Numerical analysis of ossicular chain lesion of human ear
|
|
|
- Janis Garrison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Mech Sin (2009) 25: DOI /s RESEARCH PAPER Numerical analysis of ossicular chain lesion of human ear Yingxi Liu Sheng Li Xiuzhen Sun Received: 8 January 2008 / Revised: 11 September 2008 / Accepted: 24 September 2008 / Published online: 11 November 2008 The Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics and Springer-Verlag GmbH 2008 Abstract Lesion of ossicular chain is a common ear disease impairing the sense of hearing. A comprehensive numerical model of human ear can provide better understanding of sound transmission. In this study, we propose a three-dimensional finite element model of human ear that incorporates the canal, tympanic membrane, ossicular bones, middle ear suspensory ligaments/muscles, middle ear cavity and inner ear fluid. Numerical analysis is conducted and employed to predict the effects of middle ear cavity, malleus handle defect, hypoplasia of the long process of incus, and stapedial crus defect on sound transmission. The present finite element model is shown to be reasonable in predicting the ossicular mechanics of human ear. Keywords Finite element model Ossicular chain lesion Acoustic structural coupled analysis Middle ear cavity Sound transmission 1 Introduction The human ear includes complex morphological structures consisting of canal, middle ear and inner ear to transfer sound from environment into central auditory system. The external The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( , , and ). Y. Liu S. Li (B) X. Sun State Key Laboratory of Structural Analysis for Industrial Equipment, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China lishengdlut@163.com X. Sun ENT Department, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China canal collets sound pressure waves and stimulate the air media in the ear canal to induce vibration of the tympanic membrane. The middle ear consists of three small ossicles (i.e., malleus, incus, and stapes) which are suspended in the airfilled middle ear cavity by attached ligaments and muscle tendons and connected by two joints: incudomalleolar and incudostapedial joints. The middle ear builds a mechanism (ossicular chain) for transmitting vibrations of the tympanic membrane. The output portion of the middle ear is a stapes footplate, which sets into the oval window and transmits vibrations into cochlear fluid. A number of parameters, such as shape and stiffness of the tympanic membrane, shape and volume of the external ear canal, and volume and pressure of the middle ear cavity, affect directly acoustic mechanical transmission through the ear. Changes of these parameters are often related to patho-physiological conditions in the ear. The ossicular chain plays an important role in auditory mechanics. If a patient suffers from different diseases, the ossicular bones may be damaged in different part and the efficiency in the sound transmission of the middle ear may also be reduced. Frequent occurrence of ossicular chain lesions is one of the factors urging physicians to seek out the most cost-effective clinical strategies for managing the condition. A number of clinical studies have been dedicated to symptoms of the diseases of ossicles in human [1 3] using experimental method. However, the effects have not been quantitatively clarified because removal of any part of ossicular bones is difficult. And, direct measurements of certain performances are difficult to carry out. When the dynamic behavior of biological structures is analyzed, the finite element method would be one of the powerful tools. The finite element method is always capable of modeling the complex geometry, ultrastructural characteristics, and non-homogenous and anisotropic material properties of biological systems. The first
2 242 Y. Liu et al. finite element model of the ear (for cat tympanic membrane) was reported by Funnell and Laszlo in 1978 [4]. In 1992, a three-dimensional finite element model of middle ear was proposed by Wada and Metoki [5] for investigating vibration patterns of the middle ear system. Since then, the finite element modeling of the static and dynamic behaviors of the middle ear subsets or entire middle ear has become a rapid growing field in ear mechanics. A thorough literature survey about the FE modeling of ear mechanics is summarized in our previous publication [6]. In 2004, Gan et al. construct a complete finite element model of the human ear on the basis of histological section images of human temporal bone [7] for analyzing the transmission of sound wave. But, the specimen has to be decalcified and embedded before the actual risky process of sectioning and mounting the slices on microscope glass plates. In 2007, Lee et al. develop a finite element model using high-resolution computed tomography for cartilage myringoplasty [8]. However, some factors have not been considered in Lee s model, e.g., the middle cavity and the canal. Using the spiral CT technology, Liu et al. [9] construct a finite element model of human ear which incorporated the canal, the tympanic membrane, the ossicular bones, the middle ear suspensory ligaments/muscles, and the inner ear fluid. The validity of the model is confirmed by comparing the displacements of tympanic membrane and stapes footplate obtained by the finite element model with published experimental data. In the present study, the effect of middle ear cavity is taken into consideration [10]. The acoustic structural coupling effect of the canal, the tympanic membrane, the ossicules, and the middle ear cavity is investigated and the effects of the middle ear cavity and the ossicular chain lesions are predicted by using the finite element model. 