Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) S urveillance Report 2007 Background Methods
|
|
|
- Edward Stafford
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 27 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services Updated: February 29 Background Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) is a core component of the Emerging Infections Program (EIP) Network sponsored by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The purpose of ABCs is to determine the incidence and epidemiologic characteristics of invasive disease due to Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, group A Streptococcus (GAS), group B Streptococcus (GBS), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The entire EIP Network represents 39.5 million persons in 1 surveillance areas around the United States. More information on the EIP/ABCs Network is found at: In Oregon, the surveillance area for MRSA comprises the Tri-County (Clackamas, Multnomah, and Washington) Portland metropolitan area with a 27 estimated population of 1,596,37. More information on the Oregon ABCs program is found at: Methods An invasive MRSA infection is defined as the isolation of MRSA from a normally sterile body site in a Tri-County resident. Tri-County hospital laboratories submit MRSA isolates to the Oregon State Public Health Laboratory for strain typing (i.e. USA1, USA3, etc.) and forwarding to a CDC laboratory for further characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Additional cases are identified through regular laboratory record reviews. Health record reviews of each case allow standardized reports of demographic characteristics, clinical syndrome manifestations, underlying conditions and diseases, healthcare-associated risk factors, and illness outcome. Cases are classified based on the presence of established healthcare risk factors and time of culture collection in relation to hospital admission. Healthcare-onset (HO-) MRSA infections are those in which the initial culture was collected >48 hours after hospital admission; Healthcareassociated, community-onset (HACO-) MRSA cases are those in which the initial culture was collected 48 hours after hospital admission or evaluation and the medical chart indicates one or more of the following risk factors: previous MRSA colonization or infection, presence of an invasive device or catheter at the time of admission or evaluation, or hospitalization, surgery, dialysis, or resident of a long-term care facility (LTCF) within the year preceding the index culture date; and community-associated (CA-) MRSA cases are those in which the initial culture was collected 48 hours after hospital admission or evaluation and none of above risk factors are noted in the medical record. Additional technical information on surveillance methodology, including data elements collected, healthcare risk factors, clinical manifestations, and underlying diseases and conditions can be found at the EIP/ABCs Network website listed above.
2 Surveillance Results Descriptive Epidemiology In 27, we identified 3 cases of invasive MRSA disease for an overall Figure 1: Incidence of Invasive MRSA Cases, by Infection Type, HO HACO CA Overall incidence of 18.8/1, persons 25 (Figure 1). Of these, 3 (1%) were recurrent cases, reported in those with a 2 previous invasive MRSA infection. Since surveillance began in 24, when 44 cases were reported (26.5/1,), the incidence of invasive MRSA disease has decreased 29%. The mean and median ages of cases reported in 27 were equivalent at 57 years (range: -96 years). Fifty-eight percent of all reported cases were male; of the 64% of cases for which race was reported, 88% were white, 9% were black, and 3% were of another race. The highest incidence of invasive MRSA disease occurred among residents of Multnomah County (25/1,); followed by residents in Clackamas (14/1,) and Washington (13/1,) Counties. Thirty-eight cases were fatal, for mortality and case fatality rates of 2.4/1, and 13%, respectively. The case fatality rate has not changed since 24. The mean and median ages of death due to invasive MRSA infection were 67 and 72 years, respectively, with a range of to 96 years. However, fatal outcome was not distributed uniformly across the age spectrum: whereas two deaths (5%) were reported among those younger than 35 years of age (case fatality rate, 5%), 31 (82%) were reported in those 5 and older and 23 (61%) were reported in those 65 and older, among whom the case fatality rate was 2%. Consequently, increasing age was associated with a fatal outcome from invasive MRSA infection (p=.27). Incidence per 1, Figure 2: Incidence of Invasive MRSA, by Infection Of the 3 total cases reported, 43 (14%) Type and Age, 27. were HO (2.7/1,); 191 (64%) were 9 HACO (12./1,); and 66 (19%) HO 8 were CA (4.1/1,). Since 24, the 7 HACO incidence of HO has decreased 59%, that CA 6 of HACO has decreased 2% and that of CA has decreased 17% (Figure 1). HO 5 cases have comprised a decreasing 4 proportion of all MRSA cases, from 25% 3 in 24 to 14% in 27 (test for trend, 2 1 p=.16), while the proportion of the other infection types did not change significantly. Although race and sex did not differ significantly by infection type, such a difference, by age, was seen (Figure 2). The mean and median ages for CA (47 for each) were significantly lower than those seen for HO (57 and 65, respectively) or HACO (6 for each) (p<.1). Mortality was highest among HACO cases (1.5/1,), followed by HO (.6/1,) and CA (.3/1,); case fatality was highest among HO (23%), followed by HACO (13%) and CA (6% each). However, after adjusting for age, the odds of death were almost two times lower (Odds Ratio [OR] 1.8; 95% Confidence Interval [CI] 1.1, 2.9]) for HACO cases than CA cases; the odds of death for HO cases was not significantly different than those for CA cases. Incidence per 1,
