Common Foot Pathologies
|
|
|
- William Ashley Martin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Common Foot Pathologies
2 Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome)
3 Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the cartilage ) is a degenerative cartilage condition wherein the cartilage on the back of the patella (knee cap) is irritated and painful because it rubs against the medial femoral condyle. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of dull, aching pain leading to sharp localized pain in the front of the knee, particularly while going up or down stairs and hills. They may feel a grinding sensation and stiffness when squatting, bending and climbing stairs. The patient may experience the sensation of the knee giving away beneath them. How is it caused? During normal walking, the femur (thigh) and the tibia (lower leg) rotate in unison. An abnormal walking pattern (over-pronation) may cause the thigh and lower leg to rotate out of sync causing misalignment of the lower extremity. The resulting counter rotation of the femur and the tibia causes the patella to rub against the medial femoral condyle instead of moving smoothly up and down in its normal track, causing pain and damage to the cartilage, leading to chondromalacia. Note: The saddle-shaped superior surface of the talus bears the weight of the body transmitted via the tibia. Hence, over-pronation may result in the tibia internally rotating beyond the end of contact phase while the femur begins rotating externally at mid-stance. How is it treated? Treatment options vary according to symptoms and the severity of the injury. The patient may respond well to quadriceps strengthening exercises and a hamstring flexibility program. Actions such as crouching, knee bends and resistance exercises with knee extension from a fully flexed position should be avoided. Most importantly, proper alignment of the patella must be maintained. Once over-pronation has been arrested, and alignment regained, healing can begin. The patient should be fitted with orthotics and will likely experience pain relief within weeks and complete recovery within months (generally 2-3 months).
4 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Spur Syndrome)
5 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Spur Syndrome) What is it? Plantar fasciitis is a condition wherein the plantar fascia is pulling on the periosteum at the calcaneus therefore causing inflammation and pain. The plantar fascia is connective tissue that acts as a stabilizer and maintains the integrity of the arch of the foot. It originates at the plantar aspect of the calcaneus and is attached to the metatarsal heads and continues forward to insert on the proximal phalanges as well as forming the fibrous flexor sheath in each toe. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of severe pain felt in the heel at the hindfoot (plantar surface of the calcaneus) particularly when they take their first few steps of the day, or after they have been off their feet for a prolonged period of time. Pain after rest! How is it caused? The plantar fascia is repeatedly over-torqued because the calcaneus in the hindfoot is stable while the forefoot is over-pronating. This shearing force causes the plantar fascia to become inflamed. Because the weakest part of the plantar fascia is the attachment to the periosteum (fibrous membrane covering the bone) at the calcaneus, pain on the medial side of the calcaneous is felt. When the plantar fascia is repeatedly twisted, it pulls the periosteum away from the calcaneus and causes the pain and inflammation. If this happens often enough, the calcaneus will eventually grow toward the plantar fascia in an effort to re-attach itself. That bone growth is called a heel spur. The pain is felt during the first few steps of the day because during the night, the fibres of the fascia try to heal themselves by forming fragile new fibre, and when the person puts weight on the foot, renewed tearing takes place and the pain becomes severe. How is it treated? Treatment options vary according to symptoms. If the pain is caused by over-pronation and continuous torquing of the fascia, an aggressive more rigid orthotic is needed to arrest the torquing and stabilize the forefoot. If the pain is found in the middle area of the plantar fascia, aggressive rearfoot control is needed and can be found with orthotics. Since the problem is the over-pronation, orthotics that control pronation and arch elongation should be prescribed. The patient can expect a 20-25% improvement every 2 weeks until complete recovery, which generally takes 2 to 3 months.
