CONTROL STRUCTURES AND STATEMENTS IN C AND CPP
|
|
|
- Lucinda Morgan
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTROL STRUCTURES AND STATEMENTS IN C AND CPP Control structures form the basic entities of a structured programming language. We all know languages like C/C++ or Java are all structured programming languages. Control structures are used to alter the flow of execution of the program. Why do we need to alter the program flow? The reason is decision making! In life, we may be given with a set of option like doing Electronics or Computer science. We do make a decision by analyzing certain conditions (like our personal interest, scope of job opportunities etc). With the decision we make, we alter the flow of our life s direction. This is exactly what happens in a C/C++ program. We use control structures to make decisions and alter the direction of program flow in one or the other path(s) available. There are three types of control structures available in C and C++ 1) Sequence structure (straight line paths) 2) Selection structure (one or many branches) 3)Loop structure (repetition of a set of activities) All the 3 control structures and its flow of execution is represented in the flow charts given below.
2 Control statements in C/C++ to implement control structures We have to keep in mind one important fact:- all program processes can be implemented with these 3 control structures only. That s why I wrote control structures are the basic entities of a structured programming language. To implements these control structures in a C/C++ program, the language provides control statements. So to implement a particular control structure in a programming language, we need to learn how to use the relevant control statements in that particular language. The control statements are:- Switch If If Else While Do While For As shown in the flow charts:- Selection structures are implemented using If, If Else and Switch statements. Looping structures are implemented using While, Do While and For statements. Selection structures Selection structure
3 Selection structures are used to perform decision making and then branch the program flow based on the outcome of decision making. Selection structures are implemented in C/C++ with If, If Else and Switch statements. If and If Else statements are 2 way branching statements whereas Switch is a multi branching statement. The simple If statement The syntax format of a simple if statement is as shown below. if (expression) // This expression is evaluated. If expression is TRUE statements inside the braces will be executed // Program control is transfered directly to this line, if the expression is FALSE The expression given inside the brackets after if is evaluated first. If the expression is true, then statements inside the curly braces that follow if(expression) will be executed. If the expression is false, the statements inside curly braces will not be executed and program control goes directly to statements after curly braces. Example program to demo If statement Problem:- A simple example program to demo the use of If, If Else and Switch is shown here. An integer value is collected from user. If the integer entered by user is 1 output on screen UNITED STATES. If the integer is 2 output SPAIN, If the integer is 3 output INDIA. If the user enters some other value output WRONG ENTRY. Note:- The same problem is used to develop example programs for if else and switch statements int num; if(num==1)
4 printf("united STATES"); if(num==2) printf("spain"); if(num==3) printf("india"); The If Else statement. Syntax format for If Else statement is shown below. if(expression 1)// Expression 1 is evaluated. If TRUE, statements inside the curly braces are executed. //If FALSE program control is transferred to immedate else if statement. else if(expression 2)// If expression 1 is FALSE, expression 2 is evaluated. else if(expression 3) // If expression 2 is FALSE, expression 3 is evaluated else // If all expressions (1, 2 and 3) are FALSE, the statements that follow this else (inside curly braces) is executed. other statements; The execution begins by evaluation expression 1. If it is TRUE, then statements inside the immediate curly braces is evaluated. If it is FALSE, program control is transferred directly to immediate else if
5 statement. Here expression 2 is evaluated for TRUE or FALSE. The process continues. If all expressions inside the different if and else if statements are FALSE, then the last else statement (without any expression) is executed along with the statements 1 and 2 inside the curly braces of last else statement. Example program to demo If Else int num; if(num==1) printf("united STATES"); else if(num==2) printf("spain"); else if(num==3) printf("india"); else printf("wrong ENTRY"); // See how else is used to output "WRONG ENTRY" Note:- Notice how the use of If Else statements made program writing easier. Compare this with above program using simple If statement only. Switch statement Switch is a multi branching control statement. Syntax for switch statement is shown below. switch(expression)// Expression is evaluated. The outcome of the expression should be an integer or a character constant case value1: // case is the keyword used to match the integer/character constant from expression.