3 Clinical Manifestations The most common clinical manifestations of invasive MRSA infections reported in 27 are provided in Table 1. This profile is not significantly different from cases reported during Cases with healthcare-associated risk factors (including HO and HACO) were more likely to manifest as bacteremia (OR 2.5; CI 1.3, 4.7) than CA cases, while CA cases were more likely to manifest as sterile abscess (OR 2.; CI 1., 3.8), cellulitis (OR 2.2; CI 1.1, 4.3), bursitis (OR 14.1; CI 4.4, 45.), and endocarditis (OR 6.5; CI 2.4, 17.5) than HO and HACO cases. Pneumonia and empyema were reported similarly across infection types. Compared with other clinical manifestations, a fatal outcome was ten times more likely with bacteremia (CI 1.3, 75.) and three times more likely with pneumonia (CI 1.2, 5.6). This effect was independent of age and infection type. Table 2: Common underlying conditions reported among invasive MRSA cases, by infection type, 27 HO HACO CA Total Diabetes 1 (23) 9 (47) 13 (2) 113 (38) Smoking 11 (26) 58 (3) 26 (39) 95 (32) Renal Failure 7 (16) 55 (29) 2 (3) 64 (21) CVD/CHF 12 (28) 7 (37) 5 (8) 87 (29) IVDU () 22 (12) 18 (27) 4 (13) Immunosuppressive Therapy 1 (23) 28 (15) 5 (8) 43 (14) COPD 8 (19) 31 (16) 6 (9) 45 (15) Solid Organ Malignancy 7 (16) 34 (18) 2 (3) 43 (14) Obesity 7 (16) 3 (16) 5 (8) 42 (14) Stroke 3 (7) 29 (15) 1 (2) 33 (11) Alcohol Abuse 6 (14) 18 (9) 4 (6) 28 (9) None 3 (7) 4 (2) 8 (12) 15 (5) Some cases report >1 condition; not all conditions shown. Table 1: Common clinical manifestations of invasive MRSA cases, by infection type, 27. HO HACO CA Total Bacteremia 36 (84) 165 (86) 47 (71) 248 (83) Pneumonia 1 (23) 29 (15) 17 (26) 56 (19) Sterile Abscess 4 (9) 31 (16) 17 (26) 52 (17) Cellulitis 1 (2) 27 (14) 15 (23) 43 (14) Bursitis 1 (2) 3 (2) 13 (2) 17 (6) Endocarditis () 7 (4) 11 (17) 18 (6) Empyema 5 (12) 4 (2) 3 (5) 12 (4) Osteomyelitis 1 (2) 2 (1) 9 (9) 27 (9) Reported in at least 1% of cases of at least one infection type. Some cases report more than 1 syndrome. Not all syndromes shown. Underlying Conditions Almost all (95%) of invasive MRSA cases were in individuals reporting one or more underlying diseases or conditions (Table 2). Cases with healthcare-associated risk factors (including HO and HACO) were more likely to report diabetes (OR 3.; CI 1.6, 5.9); renal failure (OR 11.5; CI 2.7, 48.5); cardiovascular disease or congestive heart failure (CVD/CHF) (OR 6.6; CI 2.5, 17.); solid organ malignancy (OR 6.8; CI 1.6, 28.9), and stroke (OR 1.3; CI 1.4, 76.8) than CA cases, while CA cases were more likely to report intravenous drug use (IVDU) (OR 3.6; CI 1.8, 7.3) and were more likely not to have any underlying condition reported (OR 4.5; CI 1.6, 13.) than HO and HACO cases. After controlling for age and infection type, only immunosuppressive therapy was significantly associated with a fatal outcome (adjusted OR 2.5; CI 1.1, 5.7). In 27, cases reported with presence of commonly-reported underlying conditions were associated with the clinical manifestation of invasive MRSA disease, as shown in Table 3.
4 Table 3: Associations between common underlying conditions and clinical manifestation of invasive MRSA disease, 27. Bacteremia Pneumonia Osteo. Abscess Endocarditis Diabetes 4. (1.8, 8.9) 2.2 (1., 5.) Renal Failure 2.9 (1.1, 7.7) IVDU 2.5 (1., 6.5) 4.1 (2., 8.6) 6.3 (2.3, 17.) Immuno. Therapy 2.5 (1.2, 5.1) Stroke 7.6 (1., 56.6) The upper value is the univariate odds ratio between the respective underlying condition and clinical manifestation; the lower number, in parenthesis, is the 95% confidence interval. Only positive, significant associations are shown. Antibiotic Susceptibilities By definition, all MRSA isolates are resistant to β-lactam antibiotics, including penicillin and methicillin. Additionally, a proportion of isolates displayed decreased susceptibility (intermediate or full resistance) to several commonly assayed antibiotics in 27, including: erythromycin (92%), levofloxacin (77%), clindamycin (45%), tetracycline (6%), and trimethoprim-sulfa and rifampin (1% each). No isolates displayed decreased susceptibility to vancomycin. The proportion of isolates with decreased susceptibility to these antibiotics has not changed since 24 and decreased susceptibility to antibiotics was not associated with a fatal disease outcome. In 27, HO and HACO cases, combined, were three times more likely (95% CI 1.2, 7.6) to display decreased susceptibility to levofloxacin and six times more likely to display decreased susceptibility to clindamycin (95% CI 2.9, 12.2) than community-associated cases (Figure 3). Although a greater proportion of HO and HACO cases also displayed decreased susceptibility to erythromycin, this difference was not statistically significant. Percent Figure 3: Percentage of invasive MRSA isolates with intermediate or full resistance to select antibiotics, by infection type, Erythromycin Levofloxacin Clindamycin HO HACO CA Strain Typing Strain typing, by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), was completed for a subset of invasive MRSA cases and PFGE results are available for 145/3 (48%) cases reported in 27, with no difference in the proportion of cases with isolate PFGE results, by infection type (p=.41). Of the 145 isolates, 52 (36%) of isolates were USA1, 87 (6%) were USA3, and 6 (4%) were another type. The proportion of isolates identified as USA1 has decreased 36% since 25, from 27% to 17% in 27 (p=.4). Of the 139 isolates determined to be either USA1
