MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
|
|
|
- Gregory Gaines
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS NATIONAL GUIDELINES
2 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 1.0 Introduction Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common bacterial diseases in childhood and by far the most frequent indication for long term antibiotic prophylaxis and imaging studies. Those in early childhood have a higher risk of renal damage following pyelonephritis and >90% of febrile UTI in infants are clinically consistent with pyelonephritis and even septicaemia. Fever, therefore, is considered an indication of upper urinary tract involvement or pyelonephritis in young children. At present the universally accepted method of minimizing renal damage is effective treatment of acute pyelonephritis. The primary care clinician has a major role in this initial management, which involves early and accurate diagnosis, prompt treatment and appropriate referral for further evaluation. The important reason to investigate children with UTI is to detect or exclude structural abnormalities that may predispose them to recurrent infections and kidney damage. These guidelines are prepared based on existing evidence for their appropriateness and also according to the availability and cost effectiveness. Table 1 Definitions Significant bacteriuria Asymptomatic bacteriuria Complicated UTI Simple UTI Colony count of >10 5 /ml of a single species in a midstream clean catch sample Presence of significant bacteriuria in two or more specimens in a child with no symptoms. Toxicity, persistent vomiting, dehydration, renal angle tenderness, renal impairment, clinical non response to treatment after 48 hours UTI with low grade fever, dysuria, frequency, urgency but none of the above symptoms 4 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
3 2.0 Initial evaluation 2.1 Clinical features of UTI *Dysuria, **straining, increased frequency, incontinence (*Infants usually cry when the bladder is full and also after the passage of urine due to the wet nappy. **Lots of infants also strain due to aerophagia and are usually relieved after passage of urine which very commonly leads to unnecessary investigations. But, if the baby cries while passing urine in distress - suspect UTI) Secondary enuresis, Macroscopic haematuria or pyuria Unexplained lower abdominal pain, flank pain Infant and young child with unexplained fever (> C) for more than three days or persistent vomiting or irritability Exclude UTI in all neonates with septicaemia and prolonged jaundice 2.2 Specific physical signs to look for in a child with UTI Fever Dehydration General ill health Elevated blood pressure Palpable bladder (after voiding) Can be due to acute retention. May also be due to a neurogenic bladder or posterior urethral valves (PUV) in a male child. Ballotable kidneys Renal angle tenderness Spinal defects External genitalia: - Labial adhesions - Phimosis (fore skin is usually not retractable < 4 yrs) - Signs of inflammation GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 5
4 Table 2 Specific features suggesting upper tract involvement Unexplained fever (>38.5ºC) General ill health/ toxicity Loin pain / tenderness + CRP or ESR Table 3 Other conditions with urinary symptoms mimicking lower UTI: Vulval irritation from soap, bubble baths, poor hygiene Threadworms Labial adhesions and phimosis (Also a common cause for false positive urine cultures) Sexual abuse Table 4 KEY POINTS 1. Fever is an indication of upper tract involvement in childhood UTI 2. An ill toxic child has to be evaluated carefully Table 5 Conditions predisposing to UTI VUR Obstructive uropathy Infrequent voiding habits Voiding dysfunction Urethral instrumentation Poor personal hygiene Inappropriate/ prolonged use of diapers Wiping of the perineum from back to front Sexual abuse Constipation Impaired host defenses 6 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
