[Type text] [Type text]
|
|
|
- Loraine Cole
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adult Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Spectrum of Clinical features and management in a Tertiary Health Institution and Literature Review J.A. Fasunla, O.G.B. Nwaorgu Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University College Hospital, Ibadan Nigeria Correspondence to: Dr James A. Fasunla, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University College Hospital, Ibadan. Nigeria, ayofasunla@gmail.com Background: Rhinosinusitis is defined as inflammation of the nasal and paranasal sinus mucosa. Chronic rhinosinusitis occurs when this inflammation and the symptoms persist for more than 3 months. The objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical features and management of adult chronic rhinosinusitis in a tertiary health institution and to review the literature for its current modalities of management. Methods: This is a 5-year retrospective study of all adult patients managed for clinically and radiologically diagnosed chronic rhinosinusitis at the study center. Their medical records were reviewed for essential data which included demographic data, clinical presentations, skin sensitivity test, radiologic reports and treatment offered. The data were collated and analyzed using simple descriptive statistics. Results: There were 228 patients, 97(42.54%) males and 131(57.46%) females with a male: female ratio of 1:1.35, age ranged between years (mean =35.2). The five major presenting symptoms were nasal discharge 228(100.00%), nasal obstruction 224 (98.25%), frequent throat hawking 189 (82.89%), itching of eye, ear, nose or throat 138 (60.53%) and excessive sneezing 136(59.65%). About 6% of the patients developed complications. Allergy accounted for the cause in 93 (40.79%) patients. Maxillary antral mucosal thickening and engorged inferior turbinates were the commonest radiological features. About 51% of the patients were treated with intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy with or without inferior turbinectomy. There was recurrence of symptoms in about 18% of these patients from 3 to 8months after surgery. Conclusions: Both subjective and objective measures should be employed in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis and intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy may rarely produce satisfactory clinical improvement. Introduction Rhinosinusitis is a common clinical condition which affects more than 16% of the adult population annually 1,2. It is defined as inflammation of the nasal and paranasal sinus mucosa. Chronic rhinosinusitis occurs when this inflammation and the symptoms persist for more than 3 months. Osteitis of the underlying bone may occur 3. Chronic rhinosinusitis is a multi factorial disease and obstruction at the osteomeatal complex usually accounts for most cases of chronic rhinosinusitis. This obstruction could be caused by nasal allergy, polyps, bacterial or fungal infection, anatomical abnormality like septal spurs/deviation, concha bullosa, enlarged ethmoidal bulla, tumors, immunodeficiency and mucociliary impairment 4. There are two histopathologic categories; the polypoidal mucosal change with eosinophilia variant is usually associated with a more severe damage to the nasal mucosa than the submucosal serous gland hyperplasia category 5-7. The burden of this disease on those it affects made it a challenge to the society. It impacts negatively on their quality of life thereby causing socioeconomic and academic loss. Although family physicians and pulmonologists are able to evaluate and care for some of these patients, they are usually faced with challenges of the disease recurrence, chronicity and complications. Good and adequate knowledge of the pathophysiology of this disease will bring about a better, effective treatment and good, satisfactory treatment outcome. Otorhinolaryngologists therefore have the responsibility of providing an accurate, efficient and accessible method of making diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis and also, providing an expanded knowledge about the disease process as well as developing better treatment modalities.
2 The aim of this study therefore, was to evaluate the clinical features and management modalities of chronic rhinosinusitis in our center and also, to present a review of its current management modalities. Patients and methods This is a 5-year retrospective study of all adult patients managed for clinically and radiologically diagnosed chronic rhinosinusitis at the department of Otorhinolaryngology, University College Hospital, Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria from The diagnosis was made based on the consensus reached and created in 1997 by the Rhinosinusitis Task Force of the American Academy of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) which was revised and amended in 2003 by the Sinus and Allergy Health Partnership (SAHP) 8-9. Patients data collected from their medical records included demographic data (age, sex), presenting symptoms and their duration at presentation with examination findings. Reports of the skin sensitivity test and plain radiographs of the paranasal sinuses comprising the occipito-frontal (Caldwell), occipito-mental (Water's) and lateral views were extracted as documented by the radiologist. The associated complications and treatment modalities were also collated. Those with incomplete data were excluded from the study. The data collected were analyzed using simple descriptive method and the results presented in tabular forms. Results Chronic rhinosinusitis constituted 78.2% of the total adult rhinologic cases seen during the study period. There were 228 patients, 97(42.54%) males and 131(57.46%) females with a male: female ratio of 1:1.35. The age ranged from years (mean =35.2). The five major presenting symptoms were nasal discharge 228(100.00%), nasal obstruction/congestion in 224 (98.25%), frequent hawking of throat 189 (82.89%), itching of the eye, ear, nose or throat in 138 (60.53%) and excessive sneezing in 136(59.65%) (Table 1). The clinical findings of the patients are presented in Table 2. Allergy accounted for the cause in 93 (40.79%) patients and nasal polyposis was seen in 13 (5.70%) patients. The diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis was further confirmed with plain paranasal sinus x-ray. The plain paranasal sinus radiographs of 34 (14.91%) patients appeared normal. The radiographic findings in the remaining 194 (85.09%) patients showed different abnormalities. There is involvement of more than one paranasal sinus in some of these patients and about 93% of the X- ray abnormalities showed involvement of maxillary sinuses (Figure 1). Mucosal thickening was found in 147 (75.77%) patients, soft tissue shadow in the nasal cavities suggesting engorged inferior turbinates were found in 139 (71.65%), Table 1. Clinical presentations of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Symptoms Frequency (n) Percentage (%) Nasal discharge Alternating/complete nasal blockage Frequent throat hawking & clearing Itching of eye, ear, nose or throat Excessive sneezing Hyposmia/anosmia Facial pain/pressure or headache Fatigue Ear pain Tooth ache Cheek pain/paraesthesia Hoarseness Halitosis
3 Note: All the patients had more than one symptom opacification of the maxillary antrum in 39 (20.10%) patients, diffuse opacification of the nasal cavity (ies) in 28(14.43%), septal spur/ deviation in 19 (9.79%) patients and fluid level in 2 (1.03%) patients. More than one radiologic feature was seen in some patients. The complications included Frontoethmoidal mucocele in 8 (3.51%) patients, Frontocutaneous fistula in 2 (0.88%) patients, Potts s Puffy tumor in 2 (0.88%) patients, blindness in 1 (0.44%) patient and intracranial abscess in 1 (0.44%) patient. Eighty one (35.53%) patients were successfully treated with medical treatments using nasal decongestant, ascorbic acid, steam inhalations and antibiotics. Medical and Surgical treatments were used in the remaining 147 patients. One hundred and seventeen (51.32%) patients were treated with intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy with or without inferior turbinectomy, 12 (5.26%) patients were treated with Caldwell-Luc operation and 18 (7.89%) patients were treated with external frontoethmoidectomy. Table 2. Clinical findings in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Signs Frequency (n) Percentage (%) Mucoid/Mucopurulent rhinorrhea Engorged inferior turbinate Edematous nasal mucosal Granular posterior pharyngeal wall Dull tympanic membrane Postnasal discharge Mouth breathing Nasal polyp Retracted tympanic membrane Septal deviation Note: All the patients had more than one sign.