5 (37%) or USA3 (63%), there was no difference between the strains in the proportion of cases with a fatal outcome. Figure 4: Percentage of isolates typed as USA1 and USA3, by infection type, 27. Figure 4 displays the percentage of cases of isolates determined to be USA1 or USA3, by epidemiologically classified infection type. For the first time, in 27, a greater proportion of HACO cases were USA3 than USA1. Strain type is significantly associated with age (p<.1), with the mean and median ages of cases due to USA1 (69 and years, respectively) higher than those due to USA3 (48 and 49, respectively). This HO HACO CA significant association between age and strain type was independent of the effect of infection type. Percent Among cases for which isolate PFGE results were available, USA1 comprised 63% of urinary tract infections, 4% of cellulitis cases, 38% of bacteremia cases, 33% of osteomyelitis cases, 32% of cases presenting as pneumonia, 31% of endocarditis cases, 22% of arthritis cases, and 17% of internal abscesses. None of these clinical manifestations, however, were significantly associated with strain type. Strain type did significantly (p<.5) differ by underlying condition: USA1 was identified in a higher proportion of cases with immunsuppressive therapy (79%), renal insufficiency (66%), cardiovascular disease (63%), COPD (63%), and stroke (65%); USA3 was identified in a higher proportion of cases with IVDU (95%) and smoking (8%). While cases with no reported underlying conditions also had a higher proportion of USA3 isolates (88%), the association was not significant, likely due to a small sample size. Decreased susceptibility to levofloxacin was found among all USA1 strains and 68% of USA3 strains, while decreased susceptibility to clindamycin was found among 84% of USA1 strains and 9% of USA3 strains; both differences are significant at p.2. No other differences in decreased susceptibility to antibiotics were seen by strain type. 1 9 USA1 USA3 Expanded HACO Analysis The distribution of healthcare risk factors among HACO cases is shown in Table 4. Since 24, the proportion of cases having been hospitalized and having surgery during the year prior to the date of MRSA culture significantly increased, while the proportion of cases having had dialysis significantly decreased (p<.3 for each). Among HACO cases, 36 (19%) had one healthcare risk factor; 67 (35%) had two; 47 (25%) had three; 3 (16%) had four; 1 (5%) had five; and 1 (1%) had all six. The proportion of cases with multiple reported risk factors has remained stable since 24. Table 4: Distribution of healthcare risk factors among HACO cases, Risk Factor Overall Dialysis (2) Central Venous Catheter 2 27 (24) LTCF Residence (38) Prior Surgery 1 51 (6) Hospitalization (8) Previous MRSA 3 32 (37) 1 Within year before date of culture; 2 In place at time of culture; 3 Ever documented infection or colonization Independent of age, dialysis and residence in a long-term care facility (LTCF) within the year before the date of culture and a central venous
6 Table 5: Adjusted odds ratios of significant, positive associations between healthcare risk factors and clinical manifestations and isolate strain type of HACO disease, Dialysis CVC LTCF Surgery Bacteremia 7.3 (1.7, 32.4) 5.9 (2., 17.2) 2.1 (1.3, 3.5) Abscess 3.2 (1.6, 6.3) Osteomyelitis 1.7 (1., 3.) USA1 2.2 (1.3, 3.8) 2.2 (1.5, 3.3) 1 Adjusted for age, with hospitalization within year prior to culture date as the referent group; those with previous documented MRSA colonization or infection only were excluded. catheter (CVC) in place at the time of culture were independently associated with bacteremia; the latter two risk factors were also associated with USA1 isolate strain type (Table 5). Surgery was associated with sterile abscess and osteomyelitis; and USA1 isolate strain type was associated with having a CVC in place at the time of culture and LTCF residence within a year before the date of culture. The presence of multiple risk factors also a factor: the presence of each additional risk factor was significantly associated with bacteremia (OR 1.4; CI 1.1, 1.6) and USA1 isolate strain type (OR 1.2; CI 1.1, 1.4). Discussion Four full years of surveillance have allowed for a better characterization of the epidemiology of invasive MRSA disease in the Portland Tri-County metropolitan area. Over this time, the incidence of invasive MRSA disease has decreased substantially, with the greatest decreases seen among HO and HACO cases. With the exception of invasive disease due to N. meningitidis, which has been decreasing nationally over the past several years, that the incidence rates of other pathogens under surveillance through ABCs have not shown similar decreases supports a true decreasing incidence of invasive MRSA disease. The reasons for this decrease are currently unknown and will be the subject of further investigation through the ABCs program. Results from 27 are consistent with previous years, in that invasive MRSA disease manifests largely in those with an underlying condition or behavior that is directly related to their infection. Almost all cases in those with healthcare-defining risk factors were in those with underlying chronic diseases, such as renal failure, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc., that require frequent encounters with the health care system and/or invasive medical procedures. That HO and HACO cases increase with age and occur primarily among those 65 and older reflect the increasing prevalence of these diseases among this population. Among CA cases, IVDU is the primary risk factor for invasive MRSA disease. Based on unpublished estimates of the number of persons who inject drugs in the Portland area, the risk of invasive MRSA disease in this population is 1 in 3 to 1 in 2,6. In contrast, the risk of invasive MRSA disease among those in the general population who do not inject drugs is extremely low, estimated at 1 in 35,. Looking at disease manifestation along with underlying conditions, several patterns emerge. For instance, bacteremia commonly occurs in those with systemic conditions, such as diabetes and renal failure, which involve direct introduction of the bacteria into the blood stream through medical interventions (i.e. dialysis); while type of surgery is not collected on the form, it is likely that localized joint and bone infections in the area of surgery occur after orthopedic surgeries in those areas; and injection drug use leads to the observed localized invasive infections.