6 Achilles Tendonitis
7 Achilles Tendonitis ( Achilles from Greek mythology) What is it? Achilles tendonitis is a condition wherein the achilles tendon, at or near its insertion to the posterior aspect of the calcaneus, becomes inflamed and causes pain. The achilles tendon is one of the longest and strongest tendons in the body. It is avascular and therefore slow to heal. The Achilles Tendon is formed in the lower third of the posterior aspect of the tibia. Two muscles join to form the Achilles tendon: the Gastrocnemius which originates on the posterior aspect of the femur, and the Soleus which originates on the posterior aspect of the upper third of the tibia. The Achilles tendon works as an anti-pronator. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of severe aching or burning pain felt in the back of the heel, which increases with passive dorsiflexion and resisted plantarflexion, such as rising up onto the toes. How is it caused? Over-pronation, overstress of the tendon. Risk factors include tight heel cords, foot malalignment deformities, recent change in activities or shoes. During a normal gait cycle, the femur and the tibia rotate in unison (i.e. internally during pronation and externally during supination). However, when a person over-pronates, the tibia is locked into the talus by the saddle joint and therefore continues to rotate internally past the end of the contact phase while the femur begins to rotate externally at the beginning of midstance. The Gastrocnemius muscle is attached to the femur and rotates externally while the Soleus muscle is attached to the tibia and fibula and rotates internally during pronation. The resulting counter rotation of the femur and the tibia causes a shearing force to occur in the Achilles tendon. This counter rotation twists the tendon at its weakest area, namely the Achilles tendon itself, and causes the inflammation. Since the tendon is avascular, once inflammation sets in, it tends to be chronic. How is it treated? Relieving the stress is the first course of action. Acute treatment involves ice therapy and activity modification. Active stretching and strengthening exercises will assist rehabilitation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. When placed in a heeled shoe, the patient will immediately notice a difference, compared to flat ground. It is recommended that the patient be fitted with orthotics to control the down and in movement of the talus and maintain proper alignment, relieving the stress on the achilles tendon. Tightness in the tendon itself can be helped by an extra heel lift added to the orthotics. The patient can expect a slow recovery over a period of months.
8 Bunion
9 Bunion ( Hallux Valgus ) What is it? A bunion is a medial deviation and inflammation of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint of the big toe. The capsule of the joint is subluxed (displaced), thickened and enlarged, and the cartilage of the joint is damaged. There are three degrees of bunions: mild, moderate and severe. Bunions are not hereditary, although the tendency to over-pronate, which is the cause of bunions, has a hereditary component. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of pain in the MTP joint and have a deformed (medially deviated) big toe. Often, they are only able to wear very wide shoes. How is it caused? Prolonged pressure against the medial aspect of the first MTP joint can lead to thickening of the medial capsule and bursa, resulting in severe valgus deformity of the great toe. Normally toe-off occurs from the plantar surface of the big toe. Over-pronation can cause the propulsion phase of stance to take off from the medial aspect of the phalanges of the big toe instead of the plantar surface. As a result, there is a retrograde force into the joint which pushes it out medially and stretches the joint capsule. This tearing and stretching of the joint capsule as well as the wear and tear on the cartilage causes the pain. How is it treated? Since the problem is the over-pronation, the patient should be fitted with orthotics and can expect a slow recovery over a period of months. Orthotics will not cause the physical deformity to regress, but will simply arrest any further progression and likely stop the pain. It is important to note however, that when bunions are severe and require surgery, the bunion can be corrected, but will develop again unless the root cause of over-pronation is corrected. Since overpronation is the root cause, orthotics are still necessary.
10 Hammer Toes
11 Hammer Toes What is it? Hammer toes is a condition wherein there is contracture of the proximal interphalangeal joint (usually in the second toe, but sometimes the third toe). It is extended at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, flexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint, and extended at the distal interphalangeal joint. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients may feel pressure against the shoe and under the metatarsal head, particularly the second toe, which is often caused by the retrograde pressure on the big toe. Patients complain of pain felt on the dorsal aspect at the PIP joint of the hammer toe itself usually due to a corn/callus that has developed. Once this happens, it is painful to wear regular shoes. How is it caused? A Hammer Toe may be caused by improperly fitted shoes or a dropped metatarsal head which presses on the flexor tendon (flexor complex - the group of muscles running on the plantar surface of the toes). This pressure causes the proximal phalanx to remain dorsiflexed, and the toe becomes hammered. Some other causes are diabetes, arthritis, neuromuscular disease, polio or trauma. How is it treated? First push up on the plantar surface of the metatarsal head and see if the toe straightens out. If it does, then an orthotic could correct the problem, usually with a metatarsal pad. If the toe does not straighten out when the metatarsal head is pushed up, then that indicates that contracture in the capsule and ligaments (capsule contracts because the joint was in the wrong position for too long) of the MTP joint has set in and surgery is required. Orthotics are required post-surgically.
