Tuberculosis Treatment: Drug Therapy, Case Management, & Special Considerations
|
|
|
- Myron Lewis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tuberculosis Treatment: Drug Therapy, Case Management, & Special Considerations Take Home Information for Attendees of the 2014 Intergovernmental Panel Physicians Training Summit
2 Principles of Tuberculosis Treatment Standard Drug Regimen for PanscuceptibleTuberculosis: INH, RIF, PZA, EMB Intensive Phase 2 Months Continuation Phase 4 Months 4 Drugs Isoniazid Rifampin Ethambutol Pyrazinamide 2 Drugs Isoniazid Rifampin Intake of drugs observed 5-7 days a week Intake of drugs observed 3-5 days a week
3 General Principles of Therapy Always treat with a multiple-drug regimen Never add a single drug to a failing regimen Duration of treatment depends on the drugs used (the weaker the regimen, the longer the treatment) Isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide are the basis of modern short-course chemotherapy Schecter, 2012
4 Standard Drug Therapy for Tuberculosis Treatment Initial Phase Continuation Phase Isoniazid Rifampin Pyrazinamide Ethambutol 5 mg/kg up to 300 mg 10 mg/kg up to 600 mg mg/kg mg/kg Months Schecter, 2012
5 Pansusceptible Treatment Both are equally acceptible: 7 days a week Intensive phase: 56 doses Continuation phase: 126 doses 5 days a week Intensive phase: 40 doses Continuation phase: 90 doses 8 weeks 18 weeks 8 weeks 18 weeks ATS/CDC/IDSA guidelines Table 2
6 Challenges Associated with Standard Drug Therapy for Tuberculosis What are the side effects most commonly seen in patients/applicants undergoing tuberculosis treatment? INH RIF PZA EMB be What comorbidities or drug interactions should panel sites concerned about when an applicant is under treatment? Who is permitted to provide DOT? Under what circumstances should treatment regimens be adjusted? Extended?
7 Adverse Reactions Between 8-18% have drug regimens modified Most common side effects: Rash Gastrointestinal intolerance Liver toxicity Peripheral neuropathy (INH) Optic neuritis (ethambutol)- dose and duration dependent Gout, arthropathy (pyrazinamide)
8 Rash Any of the drugs can produce rash Hold all medications until rash subsides Serial re-challenge sequentially every 3-4 days to find cause Usual sequence is INH, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol
9 GI Intolerance Discern between transient vs. persistent Transient: pill burden, indigestion Persistent: anorexia, nausea, and fatigue may signify liver toxicity If hepatotoxicity suspected, hold meds and obtain liver function tests (LFTs) If LFTs are normal, restart meds and reassure
10 Liver Toxicity Most feared adverse reaction INH, rifampin, and pyrazinamide can all cause liver injury Warn patients to seek immediate attention if anorexia, nausea, emesis, abdominal discomfort, or jaundice develops 4-5 fold increased risk with hepatitis C Liver sparing regimen of ethambutol, quinolone, and injectable agent may be necessary if early in treatment and high-burden disease Prevention: avoidance of alcohol and monitoring LFTs if other drugs with potential liver toxicity are used
11 Liver Toxicity: Order of Re-challenge Depends on Circumstances Patterns of hepatitis Hepatocellular (increased transaminases): can be caused by all three 1 st line agents Cholestasis (high Alk phos and bilirubin) is usually due to rifampin INH hepatitis: often age-dependent Pyrazinamide hepatitis: often dose-dependent
12 Isoniazid (INH) Adverse Effects Asymptomatic transaminitis Up to 5X upper limit normal in 10-20% Clinical hepatitis With INH alone approximately 0.6%; 2.7% with RIF Peripheral neurotoxicity Less than 0.2% unless predisposing factors Central nervous system effects Not well quantified Lupus-like reaction Approximately 20% develop positive ANA; Lupus in less than 1%
13 Rifampin (RIF) Adverse Effects Cutaneous reactions Pruritus with or without rash in up to 6% Gastrointestinal reactions Variable incidence but usually mild Flu-like syndrome Occurs in % receiving 600 mg twice weekly Hepatoxicity Transient asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia in 0.6% Clinical hepatitis uncommon, usually cholestatic Immunological reactions <0.1% develop platelets, anemia, renal failure
14 Ethambutol (EMB) Adverse Effects Retrobulbar neuritis Less than 1% with dose of 15 mg/kg 18% with more than 30 mg/kg/day Peripheral neuritis Rare Cutaneous reactions Approximately % require discontinuation of drug
15 Pyrazinamide (PZA) Adverse Effects Hepatotoxicity About 1% develop clinical hepatitis, can be severe Gastrointestinal symptoms Mild anorexia and nausea are common Non-gouty polyarthralgia Up to 40% receiving daily PZA, not serious Hyperuricemia Asymptomatic - expected effect Acute gouty arthritis - rare except if pre-existing gout Cutaneous reactions Transient morbilliform rash, self-limited Photosensitive dermatitis
16 Isoniazid Drug Interactions Isoniazid - Relatively potent inhibitor of several cytochrome P450 isozymes, but not CYP3A Inhibitory activity of INH increases the serum concentrations of phenytoin, carbamazepine, and diazepam Rifampin has opposite effect and outweighs inhibitory effect of INH INH may increase toxicity to acetaminophen, valproate, serotonergic antidepressants, disulfiram, warfarin, and theophylline
17 Rifamycins Drug Interactions Rifamycins - Induce various isozymes of the cytochrome P450 system resulting in a decrease in serum concentration of many drugs Enzyme induction: Rifampin>rifapentine>rifabutin Corticosteroids, steroid contraceptives, oral hypoglycemic agents, oral anticoagulants, phenytoin, cimetidine, digitalis, antiretroviral agents
18 Summary: Common Drug Side Effects Side Effects Drug G.I. Effects Ethionamide PAS Quinolones Clofazimine Aminoglycosides Rifabutin Headache Quinolones INH Cycloserine Ethambutol Ethionamide Skin Problems Clofazimine Cycloserine INH Rifabutin PAS Ethionamide Ethambutol Photosensitivity Clofazimine Quinolones Hepatotoxicity INH Pyrazinamide Rifabutin Ethionamide PAS Quinolones Behavioral Changes Cycloserine INH Quinolones Ethionamide
19 Summary: Common Drug Side Effects (Cont.) Side Effects Drug Musculoskeletal/joint Pyrazinamide Quinolones Rifabutin Rifampin INH Visual changes, eye pain Ethambutol Rifabutin Clofazimine INH (high-dose) Linezolid Hearing loss, tinnitus, loss of balance Aminoglycosides Capreomycin Dizziness Aminoglycosides/capreomycin Cycloserine Quinolones Peripheral Neuropathy INH Ethionamide Cycloserine Ethambutol Hypothyroidism Ethionamide PAS Hypokalemia/hypomagn Aminoglycoside/capreomycin Lima, Aug 2011
20 Drug Therapy for Tuberculosis Treatment: Extending Therapy Initial Continuation Phase* Isoniazid Rifampin Pyrazinamide Ethambutol 0 1 2* months *If cavitary disease and culture positive at 2 months, extend continuation phase from 4 to 7 months. Schecter, 2012
21 Alternative Regimens Drug Resistance Mono INH resistance 6 month regimen of Rif, PZA, and EMB (+/-fluoroquinolone(fqn)) 12 months Rif, EMB (+/- FQN) Mono Rifampin resistance 12 month regimen of INH, PZA, and EMB (+/-FQN) 18 month regimen of INH, EMB MDR TB 4-6 drugs, always including a FQN and injectable drug if susceptible, for months post culture conversion (the injectable drug for a minimum of 6 months) Schecter, 2012
22 Special Situations Treatment Interruptions Initial phase < 14 days Continue treatment If total not completed in 3 months re-start from the beginning 14 days Re-start from the beginning Continuation phase < 80% completed AND interruption < 3 months Continue treatment If not completed in 6 months restart from the beginning < 80% completed AND interruption 3 months Re-start from the beginning 80% completed Continue treatment Miriti, 2011
23 Treatment of Drug Resistant Cases What are the categories of drugs used for the treatment of drug-resistant cases? Once drug resistance is identified, how should a treatment regiment be determined? Describe some of the treatment concerns associated with drug-resistant cases? How can risks be minimized?