7 Several interesting points are noted in our results, with respect to antibiotic use for treatment of invasive MRSA disease. First, while strains causing CA disease display, in general, a higher sensitivity to antibiotics than do strains causing HO and HACO disease, over half of all CA strains are resistant to quinolones. Consequently, quinolones may not be an effective empiric treatment for invasive MRSA. Second, an increasing use of more effective antibiotics against invasive MRSA disease (i.e. daptomycin) would be expected to reduce its case fatality rate. That this is not supported by our surveillance results may require further research into current therapeutic practices. Third, while intermediate or full resistance to vancomycin has not been detected among invasive MRSA isolates in Oregon, based on accepted breakpoint values, the extent to which reduced susceptibility to this drug is reflected in increased minimum inhibitory concentrations has not been fully ascertained and may require additional characterization. The addition of molecular strain type information has demonstrated an increase in the traditional community-associated, USA3 strain among cases classified epidemiologically as healthcareassociated, raising two possibilities: USA3 could increasingly be transmitted within the healthcare setting at least among those with traditional healthcare risk factors an observation supported in recently-published literature; or cases may be misclassified as healthcare-associated, due to the presence of the established risk factors, when they were actually acquired in the community. 1,2 Although both factors likely play some role, further work (such as the expanded HACO analysis presented for the first time in this report) will be needed to better refine our understanding of MRSA infection and invasive disease in the healthcare and community settings. References: 1. Popovich KJ, Weinstein RA, Bota B. Are community-associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains replacing traditional nosocomial MRSA strains? Clin Infect Dis. 28;46: Boyce JM. Community-associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a cause of health care-associated infection. Clin Infect Dis. 28;46:795-8.
Introduction to Infection Control
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006
 Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Hemodialysis catheter infection
 Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
Hemodialysis catheter infection Scary facts In 2006, 82% of patients in the United States initiated dialysis via a catheter The overall likelihood of Tunneled cuffed catheters use was 35% greater in 2005
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY. Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting
 EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
EAST CAROLINA UNIVERSITY INFECTION CONTROL POLICY Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus: Management in the Outpatient Setting Date Originated: Date Reviewed: Date Approved: Page 1 of Approved by: Department
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile
 Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
Lab ID Events MRSA Bloodstream Infection and C. difficile MDRO and CDI Module Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA), Vancomycinresistant Enterococcus(VRE), certain gram negative bacilli, Clostridium
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED
 METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) COMMUNITY ACQUIRED vs. HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED Recently, there have been a number of reports about methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (MRSA) infections
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005. Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007
 Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience
 Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience L. Ammari, A. Ghoubontini, A. Berriche, R. Abdelmalek, S.Aissa, F.Kanoun, B.Kilani, H.Tiouiri Benaissa, T.Ben chaabane Department of Infectious diseases,
Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience L. Ammari, A. Ghoubontini, A. Berriche, R. Abdelmalek, S.Aissa, F.Kanoun, B.Kilani, H.Tiouiri Benaissa, T.Ben chaabane Department of Infectious diseases,
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008
 Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Highlights of the Revised Official ICD-9-CM Guidelines for Coding and Reporting Effective October 1, 2008 Please refer to the complete ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting posted on this
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
Solid Organ Transplantation
 Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Solid Organ Transplantation Infection Prevention And Control Transplant Atlantic 2011 October 13/2011 Kathy Hart Introduction In the past several years, the drugs that we use, the surgeries themselves,
Irish Wolfhound Pedigree Breed Health Survey
 Irish Wolfhound Pedigree Breed Health Survey Forms were received representing 74 living dogs & 32 deceased dogs. Mortality results A total of 32 deaths were reported, representing 0.57% of all deaths reported
Irish Wolfhound Pedigree Breed Health Survey Forms were received representing 74 living dogs & 32 deceased dogs. Mortality results A total of 32 deaths were reported, representing 0.57% of all deaths reported
Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines
 Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines March 17, 2012 National Study Day Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship prof. dr. Dirk Vogelaers, Ghent University Hospital apr. Franky Buyle, Ghent
Staphyloccus aureus sepsis: follow- up practice guidelines March 17, 2012 National Study Day Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship prof. dr. Dirk Vogelaers, Ghent University Hospital apr. Franky Buyle, Ghent
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2014 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Table of Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 21 Duration
Other Causes of Fever
 T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
T e c h n i c a l S e m i n a r s Other Causes of Fever Febrile Illness Causes Fever After Seven Days Referral Relapsing Fever - Borreliosis Overview JHR Adaptation Sore Throat Overview Prevention Management
Meningococcal Disease Among Men Who Have Sex with Men United States, January 2012 - June 2015
 Meningococcal Disease Among Men Who Have Sex with Men United States, January 2012 - June 2015 Temitope A. Folaranmi MBChB MPH MPP Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices February 24, 2016 National
Meningococcal Disease Among Men Who Have Sex with Men United States, January 2012 - June 2015 Temitope A. Folaranmi MBChB MPH MPP Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices February 24, 2016 National
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
healthcare associated infection 1.2
 healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective Endocarditis and Prosthetic Joint Infections for Dentists
 PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
Heart transplantation
 Heart transplantation A patient s guide 1 Heart transplantation Heart transplantation has the potential to significantly improve the length and quality of life for patients with severe heart failure.