4 Figure 1, Showed Plain paranasal occipitomental view with opacification of the left maxillary antrum (arrowed). Figure 2. Shows Fronto-cutaneous fistula (arrowed) in a woman with poorly managed chronic rhinosinusitis. All the patients had intranasal warm normal saline irrigations, ascorbic acid, antibiotics and decongestants post-operatively. Those with nasal polyposis had intranasal polypectomy and steroid therapy. Twenty one (17.95%) patients who had intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy had recurrence of symptoms within 3 8 months postoperative period. The patients with blindness due to sphenoidal mucocele and intracranial abscess had surgery via trans-nasal, external and skull base surgical approaches. Discussion Chronic rhinosinusitis is a common clinical presentation to the otorhinolaryngologic clinic as seen in this study where it constituted about 78% of rhinologic diseases in the adult population. The transition of rhinosinusitis from acute phase to chronicity depends largely on the predisposing factors which may be host or environmental (infective and non-infective) in origin 9, 10. Chronic rhinosinusitis occurs when the sinonasal mucosa inflammation persists for more than 3 months. This may result in defective ventilation of the paranasal sinuses when their ostia are obstructed. Irrespective of the etiologic factor, the clinical manifestations of this disease entity are similar 11. The spectra of clinical features of chronic rhinosinusitis seen in this study (Table 1) do not differ much from what had been reported in similar studies in both developing and developed countries Prior to 1997, there was no consensus reached as guideline for the diagnosis of rhinosinusitis. Some common sinonasal symptoms and signs were organized into major and minor factors in order to create a uniform diagnostic paradigm for rhinosinusitis. This was the product of consensus reached and created in 1997 by the Rhinosinusitis Task Force of the American Academy of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS). This laid emphasis on patient s history and limited physical examination findings which allow most patients to be diagnosed and effectively treated without an immediate need for further investigations. The diagnostic criteria for chronic rhinosinusitis require 2 or more major factors or 1 major factor and 2 minor factors 8. Major factors for diagnosis include facial pain or pressure, facial congestion or fullness, nasal obstruction or blockage, nasal discharge or purulence or discolored postnasal discharge and hyposmia or anosmia. Minor factors were defined as headache, fever, halitosis, fatigue, dental pain, cough, and ear pain or pressure, or fullness 9,14. However, facial pain or pressure alone does not constitute a strong history for diagnosing chronic rhinosinusitis in the absence of another major symptom or sign 9,14. The physical findings in this study (Table 2) are similar to the findings from other studies 8,9. Although these physical findings are important in chronic rhinosinusitis, they are not part of the diagnostic
5 criteria initially created by Rhinosinusitis Task Force of the American Academy of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) 8. The use of patients symptoms alone in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis has a pitfall as it does not address the cause of the problem. Obstruction at the osteomeatal complex usually accounts for most cases of chronic rhinosinusitis 4. Objective assessment measures aid in identifying the cause and the extent of the obstruction. A careful subjective and objective assessment measures are therefore the key to improving diagnostic accuracy. The anterior rhinoscopy, nasal endoscopy and Computerized Tomographic scan are objective measures that can increase the accuracy of chronic rhinosinusitis diagnosis 15. The Sinus and Allergy Health Partnership (SAHP) reviewed and amended the subjective diagnostic criteria created by Rhinosinusitis Task Force of the American Academy of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery to include physical and nasal examination findings in addition to suggestive history 13. These physical findings were divided into two groups namely; those accessible to all health care practitioners (examination of the face and anterior rhinoscopy) and to Otorhinolaryngologists (nasal endoscopy) 13,15. The expected facial findings include swelling and erythema of the maxillary, ocular, orbital and frontal areas. The anterior rhinoscopy findings include hyperemia, edema, crusts, purulence and polyps. The findings of Anterior rhinoscopy is limited as it may not reveal the pathology like grade 1 polyps, secretions and anatomical abnormalities at the osteomeatal complex due to poor exposure and visualization. Endoscopic examination by an otolaryngologist is useful in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis. The nasal endoscopy findings include bluish discoloration of turbinate, generalized or localized erythema, purulent discharge from Osteomeatal complex/sinus ostia, polypoidal swelling or granulation tissue, septal deviation, concha bullosa and paradoxical turbinates 13,15. The grading of nasal polyps was presented in the work of Lund and Mackay 16. There is a high correlation between endoscopic findings and Computerized Tomographic examination 15,17. The endoscopic observation of pus, polyps, or other significant mucosal derangements helps solidify the diagnosis. For areas that are not accessible to nasal endoscopy, Computerized Tomography can be useful in identifying disease. In our practice, examination of adult with chronic rhinosinusitis does not routinely involve nasal endoscopy. This is because the endoscopes are not readily available for use on the patients in our center. We therefore depend on the facial and anterior rhinoscopic findings in addition to the presenting symptoms in making diagnosis. Non usage of diagnostic nasal endoscope in our clinical practice would have resulted in some important clinical findings being missed thereby, resulting in incomplete clinical documentation of the disease. Radiological imaging is complementary to the clinical evaluation of patients with rhinosinusitis. Radiographic examination has evolved significantly over time. Computerized Tomographic (CT) scan has replaced plain-film radiographs as the standard for paranasal sinus imaging in health institutions in developed countries 18,19. However, in most centers in the developing countries, patients are still being evaluated with plain radiographs of the paranasal sinuses (Figure 1) because of availability and cost. In our centre, it is often those who had complications or with doubtful diagnosis on plain radiographs that are re-evaluated with CT scan. This is because most of our patients are from the low socioeconomic class and can hardly afford the investigation. The plain radiographs of the paranasal sinuses have the limitation of many structures being superimposed on one another and not being able to define the osteomeatal complex 18,20. CT scan of paranasal sinuses has the merit of better disease delineation and will show any anatomical intranasal abnormality especially at the osteomeatal complex and paranasal sinuses 18. Since the advent of antibiotics, complication of infective rhinosinusitis is uncommon However, about 6.14% of our patients with chronic rhinosinusitis still presented with different complications. Fronto-ethmoidal mucocele is the commonest complication seen in this study. These patients
