The Management of Depression in Patients with Cancer CAGPO 2015
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Thomas Townsend
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Management of Depression in Patients with Cancer CAGPO 2015 Dr. Caroline Gérin-Lajoie Psychiatrist, Psychosocial Oncology Program, The Ottawa Hospital Cancer Centre
2 Learning Objectives Review the diagnosis and treatment of depression in patients with cancer Discuss the unique precipitating factors present in the oncology patient Discuss treatment options and when to refer to a psychiatrist
3 Conflict of Interest I DO NOT have an affiliation (financial or otherwise) with a pharmaceutical, medical device or communications organization.
4 All health professionals who work with patients/families affected by cancer need to be aware of the prevalence, impact, and need to respond to the continuum of distress from mild to severe distress, up to psychiatric symptoms or disorder
5 Cancer Trajectory Also referred to as the cancer experience, continuum, journey Each phase has its unique set of stresses and challenges Normalization and education can be very helpful
6 Key Points in The Cancer Trajectory Diagnosis Acute Treatment Remission Follow-up Relapse Chronic illness or survivorship Palliation
7 DISTRESS Cancer-related distress: psychological (cognitive, behavioral, emotional), social, and/or spiritual nature that may interfere with the ability to cope effectively with cancer, its physical symptoms and its treatment (NCCN Guidelines) Prevalence: 28-87%
8 Prevalence of Depression in Cancer Clinical rule of thumb: 25% of cancer patients are likely to be depressed enough at some point in the course of disease to warrant evaluation and treatment Advanced cancer median prevalence: 15%, global suffering, total pain
9 Research in Cancer Patients Absence of strong cancer-specific evidence, insufficient new evidence in the last decade Evidence is extrapolated from primary psychiatric and other medical populations Based on NICE clinical guidelines and Depression in Adults with a Chronic Physical Health Problem
10 Other Guidelines Canadian Association of Psychosocial Oncology s depression symptoms management guideline (SMG) A Pan-Canadian Practice Guideline: Screening, Assessment and Care of Psychosocial Distress (Depression, Anxiety) in Adults with Cancer
11 Cancer Care Ontario Guideline #19-4 Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC) The Management of Depression in Patients with Cancer Report Date: May 11, 2015
12 Target Population Adult patients with cancer, diagnosed with a major depressive disorder based on a structured diagnostic interview or suspected depressive disorder based on meeting a threshold on a validated rating scale To be used by multidisciplinary health care providers
13 Guideline also includes Quick reference guide for the initial management of depression Delivery of intervention according to the stepped care model Practical tools (screening scales, diagnostic criteria, psychological interventions, antidepressant prescribing)
14 8 Recommendations 1. Screening of patients 2. General management principles 3. Pharmacological or psychological/psychosocial interventions 4. Depression severity and a stepped care approach 5. Collaborative care interventions 6. Specialist referral 7. Selection of psychological therapies 8. Use of antidepressant medication
15 Depression Management Algorithm Establish the presence of a Depressive Disorder Rule out other Medial Condition (TSH, B12, folate, anemia, ) Assess suicidal ideation, plan, intent Optimize treatment of cancer-related physical symptoms Validated Rating Scale to assess severity and monitor response to treatment Deliver intervention with intensity corresponding to Depression Severity (Stepped Care Model)
16 R1: Screening of patients with cancer for distress and depression Patients with cancer should be screened Screening for Distress, the 6 th Vital Sign, is a standard of care in multiple cancer care guidelines ESAS in Canada the most commonly used for various symptoms
17 Select Validated Depression Screening Scales Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) *Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II)
18 DSM-5 Criteria for Major Depression Is the standard for diagnosing Major Depression in people with cancer 5 or more sx, for at least 2 weeks duration, change from previous functioning, and including at least one: either depressed mood, or loss of interest/ pleasure NOTE: do not include sx attributable to another medical condition
19 DSM-5 Criteria for Major Depression Symptoms: SIG E CAPS Depressed mood Diminished interest or pleasure Significant weight loss Insomnia or hypersomnia Psychomotor agitation or retardation Fatigue or loss of energy Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt Diminished concentration or indecisiveness Suicidal ideation
20 DSM-5 Criteria for Major Depression Clinically significant distress/impairment of functioning Not secondary to substances or general medical condition Not bereavement
21 Diagnosis of Depression in Cancer May rest upon affective and cognitive sx: Depressed mood, anhedonia, loss of interest/apathy, poor concentration or memory, slowed sluggish thoughts, pessimism/negativity, worthlessness, excessive guilt, helplessness, hopelessness, suicidal ideation
22 Depression Severity Criteria Subthreshold depressive sx: <5 sx of depression Mild depression: few sx over the minimum required to make a dx, minor impairment on functioning Severe depression: many sx and markedly interfere with functioning Moderate: in between mild and severe
23 Medical Causes of Depression CNS: Parkinson s, CVA, tumors Aids Hypokalemia Hypo/Hyperthyroidism Pancreatic CA Hepatitis, Cirrhosis Mononucleosis Occult malignancy Anemia Cushing s (hypercortisolism)
24 Cancer Illness and Treatment-related Factors Tumors or metastases to CNS Metabolic complications (hypercalcemia) Tumor-related toxins Autoimmune reactions Viral infections Nutritional deficiencies (B12, Folate) Radiation to brain or head and neck
25 Pharmacological Causes of Depression Cardiac and antihypertensives Sedatives and hypnotics Steroids and hormones Stimulants and appetite suppressants Psychotropic drugs (benzo) Neurological agents Analgesics/antiinflammatory Antibacterial and antifungal NSAIDs Anticholinesterases Antineoplastic (vincristine, vinblastine, asparaginase, intrathecal methotrexate, interferon, interleukin, tamoxifen)
26 R2: General management principles Provide psychoeducation about depression in patients with cancer (NCI handouts) Inform patients about the impact of depression on cancer outcomes Destigmatize clinical depression Investigate medical contributors to depression (TSH, B12, folate, )
