Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
|
|
|
- Cornelius Chase
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scan for mobile link. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) What is Coronary CTA? Coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a heart imaging test that helps determine if plaque buildup has narrowed a patient's coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply the heart. Plaque is made of various substances circulating in the blood, such as fat, cholesterol and calcium which deposits along the inner lining of the arteries. It can reduce the blood flow, or in some cases, block it completely. This build-up occurs over several years. Coronary CTA is a special type of x-ray examination. Patients undergoing a coronary CTA scan receive an iodine-containing contrast material (dye) as an intravenous (IV) injection to ensure the best possible images of the heart blood vessels. Computed tomography, more commonly known as a CT or CAT scan, is a diagnostic medical test that, like traditional x-rays, produces multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body. The cross-sectional images generated during a CT scan can be reformatted in multiple planes, and can even generate three-dimensional images. These images can be viewed on a computer monitor, printed on film or transferred to a CD or DVD. CT images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels typically provide greater detail than traditional x-rays, particularly of soft tissues and blood vessels. What are some common uses of the procedure? Many physicians advocate the careful use of coronary CTA for patients who have: suspected abnormal anatomy of the coronary arteries. low or medium risk for coronary artery disease, including patients who have chest pain and normal, non-diagnostic or unclear lab and ECG results. non-acute chest pain. new or worsening symptoms with a previous normal stress test result. unclear or inconclusive stress test results. new onset heart failure with reduced heart function and low or medium risk for coronary artery disease. medium risk of coronary artery disease, before non-coronary cardiac surgery. coronary artery bypass grafts. For patients meeting the above indications, coronary CTA can provide important information about the Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 1 of 7
2 presence and extent of plaque in the coronary arteries. Apart from identifying coronary artery narrowing as the cause of chest discomfort, it can also detect other possible causes of symptoms, such as a collapsed lung, blood clot in the vessels leading to the lungs, or acute aortic abnormalities. Your primary care physician or cardiac specialist, possibly in consultation with a radiologist who would perform the test, will determine whether coronary CTA is appropriate for you. How should I prepare? You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your exam. You may be given a gown to wear during the procedure. Metal objects, including jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures and hairpins, may affect the CT images and should be left at home or removed prior to your exam. You may also be asked to remove hearing aids and removable dental work. Women will be asked to remove bras containing metal underwire. You may be asked to remove any piercings, if possible. You should inform the technologist if you have a pacemaker. Pacemakers do not hinder the use of CT as in MRI as long as the scanner will not be taking images repeatedly over the area of the pacemaker device in the upper chest. This is usually not an issue for cardiac CT exams. You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for a few hours beforehand, especially if a contrast material will be used in your exam. You should inform your physician of all medications you are taking and if you have any allergies. If you have a known allergy to contrast material, or "dye," your doctor may prescribe medications (usually a steroid) to reduce the risk of an allergic reaction. These medications generally need to be taken 12 hours prior to administration of contrast material. To avoid unnecessary delays, contact your doctor before the exact time of your exam. Also inform your doctor of any recent illnesses or other medical conditions and whether you have a history of heart disease, asthma, diabetes, kidney disease or thyroid problems. Any of these conditions may increase the risk of an unusual adverse effect. On the day before and day of your exam, you may be asked to avoid: diet pills and caffeinated drinks such as coffee, tea, energy drinks or sodas. These may increase heart rate and limit the ability of the exam to evaluate for plaque in the coronary arteries. Viagra or any similar medication. They are not compatible with the medications you will receive during the procedure. On the night before the procedure, you may be asked to take a beta blocker medication to lower your heart rate to optimize the quality of the exam. Ask your doctor if you have questions about the instructions given to you. Women should always inform their physician and the CT technologist if there is any possibility that they may be pregnant. See the Safety page ( for more information about pregnancy and x-rays. If you are breastfeeding at the time of the exam, you should ask your doctor how to proceed. It may help to pump breast milk ahead of time and keep it on hand for use after contrast material has cleared from your body, about 24 hours after the test. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 2 of 7