24 Potential Regimens for the Management of Patients with Drug- Resistant Tuberculosis Pattern of Drug Resistance Suggested Regimen Duration of Treatment (months) Comments INH (± SM) RIF, PZA, EMB (an FQN may strengthen the regimen for patients with extensive disease) 6 In BMRC trials, 6-month regimens have yielded 95% success rates if four drugs were used in the initial phase and RIF plus EMB or SM was used throughout.* Additional studies suggest results were best if PZA was also used throughout the 6 months. INH and RIF (± SM) FQN, PZA, EMB, IA, ± alternative agent Extended treatment is needed to lessen the risk of relapse. INH and RIF (± SM) and EMB or PZA FQN (EMB or PZA if active), IA, and two alternative agents 24 Use of first line agents to which there is susceptibility. Add two or more alternative agents in case of extensive disease. RIF INH, EMB, FQN, supplemented with PZA for the first 2 months (an IA may be included for the first 2-3 months for patients with extensive disease) Daily and thee times weekly regimens of INH, PZA and SM given for 9 months were effective in a BMRC trial. * Source: Mitchison DA, Nunn AJ. Influence of initial drug resistance on the response to short-course chemotherapy of pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986; 133: Source: Hong Kong Chest Service, British Medical Resource Council. Five year follow-up of a control trial of five 6 month regimens of chemotherapy for tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987; 136: Source: Hong Kong Chest Service, British Medical Resource Council. Controlled trail of 6-month and 9-month regimens of daily and intermediate streptomycin plus isoniazid plus pyrazinamide for pulmonary tuberculosis in Hong Kong. Am Rev Respir Dis 1977;115: Lauzardo, 2012
25 Guiding Principles for Treating MDR-TB Consult with experts in coordination with country you are screening for. Use guidelines in Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis A Survival Guide for Clinicians, 2 nd edition (Curry National TB Center). Medication regimen must be based on drug susceptibility results. A single new drug should never be added to a failing regimen. Employ at least three previously unused drugs to which there is in vitro susceptibility. One of these should be an injectable agent. Do not limit the regimen to three agents if other previously unused drugs that are likely to be active are available. Simultaneous use of two injectable agents is not recommended. Resistance to PZA is uncommon in the absence of resistance to other first-line drugs. Lauzardo, 2012
26 Guiding Principles for Treating MDR-TB Intermittent therapy should not be used for tuberculosis caused by drug-resistant organisms, except perhaps for injectable agents after an initial period of daily therapy. The use of drugs to which there is demonstrated in vitro resistance is not encouraged. The use of INH is associated with better survival rates in patients with the strain- W variety of MDR M. tuberculosis that are susceptible to higher concentrations of INH. Resistance to RIF is associated with cross-resistance to rifabutin and rifapentine. There is no cross-resistance between streptomycin and the other injectable agents, however cross-resistance between amikacin and kanamycin is universal. Lauzardo, 2012
27 DOT: The Basics What is true DOT? Why Directly Observed Therapy (DOT)? Who is permitted to provide DOT? Please discuss the importance of documentation in DOT
28 Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) Patients are observed to ingest each dose of antituberculosis medications, to maximize the likelihood of completion of therapy Enablers: assist the patient in completing therapy. e.g. follow-up missed appointments Incentives: Interventions to motivate the patient. e.g. US immigrant visa Tan, SLEC
29 Why DOT? Adherence to treatment is the single most important factor predicting cure of tuberculosis and prevention of acquired drug resistance DOT: Effect on Resistance and Relapse Self-treatment N=407 (pre 1987) DOT N=581 (1987 +) Primary Resistance 13% 6.7% Secondary Resistance 10.3% 1.4% Relapse 20.9% 5.5% MDR relapse 6.1% 0.9% schecter Schecter, 2012
30 Principles of DOT Every dose throughout the course of treatment must be observed by a health-care worker Worker watches applicant swallow each dose of medication and checks mouth for retained pills Not acceptable to dispense on a weekly or monthly basis DOT required during intensive and continuation phases. Total number of doses most important Applicant may take one-two weekend doses unobserved, but those are not counted toward total # of doses. Will not extend treatment if patient adherent to DOT. Staff must understand principles of DOT Miriti, 2011
31 Who Can and Cannot Deliver DOT for Immigration Purposes CAN Physician Nurse Other trained health worker CANNOT Family member Non trained health worker Non health care worker Miriti, 2011
32 Observing and Documenting the Dose Prepares the medications Watches the applicant swallow the medications Tan, 2011
33 Checking mouth for swallowed dose Miriti, 2011
34 Observing and Documenting the Dose Checks the mouth for retained medications Documents the doses Tan, 2011
35 Case Management What should be included in the intake process be when an applicant/patient begins treatment? Establishing a regimen Setting a treatment schedule/culture Patient education TB treatment file What are your recommendations for optimal applicant/patient management? What situations should indicate that greater patient/applicant Who is permitted to provide DOT? management is required when someone is under treatment? How does case management change when treating a drug-resistant case?