2 Methods 2.1 Construction of finite element model A healthy living volunteer (male, age 25, right ear) is scanned using spiral computerized tomography to show the whole temporal bone. The spiral data set is reconstructed with an interval of 0.1 mm, and the images from the spiral computerized tomography machine are digitized using self-programming of Matlab along the outlines of the ear structures identified by the otologic surgeon. The data of digitized images are input into ANSYS to generate a finite element model and appropriate boundary conditions. Figure 1a d show the finite element model of human ear incorporating the ear canal, the tympanic membrane, the ossicular bones, the middle ear suspensory ligaments/muscles, the middle ear cavity and the inner ear fluid. The connections of components are showed in Fig. 1e and f. The tympanic membrane is meshed by three-node shell elements with a total of 3,626 elements, the canal, the middle cavity and inner ear fluid are meshed by four-node acoustic elements with a total of 149,747 elements, and the other parts are meshed by four-node tetrahedral solid elements with a total of 36,270 elements. Fig. 1 a d Finite element models of ear components, e, f illustration for the connection of components
3 Numerical analysis of ossicular chain lesion of human ear 243 Table 1 Material properties of ear components ρ/(kg m 3 ) E/Pa Tympanic membrane [11] [12] Malleus (head) [13] [14] (neck) (handle) Incus (body) [13] [14] (short process) (long process) Stapes [13] [15] Incudomalleolar joint [6] [6] Incudostapedial joint [6] [16] Manubrium [6] [6] Tympanic annulus [6] Superior mallear ligament [17] [12] Lateral mallear ligament [12] Anterior mallear ligament [6] Superior incudal ligament [6] Posterior incudal ligament [16] Stapedial annular ligament [18] Tensor tympani tendon [16] Stapedial tendon [17] Table 2 Acoustic properties of ear components ρ/(kg m 3 ) v/(ms 1 ) Air Cochlear fluid 1,000 1, Governing equations The structural dynamics equation of the acoustic structural coupled system is Mü + C u + Ku = f + Rp, (1) 2.3 Material properties The human ear is described as a linear system under a regular sound intensity at an audible level. Material properties and boundary conditions are assigned from published data (Table 1), while acoustic properties of air and water are listed in Table 2. The Poisson s ratio is assumed to be 0.3 [7], the Raleigh damping parameters for all materials of the middle ear system are α = 0s 1 and β = s [7] and the thickness of the tympanic membrane is 0.05mm. The surfaces of acoustic elements next to the movable structure, such as the tympanic membrane, ossicles, and suspensory ligaments, are where M, C, K, and R are structural mass matrix, structural damping matrix, structural stiffness matrix, and coupling matrix, respectively; u is the displacement vector; u is the velocity vector; ü is the acceleration vector; f is the applied load vector, and p is the sound pressure on the coupled surface. The acoustic wave equation of the acoustic structural coupled system is M p p + K p p = ρ 0 R T ü, (2) where M p, K p, and R are fluid mass matrix, fluid stiffness matrix, and coupling matrix, respectively; p is the sound pressure; ü is the acceleration vector on the coupled surface; ρ 0 is mean fluid density. Fig. 2 Finite element model of the middle ear cavity with different volume. a Cavity closed I, b cavity closed II
4 244 Y. Liu et al. Fig. 3 Effects of the middle ear cavity on tympanic membrane (a) and stapes footplate (b) displacements Fig. 4 Finite element model of malleus handle defect defined as fluid structural interface (FSI) where the acoustic pressure distribution is coupled into structural analysis as the force input in ANSYS. 3 Result and discussion 3.1 Effects of middle ear cavity Effect of the middle ear cavity on sound transmission is examined in this section. The finite element models with different volumes: (a) mm 3 and (b) mm 3 are shown in Fig. 2, and the state of the middle ear cavity can be either open or closed for simulation. An open middle ear cavity refers to a finite element model in which the middle ear air space connects directly to ambient pressure, whereas a closed middle ear cavity refers to a model where the entire middle ear air space is sealed. Figures 3a and b show the calculated displacements of tympanic membrane and stapes footplate based on the finite element model with three states of cavity: cavity open, cavity closed I and cavity closed II. Opening the middle ear cavity increases the magnitude of the displacements at tympanic membrane. Moreover, the displacements will be reduced when the cavity volume is decreased. The effects of cavity states on displacements are sensitive for frequencies below 2,000 Hz. Results of stapes footplate show similar differences between the open and sealed cavity configurations. The analysis demonstrates that the volume of the middle ear cavity plays an important role in determining hearing loss. The trend of simulation results is consistent with that previously published [19]. 3.2 Effects of malleus handle defect The handle of the malleus secured to the tympanic membrane plays an important role in sound transmission from Fig. 5 Effects of malleus handle defect on tympanic membrane (a) and stapes footplate (b) displacements