5 3.0 Diagnosis a. Urinalysis - supportive b. Urine for culture / ABST Positive urine culture is the gold standard of diagnosis and its validity depends on the proper collection, transportation and inoculation of the urine specimen and accurate interpretation of results. Refer tables 6-8 Table 6 Method of urine collection Infant or young child who is not potty trained 1. Clean catch mid stream sample (CCMS) 2. Supra pubic aspiration (SPA) 3. Catheter samples (only in failed attempts of SPA) Older child CCMS SPA (in special situations) Table 7 Advice to parents on collection of CCMS urine sample Wash hands and genitalia with water - No antiseptics (Retract the prepuce of the older boys) Do not wash the urine culture bottle and do not leave the lid opened for a long time Send first few ml of urine out and collect a mid stream specimen directly into the sterile culture bottle without contamination Close the cap and hand over immediately Transportation Method and time* of collection must be stated in the request form (*to be written by the nursing officer who takes the sample) Send immediately to the lab If the specimen cannot be transported within 2 hours, refrigerate immediately at 4ºC maximum time of refrigeration is 24 hours GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 7
6 Interpretation of results Urinalysis: (centrifuged sample) WBC >10 /HPF indicates significant pyuria Nitrites (Dipstix) positive suggestive of infection Table 8 Interpretation of urine culture Method of collection Colony count (pure growth) Probability of infection CCMS SPA > Any number 80-95% Infection likely >99% Catheter sample >10 5 > (can increase sensitivity by taking second 2-4 ml of urine) 95% Infection likely 4.0 Management of the acute phase a. Correct dehydration b. Control pain & fever (Liberal fluid intake also reduces dysuria) c. Persistent vomiting domperidone may be useful d. Other investigations: Febrile child FBC Ill or septic child Blood urea, serum creatinine, Serum electrolytes Blood culture LP (if indicated) Urgent USS in complicated UTI, neonates, children with distended bladder and ballotable kidneys 8 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
7 e. Antibiotics A valid urine sample must be obtained before antibiotic therapy and this may warrant a SPA for infants and young children.(x) Prompt treatment with the best guess antibiotic in appropriate dosage must be started in all suspected cases of febrile UTI pending the urine culture result and the drug can be changed according to the ABST pattern latter. Refer tables (x) Treatment can be delayed till urine culture report is available if the child is afebrile and not ill. Urinary antiseptics like nitrofurantoin and nalidixic acid are not suitable for treatment of febrile UTI IV antibiotics are indicated for the neonate, ill and septic child and who cannot tolerate oral intake. (x) Aminoglycosides should be used with caution in children with renal impairment. Duration 7 days f. All outpatients must be reviewed after 48 hours to assess the clinical response If no response after 48 hours of antibiotic treatment: Check the drug dosage and the ABST pattern Repeat urine culture Consider urgent USS to exclude predisposing urinary tract abnormalities and complications of UTI. g. Commence prophylactic antibiotics for all children below 5 yrs and continue until follow up investigations are available. (Refer table 12) Table 9 Admission criteria 1. Neonates and young infant 2. Ill, toxic and dehydrated child 3. Persistent vomiting 4. Symptoms and / or signs suggestive of obstruction or calculi GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 9
8 Refer to a Paediatrician when: a. The child is <5 years of age b. Diagnosis of uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI) is in doubt c. It is necessary to arrange imaging of the urinary tract to rule out obstructions (including calculi), anatomical defects, and dysfunctional bladder emptying d. There is a failure to respond to appropriate therapy after 48 hours e. There are recurrent attacks of UTI Patient and parent education a. Stress on the importance of early recognition and prompt treatment of further attacks b. Advice on the importance of continuation of prophylaxis c. Increase fluid intake and maintain good urine output. d. Avoid predisposing factors. (Refer table 5) e. Double micturition in patients with VUR Include preference order Table 10 Oral antibiotics for treatment of UTI Medication mg/kg/day Doses/day Cefixime 8 2 Cephalexin Co-amoxyclav oral Amoxy content oral Amoxy content 2 (duo) Cotrimoxazole 6-10 trimethoprim or sulphamethoxazole 2 Table 11 Parenteral antibiotics for treatment of UTI Medication mg/kg/day Doses/day Cefotaxime Ceftriaxone Cefuroxime Co-amoxyclav Gentamicin GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