3 What does the equipment look like? The CT scanner is typically a large, box-like machine with a hole, or short tunnel, in the center. You will lie on a narrow examination table that slides into and out of this tunnel. Rotating around you, the x-ray tube and electronic x-ray detectors are located opposite each other in a ring, called a gantry. The computer workstation that processes the imaging information is located in a separate control room, where the technologist operates the scanner and monitors your examination in direct visual contact and usually with the ability to hear and talk to you with the use of a speaker and microphone. Coronary CTA is very much like a normal CT scan. The only difference is the speed of the CT scanner and the heart monitor hook-up. How does the procedure work? During the examination, x-rays pass through the body and are picked up by special detectors in the scanner. Typically, higher numbers (especially 64 or more) of these detectors result in clearer final images. For that reason, coronary CTA often is referred to as multi-detector or multi-slice CT scanning. The information collected during the coronary CTA examination is used to identify the coronary arteries and possible areas of plaque along the coronary artery wall with associated narrowing of the vessel lumen, or cavity. The computer is used to create three-dimensional images and images in various planes to fully evaluate the heart and coronary arteries. When a contrast material is introduced to the bloodstream during the procedure, it clearly defines the blood vessels being examined by making them appear bright white. How is the procedure performed? You will be given a gown to wear during the procedure. A nurse will insert an intravenous (IV) line into a vein in your arm to administer contrast material (dye) during your procedure. You may be given a beta blocker medication through the same IV line or orally to help slow your heart rate in order to improve image quality. Nitroglycerin, which will dilate your coronary arteries for better visualization, may also be administered as a tablet or spray underneath your tongue. You will lie on a special scanning table. The technologist will clean three small areas of your chest and place small, sticky electrode patches on these areas. Men may require a small area of hair to be shaved on their chest to help the electrodes stick. The electrodes are attached to an electrocardiograph (ECG) monitor, which shows your heart's electrical activity during the test. While lying on the scanning table, you may be asked to raise your arms over your head for the duration of the exam. This will help improve image quality. Next, the table will move quickly through the scanner to determine the correct starting position for the scans. Then, the table will move slowly through the machine as the actual CT scanning is performed. Depending on the type of CT scan, the machine may make several passes. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 3 of 7
4 You may be asked to hold your breath during the scanning. Any motion, whether breathing or body movements, can lead to artifacts on the images. This loss of image quality can resemble the blurring seen on a photograph taken of a moving object. Inform your doctor if you have problems holding your breath for 10 to 15 seconds. Breathing during the scan creates blurring on the images and can result in an inconclusive exam. When the examination is completed, you will be asked to wait until the technologist verifies that the images are of high enough quality for accurate interpretation. Your intravenous line will be removed. Including all preparations, the coronary CTA scan usually takes about 15 minutes if the heart rate is slow and steady. It may take longer if the baseline heart rate is fast and beta-blocker is given to slow it down. If the beta-blocker is given by mouth it generally will require at least one hour to take effect. If the medication is injected into a vein (intravenously), it may still require multiple doses and up to 20 minutes to reach the slower heart rate. What will I experience during and after the procedure? Other than the needle stick when the IV line is placed, most CT exams are fast, easy and painless. Though the scanning itself causes no pain, there may be some discomfort from having to remain still for several minutes and with placement of an IV. If you have a hard time staying still, are very nervous or anxious or have chronic pain, you may find a CT exam to be stressful. The technologist or nurse, under the direction of a physician, may offer you some medication to help you tolerate the CT scanning procedure. For exams (excluding head and neck) your head will remain outside the hole in the center of the scanner. The scanner is approximately 24 inches wide, therefore, your entire body will be "inside" the scanner at one time such as with MRI. If an intravenous contrast material is used, you will feel a pin prick when the needle is inserted into your vein. You will likely have a warm, flushed sensation during the injection of the contrast materials and a metallic taste in your mouth that lasts for at most a minute or two. You may experience a sensation like you have to urinate; however, this is actually a contrast effect and subsides quickly. The medication given to slow the heart rate has been known to cause some patients to feel dizzy when they stand suddenly due to a lowering of blood pressure. Therefore, you will often be asked to sit up slowly on the table prior to standing. The dizziness is slight and only happens rarely. You may also have your blood pressure taken before the exam, during and following the examination if medications are given. When you enter the CT scanner room, special light lines may be seen projected onto your body, and are used to ensure that you are properly positioned. With modern CT scanners, you will hear only slight buzzing, clicking and whirring sounds as the CT scanner revolves around you during the imaging process. You will be alone in the exam room during the CT scan, unless there are special circumstances. For example, sometimes a parent wearing a lead shield may stay in the room with their child. However, the Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 4 of 7