5 Numerical analysis of ossicular chain lesion of human ear Effects of incus with hypoplasia Fig. 6 Finite element model of incus lesion outer ear to inner ear. The trauma may lead to defects in the malleus handle. In the section, efforts are focused on the change of vibration at tympanic membrane and stapes because of the defect in melleus handle. Figure 4 shows the finite element model of normal malleus and melleus with lesion. The finite element model of the ear is used for predicting the effects of malleus handle on tympanic membrane and stapes movements. Figure 5a and b show the displacements of tympanic membrane and stapes footplate in response to the change of malleus handle. The results suggest that the lesion of malleus handle will have tremendous effects on tympanic membrane and stapes footplate movement and thus affect sense of hearing. The defect in malleus handle results in an overall increase of tympanic membrane displacement over the auditory frequency range (Fig. 5a). However, the defect results in an extensive reduction of stapes displacement (Fig. 5b). The results predicted by the finite element model may provide useful information for the diagnosis of isolated defect occurred in malleus handle of a patient with conductive hearing loss. The incus articulates with malleus and stapes by incudomalleolar joint and incudostapedial joint, respectively. Hypoplasia of incus would result in different otological diseases. In the study, it is assumed that the long process of incus has pathologic change. In the abnormal situation, bone tissue of the long process of incus is replaced by soft tissue (Fig. 6). To simulate the disorder of the long process of incus, it is assumed that the Young s modulus of the long process is decreased from Pa to Pa. Figures 7a and b show the model-predicted displacement curves at tympanic membrane and stapes footplate in response to the stiffness change of the long process of incus. The softer long process results in an obvious increase of stapes displacement. However, the influence of the softer long process on tympanic membrane is very limited. One explanation for the change is that less acoustic energy is transported to the stapes footplate through the softer long process. The results of the section indicate that the finite element model can be used to predicting clinical manifestation of incus prostheses for improving the patient s sense of hearing. 3.4 Effects of stapedial crus defect As the name implies, the stapes looks like a stirrup. It has four components: a footplate, anterior crus, posterior crus, and a head (Fig. 8). The head of the stapes articulates with the long process of the incus, and the footplate of the stapes covers the oval window. The hypoplasia of stapes may lead to defects in anterior crus or in posterior crus, both of which would be discussed in detail in the present section. The defect in crus has a little effect on tympanic membrane movement at all frequencies (Fig. 9a). Figure 9b and c show the displacement curves of the anterior part of stapes footplate and the posterior part of stapes footplate, respectively. As shown in the figures, the defect in anterior crus and posterior crus have substantial effect on the stapes footplate movement. The defect in anterior crus decreases the Fig. 7 Effects of the long process lesion of incus on tympanic membrane (a) and stapes footplate (b) displacements
6 246 Y. Liu et al. Fig. 8 Finite element model of stapedial crus defect Fig. 9 Effects of stapedial crus defect on the displacements of tympanic membrane (a), anterior part of stapes footplate (b) and posterior part of stapes footplate (c) displacement of the anterior part of stapes footplate (Fig. 9b) and increases the displacement of the posterior part of stapes footplate (Fig. 9c). When the posterior crus is damaged, the displacement is increased at the anterior part of stapes footplate (Fig. 9b) and decreased at the posterior part of stapes footplate (Fig. 9c). The results can give a better understanding of malformation of stapes and be referenced by stapedial surgery. 4 Conclusion In this study, a three-dimensional finite element model of human ear is created based on a complete set of CT images of a living human temporal bone. Numerical analysis based on the finite element model is conducted for otological applications to predicting the effects of the middle ear cavity, malleus handle defect, hypoplasia of the long process of incus, and stapedial crus defect on sound transmission. From this study, it is clear that the finite element method has great potential for analyzing the dynamical behavior of acoustic transmission in human ear. Predictions from this model may be useful to clinicians in researching new surgical reconstruction techniques and provide useful information for the design of middle ear implants to restore sense of hearing. Acknowledgments A special note of thanks is extended to all the doctors of the Department of ENT, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian
7 Numerical analysis of ossicular chain lesion of human ear 247 Medical University for their assistance in the design and organization of this research. References 1. Iurato, S., Quaranta, A.: Malleus-handle fracture: historical review and three new cases. Am. J. Otol. 20, (1999) 2. Park, K., Choung, Y.-H., Shin, Y.R.: Conductive deafness with normal eardrum absence of the long process of the incus. Acta Otolaryngol. 127, (2007) 3. Gomes, G., Felix, F., Tomita, S.: Improvements of bone conduction after stapes surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 133, 240 (2005) 4. Funnell, W.R.J., Laszlo, C.A.: Modeling of the cat eardrum as a thin shell using the finite-element method. J Acoust. Soc. Am. 63, (1978) 5. Wada, H., Metoki, T.: Analysis of dynamic behavior of human middle ear using a finite method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 92, (1992) 6. Sun, Q., Gan, R.Z., Chang, K.-H., Dormer, K.J.: Computerintegrated finite element modeling of human middle ear. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 1, (2002) 7. Gan, R.Z., Feng, B., Sun, Q.: Three-dimensional finite element modeling of human ear for sound transmission. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32, (2004) 8. Lee, C.F., Chen, J.H., Chou, Y.F.: Optimal graft thickness for different sizes of tympanic membrane perforation in cartilage myringoplasty a finite element analysis. Laryngoscope 117, (2007) 9. Liu, Y.X., Li, S., Sun, X.Z. : Numerical modeling of human ear for sound transmission. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 40, (in Chinese) (2008) 10. Voss, S.E., Rosowski, J.J., Merchant, S.N., Peake, W.T.: Acoustic respones of the human middle ear. Hear. Res. 150, (2000) 11. Williams, K.R., Lesser, T.H.: A finite element analysis of the natural frequencies of vibration of the human tympanic membrane. Part I. Br. J. Audiol. 24, (1990) 12. Beer, H.J., Bornitz, M., Drescher, J.: Finite element modeling of the human eardrum and applications. In: Huttenbrink, K.B. (ed.) Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otosurgery, pp Dresden University of Technology, Dresden (1996) 13. Kirikae, I.: The Structure and Function of the Middle Ear. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo (1960) 14. Speirs, A.D., Hotz, M.A., Oxland, T.R.: Biomechanical properties of sterilized human auditory ossicles. J. Biomech. 32, (1999) 15. Herrmann, G., Liebowitz, H.: Mechanics of bone fractures. In: Liebowitz, H. (ed.) Fracture: an Advanced Treatise, pp Academic Press, New York (1972) 16. Wada, H., Koike, T., Kobayashi, T.: Three-dimensional finiteelement method (FEM) analysis of the human middle ear. In: Huttenbrink, K.B. (ed.) Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otosurgery. pp Dresden University of Technology, Dresden (1996) 17. Koike, T., Wada, H., Kobayashi, T.: Modeling of the human middle ear using the finite-element method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111, (2002) 18. Gan, R.Z., Sun, Q., Feng, B., Wood, M.W.: Acoustic structural coupled finite element analysis for sound transmission in human ear-pressure distributions. Med. Eng. Phys. 28, (2006) 19. Mehta, R.P., Rosowski, J.J., Voss, S.E.: Determinants of hearing loss in perforations of the tympanic membrane. Otol. Neurotol. 27, (2006)
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
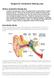 Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss What is conductive hearing loss Conductive hearing loss is a form of hearing loss due to abnormalities in mobile portions of the ear. Theses are the movable parts (including
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Diseases of the middle ear
 Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
Diseases of the middle ear Acute Suppurative Otitis Media: Acute suppurative otitis media may be viral or bacterial and is accompanied by signs of pain, pressure sensation, diminished hearing and occasional
Auditory System. Chaos Healthcare
 Medical Coding Auditory System Chaos Healthcare AUDITORY SYSTEM: Anatomy AUDITORY SYSTEM: Physiology AUDITORY SYSTEM MYRINGOPLASTY: Myringoplasty is an operative procedure used in the reconstruction of
Medical Coding Auditory System Chaos Healthcare AUDITORY SYSTEM: Anatomy AUDITORY SYSTEM: Physiology AUDITORY SYSTEM MYRINGOPLASTY: Myringoplasty is an operative procedure used in the reconstruction of
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
SEMI-IMPLANTABLE AND FULLY IMPLANTABLE MIDDLE EAR HEARING AIDS
 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be read in its
Ear, Nose, Throat, Teeth and the Jaw
 Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 REDISTRIBUTION OF LOAD OF INJURED LOWER CERVICAL SPINE UNDER AXIAL COMPRESSION USING FEM E. C. Teo 1 and H. W. Ng 1 1 School of Mechanical and Production Engineering, Nanyang Technological University,
REDISTRIBUTION OF LOAD OF INJURED LOWER CERVICAL SPINE UNDER AXIAL COMPRESSION USING FEM E. C. Teo 1 and H. W. Ng 1 1 School of Mechanical and Production Engineering, Nanyang Technological University,
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell
 Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
Light wear for a powerful hearing. Bone Conduction Headset
 Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Light wear for a powerful hearing Bone Conduction Headset 2 Light wear for a powerful hearing Melody Flex, the new bone conduction headset is AUTEL s solution to improve hearing quality of those affected
Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant
 International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. 3 Issue. 3 Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) Techniques Applied To Hip Implant 1, M. S. Abo_Elkhair, 2, M. E. Abo-Elnor,
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
OSSICULOPLASTY CHAPTER 4. James S. Batti, MD Charles D. Bluestone, MD
 CHAPTER 4 OSSICULOPLASTY James S. Batti, MD Charles D. Bluestone, MD This chapter reviews methods for reconstructing the ossicular chain from tympanic membrane to oval window, with emphasis on specific
CHAPTER 4 OSSICULOPLASTY James S. Batti, MD Charles D. Bluestone, MD This chapter reviews methods for reconstructing the ossicular chain from tympanic membrane to oval window, with emphasis on specific
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED
 Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Your Hearing ILLUMINATED INFORMATION FROM YOUR HEARING CARE PROFESSIONAL REDISCOVER your hearing and reconnect 1 with the important things you might have been missing. Your sense of hearing is a vital
Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs
 Acoustics 8 Paris Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs J.-J. Chen and B. Bonello CNRS and Paris VI University, INSP - 14 rue de Lourmel, 7515 Paris, France chen99nju@gmail.com 41 Acoustics 8 Paris We
Acoustics 8 Paris Plate waves in phononic crystals slabs J.-J. Chen and B. Bonello CNRS and Paris VI University, INSP - 14 rue de Lourmel, 7515 Paris, France chen99nju@gmail.com 41 Acoustics 8 Paris We
Estimating Acoustic Performance of a Cell Phone Speaker Using Abaqus
 Estimating Acoustic Performance of a Cell Phone Speaker Using Abaqus C. Jackman 1, M. Zampino 1 D. Cadge 2, R. Dravida 2, V. Katiyar 2, J. Lewis 2 1 Foxconn Holdings LLC 2 DS SIMULIA Abstract: Consumers
Estimating Acoustic Performance of a Cell Phone Speaker Using Abaqus C. Jackman 1, M. Zampino 1 D. Cadge 2, R. Dravida 2, V. Katiyar 2, J. Lewis 2 1 Foxconn Holdings LLC 2 DS SIMULIA Abstract: Consumers
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation
 Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
Noise: Impact on Hearing; Regulation EOH 466A Fall 2008 Mechanism of Hearing Sound waves collected, focused by the outer ear. Humans have little control over muscles in outer ear. Many animals have the
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL
 STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL Paulo Mendes, Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Portugal Sérgio Oliveira, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia
STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL Paulo Mendes, Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Portugal Sérgio Oliveira, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia
CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
 41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM
 3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM Fabian Krome, Hauke Gravenkamp BAM Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, Unter den Eichen 87, 12205 Berlin, Germany email: Fabian.Krome@BAM.de
3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM Fabian Krome, Hauke Gravenkamp BAM Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, Unter den Eichen 87, 12205 Berlin, Germany email: Fabian.Krome@BAM.de
Mesh Moving Techniques for Fluid-Structure Interactions With Large Displacements
 K. Stein Department of Physics, Bethel College, St. Paul, MN 55112 T. Tezduyar Mechanical Engineering, Rice University, MS 321, Houston, TX 77005 R. Benney Natick Soldier Center, Natick, MA 01760 Mesh
K. Stein Department of Physics, Bethel College, St. Paul, MN 55112 T. Tezduyar Mechanical Engineering, Rice University, MS 321, Houston, TX 77005 R. Benney Natick Soldier Center, Natick, MA 01760 Mesh
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology
 The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
Noise. CIH Review PDC March 2012
 Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Constrained Tetrahedral Mesh Generation of Human Organs on Segmented Volume *
 Constrained Tetrahedral Mesh Generation of Human Organs on Segmented Volume * Xiaosong Yang 1, Pheng Ann Heng 2, Zesheng Tang 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Constrained Tetrahedral Mesh Generation of Human Organs on Segmented Volume * Xiaosong Yang 1, Pheng Ann Heng 2, Zesheng Tang 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31)
 Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor
 Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 -
 Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids. April 2013. Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids April 2013 Reference: NHSCB/ D09/P/a NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Bone Anchored Hearing Aids First published: April 2013
A Semantic Web Platform for Automating the Interpretation of Finite Element Bio-simulations
 A Semantic Web Platform for Automating the Interpretation of Finite Element Bio-simulations André Freitas, Kartik Asooja, João B. Jares, Stefan Decker, Ratnesh Sahay Insight Centre for Data Analytics National
A Semantic Web Platform for Automating the Interpretation of Finite Element Bio-simulations André Freitas, Kartik Asooja, João B. Jares, Stefan Decker, Ratnesh Sahay Insight Centre for Data Analytics National
DYNAMICAL ANALYSIS OF SILO SURFACE CLEANING ROBOT USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 190-202, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_020 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 190-202, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_020 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
 45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL
 PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL P. Kolar, T. Holkup Research Center for Manufacturing Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Czech
PREDICTION OF MACHINE TOOL SPINDLE S DYNAMICS BASED ON A THERMO-MECHANICAL MODEL P. Kolar, T. Holkup Research Center for Manufacturing Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Czech
Presbycusis. What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis?
 Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
Presbycusis What is presbycusis? Presbycusis is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most individuals as they grow older. Hearing loss is a common disorder associated with aging. About 30-35 percent
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary
 X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who has a hearing loss? How does hearing work?
