Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness
|
|
|
- Harold Byrd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TITLE: Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 20 July 2016 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m 2, and is further classified into class I (BMI 30.0 to 34.9 kg/m 2 ), class II (BMI 35.0 to 39.9 kg/m 2 ), and class III obesity (BMI 40.0 kg/m 2 ), with an increase in morbidity associated with increasing class of obesity. 1 As of 2011, 18.3% of adult Canadians were obese, which represented a 200% increase from Among the 18.3%, 71.6% were categorized as having class I obesity, 19.7% had class II obesity, and 8.7% had class III obesity. 2 Obesity is associated with considerable morbidity, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. 3 The increased prevalence of comorbidities associated with obesity results in a reduction in life expectancy in those who are obese compared to individuals with a BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m 2. 3 There are a number of bariatric surgical procedures currently available, and the most commonly performed procedures are gastric bypass (GBP), sleeve gastrectomy (SG), laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), vertical banded gastroplasty (stomach stapling), and biliopancreatic diversion. 4,5 A 2014 CADTH Rapid Response review 6 compared the clinical and cost-effectiveness of roux-en-y gastric bypass (RYGB), SG and LAGB, and found that RYGB was associated with a greater weight reduction relative to LAGB, but was also associated with a higher risk for procedural adverse events. SG appeared to be more effective than LAGB but less effective than RYGB for weight loss, and had a reduced risk for complications relative to RYGB and a higher risk for complications relative to LABG, but evidence was conflicting. Economic evaluations of RYGB and LAGB were conducted in two cost studies, with RYGB dominating LAGB in one analysis, though the generalizability of these findings to a Canadian context is unclear. The review did not identify any evidence-based guidelines recommending specific surgical procedures. Disclaimer: The Rapid Response Service is an information service for those involved in planning and providing health care in Canada. Rapid responses are based on a limited literature search and are not comprehensive, systematic review s. The intent is to provide a list of sources of the best evidence on the topic that CADTH could identify using all reasonable efforts w ithin the time allow ed. Rapid responses should be considered along w ith other types of information and health care considerations. The information included in this response is not intended to replace professional medical advice, nor should it be construed as a recommendation for or against the use of a particular health technology. Readers are also cautioned that a lack of good quality evidence does not necessarily mean a lack of effectiveness particularly in the case of new and emerging health technologies, for w hich little information can be found, but w hich may in future prove to be effective. While CADTH has taken care in the preparation of the report to ensure that its contents are accurate, complete and up to date, CADTH does not make any guarantee to that ef fect. CADTH is not liable for any loss or damages resulting from use of the information in the report. Copyright: This report contains CADTH copyright material and may contain material in w hich a third party ow ns copyright. This report may be used for the purposes of rese arch or private study only. It may not be copied, posted on a w eb site, redistributed by or stored on an electronic system w ithout the prior w ritten permission of CADTH or applicable copyright ow ner. Links: This report may contain links to other information available on the w ebsites of third parties on the Internet. CADTH does not have control over the content of such sites. Use of third party sites is governed by the owners own terms and conditions.
2 Despite bariatric surgery having been shown to be more effective than non-surgical interventions such as medications or lifestyle changes in a number of systematic reviews of clinical trials with relatively short-term follow-up, 7,8 its long-term effectiveness is unclear. There is an increasing number of revisionary surgery (repeat surgery) that are due to undesirable results of the primary bariatric procedures, with the main cause being inadequate weight loss. 9,10 This Rapid Response report aims to review the comparative long-term (at least five years) clinical and cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of class II and class III morbid obesity. RESEARCH QUESTIONS 1. What is the long-term clinical effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity? 2. What is the long-term cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity? KEY FINDINGS At five years follow-up, bariatric surgeries lead to a statistically significant reduction in weight, waist circumference, and body mass index (BMI) as compared to medical treatment in patients with morbid obesity. Evidence from cost evaluation studies showed that bariatric surgery is more cost-effective than conventional treatment in patients with morbid obesity over a life time horizon. Despite higher inpatient costs leading to higher total healthcare costs at 15 years, there was no difference in total healthcare costs in the subgroup of patients with diabetes, with savings mainly driven in reduced costs of diabetes drugs. METHODS Literature Search Strategy A limited literature search was conducted on key resources including MEDLINE via OVID, PubMed, The Cochrane Library, University of York Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) databases, Canadian and major international health technology agencies, as well as a focused Internet search. No filters were applied to limit the retrieval by study type. This report is an extension of a literature search conducted in March 2014 for a previous CADTH report. The current search was limited to English language documents published between March 25, 2014 and June 21, 2016.The search was also limited to English language documents. Selection Criteria and Methods One reviewer screened the titles and abstracts of the retrieved publications and examined the full-text publications for the final article selection. Selection criteria are outlined in Table 1. Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 2
3 Population Intervention Table 1: Selection Criteria Adults and children with a BMI 35 with severe comorbidities Adults and children with a BMI 40 with or without comorbidities Any type of bariatric surgery Comparator Outcomes Study Designs Non-surgical treatment Other surgery types (one modality of bariatric surgery compared with another modality) Long term weight loss (5 years and more); Rates of repeat bariatric surgery after 5 years, Rates of qualification for repeat bariatric surgery after 5 years Cost-effectiveness (at least 5 years) Health technology assessments (HTA), systematic reviews (SR), meta-analyses (MA), randomized controlled trials (RCTs), non-rcts, economic evaluations. Exclusion Criteria Articles were excluded if they did not meet the selection criteria in Table 1, if they were published prior to March 2014, if they were duplicate publications of the same study, or if they were referenced in a selected systematic review. Critical Appraisal of Individual Studies The quality of the included clinical trials, and cost evaluation was assessed using the Downs and Black 11 and Drummond 12 checklists, respectively. Numeric scores were not calculated. Instead, the strengths and limitations of the study are summarized and presented narratively. SUMMARY OF EVIDENCE Quantity of Research Available The literature search yielded 645 citations. After screening of abstracts from the literature search and from other sources, eight potentially relevant studies were selected for full-text review. Four studies were included in the review. The PRISMA flowchart in Appendix 1 details the process of the study selection. Summary of Study Characteristics A detailed summary on the design, population, interventions, comparators and outcomes of the included studies is provided in Appendix 2. An open-label RCT assigned 60 obese patients (BMI 35 kg/m 2 ) with type 2 diabetes to receive either conventional treatment only or bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or biliopancreatic diversion). 53 patients completed five years follow-up. Control of diabetes, Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 3