5 technologist will always be able to see, hear and speak with you through a built-in intercom system. After a CT exam, you can return to your normal activities. If you received contrast material, you may be given special instructions. Who interprets the results and how do I get them? A physician, usually a radiologist with expertise in supervising and interpreting radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care physician or physician who referred you for the exam, who will discuss the results with you. If you are actively having chest pain, your results will be given to the emergency room doctor by the radiologist, and a preliminary result will be reported right away. Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the exact reason why another exam is requested. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up examination may also be necessary so that any change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable over time. What are the benefits vs. risks? Benefits Risks Coronary CTA is not invasive. An alternative test, cardiac catheterization with a coronary angiogram, is invasive, has more complications related to the placement of a long catheter into the arteries and the movement of the catheter in the blood vessels, and requires more time for the patient to recover. A major advantage of CT is that it is able to view bone, soft tissue and blood vessels all at the same time. It is therefore suited to identify other reasons for your discomfort such as an injury to the aorta or a blood clot in the lungs. Unlike conventional x-rays, CT scanning provides very detailed images of many types of tissue. CT examinations are fast and simple. CT has been shown to be cost-effective for a wide range of medical problems. CT is less sensitive to patient movement than MRI. CT can be performed if you have an implanted medical device of any kind, unlike MRI. No radiation remains in a patient's body after a CT examination. X-rays used in CT scans should have no immediate side effects. In some people with abnormal kidney function, the dye used in CT scanning may worsen kidney function. If a large amount of x-ray contrast material leaks out from the vessel being injected and spreads under the skin where the IV is placed, skin damage or damage to blood vessels and nerves, though Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 5 of 7
6 unlikely, can result. If you feel any pain in your arm at the location of the IV during contrast material injection, you should immediately inform the technologist. There is always a slight chance of cancer from excessive exposure to radiation. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk. The effective radiation dose for this procedure varies. See the Safety page ( for more information about radiation dose. Women should always inform their physician and x-ray or CT technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. See the Safety page ( for more information about pregnancy and x-rays. CT scanning is, in general, not recommended for pregnant women unless medically necessary because of potential risk to the baby in the womb. Manufacturers of intravenous contrast indicate mothers should not breastfeed their babies for hours after contrast medium is given. However, both the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the European Society of Urogenital Radiology note that the available data suggest that it is safe to continue breastfeeding after receiving intravenous contrast. For further information please consult the ACR Manual on Contrast Media and its references. ( The risk of serious allergic reaction to contrast materials that contain iodine is extremely rare, and radiology departments are well-equipped to deal with them. What are the limitations of Coronary CTA? A person who is very large may not fit into the opening of a conventional CT scanner or may be over the weight limit usually 450 pounds for the moving table. Patients who are extremely overweight or who have abnormal heart rhythms are usually not good candidates for this test because image quality may be compromised. Although coronary CTA examinations are growing in use, coronary angiography is still the main method for detecting coronary artery stenosis, which is a significant narrowing of an artery that could require treatment such as a stent or bypass surgery. Unlike CTA, which is only a diagnostic test, coronary angiography can be used for both diagnosis and treatment in a single session. Patients with a high risk of coronary artery disease and typical symptoms might undergo coronary angiography instead of CTA. Coronary CTA is often not useful in patients with many areas of old, calcified (hardened) plaque, which is often the case in older patients. Disclaimer This information is copied from the RadiologyInfo Web site ( which is dedicated to providing the highest quality information. To ensure that, each section is reviewed by a physician with expertise in the area presented. All information contained in the Web site is further reviewed by an ACR (American College of Radiology) - RSNA (Radiological Society of North America) committee, comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas. However, it is not possible to assure that this Web site contains complete, up-to-date information on any particular subject. Therefore, ACR and RSNA make no representations or warranties about the suitability of this information for use for any particular purpose. All information is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 6 of 7
