Short-Term Insulin Requirements Following Gastric Bypass Surgery in Severely Obese Women with Type 1 Diabetes
|
|
|
- Kristian Bond
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short-Term Insulin Requirements Following Gastric Bypass Surgery in Severely Obese Women with Type 1 Diabetes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable Link Terms of Use Middelbeek, Roeland J. W., Tamarra James-Todd, Mary- Elizabeth Patti, and Florence M. Brown Short-Term Insulin Requirements Following Gastric Bypass Surgery in Severely Obese Women with Type 1 Diabetes. Obesity Surgery 24 (9): doi: /s doi: /s December 21, :10:45 PM EST This article was downloaded from Harvard University's DASH repository, and is made available under the terms and conditions applicable to Other Posted Material, as set forth at (Article begins on next page)
2 OBES SURG (2014) 24: DOI /s ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Short-Term Insulin Requirements Following Gastric Bypass Surgery in Severely Obese Women with Type 1 Diabetes Roeland J. W. Middelbeek & Tamarra James-Todd & Mary-Elizabeth Patti & Florence M. Brown Published online: 26 March 2014 # The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Background In severely obese type 2 diabetes patients, gastric bypass surgery (GB) reduces body mass index (BMI) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and allows reduced doses of insulin and other medications. Data regarding the effects of GB on severely obese patients with type 1 diabetes are limited. Methods Severely obese women with type 1 diabetes (n=9) were studied immediately before and after GB (7.7±5.8 weeks, mean ± SD). Results On average, GB reduced mean BMI by 11 % and mean HbA1c by 0.9 % (from 8.0 to 7.1 %), with a parallel 38 % decrease in basal insulin requirements (expressed per kilogram of body weight). Conclusion GB rapidly decreased BMI, HbA1c, and insulin requirements in severely obese women with type 1 diabetes. However, physiologic insulin replacement remains necessary in patients with type 1 diabetes. R. J. W. Middelbeek: M.<E. Patti : F. M. Brown Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, 330 Brookline Ave, Boston, MA, USA R. J. W. Middelbeek rmiddelb@bidmc.harvard.edu M.<E. Patti maryelizabeth.patti@joslin.harvard.edu T. James-Todd Division of Women s Health, Brigham and Women s Hospital, 1620 Tremont St., 3rd floor, Boston, MA 02120, USA tjames-todd@partners.org M.<E. Patti: F. M. Brown (*) Joslin Diabetes Center, One Joslin Place, Boston, MA 02215, USA florence.brown@joslin.harvard.edu R. J. W. Middelbeek: T. James-Todd : M.<E. Patti : F. M. Brown Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Keywords Gastric bypass surgery. Type 1 diabetes. Insulin requirements Background Recent data demonstrate that gastric bypass surgery (GB) is a highly effective strategy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. GB achieves long-term weight loss, decreases mortality [1], and rapidly normalizes hyperglycemia [2], permitting dosage reduction and/or withdrawal of diabetes medication. These effects are likely related to both the marked reduction in peripheral insulin resistance [3] and increased incretin and insulin secretion [4], which occur even prior to sustained weight loss [5 7]. By contrast, little is known about the effects of GB on severely obese patients with type 1 diabetes. Prior case reports showed mixed effects of GB on hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and insulin requirements in individuals with type 1 diabetes [8 11]. Given the limited studies in this increasingly obese population [12], we investigated the short-term effects of GB on weight, HbA1c, and insulin requirements in obese subjects with type 1 diabetes. Methods Study Population The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Joslin Diabetes Center, and informed consent was waived. The electronic medical record database of the Joslin Diabetes Center was queried for the terms type 1 diabetes and gastric bypass for visits which occurred between January 1, 2000 and April 1, 2012; a total of 27 individuals were found. Gastric bypass was defined as Roux-en-Y laparoscopic gastric
3 OBES SURG (2014) 24: bypass surgery. After excluding subjects without a date of surgery listed (14.8 %), not on insulin therapy (3.7 %), with missing pre- or postsurgery visit documentation, or a visit >20 weeks after surgery (48.1 %), nine individuals were included in the final cohort for analysis. Demographic data were collected from medical records. Subjects were treated with either continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) or multiple daily injections (MDI). For CSII-treated subjects, only the basal insulin contribution to the total daily dose of insulin was available for review. For MDItreated subjects, basal and meal bolus insulin requirements were recorded. Medical records were reviewed in detail to confirm the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes based on clinical characteristics [13]. The diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was further supported by the presence of autoantibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), insulinoma-associated (IA-2), and insulin (IAA), and/or low or undetectable C- peptide levels in four out of four patients tested. Additionally, patients were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at a mean age of 15 years (<12 years of age in 56 % of subjects). Data Analysis Body mass index (BMI), HbA1c, and basal insulin doses were considered primary outcomes. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures were considered secondary outcomes. BMI was calculated as weight in kilogram/height in square meters. HbA1c values were collected from medical record data. Insulin requirements were expressed relative to body weight and presented as units per kilogram per day, and both absolute and relative differences between pre- and postoperative requirements were calculated. Table 1 Baseline characteristics and postsurgery changes Presurgery Postsurgery p values Values are represented as mean ± SD. Baseline characteristics of type 1 diabetes subjects who underwent GB were obtained during the last presurgery visit. HbA1c, BMI, blood pressure, and insulin requirements were obtained during the first postsurgical visit (mean 7.7±5.8 weeks) and the last presurgical visit TDD total daily dose, MDI multiple dose injections Age at time of surgery (years) 40.3±8.5 Female sex N (%) 9 (100) Height (cm) 167.8±8.0 Weight (kg) 122.2±23.5 Diabetes duration at time of surgery (years) 25.3±8.9 Mean age at DM diagnosis (years) 15.0±8.2 Low or undetectable C-peptide level N (%) 4 (44 %) Autoantibodies present (GAD, IA2, IAA) N (%) 3 (33 %) Insulin pump N (%) 5 (56 %) Insulin pump and pramlintide 1 (11 %) Multiple daily injections N (%) 4 (44 %) Multiple daily injections and metformin 1 (11 %) Supplemental medications N (%) 2 (22 %) Pramlintide, metformin HbA1c (%) 8.0± ±0.9 <0.05 BMI (kg/m 2 ) 43.8± ±8.6 <0.05 Basal insulin requirement (U/day) 59.7± ±20.9 <0.05 % Basal insulin compared to presurgery (n=9) N/A 54.6 Basal insulin/kg/day (U/kg/day) 0.47± ±0.14 <0.05 % Basal insulin/kg/day compared to presurgery N/A 61.8 Meal bolus insulin requirement (U/day) (n=4) 53.0± ± % bolus insulin compared to presurgery N/A 40.1 Meal bolus dose/kg/day (U/kg/day) 0.44± ± % bolus insulin/kg/day compared to presurgery N/A 34.6 Total daily insulin requirement (U/day) (n=4) 113± ±28.2 <0.05 % TDD compared to presurgery N/A 46.9 Total daily dose/kg/day (U/kg/day) 0.93± ±0.26 <0.05 % TDD insulin/kg/day compared to presurgery N/A 50.7 Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) 124.0± ± Diastolic blood pressure (mmhg) 74.2± ± Supplemental medications N (%) 2 (22 %) 0 (0 %) Assessment postsurgery (weeks) 7.7±5.8
4 1444 OBES SURG (2014) 24: Age, age at diagnosis, length of time with diabetes, height, weight, and blood pressure were considered as continuous variables, and mean and standard deviation were calculated. Treatment with auxiliary oral or injected diabetes medications was assessed. To determine whether our primary outcomes differed before and after GB, we conducted paired t tests and defined significance as p<0.05. To compare the change in insulin dose with the change in weight, we used the Pearson correlation. Microsoft Office Excel 2007 was used for statistical analyses. Results All subjects (n=9) were female (mean age 40.3±8.5 years) and had a mean duration of type 1 diabetes of 25.3±8.9 years (range years). The mean age at diagnosis was 15.0± 8.2 years (range 8 28 years) (Table 1). All subjects were treated with insulin; five patients used CSII, while four patients used MDI. Two subjects were also treated with metformin and pramlintide as adjunctive medications to promote weight loss [14]; both of these subjects had positive autoantibodies and low or undetectable C-peptide levels, confirming type 1 diabetes. At the time of the first postsurgical visit (mean 7.7± 5.8 weeks, range 2 18 weeks), BMI had decreased by a mean of 11 % (from 43.4±8.0 to 38.7±8.6 kg/m 2, p<0.05). HbA1c also decreased significantly, from 8.0 to 7.1 % (p<0.05). The dose of basal insulin, calculated from recorded CSII and MDI regimens, decreased from 59.7±43.8 to 32.6±20.9U/day (p<0.05) (Table 1) and was also significantly decreased when expressed per kilogram of body weight (38 % reduction, from 0.47±0.28 to 0.29±0.14U/kg/day, p<0.05) (Fig. 1, Table 1). In MDI-treated subjects (n=4), the meal bolus dose showed a trend towards a decrease by 65 % (from 0.44±0.24 to 0.15± 0.9 U/kg/day, p<0.08). Similarly, total daily insulin dose in MDI-treated patients, calculated from recorded basal and bolus regimens, decreased by a mean of 53 % from 113±33.8 to 52.6 ±28.2 U/day. Total daily insulin dose per kilogram of body weight also decreased by 49 % from 0.93±0.14 to 0.49± 0.19 U/kg/day (p<0.05). Subjects with postsurgical visits at <7.7 weeks showed a greater decrease in basal insulin requirement than those assessed at >7.7 weeks ( 0.23±0.19 vs ±0.12 U/kg/day, respectively), but less weight loss ( 10.2±7.0 vs. 16.8±10.1 kg, respectively). There was no statistically significant correlation between the extent of weight loss and percentage change in basal insulin requirements (Pearson correlation coefficient r=0.34, p=0.37). None of the subjects was able to discontinue insulin therapy, consistent with their absolute insulin deficiency and type 1 diabetes, but all auxiliary oral and injectable therapy was discontinued after surgery. Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure tended to decrease, from 124±9 to 114±22 mmhg andfrom74±7to67±6mmhg(p=0.14 and p=0.06, respectively). Discussion This study demonstrates that GB rapidly and significantly reduces BMI, HbA1c, and insulin requirements in severely obese women with type 1 diabetes. These patterns are similar to those in prior studies of patients with type 2 diabetes [15]. However, the 38 % reduction in basal insulin requirements in both CSII and MDI-treated patients with type 1 diabetes and 50 % reduction in total insulin requirements in MDI-treated Fig. 1 Basal insulin requirements per day (U/kg/day) from individual study participants (n=9) were determined at the final presurgical and first postsurgical visits, between January 1, 2000 and April 1, 2012 Insulin requirement (U/kg/day)
5 OBES SURG (2014) 24: patients are less than the overall 79 % reduction of insulin therapy previously observed in studies of type 2 diabetes patients, although this reduction was reported for a mean follow-up of 19.7 months [16]. This likely reflects the persisting absolute requirement for insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes, as a result of immunological β-cell destruction and absolute insulin deficiency. Previous case reports have described mixed effects of GB on type 1 diabetes. Czupryniak et al. found marked decreases in insulin requirements and HbA1c after GB in three patients who had poorly controlled type 1 diabetes preoperatively (mean HbA1c 10.4 %) [8, 10]. By contrast, a report from Mendez et al. in three patients showed no significant improvement in HbA1c, despite significant weight loss in three patients [9]. These differences could be due to the small sample size or differences in age, gender, time of subject assessment, and variable preoperative glycemic control. A recent paper assessed six patients undergoing a variety of bariatric surgical procedures, finding reductions in weight, insulin requirements, and HbA1c 1 year postoperatively; only two of these patients had undergone GB surgery [11]. In type 2 diabetes, GB improves insulin sensitivity, as defined by hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamps [17], in parallel with reduced basal insulin levels and increased postprandial insulin secretion [6]. In type 1 diabetes, endogenous insulin levels are low to absent secondary to autoimmune beta cell destruction. Thus, the reduction in exogenous basal insulin requirement is likely related to resolution of obesityinduced insulin resistance. Additionally, reductions in total caloric intake and or altered proportions of macronutrients may also contribute to reduced insulin requirements. In our study, the reduction in basal insulin requirements did not correlate with the amount of weight loss, suggestive of a weight loss-independent mechanism. Moreover, GB yields marked effects on