All images and artwork used in this program were obtained or drawn by Shane Smith.
|
|
|
- Matthew Webster
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCS Continuing Education and Three Phase CEUs presents: Anatomy and Radiography of the Wrist, Hand, and Fingers Copyright 2006
2 Introduction: Hello and welcome to this program from SCS Continuing Education! Knowledge is the key to success for ourselves and our patients. This easy-to-use point and click program allows you to navigate through text and visual aides designed to provide a comprehensive view of the material covered. Please feel free to contact Shane Smith at ceuarmy@yahoo.com if you have any questions. Course Abstract and Objectives: The objective of this home study course is to provide the learner with a computer based tutorial that will give them the means to learn the anatomy and radiography of the ankle, foot, and toes. A mastery test will be administered at the end of this home study course in order to ensure that competency of the material has been achieved. All images and artwork used in this program were obtained or drawn by Shane Smith.
3 Anatomy and Radiography of the Ankle, Foot and Toes by Shane Smith PTA, RT(R) Copyright 2006
4 CHAPTERS: Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle...pg 5 Bony Anatomy pg 11 Positioning..pg 20 Technical Guidelines..pg 34 MRI.pg 36 Common Clinical Findings...pg 44 Conclusion..pg 55 Test.. pg 56 References.. pg 57
5 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle
6 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle: There are 28 bones and 25 joints in the foot and ankle complex. These structures are configured to accommodate the stability and mobility responsibilities of the foot and ankle on various surfaces during varying degrees of weight bearing.
7 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle: The foot is divided into 3 categories; the fore foot (metatarsals and phalanges), mid foot (cuboid, navicular and 3 cuneiforms) and hind foot (talus and calcaneous). Subtalar joint Transverse tarsal joint mid foot Tarsometatarsal joint fore foot mid foot hind foot fore foot hind foot Lateral foot Note: The joints will be discussed later in the tutorial. AP foot
8 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle: Now that we have been oriented to the basic structure of the foot and ankle, let s review the keys concepts related to motion. This section is split into two sections: joint classification and the arch. Let s begin by reviewing some terminology that will be used in the forthcoming slides. synovial joint: diathrotic; allows one or more types of free movement; contain articular cartilage, synovial fluid, synovial membrane and a fibrous capsule. inversion: combination of supination, adduction and plantar flexion.. eversion: combination of pronation, abduction and dorsiflexion. compound joint: made up of two or more bones and/or joints. uniaxial joint: 1 degree of freedom. hinge joint: monaxial; flexion/extension. syndesmosis: fibrous connection between a concave and convex surface. condyloid joint: allows all forms of angular movement except axial rotation.
9 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle: Joint Classification Joint Bones involved Type talocrural (ankle) proximal tibiofibular distal tibiofibular subtalar transverse tarsal tarsometatarsal metatarsophalangeal interphalangeal talus, tibia and fibula proximal tibia and fibula distal tibia and fibula talus and calcaneous talus, navicular, calcaneous and cuboid metatarsals, cuneiforms and cuboid metacarpal and proximal phalanx adjacent phalanges synovial; hinge synovial syndesmosis uniaxial compound synovial condyloid; synovial synovial; hinge
10 Fundamentals of the Foot and Ankle: The Arch The arch, also referred to as a twisted osteoligamentous plate, is formed by the configuration of bones and ligaments in the foot. The arch plays a role in both mobility and stability. In mobility, the arch acts as a shock absorber and allows the foot to adapt to changes in terrain. In stability, it allows for weight distribution through the foot during weight bearing and converts foot to a rigid lever when pushing off during gait. The plantar fascia tightens during extension at the metatarsophalangeal joint. This tightening results in a shortening of the plantar fascia that keeps the midfoot and hind foot locked in an supinated position as the heel lifts off the ground. This is known as the windlass mechanism.
