Lab 1 Router on a stick
|
|
|
- Nickolas Robbins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
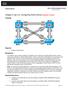
1 Lab 1 Router on a stick BEFORE YOU BEGIN Clear all router/switch configurations and VLANs, using the Introduction Lab as a guide if needed. For this lab you will need: 2 Subnets (VLANs) o VLAN /24 o VLAN /24 3 Routers (2 used for hosts) 1 Layer 2 switch Start with a diagram/drawing. In doing this task, you will find what you need for the lab topology based on your pod diagram by figuring out what equipment and ports are needed.
2 For this lab, you will need 3 routers that connect directly to the same layer 2 switch. Take the drawing above and write in hostnames and ports you will use to accomplish the task. Stuck? Ask your instructor or TA for assistance! This part is a crucial skill that you will need throughout the course. Now that you have your diagram and ports, we can start to configure the devices. Let s start with the PCs: First, use 2 routers that connect to 1 switch in your pod. These 2 routers will be used as hosts, and will not do any layer 3 routing, so the first thing we can do is shut off the routing function with the no ip routing command. Next, we need to make sure we give our host a default gateway, since we have just turned off ip routing. This will allow our host to get off its local network/subnet when it wants to. We will use the ip default gateway x.1 command to accomplish this. As always, simply replace the x with the proper subnet number. Next, let s give our host a name with the hostname command. Keep it simple. VLAN5HOST will do. Next, configure the correct interface that connects to the switch. This port will probably be a gigabit0/0, or gigabit 0/1 on the router. You will want to make sure the following commands are configured: o ip address x replace the X with whatever Subnet/VLAN you are configuring. o A no shutdown command to place the interface in an active state. Next, we will need to verify our interface is setup properly. Do a show run interface gigabit x/x where the x/x is the correct number for the interface you used. This command will allow you to verify what you configured for that particular interface. If you would like to see the entire router configuration, simply do a show run. Now let s look at the operational state of that particular interface. We can do this with the show interface gigabit x/x command. Again, substitute the correct interface numbers. Here is an example output, What we want to focus on is in Red: HOST2#show int gi 0/0
3 GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is 1cdf.0fe1.ccb8 (bia 1cdf.0fe1.ccb8) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is RJ45 output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:22, output 00:00:00, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec OUTPUT CONTINUED>>>>Omitted HOST2# Note that we see the interface is up/up at layers 1 and 2, has an IP at layer 3, and has negotiated speed and duplex in a proper manor. Next we move on to the switch configuration: Configure a hostname for the switch, using the hostname command.
4 Now we will configure our VLANs that we will use for our subnets. Remember a VLAN is used to logically separate Subnets from each other without the use of additional hardware and interfaces. We will logically separate our 2 VLANs, 5 and 6, and their associated IP traffic, and allow them to communicate via a single interface on our local router. Use the global configuration vlan command to accomplish this. Use the show vlan command to verify. Here is an example: SWITCH1(config)#vlan 5 SWITCH1(config-vlan)#name VLAN5 SWITCH1(config-vlan)#exit SWITCH1(config)#vlan 6 SWITCH1(config-vlan)#name VLAN6 SWITCH1(config-vlan)#exit SWITCH1(config)#do show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports default active Gi0/1, Gi0/2, Gi0/3, Gi0/4 Gi0/5, Gi0/6, Gi0/7, Gi0/8 Gi0/9, Gi0/10, Gi0/11, Gi0/12 Gi0/13, Gi0/14, Gi0/15, Gi0/16 Gi0/17, Gi0/18, Gi0/19, Gi0/20 Gi0/21, Gi0/22, Gi0/23, Gi0/24 5 VLAN5 active 6 VLAN6 active 1002 fddi-default act/unsup 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
5 1005 trnet-default act/unsup OUTPUT CONTINUED>>>>Omitted Now we need to associate our host ports with the appropriate VLANs. The port that we have connected to the host on VLAN 5, will need to be associated with VLAN 5. The port for the host on VLAN 6, of course, will need to be associated with VLAN 6. We should also verify that our ports are up/up, and are associated properly after configurations with the proper show commands. Use the interface command switchport access VLAN x to associate the port with the VLAN. Substitute the proper VLAN # for x. Example: SWITCH1(config)#int gi 0/3 SWITCH1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 5 SWITCH1(config-if)#exit SWITCH1(config)# Verify with the show interface switchport and show interface commands shown below: SWITCH1#show interface gigabitethernet 0/3 switchport Name: Gi0/3 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: static access Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Operational Trunking Encapsulation: native Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 5 (VLAN5) OUTPUT CONTINUED>>>>Omitted
6 SWITCH1#show int gi 0/3 GigabitEthernet0/3 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is Gigabit Ethernet, address is f866.f2f (bia f866.f2f8.6203) MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s, media type is 10/100/1000BaseTX OUTPUT CONTINUED>>>>Omitted Now that we have our host ports associated with the proper VLANs, we now need to allow this VLAN traffic to be brought up to the router to be routed. We will accomplish this by setting up a link called a trunk. A trunk will allow for multiple VLANs to traverse the connection to the other device so that it can be processed. In this case, we are allowing VLANs 5 and 6 to traverse the trunk so our router can allow the 2 VLANS to communicate with each other. The frames traversing the link are tagged with their VLAN ID, which allows for the traffic to stay separate. It will be the job of the router to make the decisions on whether the VLANs can communicate with each other. This process can involve the use of routing protocols, Access Control Lists, Quality of Services, etc. In this lab, we will use basic connected routes to allow these VLANs to communicate. In order to accomplish this task, we will need to identify the interface that you have chosen to connect to your router, and we will statically configure this link as a trunk. We will also only allow for VLANs 5 and 6 to traverse the link. This is done for bandwidth and security reasons, as you will learn later. We will also set the layer 2 trunking encapsulation type, there are 2 for these switches, ISL (Cisco) and Dot1Q, Dot1Q being an open standard. We will use Dot1Q. Use the switchport mode trunk and switchport trunk commands to accomplish this task. An example is below: SWITCH1(config)#int gi 0/1 SWITCH1(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