Heart transplantation A patient s guide 1 Heart transplantation Heart transplantation has the potential to significantly improve the length and quality of life for patients with severe heart failure.
Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib) Vaccination Position Paper. July 2013
 Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib) Vaccination Position Paper July 2013 Hib burden-pre vaccine era In 2000, before widespread introduction of Hib vaccine in resource-poor countries, Hib caused: 8.13 million
Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib) Vaccination Position Paper July 2013 Hib burden-pre vaccine era In 2000, before widespread introduction of Hib vaccine in resource-poor countries, Hib caused: 8.13 million
Big Data Health Big Health Improvements? Dr Kerry Bailey MBBS BSc MSc MRCGP FFPH Dr Kelly Nock MPhys PhD
 Big Data Health Big Health Improvements? Dr Kerry Bailey MBBS BSc MSc MRCGP FFPH Dr Kelly Nock MPhys PhD Epidemiology Infection 2006 Dec;134(6):1167-73. Epub 2006 Apr 20. Risk factors for hospital-acquired
Big Data Health Big Health Improvements? Dr Kerry Bailey MBBS BSc MSc MRCGP FFPH Dr Kelly Nock MPhys PhD Epidemiology Infection 2006 Dec;134(6):1167-73. Epub 2006 Apr 20. Risk factors for hospital-acquired
Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 2014
 Public Health Division Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 214 Chronic HCV in Oregon Since 25, when positive laboratory results for HCV infection became reportable in Oregon, 47,252 persons with
Public Health Division Hepatitis C Infections in Oregon September 214 Chronic HCV in Oregon Since 25, when positive laboratory results for HCV infection became reportable in Oregon, 47,252 persons with
Denver County Births and Deaths 2013
 Denver County Births and Deaths 2013 Selected birth characteristics: County residents, 2013... 2 Selected birth characteristics by age group of mother: County residents, 2013... 3 Selected birth characteristics
Denver County Births and Deaths 2013 Selected birth characteristics: County residents, 2013... 2 Selected birth characteristics by age group of mother: County residents, 2013... 3 Selected birth characteristics
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI
 Antibiotics in the Surgical Patient James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI Objectives Define current prophylactic recommendations for the use of antibiotics in the surgical patient List current antibiotics available
Antibiotics in the Surgical Patient James T. Dwyer DO, FACOI Objectives Define current prophylactic recommendations for the use of antibiotics in the surgical patient List current antibiotics available
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Page 1 of 5 Hialeah Nursing and Rehabilitation Center Combines Technology and Best Practices to Improve Infection Control Specific to C.diff ABSTRACT RB Health Partners, Inc., June 24,
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan
 Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Fungal Infection in Total Joint Arthroplasty Dr.Wismer Dr.Al-Sahan Delayed Reimplantation Arthroplasty for Candidal Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature David M.
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
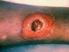 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital
 Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Surveillance cultures PRO. Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen
 Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS
 ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
Sepsis Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Sepsis Awareness Month Issue 11 September 2015 In this Issue 2 Getting to understand Sepsis 3 Stages in Sepsis Advancement 4 Diagnosis & Treatment
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013. Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group
 Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
Scottish Diabetes Survey 2013 Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group Contents Contents... 2 Foreword... 4 Executive Summary... 6 Prevalence... 8 Undiagnosed diabetes... 18 Duration of Diabetes... 18
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline
 Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infection Treatment Guideline Purpose: To provide a framework for the evaluation and management patients with Methicillin- Susceptible (MSSA) and Methicillin-Resistant
How Common is MRSA in Adult Septic Arthritis?
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE/BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT How Common is MRSA in Adult Septic Arthritis? Bradley W. Frazee, MD Christopher Fee, MD Larry Lambert, MPH From the Department of Emergency Medicine, Alameda County
INFECTIOUS DISEASE/BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT How Common is MRSA in Adult Septic Arthritis? Bradley W. Frazee, MD Christopher Fee, MD Larry Lambert, MPH From the Department of Emergency Medicine, Alameda County
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General. The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England
 Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General The Management and Control of Hospital Acquired Infection in Acute NHS Trusts in England HC 230 Session 1999-00 17 February 2000 Report by the Comptroller
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital
 Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Does referral from an emergency department to an. alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent. emergency room visits in patients with alcohol
 Does referral from an emergency department to an alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent emergency room visits in patients with alcohol intoxication? Robert Sapien, MD Department of Emergency Medicine
Does referral from an emergency department to an alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent emergency room visits in patients with alcohol intoxication? Robert Sapien, MD Department of Emergency Medicine
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
How To Plan Healthy People 2020
 Healthy California 2020 Initiative: Consensus Building on Top Priority Areas for CDPH Public Health Advisory Committee April 30, 2010 Introducing the CDPH Decision Framework Responding to public health
Healthy California 2020 Initiative: Consensus Building on Top Priority Areas for CDPH Public Health Advisory Committee April 30, 2010 Introducing the CDPH Decision Framework Responding to public health
Chapter 20: Analysis of Surveillance Data
 Analysis of Surveillance Data: Chapter 20-1 Chapter 20: Analysis of Surveillance Data Sandra W. Roush, MT, MPH I. Background Ongoing analysis of surveillance data is important for detecting outbreaks and
Analysis of Surveillance Data: Chapter 20-1 Chapter 20: Analysis of Surveillance Data Sandra W. Roush, MT, MPH I. Background Ongoing analysis of surveillance data is important for detecting outbreaks and
FOR INFORMATION CONTACT:
 NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-7854 September 10, 2014 For Immediate Release
The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in. New Brunswick
 The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in New Brunswick Introduction Diabetes is a chronic, often debilitating and sometimes fatal disease, in which the body either cannot produce insulin
The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in New Brunswick Introduction Diabetes is a chronic, often debilitating and sometimes fatal disease, in which the body either cannot produce insulin
in children less than one year old. It is commonly divided into two categories, neonatal
 INTRODUCTION Infant Mortality Rate is one of the most important indicators of the general level of health or well being of a given community. It is a measure of the yearly rate of deaths in children less
INTRODUCTION Infant Mortality Rate is one of the most important indicators of the general level of health or well being of a given community. It is a measure of the yearly rate of deaths in children less
State Health Assessment Health Priority Status Report Update. June 29, 2015 Presented by UIC SPH and IDPH
 State Health Assessment Health Priority Status Report Update June 29, 2015 Presented by UIC SPH and IDPH 1 Health Priority Presentation Objectives 1. Explain context of how this discussion fits into our
State Health Assessment Health Priority Status Report Update June 29, 2015 Presented by UIC SPH and IDPH 1 Health Priority Presentation Objectives 1. Explain context of how this discussion fits into our
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM
 ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL: AN EMERGING NEW PARADIGM AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 77th Annual Meeting March 9-12, 2010 New Orleans, Louisiana COMMITTEE ON PATIENT SAFETY PREPARED
Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes?