36 Creating a TB DOT File TB treatment file should include Referral letter and DS forms indicating basis for TB diagnosis TB Patient record card Contains current photo of patient Lists home address, telephone number, alternate number for the patient supporter, disease category, patient classification, drugs used TB treatment compliance card Side effect monitoring card Patient appointment card Miriti, 2011
37 Anti-TB Drug Patient Packs Miriti, 2011
38 Patient Education Objectives To provide correct information To prevent defaulters and ensure completion of treatment To get family support To improve success of contact investigation To improve infection control Tan, SLEC
39 Patient Education Comprehensive TB disease, transmission, control Medications and possible side effects Duration of treatment and required DOT compliance Lifestyle changes Good nutrition and hygiene Contact evaluation Treatment monitoring: sputum analysis and CXR schedule (psychological preparation and financial implications for self payers.) Miriti, 2011
40 Patient Education Explain immigration process Repeat TB testing and repeat medical examination required at the end of TB treatment TB treatment must be completed successfully to be medically cleared for travel TB patient education is a continuous process from initial visit through the end of treatment. Miriti, 2011
41 Patient Monitoring Baseline laboratories and follow up laboratory results Daily signs and symptoms check (DON T assume there are no side effects if the patient doesn t initiate conversation) Weight (weekly) Vital Signs (daily/weekly) Observe every patient swallow every pill Document the dose Pulmonary evaluation (monthly) Schedule and follow-up on results of sputum smears, cultures and DST Schedule for Chest X-ray Track patients lost to follow-up Oladele, 2013
42 Routine Monitoring and Frequency Signs and symptoms monthly Sputum conversion Weight LFTs Side effects: MD evaluations End of treatment 2 specimens monthly until cultures negative for 2 consecutive months monthly Baseline, 1 month and prn Monthly: includes visual acuity and red/green discrimination, GI complaints, check for jaundice Minimum at baseline, 3 months and end of therapy 2 sputa for smear and culture Schecter, 2012
43 Sputum Smear and Culture Monitoring During Treatment Schedule Pansusceptible, Mono or Poly-drug resistance (not MDR) No DST 1st month Two specimens* One specimen 2nd month Two specimens* One specimen 3rd month 4th month 5th month 6th month Treatment completion Two specimens* (if culture pending from 1st month) No specimens needed if cultures obtained after treatment months #1 and #2 are negative Two specimens One specimen One specimen One specimen One specimen Two specimens *Obtain at end of month Tan, SLEC
44 Management of Treatment Failure, Relapse 90-95% of patients treated for pulmonary TB will have negative sputum cultures by 3 months If still culture positive after 3 months of therapy: Recheck drug susceptibility tests Assess adherence Consider malabsorption of drugs Schecter, 2012
45 Management of Treatment Failure, Relapse Treatment failure Culture positive after 4 months of therapy: If the patient is seriously ill or sputum AFB smear +, an empirical regimen should be started with at least two new drugs If the patient is not seriously ill consider waiting for the results of drug susceptibility testing If malabsorption suspected, consider IV therapy (INH, rifampin, moxifloxacin) Schecter, 2012
MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS Dean B. Ellithorpe, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine Section of Pulmonary Diseases, Critical Care and Environmental Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine INTRODUCTION
MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS Dean B. Ellithorpe, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine Section of Pulmonary Diseases, Critical Care and Environmental Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine INTRODUCTION
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol)
 MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
MANAGEMENT OF COMMON SIDE EFFECTS of INH (Isoniazid), RIF (Rifampin), PZA (Pyrazinamide), and EMB (Ethambutol) 1. Hepatotoxicity: In Active TB Disease a. Background: 1. Among the 4 standard anti-tb drugs,
Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Tuberculosis. Anju Budhwani, MD
 Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Tuberculosis Anju Budhwani, MD Introduction Management of patients with tuberculosis (TB) can be a difficult task in any patient Drug reactions commonly occur in
Management of Adverse Drug Reactions in Tuberculosis Anju Budhwani, MD Introduction Management of patients with tuberculosis (TB) can be a difficult task in any patient Drug reactions commonly occur in
TB Drugs: Common Side Effects and Interactions. First-line Drugs 11/21/2012. Adverse Events of First-line TB Drugs
 TB Drugs: Common Side Effects and Interactions L. Beth Gadkowski MD MPH MS Assistant Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Eastern Virginia Medical School First-line Drugs Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin
TB Drugs: Common Side Effects and Interactions L. Beth Gadkowski MD MPH MS Assistant Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Eastern Virginia Medical School First-line Drugs Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin
Chapter 6 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease
 Chapter 6 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 139 Introduction.... 141 Treatment and Monitoring Plan.... 143 Adherence Strategies... 143 TB Disease Treatment Regimens....
Chapter 6 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 139 Introduction.... 141 Treatment and Monitoring Plan.... 143 Adherence Strategies... 143 TB Disease Treatment Regimens....
San Francisco Treatment Guidelines for Latent Tuberculosis Infection
 City and County of San Francisco Department of Public Health Tuberculosis Control Unit Julie Higashi, MD, PhD Director Population Health Division Edwin M. Lee Mayor Disease Prevention and Control Branch
City and County of San Francisco Department of Public Health Tuberculosis Control Unit Julie Higashi, MD, PhD Director Population Health Division Edwin M. Lee Mayor Disease Prevention and Control Branch
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tube rc ulos is Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tube rc ulos is Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents
 Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents Ritu Banerjee, MD, Ph.D TB Clinical Intensive April 8, 2015 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2014 MFMER slide-2 Objectives Describe the epidemiology of pediatric
Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents Ritu Banerjee, MD, Ph.D TB Clinical Intensive April 8, 2015 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2014 MFMER slide-2 Objectives Describe the epidemiology of pediatric
Recent Advances in The Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
 Recent Advances in The Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Dr Mohd Arif Mohd Zim Senior Lecturer & Respiratory Physician Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Teknologi MARA mohdarif035@salam.uitm.edu.my
Recent Advances in The Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Dr Mohd Arif Mohd Zim Senior Lecturer & Respiratory Physician Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Teknologi MARA mohdarif035@salam.uitm.edu.my
Guideline. Treatment of tuberculosis in adults and children Version 2.1 July 2015
 Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in adults and children Version 2.1 July 2015 Contents What this guideline covers:... 1 What this guideline does not cover:... 1 Standard regimens for pulmonary tuberculosis...
Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in adults and children Version 2.1 July 2015 Contents What this guideline covers:... 1 What this guideline does not cover:... 1 Standard regimens for pulmonary tuberculosis...
CDHS/CTCA JOINT GUIDELINES Guidelines for the Treatment of Active Tuberculosis Disease. Table of Contents
 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CDHS/CTCA JOINT GUIDELINES Table of Contents I. Basic Principles 1 A. Organization and Treatment 1 B. Treatment 1 C. Clinical Management Issues 2 II. Diagnosis 2 III.
Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CDHS/CTCA JOINT GUIDELINES Table of Contents I. Basic Principles 1 A. Organization and Treatment 1 B. Treatment 1 C. Clinical Management Issues 2 II. Diagnosis 2 III.
