Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
|
|
|
- Dorothy Hardy
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract Bleeding in the digestive tract is a symptom of a disease rather than a disease itself. Bleeding can occur as the result of a number of different conditions, some of which are life threatening. Most causes of bleeding are related to conditions that can be cured or controlled, such as ulcers or hemorrhoids. The cause of bleeding may not be serious, but locating the source of bleeding is important. The digestive or gastrointestinal (GI) tract includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine or colon, rectum, and anus. Bleeding can come from one or more of these areas, that is, from a small area such as an ulcer on the lining of the stomach or from a large surface such as an inflammation of the colon. Bleeding can sometimes occur without the person noticing it. This type of bleeding is called occult or hidden. Fortunately, simple tests can detect occult blood in the stool. What causes bleeding in the digestive tract? Stomach acid can cause inflammation that may lead to bleeding at the lower end of the esophagus. This condition, usually associated with the symptom of heartburn, is called esophagitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Sometimes a muscle between the esophagus and stomach fails to close properly and allows the return of food and stomach juices into the esophagus, which can lead to esophagitis. In another, unrelated condition, enlarged veins (varices) at the lower end of the esophagus may rupture and bleed massively. Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of esophageal varices. Esophageal bleeding can be caused by a tear in the lining of the esophagus (Mallory-Weiss syndrome). Mallory-Weiss syndrome usually results from vomiting but may also be caused by increased pressure in the abdomen from coughing, hiatal hernia, or childbirth. Esophageal cancer can cause bleeding. The stomach is a frequent site of bleeding. Infections with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), alcohol, aspirin, aspirin-containing medicines, and various other medicines (NSAIDs, particularly those used for arthritis) can cause stomach ulcers or inflammation (gastritis). The stomach is often the site of ulcer disease. Acute or chronic ulcers may enlarge and erode through a blood vessel, causing bleeding.
2 Also, patients suffering from burns, shock, head injuries, cancer, or those who have undergone extensive surgery may develop stress ulcers. Bleeding can also occur from benign tumors or cancer of the stomach, although these disorders usually do not cause massive bleeding. A common source of bleeding from the upper digestive tract is ulcers in the duodenum (the upper small intestine). Duodenal ulcers are most commonly caused by infection with H. pylori bacteria or drugs such as aspirin or NSAIDs. In the lower digestive tract, the large intestine and rectum are frequent sites of bleeding. Hemorrhoids are the most common cause of visible blood in the digestive tract, especially blood that appears bright red. Hemorrhoids are enlarged veins in the anal area that can rupture and produce bright red blood, which can show up in the toilet or on toilet paper. If red blood is seen, however, it is essential to exclude other causes of bleeding since the anal area may also be the site of cuts (fissures), inflammation, or cancer. Benign growths or polyps of the colon are very common and are thought to be forerunners of cancer. These growths can cause either bright red blood or occult bleeding. Colorectal cancer is the third most frequent of all cancers in the United States and often causes occult bleeding at some time, but not necessarily visible bleeding. Inflammation from various causes can produce extensive bleeding from the colon. Different intestinal infections can cause inflammation and bloody diarrhea. Ulcerative colitis can produce inflammation and extensive surface bleeding from tiny ulcerations. Crohn s disease of the large intestine can also produce bleeding. What are the common causes of bleeding in the digestive tract? Esophagus inflammation (esophagitis) enlarged veins (varices) tear (Mallory-Weiss syndrome) liver disease Stomach ulcers inflammation (gastritis) Small intestine duodenal ulcer inflammation (irritable bowel disease) Large intestine and rectum hemorrhoids infections inflammation (ulcerative colitis) colorectal polyps colorectal cancer diverticular disease Diverticular disease caused by diverticula pouches in the colon wall can result in massive bleeding. Finally, as one gets older, abnormalities may develop in the blood vessels of the large intestine, which may result in recurrent bleeding. Patients taking blood thinning medications (warfarin) may have bleeding from the GI tract, especially if they take drugs like aspirin. 2 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
3 How is bleeding in the digestive tract recognized? The signs of bleeding in the digestive tract depend upon the site and severity of bleeding. If blood is coming from the rectum or the lower colon, bright red blood will coat or mix with the stool. The stool may be mixed with darker blood if the bleeding is higher up in the colon or at the far end of the small intestine. When there is bleeding in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum, the stool is usually black or tarry. Vomited material may be bright red or have a coffeegrounds appearance when one is bleeding from those sites. If bleeding is occult, the patient might not notice any changes in stool color. If sudden massive bleeding occurs, a person may feel weak, dizzy, faint, short of breath, or have crampy abdominal pain or diarrhea. Shock may occur, with a rapid pulse, drop in blood pressure, and difficulty in producing urine. The patient may become very pale. If bleeding is slow and occurs over a long period of time, a gradual onset of fatigue, lethargy, shortness of breath, and pallor from the anemia will result. Anemia is a condition in which the blood s iron-rich substance, hemoglobin, is diminished. How is bleeding in the digestive tract diagnosed? The site of the bleeding must be located. A complete history and physical examination are essential. Symptoms such as changes in bowel habits, stool color (to black or red) and consistency, and the presence of pain or tenderness may tell the doctor which area of the GI tract is affected. Because the intake of iron, bismuth (Pepto