4 reduction in weight, waist circumference, and BMI were compared between the two groups at five years follow-up. 13 A cost study in Sweden examined the cost savings for the treatment of 4030 obese patients with different baseline fasting blood glucose levels undergoing different types of bariatric surgeries (mean age 41; mean BMI 42.7 in men, and 41.2 in women) compared to conventional treatment (ranging from advanced lifestyle modification to no treatment) over 15 years. Drug costs, inpatient and outpatient costs, and total health care costs were reported in 2013 US dollars. 14 An economic evaluation study in Sweden evaluated the cost-utility for obese patients undergoing different types of bariatric surgeries (mean age 41; mean BMI 42.8) compared to conventional treatment using Markov modeling with a life time horizon. The model functions by predicting the risk of cardiovascular events, type 2 diabetes, and complications of surgery. Direct medical costs of bariatric surgery and medical treatment were reported in 2012 Euros ( ). 15 A cost evaluation study in Spain assessed the cost-utility for severely obese patients undergoing gastric bypass (aged 18-55; mean BMI 50.7) compared to conventional treatment using a discrete-event simulation model with various time horizons. The model assumes that all patients may develop type 2 diabetes. Direct medical costs of bariatric surgery and medical treatment were reported in Summary of Critical Appraisal The included clinical trial 13 is an open label RCT, with the hypothesis, method of selection of participants from the source population and representation, method of randomization, main outcomes, interventions, patient characteristics, and main findings clearly described. Estimates of random variability and actual probability values were provided and losses to follow-up were described. The study had sufficient power to detect a clinically important effect. The patients were not blinded to the intervention, but since patients undergoing surgery had to sign informed consent and be aware of the specific risks of procedures, this is a limitation that is inherent to the nature of the intervention. The cost study 14 had outcomes and costs assessed and compared appropriately, all the important and relevant outcomes and costs for each alternative identified. The presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users. There was no economic evaluation, incremental analysis, or sensitivity analysis performed. The economic evaluations 15,16 are likely to be usable, outcomes and costs were assessed and compared appropriately; all the important and relevant outcomes and costs for each alternative were identified; outcomes and costs were measured accurately in appropriate units prior to evaluation; outcomes and costs were valued credibly; outcomes and costs were adjusted for different times at which they occurred. An incremental analysis of the outcomes and costs of alternatives and a sensitivity analysis were performed. The presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users. The economic evaluations did not base the clinical outcomes on well-designed clinical studies. The economic models had to assume the risk of long-term complications of obesity such as cardiovascular events and type 2 diabetes. The generalizability of the results of the economic studies to a Canadian context may be limited since costs data used Swedish 14,15 or Spanish 16 sources. Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 4
5 Details of the strengths and limitations of the included studies are summarized in Appendix 3. Summary of Findings Main findings of included studies are summarized in detail in Appendix What is the long-term clinical effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity? An open-label RCT assigned 60 obese patients (BMI 35 kg/m 2 ) with type 2 diabetes to receive either conventional treatment only or bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or biliopancreatic diversion). 13 In all groups, diet, life style modification and dosage of insulin were optimized on an individual basis with the aim to reach adequate glycaemic control (HbA 1c <7.0%). At five years of follow-up, both surgical procedures lead to a statistically significant reduction in weight, waist circumference and BMI, and better control of diabetes, as compared to medical treatment. At five years, the mean patient weight (kg) was 127.1, 90.3 and 92.8 in only medically treated, gastric bypass, and biliopancreatic diversion groups, respectively. Mean waist circumference (cm) was 113.9, and in only medically treated, gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion groups, respectively. Mean BMI (kg/m 2 ) was 42.1, 31.3 and 30.3 in only medically treated, gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion groups, respectively. The differences in all outcomes between medical treatment and surgery were statistically significant. Details on diabetes control are in presented in Appendix 4. The authors concluded that surgery is more effective than medical treatment for the long-term control of obese patients with type 2 diabetes. 2. What is the long-term cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity? In general, data from cost studies showed that bariatric surgery is more cost-effective than conventional treatment in patients with morbid obesity over a life time horizon, despite the fact that surgery may generate additional costs in the first 15 years. Despite higher inpatient costs at 15 years, there was no difference in total health care costs in the subgroup of patients with diabetes, with savings mainly driven in reduced costs of diabetes drugs. A cost study in Sweden examined the cost savings for the treatment of obese patients with different baseline glucose status undergoing different types of bariatric surgeries (mean age 41; mean BMI 42.7 in men, and 41.2 in women) compared to conventional treatment over 15 years. 14 Drug costs, inpatient and outpatient costs, and total health care costs were reported in 2013 US dollars. Drug costs did not differ between the surgery and conventional treatment group in patients with euglycaemia, but were lower in the surgery group in the prediabetes (-$3,329) and diabetes group (-$5,487). Inpatient costs were higher in the surgery group for all 3 diabetes statuses than in the conventional treatment group (euglycaemia group +$22,931, prediabetes group +$27,152, and diabetes group +$18 697). There was no difference in outpatient costs regardless of diabetes status. Total health-care costs were higher in the surgery group in the euglycaemic (+$22 390) and prediabetes (+$26 292) groups than in the conventional treatment group; there was no difference between treatment groups in patients with diabetes. Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 5