Chapter Four: Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease
 Chapter Four: Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease The standard of tuberculosis (TB) treatment in Los Angeles County (LAC) is to initiate an appropriate chemotherapeutic regimen along with Directly Observed
Chapter Four: Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease The standard of tuberculosis (TB) treatment in Los Angeles County (LAC) is to initiate an appropriate chemotherapeutic regimen along with Directly Observed
INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY
 FOR YOUR PATIENTS WITH RELAPSING FORMS OF MS INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been
FOR YOUR PATIENTS WITH RELAPSING FORMS OF MS INITIATING ORAL AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) THERAPY WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND RISK OF TERATOGENICITY Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been
CHAPTER 9: TREATMENT OF ACTIVE TB DISEASE
 CHAPTER 9: TREATMENT OF ACTIVE TB DISEASE 9.1 Treatment Regimens....... 2 9.1.1 Standard TB Treatment Regimen......2 9.1.2 Alternate TB Treatment Regimens.3 9.2 Phases of TB Treatment....3 9.3 TB Medications
CHAPTER 9: TREATMENT OF ACTIVE TB DISEASE 9.1 Treatment Regimens....... 2 9.1.1 Standard TB Treatment Regimen......2 9.1.2 Alternate TB Treatment Regimens.3 9.2 Phases of TB Treatment....3 9.3 TB Medications
TB Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment. Accelerating advocacy on TB/HIV 15th July, Vienna
 TB Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment Accelerating advocacy on TB/HIV 15th July, Vienna Diagnosis Microscopy of specially stained sputum is the main test for diagnosing TB (1 2 days) TB bacilli seen in
TB Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment Accelerating advocacy on TB/HIV 15th July, Vienna Diagnosis Microscopy of specially stained sputum is the main test for diagnosing TB (1 2 days) TB bacilli seen in
Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease
 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CONTENTS Introduction... 6.2 Purpose... 6.2 Policy... 6.2 Forms... 6.3 Basic Treatment Principles... 6.4 Treatment Regimens and Dosages... 6.6 Regimens... 6.6 Dosages...
Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CONTENTS Introduction... 6.2 Purpose... 6.2 Policy... 6.2 Forms... 6.3 Basic Treatment Principles... 6.4 Treatment Regimens and Dosages... 6.6 Regimens... 6.6 Dosages...
MODULE THREE TB Treatment. Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit
 MODULE THREE TB Treatment Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit 1 Topics to be covered TB treatment fundamentals Treatment of TB infection and disease TB treatment research Advocacy issues 2 Section
MODULE THREE TB Treatment Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit 1 Topics to be covered TB treatment fundamentals Treatment of TB infection and disease TB treatment research Advocacy issues 2 Section
New York City Department of Health Protocols for Latent TB Infection Treatment
 New York City Department of Health Protocols for Latent TB Infection Treatment CONTENT A. Medical evaluation for latent TB infection (LTBI) treatment 1. Medical history and physical examination 2. Chest
New York City Department of Health Protocols for Latent TB Infection Treatment CONTENT A. Medical evaluation for latent TB infection (LTBI) treatment 1. Medical history and physical examination 2. Chest
How To Treat Tuberculitis
 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CONTENTS Introduction... 6.2 Purpose... 6.2 Policy... 6.2 Forms... 6.3 Reporting Requirements... 6.3 Basic Treatment Principles... 6.4 Treatment Regimens and Dosages...
Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease CONTENTS Introduction... 6.2 Purpose... 6.2 Policy... 6.2 Forms... 6.3 Reporting Requirements... 6.3 Basic Treatment Principles... 6.4 Treatment Regimens and Dosages...
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA
 GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
TUBERCULOSIS SCREENING AND TREATMENT IN PREGNANCY. Stephanie N. Lin MD 2/12/2016
 TUBERCULOSIS SCREENING AND TREATMENT IN PREGNANCY Stephanie N. Lin MD 2/12/2016 Epidemiology of TB 9.6 million new cases in 2014 12% of them are in HIV positive patients 1.5 million deaths in 2014 ~646
TUBERCULOSIS SCREENING AND TREATMENT IN PREGNANCY Stephanie N. Lin MD 2/12/2016 Epidemiology of TB 9.6 million new cases in 2014 12% of them are in HIV positive patients 1.5 million deaths in 2014 ~646
Tuberculousmeningitis: what is the best treatment regimen?
 Tuberculousmeningitis: what is the best treatment regimen? H S Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Stellenbosch University
Tuberculousmeningitis: what is the best treatment regimen? H S Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Stellenbosch University
Treatment of Tuberculosis
 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports June 20, 2003 / Vol. 52 / No. RR-11 Treatment of Tuberculosis American Thoracic Society, CDC, and Infectious Diseases Society of America
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports June 20, 2003 / Vol. 52 / No. RR-11 Treatment of Tuberculosis American Thoracic Society, CDC, and Infectious Diseases Society of America
Tuberculosis And Diabetes. Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University
 Tuberculosis And Diabetes Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University TUBERCULOSIS FACTS More than 9 million people fall sick with tuberculosis (TB) every year. Over 1.5 million die
Tuberculosis And Diabetes Dr. hanan abuelrus Prof.of internal medicine Assiut University TUBERCULOSIS FACTS More than 9 million people fall sick with tuberculosis (TB) every year. Over 1.5 million die
Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection
 Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 109 Introduction.... 111 Candidates for the Treatment of LTBI.... 112 LTBI Treatment Regimens.... 118 LTBI
Chapter 5 Treatment for Latent Tuberculosis Infection Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 109 Introduction.... 111 Candidates for the Treatment of LTBI.... 112 LTBI Treatment Regimens.... 118 LTBI
New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. Standards of Care for Tuberculosis Disease and Latent TB Infection
 New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services Standards of Care for Tuberculosis Disease and Latent TB Infection Tuberculosis Medical Advisory Board March 2007 Table of Contents Standard # 1: Diagnosis
New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services Standards of Care for Tuberculosis Disease and Latent TB Infection Tuberculosis Medical Advisory Board March 2007 Table of Contents Standard # 1: Diagnosis
Management of Tuberculosis: Indian Guidelines
 Chapter 105 Management of Tuberculosis: Indian Guidelines Kuldeep Singh Sachdeva INTRODUCTION Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused predominantly by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and among the
Chapter 105 Management of Tuberculosis: Indian Guidelines Kuldeep Singh Sachdeva INTRODUCTION Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused predominantly by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and among the
AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS (UPDATE 2004) Internal guidelines of the Tuberculosis & Chest Service of the Department of Health
AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS (UPDATE 2004) Internal guidelines of the Tuberculosis & Chest Service of the Department of Health
Treatment. Introduction... 32. Individualized Regimens.. 33. Selection and Dosing of Drugs... 41. Administration of the Regimen...
