MAP - Mobile Application Part
|
|
|
- Jodie Welch
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 - Mobile Application Part Mobility Management in GSM GSM services Short Message Service CAMEL = IN+GSM integration Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-1 Course scope - lecture scope H.323 or SIP IP SIP or ISUP CAS, R2 IP PABX ISDN Switching Fabric Voice path CCS7 ISUP AN V5 Control Part INAP SCP Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-2
2 GSM system consists of 4 sub-systems Radio or Air i/f A-interface MS = ME+SIM Base Station Sub-system (BSS) Network Sub-System (NSS) O&M Network Management Sub-system MS - Mobile Station ME - Mobile Equipment SIM - Subscriber Identity Module BSS - Base Station Subsystem NSS - Network Sub-System Main differences cmp to wire-line networks - air interface for the subscribers - mobility and roaming of users NB: the whole system is digital incl the ME. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-3 NSS interfaces are G E (B) D C F EIR std A Base Station sub-system - Mobile Switching Center - Home Location Register - Visitor Location Register EIR - Equipment Identity Register NB: + always in the same node +H-interface: - SMS Gateway interface +I - interface: MS - (MS-/-) All NSS interfaces: B-H conform to the protocol Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-4
3 Milestones in development 1 phase 1 2 phase 2 Phase 2+ Release96 Release97 In phase 2+ versioning is per operation package.... This supports the idea of deploying small sets of features at a time in the network. If the remote systems does not understand the newest tricks, fall-back negotiation restores operation on the level of the previous version. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology operations can be mapped to interfaces I/f Elements Mobility management O&M Call handling Supplementary services Short messages B C G- 1 1 D E F -EIR 1 1 G SMSGW SMSGW 1 1 Sum Sum The table corresponds to v2 This lecture does not discuss - interface operations nor O&M -operations. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-6
4 Addressing messages GT= , PC=7896 EIR AuC (Authentication GT= , PC=7895 centre) TCAP SSN=8 TCAP SSN=7 TCAP SSN=6 TCAP SSN=9 TCAP SSN=6 SCCP MTP SCCP MTP GT formats: IMSI MCC MSISDN CC Hybrid CC MNC NDC NDC MSIN SN MSIN GT - Global Title PC - Point Code MCC - Mobile Country Code CC - Country Code MNC - Mobile Network Code NDC - National Destination Code MSIN - Mobile Subscriber Identity Number SN - Subscriber Number Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-7 uses the structured dialogue provided by TCAP TC-INVOKE-req TC-INVOKE-req TC TR TC- BEGIN-req TR-BEGIN-req BEGIN TC- CONTINUE-req TR-CONTINUE-req CONTINUE TC-CONTINUE-ind TC-END-ind TR-CONTINUE-ind TR-END-ind CONTINUE END Begin causes a transaction identifier to be reserved. The remote system can either continue the transaction or close it. Continue - messages are exchanged in a full-duplex mode. Closing options: based on pre-arrangement independently normally by the End-message or abnormally by an Abort message Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-8
5 Mobility management is the most important feature in Location management Handover - during a call handover is supported on many levels - also BSSAP (A- i/f protocol) is needed, but we do not cover that here Authentication and security IMEI - mobile equipment id queries Subscriber management Fault recovery Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-9 Home Location Register - - contains subscriber and service information IMSI Subscriber information (location, etc) MSISDN Service info (voice, fax, blocking modes, etc) In a mobile terminated call, the right can be found based on a prefix in MSISDN or if free numbering within the operator network is supported, a Global Title (MSISDN is embedded in the GT in SCCP) translation needs to be done first e.g. in a specific network element. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-10
6 Location management maintains the location of the MSs in the () SendIdentification () /D UpdateLocation CancelLocation PurgeMS SendIdentification requests MS info (IMSI, authentication) from the previous. UpdateLocation updates the new location with the accuracy of a area With PurgeMS tells to that MS is unreachable. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology With query the MS is found in a Mobile terminated call /C /D PSTN G ISUP - IAM SendRoutingInformation ProvideRoamingNumber ProvideRoamingNumberACK SendRoutingInformationACK ISUP - IAM MSRN - Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number - conforms to E.164 format (any exchange can pass along the number) - each has a limited range of MSRNs - MSRN has a validity timeout - MSRN may be allocated on a call be call basis or for the duration of the visit Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-12