27 R2: General management principles Assess and optimize cancer-related physical symptom control Involve and educate family members Discuss treatment options Consider a validated depression rating scale to monitor over time
28 R3: Pharmacological or psychological/psychosocial interventions Patients with cancer and a diagnosed major depression may benefit from pharmacological or psychosocial interventions either alone or in combination Effectiveness for psychosocial and pharmacological interventions for moderate depression is equal Pharmacological treatment most effective in more severe depression Combined psychosocial and pharmacologic interventions should be considered for severe depression
29 R4: Depression severity and stepped care approach Provision of support and psychoeducation for all patients Assessment of severity of depression for each patient Low-intensity interventions for mildmoderate depression or persistent subthreshold High-intensity interventions for nonresponsive or moderate-severe depression
30 R4: Depression severity and stepped care approach Low-intensity psychosocial intervention Group physical activity programs Group-based peer support or self-help programs Guided self-help programs (CBT based) Behavioural activation Problem solving High-intensity psychosocial intervention Individual or group CBT Behavioural couples therapy Individual or group supportiveexpressive psychotherapies
31 R5: Collaborative care interventions Active collaboration between oncologist or primary care provider and a patient care manager (nurse, SW, psychologist) with pharmacological treatment supervised by a consulting psychiatrist as needed Multi-component interventions, at a range of intensity levels, depending on local resources Typically include measurement-based care Follows principles of stepped care
32 R5: Collaborative care interventions Meta-analysis of collaborative care interventions in patients with moderate to severe major depression and cancer Significantly more likely to experience 50% reduction of score on rating scale, lower mean scores, remission more likely
33 R6: Specialist referral Risk of harm Complex psychosocial cases Patients experience persistent symptoms after initial intervention or severe depression Diagnosis is unclear Delivery of specific psychotherapies requiring specialized training
34 R7: Selection of psychological therapies Insufficient evidence for superiority of one modality over another Selection based on patient factors and local resource availability Considered first for mild to moderate depression (most cancer patients) Non-mental health specialists can be trained in basic psychosocial interventions
35 R7: Selection of psychological therapies Trained health-care professionals Empathic communication (PEBC Guideline 19-2 on Provider-patient communication) Psychoeducation (National Cancer Institute handouts) Problem solving Behavioural activation Specially trained therapists Individual or group CBT Behavioural couples therapy Individual or group supportive-expressive psychotherapies
36 Psychological interventions used for depression in cancer Group-based peer support (self-help) programs Structured group physical activity programs Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction and Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Behavioural activation therapy Problem solving therapy Interpersonal therapy Behavioural couples therapy Supportive-expressive therapy Core conflictual relationship theme Dignity therapy Meaning-Centred psychotherapy Managing Cancer and Living Meaningfully (CALM)
37 R8: Use of antidepressant medication Do not use it routinely for subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild depression (higher risk:benefit ratio) Considered first for severe depression SSRI s (citalopram, escitalopram) should be first resort due to best tolerability and least potential for drug interactions Roles also for anxiety, hot flashes, sleep disturbances, appetite enhancement, neuropathic pain, nausea
38 Standard first-line antidepressants for patients with cancer Citalopram/Escitalopram Start: mg daily/ 5-10 mg qhs Goal: mg daily/ mg qhs Max: 40 mg daily/ 20 mg qhs Escitalopram may have more rapid onset than other SSRIs (1-3 weeks) Venlafaxine/Desvenlafaxine Start: mg qam/50mg qam Goal: mg qam/50-100mg qam Max: 300mg qam/100mg qam Optimal for tamoxifen, consider when hot flashes
39 Standard first-line antidepressants for patients with cancer Mirtazapine Start: mg qhs Goal: 15-45mg qh Max: 60mg qhs Consider for insomnia, anorexia, nausea, rapid dissolve formulation Duloxetine Start: 30mg qam Goal: mgqam Max: 120mg qam Separate indication for neuropathic pain and chronic pain
40 Standard first-line antidepressants for patients with cancer Buproprion XL Start: 150mg qam Goal: mg qam Max: 450mg qam Consider for prominent fatigue, aids sexual function, smoking cessation aid, weight neutral
41 Practical tools: Selecting an Antidepressant Past psychiatric history (positive response) Family psychiatric history (positive response) Concurrent medication (drug interactions) Somatic symptoms profile (sedation, weight gain) Potential dual benefit (neuropathic pain, hot flashes) Type of cancer (avoid bupropion in CNS) Comorbidities (avoid TCA s in cardiac disease) Cancer prognosis (consider psychostimulants if very short life expectancy)
42 Practical tools: Initiating an Antidepressant Screen for medical contributors and substance use (TSH, vitamin B12, folate ) Start at lowest dose (avoid side effects) Discuss that side effects should resolve within a week Therapeutic benefit can take 4 to 6 weeks to reach full effect Need to take medications daily and even after remission Counsel about potential discontinuation symptoms if stopped abruptly Reassure that dependence and tolerance does not occur Discuss concerns related to antidepressants and potential increased suicidality
43 Practical tools: Maintaining an Antidepressant Follow every 2 to 4 weeks until remission Assess response after 3 to 4 weeks at therapeutic dose, increase dose if no response Switch medication if no response after 6 weeks Continue at effective dose for at least 6 months after full remission If history of recurrent depression should continue at least 2 years or indefinitely
44 Practical tools: Maintaining an Antidepressant Discontinuation syndromes (malaise, dizziness, agitation, headache, nausea) may occur with abrupt termination or missed doses at high dosage levels Discontinuation syndromes more common with antidepressants that have a short half-life (venlafaxine, paroxetine) Taper over 4 weeks, symptoms may be more prominent toward the end of the taper Symptoms self-limiting over 1 week