11 Bony Anatomy
12 Bony Anatomy: The Ankle The ankle joint or talocrural joint is a synovial hinge joint that is made up of the articulation of 3 bones. The 3 bones are the tibia, the fibula and the talus. The articulations are between the talus and the tibia and the talus and the fibula. distal tibiofibular joint Anterior View TIBIA Tibia Mortise The mortise is the concaved surface formed by the tibia and fibula. The mortise is adjustable and is controlled by the proximal and distal tibiofibular joints. The talus articulates with this surface and allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. talofibular articulation Fibula Talus tibiotalar articulation
13 Bony Anatomy: Talocrural joint: Most congruent joint in the body. It allows 1 of freedom: dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. In open chain activity (non-weight bearing), the convex talus slides posteriorly during dorsiflexion and anteriorly during plantar flexion on the concave tibia and fibula. Fibula Tibia Mortise Talus talocrural joint In closed chain activity (weight bearing), the tibia and fibula move on the talus. Total talocrural joint motion is approximately: plantar flexion: dorsiflexion: 20
14 Bony Anatomy: Subtalar joint: Also known as the talocalcaneal joint. It is a triplanar, uniaxial joint which allows 1 of freedom: supination (closed packed position) and pronation (open). Supination is accompanied by calcaneal inversion (calcaneovarus) and pronation is accompanied by calcaneal eversion (calcaneovalgus). subtalar joint Fibula Tibia Talus Total subtalar joint motion is approximately: inversion: 20 eversion: 10 Calcaneous
15 Bony Anatomy: The Foot Let s identify the bones of the foot. Notice that the great toe only has a proximal and distal phalange. There are also 2 sesamoid bones (not shown) located under the 1 st MTP joint. The toes are also known as rays. The great toe is the 1 st ray, the next toe is the 2 nd ray, the middle toe is the 3 rd ray, the next lateral toe is the 4 th ray and the little toe is the 5 th ray. distal phalange proximal phalange middle cuneiform medial cuneiform navicular 1 st ray 2 nd ray middle phalange 3 rd ray 4 th ray 5 th ray metatarsal lateral cuneiform cuboid talus calcaneous
16 Bony Anatomy: Transverse tarsal joint: Also known as the midtarsal joint. It is a compound joint which allows compensation between the hind foot and fore foot on uneven terrain. It is made up of four bones (talus, calcaneous, cuboid and navicular) and two joints (talonavicular and calcaneocuboid). transverse tarsal joint
17 Bony Anatomy: Tarsometatarsal joint: Plane synovial joint formed by articulations with: 1 st metatarsal and medial cuneiform 2 nd metatarsal and middle cuneiform 3 rd metatarsal and lateral cuneiform 4 th and 5 th metatarsals and cuboid Continues the compensating movement available at the transverse tarsal joint once the maximum range of motion of that joint has been reached. tarsometatarsal joint
18 Bony Anatomy: Metatarsophalangeal joint: Also known as the ball of the foot. It is a condyloid synovial joint with 2 of freedom: flexion/extension and abduction/adduction. Total MTP joint motion is approximately: great toe flexion: 0-45 toe flexion: 0-40 great toe and toe extension: 0-80 metatarsophalangeal joint
19 Bony Anatomy: Interphalangeal joint: IP joints are synovial hinge joints with 1 of freedom: flexion/extension. Total IP joint motion is approximately: IP flexion of great toe: 0-90 PIP flexion: 0-35 DIP flexion: 0-60 great toe and toe extension: 0-80 interphalangeal joint
20 Positioning
21 Positioning: General Guidelines remove any jewelry that will interfere with the anatomy being radiographed. make patient as comfortable as possible; some positions that the patient must conform to and maintain in order for a diagnostic image to be obtained can be difficult due to disease process, trauma, etc. It is important to keep that in mind when positioning patients for an exam. always shield when possible; for the purpose of this program, shielding should always be utilized for radiography of the foot and ankle. use collimation; at minimum, collimation should not exceed the cassette size. the body part should be parallel to the film; the central ray (centering) should be perpendicular (90 ) to the body part and the film. Lead markers should be used to identify RIGHT or LEFT.