7 SWITCH1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk SWITCH1(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 5,6 SWITCH1(config-if)#exit Verify our trunk configurations using your show interface and show interface switchport commands as you did above for the access ports (PCs). Also, verify your trunk using the show interfaces trunk command. Example: SWITCH1#show int trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Gi0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Gi0/1 5-6 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Gi0/1 5-6 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi0/1 none SWITCH1# Don t see a trunk? Check you router to make sure the interface is at least up/up. Do a no shut if needed, and verify again. Also, check your interface configuration using the show run interface command. At this point we will move on to the router. The switch configuration is complete.
8 Router configuration: We will need to configure our router to accept frames over our trunk for both VLANs 5 and 6. We will also need to configure the Gigabit interface for both VLANs, which will allow for us to route between these VLANs. Essentially, we are configuring the default gateways for both of our subnets. Let s begin: First, configure a hostname for the router, see above for commands to accomplish this. Next, identify the interface on the router you used for the trunk to the switch. The first command you should do is a no shutdown, if you have not done so already, allowing for layer 1 and 2 connectivity to the switch. Verify this with your show interface command that you used above, remember, you are looking for an up/up state on the interface. Now let s configure the trunk and layer 3 IP commands: We will need to use Sub-Interfaces in order to use one physical interface to represent two virtual interfaces. Here is an example of how to configure a sub-interface : ROUTER1(config-if)#int gi 0/0.5 Note the use of the.5 on the end of the interface gig0/0 command. This is a logical separation of the interface, and we are choosing.5 because this will be used for VLAN 5. This is an arbitrary number..however we will use 5 for documentation and clarity. Next we will need to set the encapsulation type, and the VLAN 5 used for this sub-interface. This number is NOT arbitrary, and needs to match the exact VLAN used on the trunk. Example: ROUTER1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 5 Next we will need to set the default gateway IP address for our hosts. This will be the assigned IP for this sub-interface. Here is an example for VLAN 5. ROUTER1(config-subif)#ip address Perform this same configuration for both VLANs. Use the.6 sub-interface for VLAN 6. Verify your configurations using the show interface commands above, but let s also add a new command, the show interface brief command: ROUTER1#show ip interface brief
9 Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up up GigabitEthernet0/1 Serial0/0/0 Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down unassigned YES unset administratively down down unassigned YES unset administratively down down ROUTER1# Note with this command we see that the main Gig interface is up/up, but has no IP address assigned. We also see that our 2 sub-interfaces have the IPs, and they are up/up as well. At this point, we can start to verify our connectivity! Lab connectivity verification: We can now begin the process of verifying our configurations. First, do a double check of your configurations and make sure everything appears as you configured it using your show run commands. Next, let s check our hosts. First, ping their gateway to see if they can reach the router. HOST2#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:..!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms HOST2# Did you lose a couple of pings at first? This is usually due to the time it takes to do the first ARP lookups. Can t ping your gateway??? Start you troubleshooting by choosing a method. (Top down, bottom up, divide and conquer, etc) Next follow the packet!!!! Remember we will leave the NIC on our host, then switch through to the router, and then we follow the same path back to the PC. Check things like port status, trunk status, VLAN assignments, etc. If the ping to the gateway is successful, check to see if you can ping the other host on the different subnet. VLAN 5 to VLAN 6. This will verify that routing is working as well. We should now be able to
10 take a packet from VLAN 5, destined for VLAN 6, and the router will use its internal routing table to forward the packet. HOST1#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms HOST1# Also, we can verify the router has the right routes with a new command, a show ip route. Perform this command on your router. Note these are listed as CONNECTED routes. ROUTER1#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, + - replicated route Gateway of last resort is not set /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C L /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0.6
11 L /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0.6 ROUTER1# At this point you have successfully completed Lab1. Save all configurations as you will need them for upcoming labs!