45 R8: Use of antidepressant medication Concerns about interactions between Tamoxifen and antidepressants that inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) Meta-analyses suggest this does not translate into increased breast cancer recurrent rates or mortality rates Existing recommendations still caution avoidance of potent CYP2D6 inhibitors (paroxetine, fluoxetine, high-dose sertraline, buproprion) Prefer low CYP2D6 inhibition: citalopram/escitalopram, venlafaxine/desvenlafaxine, mirtazapine) as first-line agents
Depression Flow Chart
 Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depression Flow Chart SCREEN FOR DEPRESSION ANNUALLY Assess for depression annually with the PHQ-9. Maintain a high index of suspicion in high risk older adults. Consider suicide risk and contributing
Depre r s e sio i n o i n i a dults Yousuf Al Farsi
 Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
Depression in adults Yousuf Al Farsi Objectives 1. Aetiology 2. Classification 3. Major depression 4. Screening 5. Differential diagnosis 6. Treatment approach 7. When to refer 8. Complication 9. Prognosis
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA
 MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA MAJOR DEPRESSION IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE HEALTH CARE GUIDELINE (ICSI) Health Care Guideline Twelfth Edition May 2009. The guideline was reviewed and adopted by the Molina
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA MAJOR DEPRESSION IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE HEALTH CARE GUIDELINE (ICSI) Health Care Guideline Twelfth Edition May 2009. The guideline was reviewed and adopted by the Molina
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease
 Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
Recognition and Treatment of Depression in Parkinson s Disease Web Ross VA Pacific Islands Health Care System What is depression? Depression is a serious medical condition that affects a person s feelings,
DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource
 E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
E-Resource March, 2015 DEPRESSION Depression Assessment PHQ-9 Screening tool Depression treatment Treatment flow chart Medications Patient Resource Depression affects approximately 20% of the general population
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION
 MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 6/2011 DEPRESSION Executive summary of recommendations Details of recommendations can be found in the main text at the pages indicated. Clinical evaluation D The basic
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic Nomenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions
 Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic omenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions Conditions Diagnostic Criteria Duration Major Depression 5 of the following
Major Depressive Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Guideline Diagnostic omenclature for Clinical Depressive Conditions Conditions Diagnostic Criteria Duration Major Depression 5 of the following
Depression Assessment & Treatment
 Depressive Symptoms? Administer depression screening tool: PSC Depression Assessment & Treatment Yes Positive screen Safety Screen (see Appendix): Administer every visit Neglect/Abuse? Thoughts of hurting
Depressive Symptoms? Administer depression screening tool: PSC Depression Assessment & Treatment Yes Positive screen Safety Screen (see Appendix): Administer every visit Neglect/Abuse? Thoughts of hurting
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem Treatment and management Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 91 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg91 NICE has accredited the process used by the
Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller
 Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller School of Medicine/University of Miami Question 1 You
Elizabeth A. Crocco, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Miller School of Medicine/University of Miami Question 1 You
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder. Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice
 Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
Update on guidelines on biological treatment of depressive disorder Dr. Henry CHEUNG Psychiatrist in private practice 2013 update International Task Force of World Federation of Societies of Biological
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå. aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí=
 `çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
`çããçå=jéåí~ä= aáëçêçéêëw=^åñáéíó=~åç= aééêéëëáçå aêk=`=f=lâçåü~ jéçáå~ä=aáêéåíçê lñäé~ë=kep=cçìåç~íáçå=qêìëí= Overview: Common Mental What are they? Disorders Why are they important? How do they affect
Managing depression after stroke. Presented by Maree Hackett
 Managing depression after stroke Presented by Maree Hackett After stroke Physical changes We can see these Depression Emotionalism Anxiety Confusion Communication problems What is depression? Category
Managing depression after stroke Presented by Maree Hackett After stroke Physical changes We can see these Depression Emotionalism Anxiety Confusion Communication problems What is depression? Category
DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
1 DEPRESSION CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for depression and any history of depression? 2. Did staff
NICE Clinical guideline 23
 NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
NICE Clinical guideline 23 Depression Management of depression in primary and secondary care Consultation on amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised
Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth
 Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth Aisha Mays, MD UCSF Department of Family And Community Medicine Native American Health Center Oakland, CA July 8, 2015 Presenter Disclosures No relationships
Depression, Mental Health and Native American Youth Aisha Mays, MD UCSF Department of Family And Community Medicine Native American Health Center Oakland, CA July 8, 2015 Presenter Disclosures No relationships
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
 TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
TREATING MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER A Quick Reference Guide Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Second Edition, originally published in April 2000.
