IEC CONFORMANCE TEST
|
|
|
- Kristopher Bishop
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IEC CONFORMNCE TEST Conformance test report of the IEC Unbalanced protocol implementation in the SICM TM CP6014 (version ) tested as controlled station implementation in Normal direction Siemens G Report no.: , Rev. 0 Date: 15th September 2016
2 Project name: IEC Conformance test DNV GL - Energy Report title: Conformance test report of the IEC Unbalanced protocol implementation in the SICM TM CP6014 (version ) tested as controlled station implementation in Normal direction Customer: Siemens G, Nuremberg (Germany) Contact person: Johan Huybreghs Date of issue: 15th September 2016 Project No.: Organisation unit: OPE/INC Report No.: , Rev. 0 Energy dvisory P.O. Box ET RNHEM Tel: Registered rnhem Task and objective: ssess if the protocol implementation conforms to the IEC Companion Standard and the TenneT PID Prepared by: pproved by: E. Henriquez P. Cioci Consultant Head of Section Intelligent Networks & Communication Unrestricted distribution (internal and external) Unrestricted distribution within DNV GL Limited distribution within DNV GL after 3 years No distribution (confidential) Secret
3 IMPORTNT NOTICE ND DISCLIMER This document is protected by copyright and may not be made available to third parties without the express and prior written consent of the DNV GL entity issuing this document ( DNV GL ). This document is intended for the sole use of the Customer as detailed on the front page of this document to whom the document is addressed and who has entered into a written agreement with the DNV GL. To the extent permitted by law, neither DNV GL nor any group company (the "Group") assumes any responsibility whether in contract, tort including without limitation negligence, or otherwise howsoever, to third parties (being persons other than the Customer), and no company in the Group other than DNV GL shall be liable for any loss or damage whatsoever suffered by virtue of any act, omission or default (whether arising by negligence or otherwise) by DNV GL, the Group or any of its or their servants, subcontractors or agents. This document must be read in its entirety and is subject to any assumptions and qualifications expressed therein as well as in any other relevant communications in connection with it. This document may contain detailed technical data which is intended for use only by persons possessing requisite expertise in its subject matter. This document has been produced from information relating to dates and periods referred to in this document. This document does not imply that any information is not subject to change. Except and to the extent that checking or verification of information or data is expressly agreed within the written scope of its services, DNV GL shall not be responsible in any way in connection with erroneous information or data provided to it by the Customer or any third party, or for the effects of any such erroneous information or data whether or not contained or referred to in this document Reference to part of this report which may lead to misinterpretation is not permissible. Rev. No. Date Reason for Issue Prepared by pproved by First issue E. Henriquez P. Cioci 2016 KEM Nederland B.V.
4 Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION Background Testing Viewpoints Purpose of this document Contents of this document Glossary 3 2 REFERENCES Normative Other 4 3 THE CONFORMNCE TEST Components in the test environment SUT configuration Overview of the test suite 7 4 TEST RESULTS CONCLUSION ND RECOMMENDTIONS Exceptions with the [PICS] Remarks & Recommendations following from the test 10 6 PROTOCOL IMPLEMENTTION CONFORMNCE STTEMENT (PICS) System or device Network configuration Physical layer Link layer pplication layer Basic application functions 19 7 TEST RESULTS CONFORMNCE TESTING IEC Test results chart Test results of command transmission 37 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page i
5 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background Siemens G manufactures digital equipment that can be used in substations. Siemens has implemented the IEC Telecontrol Companion Standard 101 (Unbalanced) in the SICM TM CP6014(Communication module SM2551) product for communication with a controlling system. The IEC Telecontrol Companion Standard 101 (TCS101) can be used as a communication protocol for exchanging information between Control Center(s) (controlling station) and their substations (controlled stations). The information exchanged can be for example measurands, status messages and commands. DNV KEM s assignment was to answer the following question: Does the Siemens IEC controlled station protocol implementation (CP6014 Firmware version 08, 101 Communication module SM2551 firmware version 05.07) for the SICM TM CP6014 conform to the IEC Companion Standard in Standard Direction and the TenneT Telemetry IEC Protocol Implementation Document Unbalanced Mode, version 4.6? To answer this question, DNV KEM has performed a type conformance test of the Siemens IEC Controlled station protocol implementation in the SICM TM CP6014 SM Testing Viewpoints There are two common viewpoints for testing communication protocol implementations: Conformance testing and Interoperability testing. The first testing viewpoint, Conformance testing, is the process of verifying that an implementation performs in accordance with a particular standard. manufacturer may claim: my equipment conforms to standard ISO/IEC xxx-x. Conformance testing enables such a claim to be investigated and assessed by an objective and independent institute, like DNV GL, to establish its validity. The type test may result in an ttestation of Conformity, guaranteed by DNV GL, for the tested implementation version in that equipment. DNV KEM maintains a list of type-tested and approved equipment with IEC implementations (see Conformance testing extends the normal conformance test process by adding negative and boundary test items to the testing process. The second viewpoint, Interoperability testing (IOP), shows whether or not a protocol implementation, installed in one product, can be used to exchange information with another product which has implemented the same protocol. No direct attention is paid to the implementation of the protocol itself. fter completion of the tests, there is no guarantee that the protocol implementation is in accordance with that particular standard. It is clear, however, whether or not the protocol functions required in order to exchange information can work together to accomplish the required task. This document describes the result of a Conformance test. lthough a positive outcome of the test is a proof of independent verification (according to the applicable test procedures), it does not guarantee complete interoperability with other devices. Even when the same protocol options are DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 2
6 implemented in two devices (see PICS), some further fine configuration may be necessary to guarantee complete interoperability. The second viewpoint, Interoperability testing, shows whether or not a protocol implementation, installed in one product, can be used to exchange information with another product which has implemented the same protocol. No direct attention is paid to the implementation of the protocol itself. fter completion of the tests, there is no guarantee that the protocol implementation is in accordance with that particular standard. It is clear, however, whether or not the protocol functions required in order to exchange information can work together to accomplish the required task. 1.3 Purpose of this document The purpose of this document is to describe the results of the type test of the IEC implementation in the System Under Test (further SUT). The type test was executed at Siemens, Huizingen (Belgium) from ugust 4 th till 5 th ugust and ugust 31 st The results will form the basis for an (potential) ttestation of Conformance. This ttestation is primarily of interest to product marketers and customers, as a proof of independent verification of minimized interoperability risks. 1.4 Contents of this document Chapter 2 shows the list of relevant normative and other references, used to provide input for the type test. Chapter 3 describes the various relevant components for the type test and their configuration as used in the conformance test, including the System Under Test. This chapter also gives an overview and introduction to the various test groups that together constitute the type test. Chapter 4 and 5 give an overview and summary of the test results, the conclusion(s) and recommendations. The summary contains a Defects and a Remarks entry next to each group of test cases. ppendix specifies the detailed test cases and their outcome, appendix B contains detailed comments on test results, for instance when a defect is detected, including the actual message flow if appropriate. 1.5 Glossary SUT = System Under Test 1. PICS = Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement. template document (IEC ed.2 Clause 8 Interoperability) where all the basic characteristics of an IEC ed.2 implementation are stated PID = Protocol Implementation Document. document issued by a manufacturer or system integrator where on top of the PICS template, additional detailed information regarding requirements and fine options is added 1 This can either be an embedded device or an industrial pc. DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 3
7 2 REFERENCES 2.1 Normative The tests defined in this document are based on the following IEC (International Electrotechnical Committee) documents in the IEC range: Telecontrol equipment and systems part 5: Transmission protocols: 1. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: Transmission Frame Formats, IS (International Standard), 1990, further referred to as [IEC5-1] 2. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: Link Transmission Procedures, IS, 1992, further referred to as [IEC5-2] 3. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: General Structure of pplication Data, IS, 1992, further referred to as [IEC5-3] 4. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: Definition and Coding of pplication Information Elements, IS, 1993, further referred to as [IEC5-4] 5. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: Basic pplication Functions, IS, 1995, further referred to as [IEC5-5] 6. IEC : TELECONTROL EQUIPMENT ND SYSTEMS, PRT 5, Transmission protocols: Companion standard for basic Telecontrol tasks, IS, second edition , further referred to as [IEC5-101]. 7. IEC : Telecontrol equipment and systems, Part 5-601, Conformance test cases for the IEC Companion Standard, second edition, Other 1. TenneT Telemetry IEC Protocol Implementation Document Unbalanced Mode, version February, 2014 [PID]. DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 4
8 3 THE CONFORMNCE TEST 3.1 Components in the test environment The test environment consists of the following components: The SUT: the SICM TM CP6014-SM2551 controlled station implementation featuring: Hardware name Firmware name FW version Main System SICM TM CP6014 CPCX65 08 IEC SM2551 UMPS Communication module The DNV GL Unigrid Telecontrol Simulator v1.1.1.beta 1 (2016) and UnIECim version (2013) protocol test platform, which runs the CS101UNBMaster Version1_26.UTS simulator test suite and acts as a single-node Controlling station in Unbalanced mode; One Connection cable sub-d 9pins from the test system to the SUT based on RS232 communication. SYSTEM UNDER TEST MMI DNV GL UniGrid Telecontrol Simulator Conformance Test System & Simulator Figure 1 Connection and set-up of the test environment The system under test (DUT) is a protocol gateway and it was tested connecting to a PC based simulation of RTU, considering the final implementation, in which the RTU will be the control unit of the substation and the Sicam TM is the protocol gateway. CS 104 SUT PC Based RTU PRE01 SM/2558 Sicam TM PRE02 SM/2551 DNV GL 101 Master Simulator DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 5