7 Handover from to /E /E -A -B -B PrepareHandover Call control responsibility remains in -A ProcessAccessSignalling SendEndSignal (-B and MS have radio channel) ForwardAccessSignalling PrepareSubsequentHandover mirrors A-interface to -A Transports messages to be sent to the A-interface PrepareHandover SendEndSignal Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Security operations ensure that only authorized subscribers can use the service /D EIR SendAuthenticationInfo CheckIMEI Black list of suspect stolen phones ensures that stolen equipment can not be used for long Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-14
8 Subscriber management takes care of the subscriber data /D InsertSubscriberData DeleteSubscriberData When the operator or the subscriber have changed any of subscriber data. When location has been updated. When a basic or a supplementary service is cancelled. With these operations all information residing in the, can be manipulated, when the has the master copy of the information. ( does not have some detailed location info ) Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Supplementary service operations are passed from MS via / to MS --> / --> RegisterSS EraseSS ActivateSS DeactivateSS InterrogateSS RegisterPassword Activation of call forwarding Switching off supplementary services Activation of call blocking Deactivation of supplementary services Interrogation of supplementary service settings Password setting for SS GetPassword USSD operations Password query to MS Unstructured SS data transport Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-16
9 USSD - Unstructured Supplementary Service Data transports SS data between MS and the network Network destinations can be e.g.,, -> SCP, WWW-server Data is in ascii (cmp DTMF) E.g. WAP - Wireless Application Protocol can in principle use the USSD service a latecomer among features Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology USSD uses the structured dialogue of TCAP Dialogue is connection oriented A Dialogue has an identity Are independent of calls Message length is 80 octets, having max 91 Ascii characters a 7-bits 1 octet 80 octets DCS DCS - Data Coding Scheme USSD-string Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-18
10 USSD dialogue can be initiated by MS (pull) or by a server (push) / ProcessUnstructuredSSRequest ProcessUnstructuredSSRequest Server UnstructuredSSRequest UnstructuredSSRequest ACK UnstructuredSSRequest UnstructuredSSRequest ACK Release UnstructuredSSRequest UnstructuredSSRequest ACK UnstructuredSSRequest UnstructuredSSRequest ACK An arbitrary nrof of requests Release Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Short Message Service SMS-IW S store SMS-G MO-SMS MT-SMS S SMS-G - Short Message Service Center (or SC - Service Center) - Short message Gateway, issuer of routing information query to in MT-SMS SMS-IW - Short message Inter-working, routing in MO-SMS service SMS-GW = SMS-IW + SMS-G MO - Mobile Originated MT - Mobile Terminated S - operations: - MS short message buffer full - MS reachability - successful delivery of message Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-20
11 Short message transport protocol stack SME S SMS-G/ SMS-IW MS/SCP SM-AP SM-TP SM-RP SM-LP SM-RP SM-LP SM-RP SM-LP SM-AP SM-TP SM-RP SM-LP ForwardShortMessage User Info TCAP SCCP MTP Non standard SME - Short Message Entity SM-LP - Short Message Link Protocol SM-RP - Short Message Relay Protocol SM-TP - Short Message Transfer Protocol SM-AP - Short Message Application Protocol Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Messages in MO-SMS service DTAP /E Vendor specific SMS- IW S ForwardSM ForwardSM ACK SubmitSM SubmitSM ACK Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-22
12 Messages in MT-SMS service S Vendor specific DeliverSM SMS- G SendRoutingInfoForSM SRIForSMResult ForwardSM DeliverSM ACK ForwardSM ACK Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Status information is kept in SMS- G ReadyForSM MS has again a non-full buffer or it has become reachable ReportSMDeliveryStatus InformServiceCenter Messages waiting/ successful delivery SMS- IW AlertServiceCenter SM destination subscriber can tell the network, that its SM buffer is full or that the subscriber has become unreachable. stores the status. When Status is good for receiving, gets the info and sends it to. informs those Ss that have reported themselves onto the waiting list. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-24
13 Addressing of Short messages MO-SMS Submit service MT-SMS Deliver service S+ SMS-IW SMS-G SCCP-DA: S(GT) -DA: S(GT) -OA: A-MSISDN SM-TP-DA: B-MSISDN SCCP-DA: (GT) -DA: IMSI(GT) -OA: S(GT) SM-TP-OA: A-MSISDN S gets the IMSI of the B subscriber and the address of the V by SRIForSM operation from the. NB: Addresses are on three protocol layers! Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology CAMEL adapts the IN technology to GSM CAMEL - Customized Application for Mobile network Enhanced Logic The goal is the capability of providing the home network services to visiting subscribers CAP - CAMEL Application Part is a subset of ETSI CoreINAP phases (Capability Sets) 1 and 2 are ready Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-26