hepatic glucose metabolism as early as 1 week postoperatively, and although these data are derived from studies of individuals with type 2 diabetes [18], we hypothesize that similar effects could also be observed in severely obese patients with type 1 diabetes. This study has several limitations. First, this is a small study of nine subjects, and the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was defined clinically. However, five of nine subjects were diagnosed at <12 years of age, and laboratory confirmation was available in four subjects, including low or undetectable C-peptide levels and positive autoantibodies. Second, we assessed the impact on basal insulin levels in all subjects and meal bolus and total daily insulin doses as reported for MDI regimens, but we were unable to fully assess prandial doses in CSII-treated patients, since only insulin-to-carbohydrate ratios were reported. Third, our cohort was all female; while this is consistent with the preponderance of females undergoing bariatric surgery, these findings may not extend to men with type 1 diabetes who are treated with GB [7]. Despite these limitations, the present study is the largest to date which evaluates weight loss, glycemic control, and shortterm changes in insulin requirements in patients with type 1 diabetes following GB. We specifically chose to follow subjects at short term (<20 weeks), to assess their insulin requirements before more major weight loss occurs and to provide guidance to clinicians who see these patients during the immediate postoperative and short-term follow-up visits after surgery. Further studies are clearly required to assess the durability of weight loss and improved glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes. Moreover, GB markedly alters patterns of early postprandial glycemia [4], contributing to a potential mismatch between nutrient absorption and timing of prandial insulin, with risk of subsequent hypoglycemia. Thus, it is often challenging to optimize prandial insulin therapy in post-gb patients. Additional studies will be required to determine optimal dose and timing of prandial insulin replacement in post-gb patients in the clinical setting. In conclusion, we demonstrate that GB decreases BMI, HbA1c, and insulin requirements in severely obese women with type 1 diabetes. Consistent with the absolute requirement for insulin in type 1 diabetes, none of the subjects was able to discontinue insulin. Continuing an insulin regimen with post- GB patients with type 1 diabetes is critical in order to prevent onset of diabetic ketoacidosis, and frequent postoperative follow-up for adjustment of prandial insulin requirements is absolutely required. Longitudinal assessment will be important to evaluate long-term metabolic changes in our study population. Future larger and prospective studies will be needed to confirm these findings, assess the underlying metabolic changes, and evaluate the impact of GB on long-term morbidity and mortality in type 1 diabetes. Conflict of Interest R.J.W.M., T.J-T, M.E.P., and F.M.B. have no conflict of interest to disclose. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited. References 1. Adams TD et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(8): Mingrone G et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17): Salinari S et al. Insulin sensitivity and secretion changes after gastric bypass in normotolerant and diabetic obese subjects. Ann Surg. 2013;257(3): Goldfine AB et al. Patients with neuroglycopenia after gastric bypass surgery have exaggerated incretin and insulin secretory
6 1446 OBES SURG (2014) 24: responses to a mixed meal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(12): Saliba J, Wattacheril J, Abumrad NN. Endocrine and metabolic response to gastric bypass. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009;12(5): Schauer PR et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(17): Sjostrom L et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(26): Czupryniak L et al. Gastric bypass surgery in severely obese type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(10): Mendez CE, Tanenberg RJ, Pories W. Outcomes of Roux-en- Y gastric bypass surgery for severely obese patients with type 1 diabetes: a case series report. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2010;3: Czupryniak L et al. Long-term results of gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese type 1 diabetes patients. Obes Surg. 2010;20(4): Raab H et al. Obesity and metabolic surgery in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28 Suppl 2: Conway B et al. Temporal patterns in overweight and obesity in Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2010;27(4): American Diabetes, A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(Supplement 1):p. S Lebovitz HE. Adjunct therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6(6): Buchwald H et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122(3):p e Schauer PR et al. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 2003;238(4): discussion Muscelli E et al. Differential effect of weight loss on insulin resistance in surgically treated obese patients. Am J Med. 2005;118(1): Bojsen-Moller KN et al. Early enhancements of hepatic and later of peripheral insulin sensitivity combined with increased postprandial insulin secretion contribute to improved glycemic control after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetes doi: /db
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx:
 James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
James Cromie The Arguments: T2DM - tremendous economic burden globally Lifestyle / Pharm Rx: INEFFECTIVE and UNSUSTAINED Bariatric surgery is an Effective and Durable treatment option Well established
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY. Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN CHILDREN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Ines Guttmann- Bauman MD Clinical Associate Professor, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, OHSU Objectives: 1. To discuss epidemiology and presentation
Reversing type 2 diabetes: pancreas composition and function during return to normal glucose tolerance
 Reversing type 2 diabetes: pancreas composition and function during return to normal glucose tolerance Dr Sarah Steven Clinical Research Fellow to Professor Roy Taylor Observations from bariatric surgery
Reversing type 2 diabetes: pancreas composition and function during return to normal glucose tolerance Dr Sarah Steven Clinical Research Fellow to Professor Roy Taylor Observations from bariatric surgery
INSULIN AND INCRETIN THERAPIES: WHAT COMBINATIONS ARE RIGHT FOR YOUR PATIENT?