6 An economic evaluation study in Sweden evaluated the cost-utility for obese patients undergoing different types of bariatric surgeries (mean age 41; mean BMI 42.8) compared to conventional treatment using Markov modeling with a life time horizon. 15 Costs were direct medical costs of bariatric surgery and medical treatment and reported in Over a lifetime horizon, surgery lead to cost savings in 99.1% of cases (- 8,408), and generated an additional 4.1 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) per patient compared to medical treatment. Bariatric surgery was cost-effective with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of 26,985/QALY after 2 years (willingness to pay threshold of 35,526/QALYs). In the diabetic cohort, bariatric surgery was cost-effective in all 4 categories: moderately (BMI 30 to 34), severely (BMI 35 to 39), morbidly (BMI 40 to 50) and super obese (BMI >50). In the non-diabetic cohort, bariatric surgery was cost-effective in all categories except for moderately obese patients (BMI 30 to 34) A cost evaluation study in Spain assessed the cost-utility for severely obese patients undergoing gastric bypass (aged 18-55; mean BMI 50.7) compared to conventional treatment using a discrete-event simulation model with various time horizons. 16 Costs were direct medical costs of bariatric surgery and medical treatment and reported in At five years, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 3,350, and generated a loss of 0.13 QALYs per patient compared to medical treatment which may be due to high cost of surgery and the surgery-related deaths. At 10 years, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 1,803, and generated an additional 0.45 QALYs per patient. At 15 years, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 89.21, and generated an additional 1.12 QALYs per patient. At 20 years, gastric bypass result in a saving of 1,764, and generated an additional 1.82 QALYs per patient. Over a life time, compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in a saving of 13,994, and generated an additional 5.63 QALYs per patient. Limitations The evidence on the comparative long-term clinical effectiveness of bariatric surgery to conventional treatment is limited to one RCT with a relatively short 5 year follow-up period. The economic evaluations considered bariatric surgery as a whole, so it is unclear whether there are differences between different surgical approaches. The generalizability of the results of the economic studies to a Canadian context may be limited since context and cost data were based on foreign sources. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR DECISION OR POLICY MAKING At five years follow up, bariatric surgeries lead to a statistically significant reduction in weight, waist circumference and body mass index as compared to medical treatment in patients with morbid obesity. Evidence from cost evaluation studies showed that bariatric surgery is more cost-effective than conventional treatment in patients with morbid obesity over a life time horizon. Despite higher inpatient costs at 15 years with surgery, there was no difference in total health care costs in the subgroup of patients with diabetes, with savings mainly driven in reduced costs of diabetes drugs. Economic results should be interpreted with caution since context and cost data used foreign sources. Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 6
7 PREPARED BY: Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health Tel: Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 7
8 REFERENCES 1. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation [Internet]. Geneva (CH): World Health Organization; (WHO Technical report series; no. 894). [cited 2016 Jun 23]. Available from: 2. Twells LK, Gregory DM, Reddigan J, Midodzi WK. Current and predicted prevalence of obesity in Canada: a trend analysis. CMAJ Open [Internet] [cited 2016 Jun 23];2:E Available from: 3. Lau DCW, Douketis JD, Morrison KM, Hramiak IM, Sharma AM, Ur E, et al Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the management and prevention of obesity in adults and children. CMAJ [Internet] Apr 10 [cited 2016 Jun 23];176(8 suppl): Available from: 4. Schroeder R, Harrison TD, McGraw SL. Treatment of adult obesity with bariatric surgery. Am Fam Physician Jan 1;93(1): Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide Obes Surg Dec;19(12): Bariatric surgical procedures for obese and morbidly obese patients: a review of comparative clinical and cost-effectiveness, and guidelines [Internet]. Ottawa: CADTH; 2014 Apr 24. [cited 2016 Jun 16]. (Rapid repsonse report: summary with critical appraisal). Available from: 7. Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, Frampton GK. Surgery for weight loss in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;8:CD Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. Bariatric surgery: final evidence report [Internet]. Olympia (WA): Washington State Healthcare Authority; 2015 Apr 10. [cited 2016 Jun 23]. Available from: 9. Kuchinka J, Nawacki L, Bryk P, Matykiewicz J, Wawrzycka I, Koziel D, et al. Reoperations in bariatric surgery - indications and initial evaluation of postoperative complications. Pol Przegl Chir Mar 1;88(2): Park JY, Song D, Kim YJ. Causes and outcomes of revisional bariatric surgery: initial experience at a single center. Ann Surg Treat Res [Internet] Jun [cited 2016 Jun 22];86(6): Available from: Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health [Internet] Jun [cited 2016 Jun 22];52(6): Available from: Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 8
9 12. Higgins JPT, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions [Internet]. Version Oxford (U.K.): The Cochrane Collaboration; Figure 15.5.a: Drummond checklist (Drummond 1996). [cited 2016 Jun 22]. Available from: _1996.htm 13. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Nanni G, et al. Bariatricmetabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Sep 5;386(9997): Keating C, Neovius M, Sjoholm K, Peltonen M, Narbro K, Eriksson JK, et al. Health-care costs over 15 years after bariatric surgery for patients with different baseline glucose status: results from the Swedish Obese Subjects study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol Nov;3(11): Borisenko O, Adam D, Funch-Jensen P, Ahmed AR, Zhang R, Colpan Z, et al. Bariatric surgery can lead to net cost savings to health care systems: results from a comprehensive European decision analytic model. Obes Surg [Internet] Sep [cited 2016 Jun 22];25(9): Available from: Castilla I, Mar J, Valcarcel-Nazco C, Arrospide A, Ramos-Goni JM. Cost-utility analysis of gastric bypass for severely obese patients in Spain. Obes Surg Dec;24(12): Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 9
10 Appendix 1: Selection of Included Studies 645 citations identified from electronic literature search and screened 639 citations excluded 6 potentially relevant articles retrieved for scrutiny (full text, if available) 2 relevant reports retrieved from other sources (grey literature, hand search) 8 potentially relevant reports 4 reports excluded (irrelevant population, interventions or outcomes) 4 reports included in review Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 10
11 Appendix 2: Characteristics of Included Studies Table A1: Characteristics of Included studies First Author, Year, Country, Study Objectives Interventions/Com parators Patients Main Study Outcomes Clinical studies Mingrone, , Italy, Germany, UK Cost studies We aimed to assess 5 year outcomes from our randomised trial designed to compare surgery with conventional medical treatment for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in obese patients (p 964) Roux-en-Y (19 patients) Biliopancreatic diversion (19 patients) Medical treatment (15 patients) Patients aged years with a body-mass index of 35 kg/m 2 or more and a history of type 2 diabetes lasting at least 5 years (p 964) Diabetic remission (at 5 years) Changes in weight, waist circumference and BMI (at 5 years) Keating, , Sweden Borisenko, , Sweden We aimed to assess health-care costs over 15 years for patients with obesity treated conventionally or with bariatric surgery and who had either euglycaemia, prediabetes, or type 2 diabetes before intervention (p 855) The objective of the present study was to evaluate the cost-utility of bariatric surgery in a lifetime horizon from a Swedish health care payer perspective (p 1559) Bariatric surgery (GBP, VBG, GB) Medical treatment Bariatric surgery (GBP, SG, GB) Medical treatment Obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery (mean age 47, SD 6; mean BMI 42.7 in men, SD 4.2 and 41.2 in women, SD 4.7) Obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery (mean age 41; range 25 65; mean BMI 42.8; range 30 60) Cost savings (2013 US$) (costs of health care use retrieved from Swedish registers: drug costs, inpatient costs, outpatient costs) Cost evaluation: using Markow modeling with life time horizon; direct medical costs (2012 ): costs of bariatric surgery; costs of medical treatment ICER QALY Castilla, , Spain To assess the cost utility of gastric bypass versus usual care for patients with severe obesity in Spain (p 2061) Bariatric surgery (GBP) Obese patients undergoing gastric bypass (aged 18-55; mean BMI 50.7; range ) Cost evaluation: using a discrete-event simulation (DES) modeling with various time horizons; direct medical costs (2012 ): costs of bariatric surgery; costs of medical treatment ICER QALY GB : gastric banding; GBP: gastric bypass; ICER : incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALY : quality-adjusted life years; SD : standard deviation; SG : sleeve gastrectomy; VBG : vertical-banded gastroplasty Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 11
