Protocol Title: One Step PCR Preparation of Samples for Illumina Sequencing Current Revision Date: 11/10/2012 RNAi Platform,, trc_info@broadinstitute.org Brief Description: This
Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene. genesig Advanced Kit. DNA testing
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Epstein Barr Virus (Human Herpes virus 4) nonglycosylated membrane protein (BNRF1) gene genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere...
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds. Overview. Data Analysis Tutorial
 Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
RT31-020 20 rxns. RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl
 Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
USER GUIDE. Encore PART NOS. 8041 and 8042. SP Rapid Library Systems
 USER GUIDE Encore PART NOS. 8041 and 8042 SP Rapid Library Systems Patents, Licensing and Trademarks 2012 2013 NuGEN Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Encore, Ovation and Applause families of
USER GUIDE Encore PART NOS. 8041 and 8042 SP Rapid Library Systems Patents, Licensing and Trademarks 2012 2013 NuGEN Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Encore, Ovation and Applause families of
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
How To Use An Enzymatics Spark Dna Sample Prep Kit For Ion Torrent
 SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit Ion Torrent (SPK0002-V08) Frequently Asked Questions Under what circumstances would I use SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit for Ion Torrent? Enzymatics SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit for Ion
SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit Ion Torrent (SPK0002-V08) Frequently Asked Questions Under what circumstances would I use SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit for Ion Torrent? Enzymatics SPARK DNA Sample Prep Kit for Ion
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
Troubleshooting Guide for DNA Electrophoresis
 Troubleshooting Guide for Electrophoresis. ELECTROPHORESIS Protocols and Recommendations for Electrophoresis electrophoresis problem 1 Low intensity of all or some bands 2 Smeared bands 3 Atypical banding
Troubleshooting Guide for Electrophoresis. ELECTROPHORESIS Protocols and Recommendations for Electrophoresis electrophoresis problem 1 Low intensity of all or some bands 2 Smeared bands 3 Atypical banding
Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests
 Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests Role in quality management system Quality Control (QC) is a component of process control, and is a major element of the quality management
Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests Role in quality management system Quality Control (QC) is a component of process control, and is a major element of the quality management
Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit Guide
 Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit Guide Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2009, 2013 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means
Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit Guide Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Agilent Technologies Notices Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2009, 2013 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means
TruSeq DNA Methylation Library Preparation Guide
 TruSeq DNA Methylation Library Preparation Guide Kit Contents 3 Consumables and Equipment 4 Preparation 5 Quality Control of Bisulfite-Converted DNA 6 TruSeq DNA Methylation Kit Protocol 7 Sequencing the
TruSeq DNA Methylation Library Preparation Guide Kit Contents 3 Consumables and Equipment 4 Preparation 5 Quality Control of Bisulfite-Converted DNA 6 TruSeq DNA Methylation Kit Protocol 7 Sequencing the
360 Master Mix. , and a supplementary 360 GC Enhancer.
 Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
Illumina Sequencing Technology
 Illumina Sequencing Technology Highest data accuracy, simple workflow, and a broad range of applications. Introduction Figure 1: Illumina Flow Cell Illumina sequencing technology leverages clonal array
Illumina Sequencing Technology Highest data accuracy, simple workflow, and a broad range of applications. Introduction Figure 1: Illumina Flow Cell Illumina sequencing technology leverages clonal array
quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476
 BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
Co Extra (GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability) Outcomes of Co Extra
 GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
RealLine HCV PCR Qualitative - Uni-Format
 Instructions for use PCR KIT FOR EXTRACTION OF RNA AND REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT FOR HEPATITIS C VIRUS RNA Research Use Only Qualitative Uni Format VBD0798 48 tests valid from: December 2013 Rev11122013
Instructions for use PCR KIT FOR EXTRACTION OF RNA AND REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT FOR HEPATITIS C VIRUS RNA Research Use Only Qualitative Uni Format VBD0798 48 tests valid from: December 2013 Rev11122013
Introduction. Preparation of Template DNA
 Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit
 Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit Store kit at -20 C on receipt (ver. 3-060901) A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you accept the terms and conditions outlined in
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit Store kit at -20 C on receipt (ver. 3-060901) A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you accept the terms and conditions outlined in
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS)
 Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS) A typical RNA Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS) A typical RNA Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma. Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System
 Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green)
 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
DNA quality: electrophoresis, spectrophotometry and fluorometry
 DNA quality: electrophoresis, spectrophotometry and fluorometry Ambika B Gaikwad ambika@nbpgr.ernet.in After isolation of DNA, quantification and analysis of quality are necessary to ascertain the approximate
DNA quality: electrophoresis, spectrophotometry and fluorometry Ambika B Gaikwad ambika@nbpgr.ernet.in After isolation of DNA, quantification and analysis of quality are necessary to ascertain the approximate
MMLV High Performance Reverse Transcriptase
 MMLV High Performance Reverse Transcriptase Cat. Nos. RT80110K and RT80125K Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio).
MMLV High Performance Reverse Transcriptase Cat. Nos. RT80110K and RT80125K Connect with Epicentre on our blog (epicentral.blogspot.com), Facebook (facebook.com/epicentrebio), and Twitter (@EpicentreBio).
Inc. Wuhan. Quantity Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate 1 Plate sealer for 96 wells 4 Standard (liquid) 2
 Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
Quantification of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. 150 tests
 Quantification of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis rep 13E12 For general laboratory and research use only 150 tests Introduction to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that
Quantification of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis rep 13E12 For general laboratory and research use only 150 tests Introduction to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR
 Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4. genesig Standard Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) 150 tests
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory
Application Note. Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics. Kit: A Real-Time PCR Extension
 Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
amplification tech Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye
 amplification tech note 6047 Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye Liz Jordan and Richard Kurtz, Gene Expression Division, io-rad
amplification tech note 6047 Optical Design of CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System Eliminates the Requirement of a Passive Reference Dye Liz Jordan and Richard Kurtz, Gene Expression Division, io-rad
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
VLLM0421c Medical Microbiology I, practical sessions. Protocol to topic J10
 Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