22 Positioning: AP foot Place foot flat onto the casette. Angle tube 10 toward the heel (calcaneus). Center to the base of the 3 rd metatarsal. Include toes, metatarsals, navicular, cunieforms and cuboid.
23 Positioning: Oblique foot Place foot onto the casette at a angle medially. (45 is recommended) Center to the base of the 3 rd metatarsal. Include the entire foot and talus.
24 Positioning: Lateral foot Place foot onto the cassette for a mediolateral projection (recommended). Center to the medial cunieform (base of the 3 rd metatarsal). Include the entire foot and 1 inch of distal tibia and fibula.
25 Positioning: AP toe Place foot flat onto the cassette. Angle tube toward the heel. Center to the appropriate MP joint. Include the entire toe and ½ of the metatarsal.
26 Positioning: Oblique toe Place foot onto the cassette at a 45 angle medially. Center to the appropriate MP joint. Include the entire toe and ½ of the metatarsal.
27 Positioning: Lateral toe Place foot onto the cassette for a lateromedial projection of the 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd toes and a mediolateral projection of the 4 th and 5 th toes. Center to the IP joint for the 1 st toe and the appropriate PIP joint for the other toes. Include the entire toe (phalanges).
28 Positioning: AP ankle Place ankle onto the cassette. (the intermalleolar line will not be parallel in a true AP projection). Center between the malleoli. Include the distal third of the tibia/fibula and proximal half of the metatarsals.
29 Positioning: Oblique ankle Place ankle onto the cassette at 45 of medial rotation. Center between the malleoli. Include the distal third of the tibia/fibula and proximal half of the metatarsals.
30 Positioning: AP mortise Place ankle onto the cassette at of medial rotation. Center between the malleoli. Include the distal third of the tibia/fibula and proximal half of the metatarsals.
31 Positioning: Lateral ankle Place ankle onto the cassette for a mediolateral projection. (recommended) Center to the medial malleolus. Include the calcaneus, talus, tarsals and the base of the 5 th metatarsal.
32 Positioning: Axial calcaneous Place ankle onto the cassette with the heel close to the bottom edge. Dorsiflex until plantar (bottom) surface of the foot is perpendicular to the cassette. (assistance may be necessary to achieve this). Angle tube 40 cephalad (cross-hairs seen on the bottom of the foot). Center to the base of the 3 rd metatarsal. Include entire calcaneus to the talocalcaneal joint. Due to the reproduction quality of this x-ray to fit the format of this tutorial, the talocalcaneal joint is not visualized.
33 Positioning: Lateral calcaneus Place ankle onto the cassette for a mediolateral projection. Center to 1½ inches below the medial malleolus. Include the calcaneus and talus.
34 Technical Guidelines
35 Technical Guidelines: Radiography of the foot and ankle is done at a 40 inch SID (source image distance). Keep the body part as close to the cassette as possible in order to reduce OID (object image distance). Radiographs of the ankle and foot are of better diagnostic quality when an extremity cassette is utilized. CR (computerized radiography) does not use conventional cassettes or film. Instead, a digitized plate is utilized which can be programmed to act like an extremity cassette. The difference is, however, that it is advised to only put one image per cassette. Multiple images on one cassette do not always appear properly and are difficult to window correctly. Although x-ray machines vary, the general kvp ranges for radiography of the ankle and foot is between kvp. Adjustments in kvp and MAs should be considered in cases involving splints, casts, wraps, swelling, braces, etc.
36 MRI
37 MRI: Overview A comprehensive explanation of MRI physics is outside the scope of this program but in order to appreciate the following slides and gain the most value from them, a simplistic overview is provided. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an imaging process that utilizes a magnetic field to magnetize tissues of the body in order to create a radio frequency signal (RF) that will, with the assistance of coils and a computer, produce an image. The magnetic field primarily affects tissues with an adequate amount of hydrogen. A high concentration of hydrogen will produce a strong signal and a bright area on the image while a low concentration will produce little or no signal. No signal will produce a black area with the signals in between producing gray areas, contrast.