6 commonly presented with frontal headache, scanty anterior mucoid nasal discharge and frontal swelling. Fronto-cutaneous fistula was seen in two patients (Figure 2). Self medication and delayed presentation for appropriate management were the factors identified to have contributed to the development of fronto-cutaneous fistula in these patients. The principles of management of chronic rhinosinusitis include treatment of the underlying cause, reduction of nasal mucosa inflammation and swelling, and restoration of ventilation of the paranasal sinuses 23. In this study, medical treatment alone was successfully used to treat 36% of cases. This treatment includes the use of steam inhalation, nasal decongestant, ascorbic acids and antibiotics. Those patients with allergy and allergic nasal polyposis also had steroid therapy. The use of steroid in the treatment of nasal polyps has been reported 10-11,23. All patients in this study had initial medical treatment and surgery was indicated only if the symptoms persisted or worsened and when there is an obvious growth or polyps in the nasal cavity. Surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis is indicated when there is failure of medical treatment and when there is an obvious growth or anatomical abnormalities within the nasal cavity preventing drainage and aeration of the sinuses 24. In this study, intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy with or without inferior turbinectomy was performed in 51% of the cases. This surgical procedure is usually performed with the intention of providing dependent drainage for the maxillary sinus which is believed to be the site commonly affected by the disease. Perhaps, this procedure is justified as about 93% of the paranasal sinus radiograph in this study showed involvement of the maxillary sinus. Recurrence of symptoms was seen in 18% cases within 3 8 months after the surgery in this study. When this fails to achieve the desire outcome and improvement then, removal of the entire maxillary mucosa is performed through Caldwell-Luc procedure 25. Twelve (5.26%) patients in this study were treated with Caldwell-Luc operation. The invention and use of nasal endoscope has brought about better understanding of the disease pathogenesis and osteomeatal complex is now known to be more frequently involved in the disease. The inflammation in this area usually spread to obstruct the drainage of paranasal sinuses and produce repeated infection and hence, persistent mucosa inflammation 4, 9-10,26. Surgical management that focuses on the removal of the obstructive pathology at the osteomeatal complex region have been efficacious and has provided a better improved surgical outcome of this disease 24, The goal of this procedure is to reestablish the patency of the paranasal sinuses natural ostia for aeration and drainage. This is thought to bring about a reversal of the damaged sinonasal mucosa to normal state 27,28. Septoplasty should be performed to correct septal spur/deviation contributing to nasal obstruction. This was never part of the surgical management of these patients in this study. This may be the reason while some of these patients had recurrence of their nasal symptoms 29. Conclusion In making diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis in adults, both subjective and objective measures should be employed for the purpose of an improved accuracy. Emphasis should be laid on the therapy that will remove the cause of the disease and restore the patency of natural ostia for improved sinus aeration and physiologic drainage. References 1. Anand VK. Epidemiology and economic impact of rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 2004;193: McCaig LF, Nghi L. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2000 Emergency Department Summary. Adv Data 2002;326: Giacchi RJ, Lebowitz RA, Yee HT, Light JP, Jacobs JB. Histopathologic evaluation of the ethmoid bone in chronic sinusitis. Am J Rhinol 2001;15:193 7.
7 4. Cauwenberge PV, Hoecke HV, Bachert C. Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2006;6: Szucs E, Ravandi S, Goosens A, Beal M, Clement PA. Eosinophilia on the ethmoid mucosa and its relationship to the severity of inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol 2002;16: Malekzadeh S, McGuire JF. The new histologic classification of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2003;3: Berger G, Kattan A, Bernheim J, Ophir D. Polypoid mucosa with eosinophilia and glandular hyperplasia in chronic sinusitis: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study. Laryngoscope 2002;112: Lanza DC, Kennedy DW. Adult rhinosinusitis defined, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997; 117: S1 S7. 9. Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003; 129: S Lane AP, Kennedy DW. Sinusitis and Polyposis. In Ballenger s Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 16 th edition, Spain: Williams and Wilkins 1996: Weir N, Golding-Wood D G. Infective rhinitis and sinusitis. In Scott-Brown's Rhinology 6th edition (Mackay I S, Bull T R eds) Butterworth-Heinemann, London. 1997: pp4/8/ da Lilly-Tariah O.B. Pattern of clinical features of simple chronic rhinosinusitis in Port Harcourt. Niger J Clin Pract 2006;9: Hadley JA, Schaefer SD. Clinical evaluation of rhinosinusitis: history and physical examination. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997;117: Frederick J, Braude AL. Anaerobic infection of the paranasal sinuses. N Engl J Med 1974; 200: Anand K. Devaiah MD. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: diagnosis and dilemmas. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2004;37: Lund VJ, Mackay IS. Staging in rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 1993;31: Kennedy DW. Prognostic factors, outcomes and staging in ethmoid sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 1992; 102: Zinreich SJ. Rhinosinusitis: radiologic diagnosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997; 117:S Cousin JN, Har-El G, Li J. Is there a correlation between radiographic and histologic findings in chronic sinusitis? J Otolaryngol 2000;29: Osguthorpe JD, Charleston SC. Adult Rhinosinusitis: Diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician 2001; 63: Brook I, Frazier EH, Foote PA. Microbiology of the transition from acute to chronic maxillary sinusitis. J Med Microbiol 1996;45: Poole MD, Portugal LG. Treatment of rhinosinusitis in the outpatient setting. Am J Med 2005;118: Watelet JB, Eloy PH, van Cauwenberge PV. Drug management in chronic rhinosinusitis: identification of the needs. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2007;3: Orlandi RR, Kennedy DW. Surgical management of rhinosinusitis. Am J Med Scis 1998; 316: Stefansson P, Andreasson L, Jannert M. Caldwell-Luc operation: long-term results and sequelaes. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 1988;449: Kennedy DW, Zinreich SJ, Rosenbaum AE, Johns ME. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Theory and diagnostic evaluation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1985;111: Smith TL, Batra PS, Seiden AM, Hannley M. Evidence supporting Endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of Adult Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Am J Rhinol 2005;19: Lund VJ, Mackay IS. Outcome assessment of endoscopic sinus surgery. J R Soc Med 1994;87:70-72.
