GUIDANCE ON THE PREVENTION, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IN PRIMARY CARE
|
|
|
- Adam Harrell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GUIDANCE ON THE PREVENTION, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IN PRIMARY CARE Prevention: An estimated 60-70% of the UK population could be vitamin D insufficient. For this reason: o Population screening of vitamin D blood levels is not recommended. o Lifestyle advice and use of over the counter vitamin D preparations are recommended for prevention. Patient information resources are included in this guideline. o The government Healthy Start Scheme offers free vitamin supplements (containing vitamin D) to eligible patients. They can also be purchased cheaply by those not eligible for free supplies. o Prescriptions of vitamin D preparations should be reserved for treatment of patients with symptoms AND low vitamin D levels and those patients who have an indication for supplementation but are unable to access non-prescription vitamin D supplementation such as the elderly and infirm. Fultium D 3,200 units and InVita D3 25,000 units are the preferred formulary choice for high dose colecalciferol Pro D3 is an alternative option for children as it allows flexible dosing and formulations. It may also be an option in patients with swallowing difficulties Vitamin D products should be prescribed by brand name Fultium D3 800 units, InVita D3 and Desunin 800 units can be prescribed for maintenance therapy following treatment courses but for supplementation in exceptional cases only.
2 SUMMARY: Diagnosis and management of Vitamin D deficiency in primary care Population screening by measuring Vitamin D levels is unnecessary, even in high risk populations. Symptoms of rickets or osteomalacia? (See table 1 p5) Yes No Investigations: U&Es, LFTs, calcium, phosphate, PTH and 25-OH Vitamin D Risk factors for Vitamin D deficiency? (See table 2 p5) No Yes Vit D <30nmol/l: Prescription* Vit D 30-50nmol/l: Lifestyle advice & OTC supplements + Vit D >50nmol/l: Normal- no indication for supplementation No investigation required Offer lifestyle advice Suggest OTC supplements at doses outlined (table 4 p 8) Referral to specialist indicated? Children under 1 year Children with biochemical rickets or raised PTH Renal disease (CKD 4&5) Atypical biochemistry- including hypercalcaemia Failure to respond to treatment after 3 months Short stature / skeletal deformity Focal bone pain Unexplained severe deficiency Yes No Note *Cut off for high dose vitamin D prescription Symptomatic deficiency is unlikely when 25(OH)D is greater than 30 nmol/l but there is no clear threshold. If symptoms are strongly suspected to be vitamin D related it is reasonable to offer high dose treatment when levels are between 30 and 35 nmol/l. Refer GP to prescribe as per table 3 (p6) +Prescription of vitamin D occasionally indicated with Specialist advice (e.g. in preparation for parenteral treatment of osteoporosis 2
3 Diagnosis and management of Vitamin D deficiency in primary care Contents: 1: Vitamin D physiology p4 2: Prevention of Vitamin D deficiency p4 3. Diagnosis p4 Assessing the patient Investigations Measurement and interpretation of Vitamin D levels 4: Management of Vitamin D deficiency p6 5: Management of Vitamin D insufficiency p7 6: Special Circumstances p8 7: Referral p9 8: References p9 Appendix 1: Patient information: national examples Appendix 2: Over the counter (OTC) preparations p10 p10 Introduction Vitamin D deficiency is an important public health issue concerning infants, young children, adults & elderly people. Recent evidence estimates that 60-70% of population could be vitamin D insufficient, particularly ethnic minority and the immigrant population. This guideline has been revised for 2013 following the publication of the National Osteoporosis Society Vitamin D and Bone Health document and new developments in the commercial field of vitamin D supplements. The document provides information on vitamin D, diagnosis and management of deficiency and advice for patients with insufficiency 3
4 1: Vitamin D physiology: What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a group of fat soluble vitamins that is essential bone formation in all age groups. The 2 main forms are D 2 (ergocalciferol), predominantly from plants and D 3 (colecalciferol), mainly from animal sources. Both have similar actions. Vitamin D is activated in the liver to 25- hydroxycolecalciferol and then in the kidney to 1,25-dihydroxycolecalciferol (active vitamin D). The most well established action of vitamin D is to promote calcium absorption by the GI tract. 90% of our daily vitamin requirement is obtained by the action of UVB sunlight on the skin (only during April to September in the United Kingdom) 10% is obtained through diet such as oily fish (sardines, salmon), liver, egg yolks, fortified margarine and fortified breakfast cereals) Does Vitamin D have other functions? Research has identified epidemiological links between vitamin D levels and various disease states. It remains unclear whether vitamin D could offer pharmacological benefit for any of these conditions. At the present time the indications for vitamin D treatment relate to maintenance of calcium homeostasis and bone health via the primary mode of action to aid absorption of calcium at the gut. 2: Prevention of Vitamin D deficiency: All UK Health Departments recently recommended (CMO letter 2012) that: All pregnant and breastfeeding women should take a daily supplement containing 400 international units (iu) (10micrograms (μg)) of vitamin D, to fulfil mother s requirements for vitamin D and to build adequate foetal stores All infants and young children aged 6 months to 5 years should take a daily supplement containing iu (7-8.5μg) vitamin D in the form of vitamin drops. However, those infants who are fed infant formula will not need vitamin drops until they are receiving less than 500ml of infant formula a day. Breastfed infants may need to receive drops containing vitamin D from one month of age if their mother has not taken vitamin D supplements throughout pregnancy. People aged 65 years and over and people who are not exposed to much sun should also take a daily supplement containing 400iu (10μg) of vitamin D. Most of these patients should be offered lifestyle advice as detailed in section 5 (p6) and advised to purchase supplementation over the counter in the first instance (eligible patients can obtain free supplements through the Healthy Start scheme). More information on available products for supplementation and the Healthy Start scheme can be found in appendix 2 (p8). Patients who are unable to access over the counter supplements and are unable to modify lifestyle behaviour adequately should be prescribed the relevant supplement. Relevant groups include patients in Residential and Nursing homes and those unable to afford supplements. 3: Diagnosis: Vitamin D deficiency is best assessed by measurement of serum 25-OH vitamin D. Measurement of other vitamin D metabolites or sub-fractions adds nothing further and is not recommended. Population screening is NOT recommended. Vitamin D deficiency should be suspected in patients presenting with clinical features as detailed in table 1 below and the general principle is to test only those individuals who have symptoms or features suggestive of vitamin D deficiency or osteomalacia. 4