38 MRI: Tissue Characteristics and Contrast: One advantage to MRI is the ability to utilize the variety of tissues in the body to produce contrast. The tissues of the body are divided into three characteristics: T1, PD and T2. Images produced in MRI are often described as being T1, PD or T2 weighted. Let s use the diagram below to help define these terms as they relate to the image that is produced. T1: on a T1 weighted image, fat is bright and water is dark. PD: on a proton density image, water is bright and fat is dark but the contrast between the two is less define. T2: on a T2 weighted image, water is bright and fat is dark but the contrast is greater. fat PD water bright T1 T2 water fat T1 PD T2 dark
39 MRI: Axial T1 The axial view of the foot in MRI is comparable to the AP view of the foot in x-ray. The image to the right is one slice of an axial sequence. medial cuneiform 1 st metatarsal middle cuneiform lateral cuneiform navicular talus Achilles tendon
40 MRI: Axial T1 The axial view of the foot in MRI is comparable to the AP view of the foot in x-ray. The image to the right is one slice of an axial sequence. 1 st metatarsal medial cuneiform cuboid abductor hallicus ms. calcaneus Achilles tendon
41 MRI: Sagittal T2 The sagittal view of the foot in MRI is comparable to the lateral view of the foot in x-ray. The image to the right is one slice of a sagittal sequence. Achilles tendon tibia talus metatarsal fluid calcaneus
42 MRI: Coronal T2 The coronal view of the foot in MRI has no comparable view in x- ray. The coronal slice is similar to slices in a loaf of bread. The image to the right is one slice of a coronal sequence. 1st metatarsal 3rd metatarsal 4 th metatarsal 5 th metatarsal
43 MRI: Coronal T2 The coronal view of the foot in MRI has no comparable view in x- ray. The coronal slice is similar to slices in a loaf of bread. The image to the right is one slice of a coronal sequence. 1st metatarsal 2nd metatarsal 3rd metatarsal 4 th metatarsal 5 th metatarsal
44 Common Clinical Findings
45 Common Clinical Findings: Ligaments: The MCL (medial collateral ligaments) is made up of the three fan-shaped ligaments attached to the distal tibia, also known as the deltoid ligament. This group of ligaments limits valgus stresses on the ankle. This is a fairly strong group and not commonly torn. The function of the spring (or plantar calcaneonavicular) ligament is to maintain the arch of the foot. The plantar fascia (aponeurosis) is a sheet of connective tissue that runs from the calcaneous to the proximal phalanges. Medial ligaments: spring ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular) deltoid ligament plantar fascia (aponeurosis)
46 Common Clinical Findings: Ligaments: The LCL (lateral collateral ligaments) is made up of the anterior talofibular ligament, the posterior talofibular ligament and the calcaneofibular ligament. This group of ligaments limits varus stresses on the ankle. The weakest and most commonly torn of this group is the anterior talofibular ligament. The function of the long plantar and short plantar(or plantar calcaneocuboid ) ligaments is to maintain the arch of the foot. The bifurcate ligament attaches from the calcaneous to the navicular and the cuboid. The dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament is found lateral and distal to the bifurcate ligament and also attaches from the calcaneous to the cuboid. Lateral ligaments: posterior talofibular ligament calcaneofibular ligament dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament long plantar ligament anterior talofibular ligament bifurcate ligament short plantar ligament
47 Common Clinical Findings: Now that we ve reviewed and understand the basic structure and function of the foot and ankle, let s review some of the common clinical findings. 1. Achilles Tendonitis: 2. Achilles Tendonosis: -inflammation caused by repetitive motions involving the Achilles tendon. -RX: rest/immoblization, ice, ultrasound, NSAIDs, massage, stretching, exercise. -progression of the inflammation of the Achilles tendon to degeneration of the tendon. -RX: rest/immoblization, ice, ultrasound, NSAIDs, massage, stretching, exercise, surgery.