9 KEY POINTS Table 12 Antibiotics for prophylaxis of UTI Medication mg/kg/dose Remarks Cephalexin 10 Cotrimoxazole 2 (trimethoprim) Table 13 Recommended drug in first 1-3 months until trimethoprim is available in Sri Lanka Avoid in infants <1 month age Trimethoprim 2 Recommended in neonates; but require specialist supervision Nalidixic acid 12.5 Avoid <6 months Nitrofurantoin 1-2 Avoid in infants <3 months age 1. Child with UTI needs prompt antibiotic treatment in appropriate dosages to minimize kidney damage 2. A valid urine sample must be obtained before antibiotic therapy and this warrants a SPA for infants and young children. 3. Do not use urinary antiseptics for febrile UTI 4. Assess all the patients after 48 hours of therapy for clinical improvement 5. Refer the patients when indicated. 5.0 Imaging in UTI Confirm the diagnosis before planning long term prophylaxis and imaging studies. 5.1 USS USS is recommended for all children following first attack of UTI This should be performed urgently in neonates, in complicated UTI and in patients with persistently distended bladder or ballotable kidneys. It is indicated at the earliest convenient time for the other patients. Abnormal USS further investigations to be done preferably after consultation with the Radiologist. GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 11
10 If imaging shows an abnormality, a repeat USS of kidneys is recommended before discontinuation of prophylaxis to assess the renal growth. Patients must be sent with full bladder for USS and they must be well hydrated before all imaging studies. 5.2 MCUG MCUG is the best investigation to detect abnormalities of urethra and bladder and it is also useful in detecting and grading VUR, but is extremely invasive, hence should be undertaken after careful evaluation. MCUG has to be done 6 weeks after UTI except in bladder outlet obstruction where it is indicated immediately. Indications for MCUG a. Suspected bladder outlet obstruction b. Dilated ureter / dilated ureter and dilated pelvicalyceal system in the USS under 5 years of age c. Abnormal DMSA scan: Significant scarring under 5 years of age Dysplastic kidneys d. First attack of febrile UTI under 1 year of age and DMSA scan is not available e. Second attack of febrile UTI under 5 years of age f. Clinical picture is highly suggestive of acute pyelonephritis of children below 5 years and DMSA scan is not available. 5.3 DMSA DMSA scan is indicated 6 months after an attack of UTI to detect scarring. (Reversible renal parenchymal changes of acute infection can mimic permanent scarring in the DMSA scan during the first 3-4 months.) 12 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
11 Indications for DMSA scan Under 1 year of age a. All children with febrile UTI Under 5 years of age a. Clinical picture is highly suggestive of acute pyelonephritis other than fever b. Second attack of febrile UTI before 5 years of age c. Abnormal USS: hypoplastic / dysplastic kidneys, scarring d. Other structural anomalies: VUR, duplex system, ureterocele etc. 5.4 Other imaging studies Indications for DTPA scan a. Suspected pelvi-ureteric or vesico-ureteric junction obstruction Indications for X-Ray KUB a. UTI associated with persistent or recurrent microscopic or macroscopic haematuria KEY POINTS Table USS is indicated for all children with UTI. 2. DMSA, MCUG and DTPA scans are indicated after careful evaluation. 3. Please note the contrast and isotope studies are invasive, costly and carry a risk of radiation. In addition, isotope studies are not freely available. 4. If the imaging studies are abnormal a repeat USS is recommended at discontinuation of prophylaxis to assess renal growth. GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 13
12 6.0 Prophylaxis for UTI Refer Table 12. Drugs are given as a single dose in the night Antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated for all children below 5 years following the first attack of UTI until an USS of the kidneys is available. Continuation of prophylaxis is decided according to following factors. First attack <1 year a. If the USS is normal in infants with afebrile UTI it is recommended to stop the prophylaxis and to follow up without further investigations. b. In infants with febrile UTI, it is continued till recommended imaging studies are available or until their first birthday; which ever comes last. c. Those with structural abnormalities or recurrent UTI need prophylaxis till 5 years or longer. First attack between 1-5 years a. Those children with normal USS following an afebrile or a simple febrile UTI will be followed up without prophylaxis or further investigations. (Refer figure 1) b. Those with structural abnormalities or recurrent UTI need prophylaxis till 5 years or longer. 7.0 Management of recurrent attacks of UTI Confirm the diagnosis, and obtain a urine sample via a SPA for repeat culture, in children not potty trained. Treat promptly with an appropriate antibiotic pending the culture report. Identify correctable risk factors e.g.: constipation, poor hygiene, inappropriate voiding practices etc Treat phimosis or labial adhesions appropriately. (They lead to false positive culture reports) Imaging studies as indicated. Check the compliance, especially if the urine culture yields organisms sensitive to the prophylactic antibiotic used. 14 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