9 SUT requirements Next to the CS101 communication capability specified in the PID, the System Under Test must support the following requirements for control and simulation purposes during testing, e.g. via additional test equipment attached to the SUT or one or more configured and running operator MMI stations: Display the current values of the Information Elements described in I/O list, mapped to visible MMI-elements Manually shut down and restart or equivalent Manually cut-off of the connection to the communication link Manually activate the supported Basic pplication Functions Direct physical connection to the communication link. 3.2 SUT configuration The configuration of the SUT is as follows: The telecontrol communication modes are Unbalanced Master-Slave capable of using fixed (point-to-point) communication lines, and the Unigrid Telecontrol Simulator and the SICM TM CP6014 are respectively acting as the (simulated) Slave and Master FT1.2 frames at maximum bps 2, 8 data bits, even parity, and 1 stop bit 1 or 2 octets for data link address 1 or 2 octets for the Common address of SDU 1, 2, or 3 octets for the Information Object ddresses (see next section) The configured Link ddress was 512: common ddress of SDU (C) used during the test was 5, 500, 3328, Further details of the implemented protocol (interoperability sheet) subset can be found in Chapter 4, Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement (PICS). The PICS forms the basis for the applicable test cases performed as described in Chapter UniGrid Telecontrol test system The UniGrid Telecontrol IEC protocol test suite consists in DNV GL s test tools for testing IEC protocol implementations. The knowledge of the IEC protocol is in the software and it does support the test engineer. UniGrid Telecontrol supports real-time data capturing, analysis and decoding, combined with construction of frames and real-time script execution for simulation of conforming (positive) as well as non-conforming (negative) communication functions. UniGrid Telecontrol Simulator is a simulator and test system (active) for testing Controlling or Controlled station implementations based on the IEC Telecontrol Companion Standard 101 (TCS 101), including redundancy functionality UnIECim is simulator and test system (active) for testing Controlling/Master or Controlled/Slave station implementations based on the IEC Telecontrol Companion Standard 101 (TCS 101), including redundancy functionality. 2 Configurable as in the PID DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 6
10 3.3 Overview of the test suite Tests on physical level For signal transmission between both end systems the V24/V28 (the well-known EI232 standard) interface with interface connector (EI DB9) is used. UniGrid checks constantly physical level failures. The SUT can send and receive octets after connecting the systems. The tests are passed if the physical connection doesn t fail permanently. Some of the additional tests defined in Chapter 5 are performed on physical level Tests on link level The tests on link level are automatically performed by the UniGrid test system on each transmitted frame. The tests are passed if no error is reported during a test session. If relevant, redundant link tests are defined in Chapter Tests on application level The Basic pplication Functions (BFs) tests defined in the tables of Chapter 5 are performed by a combination of automatic verification and manual expert analysis for each test case if applicable. The tests have passed if no defects are found during a test session Negative tests The Negative tests defined in Chapter 5 are performed by a combination of automatic verification and manual expert analysis for each applicable test case. The tests have passed if the SUT continues correct operation, that is: does not send corrupted frames and reacts in a correct and sensible manner. The SUT may not fail permanently when receiving: Corrupted frames Illegal functions Not supported functions Not supported Basic pplication Functions (BF) or SDU s. DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 7
11 4 TEST RESULTS This Chapter gives a summary of the test results. Numbers shown in the table refer to test numbers of individual test cases in IEC If applicable, an end note describing a defect is added in appendix. Defects are a certain cause for operational risks: these MUST be corrected before going into an operational situation! They imply the overall test outcome to be failed. Remarks introduce additional observations about the test case results, like limitations in the implementation or implementation choices. The PICS in Chapter 6 is the basis for the applicable test cases in ppendix. The PICS gives an overview of the tested protocol implementation, but this isn t a guarantee that the complete function or SDU, as enabled in the PICS, is tested and supported. Partial testing is possible and the completeness of the tests for the specific function or SDU must be consulted in ppendix. Table 1 Summary of test results for the System Under Test Test Group Defects Remarks Verdict Table 1 Supported Configuration Parameter Passed Values Table 2 Verification of the Physical Level Passed Table 3 Verification of the Link Level Passed Table 4 Verification of the Data Unit Identifier Passed Table 5 Verification of the Object ddress Passed Table 6 SDUs for process information in monitor Passed direction Table 7 SDUs for process information in control Passed direction Table 8 SDUs for system information in monitor Passed direction Table 9 SDUs for system information in control Passed direction Table 10 SDUs for parameters in control. direction Table 11 SDUs for file transfer in normal and. control direction Table 12 Link layer Conformance Test Procedure Passed Table 13 Data Unit Identifier Conformance Test Passed Procedure Table 14 Information Object ddress Passed Conformance Test Procedure Table 15 Station Initialisation Unbalanced Passed Systems Table 16 Data cquisition by Polling Passed Table 17 Station Initialisation Balanced Systems. Table 18 Redundant Links Passed Table 19 Cyclic Data Transmission Passed Table 20 Data cquisition through Read. Table 21 cquisition of Events (2) Passed Table 22 General Interrogation Passed Table 23 Clock Synchronisation Passed. Table 24 Command Transmissions X, Passed Table 25 Transmission of Integrated Totals. Table 26 Parameter Loading. Table 27 Test Command. Table 28 File Transfer Procedure. Table 29 Delay cquisition Procedure. Table 30 dditional Conformance Tests Passed Table 31 Negative Conformance Test Procedure Passed Table 32 PIXIT Related Conformance Test. TOTLS 0 10 Passed *. = Not pplicable DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 8
12 5 CONCLUSION ND RECOMMENDTIONS The assignment was to give a well-founded answer on the question: Does the Siemens IEC controlled station protocol implementation (CP6014 Firmware version 08, 101 Communication module SM2551 firmware version 05.07) for the SICM TM CP6014 conform to the IEC Companion Standard in Standard Direction and the TenneT Telemetry IEC Protocol Implementation Document Unbalanced Mode, version 4.6? Based on the test results described in this report, DNV GL declares the tested Siemens IEC Unbalanced Controlled Station protocol implementation in conformance with the IEC standard, and the TenneT Telemetry IEC Protocol Implementation Document Unbalanced Mode, version 4.6 for the tested configuration. 5.1 Exceptions with the [PICS] Requirements set in the PID in chapter for the acquisition of cyclic analogues values according to a certain dead band was not possible to test, as the SICM TM was tested just in its configuration as protocol gateway that will convert to CS101 the events received for the RTUs in the substation. The device does support the possibility to directly connect peripheral elements. This means the TM has a peripheral bus to which DI, DO, I, O,- modules can be connected. Telegrams generated by changing state of inputs get timestamp of the CP6014. This configuration however was not object of the test, as it was decided to test according to the configuration that it is going to be used in the connection to Tennet s SCD system. SUT implements 2 serial interfaces and the buffering can be done according to the requirement set in PID chapter (Buffering of data in the RTU). However this will not be the default configuration of the device as used in the connection towards Tennet s Control Center. In the default connection 2 SICM TM units will be used with 1 connection each, the second interface in the SUT will be disabled. The connection scheme is shown in the figure: DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 9
13 SICM TM 1 SICM TM 2 RTU 1 SICM 230 RTU 2 SICM 230 RTU 3 SICM Remarks & Recommendations following from the test The following remarks apply: The responses to the command messages (activation confirmation and activation termination) where manually simulated at the RTU simulator, not generated at the SUT, that as protocol gateway just converted the message to 104 and send it to the RTU. The events telegramms were simulated at the RTU simulator therefore their time stamp did not reflect the time of the SUT and could not be taken into account when testing time synchronization or pausability of the time stamp in acquisition of events.. DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 10
14 6 PROTOCOL IMPLEMENTTION CONFORMNCE STTEMENT (PICS) IMPORTNT The Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement (PICS) in this paragraph is the basis for the applicable test cases in Chapter 5. This PICS gives an overview of the tested protocol implementation, but this isn t a guarantee that the complete function or SDU, as enabled in the PICS, is tested and supported. Partial testing is possible and the completeness of the tests for the specific function or SDU should be consulted in Chapter 5. The selected parameters should be marked in the white boxes as follows: Function or SDU is not used X R B Function or SDU is used as standardized (default) Function or SDU is used in reverse mode Function or SDU is used in standard and reverse mode The possible selection (blank, X, R, or B) is specified for each specific clause or parameter. NOTE: In addition, the full specification of a system may require individual selection of certain parameters for certain parts of the system, such as the individual selection of scaling factors for individually addressable measured values. 6.1 System or device (System-specific parameter, indicate the definition of a system or a device by marking one of the following with X ). System definition Controlling station definition X Controlled station definition 6.2 Network configuration (Network-specific parameter, all configurations that are used are to be marked X ). X Point-to-point X Multipoint-partyline X Multiple point-to-point X Multipoint-star 6.3 Physical layer (network-specific parameter, all interfaces and data rates that are used are to be marked X ). Transmission speed (control direction) Unbalanced interchange Circuit V.24/V.28 Standard Unbalanced interchange Circuit V.24/V.28 Recommended if >1 200bit/s Balanced interchange Circuit X.24/X bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 11
15 200 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s 300 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s 600 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s X bit/s bit/s Transmission speed (monitor direction) Unbalanced interchange Circuit V.24/V.28 Standard Unbalanced interchange Circuit V.24/V.28 Recommended if >1 200bit/s Balanced interchange Circuit X.24/X bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s 200 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s 300 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s 600 bit/s X bit/s bit/s bit/s X bit/s bit/s 6.4 Link layer (network-specific parameter, all options that are used are to be marked X. Specify the maximum frame length. If a non-standard assignment of class 2 messages is implemented for unbalanced transmission, indicate the type ID and COT of all messages assigned to class 2.) Frame format FT 1.2, single character 1 and the fixed time out interval are used exclusively in this companion standard. Link transmission Balanced transmission ddress of the link not present (balanced transmission only) X Unbalanced transmission X One octet X Two octets Frame length Structured 100 Maximum length L (control dir.) X Unstructured 255 Maximum length L (monitor dir.) When using an unbalanced link layer, the following SDU types are returned in class 2 messages (low priority) with the indicated causes of transmission: X The standard assignment of SDUs to class 2 messages is used as follows: Type identification Cause of transmission DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 12