5 Clinical features of Vitamin D deficiency (Table 1): Children Poor growth, delayed fontanelle closure Delayed walking or a waddling gait Tender or swollen joints, classically the wrists or costochondral junctions Deformed bones (bow legs or knock knees) Bone pain or tenderness Muscle pain or proximal myopathy Delayed eruption of teeth, or enamel hypoplasia Carpopedal spasm, tetany, seizures or irritability due to hypocalcaemia & requiring urgent treatment Adults Gradual onset & persistent bone pain without preceding mechanical injury (frequently in back, ribs or lower limb) Fragility fracture Proximal muscle weakness (difficulty with stairs, getting up off the floor or standing after sitting in a low chair, waddling gait) or muscle pain Carpopedal spasm, tetany, seizures or irritability due to hypocalcaemia & requiring urgent treatment GPs should consider a diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency in a patient with risk factors (table 2) who presents with chronic musculoskeletal (MSK) pain. NB. The relationship between chronic MSK pain and vitamin D deficiency is not clear and treatment does not necessarily resolve symptoms. Risk factors for Vitamin D deficiency (Table 2) Age Groups 65years <5 years Pregnant women Breastfeeding women Poor exposure to UVB light Pigmented skin Occlusive garments Housebound Use of sun blocking creams Poor dietary intake Vegetarian (or fish-free diet) Malabsorption, including bariatric surgery patients Cholestatic liver disease Breast fed infants Metabolic risk Elderly (reduced synthesis) Liver disease (reduced stores) Renal disease (reduced synthesis of active vitamin D) Obese people (excess storage in fat) Drugs: Rifampicin, Antiretroviral drugs, anticonvulsants, cholestyramine, glucocorticoids. Investigations (to be arranged by primary care): U&Es, LFTs, calcium, phosphate and 25-OH Vitamin D PTH should be measured when the adjusted calcium is significantly low (<2.15) Children: In addition, albumin & PTH should be measured routinely in children (refer if PTH high) The findings in osteomalacia are a low/ normal calcium, low/normal phosphate, raised alkaline phosphatase, low vitamin D and raised PTH (secondary hyperparathyroidism) Vitamin D levels are expressed as nmol/l (ng/ml x 2.5 = nmol/l). The definition of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency is based on blood measurements of 25- OH vitamin D: >50 nmol/l Satisfactory Vitamin D levels nmol/l Vitamin D insufficiency <30 nmol/l Vitamin D deficiency Note: In patients with a Vitamin D level >30 nmol/l, symptoms are unlikely to be due to Vitamin D deficiency. However, clinicians should use clinical judgment when considering the diagnosis and treatment plan for an individual patient. 5
6 4: Management of Vitamin D deficiency: i.e.: Vitamin D level <30nmol/l Patients meeting the above criteria should be managed according to the following principles; For the purposes of this document we define treatment to be high dose therapy to reverse vitamin D deficiency. This is different from lower doses used as long term daily supplementation or as maintenance following high dose treatment. Symptomatic patients need high dose colecalciferol treatment to reverse deficiency and eradicate symptoms. Asymptomatic patients can usually be commenced on lower doses of colecalciferol (see Maintenance Therapy in section 3 of Table 3) and deficiency will gradually be resolved. When indicated a single course of high dose therapy should be followed by lifestyle advice and maintenance with lower dose supplementation. Available evidence suggests that oral colecalciferol offers greater improvements in serum 25- OH Vitamin D compared with oral ergocalciferol or intramuscular preparations at equivalent doses. As such, oral colecalciferol is the first line treatment option. Alfacalcidol and calcitriol are completely inappropriate for treatment of vitamin D deficiency outside of CKD 4-5, due to high risk of toxicity. ADULTS CHILDREN (>6 months) Drug Colecalciferol Colecalciferol Dose Length of course 20,000iu daily orally Hux D3 is recommended as an available, cost-effective option for symptomatic patients. Standard course 300,000* iu total dose colecalciferol (15 days x 20,000 units) (Consider increase total dose to 400, ,000 units if very low baseline or poor absorption anticipated) 6 months 12 years 6000iu daily orally for 4 8 weeks** years 10,000iu daily orally for 4 8 weeks** Pro D3 is recommended in children as it is available in a liquid formulation 4 8 weeks Ensure dietary factors improved. Check PTH normalised indicating deficiency has resolved 6 Monitoring Follow up Maintenance therapy (This can be used as initial treatment in asymptomatic individuals) Long term monitoring 6 weeks; Calcium, phosphate, ALP. Repeat vitamin D levels only if symptoms persist. No further monitoring or follow up needed. 800iu daily. To be continued long term. Fultium D3 is recommended for prescribing as it is a licensed preparation, available as 800iu capsules. Higher doses up to 2400iu daily may be needed in some patients (e.g. malabsorption). 1 month (or 1 week if symptomatic hypocalcaemia): calcium, phosphate, ALP and PTH. Repeat 3 monthly until treatment stopped. If ALP does not improve, check compliance. Where treatment continues >6months, check early morning urine calcium:creatinine. Review and investigate family members. Give prevention advice as a minimum iu daily. To be continued long term. Healthy Start vitamins, Abidec or Dalivit vitamin drops are recommended. No routine monitoring or rechecking of serum 25OHD levels is needed whilst on maintenance therapy. Recheck biochemistry if symptoms return or malabsortion/ poor compliance suspected.