Depression Treatment Guide
 Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
Depression Treatment Guide DSM V Criteria for Major Depressive Disorders A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous
Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Issue date: October 2009 Depression Treatment and management of depression in adults, including adults with a chronic physical health problem This is an update of NICE clinical guideline 23 Developed by
Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90
 Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
Depression in adults: recognition and management Clinical guideline Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90 NICE 2009. All rights reserved. Last updated April 2016 Your responsibility The
What are the best treatments?
 What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
What are the best treatments? Description of Condition Depression is a common medical condition with a lifetime prevalence in the United States of 15% among adults. Symptoms include feelings of sadness,
Anxiety and depression appropriate terms for cancer survivorship research?
 Anxiety and depression appropriate terms for cancer survivorship research? Jon Håvard Loge Regional Centre for Excellence in Palliative Care, Dept. of Oncol., Oslo University Hospital/ Dept. of Behavioural
Anxiety and depression appropriate terms for cancer survivorship research? Jon Håvard Loge Regional Centre for Excellence in Palliative Care, Dept. of Oncol., Oslo University Hospital/ Dept. of Behavioural
in young people Management of depression in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management
 Management of depression in young people in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management A young person with mild or moderate depression should typically be managed within primary care services A strength-based
Management of depression in young people in primary care Key recommendations: 1 Management A young person with mild or moderate depression should typically be managed within primary care services A strength-based
A Depression Education Toolkit
 A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
A Depression Education Toolkit Facts about Depression in Older Adults What is Depression? Depression is a medical illness. When sadness persists or interferes with everyday life, it may be depression.
Depression: Facility Assessment Checklists
 Depression: Facility Assessment Checklists A facility system assessment is a starting point for a quality improvement project. The checklists included in this booklet will be most useful if you take a
Depression: Facility Assessment Checklists A facility system assessment is a starting point for a quality improvement project. The checklists included in this booklet will be most useful if you take a
Mental health issues in the elderly. January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca
 Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Mental health issues in the elderly January 28th 2008 Presented by Éric R. Thériault etheriau@lakeheadu.ca Cognitive Disorders Outline Dementia (294.xx) Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (early and late
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression
 Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
Step 2: Recognised depression in adults persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to moderate depression A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents.
 Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
Recognizing and Treating Depression in Children and Adolescents. KAREN KANDO, MD Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Center for Neuroscience and Behavioral Medicine Phoenix Children s Hospital
NICE clinical guideline 90
 Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Depression in adults The treatment and management of depression in adults Issued: October 2009 NICE clinical guideline 90 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg90 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine
 Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Amendments to recommendations concerning venlafaxine On 31 May 2006 the MHRA issued revised prescribing advice for venlafaxine*. This amendment brings the guideline into line with the new advice but does
Depression Screening in Primary Care
 Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Our Vision Make Greater Cleveland a healthier place to live and a better place to do business. 2
Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Our Vision Make Greater Cleveland a healthier place to live and a better place to do business. 2
Depression. The treatment and management of depression in adults. This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23
 Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: October 2009 Depression The treatment and management of depression in adults This is a partial update of NICE clinical guideline 23 NICE clinical guideline 90 Developed by the National Collaborating
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults
 Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Step 4: Complex and severe depression in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview
 Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Post-traumatic stress disorder overview A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive
Common mental health disorders
 Issue date: May 2011 Common mental health disorders Identification and pathways to care NICE clinical guideline 123 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health NICE clinical guideline
Issue date: May 2011 Common mental health disorders Identification and pathways to care NICE clinical guideline 123 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health NICE clinical guideline
Depression in children and young people. Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care
 NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
NICE guideline May 2005 Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the
Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care
 Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Issue date: December 2004 Quick reference guide Depression: management of depression in primary and secondary care Clinical Guideline 23 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health
Depression in Long-Term Care
 Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
Depression in Long-Term Care Annette Carron, DO, CMD, FACOI, FAAHPM Director Geriatrics and Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Slide 1 OBJECTIVES Know and understand: Incidence and morbidity of depressive
Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too.