14 IN is a way of implementing services in nodes separate from exchanges SRF SCE INAP Network of STP nodes SSF CCF exchange SMP SCF INAP INAP SDF SSF CCF exchange INAP = IN Application Part = main protocol SSF - Service Switching Function maintains call state with CCF SCF - Service Control Function implements service logic SRF - Special Resource Function processes in-band signals SDF - Service Data Function is a database SCE - Service Creation Environment for creating new service logic SMP - Service Management Point implements mgt functions Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology Features of the IN architecture... BCSM - Basic Call State Model is a standardized state machine in SSP - couples/ de-couples IN service logic from connection resources BCSM states (detection points) can be programmed to trigger on conditions queries to an SCF concerning a certain call BCSM architectural issue is that a call is also a service and therefore the architecture is service dependent INAP messages are independent of voice channel connections Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-28
15 Phase 1 CAMEL architecture Home network gsmscf Requesting network CAP CAP Visited network Incoming call gsmssf G roaming leg gsmssf rerouteing MO outgoing call or rerouteing Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology MS originated CAMEL call / + gsmssf A C CAP-InitialDP CAP-Connect ISUP-IAM gsmscf B PSTN A - gets the CAMEL service info from the concerning the A subscriber, sees an active CAMEL service and hands the call to gsmssf. gsmssf queries gsmscf:lle (service key, A-nr, B-nr, IMSI, location... B - gsmscf can for example do a number translation C - sets up a call using the received info Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-30
16 Mobile terminated CAMEL call PSTN G + gsmssf gsmscf ISUP-IAM ISUP-IAM A B -SendRoutingInfo -SRInfoResult CAP-InitialDP CAP-Connect C A - G queries of the location of the MS. sends the terminating CAMEL service data of the subscriber. B - G hands the call to gsmssf, which queries gsmscf gsmscf returns C-number that is used for routeing the call C - G sets up the call to C-number. If needed, G can first do a new query. Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology IN+GSM integration based on CAMEL is a step towards 3G CAPv1 supports only 7 operations CAPv1 call model has only a few triggering points (TDP - trigger detection point) CAPv2 has 22 operations Still no triggering for Short Messages CAMEL compatible equipment is in use in many networks Raimo Kantola/ k2002 Telecommunications Switching Technology 17-32
GSM and IN Architecture
 GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP Raimo.Kantola@netlab.hut.fi Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET
 Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Dodatek 1 - wyja nienie skrótów UTE Marek redniawa
 skrótów AC AE AEI AIN ASE APDU ASN.1 BCP BCSM CAMEL CAP CCAF CCF CID CK CPH Application Context Application Entity Application Entity Invocation Advanced Intelligent Network Application Service Element
skrótów AC AE AEI AIN ASE APDU ASN.1 BCP BCSM CAMEL CAP CCAF CCF CID CK CPH Application Context Application Entity Application Entity Invocation Advanced Intelligent Network Application Service Element
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network
 Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin (po@p1sec.com) Alexandre De Oliveira (alex@p1sec.com) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
SS7: Locate. Track. Manipulate.
 You have a remote-controlled tracking device in your pocket Tobias Engel @2b_as 2 Signalling System #7 Protocol suite used by most telecommunications network operators throughout the world
You have a remote-controlled tracking device in your pocket Tobias Engel @2b_as 2 Signalling System #7 Protocol suite used by most telecommunications network operators throughout the world
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols
 Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols SS7 is a set of telephony signaling protocols that are used to set up
Introduction to SS7 Signaling This tutorial provides an overview of Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network architecture and protocols SS7 is a set of telephony signaling protocols that are used to set up
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Intelligent Networks. John Anderson. Principles and ApplicaHons. The Institution of Electrical Engineers
 Intelligent Networks Principles and ApplicaHons John Anderson The Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Preface Acknowledgments Introduction to intelligent networks. The basics of intelligent networks..
Intelligent Networks Principles and ApplicaHons John Anderson The Institution of Electrical Engineers Contents Preface Acknowledgments Introduction to intelligent networks. The basics of intelligent networks..