8 29. Grymer LF, Pedersen OF, Hilberg O, Elbrond O. Acoustic rhinometry: Evaluation of the nasal cavity with septal deviations, before and after septoplasty. Laryngoscope 1989; 99:
GUIDELINE Sinusitis. David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor. Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery
 GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations
 Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations Shannon Hunter, MD Board-Certified Otolaryngologist Thank you for joining us today We are recording this webinar and will be sending
Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis: The Latest Recommendations Shannon Hunter, MD Board-Certified Otolaryngologist Thank you for joining us today We are recording this webinar and will be sending
Nasal and Sinus Disorders
 Nasal and Sinus Disorders Chronic Nasal Congestion When nasal obstruction occurs without other symptoms (such as sneezing, facial pressure, postnasal drip etc.) then a physical obstruction might be the
Nasal and Sinus Disorders Chronic Nasal Congestion When nasal obstruction occurs without other symptoms (such as sneezing, facial pressure, postnasal drip etc.) then a physical obstruction might be the
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine
 Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Sinus Headache vs. Migraine John M. DelGaudio, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology Emory University School of Medicine 1 Sinus Headache Problems
Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in. Children
 Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Children Fuad M. Baroody, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatrics The University of Chicago Medicine and Biological
Surgical Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Children Fuad M. Baroody, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatrics The University of Chicago Medicine and Biological
Nasal polyps differ in terms of origin, as well
 Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Clearing the Air on Nasal Polyps By Gordon Franke, MD, BSc, FRCS(C) Presented at the University of Saskatchewan Practical Otolaryngology Conference 2003,
Focus on CME at the University of Saskatchewan Clearing the Air on Nasal Polyps By Gordon Franke, MD, BSc, FRCS(C) Presented at the University of Saskatchewan Practical Otolaryngology Conference 2003,
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Transition Spaces. LJ Mariotti, DO Associate Professor of Surgery The Commonwealth Medical College Scranton, PA
 Transition Spaces LJ Mariotti, DO Associate Professor of Surgery The Commonwealth Medical College Scranton, PA Messerklinger considered these the spaces between the sinus proper and the nose He called
Transition Spaces LJ Mariotti, DO Associate Professor of Surgery The Commonwealth Medical College Scranton, PA Messerklinger considered these the spaces between the sinus proper and the nose He called
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty
 Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2015 8/2016 8/2015 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2015 8/2016 8/2015 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
By James D. Gould, MD FACS
 By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
New treatment options for chronic sinusitis
 New treatment options for chronic sinusitis Balloon Sinuplasty Technology Vishram Jalukar, MD Mason City Clinic ENT & Allergy MKT01014 Rev. D Sinusitis Overview Inflammation of the sinus lining caused
New treatment options for chronic sinusitis Balloon Sinuplasty Technology Vishram Jalukar, MD Mason City Clinic ENT & Allergy MKT01014 Rev. D Sinusitis Overview Inflammation of the sinus lining caused
YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY What is functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)? Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE: SECTION OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY PATIENT INFORMATION FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY What is functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)? Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA 2010 Allergy Symposium November 6, 2010 David Keschner, MD, JD HNS Orange County General Introduction Overview of material Anatomy and Clinical Features
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF NASAL CONGESTION AND RHINORRHEA 2010 Allergy Symposium November 6, 2010 David Keschner, MD, JD HNS Orange County General Introduction Overview of material Anatomy and Clinical Features
Underestimation of Rhinogenic Causes in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Acute Headache
 Original Article 37 Underestimation of Rhinogenic Causes in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Acute Headache Jae-Heon Lee, Hyun-Jik Kim, Young-Ho Hong, Kyung-Soo Kim Abstract- Objectives:
Original Article 37 Underestimation of Rhinogenic Causes in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Acute Headache Jae-Heon Lee, Hyun-Jik Kim, Young-Ho Hong, Kyung-Soo Kim Abstract- Objectives:
Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Audio Seminar/Webinar July 31, 2008 Practical Tools for Seminar Learning Copyright 2008 American Health Information Management Association. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Coding Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Audio Seminar/Webinar July 31, 2008 Practical Tools for Seminar Learning Copyright 2008 American Health Information Management Association. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Sinusitis. Health Promotion and Education Program. Rev. 2014 MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E
 Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Sinusitis Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-766-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
What is Balloon Sinuplasty?
 What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
What is Balloon Sinuplasty? The painful symptoms associated with chronic sinusitis can be overwhelming. If symptoms are difficult to control with medications alone, your primary doctor may refer you to
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis can include:
 Rhinitis Rhinitis is an irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. There are two types of rhinitis, allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and nonallergic (such as vasomotor) rhinitis.
Rhinitis Rhinitis is an irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. There are two types of rhinitis, allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and nonallergic (such as vasomotor) rhinitis.
Get Your Head In The Game. Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016
 Get Your Head In The Game Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016 About Me Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Geisinger Medical Center General Surgery University of California San Francisco
Get Your Head In The Game Matthew Voorman, MD Hutchinson Clinic March 21, 2016 About Me Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Geisinger Medical Center General Surgery University of California San Francisco
fig.1: CT scan of sinuses: Right isolated sphenoid sinus opacification
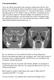 Case presentation: An 8 year old boy presented to the emergency department with few days history of severe headache. Pain is described as fronto-occipital, continuous and not relieved by pain medications.
Case presentation: An 8 year old boy presented to the emergency department with few days history of severe headache. Pain is described as fronto-occipital, continuous and not relieved by pain medications.
BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION
 BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION Effective Date: March 11, 2014 Review Dates: 12/11, 12/12, 2/13, 2/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: December 14, 2011 Status: Current I. POLICY/CRITERIA A. The use of balloon sinus
BALLOON SINUS OSTIAL DILATION Effective Date: March 11, 2014 Review Dates: 12/11, 12/12, 2/13, 2/14, 2/15 Date Of Origin: December 14, 2011 Status: Current I. POLICY/CRITERIA A. The use of balloon sinus
Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure?
 Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure? Instant relief that lasts Quick recovery Sinusitis, Balloon Sinus Dilation, and You 1 What are the Sinuses? How do Healthy Sinuses Work? Paranasal sinuses are air
Tired of Sinusitis Pain and Pressure? Instant relief that lasts Quick recovery Sinusitis, Balloon Sinus Dilation, and You 1 What are the Sinuses? How do Healthy Sinuses Work? Paranasal sinuses are air
Pulsating Aerosol. The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy. For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis
 The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases of the upper airways www.parimedical.co.uk
The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases of the upper airways www.parimedical.co.uk
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Introduction. 31 million Americans suffer from chronic sinusitis Surgical treatment for chronic sinusitis has evolved tremendously since its inception
 Balloon Sinuplasty Ki-Hong Kevin Ho, MD Faculty Advisor: Patricia Maeso, MD Department of Otolaryngology The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation December 16, 2009 Introduction
Balloon Sinuplasty Ki-Hong Kevin Ho, MD Faculty Advisor: Patricia Maeso, MD Department of Otolaryngology The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation December 16, 2009 Introduction
Endoscopic Surgical Treatment of Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis of Dental Origin
 Endoscopic Surgical Treatment of Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis of Dental Origin Fabio Costa, MD,* Enzo Emanuelli, MD, Massimo Robiony, MD, FEBOMS, Nicoletta Zerman, MD, Francesco Polini, MD, and Massimo
Endoscopic Surgical Treatment of Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis of Dental Origin Fabio Costa, MD,* Enzo Emanuelli, MD, Massimo Robiony, MD, FEBOMS, Nicoletta Zerman, MD, Francesco Polini, MD, and Massimo
Clinical Features and Treatments of Odontogenic Sinusitis
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.932 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(6):932-937, 2010 Clinical Features and Treatments of Odontogenic Sinusitis Kyung Chul Lee and Sung Jin
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.932 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(6):932-937, 2010 Clinical Features and Treatments of Odontogenic Sinusitis Kyung Chul Lee and Sung Jin
Balloon catheter sinusotomy: One-year follow-up Outcomes and role in functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 139, S27-S37 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Balloon catheter sinusotomy: One-year follow-up Outcomes and role in functional endoscopic sinus surgery Frederick A. Kuhn, MD,
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 139, S27-S37 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Balloon catheter sinusotomy: One-year follow-up Outcomes and role in functional endoscopic sinus surgery Frederick A. Kuhn, MD,
Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY
 Advanced Sinus /Skull Base Center ENT & Allergy Associates, LLP Fall 2014 Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY www.schaeffermd.com New Treatments for Nasal Polyps Dr Schaeffer
Advanced Sinus /Skull Base Center ENT & Allergy Associates, LLP Fall 2014 Nasal Polyps B. Todd Schaeffer, MD, FACS Lake Success, Long Island, NY www.schaeffermd.com New Treatments for Nasal Polyps Dr Schaeffer
Endoscopic Aided Septoplasty Versus Conventional Septoplasty
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (1): 33-38, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.1.83185 Endoscopic Aided Septoplasty Versus Conventional Septoplasty Magdy
World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (1): 33-38, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.1.83185 Endoscopic Aided Septoplasty Versus Conventional Septoplasty Magdy
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Prevention and Management of Complications in Maxillary Sinus Surgery
 Prevention and Management of Complications in Maxillary Sinus Surgery Esther Kim, MD, James A. Duncavage, MD* KEYWORDS Maxillary antrostomy Management of complications Prevention of complications Caldwell-Luc
Prevention and Management of Complications in Maxillary Sinus Surgery Esther Kim, MD, James A. Duncavage, MD* KEYWORDS Maxillary antrostomy Management of complications Prevention of complications Caldwell-Luc
Study to Compare and Evaluate Traditional vs. Endoscopic Septoplasty Shrestha I, Pokharel M, Dhakal A, Amatya RCM
 Original Article VOL. 13 NO. 2 ISSUE 50 APRIL-JUNE 2015 Study to Compare and Evaluate Traditional vs. Endoscopic Septoplasty Shrestha I, Pokharel M, Dhakal A, Amatya RCM ABSTRACT Background Department
Original Article VOL. 13 NO. 2 ISSUE 50 APRIL-JUNE 2015 Study to Compare and Evaluate Traditional vs. Endoscopic Septoplasty Shrestha I, Pokharel M, Dhakal A, Amatya RCM ABSTRACT Background Department
ACUTE SINUSITIS. Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997
 ACUTE SINUSITIS Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997 ANATOMY There are four paired paranasal sinuses, the maxillary, ethmoid,, frontal and sphenoid sinuses Anterior and posterior sinuses
ACUTE SINUSITIS Michael E. Prater, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 19, 1997 ANATOMY There are four paired paranasal sinuses, the maxillary, ethmoid,, frontal and sphenoid sinuses Anterior and posterior sinuses
Sinusitis is ubiquitous among humans and one of the most common reasons
 Sinusitis Kathleen Fitch, MSN, APRN,BC, FNP Gennine Zinner, RNC, ANP Sinusitis is ubiquitous among humans and one of the most common reasons health care office visits in the USA. In 1991 sinusitis accounted
Sinusitis Kathleen Fitch, MSN, APRN,BC, FNP Gennine Zinner, RNC, ANP Sinusitis is ubiquitous among humans and one of the most common reasons health care office visits in the USA. In 1991 sinusitis accounted
The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Relationship to Nasal Septal Deviation and Paranasal Sinus Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1613 1618, October 2004 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Relationship to Nasal Septal Deviation and Paranasal Sinus Disease Jamie S. Stallman, Joao N. Lobo, and Peter M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1613 1618, October 2004 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Relationship to Nasal Septal Deviation and Paranasal Sinus Disease Jamie S. Stallman, Joao N. Lobo, and Peter M.