12 Appendix 3: Summary of Critical Appraisal of Included Study Table A2: Summary of Critical Appraisal of Included Study First Author, Strengths Publication Year Critical appraisal of included clinical trials (Downs and Black)11) Limitations Mingrone, hypothesis clearly described patients randomized method of selection from source population and representation described main outcomes, interventions, patient characteristics, and main findings clearly described estimates of random variability and actual probability values provided losses to follow-up described study had sufficient power to detect a clinically important effect Critical appraisal of included cost study (Drummond 12 ) Keating, outcomes and costs assessed and compared appropriately (all the important and relevant outcomes and costs for each alternative identified; outcomes and costs measured accurately in appropriate units prior to evaluation; outcomes and costs valued credibly; outcomes and costs adjusted for different times at which they occurred) the presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users Borisenko, the economic evaluation is likely to be usable (a well-defined question posed in an answerable form; a comprehensive description of the competing alternatives given; evidence for the programme s effectiveness established) outcomes and costs assessed and compared appropriately (all the important and relevant outcomes and costs for each alternative identified; outcomes and costs measured accurately in appropriate units prior to evaluation; outcomes and costs valued credibly; outcomes and costs adjusted for different times at which they occurred) an incremental analysis of the outcomes and costs of alternatives performed a sensitivity analysis performed the presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users Participants not blinded there was no economic evaluation performed there was no incremental analysis performed there was no sensitivity analysis performed the generalizability of the results to a Canadian context may be limited since costs data used Swedish sources the generalizability of the results to a Canadian context may be limited since costs data used Swedish sources Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 12
13 Table A2: Summary of Critical Appraisal of Included Study First Author, Strengths Publication Year Castilla, the economic evaluation is likely to be usable (a well-defined question posed in an answerable form; a comprehensive description of the competing alternatives given; evidence for the programme s effectiveness established) outcomes and costs assessed and compared appropriately (all the important and relevant outcomes and costs for each alternative identified; outcomes and costs measured accurately in appropriate units prior to evaluation; outcomes and costs valued credibly; outcomes and costs adjusted for different times at which they occurred) an incremental analysis of the outcomes and costs of alternatives performed a sensitivity analysis performed the presentation and discussion of study results include all issues of concern to users Limitations the generalizability of the results to a Canadian context may be limited since costs data used Spanish sources Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 13
14 Appendix 4: Main Study Findings and Authors Conclusions Table A3: Main Study Findings and Authors Conclusions First Author, Publication Year Main Study Findings Authors Conclusions Research question 1 (long-term clinical effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity) Mingrone, At 5 years In summary, surgery is more effective than medical treatment for the Weight (kg) (mean; SD) Medical treatment: (20.5) Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y): 90.3 (12.7) Biliopancreatic diversion: 92.8 (14.0) P < long-term control of obese patients with type 2 diabetes (p 972) Waist circumference (cm) Medical treatment: (14.2) Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y): (12.8) Biliopancreatic diversion: (12.6) P < BMI (kg/m 2 ) Medical treatment: 42.1 (5.8) Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y): 31.3 (2.5) Biliopancreatic diversion: 30.3 (4.0) P < Diabetes remission (number of participants, %) Medical treatment: 0 (0%) Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y): 7 (37%) Biliopancreatic diversion: 12 (63%) P = HbA1c concentration 6.5% Medical treatment: 4 (27%) Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y): 8 (42%) Biliopancreatic diversion: 13 (68%) P = Research question 2 (long-term cost effectiveness of bariatric surgery for the treatment of obesity and morbid obesity) Keating, 14 Costs over 15 years 2015 Drug costs did not differ between the surgery and conventional treatment group in patients with euglycaemia ($ vs $10 680; adjusted mean difference -$225; P=0.812), but were lower in the surgery group in the prediabetes ($ vs $13 186; $3329; P=0.007) and diabetes group ($ vs $19 511; $5487 P<0.0001) Inpatient costs: higher in the surgery group for all 3 groups than in the conventional treatment. Euglycaemia group ($ vs $25 313; $22 931; P<0.0001), prediabetes ($ vs $32 861; $27 152; P<0.0001), and diabetes ($ vs $47 569; $18 697; P<0.0001) Outpatient costs: no difference in all 3 groups Total health-care costs: higher in the surgery group in the Total health-care costs were higher for patients with euglycaemia or prediabetes in the surgery group than in the conventional treatment group, but we detected no difference between the surgery and conventional treatment groups for patients with diabetes (p 855) Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 14
15 Table A3: Main Study Findings and Authors Conclusions First Author, Publication Year Borisenko, Main Study Findings euglycaemic ($ vs $45 542; $22 390; P<0.0001) and prediabetes ($ vs $54 864; $26 292; P<0.0001) groups than in the conventional treatment group; no difference between treatment groups in patients with diabetes ($ vs $79 967; $9081; P=0.090). Costs over a life time Compared to medical treatment, surgery lead to a saving of 8,408 ( 26,258 vs 34,665), and generated an additional 4.1 QALYs per patient. Authors Conclusions Bariatric surgery, over a lifetime horizon, may lead to significant cost savings to health care systems in addition to the known clinical benefits (p 1559) Castilla, Sensitivity analysis showed that bariatric surgery produced clinical benefits (additional QALYs) in all patients and was cost saving in 99.1% of cases In general, bariatric surgery was cost-effective: ICER: 26,985/QALY after 2 years (willingness to pay threshold of 35,526/QALYs) In the diabetic cohort, bariatric surgery was cost-effective in all 4 categories: moderately (BMI 30 34), severely (BMI 35 39), morbidly (BMI 40 50) and super obese (BMI >50) In the non-diabetic cohort, bariatric surgery was cost-effective in all categories except for moderately obese patients (BMI 30 34) Costs at 5 years Compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 3,350, and generated a loss of 0.13 QALYs per patient (medical treatment is better). Costs at 10 years Compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 1,803, and generated an additional 0.45 QALYs per patient. Costs at 15 years Compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in an additional spending of 89.21, and generated an additional 1.12 QALYs per patient. Costs at 20 years Compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in a saving of 1,764, and generated an additional 1.82 QALYs per patient. Costs over a life time Compared to medical treatment, gastric bypass result in a saving of 13,994, and generated an additional 5.63 QALYs per patient. Gastric bypass is an intervention that dominates over the option of not intervening when a lifetime horizon is considered (p 2061) Bariatric Surgery for the Long-Term Treatment of Obesity 15