Mobile Networking. SS7 Network Architecture. Purpose. Mobile Network Signaling
 Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Service aspects; Advanced Addressing (UMTS 22.75 version 3.0.0)
 TSG-SA Working Group 1 (Services) meeting #2 Edinburgh, Scotland 9 th -12 th March 1999 TSGS1#2(99)122 Agenda Item: 9.10 Source: Coordinator Title: Document for: Information I Universal Mobile Telecommunications
TSG-SA Working Group 1 (Services) meeting #2 Edinburgh, Scotland 9 th -12 th March 1999 TSGS1#2(99)122 Agenda Item: 9.10 Source: Coordinator Title: Document for: Information I Universal Mobile Telecommunications
GSM Voice Mail Service TDM Call Control
 IT 12 072 Examensarbete 30 hp December 2012 GSM Voice Mail Service TDM Call Control Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Institutionen för informationsteknologi Department of Information Technology Abstract GSM Voice
IT 12 072 Examensarbete 30 hp December 2012 GSM Voice Mail Service TDM Call Control Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Institutionen för informationsteknologi Department of Information Technology Abstract GSM Voice
Introduction. Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Common Channel Signaling (CCS) Still widely deployed today Considered as old technology
 VoIP and SS7 Introduction Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Still widely deployed today Considered as old technology Common Channel Signaling (CCS) Separation of signaling and call paths Signaling System
VoIP and SS7 Introduction Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Still widely deployed today Considered as old technology Common Channel Signaling (CCS) Separation of signaling and call paths Signaling System
ETSI TR 122 975 V3.1.0 (2000-01)
 ETSI TR 122 975 V3.1.0 (2000-01) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Service aspects; Advanced Addressing (3G TR 22.975 version 3.1.0 Release 1999) (3G TR 22.975 version
ETSI TR 122 975 V3.1.0 (2000-01) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Service aspects; Advanced Addressing (3G TR 22.975 version 3.1.0 Release 1999) (3G TR 22.975 version
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
An Oracle White Paper November 2013. Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers
 An Oracle White Paper November 2013 Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers Disclaimer The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended
An Oracle White Paper November 2013 Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers Disclaimer The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration
 Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Definition The convergence of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol (IP) data networks promises exciting opportunities
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Definition The convergence of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol (IP) data networks promises exciting opportunities
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting. Tcl used for testing in the mobile world
 4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
ETSI TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12)
 TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN. Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
ETSI ETR 186-1 TECHNICAL September 1995 REPORT
 ETSI ETR 186-1 TECHNICAL September 1995 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SPS Reference: DTR/SPS-03011-1 ICS: 33.080 Key words: IN, INAP, CS1, ISDN, interaction, signalling Intelligent Network (IN); Interaction between
ETSI ETR 186-1 TECHNICAL September 1995 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SPS Reference: DTR/SPS-03011-1 ICS: 33.080 Key words: IN, INAP, CS1, ISDN, interaction, signalling Intelligent Network (IN); Interaction between
1. Public Switched Telephone Networks vs. Internet Protocol Networks
 Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
Internet Protocol (IP)/Intelligent Network (IN) Integration Tutorial Definition Internet telephony switches enable voice calls between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Internet protocol
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
MODELLING OF INTELLIGENCE IN INTERNET TELEPHONE SYSTEM
 MODELLING OF INTELLIGENCE IN INTERNET TELEPHONE SYSTEM Evelina Nicolova Pencheva, Vessela Liubomirova Georgieva Department of telecommunications, Technical University of Sofia, 7 Kliment Ohridski St.,
MODELLING OF INTELLIGENCE IN INTERNET TELEPHONE SYSTEM Evelina Nicolova Pencheva, Vessela Liubomirova Georgieva Department of telecommunications, Technical University of Sofia, 7 Kliment Ohridski St.,
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
How To Connect Gsm To Ip On A Gsm Network On A Pnet On A Microsoft Cell Phone On A Pc Or Ip On An Ip Onc (Gsm) On A Network On An Iph (Gms) On An
 THE STUDY OF THE INTERCONNECTION OF GSM MOBILE COMMUNCATION SYSTEM OVER IP BASED NETWORK+ Le-Pond Chin. Jyh-Hong Wen2, and Ting-Way Liu Department of Information Management Shih-Chien University, Taipei,
THE STUDY OF THE INTERCONNECTION OF GSM MOBILE COMMUNCATION SYSTEM OVER IP BASED NETWORK+ Le-Pond Chin. Jyh-Hong Wen2, and Ting-Way Liu Department of Information Management Shih-Chien University, Taipei,
Tutorial on Signaling System 7 (SS7) Performance Technologies www.pt.com
 Tutorial on Signaling System 7 (SS7) Performance Technologies Table of Contents Topic Page Overview...3 Signaling Links...3 Signaling Points...3 SS7 Signaling Link Types...4 SS7 Protocol Stack...6 Message
Tutorial on Signaling System 7 (SS7) Performance Technologies Table of Contents Topic Page Overview...3 Signaling Links...3 Signaling Points...3 SS7 Signaling Link Types...4 SS7 Protocol Stack...6 Message
Draft ETSI EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08)
 Draft EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Support of Mobile Number Portability (MNP); Technical Realisation;
Draft EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Support of Mobile Number Portability (MNP); Technical Realisation;
Session 6 - Operator Implementation Overview