 Treatment 3 Introduction............ 32 Individualized Regimens.. 33 Monoresistance......... 33 Polyresistance.......... 34 Multidrug Resistance..... 35 Extensive Drug Resistance 39 Selection and Dosing
Treatment 3 Introduction............ 32 Individualized Regimens.. 33 Monoresistance......... 33 Polyresistance.......... 34 Multidrug Resistance..... 35 Extensive Drug Resistance 39 Selection and Dosing
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination Public
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination Public
CIRCULATED FOR COMMENTS - Feb04 DRAFT. BHIVA treatment guidelines for TB/HIV infection
 BHIVA treatment guidelines for TB/HIV infection February 2004 (DRAFT) Dr Anton Pozniak Contents 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Aims of TB treatment 3.0 Treatment Regimens 4.0 Drug/drug interactions 5.0 Overlapping
BHIVA treatment guidelines for TB/HIV infection February 2004 (DRAFT) Dr Anton Pozniak Contents 1.0 Introduction 2.0 Aims of TB treatment 3.0 Treatment Regimens 4.0 Drug/drug interactions 5.0 Overlapping
Guideline. Treatment of tuberculosis in renal disease. Version 3.0
 Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in renal disease Version 3.0 Key critical points Renal failure is recognised as a risk factor for developing tuberculosis. Renal failure is recognised as a risk factor
Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in renal disease Version 3.0 Key critical points Renal failure is recognised as a risk factor for developing tuberculosis. Renal failure is recognised as a risk factor
Treatment of Tuberculosis
 Treatment of Tuberculosis 1a Taking TB Treatment 2 Learning outcomes Describe the use of TB case definitions & the management of TB patients Successfully treat TB using the appropriate regimen for the
Treatment of Tuberculosis 1a Taking TB Treatment 2 Learning outcomes Describe the use of TB case definitions & the management of TB patients Successfully treat TB using the appropriate regimen for the
Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
 Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Indication: In combination with docetaxel in locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent NSCLC of adenocarcinoma
Lung Pathway Group Nintedanib (Vargatef) in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Indication: In combination with docetaxel in locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent NSCLC of adenocarcinoma
12 Points of Tuberculosis (TB) Patient Education
 12 Points of Tuberculosis (TB) Patient Education Transmission of TB TB is a disease caused by the TB germ. The disease is mainly in the lungs (pulmonary TB), but the germ can travel to other parts of the
12 Points of Tuberculosis (TB) Patient Education Transmission of TB TB is a disease caused by the TB germ. The disease is mainly in the lungs (pulmonary TB), but the germ can travel to other parts of the
Case Management Treatment Plan for Active TB Disease
 Case Management Treatment Plan for Active TB Disease The purpose of this form is to provide a checklist to organize the gathering of information in a TB case to ensure the best medical and public health
Case Management Treatment Plan for Active TB Disease The purpose of this form is to provide a checklist to organize the gathering of information in a TB case to ensure the best medical and public health
Dr Malgosia Grzemska Global TB programme, WHO/HQ Meeting of manufacturers Copenhagen, Denmark, 23-26 November 2015
 TB burden and treatment guidelines Dr Malgosia Grzemska Global TB programme, WHO/HQ Meeting of manufacturers Copenhagen, Denmark, 23-26 November 2015 Outline Latest epidemiological data Global programme
TB burden and treatment guidelines Dr Malgosia Grzemska Global TB programme, WHO/HQ Meeting of manufacturers Copenhagen, Denmark, 23-26 November 2015 Outline Latest epidemiological data Global programme
American Thoracic Society Documents
 American Thoracic Society Documents American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: Treatment of Tuberculosis This Official Joint Statement
American Thoracic Society Documents American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: Treatment of Tuberculosis This Official Joint Statement
LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services
 Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Tuberculosis and You A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease that can damage the lungs or other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys or spine. There are
Introduction to TB Nurse Case Management Online February 4, 11, 18 and 25, 2015
 Introduction to TB Nurse Case Management Online February 4, 11, 18 and 25, 2015 Completion of Treatment: Case Studies or A Little Bit of Everything Presented by Cherie Fulk February 25, 2015 Cherie Fulk
Introduction to TB Nurse Case Management Online February 4, 11, 18 and 25, 2015 Completion of Treatment: Case Studies or A Little Bit of Everything Presented by Cherie Fulk February 25, 2015 Cherie Fulk
5.07.09. Aubagio. Aubagio (teriflunomide) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.07.09 Subject: Aubagio Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: December 5, 2014 Aubagio Description Aubagio (teriflunomide)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.07.09 Subject: Aubagio Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: December 5, 2014 Aubagio Description Aubagio (teriflunomide)
DIRECTLY OBSERVED TREATMENT SHORT-COURSE (DOTS)
 DIRECTLY OBSERVED TREATMENT SHORT-COURSE (DOTS) Protocol for Tuberculosis Demonstration Projects in Russia U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and U.S. Agency for International Development
DIRECTLY OBSERVED TREATMENT SHORT-COURSE (DOTS) Protocol for Tuberculosis Demonstration Projects in Russia U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and U.S. Agency for International Development
This regimen has low emetogenic potential refer to local protocol None required routinely. Baseline results valid for 7 days. Results valid for 72 hrs
 Regimen : Ipilimumab for Advanced Melanoma ICD10 code Codes pre-fixed with C43. Indication Regimen detail Ipilimumab is recommended as an option for treating advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma
Regimen : Ipilimumab for Advanced Melanoma ICD10 code Codes pre-fixed with C43. Indication Regimen detail Ipilimumab is recommended as an option for treating advanced (unresectable or metastatic) melanoma
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS Ministry of Health Malaysia Academy of Medicine Malaysia Malaysian Thoracic Society KEY MESSAGES 1. Tuberculosis (TB) is a notifiable infectious disease. Timely
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS Ministry of Health Malaysia Academy of Medicine Malaysia Malaysian Thoracic Society KEY MESSAGES 1. Tuberculosis (TB) is a notifiable infectious disease. Timely
Guideline. Treatment of tuberculosis in patients with HIV co-infection. Version 3.0
 Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in patients with HIV co-infection Version 3.0 Key critical points Co-infection with Tuberculosis (TB) and HIV is common in many parts of the world, especially sub-saharan
Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in patients with HIV co-infection Version 3.0 Key critical points Co-infection with Tuberculosis (TB) and HIV is common in many parts of the world, especially sub-saharan
Maximizing Rifamycins
 Maximizing Rifamycins Charles A. Peloquin, Pharm.D. Director Infectious Disease Pharmacokinetics Laboratory Professor, College of Pharmacy & The Emerging Pathogens Institute University of Florida Page
Maximizing Rifamycins Charles A. Peloquin, Pharm.D. Director Infectious Disease Pharmacokinetics Laboratory Professor, College of Pharmacy & The Emerging Pathogens Institute University of Florida Page
Massachusetts Tuberculosis Nursing Case Management Protocols. Tuberculosis Elimination Achieved through Management
 Massachusetts Tuberculosis Nursing Case Management Protocols Tuberculosis Elimination Achieved through Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Page I. Introduction Theoretical Framework 5 5 Goal of Case Management
Massachusetts Tuberculosis Nursing Case Management Protocols Tuberculosis Elimination Achieved through Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Page I. Introduction Theoretical Framework 5 5 Goal of Case Management
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices
 Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Exposure Control Plan for Low Risk Dental Offices A. BACKGROUND According to the CDC, approximately one-third of the world s population, almost two billion people, are infected with tuberculosis.