48 Common Clinical Findings: 3. Ankle Sprain: -injury involving one or more ligaments in the ankle. -severity dependent upon number of ligaments involved, stretched vs torn and to the degree the ligament is torn. -RX: rest/immoblization, ice, NSAIDs, compression wrap, elevation, surgery. 4. Ankle Fracture: -injury involving one or more bones of the ankle. -severity dependent upon number of bones involved, displaced vs non-displaced, protruding through skin. -RX: rest/immoblization, ice, NSAIDs, compression wrap, elevation, surgery.
49 Common Clinical Findings: 5. Plantar Fascitis: 6. Pes Planus: -inflammation to the plantar fascia resulting in heel pain due to prolonged non-weight bearing (sitting) in some cases and prolonged weight bearing (standing) in others. -RX: stretching exercises, ice, rest, NSAIDs, orthotics and/or shoe modification. -also known as flat foot ; partial or complete loss of arch. -RX: weight loss, rest, NSAIDs, orthotics and/or shoe modification, surgery.
50 Common Clinical Findings: 7. Chronic Instability : -usually caused by a lateral ankle sprain that has not healed properly and/or repeated ankle sprains resulting in laxity in the LCL. -RX: strengthening exercises, bracing, NSAIDs. 8. Osteoarthritis : -breakdown and loss of cartilage in one or more joints. -could be caused by flatfoot, jamming toe(s), fracture, severe sprain. -RX: strengthening exercises, rest, NSAIDs, orthotics and/or shoe modification, bracing, steroid injections, surgery.
51 Common Clinical Findings: 9. Pes cavus: -excessively supinated foot as a result of a high arch -loss of shock absorption ability or adaptation to uneven terrain -RX: questionable results with conservative intervention.
52 Common Clinical Findings: fracture of the lateral malleolus
53 Common Clinical Findings: amputation of great toe
54 Common Clinical Findings: fracture of base of 5 th metatarsal fracture of base of 5 th metatarsal fracture of cuboid fracture of cuboid
55 Conclusion: Radiography of the foot, ankle and toes is done at a 40 inch SID (source image distance). Keep the body part as close to the cassette as possible in order to reduce OID (object image distance). Although x-ray machines vary, the general kvp ranges for radiography of the wrist and hand is between kvp. Adjustments in kvp and MAs should be considered in cases involving splints, casts, wraps, swelling, braces, etc. The body part should be parallel to the film and the central ray (centering) should be perpendicular (90 ) to the body part and the film unless otherwise indicated. Always shield when possible; use collimation, identify LEFT or RIGHT by utilizing lead markers, remove jewelry that may interfere with anatomy and be conscious of patient comfort when positioning.
56 Test: There are 60 questions on this test. All answers can be found within the context of this program. The hint button located next to each question will provide you the information needed to answer the question. At any time during the test you may skip a question and return to it later. You must successfully answer 70% of the questions in order to receive credit for the course. To access the test, please close out of this course by clicking the x in the top right corner. Good luck!!!
57 References: Norkin, Cynthia C. and Levangie, Pamela K.; Joint Structure & Function: A Comprehensive Analysis, Second Edition, F.A. Davis Co. Philadelphia, PA.1992 Malone,Terry R., McPoil, Thomas, Nitz, Arthur J.; Orthopedic and Sports Physical Therapy, Third Edition, Mosby-Year Book Inc. St. Louis, MS Hislop, Helen J. and Montgomery, Jacqueline; Daniels and Worthingham s Muscle Testing: Techniques of Manual Examination, Sixth Edition, W.B. Saunders Co. Philadelphia, PA Stalheim-Smith, Ann and Fitch, Greg K.; Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology, West Publishing Co. St. Paul, MN Thomas, Clayton L.; Taber s Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary, Seventeenth Edition, F.A. Davis Co.Philadelphia, PA Bontrager, Kenneth L.: Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy, Fourth Edition, Mosby Inc. St. Louis, MO Tortora, Gerard J. and Grabowski, Sandra R.; Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc New York, NY Footphysicians.com. Healthy Feet for an Active Life. Foot & Ankle Information Feb Stoller, David W.; Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine, J.B. Lippincott Co. Philadelphia, PA Sprawls, Perry; Magnetic Resonance Imaging Principles, Methods, and Techniques, Medical Physics Publishing, Madison, WI. 2000
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás
 Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better. By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the
 The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics
 Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete
 Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Syndesmosis Injuries
 Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Ankle Sports injuries. Ben Yates
 Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which
 To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses
 Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Pathology-Designed Custom Molded Foot Orthoses Kevin B. Rosenbloom, CPed KEYWORDS Foot orthoses Custom orthoses Orthotic devices Pathology-designed orthoses Orthosis design Treating patients with custom
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Deformities. Assessment of Foot. The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized.
 Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
Assessment of Foot Deformities in the Infant By Maureen Baxter, MDCM, FRCS The majority of foot deformities occur in otherwise healthy infants. However most generalized neurologic disorders (spina bifida,
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY. Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery. Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch
 CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation
 RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis
 Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis Dani Martínez November 2013 Chicago, IL 1 Abstract This paper assesses the use of Pilates to decrease over-supination in the forefoot and thus alleviate associated
Over-Supination and Peroneal Tendinosis Dani Martínez November 2013 Chicago, IL 1 Abstract This paper assesses the use of Pilates to decrease over-supination in the forefoot and thus alleviate associated
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet.
 WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC. Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program
 J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO
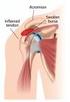 AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology
 Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
How To Treat Heel Pain
 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints
 Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis
 C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears. Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014
 The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 16 (2005) 779 799 Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners Karen P. Barr, MD a, *, Mark A. Harrast, MD a,b a Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Box
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 16 (2005) 779 799 Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners Karen P. Barr, MD a, *, Mark A. Harrast, MD a,b a Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Box
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Appendix An Acupuncturist s Guide to the Treatment and Assessment of Plantar Fasciitis and Excessive Foot Pronation
 Appendix An Acupuncturist s Guide to the Treatment and Assessment of Plantar Fasciitis and Excessive Foot Pronation By Matt Callison, M.S., L.A.c I An Acupuncturist s Guide to the Treatment and Assessment
Appendix An Acupuncturist s Guide to the Treatment and Assessment of Plantar Fasciitis and Excessive Foot Pronation By Matt Callison, M.S., L.A.c I An Acupuncturist s Guide to the Treatment and Assessment
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine
 Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Family Medicine / Emergency Medicine / Orthopedic: Ankle sprain Author: Joe Lau OMS-IV, Theodore Flaum, DO Introduction: Ankle sprain, a.k.a. sprained
Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Family Medicine / Emergency Medicine / Orthopedic: Ankle sprain Author: Joe Lau OMS-IV, Theodore Flaum, DO Introduction: Ankle sprain, a.k.a. sprained
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries
 Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Evaluating Knee Pain
 Evaluating Knee Pain Matthew T. Boes, M.D. Raleigh Orthopaedic Clinic September 24, 2011 Introduction Approach to patient with knee pain / injury History Examination Radiographs Guidelines for additional
Evaluating Knee Pain Matthew T. Boes, M.D. Raleigh Orthopaedic Clinic September 24, 2011 Introduction Approach to patient with knee pain / injury History Examination Radiographs Guidelines for additional
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY.
 QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot
 Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
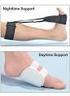 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
Rehabilitation with Pilates
 Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Last Review Date August 2015 Version 1.1 Page 1 of 11
 Title: Protocol for the Management of Lower Leg, Ankle and Foot Injuries Document Owner: Deirdre Molloy Document Author: Deirdre Molloy Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: August 2015 Ratified
Title: Protocol for the Management of Lower Leg, Ankle and Foot Injuries Document Owner: Deirdre Molloy Document Author: Deirdre Molloy Presented to: Care & Clinical Policies Date: August 2015 Ratified
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries
 How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
How To Treat Turf Toe Injuries Turf toe injuries can have a significant impact upon the playing time of professional athletes. Accordingly, this author reviews the etiology of these injuries and assesses
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