Bismol), or foods such as beets can give the stool the same appearance as bleeding from the digestive tract, a doctor must test the stool for blood before offering a diagnosis. A blood count will indicate whether the patient is anemic and also will give an idea of the extent of the bleeding and how chronic it may be. Endoscopy Endoscopy is a common diagnostic technique that allows direct viewing of the bleeding site. Because the endoscope can detect lesions and confirm the presence or absence of bleeding, doctors often choose this method to diagnose patients with acute bleeding. In many cases, the doctor can use the endoscope to treat the cause of bleeding as well. The endoscope is a flexible instrument that can be inserted through the mouth or rectum. The instrument allows the doctor to see into the esophagus, stomach, duodenum (esophago-duodenoscopy), colon (colonoscopy), and rectum (sigmoidoscopy); to collect small samples of tissue (biopsies); to take photographs; and to stop the bleeding. Small bowel endoscopy, or enteroscopy, is a procedure using a long endoscope. This endoscope may be used to localize unidentified sources of bleeding in the small intestine. A new diagnostic instrument called a capsule endoscope is swallowed by the patient. The capsule contains a tiny camera that transmits images to a video monitor. It is used most often to find bleeding in portions of the small intestine that are hard to reach with a conventional endoscope. 3 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
4 Other Procedures Several other methods are available to locate the source of bleeding. Barium x rays, in general, are less accurate than endoscopy in locating bleeding sites. Some drawbacks of barium x rays are that they may interfere with other diagnostic techniques if used for detecting acute bleeding, they expose the patient to x rays, and they do not offer the capabilities of biopsy or treatment. Another type of x ray is CT scan, particularly useful for inflammatory conditions and cancer. Angiography is a technique that uses dye to highlight blood vessels. This procedure is most useful in situations when the patient is acutely bleeding such that dye leaks out of the blood vessel and identifies the site of bleeding. In selected situations, angiography allows injection of medicine into arteries that may stop the bleeding. Radionuclide scanning is a noninvasive screening technique used for locating sites of acute bleeding, especially in the lower GI tract. This technique involves injection of small amounts of radioactive material. Then, a special camera produces pictures of organs, allowing the doctor to detect a bleeding site. How is bleeding in the digestive tract treated? Endoscopy is the primary diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for most causes of GI bleeding. Active bleeding from the upper GI tract can often be controlled by injecting chemicals directly into a bleeding site with a needle introduced through the endoscope. A physician can also cauterize, or heat treat, a bleeding site and surrounding tissue with a heater probe or electrocoagulation device passed through the endoscope. Laser therapy is useful in certain specialized situations. Once bleeding is controlled, medicines are often prescribed to prevent recurrence of bleeding. Medicines are useful primarily for H. pylori, esophagitis, ulcer, infections, and irritable bowel disease. Medical treatment of ulcers, including the elimination of H. pylori, to ensure healing and maintenance therapy to prevent ulcer recurrence can also lessen the chance of recurrent bleeding. Removal of polyps with an endoscope can control bleeding from colon polyps. Removal of hemorrhoids by banding or various heat or electrical devices is effective in patients who suffer hemorrhoidal bleeding on a recurrent basis. Endoscopic injection or cautery can be used to treat bleeding sites throughout the lower intestinal tract. Endoscopic techniques do not always control bleeding. Sometimes angiography may be used. However, surgery is often needed to control active, severe, or recurrent bleeding when endoscopy is not successful. 4 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
5 How do you recognize blood in the stool and vomit? bright red blood coating the stool dark blood mixed with the stool black or tarry stool bright red blood in vomit coffee-grounds appearance of vomit What are the symptoms of acute bleeding? any of bleeding symptoms above weakness shortness of breath dizziness crampy abdominal pain faintness diarrhea What are the symptoms of chronic bleeding? any of bleeding symptoms above weakness fatigue shortness of breath lethargy faintness Hope Through Research NIDDK, through the Division of Digestive Diseases and Nutrition, supports several programs and studies devoted to improving treatment for patients with digestive diseases that cause bleeding in the digestive tract, including Helicobacter pylori and inflammatory bowel disease. For More Information American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 4900-B South 31st Street Alexandria, VA Phone: Fax: Internet: The U.S. Government does not endorse or favor any specific commercial product or company. Trade, proprietary, or company names appearing in this document are used only because they are considered necessary in the context of the information provided. If a product is not mentioned, the omission does not mean or imply that the product is unsatisfactory. 5 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
GI Bleeding. Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics
 GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
SMALL BOWEL BLEEDING: CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT By Anne C. Travis, M.D., M.Sc. and John R. Saltzman, M.D., FACG Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA 1. What is the small
understanding GI bleeding
 understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Crohn s Disease. What I need to know about. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
 What I need to know about Crohn s Disease NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Crohn
What I need to know about Crohn s Disease NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Crohn
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING
 COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING By Douglas K. Rex, M.D., FACG & Suthat Liangpunsakul, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis,
What are peptic ulcers?
 Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
Information about Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are the symptoms? What are the causes? What are peptic ulcers? When should I consult a doctor? What will the doctor do? How should I treat peptic
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16
 Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers
 NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore
NSAIDs and Peptic Ulcers National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a peptic ulcer? A peptic ulcer is a sore
Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System
 Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS)
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What you need to know before your procedure Your Doctor has decided that an EUS is necessary for further evaluation and treatment of your condition. This information sheet has
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
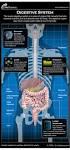 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Colon Polyps. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Colon Polyps U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Colon
What I need to know about Colon Polyps U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Colon
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H. pylori even be good for us?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Helicobacter pylori? What is Helicobacter pylori? hat problems can H. pylori cause? Does H. pylori cause cancer? ight H.
I can t empty my rectum without pressing my fingers in or near my vagina
 Since the birth of my baby, I can t control my bowel movements Normally bowel movements (stools) are stored in the rectum until the bowel sends a message to the brain that it is full, and the person finds
Since the birth of my baby, I can t control my bowel movements Normally bowel movements (stools) are stored in the rectum until the bowel sends a message to the brain that it is full, and the person finds
What is Helicobacter pylori? The Life Cycle (Pathogenesis) of Helicobacter pylori
 Helicobacter pylori Source: http://www.medicaltribune.net/put/default.htm Source: http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/djk010.gif What is Helicobacter pylori? Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a
Helicobacter pylori Source: http://www.medicaltribune.net/put/default.htm Source: http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/djk010.gif What is Helicobacter pylori? Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) are a
Millions of Americans suffer from abdominal pain, bloating, constipation and diarrhea. Now new treatments can relieve your pain and discomfort.
 3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children. David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians
 It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
Bowel cancer: should I be screened?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
Patient information from the BMJ Group Bowel cancer: should I be screened? Bowel cancer is a serious condition, but there are good treatments. Treatment works best if it's started early.to pick up early
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families
 Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Complications that may occur with ulcerative colitis:
 Ulcerative Colitis What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is one of the major forms of inflammatory bowel disease. The other major form is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis is felt to be due
Ulcerative Colitis What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is one of the major forms of inflammatory bowel disease. The other major form is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis is felt to be due
Introduction. Physiology of the Abdomen. Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Pain Introduction (2 of 2) Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies
 Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you
 Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE (C. DIFF)
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What can I eat? Peptic ulcers. What are peptic ulcers? What tests are needed? Will the ulcer come back? What causes a peptic ulcer?
 In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable. American Cancer Society
 Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2016 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2016 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable. American Cancer Society
 Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2013 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Colorectal Cancer: Preventable, Beatable, Treatable American Cancer Society Reviewed January 2013 What we ll be talking about How common is colorectal cancer? What is colorectal cancer? What causes it?
Neuroendocrine Tumors
 Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure
 Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure Please review this information before your procedure. Please talk to your doctor if you have any questions or do not understand any of this information.
Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure Please review this information before your procedure. Please talk to your doctor if you have any questions or do not understand any of this information.