16 ll SDU s <1> special assignment of SDUs to class 2 messages is used as follows: Type identification Cause of transmission Note: In response to a class 2 poll, a controlled station may respond with class 1 data when there is no class 2 data available. DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 13
17 6.5 pplication layer Transmission mode for application data Mode 1 (least significant octet first), as defined in 4.10 of IEC , is used exclusively in this companion standard. Common address of SDU (system-specific parameter, all configurations that are used are to be marked X ). X One octet X Two octets (Default) Information object address (system-specific parameter, all configurations that are used are to be marked X ). X One octet X Structured X Two octets X Unstructured X Three octets Cause of transmission (system-specific parameter, all configurations that are used are to be marked X ). X One octet X Two octets (with originator address) Originator address is set to zero if not used Selection of standard SDUs Process information in monitor direction (station-specific parameter, mark each type ID X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions). X <1>:=Single-point information M_SP_N_1 X <2>:=Single-point information with time tag M_SP_T_1 X <3>:=Double-point information M_DP_N_1 X <4>:=Double-point information with time tag M_DP_T_1 X <5>:=Step position information M_ST_N_1 <6>:=Step position information with time tag M_ST_T_1 <7>:=Bitstring of 32 bit M_BO_N_1 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 14
18 <8>:=Bitstring of 32 bit with time tag M_BO_T_1 X <9>:=Measured value, normalized value M_ME_N_1 <10>:=Measured value, normalized value with time tag M_ME_T_1 X <11>:=Measured value, scaled value M_ME_NB_1 <12>:=Measured value, scaled value with time tag M_ME_TB_1 X <13>:=Measured value, short floating point value M_ME_NC_1 <14>:=Measured value, short floating point value with time tag M_ME_TC_1 <15>:=Integrated totals M_IT_N_1 <16>:=Integrated totals with time tag M_IT_T_1 <17>:=Event of protection equipment with time tag M_EP_T_1 <18>:=Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag M_EP_TB_1 <19>:=Packed output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag M_EP_TC_1 <20> :=Packed single-point information with status change detection M_PS_N_1 <21> := Measured value, normalized value without quality descriptor M_ME_ND_1 X <30> := Single-point information with time tag CP56Time2a M_SP_TB_1 X <31> := Double-point information with time tag CP56Time2a M_DP_TB_1 X <32> := Step position information with time tag CP56Time2a M_ST_TB_1 <33> := Bitstring of 32 bit with time tag CP56Time2a M_BO_TB_1 <34> := Measured value, normalized value with time tag CP56Time2a M_ME_TD_1 <35> := Measured value, scaled value with time tag CP56Time2a M_ME_TE_1 <36> := Measured value, short floating point value with time tag CP56Time2a M_ME_TF_1 <37> := Integrated totals with time tag CP56Time2a M_IT_TB_1 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 15
19 <38> := Event of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a M_EP_TD_1 <39> := Packed start events of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a M_EP_TE_1 <40> := Packed output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a M_EP_TF_1 Either SDUs of the set <2>, <4>, <6>, <8>, <10>, <12>, <14>, <16>, <17>, <18>, <19> or of the set <30 40> are used. Process information in control direction (station-specific parameter, mark each type ID X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions). X <45> := Single command C_SC_N_1 X <46> := Double command C_DC_N_1 X <47> := Regulating step command C_RC_N_1 X <48> := Set point command, normalized value C_SE_N_1 X <49> := Set point command, scaled value C_SE_NB_1 X <50> := Set point command, short floating point value C_SE_NC_1 <51> := Bitstring of 32 bit C_BO_N_1 System information in monitor direction (station-specific parameter, mark X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) X <70> := End of initialization M_EI_N_1 System information in control direction (station-specific parameter, mark each type ID X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) X <100>:= Interrogation command C_IC_N_1 <101>:= Counter interrogation command C_CI_N_1 <102>:= Read command C_RD_N_1 X <103>:= Clock synchronization command C_CS_N_1 <104>:= Test command C_TS_N_1 <105>:= Reset process command C_RP_N_1 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 16
20 <106>:= Delay acquisition command C_CD_N_1 Parameter in control direction (station-specific parameter, mark each type ID X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) <110>:= Parameter of measured value, normalized value P_ME_N_1 <111>:= Parameter of measured value, scaled value P_ME_NB_1 <112>:= Parameter of measured value, short floating point value P_ME_NC_1 <113>:= Parameter activation P_C_N_1 File Transfer (station-specific parameter, mark each type ID X if it is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) <120>:= File ready F_FR_N_1 <121>:= Section ready F_SR_N_1 <122>:= Call directory, select file, call file, call section F_SC_N_1 <123>:= Last section, last segment F_LS_N_1 <124>:= ck file, ack section F_F_N_1 <125>:= Segment F_SG_N_1 <126>:= Directory {blank or X, only available in monitor (standard) direction} F_DR_T_1 <127>:= Query log Request archive file F_SC_NB_1 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 17
21 Type identifier and cause of transmission assignments (station-specific parameters) Shaded boxes are not required. Blank = function or SDU is not used. Mark type identification/cause of transmission combinations: X if only used in the standard direction R if only used in the reverse direction B if used in both directions Type identification Cause of transmission to <1> M_SP_N_1 X X <2> M_SP_T_1 X <3> M_DP_N_1 X X <4> M_DP_T_1 X <5> M_ST_N_1 X X <6> M_ST_T_1 <7> M_BO_N_1 <8> M_BO_T_1 <9> M_ME_N_1 X X X <10> M_ME_T_1 <11> M_ME_NB_1 X X X <12> M_ME_TB_1 <13> M_ME_NC_1 X X X <14> M_ME_TC_1 <15> M_IT_N_1 <16> M_IT_T_1 <17> M_EP_T_1 <18> M_EP_TB_1 <19> M_EP_TC_1 <20> M_PS_N_1 <21> M_ME_ND_1 <30> M_SP_TB_1 X <31> M_DP_TB_1 X <32> M_ST_TB_1 X <33> M_BO_TB_1 <34> M_ME_TD_1 <35> M_ME_TE_1 <36> M_ME_TF_1 <37> M_IT_TB_1 <38> M_EP_TD_1 <39> M_EP_TE_1 <40> M_EP_TF_1 <45> C_SC_N_1 X X X <46> C_DC_N_1 X X X <47> C_RC_N_1 X X X <48> C_SE_N_1 X X X to DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 18
22 Type identification Cause of transmission to <49> C_SE_NB_1 X X X <50> C_SE_NC_1 <51> C_BO_N_1 <70> M_EI_N_1 X <100> C_IC_N_1 X X X <101> C_CI_N_1 <102> C_RD_N_1 <103> C_CS_N_1 X X X <104> C_TS_N_1 <105> C_RP_N_1 <106> C_CD_N_1 <110> P_ME_N_1 <111> P_ME_NB_1 <112> P_ME_NC_1 <113> P_C_N_1 <120> F_FR_N_1 <121> F_SR_N_1 <122> F_SC_N_1 <123> F_LS_N_1 <124> F_F_N_1 <125> F_SG_N_1 <126> F_DR_T_1* *) blank or X only to Basic application functions Station initialization (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used). Remote initialization Cyclic data transmission (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions). X Cyclic data transmission Read procedure (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions). Read procedure DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 19
23 Spontaneous transmission (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions). X Spontaneous transmission Double transmission of information objects with cause of transmission spontaneous (station-specific parameter, mark each information type X where both a type ID without time and corresponding type ID with time are issued in response to a single spontaneous change of a monitored object). The following type identifications may be transmitted in succession caused by a single status change of an information object. The particular information object addresses for which double transmission is enabled are defined in a project-specific list. Single-point information M_SP_N_1, M_SP_T_1, M_SP_TB_1 and M_PS_N_1 Double-point information M_DP_N_1, M_DP_T_1 and M_DP_TB_1 Step position information M_ST_N_1, M_ST_T_1 and M_ST_TB_1 Bitstring of 32 bit M_BO_N_1, M_BO_T_1 and M_BO_TB_1 (if defined for a specific project) Measured value, normalized value M_ME_N_1, M_ME_T_1, M_ME_ND_1 and M_ME_TD_1 Measured value, scaled value M_ME_NB_1, M_ME_TB_1 and M_ME_TE_1 Measured value, short floating point number M_ME_NC_1, M_ME_TC_1 and Station interrogation (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) X global group 1 group 7 group 13 group 2 group 8 group 14 group 3 group 9 group 15 group 4 group 10 group 16 group 5 group 11 group 6 group 12 Information Object ddresses assigned to each group must be shown in a separate table Clock synchronization (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) X Clock synchronization DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 20
24 Command transmission (object-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) X X X X X Direct command Direct set point command transmission Select and execute command (Only for the commands without timetag) Select and execute set point command (Only for the commands without timetag) C_SE CTTERM used X X X No additional definition Short pulse duration (duration determined by a system parameter in the outstation) Long pulse duration (duration determined by a system parameter in the outstation) Persistent output Transmission of integrated totals (station- or object-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) Mode : Local freeze with spontaneous Mode B: Local freeze with counter Mode C: Freeze and transmit by counter interrogation Mode D: Freeze by counter interrogation command, frozen values reported Counter read Counter freeze without reset Counter freeze with reset Counter reset General request Request counter group 1 Request counter group 2 Request counter group 3 DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 21
25 Request counter group 4 Parameter loading (object-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) Threshold value Smoothing factor Low limit for transmission of measured High limit for transmission of measured Parameter activation (object-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) ct/deact of persistent cyclic or periodic transmission of the addressed Test procedure (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used only in the standard direction, R if used only in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) Test procedure File transfer (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is used) File transfer in monitor direction Transparent file Transmission of disturbance data of protection Transmission of sequences of events Transmission of sequences of recorded analogue values File transfer in control direction Transparent file Background scan (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) Background scan DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 22
26 cquisition of transmission delay (station-specific parameter, mark X if function is only used in the standard direction, R if only used in the reverse direction, and B if used in both directions) cquisition of transmission delay DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 23
27