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Configuring Link Aggregation
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router
 Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module
 CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI
 CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite
 Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN
 Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH
 APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH 1 1. Criando um Banner de Login REDE DE COMPUTADORES VI SALESIANO#conf t SALESIANO(config)#banner motd c Enter TEXT message. End with the character 'c'.
APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH 1 1. Criando um Banner de Login REDE DE COMPUTADORES VI SALESIANO#conf t SALESIANO(config)#banner motd c Enter TEXT message. End with the character 'c'.
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
- Switch Port Configuration -
 1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Laboratorio 4. Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite
 Laboratorio 4 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Laboratorio 4 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Study Guide Allan Johnson
 Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi
 How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide support
How to Create VLANs Within a Virtual Switch in VMware ESXi I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide support
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R
 VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
Network Simulator Lab Study Plan
 The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
IST 220 Honors Project. Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks
 IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing
 Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
Frame Mode MPLS Implementation
 CHAPTER 4 Frame Mode MPLS Implementation Lab 4-1: Configuring Frame Mode MPLS (4.5.1) In this lab, you learn how to do the following: Configure EIGRP on a router. Configure LDP on a router. Change the
CHAPTER 4 Frame Mode MPLS Implementation Lab 4-1: Configuring Frame Mode MPLS (4.5.1) In this lab, you learn how to do the following: Configure EIGRP on a router. Configure LDP on a router. Change the
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000
 Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP -
 1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
Cisco Quality of Service and DDOS
 Cisco Quality of Service and DDOS Engineering Issues for Adaptive Defense Network MITRE 7/25/2001 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. TESTBED SETUP...1 3. QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) TESTS...3 3.1. FIRST IN,
Cisco Quality of Service and DDOS Engineering Issues for Adaptive Defense Network MITRE 7/25/2001 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. TESTBED SETUP...1 3. QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) TESTS...3 3.1. FIRST IN,
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN
 Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN Help us help you. Please rate this document. Contents Introduction Conventions Hardware and Software Versions Network Diagram Configuration Procedures Enabling Configuring
Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN Help us help you. Please rate this document. Contents Introduction Conventions Hardware and Software Versions Network Diagram Configuration Procedures Enabling Configuring
Cisco Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs
 Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. 1. IP address for this host computer 2. Subnet mask 3. Default gateway address
 Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
Objectives University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab.4 Basic Network Operation and Troubleshooting 1. To become familiar
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting
 Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Analysis of Basic Quality of Service Mechanism for Voice over IP In Hamdard University Network Campus
 Analysis of Basic Quality of Service Mechanism for Voice over IP In Hamdard University Network Campus Shahbaz Akhatar Siddiqui Student MS (Telecom) Hamdard University Karachi Junior Lecturer in National
Analysis of Basic Quality of Service Mechanism for Voice over IP In Hamdard University Network Campus Shahbaz Akhatar Siddiqui Student MS (Telecom) Hamdard University Karachi Junior Lecturer in National
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP. Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration. VoIP Network Switch. Control Network Switch
 Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
Vocia MS-1 Network Considerations for VoIP Vocia software rev. 1.4 or higher required Vocia MS-1 and Network Port Configuration The Vocia Message Server 1 (MS-1) has a number of roles in a Vocia Paging
Configuring IPsec VPN Fragmentation and MTU
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about configuring IPsec VPN fragmentation and the maximum transmission unit (MTU). It includes the following sections: Understanding IPsec VPN Fragmentation
CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about configuring IPsec VPN fragmentation and the maximum transmission unit (MTU). It includes the following sections: Understanding IPsec VPN Fragmentation
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
CertificationKits.com EIGRP Sample CCNA Lab. EIGRP Routing. The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol.