 INSULIN AND INCRETIN THERAPIES: WHAT COMBINATIONS ARE RIGHT FOR YOUR PATIENT? MARTHA M. BRINSKO, MSN, ANP-BC CHARLOTTE COMMUNITY HEALTH CLINIC CHARLOTTE, NC Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes in the United
INSULIN AND INCRETIN THERAPIES: WHAT COMBINATIONS ARE RIGHT FOR YOUR PATIENT? MARTHA M. BRINSKO, MSN, ANP-BC CHARLOTTE COMMUNITY HEALTH CLINIC CHARLOTTE, NC Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes in the United
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS
 BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
BARIATRIC SURGERY MAY CURE TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOME PATIENTS Thomas Rogula MD, Stacy Brethauer MD, Bipand Chand MD, and Philip Schauer, MD. "Gastric bypass surgery has become a popular option for obese
3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico
 3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico Recidive del diabete dopo terapia chirurgica La quantificazione
3 WORKSHOP CONGIUNTO SICOb SID SIO 7 MARZO 2014 L integrazione tra terapia medica e chirurgica nel trattamento del paziente obeso diabetico Recidive del diabete dopo terapia chirurgica La quantificazione
Intensive Insulin Therapy in Diabetes Management
 Intensive Insulin Therapy in Diabetes Management Lillian F. Lien, MD Medical Director, Duke Inpatient Diabetes Management Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, & Nutrition
Intensive Insulin Therapy in Diabetes Management Lillian F. Lien, MD Medical Director, Duke Inpatient Diabetes Management Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, & Nutrition
Sponsor. Novartis Generic Drug Name. Vildagliptin. Therapeutic Area of Trial. Type 2 diabetes. Approved Indication. Investigational.
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Generic Drug Name Vildagliptin Therapeutic Area of Trial Type 2 diabetes Approved Indication Investigational Study Number CLAF237A2386 Title A single-center,
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
Objectives. What Is Diabetes? 1/26/2015. Carbs & Meds & Meters, Oh My!: Diabetes in Pregnancy
 Carbs & Meds & Meters, Oh My!: Diabetes in Pregnancy Jan Tisdale RD, MPH, CDE Nutritionist / Certified Diabetes Educator UAB School of Medicine OB/GYN Maternal-Fetal Medicine 02/2015 Objectives Review
Carbs & Meds & Meters, Oh My!: Diabetes in Pregnancy Jan Tisdale RD, MPH, CDE Nutritionist / Certified Diabetes Educator UAB School of Medicine OB/GYN Maternal-Fetal Medicine 02/2015 Objectives Review
Inpatient Treatment of Diabetes
 Inpatient Treatment of Diabetes Alan J. Conrad, MD Medical Director Diabetes Services EVP, Physician Alignment Diabetes Symposium November 12, 2015 Objectives Explain Palomar Health goals for inpatient
Inpatient Treatment of Diabetes Alan J. Conrad, MD Medical Director Diabetes Services EVP, Physician Alignment Diabetes Symposium November 12, 2015 Objectives Explain Palomar Health goals for inpatient
The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes
 DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
There seem to be inconsistencies regarding diabetic management in
 Society of Ambulatory Anesthesia (SAMBA) Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Review of the consensus statement and additional
Society of Ambulatory Anesthesia (SAMBA) Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Review of the consensus statement and additional
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy. Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15
 Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Subject: Weight Loss Surgery Policy Effective Date: 1/00 Revision Date: 10/15 DESCRIPTION OSU Health Plans supports covered members with a spectrum of service for obesity and weight loss attempts. The
Subcutaneous Infusion of GLP-1 for 7 Days Improves Glycemic Control Over a Broad Dose Range in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Subcutaneous Infusion of GLP-1 for 7 Days Improves Glycemic Control Over a Broad Dose Range in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mario R. Ehlers, 1,2 Roderick E. Harley, 1 Annette L. Mathisen, 1 Roberta Schneider,
Subcutaneous Infusion of GLP-1 for 7 Days Improves Glycemic Control Over a Broad Dose Range in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mario R. Ehlers, 1,2 Roderick E. Harley, 1 Annette L. Mathisen, 1 Roberta Schneider,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Afrezza Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Afrezza (human insulin) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests Prior Authorization
Afrezza Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Afrezza (human insulin) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests Prior Authorization
Traditional View of Diabetes. Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? 8/9/2012. Change in Traditional View of Diabetes
 Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Diabetes Mellitus. Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes Mellitus
 Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Melissa Meredith M.D. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Diabetes is a chronic,
Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery
 WHITE PAPER Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery Treat the cause. Cure the symptom. Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Written July 2011 Bariatric Surgery: The Cure for Type II Diabetes? For most individuals
WHITE PAPER Diabetes and Weight-Loss Surgery Treat the cause. Cure the symptom. Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Written July 2011 Bariatric Surgery: The Cure for Type II Diabetes? For most individuals
Getting Off the Chronic Disease Merry-Go-Round: What s the Weight of the Research?
 Getting Off the Chronic Disease Merry-Go-Round: What s the Weight of the Research? Jody Dushay, MD MMSc Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA Session 445 No disclosures Disclosure Jody Dushay,
Getting Off the Chronic Disease Merry-Go-Round: What s the Weight of the Research? Jody Dushay, MD MMSc Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA Session 445 No disclosures Disclosure Jody Dushay,
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention.
 Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
Double Diabetes: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prediction and Prevention. Professor Paolo Pozzilli University Campus Bio-Medico, Rome Institute of Cell & Molecular Science, Queen Mary, University of
NCT00272090. sanofi-aventis HOE901_3507. insulin glargine
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: Generic drug name:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: Generic drug name:
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients
 Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Type 2 diabetes mellitus current therapies and the emergence of surgical options
 Type 2 diabetes mellitus current therapies and the emergence of surgical options Harold E. Lebovitz Abstract Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are usually treated with pharmacologic agents
Type 2 diabetes mellitus current therapies and the emergence of surgical options Harold E. Lebovitz Abstract Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are usually treated with pharmacologic agents
12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16
 HEALTHSPAN BARIATRIC SURGERY Methodology: Expert Opinion Champion: Surgery Issue Date: Review Date: 12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16 RELEVANCE: The CPG for
HEALTHSPAN BARIATRIC SURGERY Methodology: Expert Opinion Champion: Surgery Issue Date: Review Date: 12-05 1-13, 4-14, 6-15 Key Stakeholders: Surgery, IM Depts. Next Update: 6-16 RELEVANCE: The CPG for
Algorithms for Glycemic Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 KENTUCKY DIABETES NETWORK, INC. Algorithms for Glycemic Management of Type 2 Diabetes The Diabetes Care Algorithms for Type 2 Diabetes included within this document are taken from the American Association
KENTUCKY DIABETES NETWORK, INC. Algorithms for Glycemic Management of Type 2 Diabetes The Diabetes Care Algorithms for Type 2 Diabetes included within this document are taken from the American Association
Glucose Management University of Colorado Hospital
 Glucose Management University of Colorado Hospital Bridget Everhart, MSN, NP, CDE Inpatient Diabetes Educator Bridget.Everhart@uch.edu M F Pager 303 266-7898 UCH Diabetes Program Michael McDermott MD Diabetes
Glucose Management University of Colorado Hospital Bridget Everhart, MSN, NP, CDE Inpatient Diabetes Educator Bridget.Everhart@uch.edu M F Pager 303 266-7898 UCH Diabetes Program Michael McDermott MD Diabetes
Dealing with weight regain after Rouxen-Y gastric bypass: surgical approach
 Dealing with weight regain after Rouxen-Y gastric bypass: surgical approach Robin Blackstone, MD, FACS Masters of Minimally Invasive Bariatric Surgery April 5, 2013 Orlando, Florida Disclosures PI Enteromedics
Dealing with weight regain after Rouxen-Y gastric bypass: surgical approach Robin Blackstone, MD, FACS Masters of Minimally Invasive Bariatric Surgery April 5, 2013 Orlando, Florida Disclosures PI Enteromedics
CARDIAC SURGERY INTRAVENOUS INSULIN PROTOCOL PHYSICIAN ORDERS INDICATIONS EXCLUSIONS. Insulin allergy
 Page 1 of 5 INDICATIONS EXCLUSIONS 2 consecutive blood glucose measurements greater than 110 mg per dl AND NPO with a continuous caloric source AND Diagnosis of : Cardio-thoracic Surgery NOTE: This protocol
Page 1 of 5 INDICATIONS EXCLUSIONS 2 consecutive blood glucose measurements greater than 110 mg per dl AND NPO with a continuous caloric source AND Diagnosis of : Cardio-thoracic Surgery NOTE: This protocol
Diabetes Mellitus 1. Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions
 Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
Diabetes Mellitus 1 Chapter 43. Diabetes Mellitus, Self-Assessment Questions 1. A 46-year-old man presents for his annual physical. He states that he has been going to the bathroom more frequently than
INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENTS NOON CONFERENCE: INPATIENT GLYCEMIC CONTROL
 INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENTS NOON CONFERENCE: INPATIENT GLYCEMIC CONTROL Presented by: Leyda Callejas PGY5 Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Acknowledgements: Dr. P Orlander Dr. V Lavis Dr. N Shah
INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENTS NOON CONFERENCE: INPATIENT GLYCEMIC CONTROL Presented by: Leyda Callejas PGY5 Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Acknowledgements: Dr. P Orlander Dr. V Lavis Dr. N Shah
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Abstract Background Methods:
 Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
Sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass as revisional bariatric procedures: retrospective evaluation of outcomes. Mousa Khoursheed, Ibtisam Al-Bader, Ali Mouzannar, Abdulla Al-Haddad, Ali Sayed, Ali Mohammad,
Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075
 Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE - 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE - 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE - 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
Is surgery better? Jordan Kautz, MS IV A b atory are C erence, an 08 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine
 Is surgery better? Bariatric surgery versus medical management in type 2 diabetes mellitus Jordan Kautz, MS IV Ambulatory Care Conference, Jan 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine For the soon-to-be medical resident
Is surgery better? Bariatric surgery versus medical management in type 2 diabetes mellitus Jordan Kautz, MS IV Ambulatory Care Conference, Jan 08 UNC-CH School of Medicine For the soon-to-be medical resident
Intensifying Insulin In Type 2 Diabetes
 Intensifying Insulin In Type 2 Diabetes Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine University of North Dakota School of Medicine and Health Sciences Assistant
Intensifying Insulin In Type 2 Diabetes Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine University of North Dakota School of Medicine and Health Sciences Assistant
INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT
 INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT APIRADEE SRIWIJITKAMOL DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITOL QUESTION 1 1. ท านเคยเป นแพทย
INSULIN TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT APIRADEE SRIWIJITKAMOL DIVISION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITOL QUESTION 1 1. ท านเคยเป นแพทย
Short-term Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Severely Obese Subjects
 Obesity Surgery, 17, 1069-1074 Research Articles Short-term Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Severely Obese Subjects J. Vidal, MD, PhD; A. Ibarzabal, MD; J. Nicolau, MD; M.
Obesity Surgery, 17, 1069-1074 Research Articles Short-term Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Severely Obese Subjects J. Vidal, MD, PhD; A. Ibarzabal, MD; J. Nicolau, MD; M.