28 Controlling station test (Master) Controlled station test (Slave) Max. Transmission speed in control direction Min. Transmission speed in control direction Max. Transmission speed in monitor direction Min. Transmission speed in monitor direction Unbalanced transmission Balanced transmission Zero (0) octets for address (balanced only) One (1) octet for address Two (2) octets for address Standard assignment of class 2 messages Special assignments of class 2 messages One (1) octet for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) Two (2) octets for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) One (1) octet for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Two (2) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Three (3) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) One (1) octet for COT Two (2) octets for COT (2 nd octet is Originator address) 7 TEST RESULTS CONFORMNCE TESTING IEC The test result charts described in this chapter are based upon the conformance test procedures as described in the IEC document. For a full description of the test cases is presented in that document. 7.1 Test results chart Record the conformance test procedure result for each of the supported configuration parameter values on the right Station type Transmission speed Transmission type ddress of the link ssignment class 2 Common address of SDU Information object address Cause of transmission FIL. Empty indicates the test procedure passed for that configuration value. indicates Test Procedure failed for at least one of the Test Cases. indicates that configuration value is not supported by the device. indicates the Test Procedure was not performed. (There should be no empty boxes when testing is complete). Frame length Physical layer Verification of link level Verification of data unit identifier Maximum length L (control direction) Maximum length L (monitor direction) Byte frame FT1.2 Frame Layout Byte lag Control Field Unbalanced Transmission Procedure Balanced Transmission Procedure Time Out Interval Type Identification Variable Structure Qualifier Cause of Transmission Test bit is not supported DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 25
29 Controlling station test (Master) Controlled station test (Slave) Max. Transmission speed in control direction Min. Transmission speed in control direction Max. Transmission speed in monitor direction Min. Transmission speed in monitor direction Unbalanced transmission Balanced transmission Zero (0) octets for address (balanced only) One (1) octet for address Two (2) octets for address Standard assignment of class 2 messages Special assignments of class 2 messages One (1) octet for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) Two (2) octets for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) One (1) octet for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Two (2) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Three (3) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) One (1) octet for COT Two (2) octets for COT (2 nd octet is Originator address) Record the conformance test procedure result for each of the supported configuration parameter values on the right Station type Transmission speed Transmission type ddress of the link ssignment class 2 Common address of SDU Information object address Cause of transmission indicates the test procedure passed for that configuration value. FIL indicates Test Procedure failed for at least one of the Test Cases.. indicates that configuration value is not supported by the device. Empty indicates the Test Procedure was not performed. (There should be no empty boxes when testing is complete). Verification of SDUs SDU 1 Single-point Information SDU 2 Single-point Information with Timetag SDU 3 Double-point Information SDU 4 Double-point Information with Timetag SDU 5 Step-position Information SDU 6 Step-position Information with Timetag SDU 7 Bitstring of 32 bit SDU 8 Bitstring of 32 bit with Timetag SDU 9 Measured value, normalised value SDU 10 Measured value, normalised value with Timetag SDU 11 Measured value, scaled value SDU 12 Measured value, scaled value with Timetag SDU 13 Measured value, short floating point number SDU 14 Measured value, short floating point number with Timetag SDU 15 Integrated Totals DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 26
30 Controlling station test (Master) Controlled station test (Slave) Max. Transmission speed in control direction Min. Transmission speed in control direction Max. Transmission speed in monitor direction Min. Transmission speed in monitor direction Unbalanced transmission Balanced transmission Zero (0) octets for address (balanced only) One (1) octet for address Two (2) octets for address Standard assignment of class 2 messages Special assignments of class 2 messages One (1) octet for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) Two (2) octets for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) One (1) octet for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Two (2) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Three (3) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) One (1) octet for COT Two (2) octets for COT (2 nd octet is Originator address) Record the conformance test procedure result for each of the supported configuration parameter values on the right Station type Transmission speed Transmission type ddress of the link ssignment class 2 Common address of SDU Information object address Cause of transmission indicates the test procedure passed for that configuration value. FIL indicates Test Procedure failed for at least one of the Test Cases.. indicates that configuration value is not supported by the device. Empty indicates the Test Procedure was not performed. (There should be no empty boxes when testing is complete) SDU 16 Integrated Totals with Timetag SDU 17 Event of protection equipment with Timetag SDU 18 Packed start events of protection equipment with time-tag SDU 19 Packet output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag SDU 20 Packed single-point information with status change detection SDU 21 Measured value, normalised value without quality descriptor SDU 30 Single-point information with time tag CP56Time2a SDU 31 Double-point information with time tag CP56Time2a SDU 32 Step-position information with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 33 Bitstring of 32 bit with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 34 Measured value, normalised value with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 35 Measured value, scaled value with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 36 Measured value, short floating point number with time-tag CP56Time2a DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 27
31 Controlling station test (Master) Controlled station test (Slave) Max. Transmission speed in control direction Min. Transmission speed in control direction Max. Transmission speed in monitor direction Min. Transmission speed in monitor direction Unbalanced transmission Balanced transmission Zero (0) octets for address (balanced only) One (1) octet for address Two (2) octets for address Standard assignment of class 2 messages Special assignments of class 2 messages One (1) octet for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) Two (2) octets for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) One (1) octet for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Two (2) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Three (3) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) One (1) octet for COT Two (2) octets for COT (2 nd octet is Originator address) Record the conformance test procedure result for each of the supported configuration parameter values on the right Station type Transmission speed Transmission type ddress of the link ssignment class 2 Common address of SDU Information object address Cause of transmission FIL. Empty indicates the test procedure passed for that configuration value. indicates Test Procedure failed for at least one of the Test Cases. indicates that configuration value is not supported by the device. indicates the Test Procedure was not performed. (There should be no empty boxes when testing is complete) SDU 37 Integrated totals with time tag CP56Time2a SDU 38 Event of protection equipment with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 39 Packed start events of protection equipment with time-tag CP56Time2a SDU 40 Packet output circuit information of protection equipment with time tag CP56Time2a SDU 45 Single Command SDU 46 Double Command SDU 47 Regulating step command SDU 48 Set point command, normalised value SDU 49 Set point command, scaled value SDU 50 Set point command, short floating point value SDU 51 Bitstring of 32 bits SDU 70 End of Initialisation SDU 100 Interrogation command SDU 101 Counter interrogation command 4 SUT supports the following COI during End Of Init: UI=1 ("local manual reset") and BS=1 ("unchanged local parameters"). DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 28
32 Controlling station test (Master) Controlled station test (Slave) Max. Transmission speed in control direction Min. Transmission speed in control direction Max. Transmission speed in monitor direction Min. Transmission speed in monitor direction Unbalanced transmission Balanced transmission Zero (0) octets for address (balanced only) One (1) octet for address Two (2) octets for address Standard assignment of class 2 messages Special assignments of class 2 messages One (1) octet for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) Two (2) octets for Common ddress of SDU (CSDU) One (1) octet for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Two (2) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) Three (3) octets for Information Object ddress (structured or unstructured) One (1) octet for COT Two (2) octets for COT (2 nd octet is Originator address) Record the conformance test procedure result for each of the supported configuration parameter values on the right Station type Transmission speed Transmission type ddress of the link ssignment class 2 Common address of SDU Information object address Cause of transmission FIL. Empty indicates the test procedure passed for that configuration value. indicates Test Procedure failed for at least one of the Test Cases. indicates that configuration value is not supported by the device. indicates the Test Procedure was not performed. (There should be no empty boxes when testing is complete) SDU 102 Read command SDU 103 Clock synchronisation command SDU 104 Test command SDU 105 Reset process command SDU 106 Delay acquisition command SDU 110 Parameter of measured value, normalised value SDU 111 Parameter of measured values, scaled value SDU 112 Parameter of measured values, short floating point number SDU 113 Parameter activation SDU 120 File ready SDU 121 Section ready SDU 122 Call directory, select file, call file, call section SDU 123 Last section, last segment SDU 124 CK file, CK section SDU 125 Segment Link Layer SDU 126 Directory Frame Count Bit Invalid Checksum DNV GL - Energy Report No , Rev. 0 Page 29
INDEX. IEC 60870-5-104 Controlled Station Interoperability com.tom WEB-PLC 8.0.2
 INDEX 1 Interoperability... 2 2 History... 2 3 IEC 60870-5-104 Interoperability... 3 3.1 System or Device...3 3.2 Network Configuration...3 3.3 Physical Layer...3 3.3.1 Transmission speed...3 3.4 Link
INDEX 1 Interoperability... 2 2 History... 2 3 IEC 60870-5-104 Interoperability... 3 3.1 System or Device...3 3.2 Network Configuration...3 3.3 Physical Layer...3 3.3.1 Transmission speed...3 3.4 Link
SAGE Sistema Aberto de Gerenciamento de Energia. Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-104 no SAGE
 Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-104 no SAGE OUTUBRO 2008 Documento de Interoperabilidade 1 System or/and Device (system-specific parameter, indicate definition of a system or a
Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-104 no SAGE OUTUBRO 2008 Documento de Interoperabilidade 1 System or/and Device (system-specific parameter, indicate definition of a system or a
SAGE Sistema Aberto de Gerenciamento de Energia. Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-101 no SAGE
 Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-101 no SAGE MAIO 2003 Documento de Interoperabilidade A comunicação do SAGE sob o protocolo IEC/60870-5-101 pode ser estabelecida em canais de comunicação
Documento de Interoperabilidade do Protocolo IEC/60870-5-101 no SAGE MAIO 2003 Documento de Interoperabilidade A comunicação do SAGE sob o protocolo IEC/60870-5-101 pode ser estabelecida em canais de comunicação
SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5 Interoperability Profile Documents
 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5 Interoperability Profile Documents 2 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5 Interoperability Profile Documents Table of Contents Part I IEC 60870-5-101 Slave Interoperability Profile Document
SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5 Interoperability Profile Documents 2 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5 Interoperability Profile Documents Table of Contents Part I IEC 60870-5-101 Slave Interoperability Profile Document