13 8.0 Asymptomatic bacteriuria Do not treat the asymptomatic patients with positive urine cultures as this will lead to resistance and true pyelonephritis. But always exclude urinary symptoms by direct questioning. Routine urine cultures are not necessary. 9.0 Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR) VUR can be a risk factor for recurrent UTI. With bladder growth and maturation there is a tendency for reflux to resolve or improve. Management of VUR: a. Prophylaxis is recommended for VUR till 5 years of age. Longer regimes are indicated for recurrent UTI. b. Advice on double micturition. c. Recurrent attacks of UTI need prompt treatment. d. A repeat DMSA scan to assess new scar formation might be recommended in case of repeat attacks of febrile UTI e. Repeat MCUG to assess the improvement of reflux is not usually recommended unless there is a plan for surgery. There is no world wide consensus regarding the indications for surgical intervention in VUR. Each patient with reflux has to be assessed individually. Definite indications a. Recurrent break through infections Relative indications a. Poor compliance for prophylaxis b. Recurrent infections in spite of prophylaxix. c. New scar formation d. Impaired renal function e. Persistent gross VUR (Grade IV - V) or persistent moderate VUR (grade III) with recurrent infections after discontinuation of prophylaxis GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 15
14 Figure 1. Long term management of patients following UTI USS Normal Abnormal Management depends on specific conditions Age <1 year Age 1-5 yr Febrile Afebrile Advice Treat promptly if recurs Afebrile Febrile Prophylaxis *DMSA after 6/12 No Scarring Prophylaxis till 1 year y of of age Follow up Ill septic or features of pyelonephritis other than fever Scarring Scaring MCUG Scarring Scaring DMSA after 6/12 Yes No VUR No scarring VUR Prophylaxis Follow up on individual basis VUR ±Scarring No scarring No VUR Prophylaxis MCUG >6/52 DMSA >6/12 Stop prophylaxis Follow up Scarring No VUR No Second attack of febrile UTI < 5 yrs of age *MCUG is indicated when DMSA is not available Prophylaxis till 5 years Check blood pressure, growth, renal functions and urinalysis urine for proteinuria analysis for yearly proteinuria yearly Continue follow up into adult life Girls - advice on possible pregnancy related complications 16 GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
15 Members of Guideline Committee Dr Sarath de Silva (Coordinator) Dr Chandra Abeysekera Former Consultant Paediatrician, Lady Ridgeway Hospital, Colombo. Senior Lecturer, Head, Dept. of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Peradeniya. Dr Asiri Abeyagunawardana Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Peradeniya. Dr I N A Gooneratne Dr U K Jayantha Dr Vindya Goonasekera Dr Kumudu Karunarathna Dr Ranjan Dias Consultant Radiologist, Lady Ridgeway Hospital, Colombo. Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Galle. Senior Registrar in Paediatric Nephrology, Lady Ridgeway Hospital, Colombo. Consultant Microbiologist, Lady Ridgeway Hospital, Colombo. Consultant Paediatric Surgeon, Lady Ridgeway Hospital, Colombo. GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 17
16 NATIONAL GUIDELINES
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Urinary tract infection in children. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 Urinary tract infection in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management NICE clinical guideline 54 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: August 2007 Urinary tract infection in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management NICE clinical guideline 54 Developed by the National Collaborating
Urinary tract infection in children
 Urinary tract infection in children Diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Issued: August 2007 NICE clinical guideline 54 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg54 NICE 2007 Vad är Hypotoni? Contents Introduction...
Urinary tract infection in children Diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Issued: August 2007 NICE clinical guideline 54 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg54 NICE 2007 Vad är Hypotoni? Contents Introduction...