Guideline. Treatment of tuberculosis in pregnant women and newborn infants. Version 3.0
 Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in pregnant women and newborn infants Version 3.0 Key critical points The decision to treat tuberculosis (TB) in pregnancy must consider the potential risks to mother
Guideline Treatment of tuberculosis in pregnant women and newborn infants Version 3.0 Key critical points The decision to treat tuberculosis (TB) in pregnancy must consider the potential risks to mother
patient group direction
 DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
DICLOFENAC v01 1/8 DICLOFENAC PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
Guidelines for the Management of Adverse Drug Effects of Antimycobacterial Agents
 Guidelines for the of Adverse Drug Effects of Antimycobacterial Agents Lawrence Flick Memorial Tuberculosis Clinic Philadelphia Tuberculosis Control Program November 1998 Table of Contents Subject Page(s)
Guidelines for the of Adverse Drug Effects of Antimycobacterial Agents Lawrence Flick Memorial Tuberculosis Clinic Philadelphia Tuberculosis Control Program November 1998 Table of Contents Subject Page(s)
Current trends in chemotherapy of tuberculosis
 Review Article Indian J Med Res 120, October 2004, pp 398-417 Current trends in chemotherapy of tuberculosis M.S. Jawahar Tuberculosis Research Centre (ICMR), Chennai, India Received August 28, 2003 After
Review Article Indian J Med Res 120, October 2004, pp 398-417 Current trends in chemotherapy of tuberculosis M.S. Jawahar Tuberculosis Research Centre (ICMR), Chennai, India Received August 28, 2003 After
Elisabeth Patton, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM
 Brian Odegaard, RN BSN Public Health Madison & Dane County Diana Haley, RN BSN Sauk County Health Department Elisabeth Patton, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Veterinary Program Manager Wisconsin Department
Brian Odegaard, RN BSN Public Health Madison & Dane County Diana Haley, RN BSN Sauk County Health Department Elisabeth Patton, DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM Veterinary Program Manager Wisconsin Department
Management of HIV and TB Co-infection in South Africa
 Management of HIV and TB Co-infection in South Africa Halima Dawood Department of Medicine Case Report 39 yr old female Referred to clinic on 14/06/2006 for consideration to commence antiretroviral therapy
Management of HIV and TB Co-infection in South Africa Halima Dawood Department of Medicine Case Report 39 yr old female Referred to clinic on 14/06/2006 for consideration to commence antiretroviral therapy
Clinical Scenarios In Childhood TB. Josefina Cadorna Carlos M.D., FPPS, FPIDSP, FSMID Associate Professor of Pediatrics U E R M M M C
 Clinical Scenarios In Childhood TB Josefina Cadorna Carlos M.D., FPPS, FPIDSP, FSMID Associate Professor of Pediatrics U E R M M M C Objectives: To present different commonly encountered clinical scenarios
Clinical Scenarios In Childhood TB Josefina Cadorna Carlos M.D., FPPS, FPIDSP, FSMID Associate Professor of Pediatrics U E R M M M C Objectives: To present different commonly encountered clinical scenarios
Monitoring Patients. Initial Evaluation... 128. Documentation... 129. General Monitoring... 129. Specific Monitoring... 130. Monitoring Tools...
 6 Monitoring Patients Initial Evaluation........ 128 Documentation......... 129 General Monitoring..... 129 Specific Monitoring..... 130 Drug Administration..... 130 Absorption, Interactions. 130 Weight,
6 Monitoring Patients Initial Evaluation........ 128 Documentation......... 129 General Monitoring..... 129 Specific Monitoring..... 130 Drug Administration..... 130 Absorption, Interactions. 130 Weight,
FUNDAMENTALS OF TB CASE MANAGEMENT
 CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE FUNDAMENTALS OF TB CASE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe several components of the tuberculosis
CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE FUNDAMENTALS OF TB CASE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe several components of the tuberculosis
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) Dr. NAVPREET
 Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) Dr. NAVPREET Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH Chandigarh Problem Statement of TB in India India accounts for nearly 1/4 th of global
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) Dr. NAVPREET Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH Chandigarh Problem Statement of TB in India India accounts for nearly 1/4 th of global
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis. Information for clinicians
 Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Pregnancy and Tuberculosis Information for clinicians When to suspect Tuberculosis (TB)? Who is at risk of TB during pregnancy? Recent research suggests that new mothers are at an increased risk of TB
Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis
 Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis 2014 Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis 2014 Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis ( TB) was written to provide information on the diagnosis and treatment
Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis 2014 Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis 2014 Questions and Answers About Tuberculosis ( TB) was written to provide information on the diagnosis and treatment
You. guide to tuberculosis treatment and services
 Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Adapted from TB and You: A Guide to Tuberculosis Treatment and Services with permission from Division of Public Health TB Control Program State of North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
Pediatric Latent TB Diagnosis and Treatment
 Date Updated: April 2015 Guidelines Reviewed: 1. CDC Latent TB Guidelines 2. Harborview Pediatric Clinic Latent TB Management, 2010 3. Pediatric Associates Latent TB Guidelines, 2013 4. Seattle Children
Date Updated: April 2015 Guidelines Reviewed: 1. CDC Latent TB Guidelines 2. Harborview Pediatric Clinic Latent TB Management, 2010 3. Pediatric Associates Latent TB Guidelines, 2013 4. Seattle Children
The Global Epidemic 3/25/14. Roadmap to the Future: TB Control & Elimination. TB Exposed: Pharmacologic Management of TB April 11, 2014
 Diana Fortune RN BSN TB Program Manager New Mexico Department of Health TB Exposed: Pharmacologic Management of TB April 11, 2014 The Global Epidemic http://exposed.aeras.org/#_video2 Roadmap to the Future:
Diana Fortune RN BSN TB Program Manager New Mexico Department of Health TB Exposed: Pharmacologic Management of TB April 11, 2014 The Global Epidemic http://exposed.aeras.org/#_video2 Roadmap to the Future:
Adverse Reactions. Introduction... 146. Gastrointestinal... 147. Dermatologic and Hypersensitivity... 151. Hematologic Abnormalities...