How To Configure An Iec 60870-5 (Runtu) For A Testnet (Rntu)
 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical Manual 2 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical Manual Table of Contents Part I IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical 4 1 Technical... Support 4 2
SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical Manual 2 SCADAPack E IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical Manual Table of Contents Part I IEC 60870-5-101/104 Slave Technical 4 1 Technical... Support 4 2
Modbus and ION Technology
 70072-0104-14 TECHNICAL 06/2009 Modbus and ION Technology Modicon Modbus is a communications protocol widely used in process control industries such as manufacturing. PowerLogic ION meters are compatible
70072-0104-14 TECHNICAL 06/2009 Modbus and ION Technology Modicon Modbus is a communications protocol widely used in process control industries such as manufacturing. PowerLogic ION meters are compatible
Modbus and ION Technology
 Modbus and ION Technology Modicon Modbus is a communications protocol widely used in process control industries such as manufacturing. ACCESS meters are compatible with Modbus networks as both slaves and
Modbus and ION Technology Modicon Modbus is a communications protocol widely used in process control industries such as manufacturing. ACCESS meters are compatible with Modbus networks as both slaves and
IEC-101 Slave. ProLinx Communication Gateway IEC 60870-5-101 v3 Slave (Firmware version 3.xx) PROTOCOL MANUAL
 IEC-101 Slave ProLinx Communication Gateway IEC 60870-5-101 v3 Slave (Firmware version 3.xx) PROTOCOL MANUAL Your Feedback Please We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our
IEC-101 Slave ProLinx Communication Gateway IEC 60870-5-101 v3 Slave (Firmware version 3.xx) PROTOCOL MANUAL Your Feedback Please We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our
ESPA 4.4.4 Nov 1984 PROPOSAL FOR SERIAL DATA INTERFACE FOR PAGING EQUIPMENT CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. CHARACTER DESCRIPTION
 PROPOSAL FOR SERIAL DATA INTERFACE FOR PAGING EQUIPMENT CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. CHARACTER DESCRIPTION 2.1 CHARACTER STRUCTURE 2.2 THE CHARACTER SET 2.3 CONTROL CHARACTERS 2.3.1 Transmission control
PROPOSAL FOR SERIAL DATA INTERFACE FOR PAGING EQUIPMENT CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. CHARACTER DESCRIPTION 2.1 CHARACTER STRUCTURE 2.2 THE CHARACTER SET 2.3 CONTROL CHARACTERS 2.3.1 Transmission control
RS-485 Protocol Manual
 RS-485 Protocol Manual Revision: 1.0 January 11, 2000 RS-485 Protocol Guidelines and Description Page i Table of Contents 1.0 COMMUNICATIONS BUS OVERVIEW... 1 2.0 DESIGN GUIDELINES... 1 2.1 Hardware Design
RS-485 Protocol Manual Revision: 1.0 January 11, 2000 RS-485 Protocol Guidelines and Description Page i Table of Contents 1.0 COMMUNICATIONS BUS OVERVIEW... 1 2.0 DESIGN GUIDELINES... 1 2.1 Hardware Design
Single channel data transceiver module WIZ2-434
 Single channel data transceiver module WIZ2-434 Available models: WIZ2-434-RS: data input by RS232 (±12V) logic, 9-15V supply WIZ2-434-RSB: same as above, but in a plastic shell. The WIZ2-434-x modules
Single channel data transceiver module WIZ2-434 Available models: WIZ2-434-RS: data input by RS232 (±12V) logic, 9-15V supply WIZ2-434-RSB: same as above, but in a plastic shell. The WIZ2-434-x modules
EDK 350 (868 MHz) EDK 350U (902 MHz) EnOcean Developer Kit
 EDK 350 (868 MHz) EDK 350U (902 MHz) EnOcean Developer Kit EDK 350 User Manual Important Notes This information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics. No
EDK 350 (868 MHz) EDK 350U (902 MHz) EnOcean Developer Kit EDK 350 User Manual Important Notes This information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics. No
PCS0100en 02.2008. Persy Control Services B.V. Netherlands
 P-Bus Gateway PBGW2.128 Universal gateway between the P-bus protocol and open standard protocols. The variety of available electrical interfaces on the gateway offers a wide range of possibilities for
P-Bus Gateway PBGW2.128 Universal gateway between the P-bus protocol and open standard protocols. The variety of available electrical interfaces on the gateway offers a wide range of possibilities for
Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card)
 Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card) ISO 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, managed jointly by
Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card) ISO 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, managed jointly by
Modbus Communications for PanelView Terminals
 User Guide Modbus Communications for PanelView Terminals Introduction This document describes how to connect and configure communications for the Modbus versions of the PanelView terminals. This document
User Guide Modbus Communications for PanelView Terminals Introduction This document describes how to connect and configure communications for the Modbus versions of the PanelView terminals. This document
WAGO-I/O-SYSTEM in ABB robot control systems Application note
 WAGO-I/O-SYSTEM in ABB robot control systems A100500, English Version 1.0.0 ii General Copyright 2001 by WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH All rights reserved. WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH Hansastraße 27 D-32423 Minden
WAGO-I/O-SYSTEM in ABB robot control systems A100500, English Version 1.0.0 ii General Copyright 2001 by WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH All rights reserved. WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH Hansastraße 27 D-32423 Minden
ROC Protocol Specifications Manual
 Part Number D301053X012 June 2015 ROC Protocol Specifications Manual Remote Automation Solutions ROC Protocol Specifications Manual Revision Tracking Sheet June 2015 This manual may be revised periodically
Part Number D301053X012 June 2015 ROC Protocol Specifications Manual Remote Automation Solutions ROC Protocol Specifications Manual Revision Tracking Sheet June 2015 This manual may be revised periodically
TCP/IP MODULE CA-ETHR-A INSTALLATION MANUAL
 TCP/IP MODULE CA-ETHR-A INSTALLATION MANUAL w w w. c d v g r o u p. c o m CA-ETHR-A: TCP/IP Module Installation Manual Page Table of Contents Introduction...5 Hardware Components... 6 Technical Specifications...
TCP/IP MODULE CA-ETHR-A INSTALLATION MANUAL w w w. c d v g r o u p. c o m CA-ETHR-A: TCP/IP Module Installation Manual Page Table of Contents Introduction...5 Hardware Components... 6 Technical Specifications...
User Manual. AS-Interface Programmer
 AS-Interface Programmer Notice: RESTRICTIONS THE ZMD AS-INTERFACE PROGRAMMER HARDWARE AND ZMD AS-INTERFACE PROGRAMMER SOFTWARE IS DESIGNED FOR IC EVALUATION, LABORATORY SETUP AND MODULE DEVELOPMENT ONLY.
AS-Interface Programmer Notice: RESTRICTIONS THE ZMD AS-INTERFACE PROGRAMMER HARDWARE AND ZMD AS-INTERFACE PROGRAMMER SOFTWARE IS DESIGNED FOR IC EVALUATION, LABORATORY SETUP AND MODULE DEVELOPMENT ONLY.
Using the AnyBus -X Gateway to Communicate between a DVT camera and a Profibus Master
 Using the AnyBus -X Gateway to Communicate between a DVT camera and a Profibus Master Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 3 2 INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING THE ANYBUS -X GENERIC GATEWAY AND ETHERNET
Using the AnyBus -X Gateway to Communicate between a DVT camera and a Profibus Master Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 3 2 INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING THE ANYBUS -X GENERIC GATEWAY AND ETHERNET
Process Control and Automation using Modbus Protocol
 Process Control and Automation using Modbus Protocol Modbus is the fundamental network protocol used in most industrial applications today. It is universal, open and an easy to use protocol. Modbus has
Process Control and Automation using Modbus Protocol Modbus is the fundamental network protocol used in most industrial applications today. It is universal, open and an easy to use protocol. Modbus has
Remote Monitoring of Woodward easygen-3000
 Remote Monitoring of Woodward easygen-3000 HMS Industrial Networks AB Page 1 (22) About this Document HMS application notes are not binding and do not claim to be complete in regard to configuration and
Remote Monitoring of Woodward easygen-3000 HMS Industrial Networks AB Page 1 (22) About this Document HMS application notes are not binding and do not claim to be complete in regard to configuration and
Master-Touch and ValuMass. Modbus Communications. INSTRUCTION MANUAL 80202201 (Rev. 2.1)
 Master-Touch and ValuMass Modbus Communications INSTRUCTION MANUAL 80202201 (Rev. 2.1) Eldridge Products, Inc. 2700 Garden Road, Building A Monterey, CA 93940 Tel: 800/321-3569 or 831/648-7777 Fax: 831/648-7780
Master-Touch and ValuMass Modbus Communications INSTRUCTION MANUAL 80202201 (Rev. 2.1) Eldridge Products, Inc. 2700 Garden Road, Building A Monterey, CA 93940 Tel: 800/321-3569 or 831/648-7777 Fax: 831/648-7780
Programming Flash Microcontrollers through the Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface
 Programming Flash Microcontrollers through the Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface Application te Programming Flash Microcontrollers through the Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface Abstract This
Programming Flash Microcontrollers through the Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface Application te Programming Flash Microcontrollers through the Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface Abstract This
The I2C Bus. NXP Semiconductors: UM10204 I2C-bus specification and user manual. 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 1
 The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
CONTROL MICROSYSTEMS DNP3. User and Reference Manual
 DNP3 User and Reference Manual CONTROL MICROSYSTEMS SCADA products... for the distance 48 Steacie Drive Telephone: 613-591-1943 Kanata, Ontario Facsimile: 613-591-1022 K2K 2A9 Technical Support: 888-226-6876
DNP3 User and Reference Manual CONTROL MICROSYSTEMS SCADA products... for the distance 48 Steacie Drive Telephone: 613-591-1943 Kanata, Ontario Facsimile: 613-591-1022 K2K 2A9 Technical Support: 888-226-6876
Computer Gateway Specification and Technical Data
 L Computer Gateway Specification and Technical Data CG03-500 R500 3/96 detergant coffee chocolate Page 2 TDC 3000X Computer Gateway Specification and Technical Data Introduction This publication defines
L Computer Gateway Specification and Technical Data CG03-500 R500 3/96 detergant coffee chocolate Page 2 TDC 3000X Computer Gateway Specification and Technical Data Introduction This publication defines
Automation Unit TM 1703 ACP Flexible automation and telecontrol
 Automation Unit Flexible automation and telecontrol Power Transmission and Distribution Outstanding performance: Automate simply with Highly complex and yet fully transparent automation solutions are not
Automation Unit Flexible automation and telecontrol Power Transmission and Distribution Outstanding performance: Automate simply with Highly complex and yet fully transparent automation solutions are not
White Paper. Technical Capabilities of the DF1 Half-Duplex Protocol
 White Paper Technical Capabilities of the DF1 Half-Duplex Protocol Introduction DF1 Protocol To meet the challenges of today s global marketplace communication and network, systems must offer customers
White Paper Technical Capabilities of the DF1 Half-Duplex Protocol Introduction DF1 Protocol To meet the challenges of today s global marketplace communication and network, systems must offer customers
Communication Unit 560CMU05 Data sheet
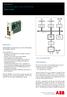 RTU560 product line Communication Unit 560CMU05 Data sheet E1 10/100 MB LAN E2 10/100 MB LAN CP1, CP2 RS232C or RS485 Ethernet Controller Ethernet Controller USART Processor bus MPU ELAN520 /Flash Memory
RTU560 product line Communication Unit 560CMU05 Data sheet E1 10/100 MB LAN E2 10/100 MB LAN CP1, CP2 RS232C or RS485 Ethernet Controller Ethernet Controller USART Processor bus MPU ELAN520 /Flash Memory
F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL
 F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL Add:J1-J2,3rd Floor,No.44,GuanRi Road,SoftWare Park,XiaMen,China 1 Zip Code:361008 Contents Chapter 1 Brief Introduction of Product... 3 1.1 General... 3 1.2 Product Features...