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is the Urinary Tract? The urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the tubes which
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN BABIES AND PRE-SCHOOL CHILDREN Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is the Urinary Tract? The urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the tubes which
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
The American Academy of Pediatrics
 Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis
 Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis Male Pelvic Anatomy Female Pelvic Anatomy What does a urinary catheter do? Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Why do patients have catheters?
Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis Male Pelvic Anatomy Female Pelvic Anatomy What does a urinary catheter do? Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Why do patients have catheters?
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS
 SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS Introduction Summary of Recommendations taken from Guidelines for the Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection, Published on behalf of SARI by HSE Health
SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS Introduction Summary of Recommendations taken from Guidelines for the Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection, Published on behalf of SARI by HSE Health
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. (CAUTIs)
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease)
 Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management
 Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management Nursing Education Material Mohamad Fakih, MD, MPH 1 This presentation This presentation targets all nurses with patient care responsibilities including the
Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management Nursing Education Material Mohamad Fakih, MD, MPH 1 This presentation This presentation targets all nurses with patient care responsibilities including the
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Urinary Tract Infections www.kidney.org Did you know that... n Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are responsible for nearly 10 million doctor visits each year. n One in five women will have at least one
Fecal incontinence (Encopresis) It is the fecal incontinence condition observed in children with chronic constipation over 1-2 years.
 WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
Night frequency None 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10. Not enough warning before needing to urinate. none mild moderate severe
 {Patient Label} SYMPTOMS SURVEY: FREQUENCY: How many times do you urinate during the day and get up from sleep to urinate at night? Day frequency 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 More Night frequency None
{Patient Label} SYMPTOMS SURVEY: FREQUENCY: How many times do you urinate during the day and get up from sleep to urinate at night? Day frequency 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 More Night frequency None
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
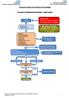 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto
 Is fever dangerous? Do we need to treat it? Episode 48 Pediatric Fever with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto prepared by Claire Heslop, edited by Anton Helman, July 2014 Pediatric Fever Fever in a child
Is fever dangerous? Do we need to treat it? Episode 48 Pediatric Fever with Dr. Sarah Reid & Dr. Gina Neto prepared by Claire Heslop, edited by Anton Helman, July 2014 Pediatric Fever Fever in a child
Bladder and Bowel Control
 Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Bladder and Bowel Control Dr Sue Woodward Lecturer, Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery 2 Why do we need to understand anatomy? Normal physiology Normal adult bladder capacity = 450-500mls
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Enuresis BOWEL AND BLADDER CONTROL. Voiding disorders. Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting
 Enuresis Why does my child have damp pants? Douglas E. Coplen Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting Division of Pediatric Urology Washington University School
Enuresis Why does my child have damp pants? Douglas E. Coplen Involuntary voiding at an inappropriate time or in a socially unacceptable setting Division of Pediatric Urology Washington University School
Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1. Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs
 Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
PATIENT URINARY CATHETER PASSPORT
 n PATIENT URINARY CATHETER PASSPORT A guide on how to look after your Catheter NHS Hertfordshire Patient Experience Team Charter House Parkway Welwyn Garden City Hertfordshire AL8 6JL Telephone: 01707
n PATIENT URINARY CATHETER PASSPORT A guide on how to look after your Catheter NHS Hertfordshire Patient Experience Team Charter House Parkway Welwyn Garden City Hertfordshire AL8 6JL Telephone: 01707
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT)
 Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) This tool and additional educational resources can be found at www.stopbedwetting.org Zinc Code: DN/360/2010/UKe(1)a Date of Preparation of website: August
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) This tool and additional educational resources can be found at www.stopbedwetting.org Zinc Code: DN/360/2010/UKe(1)a Date of Preparation of website: August
VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters. UC Access/ Maintenance
 VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters UC Insertion Preparation & Procedure Indications for insertion and continued use of indwelling urinary catheters include: Urinary retention
VUMC Guidelines for Management of Indwelling Urinary Catheters UC Insertion Preparation & Procedure Indications for insertion and continued use of indwelling urinary catheters include: Urinary retention
Self Catheterization Guide
 Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT)
 Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool Why this management tool? 1. The aim of this tool is to use a simple questionnaire and non-invasive screening,
Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool (CMT) Nocturnal Enuresis Clinical Management Tool Why this management tool? 1. The aim of this tool is to use a simple questionnaire and non-invasive screening,
Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD)
 Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD) Fetal Medicine Unit Your baby has been found to have more fluid in its kidneys than normal. This leaflet will explain what this means for your baby. First of all,
Maternity Renal Pelvis Dilation (RPD) Fetal Medicine Unit Your baby has been found to have more fluid in its kidneys than normal. This leaflet will explain what this means for your baby. First of all,
Title: Microbiology Urine Screening Effective date: 05/08/2013. Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision
 COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Add maintenance procedure and not doing dipstick from urine collected into boric acid Purpose and Scope Items Required The purpose of this process is
COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Add maintenance procedure and not doing dipstick from urine collected into boric acid Purpose and Scope Items Required The purpose of this process is
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Foley Catheter Placement
 Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening
 East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis)
 Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Diabetic ketoacidosis in children and young people bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They
Diabetic ketoacidosis in children and young people bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
ESPR-Meeting, Barcelona/Spain, June 2007
 Imaging recommendations in paediatric uroradiology: Minutes of the ESPR workgroup session on urinary tract infection, fetal hydronephrosis, urinary tract ultrasonography and voiding cystourethrography
Imaging recommendations in paediatric uroradiology: Minutes of the ESPR workgroup session on urinary tract infection, fetal hydronephrosis, urinary tract ultrasonography and voiding cystourethrography
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN
 NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN Constipation in Children Version: 1 Page 1 of 8 Background Constipation is a common complaint in infants and children. The aetiology
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN Constipation in Children Version: 1 Page 1 of 8 Background Constipation is a common complaint in infants and children. The aetiology
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE
 PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
VAGINAL MESH FAQ. How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair?
 VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
The Diagnosis, Treatment, and Evaluation of the Initial Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Infants and Young Children (AC9830)
 Practice Guideline Pediatrics Volume 103, Number 4 April 1999, pp 843-852 The Diagnosis, Treatment, and Evaluation of the Initial Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Infants and Young Children (AC9830)
Practice Guideline Pediatrics Volume 103, Number 4 April 1999, pp 843-852 The Diagnosis, Treatment, and Evaluation of the Initial Urinary Tract Infection in Febrile Infants and Young Children (AC9830)
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections
 Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
Guideline for Preventing Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infections Craig Umscheid, MD, MSCE Carolyn Gould, MD, MSCR and David A. Pegues, MD HICPAC Meeting November 13, 2008 Washington, DC Outline Progress
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections
 Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE. Sandra Reading, Women s CAG Deputy Director
 MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE Sandra Reading, APPROVING COMMITTEE(S) Women s CAG Date approved: Deputy Director EFFECTIVE FROM 9 th September 2013 DISTRIBUTION All staff in the maternity
MATERNITY SERVICES GUIDELINE POSTPARTUM BLADDER CARE Sandra Reading, APPROVING COMMITTEE(S) Women s CAG Date approved: Deputy Director EFFECTIVE FROM 9 th September 2013 DISTRIBUTION All staff in the maternity
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS
 THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS Definition Urinary Incontinence is AN INABILITY TO HOLD URINE until
THE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE WITHIN A STROKE UNIT POPULATION REENA DHAMI STROKE CNS EPSOM & ST.HELIER UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS Definition Urinary Incontinence is AN INABILITY TO HOLD URINE until
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
EVERYBODY'S GUIDE TO PEDIATRIC UROLOGY
 EVERYBODY'S GUIDE TO PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Catherine R. devries, M.D. Patrick C. Cartwright, M.D. Brent Snow, M.D. M. Chad Wallis, M.D. Siam Oottamasathien, M.D. Heidi White, C.P.N.P. AnnMarie Hannon, C.P.N.P.