12 Posterior view of right leg and foot
13 What is it? Shin Splints Medial = tibialis posterior Anterior = tibialis anterior Medial shin splints are a condition wherein the periosteum of the tibia is damaged when it is pulled away by an overstressed tibialis posterior muscle. Anterior shin splints are a condition wherein the blood flow is obstructed from the anterior compartment due to the hypertrophy of the overstressed tibialis anterior compartment. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Medial shin splints: Patients complain of a dull, aching pain felt along the medial side of the tibia. Once it starts, any activity will aggravate it. Anterior shin splints: Patients complain of dull, aching pain felt along the anterior side of the tibia. This can be a medical emergency due to lack of blood flow leading to neurosis and gangrene of muscle in the anterior compartment. How is it caused? Medial shin splints: The tibialis posterior muscle plantarflexes and inverts the foot (anti-pronator) due to its distal attachment (insertion) on the medial aspect of the foot. During over-pronation the tendon of the tibialis posterior is stretched and pulled upon excessively, thereby attacking the weakest area, namely its origin (proximal attachment) on the periosteum of the tibia. The small pain fibres of the periosteum are torn away causing pain and chronic inflammation. Anterior shin splints: The tibialis anterior muscle dorsiflexes and inverts the foot, acting as an antipronator due to its distal attachment (insertion) on the medial aspect and base of the first metatarsal. During over-pronation the tibialis anterior muscle fibres must fire constantly to oppose (re-supinate) the over-pronation, thus causing hypertrophy (swelling) of the tibialis anterior compartment. With the anterior compartment being tightly constricted, the swollen tibialis anterior can cause an obstruction of blood flow, which, in turn can cause severe pain due to ischemia (lack of oxygen). This can be very serious, and may require emergency surgery. An example of Ischemia is angina. How is it treated? Medial and anterior shin splints: Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment may include standard acute care, restricted activity and an orthotic device that corrects the over-pronation and stops the foot from falling too far medially (reducing the strain on the tibialis posterior) and facilitates proper foot function and timing, reducing the stress on the tibialis anterior.
14 Corns
15 Corns (from the Latin cornu meaning horn ) What is it? A corn (heloma) is an area of thickened skin tissue on the top of the toes (due to shoe irritation) or in between the toes due to irritation and friction (usually 2nd metatarsal) from a bony prominence. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients will complain of pain at the site of the corn. Soft corns at the webspace may become infected. How is it caused? Corns are caused or aggravated by abnormal friction (instability or over-pronation) occurring between a bony prominence and also because pronation causes the foot to function like a loose bag of bones. The result is hypermobility of the foot, causing the bony prominences to irritate and break down the soft tissue between the toes. When the loose bag of bones phase goes on too long, the skin is trapped between the bony prominences in the foot and the inside of the shoe, causing friction and irritation. The skin of the foot thickens to protect itself from the irritation but then leaves even less room between itself and the inside of the shoe, resulting in pain. How is it treated? Temporarily the corns can be cut away, however, since the problem is made worse by overpronation, the patient should be fitted with an orthotic device that restricts the instability and reduces friction. The patient will likely experience comfort and relief within weeks.