F2103 GPRS DTU USER MANUAL Add:J1-J2,3rd Floor,No.44,GuanRi Road,SoftWare Park,XiaMen,China 1 Zip Code:361008 Contents Chapter 1 Brief Introduction of Product... 3 1.1 General... 3 1.2 Product Features...
The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions
 Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
Data sheet SLIO CPU 015 (015-CEFPR00)
 Data sheet SLIO CPU 015 (015-CEFPR00) Technical data Order no. 015-CEFPR00 SLIO CPU 015 Module ID - General information Note - Features SPEED7 technology 256 kb work memory Memory extension (max. 512 kb)
Data sheet SLIO CPU 015 (015-CEFPR00) Technical data Order no. 015-CEFPR00 SLIO CPU 015 Module ID - General information Note - Features SPEED7 technology 256 kb work memory Memory extension (max. 512 kb)
I.S. 1 remote I/O system Redundant coupling via PROFIBUS DP
 I.S. 1 remote I/O system Redundant coupling via PROFIBUS DP 1. Functions An I. S. 1 fieldstation can be equipped with a primary and a redundant central unit (), whereby each has its own independent PROFIBUS
I.S. 1 remote I/O system Redundant coupling via PROFIBUS DP 1. Functions An I. S. 1 fieldstation can be equipped with a primary and a redundant central unit (), whereby each has its own independent PROFIBUS
Different Ways of Connecting to. 3DLevelScanner II. A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0
 3DLevelScanner II Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0 2 Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II Version 3.0 Table
3DLevelScanner II Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II A.P.M Automation Solutions LTD. www.apm-solutions.com Version 3.0 2 Different Ways of Connecting to 3DLevelScanner II Version 3.0 Table
Omron I/O Driver (Series 2) Programmable Serial Interface Card
 Omron I/O Driver (Series 2) Programmable Serial Interface Card USER MANUAL Rev. P1.55 June 8, 2012 DeltaV is a trademark of Emerson Process Management, Inc Emerson Process Management, Inc. 1998, 1999.
Omron I/O Driver (Series 2) Programmable Serial Interface Card USER MANUAL Rev. P1.55 June 8, 2012 DeltaV is a trademark of Emerson Process Management, Inc Emerson Process Management, Inc. 1998, 1999.
A DNP3 Protocol Primer
 A Protocol Primer Introduction This is a primer for people who want a quick understanding of without having to comb through the tedious details of a complex specification. The writing style is meant to
A Protocol Primer Introduction This is a primer for people who want a quick understanding of without having to comb through the tedious details of a complex specification. The writing style is meant to
RS485 & Modbus Protocol Guide
 RS485 & Modbus Protocol Guide Products Covered Quadratic Integra 1000 Switchboard Integra 1000 Integra 1540 Integra 1560 Integra 1580 Quadratic Integra 2000 System Protection Relay (SPR) Tyco Electronics
RS485 & Modbus Protocol Guide Products Covered Quadratic Integra 1000 Switchboard Integra 1000 Integra 1540 Integra 1560 Integra 1580 Quadratic Integra 2000 System Protection Relay (SPR) Tyco Electronics
Plant automation and telecontrol in one system. SIMATIC PCS 7 TeleControl SIMATIC PCS 7. Answers for industry.
 Plant automation and telecontrol in one system SIMATIC TeleControl SIMATIC Answers for industry. SIMATIC TeleControl The intelligent solution for installations with local and widely distributed automation
Plant automation and telecontrol in one system SIMATIC TeleControl SIMATIC Answers for industry. SIMATIC TeleControl The intelligent solution for installations with local and widely distributed automation
Disturbance Recoder SPCR 8C27. Product Guide
 Issued: April 1999 Status: Updated Version: C/26.04.2006 Data subject to change without notice Features Versatile digital disturbance recorder module for recording various phenomena in the electric power
Issued: April 1999 Status: Updated Version: C/26.04.2006 Data subject to change without notice Features Versatile digital disturbance recorder module for recording various phenomena in the electric power
BLUETOOTH SERIAL PORT PROFILE. iwrap APPLICATION NOTE
 BLUETOOTH SERIAL PORT PROFILE iwrap APPLICATION NOTE Thursday, 19 April 2012 Version 1.2 Copyright 2000-2012 Bluegiga Technologies All rights reserved. Bluegiga Technologies assumes no responsibility for
BLUETOOTH SERIAL PORT PROFILE iwrap APPLICATION NOTE Thursday, 19 April 2012 Version 1.2 Copyright 2000-2012 Bluegiga Technologies All rights reserved. Bluegiga Technologies assumes no responsibility for
WA Manager Alarming System Management Software Windows 98, NT, XP, 2000 User Guide
 WA Manager Alarming System Management Software Windows 98, NT, XP, 2000 User Guide Version 2.1, 4/2010 Disclaimer While every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this guide is accurate
WA Manager Alarming System Management Software Windows 98, NT, XP, 2000 User Guide Version 2.1, 4/2010 Disclaimer While every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this guide is accurate
AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI. Introduction. Features. Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller APPLICATION NOTE
 Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
4511 MODBUS RTU. Configuration Manual. HART transparent driver. No. 9107MCM100(1328)
 4511 MODBUS RTU Configuration Manual HART transparent driver No. 9107MCM100(1328) 9107 CONTENTS Introduction... 3 Modbus basics... 3 Modbus RTU... 3 Supported Function Codes... 3 Modbus Parameters and
4511 MODBUS RTU Configuration Manual HART transparent driver No. 9107MCM100(1328) 9107 CONTENTS Introduction... 3 Modbus basics... 3 Modbus RTU... 3 Supported Function Codes... 3 Modbus Parameters and
PROFIBUS AND MODBUS: A COMPARISON
 Real-Time Information for the Automation Professional TM PROFIBUS AND MODBUS: A COMPARISON By James Powell, Siemens October 2013 We live in a multi-protocol world and this will likely not change anytime
Real-Time Information for the Automation Professional TM PROFIBUS AND MODBUS: A COMPARISON By James Powell, Siemens October 2013 We live in a multi-protocol world and this will likely not change anytime
User Manuals. Connection to Siemens S5 PU (AS511) Part Number: 80860.699. Version: 2. Date: 18.10.2006
 User Manual Connection to Siemens S5 PU (AS511) Part Number: 80860.699 Version: 2 Date: 18.10.2006 Valid for: User Manuals Version Date Modifications 1 09.06.2006 First Edition 2 18.10.2006 Optimized data
User Manual Connection to Siemens S5 PU (AS511) Part Number: 80860.699 Version: 2 Date: 18.10.2006 Valid for: User Manuals Version Date Modifications 1 09.06.2006 First Edition 2 18.10.2006 Optimized data
TOP Server DNP 3.0 Suite. Background & Best Practices
 TOP Server DNP 3.0 Suite Background & Best Practices Page 2 of 31 Table of Contents OVERVIEW 4 BACKGROUND 5 TECHNICAL DNP PROTOCOL INFORMATION 6 Master and Outstation Databases 6 Layering 7 Device Addressing
TOP Server DNP 3.0 Suite Background & Best Practices Page 2 of 31 Table of Contents OVERVIEW 4 BACKGROUND 5 TECHNICAL DNP PROTOCOL INFORMATION 6 Master and Outstation Databases 6 Layering 7 Device Addressing
MTS Master Custom Communications Protocol APPLICATION NOTES
 MTS Master Custom Communications Protocol APPLICATION NOTES Rev. 0 12/6/94 Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 ACCOL TERMINAL ASSIGNMENTS... 1 MTS PROTOCOL SIGNAL LIST... 2 COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE... 3 Line Parameter
MTS Master Custom Communications Protocol APPLICATION NOTES Rev. 0 12/6/94 Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 ACCOL TERMINAL ASSIGNMENTS... 1 MTS PROTOCOL SIGNAL LIST... 2 COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE... 3 Line Parameter
DNP 3.0 Remote Communication Protocol for REC 523 Technical Description
 DNP 3.0 Remote Communication Protocol for REC 523 Industrial IT enabled products from ABB are the building blocks for greater productivity, featuring all the tools necessary for lifecycle product support
DNP 3.0 Remote Communication Protocol for REC 523 Industrial IT enabled products from ABB are the building blocks for greater productivity, featuring all the tools necessary for lifecycle product support
Application Unit, MDRC AB/S 1.1, GH Q631 0030 R0111
 , GH Q631 0030 R0111 SK 0010 B 98 The application unit is a DIN rail mounted device for insertion in the distribution board. The connection to the EIB is established via a bus connecting terminal at the
, GH Q631 0030 R0111 SK 0010 B 98 The application unit is a DIN rail mounted device for insertion in the distribution board. The connection to the EIB is established via a bus connecting terminal at the
Comparison of protocols used in remote monitoring: DNP 3.0, IEC 870-5-101 & Modbus
 M.Tech. Credit Seminar Report, Electronics Systems Group, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, submitted November 03 Comparison of protocols used in remote monitoring: DNP 3.0, IEC 870-5-101 & Modbus Jay Makhija (03307905)
M.Tech. Credit Seminar Report, Electronics Systems Group, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, submitted November 03 Comparison of protocols used in remote monitoring: DNP 3.0, IEC 870-5-101 & Modbus Jay Makhija (03307905)
Software Manual RS232 Laser Merge Module. Document # SU-256521-09 Rev A
 Laser Merge Module Document # SU-256521-09 Rev A The information presented in this document is proprietary to Spectral Applied Research Inc. and cannot be used for any purpose other than that for which
Laser Merge Module Document # SU-256521-09 Rev A The information presented in this document is proprietary to Spectral Applied Research Inc. and cannot be used for any purpose other than that for which
Modicon Modbus Protocol Reference Guide. PI MBUS 300 Rev. J
 Modicon Modbus Protocol Reference Guide PI MBUS 300 Rev. J 1 Modicon Modbus Protocol Reference Guide PI MBUS 300 Rev. J June 1996 MODICON, Inc., Industrial Automation Systems One High Street North Andover,
Modicon Modbus Protocol Reference Guide PI MBUS 300 Rev. J 1 Modicon Modbus Protocol Reference Guide PI MBUS 300 Rev. J June 1996 MODICON, Inc., Industrial Automation Systems One High Street North Andover,
Modbus Protocol. PDF format version of the MODBUS Protocol. http://www.http://www.modicon.com/techpubs/toc7.html. The original was found at:
 Modbus Protocol PDF format version of the MODBUS Protocol The original was found at: http://www.http://www.modicon.com/techpubs/toc7.html (In case of any discrepancies, that version should be considered
Modbus Protocol PDF format version of the MODBUS Protocol The original was found at: http://www.http://www.modicon.com/techpubs/toc7.html (In case of any discrepancies, that version should be considered
CPUs - CPU 315-2 PN/DP
 Overview The CPU with a medium program memory and quantity framework High processing performance in binary and floating-point arithmetic Used as a central controller on production lines with central and
Overview The CPU with a medium program memory and quantity framework High processing performance in binary and floating-point arithmetic Used as a central controller on production lines with central and
Documentation. M-Bus 130-mbx
 Documentation M-Bus 130-mbx Introduction The mx M-Bus module is part of the mx Smart Slot communications family. With the integrated SmartSlot technology, mx systems ag offers automatic consumer data read-out
Documentation M-Bus 130-mbx Introduction The mx M-Bus module is part of the mx Smart Slot communications family. With the integrated SmartSlot technology, mx systems ag offers automatic consumer data read-out
Data Transfer Management with esync 1.5
 ewon Application User Guide AUG 029 / Rev 2.1 Content Data Transfer Management with esync 1.5 This document explains how to configure the esync 1.5 Server and your ewons in order to use the Data Transfer
ewon Application User Guide AUG 029 / Rev 2.1 Content Data Transfer Management with esync 1.5 This document explains how to configure the esync 1.5 Server and your ewons in order to use the Data Transfer
ABB i-bus EIB Logic Module LM/S 1.1
 Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB Logic Module LM/S 1.1 Intelligent Installation System Contents page 1 General... 3 1.1 About this manual... 3 1.2 Product and functional overview... 3 2 Device technology...