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 27 June 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES In 2009, CADTH reviewed the clinical
TITLE: Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 27 June 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES In 2009, CADTH reviewed the clinical
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients
 Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines
 TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines DATE: 15 June 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES People with type 2 diabetes, also known
TITLE: Diabetic Diets for Frail Elderly Long-Term Care Residents with Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Guidelines DATE: 15 June 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES People with type 2 diabetes, also known
Bariatric surgery vs. conservative treatment for obesity and overweight
 Bariatric surgery vs. conservative treatment for obesity and overweight Assessment / Summary January 29, 2016 Authors (Assessment Team en ordre alphabétique): Zanfina Ademi 1, Heiner C. Bucher 2, Dominik
Bariatric surgery vs. conservative treatment for obesity and overweight Assessment / Summary January 29, 2016 Authors (Assessment Team en ordre alphabétique): Zanfina Ademi 1, Heiner C. Bucher 2, Dominik
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
DATE: 06 May 2013 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
TITLE: Low Molecular Weight Heparins versus New Oral Anticoagulants for Long-Term Thrombosis Prophylaxis and Long-Term Treatment of DVT and PE: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 06
The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx:
 James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation
 The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Abstract Background Methods:
 Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI)
 Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
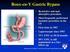 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Bariatric Surgery. OHTAC Recommendation. Bariatric Surgery
 OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
The weight of the world.
 The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
January 18, 2013. Dear Dr. Schafer,
 Medical School Center for Healthcare Outcomes & Policy Bldg 520, Room 31658 2800 Plymouth Rd, SPC 2800 Ann Arbor, Ml48109 (734) 998-7470 (734) 998-7473 fax January 18, 2013 Jyme H. Schafer, MD, MPH Director,
Medical School Center for Healthcare Outcomes & Policy Bldg 520, Room 31658 2800 Plymouth Rd, SPC 2800 Ann Arbor, Ml48109 (734) 998-7470 (734) 998-7473 fax January 18, 2013 Jyme H. Schafer, MD, MPH Director,
TITLE: Extension Tubing Changes for Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters: A Review of the Clinical Evidence and Guidelines
 TITLE: Extension Tubing Changes for Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters: A Review of the Clinical Evidence and Guidelines DATE: 21 October 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Vascular access devices (VADs)
TITLE: Extension Tubing Changes for Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters: A Review of the Clinical Evidence and Guidelines DATE: 21 October 2015 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Vascular access devices (VADs)
Subject: Obesity: Surgical Management
 Page 1 of 5 Approved: Robert Neal Mills, MD Date: 7/12/2012 (This criteria is for plans that provide an obesity surgery benefit and do NOT have their own specific criteria.) (Please refer to the member
Page 1 of 5 Approved: Robert Neal Mills, MD Date: 7/12/2012 (This criteria is for plans that provide an obesity surgery benefit and do NOT have their own specific criteria.) (Please refer to the member
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes
 Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Jill Malcolm, Karen Moir
 Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery
 WHITE PAPER Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery Treat the cause. Cure the symptom. Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Written July 2011 Bariatric Surgery: The Cure for Type II Diabetes? For most individuals
WHITE PAPER Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery Treat the cause. Cure the symptom. Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Written July 2011 Bariatric Surgery: The Cure for Type II Diabetes? For most individuals
DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES
 TITLE: Dual Antiplatelet Therapy and Enoxaparin or Unfractionated Heparin for patients with ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Dual Antiplatelet Therapy and Enoxaparin or Unfractionated Heparin for patients with ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 29 August 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of obesity (Update and re-appraisal)
Surgery for weight loss in adults (Review)
 Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, Frampton GK This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2014, Issue 8 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, Frampton GK This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2014, Issue 8 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures*
 Subject: Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures* Updated: February 24, 2009 Department(s): Policy: Objective: Utilization Management Medically necessary bariatric surgical procedures are
Subject: Gastric Bypass and Other Bariatric Surgical Procedures* Updated: February 24, 2009 Department(s): Policy: Objective: Utilization Management Medically necessary bariatric surgical procedures are
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS
 BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16
 HEALTHSPAN BARIATRIC SURGERY Methodology: Expert Opinion Champion: Surgery Issue Date: Review Date: 12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16 RELEVANCE: The CPG for
HEALTHSPAN BARIATRIC SURGERY Methodology: Expert Opinion Champion: Surgery Issue Date: Review Date: 12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16 RELEVANCE: The CPG for
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity. in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
Is surgery better? Jordan Kautz, MS IV A b atory are C erence, an 08 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine
 Is surgery better? Bariatric surgery versus medical management in type 2 diabetes mellitus Jordan Kautz, MS IV Ambulatory Care Conference, Jan 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine For the soon-to-be medical resident
Is surgery better? Bariatric surgery versus medical management in type 2 diabetes mellitus Jordan Kautz, MS IV Ambulatory Care Conference, Jan 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine For the soon-to-be medical resident
Cost Consequences of Bariatric Surgery
 The Economic Impact of Bariatric Surgery Anke-Peggy Holtorf 1,2, Harald Rinde 2, Frederic Rupprecht 3, Henry Alder 3 and Diana Brixner 1 3 1 University of Utah, 2 BioBridge Strategies LLC, 3 Ethicon Endosurgery
The Economic Impact of Bariatric Surgery Anke-Peggy Holtorf 1,2, Harald Rinde 2, Frederic Rupprecht 3, Henry Alder 3 and Diana Brixner 1 3 1 University of Utah, 2 BioBridge Strategies LLC, 3 Ethicon Endosurgery
MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY. SERVICE: Bariatric (Weight Loss) Surgery Policy Number: 053 Effective Date: 5/27/2014 Last Review: 4/24/2014
 Page 1 of 6 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms
Page 1 of 6 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY Important note Even though this policy may indicate that a particular service or supply is considered covered, this conclusion is not necessarily based upon the terms