 Session 6 - Operator Implementation Overview Orange Labs Philippe Fouquart, Research & Development 21 May 2011 Restricted ITU-T NP regional seminar Overview Introduction Problem statement for NP for an
Session 6 - Operator Implementation Overview Orange Labs Philippe Fouquart, Research & Development 21 May 2011 Restricted ITU-T NP regional seminar Overview Introduction Problem statement for NP for an
EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server
 Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Cleep Solution Description
 Cleep Solution Description LLC "Big Data Technology" ID: 1137746981932 www.carriers-capital.com Contents 1 Cleep Solution Overview... 1 2 Solution components... 1 3 Call Flow... 2 4 Physical Connectivity
Cleep Solution Description LLC "Big Data Technology" ID: 1137746981932 www.carriers-capital.com Contents 1 Cleep Solution Overview... 1 2 Solution components... 1 3 Call Flow... 2 4 Physical Connectivity
Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification
 Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Version 1.1 Edition 7.20141001 Updated October 25, 2014 Distributed with Package openss7-1.1.7.20141001
Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Version 1.1 Edition 7.20141001 Updated October 25, 2014 Distributed with Package openss7-1.1.7.20141001
This tutorial gives provides an introduction to the terms and structure of the Signalling System Number 7 (SS7) protocol.
 Public Network Signalling This tutorial gives provides an introduction to the terms and structure of the Signalling System Number 7 (SS7) protocol. What is a signalling protocol? The SS7 Protocol Message
Public Network Signalling This tutorial gives provides an introduction to the terms and structure of the Signalling System Number 7 (SS7) protocol. What is a signalling protocol? The SS7 Protocol Message
EP 1 675 420 A1 (19) (11) EP 1 675 420 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: 28.06.2006 Bulletin 2006/26
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 67 4 A1 (43) Date of publication: 28.06.06 Bulletin 06/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04Q 7/34
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 67 4 A1 (43) Date of publication: 28.06.06 Bulletin 06/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04Q 7/34
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS)
 Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) Definition Short message service (SMS) is a globally accepted wireless service that enables the transmission of alphanumeric messages between mobile subscribers and
3G TR 21.978 V3.0.0 (2000-06)
 Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Feasibility Technical Report CAMEL Control of VoIP Services (Release 1999) The present document has been
Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Feasibility Technical Report CAMEL Control of VoIP Services (Release 1999) The present document has been
Technical Specification Railway Telecommunications (RT); Rel-4 Core Network requirements for GSM-R
 TS 103 066 V1.1.2 (2012-04) Technical Specification Railway Telecommunications (RT); Rel-4 Core Network requirements for GSM-R 2 TS 103 066 V1.1.2 (2012-04) Reference RTS/RT-00019 Keywords BICC, R-GSM
TS 103 066 V1.1.2 (2012-04) Technical Specification Railway Telecommunications (RT); Rel-4 Core Network requirements for GSM-R 2 TS 103 066 V1.1.2 (2012-04) Reference RTS/RT-00019 Keywords BICC, R-GSM
Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions
 Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions Today s and the next generation networks use the Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) to exchange information within and between the networks.
Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions Today s and the next generation networks use the Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) to exchange information within and between the networks.
II. Service deployment
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 9, No 3 Sofia 2009 Integration of Services Implemented on Different Service Platforms Evelina Pencheva, Ivaylo Atanasov Technical
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 9, No 3 Sofia 2009 Integration of Services Implemented on Different Service Platforms Evelina Pencheva, Ivaylo Atanasov Technical
SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005
 UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
( ETSI Ad Hoc Group on Fixed/Mobile Convergence - Final Report - 11 March 1998) (1) Telecom Italia, V. di Valcannuta 250, Rome (Italy)
 (1) Telecom Italia, V. di Valcannuta 250, Rome (Italy) (2) Telecom Italia, V. di Valcannuta 250, Rome (Italy (3) CSELT, V. R. Romoli, 274 Turin (Italy) The term convergence is more and more associated
(1) Telecom Italia, V. di Valcannuta 250, Rome (Italy) (2) Telecom Italia, V. di Valcannuta 250, Rome (Italy (3) CSELT, V. R. Romoli, 274 Turin (Italy) The term convergence is more and more associated
GeoMatrix. Positioning of Mobile Phones System
 GeoMatrix Positioning of Mobile Phones System Geographic intelligence is one of the oldest forms of military intelligence, and one of the most important. From earliest times, an accurate knowledge and
GeoMatrix Positioning of Mobile Phones System Geographic intelligence is one of the oldest forms of military intelligence, and one of the most important. From earliest times, an accurate knowledge and
3GPP TS 23.082 V8.0.0 (2008-12)
 TS 23.082 V8.0.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Call Forwarding (CF) supplementary services; Stage 2 (Release
TS 23.082 V8.0.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Call Forwarding (CF) supplementary services; Stage 2 (Release
Error and Confirmation Codes
 Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
Error and Confirmation s The following two tables list the error and confirmation codes that can be returned within SMS replies or notifications. Table 14: Error s 8 008 10 00A 21 015 27 01B 28 01C 29
ISDN User Part - ISUP
 ISDN User Part - - ISDN User Part /TUP brief comparison additional features Interworking of signaling systems is an international and national network signaling system for call setup, supervision and release.