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail?
 Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
Why Do Some Antibiotics Fail? Patty W. Wright, M.D. April 2010 Objective To outline common reasons why antibiotic therapy is not successful and how this can be avoided. And to teach you a little bit about
CCG Outcomes Indicator Set: Emergency Admissions
 CCG Outcomes Indicator Set: Emergency Admissions Copyright 2013, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
CCG Outcomes Indicator Set: Emergency Admissions Copyright 2013, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 The NHS Information Centre is England s central, authoritative source
35-40% of GBS disease occurs in the elderly or in adults with chronic medical conditions.
 What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
What is Group B Strep (GBS)? Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that is found in the lower intestine of 10-35% of all healthy adults and in the vagina and/or lower intestine of 10-35% of
June 10, 2015. Dear Mr. Slavitt:
 1275 K Street, NW, Suite 1000 Washington, DC 20005-4006 Phone: 202/789-1890 Fax: 202/789-1899 apicinfo@apic.org www.apic.org June 10, 2015 Andrew M. Slavitt Acting Administrator Centers for Medicare &
1275 K Street, NW, Suite 1000 Washington, DC 20005-4006 Phone: 202/789-1890 Fax: 202/789-1899 apicinfo@apic.org www.apic.org June 10, 2015 Andrew M. Slavitt Acting Administrator Centers for Medicare &
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
Urinary Tract Infections Leading cause of morbidity and health care expenditures in persons of all ages. An estimated 50 % of women report having had a UTI at some point in their lives. 8.3 million office
49. INFANT MORTALITY RATE. Infant mortality rate is defined as the death of an infant before his or her first birthday.
 49. INFANT MORTALITY RATE Wing Tam (Alice) Jennifer Cheng Stat 157 course project More Risk in Everyday Life Risk Meter LIKELIHOOD of exposure to hazardous levels Low Medium High Consequences: Severity,
49. INFANT MORTALITY RATE Wing Tam (Alice) Jennifer Cheng Stat 157 course project More Risk in Everyday Life Risk Meter LIKELIHOOD of exposure to hazardous levels Low Medium High Consequences: Severity,
Methodology Understanding the HIV estimates
 UNAIDS July 2014 Methodology Understanding the HIV estimates Produced by the Strategic Information and Monitoring Division Notes on UNAIDS methodology Unless otherwise stated, findings in this report are
UNAIDS July 2014 Methodology Understanding the HIV estimates Produced by the Strategic Information and Monitoring Division Notes on UNAIDS methodology Unless otherwise stated, findings in this report are
STATISTICAL BRIEF #151
 HEALTHCARE COST AND UTILIZATION PROJECT STATISTICAL BRIEF #151 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality March 2013 Trends in Potentially Preventable Hospital Admissions among Adults and Children, 2005
HEALTHCARE COST AND UTILIZATION PROJECT STATISTICAL BRIEF #151 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality March 2013 Trends in Potentially Preventable Hospital Admissions among Adults and Children, 2005
Oregon s Death with Dignity Act--2013
 Oregon s Death with Dignity Act--2 Oregon s Death with Dignity Act (DWDA), enacted in late 997, allows terminallyill adult Oregonians to obtain and use prescriptions from their physicians for selfadministered,
Oregon s Death with Dignity Act--2 Oregon s Death with Dignity Act (DWDA), enacted in late 997, allows terminallyill adult Oregonians to obtain and use prescriptions from their physicians for selfadministered,
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
 Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Guidance for Industry Diabetes Mellitus Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Data Analysis Capabilities
 Electronic Health Record (EHR) Data Analysis Capabilities January 2014 Boston Strategic Partners, Inc. 4 Wellington St. Suite 3 Boston, MA 02118 www.bostonsp.com Boston Strategic Partners is uniquely positioned
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Data Analysis Capabilities January 2014 Boston Strategic Partners, Inc. 4 Wellington St. Suite 3 Boston, MA 02118 www.bostonsp.com Boston Strategic Partners is uniquely positioned
Southern NSW Local Health District: Our Population s Health
 Page 1 of 5 This Factsheet summarises a selection of health indicators (health behaviours & risk factors, hospitalisations and deaths) for the of the Southern NSW Local Health District (LHD). Health services
Page 1 of 5 This Factsheet summarises a selection of health indicators (health behaviours & risk factors, hospitalisations and deaths) for the of the Southern NSW Local Health District (LHD). Health services
DRG 416 Septicemia. ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines
 oding uidelines Septicemia ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines The below listed septicemia guidelines are not inclusive. The coder should refer to the applicable Coding Clinic guidelines for additional information.
oding uidelines Septicemia ICD-9-CM Coding Guidelines The below listed septicemia guidelines are not inclusive. The coder should refer to the applicable Coding Clinic guidelines for additional information.