 7 Adverse Reactions Introduction........... 146 Gastrointestinal........ 147 Dermatologic and Hypersensitivity........ 151 Hematologic Abnormalities.......... 155 Severe Drug Reactions.. 156 Hypersensitivity
7 Adverse Reactions Introduction........... 146 Gastrointestinal........ 147 Dermatologic and Hypersensitivity........ 151 Hematologic Abnormalities.......... 155 Severe Drug Reactions.. 156 Hypersensitivity
Drugs for Alcohol Dependence: Clinical Guidance and Three Way Agreement
 Drugs for Alcohol Dependence: Clinical Guidance and Three Way Agreement for County Durham In partnership with the GP, the client, and the County Durham Drug and Alcohol Service December 2015 Version 1.0
Drugs for Alcohol Dependence: Clinical Guidance and Three Way Agreement for County Durham In partnership with the GP, the client, and the County Durham Drug and Alcohol Service December 2015 Version 1.0
Targeted Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Adults and Children
 C D H S / C T C A J O I N T G U I D E L I N E S Targeted Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Adults and Children Targeted Skin Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection
C D H S / C T C A J O I N T G U I D E L I N E S Targeted Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Adults and Children Targeted Skin Testing and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection
Patient Education CONTENTS. Introduction... 12.2
 CONTENTS Introduction... 12.2 Purpose... 12.2 General Guidelines... 12.3 Language and Comprehension Barriers... 12.4 Education Topics... 12.5 Medical Diagnosis... 12.5 Contact Investigation... 12.6 Isolation...
CONTENTS Introduction... 12.2 Purpose... 12.2 General Guidelines... 12.3 Language and Comprehension Barriers... 12.4 Education Topics... 12.5 Medical Diagnosis... 12.5 Contact Investigation... 12.6 Isolation...
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
 DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
DVT/PE Management with Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Rivaroxaban is FDA approved for the acute treatment of DVT and PE and reduction in risk of recurrence of DVT and PE. FDA approved indications: Non valvular
TB preventive therapy in children. Introduction
 TB preventive therapy in children H S Schaaf Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, and Desmond Tutu TB Centre Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital Introduction Children are
TB preventive therapy in children H S Schaaf Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, and Desmond Tutu TB Centre Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital Introduction Children are
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Ottawa Public Health Tuberculosis Screening and Contact Management Guidelines 2012
 Ottawa Public Health Tuberculosis Screening and Contact Management Guidelines 2012 ottawa.ca/health ottawa.ca/sante 613-580-6744 TTY/ATS : 613-580-9656 Tuberculosis Screening and Contact Management Guidelines
Ottawa Public Health Tuberculosis Screening and Contact Management Guidelines 2012 ottawa.ca/health ottawa.ca/sante 613-580-6744 TTY/ATS : 613-580-9656 Tuberculosis Screening and Contact Management Guidelines
Treatment of TB a pharmacy perspective
 Treatment of TB a pharmacy perspective Colm McDonald, Antimicrobial Stewardship Pharmacist (Acting) National TB Conference, St. James s Hospital 6 th May 2011 Overview of presentation Role of the pharmacist
Treatment of TB a pharmacy perspective Colm McDonald, Antimicrobial Stewardship Pharmacist (Acting) National TB Conference, St. James s Hospital 6 th May 2011 Overview of presentation Role of the pharmacist
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION
 ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 TEACHING YOUR STROKE PATIENTS ABOUT THEIR MEDICATION Please refer to Module 8: Secondary Stroke Prevention for additional information Blood Pressure Medication Angiotensin
LEARNING OUTCOMES. Identify children at risk of developing TB disease. Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB. Manage child contacts
 TB in Children 1a TB IN CHILDREN 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES Identify children at risk of developing TB disease Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB Manage child contacts 3 TB Infection and Disease
TB in Children 1a TB IN CHILDREN 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES Identify children at risk of developing TB disease Correctly manage and refer children suspected of TB Manage child contacts 3 TB Infection and Disease
NOTICE OF PUBLIC HEARING REGARDING PROPOSED CHANGES IN HEALTH CARE SERVICES PROVIDED BY FRESNO COUNTY
 NOTICE IS HEREBY GIVEN that a public hearing will commence on Tuesday, September 23, 2008, at 9:00 a.m. (subject to continuance on that date of the hearing) at the Fresno County Board of Supervisors Chambers,
NOTICE IS HEREBY GIVEN that a public hearing will commence on Tuesday, September 23, 2008, at 9:00 a.m. (subject to continuance on that date of the hearing) at the Fresno County Board of Supervisors Chambers,
Tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS Co-Infection: Epidemiology and Public Health Challenges
 Tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS Co-Infection: Epidemiology and Public Health Challenges John B. Kaneene, DVM, MPH, PhD University Distinguished Professor of Epidemiology Director, Center for Comparative Epidemiology
Tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS Co-Infection: Epidemiology and Public Health Challenges John B. Kaneene, DVM, MPH, PhD University Distinguished Professor of Epidemiology Director, Center for Comparative Epidemiology
Santa Clara County Tuberculosis Screening Requirement for School Entrance Effective June 1, 2014. Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions A child has history of BCG vaccination, should they have TST or IGRA? According to the American Academy of Pediatrics Red Book (2012), Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) is
Frequently Asked Questions A child has history of BCG vaccination, should they have TST or IGRA? According to the American Academy of Pediatrics Red Book (2012), Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) is
Management of a child failing first line TB treatment.
 Management of a child failing first line TB treatment. Robert Gie Desmond Tutu Tuberculosis Centre Department of Paediatric and Child Health Stellenbosch University South Africa. Tygerberg Hospital Complex
Management of a child failing first line TB treatment. Robert Gie Desmond Tutu Tuberculosis Centre Department of Paediatric and Child Health Stellenbosch University South Africa. Tygerberg Hospital Complex
Tuberculosis Trials Consortium (TBTC) Update on New Drug Work for DS TB 2012
 Tuberculosis Trials Consortium (TBTC) Update on New Drug Work for DS TB 2012 Stop TB Work Group on New Drugs Annual Meeting, Kuala Lumpur, 2012 Clinical Development of TB Drugs Payam Nahid, MD, MPH Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis Trials Consortium (TBTC) Update on New Drug Work for DS TB 2012 Stop TB Work Group on New Drugs Annual Meeting, Kuala Lumpur, 2012 Clinical Development of TB Drugs Payam Nahid, MD, MPH Tuberculosis
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS. Hot topics / Unresolved issues in Clinical Practice
 PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Hot topics / Unresolved issues in Clinical Practice Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Legacy Emanuel Children s Hospital Portland, OR Faculty Consultant Francis J. Curry National TB Center February
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Hot topics / Unresolved issues in Clinical Practice Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Legacy Emanuel Children s Hospital Portland, OR Faculty Consultant Francis J. Curry National TB Center February
Each discipline will perform activities within the constraints of their respective practice acts, job descriptions and protocols.