500 EXCHANGE STREET, PROVIDENCE, RI 02903-2699 MEDICAL COVERAGE POLICY 1 (401) 274-4848 WWW.BCBSRI.COM
 Medical Coverage Policy Implantable Sinus Spacers and Stents for Postoperative Use Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery EFFECTIVE DATE: 09 18 2012 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 00 00 2013 sad OVERVIEW Sinus spacers/stents
Medical Coverage Policy Implantable Sinus Spacers and Stents for Postoperative Use Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery EFFECTIVE DATE: 09 18 2012 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 00 00 2013 sad OVERVIEW Sinus spacers/stents
Clinical Consensus Statement: Septoplasty with or without Inferior Turbinate Reduction
 Clinical Consensus Statement Clinical Consensus Statement: Septoplasty with or without Inferior Turbinate Reduction Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015, Vol. 153(5) 708 720 Ó American Academy of
Clinical Consensus Statement Clinical Consensus Statement: Septoplasty with or without Inferior Turbinate Reduction Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015, Vol. 153(5) 708 720 Ó American Academy of
Chronic sinusitis is a symptomatic inflammation of the. The Role of Balloon Sinuplasty in the Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis. balloon sinuplasty
 The Role of Balloon Sinuplasty in the Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Joseph P. Cummings, PhD, Hoyee Leong, PhD, and Karl A. Matuszewski, MS, PharmD Abstract Objective: To evaluate the status of balloon
The Role of Balloon Sinuplasty in the Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Joseph P. Cummings, PhD, Hoyee Leong, PhD, and Karl A. Matuszewski, MS, PharmD Abstract Objective: To evaluate the status of balloon
Balloon Catheter Dilation for Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 1 (Note: A mini HTA report consists of two parts. The first is completed by the applicant at the time the new technology is requested. The second consists of a commentary and possibly additional evidence
1 (Note: A mini HTA report consists of two parts. The first is completed by the applicant at the time the new technology is requested. The second consists of a commentary and possibly additional evidence
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Frontal Headache. Chapter 14. Core Messages. Introduction. Allen M. Seiden
 Chapter Frontal Headache Core Messages Frontal headache frequently accompanies obstruction and inflammation of the frontal sinuses, but may also reflect other sources of head pain not related to sinus
Chapter Frontal Headache Core Messages Frontal headache frequently accompanies obstruction and inflammation of the frontal sinuses, but may also reflect other sources of head pain not related to sinus
Headaches due to nasal and paranasal sinus disease
 Neurol Clin N Am 22 (2004) 1 19 Headaches due to nasal and paranasal sinus disease Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Jefferson Headache Center, 111 South Eleventh Street,
Neurol Clin N Am 22 (2004) 1 19 Headaches due to nasal and paranasal sinus disease Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Jefferson Headache Center, 111 South Eleventh Street,
Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) Ear, Nose and Throat Surgery
 Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) Ear, Nose and Throat Surgery 31 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact
Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) Ear, Nose and Throat Surgery 31 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact
ENDOSCOPIC VERSUS TRADITIONAL SEPTOPLASTY
 ENDOSCOPIC VERSUS TRADITIONAL SEPTOPLASTY Ahmed Shehata, Mohamed EL-Sayed and Taha Mohamed Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Egypt ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of
ENDOSCOPIC VERSUS TRADITIONAL SEPTOPLASTY Ahmed Shehata, Mohamed EL-Sayed and Taha Mohamed Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Egypt ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of
Normal CT scan of the chest
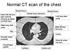 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Effect of Septoplasty on Inferior Turbinate
 Effect of Septoplasty on Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy * (M.D, Ph. D) **Hawar Mazhar (M.B.Ch.B) Abstract Background: Septal deviation usually associated with compensatory hypertrophy of the contralateral
Effect of Septoplasty on Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy * (M.D, Ph. D) **Hawar Mazhar (M.B.Ch.B) Abstract Background: Septal deviation usually associated with compensatory hypertrophy of the contralateral
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
This assessment is effective as of October 2014. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, e-mail certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
Sinus Infection Overview
 Sinus Infection Sinus Infection Overview Sinus infection, or sinusitis, is an inflammation of the sinuses and nasal passages. A sinus infection can cause aheadache or pressure in the eyes, nose, cheek
Sinus Infection Sinus Infection Overview Sinus infection, or sinusitis, is an inflammation of the sinuses and nasal passages. A sinus infection can cause aheadache or pressure in the eyes, nose, cheek
Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
 Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic
Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic
Image. 3.11.3 SW Review the anatomy of the EAC and how this plays a role in the spread of tumors.
 Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Neoplasms of the Ear and Lateral Skull Base Image 3.11.1 SW What are the three most common neoplasms of the auricle? 3.11.2 SW What are the four most common neoplasms of the external auditory canal (EAC)
Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information
 Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information PREOPERATIVE DISCUSSION FOR SEPTOPLASTY and TURBINATE REDUCTION Septoplasty The nasal septum is made of cartilage and bone covered with a lining
Septoplasty and Turbinate Reduction Surgical Information PREOPERATIVE DISCUSSION FOR SEPTOPLASTY and TURBINATE REDUCTION Septoplasty The nasal septum is made of cartilage and bone covered with a lining
Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis
 Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis Umadevi P. Nair, DMD, MDS, a and Madhu K. Nair, DMD, MS, PhD, b Gainesville, Florida UNIVERSITY OF
Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin: cone-beam volumetric computerized tomography aided diagnosis Umadevi P. Nair, DMD, MDS, a and Madhu K. Nair, DMD, MS, PhD, b Gainesville, Florida UNIVERSITY OF
NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS. Sinusitis
 NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS Sinusitis The sinuses also called paranasal sinuses are 4 pairs of air-containing spaces in the head (maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid). They extend from the nasal passages
NOSE AND SINUS PROBLEMS Sinusitis The sinuses also called paranasal sinuses are 4 pairs of air-containing spaces in the head (maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid). They extend from the nasal passages
Toothaches of Non-dental Origin
 Toothaches of Non-dental Origin This brochure is produced by the American Academy of Orofacial Pain The American Academy of Orofacial Pain is an organization of health care professionals dedicated to alleviating
Toothaches of Non-dental Origin This brochure is produced by the American Academy of Orofacial Pain The American Academy of Orofacial Pain is an organization of health care professionals dedicated to alleviating
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
HealthPACT. Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology Australia and New Zealand. Technology Brief
 HealthPACT Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology Australia and New Zealand Technology Brief Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Rhinosinusitis February 2012 State of Queensland (Queensland Health)
HealthPACT Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology Australia and New Zealand Technology Brief Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Rhinosinusitis February 2012 State of Queensland (Queensland Health)
Test Request Tip Sheet
 With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely necessary. The study
Sore Throat. Definition. Causes. (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis
 Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Sore Throat (Pharyngitis; Tonsillopharyngitis; Throat Infection) Pronounced: Fare-en-JY-tis /TAHN-sill-oh-fare-en-JY-tis by Jennifer Lewy, MSW En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A sore throat is the
Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors. Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery
 Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Pituitary Tumors Pituitary adenoma: common intracranial neoplasm
Update on Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors Kristen Riley, MD, FACS Associate Professor, Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Pituitary Tumors Pituitary adenoma: common intracranial neoplasm
Cervical lymphadenopathy
 Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Cervical lymphadenopathy Introduction There are various classifications of lymphadenopathy, but a simple and clinically useful system is to classify lymphadenopathy as "generalized" if lymph nodes are
Acoustic Rhinometry and Nasal Congestion in Patients with mild Sleep Apnea
 Acoustic rhinometry findings in patients with mild sleep apnea STEVEN M. HOUSER, MD, FAAOA, BULENT MAMIKOGLU, MD, BENJAMIN F. AQUINO, MS, MD, RIZWAN MOINUDDIN, BA, and JACQUELYNNE P. COREY, MD, FACS, FAAOA,
Acoustic rhinometry findings in patients with mild sleep apnea STEVEN M. HOUSER, MD, FAAOA, BULENT MAMIKOGLU, MD, BENJAMIN F. AQUINO, MS, MD, RIZWAN MOINUDDIN, BA, and JACQUELYNNE P. COREY, MD, FACS, FAAOA,
Jose M. Busquets Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine
 Jose M. Busquets Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine Personal Work Address: Puerto Rico Nasal and Sinus Institute 299 Ave.