 The Family Library DEPRESSION What is depression? Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too. Also called
The Family Library DEPRESSION What is depression? Depression is a medical illness that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Depression can cause physical symptoms, too. Also called
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression
 Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Algorithm for Initiating Antidepressant Therapy in Depression Refer for psychotherapy if patient preference or add cognitive behavioural office skills to antidepressant medication Moderate to Severe depression
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing specific issues Aaron, diagnosed in 1995. The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky.
Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31
 Obsessive-compulsive e disorder and body dysmorphic disorder: treatment Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31 NICE 2005. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction...
Obsessive-compulsive e disorder and body dysmorphic disorder: treatment Clinical guideline Published: 29 November 2005 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg31 NICE 2005. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction...
IMR ISSUES, DECISIONS AND RATIONALES The Final Determination was based on decisions for the disputed items/services set forth below:
 Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Number: CM13-0018009 Date Assigned: 10/11/2013 Date of Injury: 06/11/2004 Decision Date: 01/13/2014 UR Denial Date: 08/16/2013 Priority: Standard Application Received: 08/29/2013 HOW THE IMR FINAL
1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the
 1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
1 Chapter 38. Major Depressive Disorders, Self-Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following SSRIs requires up to a 5-week washout period because of the long half-life of its potent active metabolite?
Medicines for Treating Depression. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
Medicines for Treating Depression A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor or other health care professional has told you that you have depression. Your doctor
Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment LOUIS A. CANCELLARO, PhD, MD, EFAC Psych Professor Emeritus and Interim Chair ETSU Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Diagnosis
Depression in the Elderly: Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment LOUIS A. CANCELLARO, PhD, MD, EFAC Psych Professor Emeritus and Interim Chair ETSU Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences Diagnosis
Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults
 Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine B: Competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine
Guidance on competencies for management of Cancer Pain in adults Endorsed by: Contents Introduction A: Core competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine B: Competencies for practitioners in Pain Medicine
TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY
 University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
University of Washington 2012 TREATMENT-RESISTANT DEPRESSION AND ANXIETY Catherine Howe, MD, PhD University of Washington School of Medicine Definition of treatment resistance Failure to remit after 2
When You Are More Than Down in the Dumps Depression in Older Adults
 When You Are More Than Down in the Dumps Depression in Older Adults Revised by M. Smith (2006) from K.C. Buckwalter & M. Smith (1993), When You Are More Than Down in the Dumps : Depression in the Elderly,
When You Are More Than Down in the Dumps Depression in Older Adults Revised by M. Smith (2006) from K.C. Buckwalter & M. Smith (1993), When You Are More Than Down in the Dumps : Depression in the Elderly,
INDEX. and side effects of light therapy, 73 Bulimia nervosa See Eating disorders Bupropion, in treatment of SAD, 91
 INDEX 5-hydroxytryptophan, and neuroendocrine responses in SAD patients, 46 Alcoholism, and light therapy, 78 Alzheimer s disease, and light therapy, 78, 79 American Sleep Disorders Association, 78 Anorexia
INDEX 5-hydroxytryptophan, and neuroendocrine responses in SAD patients, 46 Alcoholism, and light therapy, 78 Alzheimer s disease, and light therapy, 78, 79 American Sleep Disorders Association, 78 Anorexia
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis. Managing Specific Issues
 Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing Specific Issues Feeling blue The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky. True depression
Depression & Multiple Sclerosis Managing Specific Issues Feeling blue The words depressed and depression are used so casually in everyday conversation that their meaning has become murky. True depression
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Depression
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Depression MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 6/2011 3 1 Published by Ministry of Health, Singapore 16 College Road, College of Medicine Building Singapore 169854 Printed by
Some helpful reminders on depression in children and young people. Maria Moldavsky Consultant Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist
 Some helpful reminders on depression in children and young people Maria Moldavsky Consultant Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist The clinical picture What art and my patients taught me Albert Durer (1471-1528)
Some helpful reminders on depression in children and young people Maria Moldavsky Consultant Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist The clinical picture What art and my patients taught me Albert Durer (1471-1528)
Presently, there are no means of preventing bipolar disorder. However, there are ways of preventing future episodes: 1
 What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
What is bipolar disorder? There are two main types of bipolar illness: bipolar I and bipolar II. In bipolar I, the symptoms include at least one lifetime episode of mania a period of unusually elevated