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
 Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY CONSENT FORM
 Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis
 Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is
Microscopic Colitis: Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS
 YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
YTTRIUM 90 MICROSPHERES THERAPY OF LIVER TUMORS The information regarding placement of Yttrium 90 microsphres for the management of liver tumors on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin )
 FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
FAQs about Warfarin (brand name Coumadin ) What is warfarin? Warfarin is the most commonly used anticoagulant in the US. An anticoagulant is a drug used to prevent unwanted and harmful blood clots. Although
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
PATIENT INFORMATION INSURANCE INFORMATION
 (mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
(mm/dd/yyyy): Have you been to Physicians Urgent Care before? Yes No Arrival Time: If yes, when? Is this a follow-up to a previous visit: Yes No PATIENT INFORMATION Patient s First Name: Middle Name: Last
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Irritable
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Borland-Groover Clinic PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #:
 PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Referring: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #: Place Sticker Here Directions: Please circle any of the following you have personally
PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Referring: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #: Place Sticker Here Directions: Please circle any of the following you have personally
The Digestive System
 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Crohn s Disease. What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? hat are the symptoms? What causes Crohn s Disease?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Crohn s Disease What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? What causes Crohn s Disease? hat does it do to the intestine?
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Crohn s Disease What is Crohn s Disease? ho gets Crohn s Disease? What causes Crohn s Disease? hat does it do to the intestine?
The Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre Frequently Asked Questions. What is the Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre?
 The Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre Frequently Asked Questions What is the Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre? The Forzani and MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre (CCSC) is
The Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre Frequently Asked Questions What is the Forzani MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre? The Forzani and MacPhail Colon Cancer Screening Centre (CCSC) is
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Chronic Diarrhea in Children
 Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Chronic Diarrhea in Children National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is chronic diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Chronic, or long lasting, diarrhea typically lasts for more
Upper Endoscopy (EGD)
 Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
OGD (Gastroscopy) Information for patients. Liver, Renal & Surgery. Confirming your identity
 Liver, Renal & Surgery OGD (Gastroscopy) Information for patients This leaflet answers some of the questions you may have about having an OGD. It explains the risks and the benefits of the test and what
Liver, Renal & Surgery OGD (Gastroscopy) Information for patients This leaflet answers some of the questions you may have about having an OGD. It explains the risks and the benefits of the test and what
Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for the night will have their procedure cancelled immediately.
 Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Preparing for your Colonoscopy You must have someone and/or a driver accompany you and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure. Patients who fail to bring a driver/someone to stay with them for
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery
 Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
Gallbladder - gallstones and surgery Summary Gallstones are small stones made from cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium salts, which form in a person s gall bladder. Medical treatment isn t necessary
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CYRAMZA ramucirumab Read this carefully before you receive CYRAMZA (pronounced "si ram - ze"). This leaflet is a
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr CYRAMZA ramucirumab Read this carefully before you receive CYRAMZA (pronounced "si ram - ze"). This leaflet is a
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) What is cancer?
 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years
Chapter. Guaiac Screening CHAPTER 4: GUAIAC TESTING SCREENING FOR OCCULT BLOOD. Page 1 of 5 Guaiac 3-5-02.doc 6/24/2005
 Chapter 4 Guaiac Screening CHAPTER 4: GUAIAC TESTING SCREENING FOR OCCULT BLOOD Page 1 of 5 Guaiac 3-5-02.doc 6/24/2005 Procedure: Guaiac Testing Screening for Fecal Occult Blood POLICY: The stool occult
Chapter 4 Guaiac Screening CHAPTER 4: GUAIAC TESTING SCREENING FOR OCCULT BLOOD Page 1 of 5 Guaiac 3-5-02.doc 6/24/2005 Procedure: Guaiac Testing Screening for Fecal Occult Blood POLICY: The stool occult
NEW PATIENT CONSULTATION FORM. Social Security Number - - Date of Birth Age. Home Address. Home phone Cell phone. Work phone Email address
 NEW PATIENT CONSULTATION FORM Welcome to our office. Please fill out the first four pages. Date Name Social Security Number - - Date of Birth Age Home Address Home phone Cell phone Work phone Email address
NEW PATIENT CONSULTATION FORM Welcome to our office. Please fill out the first four pages. Date Name Social Security Number - - Date of Birth Age Home Address Home phone Cell phone Work phone Email address
Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Colorectal Cancer Screening Introduction Colorectal cancer (cancer of the large intestine) is the second most common cause of death from cancer in the United States, after lung cancer. However, colorectal
Colorectal Cancer Screening Introduction Colorectal cancer (cancer of the large intestine) is the second most common cause of death from cancer in the United States, after lung cancer. However, colorectal
colon cancer Talk to your doctor about getting tested for colon cancer. They know how to prevent and you can, too. Take a look inside.
 2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No. 243900 Rev.01/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
2006, American Cancer Society, Inc. No. 243900 Rev.01/08 The American Cancer Society is the nationwide community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer as a major health problem
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
POEM Procedure for. Esophageal Achalasia
 POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and
Irritable Bowel Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and