BARIATRIC SURGERY. Prerequisites. Authorization, Notification and Referral
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
Overview of Bariatric Surgery
 Overview of Bariatric Surgery To better understand how weight loss surgery works, it is helpful to know how the normal digestive process works. As food moves along the digestive tract, special digestive
Overview of Bariatric Surgery To better understand how weight loss surgery works, it is helpful to know how the normal digestive process works. As food moves along the digestive tract, special digestive
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation
 Health Technology Assessment 2009; Vol. 13: No. 41 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation J Picot,
Health Technology Assessment 2009; Vol. 13: No. 41 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation J Picot,
Choices Around Bariatric Surgery
 Choices Around Bariatric Surgery What should you know? Richard Stubbs MD FRCS FRACS Wakefield Obesity Clinic, Wellington 152 kg / BMI 59 74 kg / BMI 29 Indications (NIH Consensus Statement 1991) BMI >
Choices Around Bariatric Surgery What should you know? Richard Stubbs MD FRCS FRACS Wakefield Obesity Clinic, Wellington 152 kg / BMI 59 74 kg / BMI 29 Indications (NIH Consensus Statement 1991) BMI >
Richard M Peterson, MD MPH FACS Chief UT Medicine Center for Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery Director Christus Weight Loss Institute Assistant
 Richard M Peterson, MD MPH FACS Chief UT Medicine Center for Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery Director Christus Weight Loss Institute Assistant Professor of Surgery UTHSCSA None Laparoscopic adjustable
Richard M Peterson, MD MPH FACS Chief UT Medicine Center for Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery Director Christus Weight Loss Institute Assistant Professor of Surgery UTHSCSA None Laparoscopic adjustable
Bariatric Surgery. Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS. Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University
 Bariatric Surgery Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University April 30, 2013 Why surgery? Eligibility criteria Most commonly
Bariatric Surgery Beth A. Ryder, MD FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery The Miriam Hospital Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University April 30, 2013 Why surgery? Eligibility criteria Most commonly
Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006. SUBJECT: Bariatric Surgery for Treatment of Morbid Obesity
 CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
CMS Manual System Pub 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 54 Date: APRIL 28, 2006 Change
young adults were at increased risk of nonmedical opioid use, which increases the risk of future substance use disorders. 5
 TITLE: Suboxone Versus Methadone for the Detoxification of Patients Addicted to Prescription Opioids: A Review of Comparative Clinical Effectiveness, Safety, and Guidelines DATE: 13 February 2014 CONTEXT
TITLE: Suboxone Versus Methadone for the Detoxification of Patients Addicted to Prescription Opioids: A Review of Comparative Clinical Effectiveness, Safety, and Guidelines DATE: 13 February 2014 CONTEXT
Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band
 Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band Presented by Ms Beth Murgatroyd Honorary Bariatric Nurse Practitioner Mr Ameet G Patel Consultant Surgeon Director of Bariatric Surgery at King s College
Weight loss surgery more than just a gastric band Presented by Ms Beth Murgatroyd Honorary Bariatric Nurse Practitioner Mr Ameet G Patel Consultant Surgeon Director of Bariatric Surgery at King s College
d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery-Not medically necessary procedures d EFFECTIVE DATE: 11 5 2014 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 5 29 2015 OVERVIEW Surgery for obesity, termed bariatric surgery, is a treatment
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: sara.davies@scotland.gsi.gov.uk Heather.knox@nhs.net T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: sara.davies@scotland.gsi.gov.uk Heather.knox@nhs.net T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi:
 Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi: Vad händer med mor och foster? Kari Johansson, nutritionist, med dr Martin Neovius, docent Enheten för klinisk epidemiologi, Karolinska Institutet Acknowledgement Co-authors
Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi: Vad händer med mor och foster? Kari Johansson, nutritionist, med dr Martin Neovius, docent Enheten för klinisk epidemiologi, Karolinska Institutet Acknowledgement Co-authors
Weight Loss Surgery Program
 Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy. Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15
 Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Persistence Market Research
 Persistence Market Research Global Obesity Surgery Devices Market Will Reach $2,489.5 Million in 2020 - Persistence Market Research Persistence Market Research 1 Persistence Market Research Released New
Persistence Market Research Global Obesity Surgery Devices Market Will Reach $2,489.5 Million in 2020 - Persistence Market Research Persistence Market Research 1 Persistence Market Research Released New
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness
 TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
TITLE: Metal-Ceramic and Porcelain Dental Crowns: A Review of Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 23 June 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Dental ceramics are widely used to repair damaged teeth and
Changes to Bariatric Surgery Prior Authorization Guidelines
 Update August 2011 No. 2011-44 Affected Programs: BadgerCare Plus, Medicaid To: Hospital Providers, Physician Assistants, Physician Clinics, Physicians, HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Changes to
Update August 2011 No. 2011-44 Affected Programs: BadgerCare Plus, Medicaid To: Hospital Providers, Physician Assistants, Physician Clinics, Physicians, HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Changes to
Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre
 Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre Outline Obesity as a Chronic Disease 5 A s of Obesity Management OBN & BRATC Referral Process Obesity Definition BMI Normal Weight 18.5-24.9 Overweight
Sudbury Bariatric Regional Assessment & Treatment Centre Outline Obesity as a Chronic Disease 5 A s of Obesity Management OBN & BRATC Referral Process Obesity Definition BMI Normal Weight 18.5-24.9 Overweight
Karen Kovach M.S, R.D Chief Scientific Officer Weight Watchers International Inc.
 Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi:
 Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi: Vad händer med mor och foster? Kari Johansson, PhD, nutritionist Enheten för klinisk epidemiologi, Karolinska Institutet Acknowledgement Co-authors Sven Cnattingius MD,
Graviditet och obesitaskirurgi: Vad händer med mor och foster? Kari Johansson, PhD, nutritionist Enheten för klinisk epidemiologi, Karolinska Institutet Acknowledgement Co-authors Sven Cnattingius MD,
Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks
 Background: Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Final Background and Scope November 19, 2015 The Centers for Disease Control
Background: Insulin degludec (Tresiba) for the Management of Diabetes: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Final Background and Scope November 19, 2015 The Centers for Disease Control
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS
 GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.
 www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Obesity Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater. Obesity is a serious medical
Considering Bariatric Surgery? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Obesity Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater. Obesity is a serious medical
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR.
 TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
TRANSVAGINAL MESH IN PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE REPAIR. Spanish full text SUMMARY Introduction: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterised by the descent or herniation of the uterus, vaginal vault, bladder
Marcus Wilson, PharmD. First Plenary Session
 Moderator First Plenary Session THE USE OF "BIG DATA" - WHERE ARE WE AND WHAT DOES THE FUTURE HOLD? Marcus Wilson, PharmD HealthCore Wilmington, DE, USA Speakers First Plenary Session THE USE OF "BIG DATA"
Moderator First Plenary Session THE USE OF "BIG DATA" - WHERE ARE WE AND WHAT DOES THE FUTURE HOLD? Marcus Wilson, PharmD HealthCore Wilmington, DE, USA Speakers First Plenary Session THE USE OF "BIG DATA"
Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures. Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital
 Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital Disclosures Allergan, Inc. (Past) Faculty Member Educational
Technical Aspects of Bariatric Surgical Procedures Robert O. Carpenter, MD, MPH, FACS Department of Surgery Scott & White Memorial Hospital Disclosures Allergan, Inc. (Past) Faculty Member Educational
Morbid obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) >40 kg/m2 (normal BMI range: 19-25 kg/m2)
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bariatric Surgery Date of Origin: January 1996 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 58 Effective Date: July 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico
 3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico Recidive del diabete dopo terapia chirurgica La quantificazione
3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico Recidive del diabete dopo terapia chirurgica La quantificazione
White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary?
 White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Introduction More than one
White Paper: Treating Clinical Obesity: When is Bariatric Surgery or Bariatric Surgery Revision Medically Necessary? For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Introduction More than one
Procedure Type: Metabolic and Malabsorbtion. Procedure Names. Adjustable Gastric Band (LAGB) Realize Band. Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG)
 The following table explains and compares the various weight loss surgeries, and their differences. For more information, please also read our compilation of related medical journals & articles below the
The following table explains and compares the various weight loss surgeries, and their differences. For more information, please also read our compilation of related medical journals & articles below the
Real World Data: How It s Used at a Medical Device Company
 MD MEDICAL SAFETY Real World Data: How It s Used at a Medical Device Company Myoung Kim, Ph.D., MBA. Andrew Yoo, M.D., M.S. Epidemiology and Health Informatics Medical Devices Johnson & Johnson May 29,
MD MEDICAL SAFETY Real World Data: How It s Used at a Medical Device Company Myoung Kim, Ph.D., MBA. Andrew Yoo, M.D., M.S. Epidemiology and Health Informatics Medical Devices Johnson & Johnson May 29,
SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER. Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS
 SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS GOALS The Many Benefits of Bariatric surgery and Weight Reduction Bariatric Care Center Surgical Weight Loss Program Medical
SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS GOALS The Many Benefits of Bariatric surgery and Weight Reduction Bariatric Care Center Surgical Weight Loss Program Medical
The Skinny on Bariatric Surgery. Kim A. Noble, Ph.D., RN, CPAN SCAPAN Fall Conference November 15 th, 2014 kanoble@mail.widener.
 The Skinny on Bariatric Surgery Kim A. Noble, Ph.D., RN, CPAN SCAPAN Fall Conference November 15 th, 2014 kanoble@mail.widener.edu The Skinny on Bariatric Surgery Objectives Following the completion of
The Skinny on Bariatric Surgery Kim A. Noble, Ph.D., RN, CPAN SCAPAN Fall Conference November 15 th, 2014 kanoble@mail.widener.edu The Skinny on Bariatric Surgery Objectives Following the completion of
The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes
 DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
COMMISSIONING POLICY
 COMMISSIONING POLICY Morbid Obesity in Adults: Secondary Care Referral Pathway Specialty: General Surgery Diabetic Medicine Respiratory Medicine Version: 2.3 Ratified by (name of Committee): Clinical Senate
COMMISSIONING POLICY Morbid Obesity in Adults: Secondary Care Referral Pathway Specialty: General Surgery Diabetic Medicine Respiratory Medicine Version: 2.3 Ratified by (name of Committee): Clinical Senate
The safety, effectiveness and cost effectiveness of surgical and non-surgical interventions for patients with morbid obesity.
 NZHTA TECHNICAL BRIEF November 2007 Volume 6 Number 8 The safety, effectiveness and cost effectiveness of surgical and non-surgical interventions for patients with morbid obesity. Meagan Stephenson Sarah
NZHTA TECHNICAL BRIEF November 2007 Volume 6 Number 8 The safety, effectiveness and cost effectiveness of surgical and non-surgical interventions for patients with morbid obesity. Meagan Stephenson Sarah
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS. Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence
 PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
Clinical Practice Assessment. Bariatric Surgery
 Clinical Practice Assessment Bariatric Surgery Clinical Question: In patients with obesity, do those who undergo a bariatric surgery procedure, compared to those managed medically, have better outcomes?
Clinical Practice Assessment Bariatric Surgery Clinical Question: In patients with obesity, do those who undergo a bariatric surgery procedure, compared to those managed medically, have better outcomes?
Understanding Obesity
 Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Keeping up to date with information retrieval research: Summarized Research in Information Retrieval for HTA (SuRe Info)
 Keeping up to date with information retrieval research: Summarized Research in Information Retrieval for HTA (SuRe Info) Patrice X. Chalon 1, Sari Susanna Ormstad 2, Jaana Isojärvi 3, Mick Arber 4, Sigrid
Keeping up to date with information retrieval research: Summarized Research in Information Retrieval for HTA (SuRe Info) Patrice X. Chalon 1, Sari Susanna Ormstad 2, Jaana Isojärvi 3, Mick Arber 4, Sigrid
The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure?