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals
 Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
Diabetes: When To Treat With Insulin and Treatment Goals Lanita. S. White, Pharm.D. Director, UAMS 12 th Street Health and Wellness Center Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice, UAMS College of Pharmacy
tips Insulin Pump Users 1 Early detection of insulin deprivation in continuous subcutaneous 2 Population Study of Pediatric Ketoacidosis in Sweden:
 tips Top International Publications Selection Insulin Pump Users Early detection of insulin deprivation in continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion-treated Patients with TD Population Study of Pediatric
tips Top International Publications Selection Insulin Pump Users Early detection of insulin deprivation in continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion-treated Patients with TD Population Study of Pediatric
INSULIN INTENSIFICATION: Taking Care to the Next Level
 INSULIN INTENSIFICATION: Taking Care to the Next Level By J. Robin Conway M.D., Diabetes Clinic, Smiths Falls, ON www.diabetesclinic.ca Type 2 Diabetes is an increasing problem in our society, due largely
INSULIN INTENSIFICATION: Taking Care to the Next Level By J. Robin Conway M.D., Diabetes Clinic, Smiths Falls, ON www.diabetesclinic.ca Type 2 Diabetes is an increasing problem in our society, due largely
EFFICACY OF BARIATRIC SURGERY IN OBESE INDIAN WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 EFFICACY OF BARIATRIC SURGERY IN OBESE INDIAN WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS Subodh Banzal, Abhishek Singhai, Mohit Bhandari, Padmnabh Sharma, Rajesh Kumar Jha, Piyush Manoria 1. Associate Professor, DM,
EFFICACY OF BARIATRIC SURGERY IN OBESE INDIAN WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS Subodh Banzal, Abhishek Singhai, Mohit Bhandari, Padmnabh Sharma, Rajesh Kumar Jha, Piyush Manoria 1. Associate Professor, DM,
Bariatric Surgery. OHTAC Recommendation. Bariatric Surgery
 OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies)
 Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies) Leann Olansky, MD, FACP, FACE Cleveland Clinic Endocrinology Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG Diabetes
Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies) Leann Olansky, MD, FACP, FACE Cleveland Clinic Endocrinology Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG Diabetes
Glucose Tolerance Categories. Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies)
 Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies) Leann Olansky, MD, FACP, FACE Cleveland Clinic Endocrinology Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG Diabetes
Distinguishing between Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2, (with Overview of Treatment Strategies) Leann Olansky, MD, FACP, FACE Cleveland Clinic Endocrinology Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG Diabetes
Glycemic Control Initiative: Insulin Order Set Changes Hypoglycemia Nursing Protocol
 Glycemic Control Initiative: Insulin Order Set Changes Hypoglycemia Nursing Protocol Ruth LaCasse Kalish, RPh Department of Pharmacy Objectives Review the current practice at UConn Health with sliding
Glycemic Control Initiative: Insulin Order Set Changes Hypoglycemia Nursing Protocol Ruth LaCasse Kalish, RPh Department of Pharmacy Objectives Review the current practice at UConn Health with sliding
Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy Alfonso Torquati MD, MSCI Associate Professor of Surgery Discosures NIH-NIDDK: grant support Covidien: consulting agreement, grant support
Comparative Studies and Metabolic Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy Alfonso Torquati MD, MSCI Associate Professor of Surgery Discosures NIH-NIDDK: grant support Covidien: consulting agreement, grant support
Insulin Analogues versus Pump Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Benefits from Pump Therapy
 Insulin Analogues versus Pump Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Benefits from Pump Therapy Eric RENARD, MD, PhD Endocrinology Dept, Lapeyronie Hospital Montpellier, France e-renard@chu-montpellier.fr Type 2
Insulin Analogues versus Pump Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Benefits from Pump Therapy Eric RENARD, MD, PhD Endocrinology Dept, Lapeyronie Hospital Montpellier, France e-renard@chu-montpellier.fr Type 2
Diabetes Medications: Insulin Therapy
 Diabetes Medications: Insulin Therapy Courtesy Univ Texas San Antonio Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Department of Family and Community Medicine Diabetes and Insulin Type 1 Diabetes Autoimmune destruction of beta
Diabetes Medications: Insulin Therapy Courtesy Univ Texas San Antonio Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Department of Family and Community Medicine Diabetes and Insulin Type 1 Diabetes Autoimmune destruction of beta
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
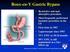 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery
 Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
Medical Coverage Policy Bariatric Surgery Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 9/1/2011 Policy Last Updated: 11/01/2011 Prospective review is recommended/required. Please check
ADJUNCTIVE THERAPIES FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES
 ADJUNCTIVE THERAPIES FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES Dr. Mohammad Alhadj Ali, MD, PgDip, MSc, PhD (UK) with Prof. David Owens (UK) Outline Type 1 Diabetes Immunology of Type 1 Diabetes Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
ADJUNCTIVE THERAPIES FOR TYPE 1 DIABETES Dr. Mohammad Alhadj Ali, MD, PgDip, MSc, PhD (UK) with Prof. David Owens (UK) Outline Type 1 Diabetes Immunology of Type 1 Diabetes Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
Intensifying Insulin Therapy
 Intensifying Insulin Therapy Rick Hess, PharmD, CDE, BC-ADM Associate Professor Gatton College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacy Practice East Tennessee State University Johnson City, Tennessee Learning
Intensifying Insulin Therapy Rick Hess, PharmD, CDE, BC-ADM Associate Professor Gatton College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacy Practice East Tennessee State University Johnson City, Tennessee Learning
Choices Around Bariatric Surgery
 Choices Around Bariatric Surgery What should you know? Richard Stubbs MD FRCS FRACS Wakefield Obesity Clinic, Wellington 152 kg / BMI 59 74 kg / BMI 29 Indications (NIH Consensus Statement 1991) BMI >
Choices Around Bariatric Surgery What should you know? Richard Stubbs MD FRCS FRACS Wakefield Obesity Clinic, Wellington 152 kg / BMI 59 74 kg / BMI 29 Indications (NIH Consensus Statement 1991) BMI >
The basal plus strategy. Denis Raccah, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University Hospital Sainte Marguerite Marseille FRANCE
 The basal plus strategy Denis Raccah, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University Hospital Sainte Marguerite Marseille FRANCE ADA/EASD guidelines recommend use of basal insulin as early as the second step
The basal plus strategy Denis Raccah, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University Hospital Sainte Marguerite Marseille FRANCE ADA/EASD guidelines recommend use of basal insulin as early as the second step
Diabetes and Obesity. The diabesity epidemic
 Diabetes and Obesity Frank B. Diamond, Jr. M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of South Florida College of Medicine The diabesity epidemic Prevalence of diabetes worldwide was over 135 million people
Diabetes and Obesity Frank B. Diamond, Jr. M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of South Florida College of Medicine The diabesity epidemic Prevalence of diabetes worldwide was over 135 million people
Insulin: Breaking Barriers Enhancing Therapies. Jerry Meece, RPh, FACA, CDE jmeece12@cooke.net
 Insulin: Breaking Barriers Enhancing Therapies Jerry Meece, RPh, FACA, CDE jmeece12@cooke.net Questions To Address Who are candidates for insulin? When do we start insulin? How do the different types of
Insulin: Breaking Barriers Enhancing Therapies Jerry Meece, RPh, FACA, CDE jmeece12@cooke.net Questions To Address Who are candidates for insulin? When do we start insulin? How do the different types of
Department of Pharmacy, Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Medical Center, San Francisco 94115, California, USA