PACKAGE LEAFLET. CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin. One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride).
 PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
PACKAGE LEAFLET CLINDAMYCIN capsules Clidamycin COMPOSITION One capsule of 75 mg contains 75 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). One capsule of 150 mg contains 150 mg Clindamycin (as hydrochloride). PROPERTIES
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe
 POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
POSITION PAPER 05 January 2011 Addressing the challenge of healthcare associated infections (HCAIs) in Europe A Call for Action Page 1 of 8 A holistic approach to combating HCAIs in Europe We must rise
Treatment of diabetes In order to survive, people with type 1 diabetes must have insulin delivered by a pump or injections.
 National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
National Diabetes Statistics What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both.
9. Substance Abuse. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption. pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs
 9. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs pg 172-173: Hospitalizations related to alcohol and substance abuse pg 174-179: Accidental
9. pg 166-169: Self-reported alcohol consumption pg 170-171: Childhood experience of living with someone who used drugs pg 172-173: Hospitalizations related to alcohol and substance abuse pg 174-179: Accidental
Seniors. health. Report. A Peel Health Status Report
 health Seniors 26 Report A Peel Health Status Report P-7-23 Acknowledgements This report was authored by: Dr. Megan Ward, Associate Medical Officer of Health; Maurizzio Colarossi, Epidemiologist and Julie
health Seniors 26 Report A Peel Health Status Report P-7-23 Acknowledgements This report was authored by: Dr. Megan Ward, Associate Medical Officer of Health; Maurizzio Colarossi, Epidemiologist and Julie
 Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Skin and Soft tissue Infections: new bugs, old drugs Disclosure Statement Sponsor: Goodman Photographic Presented by: Dr. Kristopher Wiebe, MD, CCFP (EM) Presented to: BC Chapter, Canadian Society of Hospital
Health risk assessment: a standardized framework
 Health risk assessment: a standardized framework February 1, 2011 Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Leading causes of death in the U.S. The 5 leading causes
Health risk assessment: a standardized framework February 1, 2011 Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH Director, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Leading causes of death in the U.S. The 5 leading causes
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital
 Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Open and Honest Care in your Local Hospital The Open and Honest Care: Driving Improvement Programme aims to support organisations to become more transparent and consistent in publishing safety, experience
Are venous catheters safe in terms of blood tream infection? What should I know?
 Are venous catheters safe in terms of blood tream infection? What should I know? DIAGNOSIS, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF HAEMODIALYSIS CATHETER-RELATED BLOOD STREAM INFECTIONS (CRBSI): A POSITION STATEMENT
Are venous catheters safe in terms of blood tream infection? What should I know? DIAGNOSIS, PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF HAEMODIALYSIS CATHETER-RELATED BLOOD STREAM INFECTIONS (CRBSI): A POSITION STATEMENT
Root Cause Analysis following
 Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
Butler Memorial Hospital Community Health Needs Assessment 2013
 Butler Memorial Hospital Community Health Needs Assessment 2013 Butler County best represents the community that Butler Memorial Hospital serves. Butler Memorial Hospital (BMH) has conducted community
Butler Memorial Hospital Community Health Needs Assessment 2013 Butler County best represents the community that Butler Memorial Hospital serves. Butler Memorial Hospital (BMH) has conducted community
Leading Causes of Death, by Race & Ethnicity
 Leading Causes of Death, by Race & Ethnicity African Americans had the highest rate of death. Heart disease, cancer and stroke were the top three leading causes of death for whites, African Americans and
Leading Causes of Death, by Race & Ethnicity African Americans had the highest rate of death. Heart disease, cancer and stroke were the top three leading causes of death for whites, African Americans and
Intelligent Monitoring Report. Greenford Avenue Family Health Practice 322 Greenford Avenue London W7 3AH
 Greenford Avenue Family Health Practice 322 Greenford Avenue London W7 3AH Intelligent Monitoring (IM) Report GP IM is an initial list of 37 indicators that currently cover three of our five key questions
Greenford Avenue Family Health Practice 322 Greenford Avenue London W7 3AH Intelligent Monitoring (IM) Report GP IM is an initial list of 37 indicators that currently cover three of our five key questions
HSE Health Protection Surveillance Centre. Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection
 Clostridium difficile Sub-Committee Health Protection Surveillance Centre Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection Version 3, January 2016 This document has
Clostridium difficile Sub-Committee Health Protection Surveillance Centre Sample Root Cause Analysis Tool of Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile Infection Version 3, January 2016 This document has
Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation
 Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation To whom this document applies: All staff in Colchester Hospital University Foundation Trust screening Patients for MRSA Procedural Documents Approval
Policy for Screening Patients for MRSA Colonisation To whom this document applies: All staff in Colchester Hospital University Foundation Trust screening Patients for MRSA Procedural Documents Approval
Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 1, March 2010 Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey Kelechi Austin Ofurum, M.Sc, B.Sc*,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 1, March 2010 Health-Care Associated Infection Rates among Adult Patients in Bahrain Military Hospital: A Cross Sectional Survey Kelechi Austin Ofurum, M.Sc, B.Sc*,
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive
 Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive disease)! Report immediately 24/7 by phone upon initial suspicion or laboratory test order PROTOCOL CHECKLIST Enter available information into Merlin upon
Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive disease)! Report immediately 24/7 by phone upon initial suspicion or laboratory test order PROTOCOL CHECKLIST Enter available information into Merlin upon
Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Vancouver Coastal Health & Providence Health Care Regional Guideline. September 27, 2011. (Version 3.
 Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Vancouver Coastal Health & Providence Health Care Regional Guideline Sept. 27, 2011 (Version 3.5) Developed by: Jane de Lemos, Tim Lau, Mike Legal. Endorsed by: Terri
Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Vancouver Coastal Health & Providence Health Care Regional Guideline Sept. 27, 2011 (Version 3.5) Developed by: Jane de Lemos, Tim Lau, Mike Legal. Endorsed by: Terri
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate. Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI)
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) September 1999 Updated 2007 Surgical Wound: According to 1998 Kuwait National
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Pathology, Infection, and Disease Disease: An abnormal state in which the body is not functioning normally Pathology: The study of disease Etiology: The study of
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Pathology, Infection, and Disease Disease: An abnormal state in which the body is not functioning normally Pathology: The study of disease Etiology: The study of
DISCLOSURES RISK ASSESSMENT. Stroke and Heart Disease -Is there a Link Beyond Risk Factors? Daniel Lackland, MD
 STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 29 Aalborg Viborg Herning Aarhus Hillerød Esbjerg Vejle Herlev København Hvidovre Odense Slagelse Næstved Sønderborg DEAR COLLEAGUE
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 29 Aalborg Viborg Herning Aarhus Hillerød Esbjerg Vejle Herlev København Hvidovre Odense Slagelse Næstved Sønderborg DEAR COLLEAGUE
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island
 King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
National Quality Forum (NQF) Endorsed Set of 34 Safe Practices*
 NQF Endorsed Set of Safe Practices (released 2009) 1. Leadership Structures and Systems Leadership structures and systems must be established to ensure that there is organization-wide awareness of patient
NQF Endorsed Set of Safe Practices (released 2009) 1. Leadership Structures and Systems Leadership structures and systems must be established to ensure that there is organization-wide awareness of patient
Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position Paper
 infection control and hospital epidemiology october 2008, vol. 29, no. 10 shea/hicpac position paper Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position
infection control and hospital epidemiology october 2008, vol. 29, no. 10 shea/hicpac position paper Recommendations for Metrics for Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings: SHEA/HICPAC Position
on a daily basis. On the whole, however, those with heart disease are more limited in their activities, including work.
 Heart Disease A disabling yet preventable condition Number 3 January 2 NATIONAL ACADEMY ON AN AGING SOCIETY Almost 18 million people 7 percent of all Americans have heart disease. More than half of the
Heart Disease A disabling yet preventable condition Number 3 January 2 NATIONAL ACADEMY ON AN AGING SOCIETY Almost 18 million people 7 percent of all Americans have heart disease. More than half of the
Goal 1; Objective B: Improve health care quality and patient safety: Performance measure
 TRUST FOR AMERICA S HEALTH COMMENTS ON THE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES (HHS) DRAFT STRATEGIC PLAN 2010 2015 Goal 1; Objective B: Improve health care quality and patient safety: Performance
TRUST FOR AMERICA S HEALTH COMMENTS ON THE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES (HHS) DRAFT STRATEGIC PLAN 2010 2015 Goal 1; Objective B: Improve health care quality and patient safety: Performance
3.5% 3.0% 3.0% 2.4% Prevalence 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0%
 S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in Prince Edward Island
 The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in Prince Edward Island Executive Summary Every day, Prince Edward Islanders living with type 1 diabetes take insulin to live. Many deliver insulin
The Economic Benefit of Public Funding of Insulin Pumps in Prince Edward Island Executive Summary Every day, Prince Edward Islanders living with type 1 diabetes take insulin to live. Many deliver insulin
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations
 GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
GCSE BITESIZE Examinations General Certificate of Secondary Education AQA SCIENCE A Unit Biology B1a AQA BIOLOGY Unit Biology B1a BLY1A (Human Biology) (Human Biology) FOUNDATION TIER Specimen Paper Time
No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER 5 Subject: EMPLOYMENT, SOCIAL POLICY, HEALTH AND CONSUMER AFFAIRS COUNCIL MEETING ON 9 AND 10 JUNE 2008
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 22 May 2008 9637/08 SAN 88 DENLEG 52 VETER 7 NOTE from: Committee of Permanent Representatives (Part 1) to: Council No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 22 May 2008 9637/08 SAN 88 DENLEG 52 VETER 7 NOTE from: Committee of Permanent Representatives (Part 1) to: Council No. prev. doc.: 9392/08 SAN 77 DENLEG 48 VETER
Table 1 Performance Measures. Quality Monitoring P4P Yr1 Yr2 Yr3. Specification Source. # Category Performance Measure
 Table 1 Performance Measures # Category Performance Measure 1 Behavioral Health Risk Assessment and Follow-up 1) Behavioral Screening/ Assessment within 60 days of enrollment New Enrollees who completed
Table 1 Performance Measures # Category Performance Measure 1 Behavioral Health Risk Assessment and Follow-up 1) Behavioral Screening/ Assessment within 60 days of enrollment New Enrollees who completed
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