ISDN User Part - - ISDN User Part /TUP brief comparison additional features Interworking of signaling systems is an international and national network signaling system for call setup, supervision and release.
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 03.07 TECHNICAL November 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030307Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
M E M O R A N D U M. Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities
 M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: RE: Mr. Jim Bugel, AT&T David Robinson, Syniverse Technologies Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities DATE: December 13, 2007 Automatic wireless roaming
M E M O R A N D U M TO: FROM: RE: Mr. Jim Bugel, AT&T David Robinson, Syniverse Technologies Wireless Roaming Services for Emergency Medical Facilities DATE: December 13, 2007 Automatic wireless roaming
Cellular Technology Sections 6.4 & 6.7
 Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
GSM GSM 09.08 TECHNICAL April 1997 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 09.08 TECHNICAL April 1997 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030908QR ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 09.08 TECHNICAL April 1997 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030908QR ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE
 INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE Voice over LTE SUBSCRIBER TECHNOLOGY White Paper Mobile operators have invested a lot of time and money in Intelligent Network (IN) services for
INTELLIGENT NETWORK SERVICES MIGRATION MORE VALUE FOR THE Voice over LTE SUBSCRIBER TECHNOLOGY White Paper Mobile operators have invested a lot of time and money in Intelligent Network (IN) services for
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
SS7 & LTE Stack Attack
 SS7 & LTE Stack Attack Ankit Gupta Black Hat USA 2013 akg0x11@gmail.com Introduction With the evolution of IP network, Telecom Industries are using it as their core mode of communication for their network
SS7 & LTE Stack Attack Ankit Gupta Black Hat USA 2013 akg0x11@gmail.com Introduction With the evolution of IP network, Telecom Industries are using it as their core mode of communication for their network
Global Roadmap for SMG and SA plenary WIs Document for: Information Agenda Item: 7
 Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Meeting #4, Miami, USA, 21-23 June 1999 TSGS#4(99)330 Source: MCC Title: Global Roadmap for SMG and SA plenary WIs Document for: Information Agenda
Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Meeting #4, Miami, USA, 21-23 June 1999 TSGS#4(99)330 Source: MCC Title: Global Roadmap for SMG and SA plenary WIs Document for: Information Agenda
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke uwe@iig.uni-freiburg.de Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
EUROPEAN ETS 300 374-1 TELECOMMUNICATION September 1994 STANDARD
 EUROPEAN ETS 300 374-1 TELECOMMUNICATION September 1994 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-SPS Reference: DE/SPS-03015 ICS: 33.020, 33.080 Key words: IN, CS1, INAP Intelligent Network (IN); Intelligent Network Capability
EUROPEAN ETS 300 374-1 TELECOMMUNICATION September 1994 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-SPS Reference: DE/SPS-03015 ICS: 33.020, 33.080 Key words: IN, CS1, INAP Intelligent Network (IN); Intelligent Network Capability
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
3GPP TSG CN Plenary Meeting #16 5 th - 7 th June 2002. Marco Island, USA. 3GPP TSG-CN1 Meeting #24 Tdoc N1-021455 Budapest, Hungary, 13. 17.