7 NB: *Loading regimens for treatment of deficiency up to a total of approximately 300,000 IU given either as weekly or daily split doses. The exact regimen will depend on the local availability of vitamin D. NB: **The same effect may be achieved by multiplying the dose by seven and giving it weekly if compliance is a concern NB: Where poor compliance is suspected give supervised stat oral doses (100,000 iu colecalciferol for adults) at weekly intervals NB: Liquid specials of vitamin D (unlicensed) should NOT be routinely prescribed. Cost effective alternatives are available. NB: Most vitamin D preparations contain gelatin. Hux D3 & Pro D3 are vegetarian and Halal products. NB: In patients where Fultium D3 is intolerable, or an alternative is required for maintenance, OTC preparations are advised (see Appendix 2). 5: Management of Vitamin D insufficiency: i.e.: Vitamin D level 30-50nmol/l AND risk factors for Vitamin D deficiency Patients should be offered lifestyle advice and advised to purchase supplements over the counter (OTC) at doses outlined above for maintenance therapy (see Appendix 2). Healthy start vitamins are available for children <5years. Example patient information leaflets can be found in Appendix 1. Use of colecalciferol supplements is specifically recommended for patients with 25-OH Vitamin D nmol/l and one of the following additional factors; fragility fracture, osteoporosis or high fracture risk including patients on antiresorptive mediactions increased risk of future deficiency due to e.g. reduced exposure to sunlight, cultural dress code, dark skin (see Special Circumstances 4. Asian populations) raised PTH regular prescription for antiepileptic drugs or glucocorticoids malabsorption Lifestyle advice for Vitamin D insufficiency (and deficiency) Sun exposure: Sun exposure is the main source of vitamin D and should be exploited! However, this should be balanced with the risks of excessive exposure. Time required in the sun to make sufficient vitamin D is generally short and less than the time needed for skin to burn. This should be adjusted on an individual basis and safe practices adopted. Little and often is best. The following advice was given in the New England Journal of Medicine (2007): Exposure of arms and legs for 5 to 30 minutes (depending on time of day, season, latitude, and skin pigmentation) between the hours of 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. twice a week is often adequate Note: Use of creams containing sun protection factors reduces vitamin D synthesis by >95%. Diet: Dietary sources of Vitamin D include: Oily Fish Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines, Herring, Pilchards, Fresh Tuna etc. Cod liver oil & other fish oils Red meat & Eggs yolk Infant formula milk, powdered milk Fortified breakfast cereals Soya products, fortified margarines, low fat spreads 7
8 It is difficult to obtain enough vitamin D from usual diet alone. The average daily intake from a normal diet is just iu/day (2-4µg). Where supplementation is indicated, the following doses are recommended (Table 4): Age and risk group Daily Requirement Newborn up to 1 month iu/day (7.5-10µg) 1 month 18 years iu/day (10-25µg) Pregnant and breastfeeding women People aged 65 & over* People not exposed to much sunlight 400iu/day (10µg) 400iu/day (10µg) 400iu/day (10µg) 8 NB: There is no benefit in using preparations of vitamin D combined with calcium in most patients. However calcium & vitamin D iu/day is appropriate in the elderly, most people aged 60 years or more taking bisphosphonates, and those taking corticosteroids. OTC supplementation should be continued long term in most patients. 6. Special circumstances a. Primary hyperparathyroidism/ Hypercalcaemia Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism frequently have vitamin D deficiency Vitamin D deficiency in primary hyperparathyroidism may exacerbate bone loss in this condition. Treatment with vitamin D has the potential to exacerbate hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria but is still often indicated. Specialist advice (Endocrinology) is recommended prior to vitamin D treatment in this context. Prescription supplements (eg Fultium D3) are likely to be warranted to ensure accuracy of dosing and avoid toxicity. b. Development of new hypercalcaemia during Vitamin D replacement Patients may develop hypercalcaemia during correction of vitamin D deficiency. This can indicate vitamin D toxicity although this would not be expected when using recommended doses. Most other cases are due to underlying and previously undiagnosed Primary Hyperparathyroidism although granulomatous conditions are also relevant (eg Sarcoidosis). The diagnosis can be aided by measurement of PTH- and such cases should be referred to Endocrinology for assessment. c. Elderly patients The majority of elderly patients are ambulant and community dwelling. Many will still be at risk of vitamin D deficiency but the principles of management are not different to that presented in the rest of this document. Dual supplementation with calcium and low dose vitamin D (as in numerous commercially available preparations) is more likely to be appropriate in the elderly and infirm where sun exposure is likely to be poor and gastrointestinal calcium absorption reduced. Occasionally lone vitamin D supplementation may be needed (eg concurrent primary hyperparathyroidism) and in these cases, a prescription vitamin D supplement such as Fultium D3 should be given. Meta-analysis suggests that Vitamin D supplementation may prevent falls, although this is controversial. Vitamin D supplementation (with or without calcium) will invariably be appropriate in recurrent fallers. In some cases high dose supplementation will be recommended in this context on a case by case basis by the Falls Clinic team (Vitamin D deficiency has been shown by local Audit to be almost ubiquitous in the Falls clinic population so testing of deficiency prior to treatment will not always be needed). Older people with falls should be assessed for their falls risk factors and referred as per local guidelines.