Product Manual ABB i-bus EIB Logic Module LM/S 1.1 Intelligent Installation System Contents page 1 General... 3 1.1 About this manual... 3 1.2 Product and functional overview... 3 2 Device technology...
Kurz MODBUS Client User s Guide
 Kurz MODBUS Client User s Guide Introduction The Kurz MODBUS Client program can be used to demonstrate how the Kurz MFTB and MFTA Series products can be used in a MODBUS protocol network. The program is
Kurz MODBUS Client User s Guide Introduction The Kurz MODBUS Client program can be used to demonstrate how the Kurz MFTB and MFTA Series products can be used in a MODBUS protocol network. The program is
Brunata Optuna W (171)
 Brunata Optuna W (171) Communication description Edition 1.1 UK-QB101414 / 26.02.2013 Brunata a/s is a Danish owned company. We have more than 90 years of experience within developing and producing meters,
Brunata Optuna W (171) Communication description Edition 1.1 UK-QB101414 / 26.02.2013 Brunata a/s is a Danish owned company. We have more than 90 years of experience within developing and producing meters,
SIMATIC S7-1200. It s the Interplay that makes the difference. Siemens AG 2010. All Rights Reserved.
 SIMATIC S7-1200 It s the Interplay that makes the difference SIMATIC S7-1200 Controller SIMATIC S7-1200 CPUs CPU 1211C 3 configurations per CPU Dimensions W x H x D (mm) CPU 1212C CPU 1214C DC/DC/DC, AC/DC/RLY,
SIMATIC S7-1200 It s the Interplay that makes the difference SIMATIC S7-1200 Controller SIMATIC S7-1200 CPUs CPU 1211C 3 configurations per CPU Dimensions W x H x D (mm) CPU 1212C CPU 1214C DC/DC/DC, AC/DC/RLY,
NC-12 Modbus Application
 NC-12 Modbus Application NC-12 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents... 2 2 Glossary... 3 SCADA...3 3 NC-12 Modbus in general... 3 4 Entire system... 4 4.1 PFC to PC connection alternatives...4 4.1.1
NC-12 Modbus Application NC-12 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents... 2 2 Glossary... 3 SCADA...3 3 NC-12 Modbus in general... 3 4 Entire system... 4 4.1 PFC to PC connection alternatives...4 4.1.1
SIMATIC NET. CP 243-2 AS-Interface Master B C. Preface Contents. Technical Description and Installation Instructions Interface to the User Program
 Preface Contents SIMATIC NET CP 243-2 AS-Interface Master Manual Technical Description and Installation Instructions Interface to the User Program 2 in the S7-200 CPU Access to the Data of the AS-i Slaves
Preface Contents SIMATIC NET CP 243-2 AS-Interface Master Manual Technical Description and Installation Instructions Interface to the User Program 2 in the S7-200 CPU Access to the Data of the AS-i Slaves
Using Xbee 802.15.4 in Serial Communication
 Using Xbee 802.15.4 in Serial Communication Jason Grimes April 2, 2010 Abstract Instances where wireless serial communication is required to connect devices, Xbee RF modules are effective in linking Universal
Using Xbee 802.15.4 in Serial Communication Jason Grimes April 2, 2010 Abstract Instances where wireless serial communication is required to connect devices, Xbee RF modules are effective in linking Universal
How To Set Up A Modbus Cda On A Pc Or Maca (Powerline) With A Powerline (Powergen) And A Powergen (Powerbee) (Powernet) (Operating System) (Control Microsci
 Firmware Loader User Manual CONTROL MICROSYSTEMS SCADA products... for the distance 48 Steacie Drive Telephone: 613-591-1943 Kanata, Ontario Facsimile: 613-591-1022 K2K 2A9 Technical Support: 888-226-6876
Firmware Loader User Manual CONTROL MICROSYSTEMS SCADA products... for the distance 48 Steacie Drive Telephone: 613-591-1943 Kanata, Ontario Facsimile: 613-591-1022 K2K 2A9 Technical Support: 888-226-6876
2010 Ing. Punzenberger COPA-DATA GmbH. All rights reserved.
 2010 Ing. Punzenberger COPA-DATA GmbH All rights reserved. Distribution and/or reproduction of this document or parts thereof in any form are permitted solely with the written permission of the company
2010 Ing. Punzenberger COPA-DATA GmbH All rights reserved. Distribution and/or reproduction of this document or parts thereof in any form are permitted solely with the written permission of the company
Nemo 96HD/HD+ MODBUS
 18/12/12 Pagina 1 di 28 MULTIFUNCTION FIRMWARE 2.30 Nemo 96HD/HD+ MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL CONTENTS 1.0 ABSTRACT 2.0 DATA MESSAGE DESCRIPTION 2.1 Parameters description 2.2 Data format 2.3 Description
18/12/12 Pagina 1 di 28 MULTIFUNCTION FIRMWARE 2.30 Nemo 96HD/HD+ MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL CONTENTS 1.0 ABSTRACT 2.0 DATA MESSAGE DESCRIPTION 2.1 Parameters description 2.2 Data format 2.3 Description
Library ModbusRTUlib Modbus RTU master communication. TXV 003 52.02 3 rd Issue February 2010 All rights reserved
 R Library ModbusRTUlib Modbus RTU master communication TXV 003 52.02 3 rd Issue February 2010 All rights reserved History of changes Date Issue Description of changes April 2009 1 First issue of ModbusRTULib_V10
R Library ModbusRTUlib Modbus RTU master communication TXV 003 52.02 3 rd Issue February 2010 All rights reserved History of changes Date Issue Description of changes April 2009 1 First issue of ModbusRTULib_V10
Introduction: Implementation of the MVI56-MCM module for modbus communications:
 Introduction: Implementation of the MVI56-MCM module for modbus communications: Initial configuration of the module should be done using the sample ladder file for the mvi56mcm module. This can be obtained
Introduction: Implementation of the MVI56-MCM module for modbus communications: Initial configuration of the module should be done using the sample ladder file for the mvi56mcm module. This can be obtained
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION. SIS Module SLS 1508
 ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
ACHILLES CERTIFICATION PUBLIC REPORT Final DeltaV Report SIS Module SLS 1508 Disclaimer Wurldtech Security Inc. retains the right to change information in this report without notice. Wurldtech Security
Technical Bulletin. Teledyne PDS Clock Synchronization Considerations. Version 1.2
 Teledyne PDS Clock Synchronization Considerations Version 1.2 TELEDYNE RESON B.V. Stuttgartstraat 42-44 3047 AS Rotterdam The Netherlands Tel.: +31 (0)10 245 15 00 www.teledyne-reson.com Dated: 01-05-2015
Teledyne PDS Clock Synchronization Considerations Version 1.2 TELEDYNE RESON B.V. Stuttgartstraat 42-44 3047 AS Rotterdam The Netherlands Tel.: +31 (0)10 245 15 00 www.teledyne-reson.com Dated: 01-05-2015
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 62056-21 First edition 2002-05 Electricity metering Data exchange for meter reading, tariff and load control Part 21: Direct local data exchange This English-language version
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 62056-21 First edition 2002-05 Electricity metering Data exchange for meter reading, tariff and load control Part 21: Direct local data exchange This English-language version
Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs
 Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
NortechCommander Software Operating Manual MAN-00004 R6
 NortechCommander Software Operating Manual MAN-00004 R6 If the equipment described herein bears the symbol, the said equipment complies with the applicable European Union Directive and Standards mentioned
NortechCommander Software Operating Manual MAN-00004 R6 If the equipment described herein bears the symbol, the said equipment complies with the applicable European Union Directive and Standards mentioned
SCADA Questions and Answers
 SCADA Questions and Answers By Dr. Jay Park SCADA System Evaluation Questions Revision 4, October 1, 2007 Table of Contents SCADA System Evaluation Questions... 1 Revision 4, October 1, 2007... 1 Architecture...