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 33-38 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evaluation of Glycemic Control with a Pharmacist-Managed Post-Cardiothoracic Surgery Insulin Protocol
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 33-38 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evaluation of Glycemic Control with a Pharmacist-Managed Post-Cardiothoracic Surgery Insulin Protocol
INPATIENT DIABETES MANAGEMENT Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine Director, Inpatient Diabetes University of California, San Francisco
 INPATIENT DIABETES MANAGEMENT Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine Director, Inpatient Diabetes University of California, San Francisco CLINICAL RECOGNITION Background: Appropriate inpatient glycemic
INPATIENT DIABETES MANAGEMENT Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine Director, Inpatient Diabetes University of California, San Francisco CLINICAL RECOGNITION Background: Appropriate inpatient glycemic
Insulin or GLP1 How to make this choice in Practice. Tara Kadis Lead Nurse - Diabetes & Endocrinology Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust
 Insulin or GLP1 How to make this choice in Practice Tara Kadis Lead Nurse - Diabetes & Endocrinology Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust Workshop Over View Considerations/barriers to treatments in type 2
Insulin or GLP1 How to make this choice in Practice Tara Kadis Lead Nurse - Diabetes & Endocrinology Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust Workshop Over View Considerations/barriers to treatments in type 2
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS. Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence
 PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Aspart in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
 Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2002; 11(2), 87-92 Copyright 2002 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Aspart in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Toshikazu
Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2002; 11(2), 87-92 Copyright 2002 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Aspart in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Toshikazu
Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA)
 Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA) Historically, insulin resistance (IR) was measured with an invasive test called a euglycemic clamp test. Basically it s a test to measure how much insulin a person needs
Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA) Historically, insulin resistance (IR) was measured with an invasive test called a euglycemic clamp test. Basically it s a test to measure how much insulin a person needs
Present and Future of Insulin Therapy: Research Rationale for New Insulins
 Present and Future of Insulin Therapy: Research Rationale for New Insulins Current insulin analogues represent an important advance over human insulins, but clinically important limitations of these agents
Present and Future of Insulin Therapy: Research Rationale for New Insulins Current insulin analogues represent an important advance over human insulins, but clinically important limitations of these agents
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
The first injection of insulin was given on
 EFFECTIVE USE OF INSULIN THERAPY IN TYPE 2 DIABETES * Bernard Zinman, MDCM ABSTRACT Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease; an individual s ability to secrete insulin in increasing amounts to overcome
EFFECTIVE USE OF INSULIN THERAPY IN TYPE 2 DIABETES * Bernard Zinman, MDCM ABSTRACT Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease; an individual s ability to secrete insulin in increasing amounts to overcome
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE
 DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
Long term Weight Management in Obese Diabetic Patients Osama Hamdy, MD, PhD, FACE
 Long term Weight Management in Obese Diabetic Patients Osama Hamdy, MD, PhD, FACE Medical Director, Obesity Clinical Program, Director of Inpatient Diabetes Management, Joslin Diabetes Center Assistant
Long term Weight Management in Obese Diabetic Patients Osama Hamdy, MD, PhD, FACE Medical Director, Obesity Clinical Program, Director of Inpatient Diabetes Management, Joslin Diabetes Center Assistant
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Section 2. Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery
 Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Bariatric Surgery Support NEWSLETTER. info@bariatricsurgerysupport.co.za HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US!
 info@bariatricsurgery.co.za NEWSLETTER HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US! The Christmas Holidays are nearly upon us, and, like you, our Bariatric Surgery Support is looking forward to a well-deserved rest
info@bariatricsurgery.co.za NEWSLETTER HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ALL OF US! The Christmas Holidays are nearly upon us, and, like you, our Bariatric Surgery Support is looking forward to a well-deserved rest
Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012
 Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012 In 2002, SETMA began a relationship with Joslin Diabetes
Prevention of and the Screening for Diabetes Part I Insulin Resistance By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner January 19, 2012 In 2002, SETMA began a relationship with Joslin Diabetes
The Quantified Self on Steroids: Innovation in Devices, Pumps and Monitors
 The Quantified Self on Steroids: Innovation in Devices, Pumps and Monitors Howard A. Wolpert, MD 1 Diabetes is different to many other conditions Patient/Self Managed 2 To achieve the therapeutic goals
The Quantified Self on Steroids: Innovation in Devices, Pumps and Monitors Howard A. Wolpert, MD 1 Diabetes is different to many other conditions Patient/Self Managed 2 To achieve the therapeutic goals
Insulin/Diabetes Calculations
 Insulin/Diabetes Calculations Dr. Aipoalani St Lukes Endocrinology Goals Describe various calculations for insulin dosing Understand importance of the total daily dose (TDD) of insulin Be able to calculate
Insulin/Diabetes Calculations Dr. Aipoalani St Lukes Endocrinology Goals Describe various calculations for insulin dosing Understand importance of the total daily dose (TDD) of insulin Be able to calculate
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: sara.davies@scotland.gsi.gov.uk Heather.knox@nhs.net T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: sara.davies@scotland.gsi.gov.uk Heather.knox@nhs.net T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes
 Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes This trial is conducted in Africa, Asia, Europe and the United States of America (USA). The aim
Effect of liraglutide on body weight in overweight or obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: SCALE - Diabetes This trial is conducted in Africa, Asia, Europe and the United States of America (USA). The aim
EASD/ADA 2015 Highlights- insulin. Dr Jarl Hellman
 EASD/ADA 2015 Highlights- insulin Dr Jarl Hellman Innehåll NPH Epidemiologi Nya insuliner Basinsulinets bäste vän exklusive hund och UKPDS? G.B Bolli Hypoglykemi - NPH Exogenous insulin and risk of all-cause
EASD/ADA 2015 Highlights- insulin Dr Jarl Hellman Innehåll NPH Epidemiologi Nya insuliner Basinsulinets bäste vän exklusive hund och UKPDS? G.B Bolli Hypoglykemi - NPH Exogenous insulin and risk of all-cause
Insulin Pump Therapy in children & Adolescents. Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, MBBS,DCH, FRCP(UK) Pediatric Endocrinologist
 Insulin Pump Therapy in children & Adolescents Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, MBBS,DCH, FRCP(UK) Pediatric Endocrinologist Insulin The most powerful agent we have to control glucose Banting and Best The Miracle
Insulin Pump Therapy in children & Adolescents Dr. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, MBBS,DCH, FRCP(UK) Pediatric Endocrinologist Insulin The most powerful agent we have to control glucose Banting and Best The Miracle
NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT diabetes mellitus
 0021-972X/97/$03.00/0 Vol. 82, No. 8 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1997 by The Endocrine Society An Overnight Insulin Infusion Algorithm Provides Morning
0021-972X/97/$03.00/0 Vol. 82, No. 8 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1997 by The Endocrine Society An Overnight Insulin Infusion Algorithm Provides Morning
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery.
 Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
Article from: Health Watch. January 2011 Issue 65
 Article from: Health Watch January 2011 Issue 65 Bariatric Surgery Holds Promise for Patients and for Payors by John D. Dawson, Pierre-Yves Crémieux and Arindam Ghosh John D. Dawson, FSA, MAAA, is senior
Article from: Health Watch January 2011 Issue 65 Bariatric Surgery Holds Promise for Patients and for Payors by John D. Dawson, Pierre-Yves Crémieux and Arindam Ghosh John D. Dawson, FSA, MAAA, is senior
Objectives PERINATAL INSULIN PUMPS: BASICS FOR NURSES. Historical Perspective. Insulin Pumps in Pregnancy. Insulin Pumps in the US
 Objectives PERINATAL INSULIN PUMPS: BASICS FOR NURSES Jo M. Kendrick, APN BC, CDE jkendric@utmck.edu Describe indications and contraindications for insulin pump use in hospitalized patients Differentiate
Objectives PERINATAL INSULIN PUMPS: BASICS FOR NURSES Jo M. Kendrick, APN BC, CDE jkendric@utmck.edu Describe indications and contraindications for insulin pump use in hospitalized patients Differentiate
External Insulin Pumps Corporate Medical Policy
 External Insulin Pumps Corporate Medical Policy File name: External Insulin Pumps File code: UM.DME.02 Origination: 4/2006 Last Review: 02/2014 (ICD-10 remediation only) Next Review: 10/2014 Effective
External Insulin Pumps Corporate Medical Policy File name: External Insulin Pumps File code: UM.DME.02 Origination: 4/2006 Last Review: 02/2014 (ICD-10 remediation only) Next Review: 10/2014 Effective
Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for
 SKILL COMPETENCY CHECKLIST Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for Link to Dietitian Practice and Skill Standard Met/Initials Prerequisite Skills Competency Areas Knowledge of how to conduct a
SKILL COMPETENCY CHECKLIST Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for Link to Dietitian Practice and Skill Standard Met/Initials Prerequisite Skills Competency Areas Knowledge of how to conduct a
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Pump Therapy Indications:
 Insulin Pumping Getting Started March 7, 2008 Clinical Pearls To understand the rational behind pump therapy To explore patient preferences for and against insulin pump therapy Realistic expectations for
Insulin Pumping Getting Started March 7, 2008 Clinical Pearls To understand the rational behind pump therapy To explore patient preferences for and against insulin pump therapy Realistic expectations for
Criteria: CWQI HCS-123 (This criteria is consistent with CMS guidelines for External Infusion Insulin Pumps)
 Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Origination Date: 05/15 Revision Date(s): 05/2015 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 06/24/2015 External Infusion Insulin Pumps Page 1 of
Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Origination Date: 05/15 Revision Date(s): 05/2015 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 06/24/2015 External Infusion Insulin Pumps Page 1 of
A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes at Near Normal Glucose Control: Bolus Dosing
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients Allen B.,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin Dosing Recommendations in Patients Allen B.,
Jill Malcolm, Karen Moir
 Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive. status
 Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease: its treatment the current status Associate Professor Jonathan Shaw Why is type 2 diabetes so hard to treat? How to choose the right glucose-lowering g drug? Page
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease: its treatment the current status Associate Professor Jonathan Shaw Why is type 2 diabetes so hard to treat? How to choose the right glucose-lowering g drug? Page
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes
 Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Therapy Insulin Practical guide to Health Care Providers Quick Reference F Diabetes Mellitus in Type 2
 Ministry of Health, Malaysia 2010 First published March 2011 Perkhidmatan Diabetes dan Endokrinologi Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia Practical guide to Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Quick
Ministry of Health, Malaysia 2010 First published March 2011 Perkhidmatan Diabetes dan Endokrinologi Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia Practical guide to Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Quick
Harmony Clinical Trial Medical Media Factsheet
 Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
Overview Harmony is the global Phase III clinical trial program for Tanzeum (albiglutide), a product developed by GSK for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The comprehensive program comprised eight individual
A prospective study on drug utilization pattern of anti-diabetic drugs in rural areas of Islampur, India
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure?
 Jane N. Buchwald Viewpoint Editor The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure? Robin Blackstone, MD Scottsdale Bariatric Center, Scottsdale, AZ Patients are looking to
Jane N. Buchwald Viewpoint Editor The Holy Grail of Bariatric Surgery: Which Patient Should Get What Procedure? Robin Blackstone, MD Scottsdale Bariatric Center, Scottsdale, AZ Patients are looking to
Insulin Treatment. J A O Hare. www.3bv.org. Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels
 Insulin Treatment J A O Hare www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Indications for Insulin Treatment Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetics with unstable acute illness ICU Gestational Diabetes: diet failure
Insulin Treatment J A O Hare www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Indications for Insulin Treatment Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetics with unstable acute illness ICU Gestational Diabetes: diet failure