 Jane N. Buchwald Viewpoint Editor The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure? Robin Blackstone, MD Scottsdale Bariatric Center, Scottsdale, AZ Patients are looking to
Jane N. Buchwald Viewpoint Editor The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure? Robin Blackstone, MD Scottsdale Bariatric Center, Scottsdale, AZ Patients are looking to
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY. Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010
 WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
Weight Loss Surgery Program
 Weight Loss Surgery Program Weight loss surgery helped me loose 112 pounds. - Jennifer Weaver Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When Jennifer Weaver s husband was diagnosed
Weight Loss Surgery Program Weight loss surgery helped me loose 112 pounds. - Jennifer Weaver Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When Jennifer Weaver s husband was diagnosed
Surgical Treatment. Type II Diabetes in. Obesity. for. Mathew Rawlins, MD FACS Rockwood Bariatric Specialists
 Surgical Treatment for Type II Diabetes in Obesity Mathew Rawlins, MD FACS Rockwood Bariatric Specialists Co-Morbidities of Obesity Coronary Disease Hypertension Dyslipidemias Pulmonary insufficiency
Surgical Treatment for Type II Diabetes in Obesity Mathew Rawlins, MD FACS Rockwood Bariatric Specialists Co-Morbidities of Obesity Coronary Disease Hypertension Dyslipidemias Pulmonary insufficiency
COMMISSIONING POLICY
 COMMISSIONING POLICY Morbid Obesity in Adults: Secondary Care Referral Pathway Specialty: General Surgery Diabetic Medicine Respiratory Medicine January 2013 This commissioning policy applies to patients
COMMISSIONING POLICY Morbid Obesity in Adults: Secondary Care Referral Pathway Specialty: General Surgery Diabetic Medicine Respiratory Medicine January 2013 This commissioning policy applies to patients
Some of the diseases and conditions associated with obesity include:
 WEIGHT-LOSS SURGERY facts about obesity Obesity is rapidly becoming the nation s number-one health problem. Of the 97 million Americans who are overweight, 10 million are considered morbidly obese. Obesity
WEIGHT-LOSS SURGERY facts about obesity Obesity is rapidly becoming the nation s number-one health problem. Of the 97 million Americans who are overweight, 10 million are considered morbidly obese. Obesity
Bariatric Surgery Support NEWSLETTER. info@bariatricsurgerysupport.co.za HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US!
 info@bariatricsurgery.co.za NEWSLETTER HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US! The Christmas Holidays are nearly upon us, and, like you, our Bariatric Surgery Support is looking forward to a well-deserved rest
info@bariatricsurgery.co.za NEWSLETTER HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US! The Christmas Holidays are nearly upon us, and, like you, our Bariatric Surgery Support is looking forward to a well-deserved rest
Bariatric Surgery in 2015
 Bariatric Surgery in 2015 Peter Nau, MD, MS Assistant Professor The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics 1 Objectives Define the obesity epidemic The cost of obesity Discuss the complications associated
Bariatric Surgery in 2015 Peter Nau, MD, MS Assistant Professor The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics 1 Objectives Define the obesity epidemic The cost of obesity Discuss the complications associated
Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Document Number: 001 Commercial MassHealth and Qualified Health Plans Authorization required X X Notification within 24 hours of service or next business day No notification
Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Document Number: 001 Commercial MassHealth and Qualified Health Plans Authorization required X X Notification within 24 hours of service or next business day No notification
Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy Alfonso Torquati MD, MSCI Associate Professor of Surgery Discosures NIH-NIDDK: grant support Covidien: consulting agreement, grant support
Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy Alfonso Torquati MD, MSCI Associate Professor of Surgery Discosures NIH-NIDDK: grant support Covidien: consulting agreement, grant support
Bariatric Surgical and Procedural Interventions in the Treatment of Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Bariatric Surgical and Procedural Interventions in the Treatment of Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes A position statement from the International Diabetes Federation Taskforce on Epidemiology and Prevention
Bariatric Surgical and Procedural Interventions in the Treatment of Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes A position statement from the International Diabetes Federation Taskforce on Epidemiology and Prevention
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Bariatric Surgery. Required forms: (Forms are located at OHCA Forms ) Certification Criteria for Providers. Treatment for Obesity
 Bariatric Surgery Required forms: (Forms are located at OHCA Forms ) HCA-13A HCA-12A Certification Criteria for Providers To be eligible for reimbursement, bariatric surgery providers must be certified
Bariatric Surgery Required forms: (Forms are located at OHCA Forms ) HCA-13A HCA-12A Certification Criteria for Providers To be eligible for reimbursement, bariatric surgery providers must be certified
American Society for Bariatric Surgery 100 SW 75th Street, Suite 201 Gainesville, FL 32607
 May 11, 2005 Steve E. Phurrough, MD, MPA Office of Clinical Standards & Quality Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Mail Stop C1-09-06 Baltimore, MD 21244-1850 Re: Request
May 11, 2005 Steve E. Phurrough, MD, MPA Office of Clinical Standards & Quality Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Mail Stop C1-09-06 Baltimore, MD 21244-1850 Re: Request
Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery
 Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery C Y N T H I A L. L O N G, M D, F A C S S I N A I H O S P I T A L O F B A L T I M O R E D E P A R T M E N T O F S U R G E R Y D I V I S I O N O F M I N I M A L L Y
Emerging Concepts in Bariatric Surgery C Y N T H I A L. L O N G, M D, F A C S S I N A I H O S P I T A L O F B A L T I M O R E D E P A R T M E N T O F S U R G E R Y D I V I S I O N O F M I N I M A L L Y
Weight Loss Surgery Information Session. WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program
 Weight Loss Surgery Information Session WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program What makes us different? Center of Excellence (COE) High volume center > 1000 procedures since 2003 Less complications than non-coe
Weight Loss Surgery Information Session WFBH Bariatric Surgery Program What makes us different? Center of Excellence (COE) High volume center > 1000 procedures since 2003 Less complications than non-coe
Systematic Literature Review on the Impact of Weight Loss from Adjustable Gastric Banding on Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia
 Systematic Literature Review on the Impact of Weight Loss from Adjustable Gastric Banding on Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia I. Introduction Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) surgery
Systematic Literature Review on the Impact of Weight Loss from Adjustable Gastric Banding on Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia I. Introduction Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) surgery
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
NHRMC General Surgery Specialists. Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303
 Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Type 2 Diabetes workshop notes
 Group 1 notes Abi / Nicole Type 2 Diabetes workshop notes 4.1 Population The group discussed the following sub groups that may need addressing: Men-as they tend to die earlier compared with women, their
Group 1 notes Abi / Nicole Type 2 Diabetes workshop notes 4.1 Population The group discussed the following sub groups that may need addressing: Men-as they tend to die earlier compared with women, their
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Obesity Affects Quality of Life
 Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes
 Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes This trial is conducted in Africa, Asia, Europe and the United States of America (USA). The aim
Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes This trial is conducted in Africa, Asia, Europe and the United States of America (USA). The aim
TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence
 TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 7 September 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Opioid dependence is defined as a strong desire to use the substance,
TITLE: Suboxone for Short-term Detoxification: A Review of the Clinical Evidence DATE: 7 September 2011 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Opioid dependence is defined as a strong desire to use the substance,
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery.
 Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