9 d. Asian populations A combination of skin type and cultural factors which reduce sun exposure and limit dietary and supplement choices mean that Asian patients are at particular risk of Vitamin D deficiency and have particular barriers to effective treatment. In fact vitamin D insufficiency is almost ubiquitous in this group and virtually all patients will be appropriate for supplementation. It is known that take up of Over the Counter options is low in this group. e. Parenteral Osteoporosis treatments Parenteral treatments for osteoporosis require adequate vitamin D levels in order to be safe and effective. The osteoporosis team will be involved with the care of these patients and will optimise vitamin D prior to initiation of treatment. It is vital that vitamin D levels are adequate prior to each injection to minimise the risk of severe hypocalcaemia. Vitamin D levels should be checked in patients who are not on regular supplements or in those whose compliance is suspected to be poor. The aim is to ensure 25-OH Vitamin D levels are greater than 50 nmol/l prior to treatment. 7: Referral: The following patients should be referred to secondary care for further investigation: Children under 1 year Children with biochemical rickets or raised PTH Renal disease (CKD 4&5) Atypical biochemistry- including hypercalcaemia Failure to respond to treatment after 3 months Short stature / skeletal deformity Focal bone pain Unexplained severe deficiency Unexplained weight loss 8: References Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Practical Clinical Guideline for Patient Management. National Osteoporosis Society. April Diagnosis and management of vitamin D deficiency. Pearce SHS & Cheetham TD. British Medical Journal 2010; 340:b5664. Primary vitamin D deficiency in adults. Drug & Therapeutics Bulletin. 2006; 44(4): Vitamin D Advice on supplements for at risk groups. CMO CAS letter Available from: DH_ Vitamin D Deficiency. Holick MF. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357: Vitamin D for the treatment of chronic painful conditions in adults (review). The Cochrane Collaboration Available from: Guide for Vitamin D in Childhood. Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. October 2013 ( 0for%20website.pdf) 9
10 Appendix 1: Patient information: National examples A variety of patient information leaflets are available including: Department of Health: Guide for health professionals NHS Choices Vitamin D PIL Patient.co.uk Vitamin D deficiency National Osteoporosis Society: Healthy bones: Facts about food Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital: FAQs about Vitamin D in childhood National Osteoporosis Society: Children's bone health Appendix 2: OTC preparations Healthy Start vitamins: Women and children from families who are eligible for the Government s Healthy Start scheme can get supplements which include vitamin D, in the form of tablets for women and drops for children. th Women qualify for Healthy Start from the 10 week of pregnancy or if they have a child under four years old, and if she or her family receive: Income Support, or Income-based Jobseeker s Allowance, or Income-related Employment and Support Allowance, or Child Tax Credit (but not Working Tax Credit unless the family is receiving Working Tax Credit run-on only) and has an annual family income of 16,190 or less. Women under 18 and pregnant also qualify even if not on the above benefits. For further information and application forms, visit To obtain free supplies, present a Healthy Start voucher (sent to Healthy Start recipients every 8 weeks). Patients who are not eligible for free supplies can buy Healthy Start vitamins from the local Health Centres listed above, at a cost of 1.80 for 56 tablets or 91p for a 10ml bottle of drops Vitamin drops contain Vitamins A, C & D dose 5 drops daily Vitamin tablets contain Vitamins C, D and folic acid dose 1 tablet daily Patients can also buy suitable preparations over the counter from pharmacies and other health food retailers. NB: Some vitamin D preparations contain soya oil or peanut oil; most vitamin D capsules contain gelatin. Retailers can provide information on the contents and suitability of their products. 10
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Vitamin D
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Vitamin D Purpose of guideline Provide clear advice on when to measure vitamin D and identify patients with insufficiency and deficiency. To provide
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Vitamin D Purpose of guideline Provide clear advice on when to measure vitamin D and identify patients with insufficiency and deficiency. To provide
NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions
 Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD
 GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
GUIDE FOR VITAMIN D IN CHILDHOOD October 2013 Introduction There are many different recommendations for the prevention, detection and treatment of Vitamin D deficiency in the UK. The following is a practical
Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists
 Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists January 2014 (Review date: Jan 2016) Contents Summary Flowchart... 2 Introduction... 3 Structure and mechanism
Guideline on Diagnosis & Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults for Non-Specialists January 2014 (Review date: Jan 2016) Contents Summary Flowchart... 2 Introduction... 3 Structure and mechanism
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline
 Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the UK is 16% and around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Primary Care Guideline The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the UK is 16% and around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring.
VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE. Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team
 VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team WHAT ARE THE ISSUES? A lack of suitable licensed vitamin D products in the UK for treating
VITAMIN D PRODUCTS -WHAT AND WHEN TO PRESCRIBE Claudette Allerdyce Principal Pharmacist Croydon CCG Pharmacy Team WHAT ARE THE ISSUES? A lack of suitable licensed vitamin D products in the UK for treating
Guidance on Vitamin D Deficiency/Insufficiency November 2011 (updated February 2012)
 Guidance on Vitamin D Deficiency/Insufficiency vember 2011 (updated February 2012) This guidance aims to provide general advice for clinicians in a community setting including areas where clinical uncertainty
Guidance on Vitamin D Deficiency/Insufficiency vember 2011 (updated February 2012) This guidance aims to provide general advice for clinicians in a community setting including areas where clinical uncertainty
Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Children and Adults
 Reference Number: UHB 205 Date of Next Review: 21 st January 2019 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: N/A Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Policy Statement To ensure
Reference Number: UHB 205 Date of Next Review: 21 st January 2019 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: N/A Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Policy Statement To ensure
Protecting and improving the nation s health. Vitamin D. Information for healthcare professionals
 Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
Protecting and improving the nation s health Vitamin D Information for healthcare professionals 1 Vitamin D: Information for healthcare professionals Why is vitamin D important? Some of the UK population
Vitamin D. Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough
 Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
Vitamin D Why Vitamin D is important and how to get enough Why is vitamin D vital for health? Vitamin D is needed by the body for both physical and mental health, but is best known for making sure bones
National. min. for early infancy. on Vitamin D. to get converted to action being. here. to treat an. will be insufficient
 ABUHB Prescribing Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency In ADULTS (including guidance for Non Specialists) This document aims to provide comprehensive guidance on the cost effective
ABUHB Prescribing Guideline Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency In ADULTS (including guidance for Non Specialists) This document aims to provide comprehensive guidance on the cost effective
Our main source of vitamin D is that made by our own bodies. 90% of our vitamin D is made in the skin with the help of sunlight.
 Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency is a very common problem - more than half of the UK population has insufficient levels of vitamin D Vitamin D is mostly made in the skin by exposure to sunlight
Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency is a very common problem - more than half of the UK population has insufficient levels of vitamin D Vitamin D is mostly made in the skin by exposure to sunlight
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D. Sources of vitamin D
 1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults
 Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults Around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring, whilst the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is 16%. 1 This means that in Wandsworth
Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults Around 50% of the UK adult population have vitamin D insufficiency in winter and spring, whilst the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is 16%. 1 This means that in Wandsworth
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Press Information. Vitamin D deficiency
 DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
DSM, Corporate Communications P.O. Box 6500, 6401 HJ Heerlen The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 45 578 2421 www.dsm.com Vitamin D is one of the essential nutrients for human health. Unlike other types of vitamins
Vitamin supplements and you
 Vitamin supplements and you Guidance for pregnant or breastfeeding women, babies and young children Health Improvement About this leaflet Vitamins are really important they are essential nutrients that
Vitamin supplements and you Guidance for pregnant or breastfeeding women, babies and young children Health Improvement About this leaflet Vitamins are really important they are essential nutrients that
Endocrinology. Vitamin D and bone health National Osteoporosis Society Guideline 2013. What is the GP s role? Vitamin D physiology
 Endocrinology Vitamin D and bone health... 182 - What is the GP s role?...182 - Vitamin D physiology...182 - Why do people become vitamin D deficient?...183 - Which foods contain vitamin D?...183 - What
Endocrinology Vitamin D and bone health... 182 - What is the GP s role?...182 - Vitamin D physiology...182 - Why do people become vitamin D deficient?...183 - Which foods contain vitamin D?...183 - What
Guidelines for the Treatment and Prophylaxis of vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents
 Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Guidelines
Corby Clinical Commissioning Group Kettering General Hospital NHS Trust Nene Clinical Commissioning Group Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust Northamptonshire Healthcare Foundation Trust Guidelines
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D
 Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
Selected Questions and Answers on Vitamin D Joint FAQs to the BfR, German Nutrition Society (DGE) und Max Rubner-Institute (MRI) of 03 December 2014 1 Vitamin D promotes the intake of calcium from the
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease. Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D.
 Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D Deficiency and Thyroid Disease Theodore C. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D. Vitamin D deficiency and thyroid diseases Vitamin D is an important vitamin that not only regulates calcium, but also has many
Vitamin D (serum, plasma)
 Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
Vitamin D (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Vitamin D 1.2 Alternative names The term vitamin D covers a group of closely related naturally occurring lipid soluble compounds
Volume 9; Number 13 September 2015 TREATMENT OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IN AT-RISK ADULTS (SECOND EDITION)
 Arden and Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and
Arden and Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS This guidance has been adapted from the North of Tyne Guideline Group guidelines, published in 2011. The treatment of children has been removed, as
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF VITAMIN D IN ADULTS This guidance has been adapted from the North of Tyne Guideline Group guidelines, published in 2011. The treatment of children has been removed, as
Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment
 Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
Title: Vitamin D Author: Kerry Lynn Kuffenkam Date: 4-29-09 Key words: Vitamin D Production, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Vitamin D Treatment Abstract: Since the term Vitamin D contains the word vitamin most
Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC
 Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC Vitamin D What do surfers have in abundance and maybe most of the rest of us lack? Vit D - a vitamin primarily obtained by man
Shining a light on the Sunshine Vitamin Lin A. Brown,MD Dartmouth and DHMC Vitamin D What do surfers have in abundance and maybe most of the rest of us lack? Vit D - a vitamin primarily obtained by man
HS58A. Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them
 HS58A Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them Folic acid Taking a folic acid supplement before you re pregnant and until the 12th week of your pregnancy is really important because it reduces the
HS58A Healthy Start vitamins and why you need them Folic acid Taking a folic acid supplement before you re pregnant and until the 12th week of your pregnancy is really important because it reduces the
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline
 Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Vitamin D and Calcium Guideline Vitamin D Functions of Vitamin D 2 Serum Levels 2 Deficiency 2 Toxicity 2 Dietary Reference Intakes 3 Sources of Vitamin D 3 Therapeutic Options 4 Adults 4 Children (0 18
Question I. A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth. A. True B. False. Answer A
 Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
Vitamin D Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Question I A vitamin D deficient mother will give birth to an infant with Vit D deficiency A. True B. False Answer A Question II Human breast milk has adequate amounts
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
Osteoporosis. Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist. Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013
 Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product)
 PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle. Vitamin D: All You Need to Know
 Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA 11/12/2011 Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil J. Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA, FACE, FACP Professor
Earth at Night View from the Space Shuttle Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA 11/12/2011 Vitamin D: All You Need to Know Sunil J. Wimalawansa, MD, PhD, MBA, FACE, FACP Professor
Vitamin D. Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Vitamin D Frequently Asked Questions What is vitamin D? What is a vitamin? Why do we need vitamins? Is there more than one form of vitamin D? Where do I get vitamin D? How long should I be outdoors, and
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age
 Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood)
 Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Calcium (serum, plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Calcium (total in serum, plasma, ionised in blood (see 2.1 (2)). 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description
Policy on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency / Insufficiency
 Policy on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency / Insufficiency Version no: 2.1 Issue Status: Approved Ratified by: Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date of Ratification: 20 th May 2013 Policy
Policy on the Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency / Insufficiency Version no: 2.1 Issue Status: Approved Ratified by: Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date of Ratification: 20 th May 2013 Policy
Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything?
 Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
Health problems linked to vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency: the cause of everything? Louise Gagné M.D. Family Physician Saskatoon Community Clinic Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Community
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines
 Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
Vitamin D & Iron Dosing Guidelines Ayman Khmour, MD I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program. Objectives Review Ca metabolism Review Recent AAP Guidelines Review CMH
YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS
 Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
Vitamin D YOUR TRUSTED SOURCE - FOR ALL YOUR VITAMIN D 3 NEEDS ü Natural form of vitamin D 3, cholecalciferol (from lanolin) ü Strengths from 400 iu to 10,000 iu ü Capsule and liquid forms available ü
Vitamin D. Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353
 Vitamin D Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Vitamin D Date of issue: February 2010 Review date: February 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2.
Vitamin D Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Vitamin D Date of issue: February 2010 Review date: February 2011 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2.
What s on the menu at the Ministry?
 What s on the menu at the Ministry? Dr Harriette Carr Public Health Medicine Specialist Ministry of Health PREPARED BY Dr Harriette Carr, Louise McIntyre, Diana O Neill, Virginia Mills, Martin Dutton,
What s on the menu at the Ministry? Dr Harriette Carr Public Health Medicine Specialist Ministry of Health PREPARED BY Dr Harriette Carr, Louise McIntyre, Diana O Neill, Virginia Mills, Martin Dutton,
Hypocalcaemia. Shaila Sukthankar
 Hypocalcaemia Shaila Sukthankar Ca Daily Requirements Age/ sex Ca (mg) 1-3 350 4-6 450 7-10 550 11-18 M 1000 11-18 F 800 19 + 700 Ca Dietary Sources (NDC) Milk 100 ml =120mg Cheese 15gm = 110mg Yoghurt
Hypocalcaemia Shaila Sukthankar Ca Daily Requirements Age/ sex Ca (mg) 1-3 350 4-6 450 7-10 550 11-18 M 1000 11-18 F 800 19 + 700 Ca Dietary Sources (NDC) Milk 100 ml =120mg Cheese 15gm = 110mg Yoghurt
Effect of breast cancer treatment
 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones 1 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of breast cancer treatment. You may find the
Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones 1 Effect of breast cancer treatment on the bones This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of breast cancer treatment. You may find the
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION. CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol
 (NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
(NON-PRESCRIPTION) LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION CALTRATE VITAMIN D3 600mg/400 IU, film-coated tablet Calcium and Cholecalciferol Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information
FOR HEALTH. Huldschinsky 1919. Rickets THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN. Solar UV Radiation. Treated VITAMIN D TOXIC OH FROM SUN EXPOSURE. with Mercury Arc Lamp
 THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
THE D-LIGHTFUL VITAMIN W DO YOU MAKE VITAMIN D???? FOR HEALTH Michael F. Holick Boston University Medical Center Solar UV Radiation 7-DHC UV PreD 3 UV UV Tachysterol 3 7-DHC CH2 Vitamin D 3 ΔH PreD 3 Vitamin
GP Guidance: Management of nutrition following bariatric surgery
 GP Guidance: Management of nutrition following bariatric surgery Introduction Patients who are morbidly obese will have struggled with their weight for many years before going forward for bariatric surgery.
GP Guidance: Management of nutrition following bariatric surgery Introduction Patients who are morbidly obese will have struggled with their weight for many years before going forward for bariatric surgery.
Hold the Sunscreen: Your Body Needs that Vitamin D
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hold-the-sunscreen-your-body-needs-that-vitamind/4149/
Vitamin D and You. By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com
 Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Vitamin D and You By Dr. Sherri Tenpenny www.drtenpenny.com www.osteomed2.com What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced in the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
FACTS ON LIFE STYLE DISEASES AND NUTRITION DEFICIENCY DISEASES
 FACTS ON LIFE STYLE DISEASES AND NUTRITION DEFICIENCY DISEASES INTRODUCTION We suffer from these diseases as a result of the way we live. Many are caused by Malnutrition. Malnutrition describes a partial
FACTS ON LIFE STYLE DISEASES AND NUTRITION DEFICIENCY DISEASES INTRODUCTION We suffer from these diseases as a result of the way we live. Many are caused by Malnutrition. Malnutrition describes a partial
Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency In Secure Mental Health Setting: is routine screening required?
 Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency In Secure Mental Health Setting: is routine screening required? Dr Neel Halder, Consultant Psychiatrist and Senior Honorary Lecturer, Manchester University Dhana Govindaraj,
Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency In Secure Mental Health Setting: is routine screening required? Dr Neel Halder, Consultant Psychiatrist and Senior Honorary Lecturer, Manchester University Dhana Govindaraj,
Public Assessment Report. UK National Procedure. (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048. ProStrakan Ltd.
 Public Assessment Report UK National Procedure STEXEROL-D 3 1,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS STEXEROL-D 3 25,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048 ProStrakan Ltd. 1 LAY SUMMARY
Public Assessment Report UK National Procedure STEXEROL-D 3 1,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS STEXEROL-D 3 25,000 IU FILM-COATED TABLETS (colecalciferol) PL 16508/0047 PL 16508/0048 ProStrakan Ltd. 1 LAY SUMMARY
The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Women s Health The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy Information for patients The menopause At the menopause the ovaries stop working. This means that the female
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Women s Health The Menopause and Subtotal Hysterectomy Information for patients The menopause At the menopause the ovaries stop working. This means that the female
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
HYPERCALCEMIA/HYPERCALCIURIA IN WILLIAMS SYNDROME
 HYPERCALCEMIA/HYPERCALCIURIA IN WILLIAMS SYNDROME WHAT IS CALCIUM AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? Calcium is an important mineral for building teeth and bones and in chemical reactions, such as those that cause
HYPERCALCEMIA/HYPERCALCIURIA IN WILLIAMS SYNDROME WHAT IS CALCIUM AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? Calcium is an important mineral for building teeth and bones and in chemical reactions, such as those that cause
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation
 Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Considerations With Calcium And Vitamin D Supplementation Activity Preview Calcium is an electrolyte involved in many systems in the body including bone health, nerve signaling pathways, muscle contractions,
Vitamin D. Your guide to understanding vitamin D. Title of page 1. Created by
 Vitamin D Your guide to understanding vitamin D Created by Title of page 1 Vitamin D Your guide to understanding vitamin D Created by A public health nonprofit Vitamin D Council 1241 Johnson Ave #134
Vitamin D Your guide to understanding vitamin D Created by Title of page 1 Vitamin D Your guide to understanding vitamin D Created by A public health nonprofit Vitamin D Council 1241 Johnson Ave #134
Vitamin D Deficiency in Older Patients
 Fourth Year Medical Students Required Written Patient Care Assignments Reflecting Awareness of Use of Vitamin D in Older Patients at Risk for Falling John Agens, M.D. Associate Professor in Geriatrics
Fourth Year Medical Students Required Written Patient Care Assignments Reflecting Awareness of Use of Vitamin D in Older Patients at Risk for Falling John Agens, M.D. Associate Professor in Geriatrics
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 Presentation Vit.D3 1.25 mg (equivalent to 50,000IU) capsules are presented as natural coloured, transparent, oval shaped, soft gelatin capsules, containing pale yellow coloured oil. Uses INDICATIONS Colecalciferol
Presentation Vit.D3 1.25 mg (equivalent to 50,000IU) capsules are presented as natural coloured, transparent, oval shaped, soft gelatin capsules, containing pale yellow coloured oil. Uses INDICATIONS Colecalciferol
Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Practical Clinical Guideline for Management in Children and Young People
 Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Practical Clinical Guideline for Management in Children and Young People Vitamin D and bone health: a practical clinical guideline for management in children and young people
Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Practical Clinical Guideline for Management in Children and Young People Vitamin D and bone health: a practical clinical guideline for management in children and young people
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand
 Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. Forceval Junior Capsules
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Forceval Junior Capsules Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information for you or your child. Please note this leaflet has been written as if
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Forceval Junior Capsules Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information for you or your child. Please note this leaflet has been written as if
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels. Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD
 A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
A study to Evaluate PPI s effect on vitamin D levels Rani Hanna M.D., M.S. PGY-3 Joseph Grisanti, MD The sunshine vitamin Existed over 500 million years. Prehormone, not only a vitamin. Two major sources:
What can happen if you have low iron levels?
 Iron in your diet Iron in your diet Why is iron important? Iron is important because it helps your body to make haemoglobin. Haemoglobin, or Hb, is the protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen
Iron in your diet Iron in your diet Why is iron important? Iron is important because it helps your body to make haemoglobin. Haemoglobin, or Hb, is the protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis
 Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence
 Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Christopher Kovacs, MD, FRCPC, FACP Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Memorial University of Newfoundland ckovacs@mun.ca Disclosure I am currently serving
Vitamin D in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence Christopher Kovacs, MD, FRCPC, FACP Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Memorial University of Newfoundland ckovacs@mun.ca Disclosure I am currently serving
Treatment and prophylaxis guidelines for Vitamin D deficiency in infants, children and adolescents.