 3GPP TSG CN Plenary Meeting #16 5 th - 7 th June 2002. Marco Island, USA. NP-020155 Title: Liaison Statement on 3GPP Network Domain Name usage for IMS Source: CN1 Agenda item: 5.1 Document for: INFORMATION
3GPP TSG CN Plenary Meeting #16 5 th - 7 th June 2002. Marco Island, USA. NP-020155 Title: Liaison Statement on 3GPP Network Domain Name usage for IMS Source: CN1 Agenda item: 5.1 Document for: INFORMATION
- SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Repository (as of August 2011)
 - SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Reposiry (as of August 2011) Table 1 - ANSI SS7 Translation Type (TT) code value known assignments: Use of the following TT values are recommended (although the use of other values
- SS7 TT & SSN Assignment Reposiry (as of August 2011) Table 1 - ANSI SS7 Translation Type (TT) code value known assignments: Use of the following TT values are recommended (although the use of other values
Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications
 Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications CRISTIAN TOMA, MARIUS POPA, CATALIN BOJA Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Romana Square No. 6, Bucharest ROMANIA cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
Solution for Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP Applications CRISTIAN TOMA, MARIUS POPA, CATALIN BOJA Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Romana Square No. 6, Bucharest ROMANIA cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
LTE Tutorial GSM Tutorial i
 GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
IMT-2000 Network Architecture
 IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
White paper. SIP An introduction
 White paper An introduction Table of contents 1 Introducing 3 2 How does it work? 3 3 Inside a normal call 4 4 DTMF sending commands in sip calls 6 5 Complex environments and higher security 6 6 Summary
White paper An introduction Table of contents 1 Introducing 3 2 How does it work? 3 3 Inside a normal call 4 4 DTMF sending commands in sip calls 6 5 Complex environments and higher security 6 6 Summary
3GPP TS 23.003 V5.11.0 (2006-06)
 TS 23.003 V5.11.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Numbering, addressing and identification (Release 5) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR
TS 23.003 V5.11.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Numbering, addressing and identification (Release 5) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
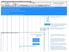 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Mobile Communication Systems: DECT Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication
 Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Message Generator and Traffic Simulator (MGTS)
 Message Generator and Traffic Simulator (MGTS) Next-generation wireless networks are evolving into "all-ip" architectures, and SS7 over Internet Protocol (IP) is becoming more prevalent as intelligent
Message Generator and Traffic Simulator (MGTS) Next-generation wireless networks are evolving into "all-ip" architectures, and SS7 over Internet Protocol (IP) is becoming more prevalent as intelligent
A Model For Network and Telecommunication Global Service Convergence
 A Model For Network and Telecommunication Global Service Convergence Claude Rigault e-mail rigault@res.enst.fr Abstract Bearer service convergence between networks and telecommunication is briefly described
A Model For Network and Telecommunication Global Service Convergence Claude Rigault e-mail rigault@res.enst.fr Abstract Bearer service convergence between networks and telecommunication is briefly described
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
SIP : Session Initiation Protocol
 : Session Initiation Protocol EFORT http://www.efort.com (Session Initiation Protocol) as defined in IETF RFC 3261 is a multimedia signaling protocol used for multimedia session establishment, modification
: Session Initiation Protocol EFORT http://www.efort.com (Session Initiation Protocol) as defined in IETF RFC 3261 is a multimedia signaling protocol used for multimedia session establishment, modification
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]
![[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]](/thumbs/26/8506801.jpg) JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
The Intel NetStructure SIU520 Signaling Interface
 The Intel NetStructure SIU520 Signaling Interface Intel in Communications The Intel NetStructure SIU520 signaling interface unit (SIU) provides Signaling System 7 (SS7) connectivity for multichassis call
The Intel NetStructure SIU520 Signaling Interface Intel in Communications The Intel NetStructure SIU520 signaling interface unit (SIU) provides Signaling System 7 (SS7) connectivity for multichassis call
Dialogic Distributed Signaling Interface Protocol Stacks
 Dialogic Dialogic (DSI) support a range of Signaling System 7 (SS7) and IETF SIGTRAN specifications to provide solid building blocks for the most advanced applications. These signaling protocols have been