Jose M. Busquets Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine Personal Work Address: Puerto Rico Nasal and Sinus Institute 299 Ave.
Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine
 Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Department of Neurology Los Angeles Kaiser Objectives 1) Identify the diagnostic features of migraine Differentiate from sinusitis 2)
Evaluation of Headache Syndromes and Migraine Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Department of Neurology Los Angeles Kaiser Objectives 1) Identify the diagnostic features of migraine Differentiate from sinusitis 2)
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis NMP307 Effective Date*: December 2006 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Balloon Sinuplasty for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis NMP307 Effective Date*: December 2006 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia
 Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Lower Respiratory Tract Dr T Avenant Recurrent or Persistent Pneumonia Definitions Recurrent pneumonia more than two episodes of pneumonia in 18 months Persistent pneumonia
Texas Sinus Center PATIENT REGISTRATION. Name Birth date Soc Sec# Address City/State Zip
 Texas Sinus Center PATIENT REGISTRATION 1. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Birth date Soc Sec# Address City/State Zip Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Marital Status S / M / W / D Student FT / PT Male / Female
Texas Sinus Center PATIENT REGISTRATION 1. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Birth date Soc Sec# Address City/State Zip Home Phone Work Phone Cell Phone Marital Status S / M / W / D Student FT / PT Male / Female
Childhood ENT disorders. When to refer to specialists. Claire Harris
 Childhood ENT disorders When to refer to specialists Claire Harris Background. Ear, nose and throat (ENT) are among the commonest reasons for attendance in general practice. Acute problems are managed
Childhood ENT disorders When to refer to specialists Claire Harris Background. Ear, nose and throat (ENT) are among the commonest reasons for attendance in general practice. Acute problems are managed
Tiffany Baugh, MD Matthew Page, MD 1/21/2015 CSF LEAK AND ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 Tiffany Baugh, MD Matthew Page, MD 1/21/2015 CSF LEAK AND ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Outline Anatomy Diagnosis intra-op Diagnosis post-op Treatment/Management Cases Question Important Anatomical Considerations
Tiffany Baugh, MD Matthew Page, MD 1/21/2015 CSF LEAK AND ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Outline Anatomy Diagnosis intra-op Diagnosis post-op Treatment/Management Cases Question Important Anatomical Considerations
Medical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Michael A Kaliner, MD
 Medical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Michael A Kaliner, MD Medical Director, Institute for Asthma and Allergy Wheaton and Chevy Chase, MD Professor of Medicine, George Washington University School
Medical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Michael A Kaliner, MD Medical Director, Institute for Asthma and Allergy Wheaton and Chevy Chase, MD Professor of Medicine, George Washington University School
Pulsating Aerosol. The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy. Cystic Fibrosis. Focus on. For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis
 The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Focus on Cystic Fibrosis Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases
The New Wave in SINUSitis Therapy Focus on Cystic Fibrosis Pulsating Aerosol For the precise, effective and gentle treatment of sinusitis PARI SINUS Inhalation treatment for acute and chronic diseases
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation. Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics
 Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Headache: Differential diagnosis and Evaluation Raymond Rios PGY-1 Pediatrics You are evaluating a 9 year old male patient at the ED brought by his mother, who says that her son has had a fever, cough,
Current reviews of allergy and clinical immunology (Supported by a grant from Astra Pharmaceuticals, Westborough, Mass)
 Current reviews of allergy and clinical immunology (Supported by a grant from Astra Pharmaceuticals, Westborough, Mass) Series editor: Harold S. Nelson, MD Chronic sinusitis Daniel L. Hamilos, MD St Louis,
Current reviews of allergy and clinical immunology (Supported by a grant from Astra Pharmaceuticals, Westborough, Mass) Series editor: Harold S. Nelson, MD Chronic sinusitis Daniel L. Hamilos, MD St Louis,
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Adult Sinusitis Guideline
 Adult Sinusitis These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They are not intended to replace a clinician
Adult Sinusitis These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They are not intended to replace a clinician
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
ORAL MAXILLO FACIAL SURGERY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines General problems include: Soft tissue conditions of the face and oral cavity
Prevention of Ear, Nose and Throat diseases for swimmers
 Prevention of Ear, Nose and Throat diseases for swimmers Dr. WAI Heung-On Jonathan 3 May 2014 Hong Kong 2014 International Swimming Teacher s Conference Prevention of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases for
Prevention of Ear, Nose and Throat diseases for swimmers Dr. WAI Heung-On Jonathan 3 May 2014 Hong Kong 2014 International Swimming Teacher s Conference Prevention of Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases for
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements
 Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Residency Competency and Proficiency Statements 1. REQUEST AND RESPOND TO REQUESTS FOR CONSULTATIONS Identify needs and make referrals to appropriate health care providers for the treatment of physiologic,
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Septoplasty/ Submucous Resection (SMR) and Turbinate Surgery. What is the nasal septum and what are turbinates?