 EIGRP Routing The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol. Hardware & Configuration Required for this Lab Two Cisco routers with two Fast Ethernet interfaces and
EIGRP Routing The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol. Hardware & Configuration Required for this Lab Two Cisco routers with two Fast Ethernet interfaces and
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs
 Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Do Not Duplicate: Post beta, not for release. Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 ICND1. Volume 1. Lab Guide. Version 2.
 ICND1 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 Volume 1 Version 2.0 Lab Guide Part Number: 97-3244-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA Asia Pacific Headquarters Cisco Systems
ICND1 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 Volume 1 Version 2.0 Lab Guide Part Number: 97-3244-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA Asia Pacific Headquarters Cisco Systems
Chapter 3 Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools & Applications Objectives
 Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools & Applications Objectives Describe & utilise Cisco IOS diagnostic tools. Explain the need for specialist tools in the troubleshooting process. Configure software
Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools & Applications Objectives Describe & utilise Cisco IOS diagnostic tools. Explain the need for specialist tools in the troubleshooting process. Configure software
Cisco Discovery 3: Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise 157.8 hours teaching time
 Essential Curriculum Computer Networking II Cisco Discovery 3: Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise 157.8 hours teaching time Chapter 1 Networking in the Enterprise-------------------------------------------------
Essential Curriculum Computer Networking II Cisco Discovery 3: Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise 157.8 hours teaching time Chapter 1 Networking in the Enterprise-------------------------------------------------
> Avaya / Cisco Interoperability Technical Configuration Guide. Ethernet Routing Switch
 Ethernet Routing Switch IP Phones Engineering > Avaya Data Solutions Document Date: April 6, 2010 Document Number: NN48500-588 Document Version: 2.0 Abstract The purpose of this TCG is to show some of
Ethernet Routing Switch IP Phones Engineering > Avaya Data Solutions Document Date: April 6, 2010 Document Number: NN48500-588 Document Version: 2.0 Abstract The purpose of this TCG is to show some of
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF
 OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
ISOM3380 Advanced Network Management. Spring 2014 15. Course Description
 ISOM3380 Advanced Network Management Spring 2014 15 Course Description In an interconnected economy, management of network applications becomes increasingly important. This course helps students develop
ISOM3380 Advanced Network Management Spring 2014 15 Course Description In an interconnected economy, management of network applications becomes increasingly important. This course helps students develop
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router
 Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
- QoS and Queuing - Queuing Overview
 1 Queuing Overview - QoS and Queuing - A queue is used to store traffic until it can be processed or serialized. Both switch and router interfaces have ingress (inbound) queues and egress (outbound) queues.
1 Queuing Overview - QoS and Queuing - A queue is used to store traffic until it can be processed or serialized. Both switch and router interfaces have ingress (inbound) queues and egress (outbound) queues.
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface
 Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1
![O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1 O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1](/thumbs/39/20242582.jpg) 1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers using HDLC and PPP.
 4357ix.fm Page 620 Thursday, August 25, 2011 11:22 AM This chapter covers the following subjects: Configuring Point-to-Point WANs: This section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers
4357ix.fm Page 620 Thursday, August 25, 2011 11:22 AM This chapter covers the following subjects: Configuring Point-to-Point WANs: This section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers
Table of Contents. Cisco How Does Load Balancing Work?
 Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Switching in an Enterprise Network
 Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR
 Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
IP Routing Between VLANs
 hp procurve 10/100-T xl module J4820A hp procurve 10/100-T xl module J4820A hp procurve Mini-GBIC xl mo d ule J4878A module IP Routing Between VLANs This example configuration provides IP routing between
hp procurve 10/100-T xl module J4820A hp procurve 10/100-T xl module J4820A hp procurve Mini-GBIC xl mo d ule J4878A module IP Routing Between VLANs This example configuration provides IP routing between