Dialogic Dialogic (DSI) support a range of Signaling System 7 (SS7) and IETF SIGTRAN specifications to provide solid building blocks for the most advanced applications. These signaling protocols have been
INTRODUCTION TO SIEMENS MOBILE NETWORKS
 INTRODUCTION TO SIEMENS MOBILE NETWORKS Algiers 28.02.2001 Imad Moussa imad.moussa@siemens.com.lb 1 Introduction to Siemens Mobile Networks Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) System Architecture Mobile
INTRODUCTION TO SIEMENS MOBILE NETWORKS Algiers 28.02.2001 Imad Moussa imad.moussa@siemens.com.lb 1 Introduction to Siemens Mobile Networks Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) System Architecture Mobile
CRs to GSM 03.03 on SSN reallocation
 ETSI SMG#29 Miami, Fl. USA, 23 25 June 1999 Document P-99-462 Source: Title: ETSI SMG3 CRs to GSM 03.03 on SSN reallocation Document for: Decision Attention: Agenda item 6.3 Introduction: SM TDoc SPEC
ETSI SMG#29 Miami, Fl. USA, 23 25 June 1999 Document P-99-462 Source: Title: ETSI SMG3 CRs to GSM 03.03 on SSN reallocation Document for: Decision Attention: Agenda item 6.3 Introduction: SM TDoc SPEC
IP Telephony and Network Convergence
 IP Telephony and Network Convergence Raimo.Kantola@hut.fi Rkantola/28.11.00/s38.118 1 Today corporations have separate data and voice networks Internet Corporate Network PSTN, ISDN Rkantola/28.11.00/s38.118
IP Telephony and Network Convergence Raimo.Kantola@hut.fi Rkantola/28.11.00/s38.118 1 Today corporations have separate data and voice networks Internet Corporate Network PSTN, ISDN Rkantola/28.11.00/s38.118
Internet, Part 2. 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support. 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility)
 Internet, Part 2 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility) 4) Mobile IP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) SIP is a protocol
Internet, Part 2 1) Session Initiating Protocol (SIP) 2) Quality of Service (QoS) support 3) Mobility aspects (terminal vs. personal mobility) 4) Mobile IP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) SIP is a protocol
Feature and Technical
 BlackBerry Mobile Voice System for SIP Gateways and the Avaya Aura Session Manager Version: 5.3 Feature and Technical Overview Published: 2013-06-19 SWD-20130619135120555 Contents 1 Overview...4 2 Features...5
BlackBerry Mobile Voice System for SIP Gateways and the Avaya Aura Session Manager Version: 5.3 Feature and Technical Overview Published: 2013-06-19 SWD-20130619135120555 Contents 1 Overview...4 2 Features...5
Product report GSM Call Service
 Product report GSM Call Service 1DT054 Project CS Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Egemen Taskin Erik Grafström Fartash M. Nejad Fredrik Pasanen Max Morén Mohammadreza Taghilu Moritz Rogalli Praveenkumar Bhadrapur
Product report GSM Call Service 1DT054 Project CS Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Egemen Taskin Erik Grafström Fartash M. Nejad Fredrik Pasanen Max Morén Mohammadreza Taghilu Moritz Rogalli Praveenkumar Bhadrapur
SIGNALING SYSTEM 7 (SS7) SECURITY REPORT
 SIGNALING SYSTEM 7 () SECURITY REPORT Page CONTENTS. Introduction. Summary 4. Research methodology 5 Preconditions for attacks 5 An attacker s profile 5 Resources required 5 4. Research overview 6 4..
SIGNALING SYSTEM 7 () SECURITY REPORT Page CONTENTS. Introduction. Summary 4. Research methodology 5 Preconditions for attacks 5 An attacker s profile 5 Resources required 5 4. Research overview 6 4..
An Example of Mobile Forensics
 An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk k.c.hilton@staffs.ac.uk www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk k.c.hilton@staffs.ac.uk www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
Protecting Mobile Networks from SS7 Attacks. Telesoft White Papers
 Protecting Mobile Networks from SS7 Attacks Telesoft White Papers Christian Feest 23rd June 2015 SS7 Networks The Challenge The problem with the current SS7 system is that messages can be altered, injected
Protecting Mobile Networks from SS7 Attacks Telesoft White Papers Christian Feest 23rd June 2015 SS7 Networks The Challenge The problem with the current SS7 system is that messages can be altered, injected
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Nokia Call Connect v1.1 for Cisco User s Guide. Part Number: N450000431 Rev 003 Issue 1
 Nokia Call Connect v1.1 for Cisco User s Guide Part Number: N450000431 Rev 003 Issue 1 Reproduction, transfer, distribution or storage of part or all of the contents in this document in any form without
Nokia Call Connect v1.1 for Cisco User s Guide Part Number: N450000431 Rev 003 Issue 1 Reproduction, transfer, distribution or storage of part or all of the contents in this document in any form without
Open IN Service Provider Access
 Open IN Service Provider Access Dr. Audun Jøsang Department of Telematics The Norwegian University of Science and Technology N-7149 Trondheim Norway email: ajos@item.ntnu.no Abstract Open IN service provider
Open IN Service Provider Access Dr. Audun Jøsang Department of Telematics The Norwegian University of Science and Technology N-7149 Trondheim Norway email: ajos@item.ntnu.no Abstract Open IN service provider