16 Calluses
17 Calluses (Hyperkeratotic Tissue) What is it? A callus is an area of thickened skin tissue on the bottom of the foot due to irritation. They are localized to high friction areas, typically under bony prominences. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients will complain of pain at the site of the callus. They will feel maximum pain with direct pressure. How is it caused? The integrity of the protective barrier the skin provides the foot is critical in maintaining weightbearing function. Callus formation occurs in areas of high vertical and shear loads and defends against blistering and ulceration. However, this process itself can cause symptoms and predispose patients with poly-neuropathy to deep infection. Even when considering a healthy foot, poor foot function can lead to callus formation. During over-pronation, the foot rolls across the metatarsal heads -- one at a time -- instead of distributing the weight equally. This happens because the foot is a loose bag of bones during pronation causing hypermobility of soft tissues. When the loose bag of bones phase goes on too long and the skin is trapped between the bones in the foot and the ground, the friction of individual metatarsal heads bearing all the weight can cause inflammation. The skin thickens in the inflamed area to protect the sore spot. This thick build up of skin so close to the nerve endings in the bottom of the foot is what causes the pain. How is it treated? Soft tissue care and maintenance is recommended. However, since the problem is high vertical and shear loading the patient should be fitted with orthotics to properly redistribute plantar pressures. Within weeks, the patient will likely feel pain relief. The calluses can be cut away or will eventually go away on their own once the irritation no longer exists.
18 Morton s Neuroma
19 Morton s Neuroma What is it? Morton s neuroma is characterized by pain located in the third interspace. The next most common locations are the second, fourth and first interspaces. What are the common symptoms/complaints? A burning sensation is present in the interspace and typically radiates to the adjacent digits. Patients will complain of numbness, a pins and needles type of tingling and loss of sensation in the corresponding toes. How is it caused? During certain kinds of over-pronation, a pivoting on the 3rd and 4th metatarsals can cause a shearing force. This shearing force between the 3rd and 4th metatarsals entraps the digital nerve and causes inflammation. The inflammation is what causes the pain. In cases of abnormal subtalar and midtarsal joint pronation, there is excessive transverse plane movement of the metatarsals. Since the 1st, 2nd and 3rd metatarsals articulate with the cuneiforms and act as one functional unit, and the 4th and 5th metatarsals articulate with the cuboid and act as another, there can be significant motion between the 3rd and 4th metatarsals which can cause an irritation to the nerve that runs between them. This inflammation causes the pain. How is it treated? Pain can be momentarily relieved by massaging the affected interspace. Control of the abnormal transverse plane motion of the foot is successful in reducing the symptoms associated with a neuroma. Orthotics should be prescribed, as they will diminish excessive transverse plane rotation between the medial and lateral columns of the foot, reducing pain and inflammation caused by Morton s neuroma. In instances where the symptoms are non-responsive, a neuroma pad should be added as accommodation to assist in diminishing transverse plane metatarsal movement and compression. Neuromas present in additional interspaces can be successfully treated with functional foot orthotics used to control abnormal foot function in the propulsive phase of gait. The patient will likely experience some pain relief within weeks and complete recovery within months (generally 2-3 months, but may take as long as 12 months).
20 Ilio Tibial Band Syndrome (a.k.a. friction syndrome)
21 Ilio Tibial Band Syndrome ( friction syndrome ) What is it? The ilio tibial band runs from the hip to the lateral side of the proximal end of the tibia. Its function is to resist internal rotation of the tibia as well as to maintain the lateral integrity of the leg. Ilio tibial band friction syndrome is a condition wherein the ilio tibial band is stretched and torqued and the distal end rubs across the lateral condyle of the femur. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of pain on the lateral side of the knee often extending up the lateral side of the thigh as high as the hip. How is it caused? Overstress of the ilio tibial band. During a normal gait cycle, the femur and the tibia rotate in unison (i.e. internally during pronation and externally during supination); however, when a person overpronates, the tibia is locked into the talus by the saddle joint and therefore continues to rotate internally past the end of the contact phase while the femur begins to externally rotate with the pelvis during midstance phase. The resulting counter rotation of the femur and the tibia causes a shearing force to occur in the ilio tibial band is torqued and stretched. The result is that the distal end of the band rubs across and is irritated by the lateral condyle of the femur. How is it treated? Massage and stretching of surrounding muscles to help ease the tightness and ice to reduce inflammation. Since the problem is the abnormal pronation, the patient should be fitted with functional orthotics to correct the prolonged pronation thereby reducing the counter rotation between the femur and the tibia, alleviating stress off of the ilio tibial band.