 This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
This e-book will answer the following questions: What is presbycusis? What are the symptoms of presbycusis? What are the causes of presbycusis? What can be done? How can I communicate with someone who
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
The NAL Percentage Loss of Hearing Scale
 The NAL Percentage Loss of Hearing Scale Anne Greville Audiology Adviser, ACC February, 2010 The NAL Percentage Loss of Hearing (PLH) Scale was developed by John Macrae of the Australian National Acoustic
The NAL Percentage Loss of Hearing Scale Anne Greville Audiology Adviser, ACC February, 2010 The NAL Percentage Loss of Hearing (PLH) Scale was developed by John Macrae of the Australian National Acoustic
An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis
 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System
 Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Vibrant Soundbridge Implantable Hearing System Kristin M. Avitabile, MS, CCC-A Clinical Manager, Southeastern U.S. MED-EL Corporation Hearing Technology Hearing Aids Mild to severe HL Problems with feedback
Food and Drug Administration 5 10(k) Notijfication - Partial & Total Ossicular Replacement Prostheses AUG I 8 2006 June 30, 2006
 5 10(k) Notijfication - Partial & Total Ossicular Replacement AUG I 8 2006 510(K) SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS Grace Medical Adjustable Length and Fixed Length Partial and Total Ossicular Replacement
5 10(k) Notijfication - Partial & Total Ossicular Replacement AUG I 8 2006 510(K) SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS Grace Medical Adjustable Length and Fixed Length Partial and Total Ossicular Replacement
Acoustical Design of Digital Stethoscope for Improved Performance
 Acoustical Design of Digital Stethoscope for Improved Performance Raj C Thiagarajan 1 *, Prema Sankaran 2, Abdul Hafeez Baig 3, Kodeeswari Elangovan 1, Raj Gururajan 3 1 ATOA Scientific Technologies, Bangalore,
Acoustical Design of Digital Stethoscope for Improved Performance Raj C Thiagarajan 1 *, Prema Sankaran 2, Abdul Hafeez Baig 3, Kodeeswari Elangovan 1, Raj Gururajan 3 1 ATOA Scientific Technologies, Bangalore,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
I Ear Your Messages A Review of Ear Disease as it Pertains to the Anatolian Shepherd Dog
 I Ear Your Messages A Review of Ear Disease as it Pertains to the Anatolian Shepherd Dog a A few months ago I received an email asking me to address the increasing prevalence of ear infections in the Anatolian
I Ear Your Messages A Review of Ear Disease as it Pertains to the Anatolian Shepherd Dog a A few months ago I received an email asking me to address the increasing prevalence of ear infections in the Anatolian
The new wide Ponto implant design clinical and surgical aspects
 The new wide Ponto implant design clinical and surgical aspects Partik Westerkull, MSc. Eng. Ph., Senior Research Consultant to Oticon Medical Lars Jinton, Director of Engineering, Oticon Medical With
The new wide Ponto implant design clinical and surgical aspects Partik Westerkull, MSc. Eng. Ph., Senior Research Consultant to Oticon Medical Lars Jinton, Director of Engineering, Oticon Medical With
Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA
 Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA Nidhi Dwivedi, Research Scholar (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P), Veerendra Kumar Principal (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P) Abstract The main objective of this paper
Burst Pressure Prediction of Pressure Vessel using FEA Nidhi Dwivedi, Research Scholar (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P), Veerendra Kumar Principal (G.E.C, Jabalpur, M.P) Abstract The main objective of this paper
8.Audiological Evaluation
 8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
8. A U D I O L O G I C A L E V A L U A T I O N 8.Audiological Evaluation The external ear of the child with Progeria Behavioral testing for assessing hearing thresholds Objective electrophysiologic tests
Cochlear Implant, Bone Anchored Hearing Aids, and Auditory Brainstem Implant
 Origination: 06/23/08 Revised: 10/13/14 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: To provide cochlear implant, bone anchored hearing aids, and auditory brainstem implant guidelines for the Medical Department staff
Origination: 06/23/08 Revised: 10/13/14 Annual Review: 11/12/15 Purpose: To provide cochlear implant, bone anchored hearing aids, and auditory brainstem implant guidelines for the Medical Department staff
Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability Based on Active Disassembly Using Smart Materials *
 Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology, 2011, 1, 80-87 doi:10.4236/jsemat.2011.12012 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsemat) Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability
Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology, 2011, 1, 80-87 doi:10.4236/jsemat.2011.12012 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsemat) Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss
 Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
Prevalence of otological disorders in diabetic patients with hearing loss Manche Santoshi Kumari *, Jangala Madhavi *, Koralla Raja Meganadh *, Akka Jyothy Institute of Genetics and Hospital for Genetic
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS
 CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
CONVENTIONAL AND DIGITAL HEARING AIDS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD. Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY
 GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
GONCA SENNAROĞLU PhD LEVENT SENNAROĞLU MD Department of Otolaryngology Hacettepe University ANKARA, TURKEY To present the audiological findings and rehabilitative outcomes of CI in children with cochlear
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Masafumi Aoyanagi Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PROBE WITH THREE DEGREE- OF-FREEDOM FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TEST USING THREE- DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Masafumi Aoyanagi Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering,
ANALYTICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF SPRING BACK EFFECTS IN A TYPICAL COLD ROLLED SHEET
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 119-130, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 2016, pp. 119-130, Article ID: IJMET_07_01_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=1
Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves
 Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves Bennie Buys Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering University of Pretoria Introduction Rock Bolts and their associated problems
Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves Bennie Buys Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering University of Pretoria Introduction Rock Bolts and their associated problems
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF CIRCULAR DISC WITH DIAMETRAL SLOTS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJMET) International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6340 (Print) ISSN 0976 6359
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJMET) International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET), ISSN 0976 6340(Print), ISSN 0976 6340 (Print) ISSN 0976 6359
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Hearing Aids (BAHA) Amended Date: October 1, 2015.
 Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
Implantable Bone Conduction Clinical Coverage Policy No: 1A-36 Table of Contents 1.0 Description of the Procedure, Product, or Service... 1 1.1 Conductive Hearing Loss... 1 1.2 Sensorineural Hearing Loss...