Depression in children and young people. Quick reference guide. Issue date: September 2005
 Quick reference guide Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the National
Quick reference guide Issue date: September 2005 Depression in children and young people Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care Clinical Guideline 28 Developed by the National
Feeling Moody? Major Depressive. Disorder. Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Mood Disorders. www.seclairer.com S Eclairer 724-468-3999
 Feeling Moody? Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Major Depressive Disorder Prevalence: 7%; 18-29 years old; Female>Male DDx: Manic episodes with irritable mood or mixed episodes, mood disorder
Feeling Moody? Is it just a bad mood or is it a disorder? Major Depressive Disorder Prevalence: 7%; 18-29 years old; Female>Male DDx: Manic episodes with irritable mood or mixed episodes, mood disorder
Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model
 Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model Larissa Elgudin, MD, Chief of Behavioral Health Services Colleen O Malley RN, BSN, Regional
Workshop: Management of Depression in the Primary Care Setting, Kaiser Permanente of Ohio s Multidisciplinary Model Larissa Elgudin, MD, Chief of Behavioral Health Services Colleen O Malley RN, BSN, Regional
Eating Disorder Treatment Protocol
 Eating Disorder Treatment Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Eating Disorders are incredibly debilitating and are associated with significant medical and psychosocial
Eating Disorder Treatment Protocol All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Eating Disorders are incredibly debilitating and are associated with significant medical and psychosocial
Psychology Externship Program
 Psychology Externship Program The Washington VA Medical Center (VAMC) is a state-of-the-art facility located in Washington, D.C., N.W., and is accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of
Psychology Externship Program The Washington VA Medical Center (VAMC) is a state-of-the-art facility located in Washington, D.C., N.W., and is accredited by the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of
Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults
 Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults Introduction The partial update of the guideline on Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder
Costing statement: Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) in adults Introduction The partial update of the guideline on Generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services
 Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
Clinical Guideline / Formulary Document Pharmacy Department Medicines Management Services DEPRESSION Pharmacological Treatment of Depression NICE guidelines suggest the following stepped care model also
CHAPTER 5 MENTAL, BEHAVIOR AND NEURODEVELOPMENT DISORDERS (F01-F99) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 CHAPTER 5 MENTAL, BEHAVIOR AND NEURODEVELOPMENT DISORDERS (F01-F99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS F01-F09 Mental disorders due to known physiological
CHAPTER 5 MENTAL, BEHAVIOR AND NEURODEVELOPMENT DISORDERS (F01-F99) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS F01-F09 Mental disorders due to known physiological
Antipsychotic drug prescription for patients with dementia in long-term care. A practice guideline for physicians and caregivers
 SUPPLEMENT 1: (Supplementary Material for online publication) Antipsychotic drug prescription for patients with dementia in long-term care. A practice guideline for physicians and caregivers About this
SUPPLEMENT 1: (Supplementary Material for online publication) Antipsychotic drug prescription for patients with dementia in long-term care. A practice guideline for physicians and caregivers About this
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults. (update) and
 Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Costing statement: Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) and Depression in adults with a chronic physical health problem: treatment and management Summary It has not
Dr. Anna M. Acee, EdD, ANP-BC, PMHNP-BC Long Island University, Heilbrunn School of Nursing
 Dr. Anna M. Acee, EdD, ANP-BC, PMHNP-BC Long Island University, Heilbrunn School of Nursing Overview Depression is significantly higher among elderly adults receiving home healthcare, particularly among
Dr. Anna M. Acee, EdD, ANP-BC, PMHNP-BC Long Island University, Heilbrunn School of Nursing Overview Depression is significantly higher among elderly adults receiving home healthcare, particularly among
Mood Disorders. What Are Mood Disorders? Unipolar vs. Bipolar
 Mood Disorders What Are Mood Disorders? In mood disorders, disturbances of mood are intense and persistent enough to be clearly maladaptive Key moods involved are mania and depression Encompasses both
Mood Disorders What Are Mood Disorders? In mood disorders, disturbances of mood are intense and persistent enough to be clearly maladaptive Key moods involved are mania and depression Encompasses both
Depression Pathway. Patient Education Box 4. Guided self help Box 18. pg 11
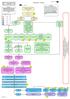 LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
LCFT localised Map pathway June 2009 Depression Pathway Instructions: Throughout this pathway if you click on the Bookmarks tab to the left of the screen and then click on the various documents you will
See also www.thiswayup.org.au/clinic for an online treatment course.
 Depression What is depression? Depression is one of the common human emotional states. It is common to experience feelings of sadness and tiredness in response to life events, such as losses or disappointments.
Depression What is depression? Depression is one of the common human emotional states. It is common to experience feelings of sadness and tiredness in response to life events, such as losses or disappointments.
DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families
 DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lori L. Altshuler, MD, and Lee S. Cohen, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
DEPRESSION DURING THE TRANSITION TO MENOPAUSE: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lori L. Altshuler, MD, and Lee S. Cohen, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm
 E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
E-Resource March, 2014 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER PTSD Diagnostic Criteria PTSD Detection and Diagnosis PC-PTSD Screen PCL-C Screen PTSD Treatment Treatment Algorithm Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Antidepressant treatment in adults
 Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Antidepressant treatment in adults A NICE pathway brings together all NICE guidance, quality standards and materials to support implementation on a specific topic area. The pathways are interactive and
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in Primary Care, Adult 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
Clinical Practice Guideline: Depression in 4 Taft Court Rockville, MD 20850 www.mamsi.com 40 05 17 035 3/03 Once a primary care patient presents with depressive symptoms, the primary care physician makes
How to Identify and Diagnose Depression
 Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
Depression Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 Depression and MS Date of issue: March 2010 Review date: March 2011 Contents Introduction 2 1.
DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview. Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions
 DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions Topics In this Session Overview Clinical Importance of Depression Types of Depression Phases of Depression Care Collaborative
DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE: An Overview Jorge R. Petit, MD Quality Health Solutions Topics In this Session Overview Clinical Importance of Depression Types of Depression Phases of Depression Care Collaborative
Appendix B NMMCP Covered Services and Exceptions
 Acute Inpatient Hospitalization MH - Adult Definition An Acute Inpatient program is designed to provide medically necessary, intensive assessment, psychiatric treatment and support to individuals with
Acute Inpatient Hospitalization MH - Adult Definition An Acute Inpatient program is designed to provide medically necessary, intensive assessment, psychiatric treatment and support to individuals with
Major Depression. What is major depression?
 Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Major Depression What is major depression? Major depression is a serious medical illness affecting 9.9 million American adults, or approximately 5 percent of the adult population in a given year. Unlike
Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa Preferred Practice Guideline
 Introduction Eating Disorders are described as severe disturbances in eating behavior which manifest as refusal to maintain a minimally normal body weight (Anorexia Nervosa) or repeated episodes of binge
Introduction Eating Disorders are described as severe disturbances in eating behavior which manifest as refusal to maintain a minimally normal body weight (Anorexia Nervosa) or repeated episodes of binge
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
Worksite Depression Screening and Treatment: An Innovative, Integrated Program
 Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Worksite Depression
Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header Worksite Depression
MOH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines
 MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
MOH CLINICL PRCTICE GUIELINES 2/2008 Prescribing of Benzodiazepines College of Family Physicians, Singapore cademy of Medicine, Singapore Executive summary of recommendations etails of recommendations
Major Depressive Disorders Questions submitted for consideration by workshop participants
 Major Depressive Disorders Questions submitted for consideration by workshop participants Prioritizing Comparative Effectiveness Research Questions: PCORI Stakeholder Workshops June 9, 2015 Patient-Centered
Major Depressive Disorders Questions submitted for consideration by workshop participants Prioritizing Comparative Effectiveness Research Questions: PCORI Stakeholder Workshops June 9, 2015 Patient-Centered
Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care
 Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Objectives Part 1: Improve ability to screen and diagnose Depression in Primary Care Increase
Part 1: Depression Screening in Primary Care Toni Johnson, MD Kristen Palcisco, BA, MSN, APRN MetroHealth System Objectives Part 1: Improve ability to screen and diagnose Depression in Primary Care Increase
Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults. Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City
 Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City What is Depression? Everyday use of the word Clinically significant depressive symptoms : more severe,
Depression and its Treatment in Older Adults Gregory A. Hinrichsen, Ph.D. Geropsychologist New York City What is Depression? Everyday use of the word Clinically significant depressive symptoms : more severe,
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
INPATIENT SERVICES. Inpatient Mental Health Services (Adult/Child/Adolescent)
 INPATIENT SERVICES Inpatient Mental Health Services (Adult/Child/Adolescent) Acute Inpatient Mental Health Services represent the most intensive level of psychiatric care and is delivered in a licensed
INPATIENT SERVICES Inpatient Mental Health Services (Adult/Child/Adolescent) Acute Inpatient Mental Health Services represent the most intensive level of psychiatric care and is delivered in a licensed
Test Content Outline Effective Date: June 9, 2014. Pain Management Nursing Board Certification Examination
 Pain Management Nursing Board Certification Examination There are 175 questions on this examination. Of these, 150 are scored questions and 25 are pretest questions that are not scored. Pretest questions
Pain Management Nursing Board Certification Examination There are 175 questions on this examination. Of these, 150 are scored questions and 25 are pretest questions that are not scored. Pretest questions