22 Dropped Metatarsal
23 Dropped Metatarsal Head What is it? A dropped metatarsal head is a condition where one of the metatarsal bones (usually the second metatarsal) is lower than the others at the distal end. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients complain of pain and the sensation that they are walking on a stone. The patient will usually have a callus under the head of the dropped metatarsal. How is it caused? This condition is very common and the cause is considered to be almost strictly hereditary. Overpronation does play a role as abnormal weight distributions in an abnormally pronated foot tend to throw too much weight to the second metatarsal. How is it treated? Orthotics should be used to redistribute the pressure and off-load the dropped metatarsal head. A metatarsal pad should be added just proximal to dropped metatarsal to off-weight it and alleviate the pain.
24 Metatarsalgia
25 Metatarsalgia What is it? Generalized pain underneath the metatarsals. What are the common symptoms/complaints? Patients will complain of pain or tenderness on the plantar surface of the foot in the metatarsal area and/or diffused pain in the metatarsal joints. How is it caused? This condition is very common and the cause is abnormal weight distribution due to abnormal pronation. How is it treated? Orthotics should be worn to correct abnormal pronation and redistribute the weight more evenly along the plantar surface. If shoe fit allows, a metatarsal bar will assist by off-loading the metatarsal heads, alleviating pain localized under the metatarsal heads. Piriformis Syndrome
26 Piriformis muscle Sciatic nerve Superficial lateral view of location of the piriformis muscle Piriformis Syndrome Posterior view of sciatic nerve running interior to the piriformis muscle Piriformis Syndrome
27 What is it? The piriformis muscle originates on the sacrum and crosses over at a slightly downward angle to the outside of the hip, attaching to the lateral side of the femur. Its function is to laterally rotate and extend the hip joint. Piriformis syndrome is a condition in which the piriformis muscle irritates the sciatic nerve, causing pain in the buttocks and referred pain down the leg along the path of the sciatic nerve. What are the common symptoms/complaints? An irritating pain in the buttocks and referring pain down the leg along the path of the sciatic nerve. Pain is aggravated by sitting, squatting or walking. When relaxed, the affected leg is often externally rotated. How is it caused? If the leg has been externally rotated for an extended period of time (i.e. driving long distances) the piriformis muscle can shorten. Continual internal rotation of the femur (result of prolonged pronation and poor foot mechanics) can cause the piriformis muscle to overwork and therefore increase in size. In both instances, when the leg tries to straighten out (i.e. walking) the involved muscle compresses the sciatic nerve. How is it treated? Stretching of the piriformis muscle is necessary. Massage is helpful in relieving tightness. Faulty pelvic and foot mechanics need to be addressed. If internal rotation of the femur and prolonged pronation is evident, an orthotic device should be prescribed to arrest over-pronation and control the leg from internally rotating too much and too long.
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
How To Treat Heel Pain
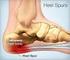 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital
 By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
PERFORMANCE RUNNING. Piriformis Syndrome
 Piriformis Syndrome Have you started to experience pain in your hip or down your leg while beginning or advancing your fitness program? This pain may be stemming from the piriformis muscle in your hip.
Piriformis Syndrome Have you started to experience pain in your hip or down your leg while beginning or advancing your fitness program? This pain may be stemming from the piriformis muscle in your hip.
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE
 KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
KINESIOLOGY TAPING GUIDE What is Kinesiology tape and how does Kinesiology tape work? How to apply Kinesiology tape Examples of application of UP Kinesiology tape for common injuries and conditions Introduction
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
Psoas Syndrome. The pain is worse from continued standing and from twisting at the waist without moving the feet.
 Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Patellofemoral/Chondromalacia Protocol
 Patellofemoral/Chondromalacia Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The knee is composed of two joints, the tibiofemoral and the patellofemoral. The patellofemoral joint is made up of the patella (knee cap)
Patellofemoral/Chondromalacia Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The knee is composed of two joints, the tibiofemoral and the patellofemoral. The patellofemoral joint is made up of the patella (knee cap)
What is Osteoarthritis? Who gets Osteoarthritis? What can I do when I am diagnosed with Osteoarthritis? What can my doctor do to help me?