Image-based simulation of the human thorax for cardio-pulmonary applications
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Image-based simulation of the human thorax for cardio-pulmonary applications F. K. Hermans and R. M. Heethaar, VU University Medical Center, Netherlands R.
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Boston Image-based simulation of the human thorax for cardio-pulmonary applications F. K. Hermans and R. M. Heethaar, VU University Medical Center, Netherlands R.
CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL
 F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
Assessment of quantitative hearing loss in relation to the morphology of central tympanic membrane perforations
 Assessment of quantitative hearing loss in relation to the morphology of central tympanic membrane perforations A Nepal, S Bhandary, SC Mishra, I Singh and P Kumar Department of Otolaryngology and Head
Assessment of quantitative hearing loss in relation to the morphology of central tympanic membrane perforations A Nepal, S Bhandary, SC Mishra, I Singh and P Kumar Department of Otolaryngology and Head
The mechanical behavior of the bone microstructure around dental implants
 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF STRUCTURAL MECHANICS The mechanical behavior of the bone microstructure around dental implants Summary and Theses of PhD dissertation ÉVA LAKATOS
BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF STRUCTURAL MECHANICS The mechanical behavior of the bone microstructure around dental implants Summary and Theses of PhD dissertation ÉVA LAKATOS
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
 Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Finite Element Analysis of a Golf Driver and Golf Ball
 Professor Suo 1/16 Solid Mechanics Finite Element Analysis of a Golf Driver and Golf Ball Abstract: This paper performs a theoretical stress and frequency analysis of both a 2D and 3D golf driver head
Professor Suo 1/16 Solid Mechanics Finite Element Analysis of a Golf Driver and Golf Ball Abstract: This paper performs a theoretical stress and frequency analysis of both a 2D and 3D golf driver head
ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS GENERATED BY MONOPOLE (PEN- CIL-LEAD BREAK) VERSUS DIPOLE SOURCES: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING AND EXPERIMENTS
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS GENERATED BY MONOPOLE (PEN- CIL-LEAD BREAK) VERSUS DIPOLE SOURCES: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING AND EXPERIMENTS M. A. HAMSTAD Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNALS GENERATED BY MONOPOLE (PEN- CIL-LEAD BREAK) VERSUS DIPOLE SOURCES: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING AND EXPERIMENTS M. A. HAMSTAD Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
Image Based-Mesh Generation for realistic Simulation of thetranscranial Current Stimulation
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Image Based-Mesh Generation for realistic Simulation of thetranscranial Current Stimulation Ash Harkara Business Manager Presentation overview Company overview
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Image Based-Mesh Generation for realistic Simulation of thetranscranial Current Stimulation Ash Harkara Business Manager Presentation overview Company overview
DURATION OF HEARING LOSS
 When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
When your child is diagnosed with a hearing loss, it may be very overwhelming. This may be a difficult time for you and your family. However, gaining a greater knowledge in this area is crucial in helping
Fluid-Structure Acoustic Analysis with Bidirectional Coupling and Sound Transmission
 VPE Swiss Workshop Acoustic Simulation 12. Sept. 2013 Fluid-Structure Acoustic Analysis with Bidirectional Coupling and Sound Transmission Reinhard Helfrich INTES GmbH, Stuttgart info@intes.de www.intes.de
VPE Swiss Workshop Acoustic Simulation 12. Sept. 2013 Fluid-Structure Acoustic Analysis with Bidirectional Coupling and Sound Transmission Reinhard Helfrich INTES GmbH, Stuttgart info@intes.de www.intes.de
Audiology Services. Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS
 Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Audiology Services Carolyn Dando Audiology Services Manager South Warwickshire NHS What are we going to cover today? General overview of the ear Hearing loss Hearing assessments, results Hearing aids Paediatric
Chapter 8. Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia. Introduction. Anatomy and Function of the Ear
 Chapter 8 Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia H. Jeffrey Kim, MD, FACS, Christopher Zalewski, MA, and Carmen C. Brewer, PhD Introduction In 1927, Guido Fanconi, MD, noticed an association between
Chapter 8 Hearing and Ear Abnormalities in Fanconi Anemia H. Jeffrey Kim, MD, FACS, Christopher Zalewski, MA, and Carmen C. Brewer, PhD Introduction In 1927, Guido Fanconi, MD, noticed an association between
Biomechanics of Joints, Ligaments and Tendons.
 Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
Hearing Aids. What Is a Hearing Aid? How Common Is Hearing Loss and What Causes It? How Do We Hear?
 Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Hearing Aids What Is a Hearing Aid? A hearing aid is an electronic, battery-operated device that amplifies and changes sound to allow for improved communication. Hearing aids receive sound through a microphone,
Cranial/Neurosurgical Implants
 MEDPOR Cranial/Neurosurgical Implants MEDPOR Biomaterial MEDPOR Porous Polyethylene Implants provide surgeons with an expanding range of options for reconstruction and augmentation. MEDPOR is a biocompatible,
MEDPOR Cranial/Neurosurgical Implants MEDPOR Biomaterial MEDPOR Porous Polyethylene Implants provide surgeons with an expanding range of options for reconstruction and augmentation. MEDPOR is a biocompatible,
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs
 FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs Berti G. and Monti M. University of Padua, DTG, Stradella San Nicola 3, I-36100 Vicenza (Italy) guido.berti@unipd.it, manuel.monti@unipd.it.