7 Please visit the RadiologyInfo Web site at to view or download the latest information. Note: Images may be shown for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to draw conclusions or make diagnoses by comparing these images to other medical images, particularly your own. Only qualified physicians should interpret images; the radiologist is the physician expert trained in medical imaging. Copyright This material is copyrighted by either the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), 820 Jorie Boulevard, Oak Brook, IL or the American College of Radiology (ACR), 1891 Preston White Drive, Reston, VA Commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method is prohibited. Copyright 2013 Radiological Society of North America, Inc. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) Page 7 of 7
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Computed Tomography (CT) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography)
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
CT Colonography. What is CT Colonography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Lymphoscintigraphy is a special type of nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
 Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
How To Prepare For A Ct Scan
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
CT Scan UHN. Information for patients and families
 CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins)
 Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
How To Use An Ultrasound For Medical Research
 Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families
 An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families What is a Cardiac Cath? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat patients who have various forms of heart disease.
An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families What is a Cardiac Cath? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat patients who have various forms of heart disease.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
MRI of the Breast. What is MRI of the Breast?
 MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
Understanding and Preparing for a CAtHeteRIZAtIon PRoCeDURe
 Understanding and Preparing for a CAtHeteRIZAtIon PRoCeDURe The Massachusetts General Hospital Heart Center and Vascular Center welcome you to the Knight Center for Interventional Cardiovascular Therapy.
Understanding and Preparing for a CAtHeteRIZAtIon PRoCeDURe The Massachusetts General Hospital Heart Center and Vascular Center welcome you to the Knight Center for Interventional Cardiovascular Therapy.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram
 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
Airport Scanner Safety
 Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
University College Hospital. Having a CT scan. Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Having a CT scan Imaging Department If you need a large print, audio, or a translated copy of this document, please contact us on: 020 345 67002 We will do our best to meet
University College Hospital Having a CT scan Imaging Department If you need a large print, audio, or a translated copy of this document, please contact us on: 020 345 67002 We will do our best to meet
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options. A Guide for Patients
 Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
CardiacAdvantage. Catheterization. Patient Guide. Cardiac
 Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know
 Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST
 CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
Cardiac Catheterization
 Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS
 INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY (IMRT) FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS HOW DOES RADIATION THERAPY WORK? Cancer is the unrestrained growth of abnormal cells within the body. Radiation therapy kills both
CT THORAX, ABDOMEN & PELVIS PREPARATION AT HOME
 CT THORAX, ABDOMEN & PELVIS PREPARATION AT HOME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Information The CT Scan Department is located in the Stockport Imaging Centre, adjacent to the
CT THORAX, ABDOMEN & PELVIS PREPARATION AT HOME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Information The CT Scan Department is located in the Stockport Imaging Centre, adjacent to the
RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL
 RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL What is Radiation Therapy? Radiation Therapy is the use of radiation to treat cancer and some non-malignant growths. A machine, called a linear accelerator, is
RADIATION THERAPY AUCKLAND CITY HOSPITAL What is Radiation Therapy? Radiation Therapy is the use of radiation to treat cancer and some non-malignant growths. A machine, called a linear accelerator, is
Cardiac catheterization Information for patients
 Cardiac catheterization Information for patients You have been scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. Your procedure is scheduled for:. Someone will call you the day before your procedure to tell you
Cardiac catheterization Information for patients You have been scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. Your procedure is scheduled for:. Someone will call you the day before your procedure to tell you
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
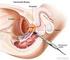 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