 Knee Osteoarthritis What is Osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis is a disease process that affects the cartilage within a joint. Cartilage exists at the surface of the ends of the bones and provides joints with
Knee Osteoarthritis What is Osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis is a disease process that affects the cartilage within a joint. Cartilage exists at the surface of the ends of the bones and provides joints with
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014
 The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
The Forefoot Valgus Foot-Type Joe Fox, MS, LAT June 10, 2014 Introduction BS Kinesiology Exercise Science and Athletic Training, University of Wisconsin-Madison MS in Exercise Science Athletic Training,
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL. Focal Weakness. Ankle Dorsiflexion Weakness COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
 Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
Pathological Gait I: Musculoskeletal - 1 PATHOLOGIC GAIT -- MUSCULOSKELETAL Normal walking is the standard against which pathology is measured Efficiency is often reduced in pathology COMMON GAIT ABNORMALITIES
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity
 Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
Biomechanical Explanations for Selective Sport Injuries of the Lower Extremity DR. LEE S. COHEN Podiatric Consultant: Philadelphia Eagles Philadelphia 76ers Philadelphia Wings Understanding Normalcy What
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Dr. O Meara s. Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com
 Dr. O Meara s Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol Hamstring Stretching & Strengthening
Dr. O Meara s Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol www.palomarortho.com Anterior Knee Pain (PatelloFemoral Syndrome) Rehabilitation Protocol Hamstring Stretching & Strengthening
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
UK HealthCare Sports Medicine Patient Education December 09
 LCL injury Description Lateral collateral knee ligament sprain is a sprain (stretch or tear) of one of the four major ligaments of the knee. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a structure that helps
LCL injury Description Lateral collateral knee ligament sprain is a sprain (stretch or tear) of one of the four major ligaments of the knee. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a structure that helps
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention. Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015
 BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015 Epidemiology Overuse injuries most common, traumatic event second
BP MS 150 lunch and learn: Stretching and injury prevention Dr. Bart Kennedy (Sports Chiropractor) and Josh Thompson February 04, 2015 Epidemiology Overuse injuries most common, traumatic event second
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction
Hip Pain HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management
 HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 About your hip 2 Common causes of hip pain 3 Trochanteric bursitis/greater trochanter pain syndrome 4 Impingement 5 Referred
HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 About your hip 2 Common causes of hip pain 3 Trochanteric bursitis/greater trochanter pain syndrome 4 Impingement 5 Referred
KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association
 Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
How To Treat A Patella Dislocation
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Realignment The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in your thigh, and attaches by ligaments and a capsule to your tibia,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Realignment The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in your thigh, and attaches by ligaments and a capsule to your tibia,
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness. and pain
 TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
TIPS and EXERCISES for your knee stiffness and pain KNEE EXERCISES Range of motion exercise 3 Knee bending exercises 3 Knee straightening exercises 5 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES 6 AEROBIC EXERCISE 10 ADDITIONAL
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Shoulder Tendonitis. Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696
 Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage
 How it works. Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage Traditional stretching techniques simply cause increases in muscle length and can actually increase your chances of injury. Self-myofascial release
How it works. Self-Myofascial Release Foam Roller Massage Traditional stretching techniques simply cause increases in muscle length and can actually increase your chances of injury. Self-myofascial release
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
ACL RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The aim of your operation is to reconstruct the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) to restore knee joint stability. A graft,
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology
 Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics
 Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Functional Anatomy and Lower Extremity Biomechanics Eric Folmar, MPT, OCS Functional Lower Extremity Biomechanics The science of foot, ankle, knee and hip biomechanics and their relationships and interactions
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
EXCESSIVE LATERAL PATELLAR COMPRESSION SYNDROME (Chondromalacia Patella)
 EXCESSIVE LATERAL PATELLAR COMPRESSION SYNDROME (Chondromalacia Patella) Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Excessive lateral patellar compression syndrome is characterized by pain in the knee
EXCESSIVE LATERAL PATELLAR COMPRESSION SYNDROME (Chondromalacia Patella) Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Excessive lateral patellar compression syndrome is characterized by pain in the knee
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella
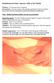 Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
BALANCED BODYWORKS LA Rejuvenate. Heal. Restore.