 Treatment and prophylaxis guidelines for Vitamin D deficiency in infants, children and adolescents. SUMMARY Who is at risk? Prophylaxis Diagnosis If Calcium is low? Treatment Monitoring When to refer to
Treatment and prophylaxis guidelines for Vitamin D deficiency in infants, children and adolescents. SUMMARY Who is at risk? Prophylaxis Diagnosis If Calcium is low? Treatment Monitoring When to refer to
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only
 For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only Cholecalciferol Granules VITOMIN D3 COMPOSITION Each sachet of 1 g contains: Cholecalciferol
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only OR for Specialist Use only Cholecalciferol Granules VITOMIN D3 COMPOSITION Each sachet of 1 g contains: Cholecalciferol
1. If I go a couple of days without my vitamin D and calcium requirements, can I make up for them?
 GOOD NUTRITION FOR BONE Calcium, Vitamin D and So Much More QUESTION & ANSWER Wednesday, March 23, 2011 (2:30 p.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET) 1. If I go a couple of days without my vitamin D and calcium requirements,
GOOD NUTRITION FOR BONE Calcium, Vitamin D and So Much More QUESTION & ANSWER Wednesday, March 23, 2011 (2:30 p.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET) 1. If I go a couple of days without my vitamin D and calcium requirements,
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution. Cyanocobalamin
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution Cyanocobalamin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER VITAMINE B12 STEROP 1mg/1ml Solution for injection / oral solution Cyanocobalamin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Quick Facts... Vitamin A. by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08)
 Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Fat-Soluble s by J. Anderson and L. Young 1 (8/08) Quick Facts... Small amounts of vitamins A, D, E and K are needed to maintain good health. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked.
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol. For use in infants, children and adults
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol For use in infants, children and adults Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Cholecalciferol mibe 500 IE, tabletten Cholecalciferol For use in infants, children and adults Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Micronutrient. Functio. Vitamin A
 EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU)
 BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen s disease). It
BOWEN S DISEASE (SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA IN SITU) What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen s disease). It
Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
 BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
PHARMACISTS AMENDMENTS TO PRESCRIPTIONS
 PHARMACISTS AMENDMENTS TO PRESCRIPTIONS May 2016 Version 2.3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions/Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
PHARMACISTS AMENDMENTS TO PRESCRIPTIONS May 2016 Version 2.3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions/Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
Scans and tests and osteoporosis
 Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
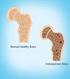 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr
 Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
Vitamin D und seine Bedeutung im Immunsystem und bei der Infektabwehr Stefan Pilz Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical University of Graz, Austria Department
Infant Feeding Survey 2010: Summary
 Infant Feeding Survey 2010: Summary Authors: Fiona McAndrew, Jane Thompson, Lydia Fellows, Alice Large, Mark Speed and Mary J. Renfrew A survey carried out on behalf of the Health and Social Care Information
Infant Feeding Survey 2010: Summary Authors: Fiona McAndrew, Jane Thompson, Lydia Fellows, Alice Large, Mark Speed and Mary J. Renfrew A survey carried out on behalf of the Health and Social Care Information
Ten top tips for the management of patients post bariatric surgery in primary care
 Ten top tips for the management of patients post bariatric surgery in primary care Obesity is recognised as a major health and economic issue for the NHS. The rate of severe obesity with BMI >40 is increasing
Ten top tips for the management of patients post bariatric surgery in primary care Obesity is recognised as a major health and economic issue for the NHS. The rate of severe obesity with BMI >40 is increasing
DIET AND ECZEMA IN CHILDREN
 DIET AND ECZEMA IN CHILDREN It has been known for many years that what children eat may have an effect on their eczema. There has been an ever-increasing interest in the part that diet plays in the development
DIET AND ECZEMA IN CHILDREN It has been known for many years that what children eat may have an effect on their eczema. There has been an ever-increasing interest in the part that diet plays in the development
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. Forceval Capsules
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Forceval Capsules Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information for you. This medicine is available without prescription. However, you still need
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET Forceval Capsules Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information for you. This medicine is available without prescription. However, you still need
MEAT AND ALTERNATIVES. Healthy Eating for Healthy Bones
 Nutrition Healthy Eating for Healthy Bones A s we get older, we often pay less attention to our diet. We may live alone and not always bother cooking a meal. We may become less active as we age, which
Nutrition Healthy Eating for Healthy Bones A s we get older, we often pay less attention to our diet. We may live alone and not always bother cooking a meal. We may become less active as we age, which
PL 17871/0208 UKPAR TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Fultium-D 3 3,200 IU Capsules PL 17871/0208 UKPAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Lay Summary Page 2 Scientific discussion Page 4 Steps taken for assessment Page 11 Summary of Product Characteristics Page 12 Patient
Fultium-D 3 3,200 IU Capsules PL 17871/0208 UKPAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Lay Summary Page 2 Scientific discussion Page 4 Steps taken for assessment Page 11 Summary of Product Characteristics Page 12 Patient
Guidelines for the Investigation and Management of Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency
 Hull and East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for the Investigation and Management of Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency Developed by:, Hull & East Yorkshire Hospital NHS Trust Hull and East Riding
Hull and East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for the Investigation and Management of Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency Developed by:, Hull & East Yorkshire Hospital NHS Trust Hull and East Riding
Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D
 Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : Presentation of advisory report Towards an adequate intake
Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D Gezondheidsraad Health Council of the Netherlands To the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport Subject : Presentation of advisory report Towards an adequate intake
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
BULLETIN. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health
 BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm (See NICE Clinical Guideline CG73 1 and Quality Standards 2 ) Who should have
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm Page 1 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm (See NICE Clinical Guideline CG73 1 and Quality Standards 2 ) Who should have
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health
 What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
Drug treatments for osteoporosis
 Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
Shared Care Guideline DRUG: Introduction: LEFLUNOMIDE (Adults) Indication: Disease modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Licensing Information: Disease modifying drug for active