 I. TITLE: Protocol for TB Targeted Testing Activities and Treatment of Latent TB Infection (previously referred to as TB screening and preventive therapy). Important Change in Nomenclature: Identification
I. TITLE: Protocol for TB Targeted Testing Activities and Treatment of Latent TB Infection (previously referred to as TB screening and preventive therapy). Important Change in Nomenclature: Identification
2011 NTP Paediatric guidelines update- final draft
 Childhood TB Investigation and management of children suspected to have tuberculosis (TB) or who are close contacts of a TB case (sputum smear positive or negative) Key facts Children who are close contacts
Childhood TB Investigation and management of children suspected to have tuberculosis (TB) or who are close contacts of a TB case (sputum smear positive or negative) Key facts Children who are close contacts
Tuberculosis (TB) remains the leading cause of mortality from infectious. Tuberculosis (TB)
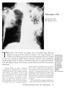 Tuberculosis (TB) John Bernardo, MD Jill S. Roncarati, PA-C Tuberculosis (TB) remains the leading cause of mortality from infectious diseases in humans in the world. In contrast to the world situation,
Tuberculosis (TB) John Bernardo, MD Jill S. Roncarati, PA-C Tuberculosis (TB) remains the leading cause of mortality from infectious diseases in humans in the world. In contrast to the world situation,
Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist
 Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist The following checklist must be completed before enrolling in the Nurse Aide Training course: Complete, sign, and date the Application Form Have the physical
Nurse Aide Training Program Application Checklist The following checklist must be completed before enrolling in the Nurse Aide Training course: Complete, sign, and date the Application Form Have the physical
Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3. Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission 4 Period of communicability 4
 Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
Tuberculosis Contents Epidemiology in New Zealand 2 Case definition 2 Clinical description 2 Laboratory test for diagnosis 3 Case classification 3 Spread of infection 4 Incubation period 4 Mode of transmission
Management of Tuberculosis (TB)
 for Professional Health Care Providers Management of Tuberculosis (TB) USAID UNITED STATES AGENCY INTERNATIONAL DEVELOPMENT USAID FROM THE AMERICAN PEOPLE SOUTHERN AFRICA WHAT IS TB? Tuberculosis (TB)
for Professional Health Care Providers Management of Tuberculosis (TB) USAID UNITED STATES AGENCY INTERNATIONAL DEVELOPMENT USAID FROM THE AMERICAN PEOPLE SOUTHERN AFRICA WHAT IS TB? Tuberculosis (TB)
Adjunctive psychosocial intervention. Conditions requiring dose reduction. Immediate, peak plasma concentration is reached within 1 hour.
 Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
Shared Care Guideline for Prescription and monitoring of Naltrexone Hydrochloride in alcohol dependence Author(s)/Originator(s): (please state author name and department) Dr Daly - Consultant Psychiatrist,
**Form 1: - Consultant Copy** Telephone Number: Fax Number: Email: Author: Dr Bernard Udeze Pharmacist: Claire Ault Date of issue July 2011
 Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Effective Shared Care Agreement for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer s Disease Donepezil tablets / orodispersible tablets (Aricept / Aricept Evess ) These forms (1 and 2) are to be completed by both
Challenges in Pediatric Tuberculosis. Mimi Emig, MD Spectrum Health Kent County Health Department
 Challenges in Pediatric Tuberculosis Mimi Emig, MD Spectrum Health Kent County Health Department Pediatric Tuberculosis: A Missed Public Health Opportunity Mimi Emig, MD Spectrum Health Kent County Health
Challenges in Pediatric Tuberculosis Mimi Emig, MD Spectrum Health Kent County Health Department Pediatric Tuberculosis: A Missed Public Health Opportunity Mimi Emig, MD Spectrum Health Kent County Health
AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS AN INFORMATION PAPER January 2013 AMBRX_1301 This information paper is an update of Chapter 17 of
AMBULATORY TREATMENT AND PUBLIC HEALTH MEASURES FOR A PATIENT WITH UNCOMPLICATED PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS AN INFORMATION PAPER January 2013 AMBRX_1301 This information paper is an update of Chapter 17 of
TB Case Management Core Components
 TB Case Management Core Components CDPH/CTCA Joint Guidelines TB Case Management Core 0 Components 1 of 24 Table of Contents PREFACE... 3 INTRODUCTION... 3 PART I. Receipt of Case Report... 4 1.1 Demographic,
TB Case Management Core Components CDPH/CTCA Joint Guidelines TB Case Management Core 0 Components 1 of 24 Table of Contents PREFACE... 3 INTRODUCTION... 3 PART I. Receipt of Case Report... 4 1.1 Demographic,
Guidelines on targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection
 Guidelines on targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection Tuberculosis and Chest Service (Last update on 31March 2015) Internal guidelines of the Tuberculosis & Chest Service
Guidelines on targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection Tuberculosis and Chest Service (Last update on 31March 2015) Internal guidelines of the Tuberculosis & Chest Service
Clinic Name and Location: 4. Clinic has specific written protocols or guidelines for treatment of TB:
 TB Clinic Survey Form Clinic Name and Location: PATIENT POPULATION 1. Number of Patients eligible for initiation of TB Treatment: 2. Number of Patients Started on TB Treatment: 3. Number of these Patients
TB Clinic Survey Form Clinic Name and Location: PATIENT POPULATION 1. Number of Patients eligible for initiation of TB Treatment: 2. Number of Patients Started on TB Treatment: 3. Number of these Patients
Tuberculosis Coding and Billing Tool
 Tuberculosis Coding and Billing Tool 2014 Georgia Department of Public Health Division of Health Protection Office of Immunization and Infectious Disease Tuberculosis Program http://dph.georgia.gov/tuberculosis-tb-prevention-and-control
Tuberculosis Coding and Billing Tool 2014 Georgia Department of Public Health Division of Health Protection Office of Immunization and Infectious Disease Tuberculosis Program http://dph.georgia.gov/tuberculosis-tb-prevention-and-control
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014 TB in the HIV Patient Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 13, 2014 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 11 14, 2014 TB in the HIV Patient Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD November 13, 2014 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
Eastern Health MS Service. Tysabri Therapy. Information for People with MS and their Families
 Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Hepatitis Update. HCV Cure As A Paradigm for Convergence of Interests. Evidence Based Nuts and Bolts For the Family Doc 11/5/2014
 Evidence Based Nuts and Bolts For the Family Doc Hepatitis Update William Carey MD MACG, FAASLD Oct 25, 2014 HCV Cure As A Paradigm for Convergence of Interests Hepatitis C Cure 1 Get Ready Get SET Go
Evidence Based Nuts and Bolts For the Family Doc Hepatitis Update William Carey MD MACG, FAASLD Oct 25, 2014 HCV Cure As A Paradigm for Convergence of Interests Hepatitis C Cure 1 Get Ready Get SET Go