 Septoplasty/ Submucous Resection (SMR) and Turbinate Surgery Mr H S Khalil, MS, FRCS(ORL-HNS),MD Consultant ENT Surgeon and Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer What is the nasal septum and what are turbinates?
Septoplasty/ Submucous Resection (SMR) and Turbinate Surgery Mr H S Khalil, MS, FRCS(ORL-HNS),MD Consultant ENT Surgeon and Honorary Clinical Senior Lecturer What is the nasal septum and what are turbinates?
Surgery of the Frontal Sinus
 Surgery of the Frontal Sinus Steven D. Pletcher MD Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco Disclosures Co-author patent application
Surgery of the Frontal Sinus Steven D. Pletcher MD Assistant Professor Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco Disclosures Co-author patent application
Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP.
 COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
COUGH Cough, as a leading symptom, would certainly be in the top 10 of reasons for seeing a GP. A cough in a child seems to cause more concern, even when it has not been present very long, whereas in adults
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review
 TECHNICAL REPORT Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review abstract In 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics published clinical practice
TECHNICAL REPORT Evidence for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Sinusitis in Children: A Systematic Review abstract In 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics published clinical practice
Recalcitrant Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Nathan Chen, M.D. Dana King, M.D. Jan 2, 2013
 Recalcitrant Chronic Rhinosinusitis Nathan Chen, M.D. Dana King, M.D. Jan 2, 2013 Outline Chronic rhinosinusitis Background Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment (medical and surgical) Workup and management
Recalcitrant Chronic Rhinosinusitis Nathan Chen, M.D. Dana King, M.D. Jan 2, 2013 Outline Chronic rhinosinusitis Background Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment (medical and surgical) Workup and management
Standalone balloon dilation versus sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial DO NOT COPY
 Standalone balloon dilation versus sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial Jeffrey Cutler, M.D., 1 Nadim Bikhazi, M.D., 2 Joshua Light, M.D.,
Standalone balloon dilation versus sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial Jeffrey Cutler, M.D., 1 Nadim Bikhazi, M.D., 2 Joshua Light, M.D.,
SARCOIDOSIS. Signs and symptoms associated with specific organ involvement can include the following:
 SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a disease that occurs when areas of inflammation develop in different organs of the body. Very small clusters of inflammation, called granulomas, are seen with sarcoidosis. They
Allergies and Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease
 Allergies and Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease Allergy is the term used to describe an over-reaction of the body to a substance that is normally harmless to most people. This substance is called an allergen,
Allergies and Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease Allergy is the term used to describe an over-reaction of the body to a substance that is normally harmless to most people. This substance is called an allergen,
Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain
 1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale
 Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale 2013 1 Table des matières 1. Pathology of acuite nose and sinus infections...3 1.1. Acute
Item 90 : Nose and sinus infections in children and adults Collège Français d'orl et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale 2013 1 Table des matières 1. Pathology of acuite nose and sinus infections...3 1.1. Acute
Protocol. Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis
 Protocol Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/15 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 07/07, 07/08, 11/08, 05/09, 01/10,
Protocol Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/15 Next Review Date: 11/16 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 07/07, 07/08, 11/08, 05/09, 01/10,
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis
 Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Policy Number: 7.01.105 Last Review: 3/2016 Origination: 3/2007 Next Review: 9/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Balloon Ostial Dilation for Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis Policy Number: 7.01.105 Last Review: 3/2016 Origination: 3/2007 Next Review: 9/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
 Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) What is? is a common virus that infects the linings of the airways - the nose, throat, windpipe, bronchi and bronchioles (the air passages of the lungs). RSV is found
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Comment prendre en charge une épistaxis sévère en médecine ambulatoire?!
 Comment prendre en charge une épistaxis sévère en médecine ambulatoire? Prof. dr. Thibaut. Van Zele Prof. dr. Jean-Baptiste Watelet dienst neus-, keel- en oorheelkunde Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 2013
Comment prendre en charge une épistaxis sévère en médecine ambulatoire? Prof. dr. Thibaut. Van Zele Prof. dr. Jean-Baptiste Watelet dienst neus-, keel- en oorheelkunde Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 2013
ENT Coding: Does Your Nose Know When You Are Coding It Correctly?
 ENT Coding: Does Your Nose Know When You Are Coding It Correctly? Presented to: AAPC Annual Meeting Orlando, Florida April 16, 2013 Presented by: Kim Pollock, RN, MBA, CPC www.karenzupko.com Kim Pollock,
ENT Coding: Does Your Nose Know When You Are Coding It Correctly? Presented to: AAPC Annual Meeting Orlando, Florida April 16, 2013 Presented by: Kim Pollock, RN, MBA, CPC www.karenzupko.com Kim Pollock,
Author correspondence: Dr. Argyro J. Bizaki, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Tampere University and
 1 Title: Facial subcutaneous emphysema after tonsillectomy Authors: Bizaki Argyro *, Kääriäinen Janne **, Harju Teemu *, Rautiainen Markus *** Institution: Department of Otolarygology, University Hospital
1 Title: Facial subcutaneous emphysema after tonsillectomy Authors: Bizaki Argyro *, Kääriäinen Janne **, Harju Teemu *, Rautiainen Markus *** Institution: Department of Otolarygology, University Hospital
Sinus and Nasal Surgery
 D E C A T U R M E M O R I A L H O S P I T A L Sinus and Nasal Surgery Introduction You are scheduled for sinus and nasal surgery. This helps open your sinuses and restore normal sinus functioning. Usually,
D E C A T U R M E M O R I A L H O S P I T A L Sinus and Nasal Surgery Introduction You are scheduled for sinus and nasal surgery. This helps open your sinuses and restore normal sinus functioning. Usually,
United States Department of Labor Employees Compensation Appeals Board DECISION AND ORDER
 United States Department of Labor L.J., Appellant and DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, BUREAU OF PRISONS, Miami, FL, Employer Appearances: Appellant, pro se Office of Solicitor, for the Director Docket No. 12-856
United States Department of Labor L.J., Appellant and DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE, BUREAU OF PRISONS, Miami, FL, Employer Appearances: Appellant, pro se Office of Solicitor, for the Director Docket No. 12-856