 Tools For Myofascial Self Massage and Stretching Foam Roller Lacrosse Ball (Hard) Stretch Strap What is Foam Rolling? Foam Rolling or Self Myofascial Release, is a form of soft tissue massage. Similar
Tools For Myofascial Self Massage and Stretching Foam Roller Lacrosse Ball (Hard) Stretch Strap What is Foam Rolling? Foam Rolling or Self Myofascial Release, is a form of soft tissue massage. Similar
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
Physical Therapy for Shoulder. Joseph Lorenzetti PT, DPT, MTC Catholic Health Athleticare Kenmore 1495 Military Road Kenmore, NY 14217
 Physical Therapy for Shoulder and Knee Pain Joseph Lorenzetti PT, DPT, MTC Catholic Health Athleticare Kenmore 1495 Military Road Kenmore, NY 14217 Physical Therapy for Shoulder and Knee Pain GOALS: Explain
Physical Therapy for Shoulder and Knee Pain Joseph Lorenzetti PT, DPT, MTC Catholic Health Athleticare Kenmore 1495 Military Road Kenmore, NY 14217 Physical Therapy for Shoulder and Knee Pain GOALS: Explain
Coccydynia. (Coccyx Pain) Information for patients. Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312
 Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy. Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego
 Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD Rady Children s Hospital - San Diego Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal hygiene problems
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation.
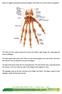 Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Physical Therapy Corner: Knee Injuries and the Female Athlete
 Physical Therapy Corner: Knee Injuries and the Female Athlete Knee injuries, especially tears of the anterior cruciate ligament, are becoming more common in female athletes. Interest in women s athletics
Physical Therapy Corner: Knee Injuries and the Female Athlete Knee injuries, especially tears of the anterior cruciate ligament, are becoming more common in female athletes. Interest in women s athletics
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Evaluating Knee Pain
 Evaluating Knee Pain Matthew T. Boes, M.D. Raleigh Orthopaedic Clinic September 24, 2011 Introduction Approach to patient with knee pain / injury History Examination Radiographs Guidelines for additional
Evaluating Knee Pain Matthew T. Boes, M.D. Raleigh Orthopaedic Clinic September 24, 2011 Introduction Approach to patient with knee pain / injury History Examination Radiographs Guidelines for additional
Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery
 Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery Sports Medicine Achilles Tendon Repair Surgery Post-operative Instructions Phase One: The First Week After Surgery Amon T. Ferry, MD Orthopedic Surgery / Sports Medicine
Pilates for Plantar Fasciitis
 Pilates for Plantar Fasciitis Written by: Heather Light Date: August, 2011 This is a student paper, submitted to BASI Pilates by the writer as a requirement for completion of the BASI Pilates Comprehensive
Pilates for Plantar Fasciitis Written by: Heather Light Date: August, 2011 This is a student paper, submitted to BASI Pilates by the writer as a requirement for completion of the BASI Pilates Comprehensive
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The arthroscope is a fibre-optic telescope that can be inserted into a joint. A camera is attached to the arthroscope and the
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME ABOUT THE OPERATION The arthroscope is a fibre-optic telescope that can be inserted into a joint. A camera is attached to the arthroscope and the
Injury Prevention. Presented by: John Furey Master Trainer, Fitcorp. jfurey@fitcorp.com
 Injury Prevention Presented by: John Furey Master Trainer, Fitcorp Injury Prevention 1. Causes of injury 2. Warm-up and stretching & cool down 3. Cross-training 4. What pain is okay? 5. What to do when
Injury Prevention Presented by: John Furey Master Trainer, Fitcorp Injury Prevention 1. Causes of injury 2. Warm-up and stretching & cool down 3. Cross-training 4. What pain is okay? 5. What to do when
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion
 A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
A Patient s Guide to Arthritis of the Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus) With Discussion on Cheilectomy and Fusion The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot
 Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
Pathomechanics, Gait Deviations, and Treatment of the Rheumatoid Foot A Clinical Report PHYLLIS DIMONTE and HOLLIS LIGHT This article describes the five major foot deformities or problems often seen in
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