Mental Health and Substance Abuse Reporting Requirements Section 425 of P.A. 154 of 2005
 Mental Health and Substance Abuse Reporting Requirements Section 425 of P.A. 154 of 2005 By April 1, 2006, the Department, in conjunction with the Department of Corrections, shall report the following
Mental Health and Substance Abuse Reporting Requirements Section 425 of P.A. 154 of 2005 By April 1, 2006, the Department, in conjunction with the Department of Corrections, shall report the following
Mental health problems in people with MS: What can we do? Eli Silber Consultant Neurologist Kings College hospital
 Mental health problems in people with MS: What can we do? Eli Silber Consultant Neurologist Kings College hospital The emotional consequences of MS MS Population General Population Depression (Lifetime
Mental health problems in people with MS: What can we do? Eli Silber Consultant Neurologist Kings College hospital The emotional consequences of MS MS Population General Population Depression (Lifetime
PCORE Depression Post Survey
 PCORE Depression Post Survey 1. Please enter your UNI. 467 answered question 467 skipped question 0 2. Please fill in the name of institution you are working at for your Clerkship. 467 answered question
PCORE Depression Post Survey 1. Please enter your UNI. 467 answered question 467 skipped question 0 2. Please fill in the name of institution you are working at for your Clerkship. 467 answered question
Henriëtte van der Horst VUmc Head of Department of General Practice and Elderly Care Medicine
 MUS and psychiatry in primary care Henriëtte van der Horst VUmc Head of Department of General Practice and Elderly Care Medicine Double Dutch: two topics Major changes in the mental health care organisation
MUS and psychiatry in primary care Henriëtte van der Horst VUmc Head of Department of General Practice and Elderly Care Medicine Double Dutch: two topics Major changes in the mental health care organisation
Welcome New Employees. Clinical Aspects of Mental Health, Developmental Disabilities, Addictive Diseases & Co-Occurring Disorders
 Welcome New Employees Clinical Aspects of Mental Health, Developmental Disabilities, Addictive Diseases & Co-Occurring Disorders After this presentation, you will be able to: Understand the term Serious
Welcome New Employees Clinical Aspects of Mental Health, Developmental Disabilities, Addictive Diseases & Co-Occurring Disorders After this presentation, you will be able to: Understand the term Serious
Treating Depression to Remission in the Primary Care Setting. James M. Slayton, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director United Behavioral Health
 Treating Depression to Remission in the Primary Care Setting James M. Slayton, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director United Behavioral Health 2007 United Behavioral Health 1 2007 United Behavioral Health Goals
Treating Depression to Remission in the Primary Care Setting James M. Slayton, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director United Behavioral Health 2007 United Behavioral Health 1 2007 United Behavioral Health Goals
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over
 Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
Depression is a common biological brain disorder and occurs in 7-12% of all individuals over the age of 65. Specific groups have a much higher rate of depression including the seriously medically ill (20-40%),
MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families
 MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lee S. Cohen, MD, and Lori L. Altshuler, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
MAJOR DEPRESSION DURING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY: A Guide for Patients and Families David A. Kahn, MD, Margaret L. Moline, PhD, Ruth W. Ross, MA, Lee S. Cohen, MD, and Lori L. Altshuler, MD www.womensmentalhealth.org
Assessment of depression in adults in primary care
 Assessment of depression in adults in primary care Adapted from: Identification of Common Mental Disorders and Management of Depression in Primary care. New Zealand Guidelines Group 1 The questions and
Assessment of depression in adults in primary care Adapted from: Identification of Common Mental Disorders and Management of Depression in Primary care. New Zealand Guidelines Group 1 The questions and
American Society of Addiction Medicine
 American Society of Addiction Medicine Public Policy Statement on Treatment for Alcohol and Other Drug Addiction 1 I. General Definitions of Addiction Treatment Addiction Treatment is the use of any planned,
American Society of Addiction Medicine Public Policy Statement on Treatment for Alcohol and Other Drug Addiction 1 I. General Definitions of Addiction Treatment Addiction Treatment is the use of any planned,
The Role of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Survivorship Care Plans, and Inter-sectoral Care in Cancer Rehabilitation
 The Role of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Survivorship Care Plans, and Inter-sectoral Care in Cancer Rehabilitation Prof. Eva Grunfeld, MD, DPhil, FCFP Ontario Institute for Cancer Research/Cancer Care
The Role of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Survivorship Care Plans, and Inter-sectoral Care in Cancer Rehabilitation Prof. Eva Grunfeld, MD, DPhil, FCFP Ontario Institute for Cancer Research/Cancer Care
Antidepressant Skills @ Work Dealing with Mood Problems in the Workplace
 Antidepressant Skills @ Work Dealing with Mood Problems in the Workplace Dr. Joti Samra PhD, R.Psych. Adjunct Professor & Research Scientist CARMHA www.carmha.ca Dr. Merv Gilbert PhD, R.Psych. Principal
Antidepressant Skills @ Work Dealing with Mood Problems in the Workplace Dr. Joti Samra PhD, R.Psych. Adjunct Professor & Research Scientist CARMHA www.carmha.ca Dr. Merv Gilbert PhD, R.Psych. Principal
SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
 E-Resource December, 2013 SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Between 10-18% of adults in the general population and up to 50% of adults in the primary care setting have difficulty sleeping. Sleep
E-Resource December, 2013 SLEEP DISTURBANCE AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Between 10-18% of adults in the general population and up to 50% of adults in the primary care setting have difficulty sleeping. Sleep