EVERYBODY'S GUIDE TO PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Catherine R. devries, M.D. Patrick C. Cartwright, M.D. Brent Snow, M.D. M. Chad Wallis, M.D. Siam Oottamasathien, M.D. Heidi White, C.P.N.P. AnnMarie Hannon, C.P.N.P.
What s new? INVESTIGATIVE PROTOCOL FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE & CATHETERS. The Revised Guidance Includes: Interpretive Guidelines
 INVESTIGATIVE PROTOCOL FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE & CATHETERS The Revised Guidance Includes: Interpretive Guidelines Investigative Protocols Compliance & Severity Guidance What s new? The new guidance for
INVESTIGATIVE PROTOCOL FOR URINARY INCONTINENCE & CATHETERS The Revised Guidance Includes: Interpretive Guidelines Investigative Protocols Compliance & Severity Guidance What s new? The new guidance for
Initial Admission Date: Interviewable: Yes No Resident Room: Care Area(s):
 Facility Name: Facility ID: Date: Surveyor Name: Resident Name: Resident ID: Initial Admission Date: Interviewable: Yes No Resident Room: Care Area(s): Use Use this protocol for a sampled resident with
Facility Name: Facility ID: Date: Surveyor Name: Resident Name: Resident ID: Initial Admission Date: Interviewable: Yes No Resident Room: Care Area(s): Use Use this protocol for a sampled resident with
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. System CAUTI Prevention Team
 Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention System CAUTI Prevention Team 1 Objectives At the end of this module, the participant will be able to: Identify risk factors for CAUTI Explain
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention System CAUTI Prevention Team 1 Objectives At the end of this module, the participant will be able to: Identify risk factors for CAUTI Explain
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization
 Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
To decrease and/or prevent the incidence of catheter associated infections and other complications associated with IUC.
 Patient Care Manual Standardized Procedure Number: PC-SP.115 Latest Revision Date: 01/27/2015 Effective Date: 10/10/2011 Standardized Procedure: Urethral Catheter (IUC), Adult, Discontinuance of FUNCTION
Patient Care Manual Standardized Procedure Number: PC-SP.115 Latest Revision Date: 01/27/2015 Effective Date: 10/10/2011 Standardized Procedure: Urethral Catheter (IUC), Adult, Discontinuance of FUNCTION
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Bladder Catheterization
 Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Blood in the Urine (Haematuria)
 Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
Information for Childhood Cancer Survivors. Kidney Problems
 Kidney problems Some chemotherapy drugs can affect the kidneys. The kidneys break down and remove many chemotherapy drugs from the body. When chemotherapy drugs get broken down, they may make products
Kidney problems Some chemotherapy drugs can affect the kidneys. The kidneys break down and remove many chemotherapy drugs from the body. When chemotherapy drugs get broken down, they may make products
SCREENING FOR SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
 SCREENING FOR SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Take history:- History of presenting problem Full sexual history (refer to guideline on sexual history taking) Relevant past medical history, including previous
SCREENING FOR SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Take history:- History of presenting problem Full sexual history (refer to guideline on sexual history taking) Relevant past medical history, including previous
es of Urinary Incontinence:
 Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Catheter Care. What you need to know. Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse
 Catheter Care What you need to know Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse Indications for Long Term Catheter Use Long term urinary catheters should only be used with clients who cannot satisfactorily be managed
Catheter Care What you need to know Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse Indications for Long Term Catheter Use Long term urinary catheters should only be used with clients who cannot satisfactorily be managed
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours using SUNItinib (SUTENT )
 BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours using SUNItinib (SUTENT ) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UGIPNSUNI Gastrointestinal Dr. Hagen
BCCA Protocol Summary for Palliative Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours using SUNItinib (SUTENT ) Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician UGIPNSUNI Gastrointestinal Dr. Hagen
Looking after your urinary catheter at home
 Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
Looking after your urinary catheter at home Information for patients and carers Useful contacts to keep: Name and title of community nurse Single point of access (SPA) for community nursing 24 hour service