FEM analysis of the forming process of automotive suspension springs Berti G. and Monti M. University of Padua, DTG, Stradella San Nicola 3, I-36100 Vicenza (Italy) guido.berti@unipd.it, manuel.monti@unipd.it.
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
FXA 2008. UNIT G485 Module 4 5.4.3 Ultrasound. Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Modeling and Numerical Blood Flow Analysis of Tibial Artery using CFD
 Modeling and Numerical Blood Flow Analysis of Tibial Artery using CFD S.Manimaran Department of Biomedical Engineering C.Muralidharan M.E Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering Surendra
Modeling and Numerical Blood Flow Analysis of Tibial Artery using CFD S.Manimaran Department of Biomedical Engineering C.Muralidharan M.E Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering Surendra
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Simulation of Couplers
 Simulation of Couplers by Søren Jønsson, Bin Liu, Lars B. Nielsen, Andreas Schuhmacher Brüel & Kjær AES, Workshop 7, 2003 March 23rd Brüel & Kjær 2003, 1 Agenda Introduction to Couplers Traditional Simulation
Simulation of Couplers by Søren Jønsson, Bin Liu, Lars B. Nielsen, Andreas Schuhmacher Brüel & Kjær AES, Workshop 7, 2003 March 23rd Brüel & Kjær 2003, 1 Agenda Introduction to Couplers Traditional Simulation
4 SENSORS. Example. A force of 1 N is exerted on a PZT5A disc of diameter 10 mm and thickness 1 mm. The resulting mechanical stress is:
 4 SENSORS The modern technical world demands the availability of sensors to measure and convert a variety of physical quantities into electrical signals. These signals can then be fed into data processing
4 SENSORS The modern technical world demands the availability of sensors to measure and convert a variety of physical quantities into electrical signals. These signals can then be fed into data processing
Hearing Conservation Procedures
 Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Hearing Conservation Procedures Purpose The University of Regina is committed to providing a safe and healthy work and educational environment for all members of the University community by ensuring that
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Integra. MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Bildgebende Verfahren als. Control 2011 Alexander Nolte CADFEM GmbH
 Bildgebende Verfahren als Basis für die FEM-Simulation Control 2011 Alexander Nolte CADFEM GmbH CADFEM: FEM Software and Services CADFEM FEM Software & Services 25+ years experience 140+ employees 40 Mio.
Bildgebende Verfahren als Basis für die FEM-Simulation Control 2011 Alexander Nolte CADFEM GmbH CADFEM: FEM Software and Services CADFEM FEM Software & Services 25+ years experience 140+ employees 40 Mio.
SDNL137 Computation of nonlinear modes of a tube curved with two non-linearities of type Summarized annular
 Titre : SDNL137 Calcul de modes non-linéaires d'un tube [...] Date : 28/10/2013 Page : 1/5 SDNL137 Computation of nonlinear modes of a tube curved with two non-linearities of type Summarized annular contact:
Titre : SDNL137 Calcul de modes non-linéaires d'un tube [...] Date : 28/10/2013 Page : 1/5 SDNL137 Computation of nonlinear modes of a tube curved with two non-linearities of type Summarized annular contact:
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Image. 3.11.3 SW Review the anatomy of the EAC and how this plays a role in the spread of tumors.
 Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
 THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
THE EARS IN CHARGE FOR THE PHYSICIAN Sandra L.H. Davenport, M.D. SensoryGenetic/Neuro-development, 5801 Southwood Drive, Bloomington MN 55437-1739 952-831-5522 slhdaven@tc.umn.edu Udayan K. Shah, M.D.
THE COMPOSITE DISC - A NEW JOINT FOR HIGH POWER DRIVESHAFTS
 THE COMPOSITE DISC - A NEW JOINT FOR HIGH POWER DRIVESHAFTS Dr Andrew Pollard Principal Engineer GKN Technology UK INTRODUCTION There is a wide choice of flexible couplings for power transmission applications,
THE COMPOSITE DISC - A NEW JOINT FOR HIGH POWER DRIVESHAFTS Dr Andrew Pollard Principal Engineer GKN Technology UK INTRODUCTION There is a wide choice of flexible couplings for power transmission applications,
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS
 BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
BONE-CONDUCTION HEARING AIDS Introduction Conventional hearing aids fit in the ear canal and amplify sounds, which the hearing aid user then hears in the normal way. However, these hearing aids are not
AN4427 Application note
 Application note Gasket design for optimal acoustic performance in MEMS microphones Introduction This application note serves as a reference for the design of gaskets in MEMS microphones, providing recommendations
Application note Gasket design for optimal acoustic performance in MEMS microphones Introduction This application note serves as a reference for the design of gaskets in MEMS microphones, providing recommendations