SCADA Questions and Answers By Dr. Jay Park SCADA System Evaluation Questions Revision 4, October 1, 2007 Table of Contents SCADA System Evaluation Questions... 1 Revision 4, October 1, 2007... 1 Architecture...
MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12
 Unity Pro MBP_MSTR 33002527 07/2011 MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12 Introduction This chapter describes the MBP_MSTR block. What s in this Chapter? This chapter contains the following topics: Topic Page
Unity Pro MBP_MSTR 33002527 07/2011 MBP_MSTR: Modbus Plus Master 12 Introduction This chapter describes the MBP_MSTR block. What s in this Chapter? This chapter contains the following topics: Topic Page
HT1632C 32 8 &24 16 LED Driver
 328 &216 LED Driver Features Operating voltage: 2.V~5.5V Multiple LED display 32 ROW /8 COM and 2 ROW & 16 COM Integrated display RAM select 32 ROW & 8 COM for 6 display RAM, or select 2 ROW & 16 COM for
328 &216 LED Driver Features Operating voltage: 2.V~5.5V Multiple LED display 32 ROW /8 COM and 2 ROW & 16 COM Integrated display RAM select 32 ROW & 8 COM for 6 display RAM, or select 2 ROW & 16 COM for
CENTRONICS interface and Parallel Printer Port LPT
 Course on BASCOM 8051 - (37) Theoretic/Practical course on BASCOM 8051 Programming. Author: DAMINO Salvatore. CENTRONICS interface and Parallel Printer Port LPT The Parallel Port, well known as LPT from
Course on BASCOM 8051 - (37) Theoretic/Practical course on BASCOM 8051 Programming. Author: DAMINO Salvatore. CENTRONICS interface and Parallel Printer Port LPT The Parallel Port, well known as LPT from
DME4 V1.23 (06-1999) V1.30 (06-2000) V1.31 (04-2001) V1.32 (09-2001) V1.33 (03-2002) V1.34 (06-2003) V1.35 (05-2004) V2.00 (12-2005) V2.
 DME4 V1.23 (06-1999) - Correction of unfounded error message 'No measurements configured' when reading measurements from DME440 (MODBUS) if special measurands hadn't been selected to be calculated. - Correction
DME4 V1.23 (06-1999) - Correction of unfounded error message 'No measurements configured' when reading measurements from DME440 (MODBUS) if special measurands hadn't been selected to be calculated. - Correction
Research of PROFIBUS PA s integration in PROFINET IO
 3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 2015) Research of PROFIBUS PA s integration in PROFINET IO Zhijia Yang 1, a *, Zhongsheng Li 1,2,b, Feng Qiao 2
3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 2015) Research of PROFIBUS PA s integration in PROFINET IO Zhijia Yang 1, a *, Zhongsheng Li 1,2,b, Feng Qiao 2
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 60870-5-103 First edition 1997-12 Telecontrol equipment and systems Part 5-103: Transmission protocols Companion standard for the informative interface of protection equipment
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IEC 60870-5-103 First edition 1997-12 Telecontrol equipment and systems Part 5-103: Transmission protocols Companion standard for the informative interface of protection equipment
IP Link Device Interface Communication Sheet
 This document provides additional assistance with wiring your Extron IP Link enabled product to your device. Different components may require a different wiring scheme than those listed below. For complete
This document provides additional assistance with wiring your Extron IP Link enabled product to your device. Different components may require a different wiring scheme than those listed below. For complete
Section 8 Scheduler. Alcatel-Lucent OmniVista 4760 Network Management System
 Alcatel-Lucent OmniVista 4760 Network Management System Section 8 Scheduler Alcatel-Lucent OmniVista 4760 Network Management System All Rights Reserved Alcatel-Lucent 2011 Legal notice: Alcatel, Lucent,
Alcatel-Lucent OmniVista 4760 Network Management System Section 8 Scheduler Alcatel-Lucent OmniVista 4760 Network Management System All Rights Reserved Alcatel-Lucent 2011 Legal notice: Alcatel, Lucent,
The Secrets of RS-485 Half-duplex Communication
 Communication Casper Yang, Senior Product Manager support@moxa.com RS-485 is a good choice for long distance serial communication since using differential transmission cancels out the vast majority of
Communication Casper Yang, Senior Product Manager support@moxa.com RS-485 is a good choice for long distance serial communication since using differential transmission cancels out the vast majority of
eztcp Technical Document Modbus/TCP of eztcp Caution: Specifications of this document may be changed without prior notice for improvement.
 eztcp Technical Document Modbus/TCP of eztcp Version 1.3 Caution: Specifications of this document may be changed without prior notice for improvement. Sollae Systems Co., Ltd. http://www.sollae.co.kr Contents
eztcp Technical Document Modbus/TCP of eztcp Version 1.3 Caution: Specifications of this document may be changed without prior notice for improvement. Sollae Systems Co., Ltd. http://www.sollae.co.kr Contents
WinCC Options. Redundancy. Manual C79000-G8263-C142-01
 WinCC Options Redundancy Manual Edition November 1998 WinCC, SIMATIC, SINEC, STEP are Siemens registered trademarks. All other product and system names in this manual are (registered) trademarks of their
WinCC Options Redundancy Manual Edition November 1998 WinCC, SIMATIC, SINEC, STEP are Siemens registered trademarks. All other product and system names in this manual are (registered) trademarks of their
Crow Limited Warranty. Print Version 017
 Crow Limited Warranty (Crow) warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service for a period of one year from the last day of the week and year whose
Crow Limited Warranty (Crow) warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service for a period of one year from the last day of the week and year whose
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
DNP Points List and Implementation
 S&C Electric Company BankGuard Plus DNP Points List and Implementation This appendix describes the DNP points and DNP implementation for the BankGuard PLUS Control, using software UPPD106S. DNP Points
S&C Electric Company BankGuard Plus DNP Points List and Implementation This appendix describes the DNP points and DNP implementation for the BankGuard PLUS Control, using software UPPD106S. DNP Points
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions
 HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Application Notes Best Practices for Using PRTG Traffic Grapher to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Application Notes Best Practices for Using PRTG Traffic Grapher to Monitor SANiQ Performance Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services
Softstarters. Type PSTX Fieldbus communication, Built-in Modbus RTU. 1SFC132089M0201 April 2015 1SFC132089M0201 1
 Softstarters Type PSTX Fieldbus communication, Built-in Modbus RTU 1SFC132089M0201 April 2015 1SFC132089M0201 1 1 Modbus RTU The Modbus protocol is a fieldbus protocol that provides full control and status
Softstarters Type PSTX Fieldbus communication, Built-in Modbus RTU 1SFC132089M0201 April 2015 1SFC132089M0201 1 1 Modbus RTU The Modbus protocol is a fieldbus protocol that provides full control and status
USER GUIDE EDBG. Description
 USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
Serial Communications / Protocol in AirTest Products
 Serial Communications / Protocol in AirTest Products General The standard sensor has two different ways of serial communication with sensor s peripherals and the outside world. One is through the UART
Serial Communications / Protocol in AirTest Products General The standard sensor has two different ways of serial communication with sensor s peripherals and the outside world. One is through the UART
Data Link Layer(1) Principal service: Transferring data from the network layer of the source machine to the one of the destination machine
 Data Link Layer(1) Principal service: Transferring data from the network layer of the source machine to the one of the destination machine Virtual communication versus actual communication: Specific functions
Data Link Layer(1) Principal service: Transferring data from the network layer of the source machine to the one of the destination machine Virtual communication versus actual communication: Specific functions
PNSPO! Modbus Solution CP1H / CP1L / CJ1 / CJ2 / CS1. Version 2.05 6/18/2009
 PNSPO!! Modbus Solution CP1H / CP1L / CJ1 / CJ2 / CS1 Version 2.05 6/18/2009 Section 1. Overview The Omron CP1H and CP1L PLCs offer a built in function called Easy Modbus, that performs a Modbus RTU Master
PNSPO!! Modbus Solution CP1H / CP1L / CJ1 / CJ2 / CS1 Version 2.05 6/18/2009 Section 1. Overview The Omron CP1H and CP1L PLCs offer a built in function called Easy Modbus, that performs a Modbus RTU Master
EMR-5000. Software-Version: 2.5.b. Protocol Implementation Extra Information for Testing (PIXIT) UCA International Users Group Testing Sub Committee
 EMR-5000 Software-Version: 2.5.b Protocol Implementation Extra Information for Testing (PIXIT) UCA International Users Group Testing Sub Committee Contents of this document This document is applicable
EMR-5000 Software-Version: 2.5.b Protocol Implementation Extra Information for Testing (PIXIT) UCA International Users Group Testing Sub Committee Contents of this document This document is applicable
TSX ETY 110 Module 8
 Module 8 Introduction Subject of this chapter What s in this Chapter? This chapter describes the implementation of a TSX ETY 110 module. This chapter contains the following sections: Section Topic Page
Module 8 Introduction Subject of this chapter What s in this Chapter? This chapter describes the implementation of a TSX ETY 110 module. This chapter contains the following sections: Section Topic Page
Rev 06 1211. GSM base station. Installation instructions
 Rev 06 1211 GSM base station Installation instructions Output string format Baud rate 115200 bps Parity none Data bits 8 Stop bits 1 Flow control none The output string is a modified version of the Sureguard
Rev 06 1211 GSM base station Installation instructions Output string format Baud rate 115200 bps Parity none Data bits 8 Stop bits 1 Flow control none The output string is a modified version of the Sureguard
Virtual Integrated Design Getting started with RS232 Hex Com Tool v6.0
 Virtual Integrated Design Getting started with RS232 Hex Com Tool v6.0 Copyright, 1999-2007 Virtual Integrated Design, All rights reserved. 1 Contents: 1. The Main Window. 2. The Port Setup Window. 3.
Virtual Integrated Design Getting started with RS232 Hex Com Tool v6.0 Copyright, 1999-2007 Virtual Integrated Design, All rights reserved. 1 Contents: 1. The Main Window. 2. The Port Setup Window. 3.
Power network telecommunication
 www.siemens.com Power network telecommunication Teleprotection Answers for infrastructure and cities. Binary I/O The best protection against high-voltage grid failures When it comes to managing power networks,
www.siemens.com Power network telecommunication Teleprotection Answers for infrastructure and cities. Binary I/O The best protection against high-voltage grid failures When it comes to managing power networks,