6 //value1, value2... are different possible values that can come in expression break; // break is a keyword used to break the program control from switch block. case value2: break; default: // default is a keyword used to execute a set of statements inside switch, if no case values match the expression value. break; Execution of switch statement begins by evaluating the expression inside the switch keyword brackets. The expression should be an integer (1, 2, 100, 57 etc ) or a character constant like a, b etc. This expression s value is then matched with each case values. There can be any number of case values inside a switch statements block. If first case value is not matched with the expression value, program control moves to next case value and so on.when a case value matches with expression value, the statements that belong to a particular case value are executed. Notice that last set of lines that begins with default. The word default is a keyword in C/C++. When used inside switch block, it is intended to execute a set of statements, if no case values matches with expression value. So if no case values are matched with expression value, the set of statements that follow default: will get executed. Note: Notice the break statement used at the end of each case values set of statements. The word break is akeyword in C/C++ used to break from a block of curly braces. The switch block has two curly braces. The keyword break causes program control to exit from switch block. Example program to demo working of switch int num; switch(num)
7 case 1: printf("united STATES"); break; case 2: printf("spain"); break; case 3: printf("india"); default: printf("wrong ENTRY"); Note:- Switch statement is used for multiple branching. The same can be implemented using nested If Else statements. But use of nested if else statements make program writing tedious and complex. Switch makes it much easier. Compare this program with above one. Loop structures
8 Loop Structure A loop structure is used to execute a certain set of actions for a predefined number of times or until a particular condition is satisfied. There are 3 control statements available in C/C++ to implement loop structures. While, Do while and For statements. The while statement Syntax for while loop is shown below: while(condition)// This condition is tested for TRUE or FALSE. Statements inside curly braces are executed as long as condition is TRUE
9 statement 3; The condition is checked for TRUE first. If it is TRUE then all statements inside curly braces are executed.then program control comes back to check the condition has changed or to check if it is still TRUE. The statements inside braces are executed repeatedly, as long as the condition is TRUE. When the condition turns FALSE, program control exits from while loop. Note:- while is an entry controlled loop. Statement inside braces are allowed to execute only if condition inside while is TRUE. Example program to demo working of while loop An example program to collect a number from user and then print all numbers from zero to that particular collected number is shown below. That is, if user enters 10 as input, then numbers from 0 to 10 will be printed on screen. Note:- The same problem is used to develop programs for do while and for loops int num; int count=0; // count is initialized as zero to start printing from zero. while(count<=num) // Checks the condition - if value of count has reached value of num or not. printf("%d",count); count=count+1; // value of count is incremented by 1 to print next number. The do while statement Syntax for do while loop is shown below: do statement 3; while(condition); Unlike while, do while is an exit controlled loop. Here the set of statements inside braces are executed first. The condition inside while is checked only after finishing the first time execution of
10 statements inside braces. If the condition is TRUE, then statements are executed again. This process continues as long as condition is TRUE. Program control exits the loop once the condition turns FALSE. Example program to demo working of "do while" int num; int count=0; // count is initialized as zero to start printing from zero. do printf("%d",count); // Here value of count is printed for one time intially and then only condition is checked. count=count+1; // value of count is incremented by 1 to print next number. while(count<=num); The for statement Syntax of for statement is shown below: for(initialization statements;test condition;iteration statements) statement 3; The for statement is an entry controlled loop. The difference between while and for is in the number of repetitions. The for loop is used when an action is to be executed for a predefined number of times. The while loop is used when the number of repetitions is not predefined. Working of for loop: The program control enters the for loop. At first it execute the statements given as initialization statements. Then the condition statement is evaluated. If conditions are TRUE, then the block of statements inside curly braces is executed. After executing curly brace statements fully, the control moves to the "iteration" statements. After executing iteration statements, control comes back to
11 condition statements. Condition statements are evaluated again for TRUE or FALSE. If TRUE the curly brace statements are executed. This process continues until the condition turns FALSE. Note 1:- The statements given as "initialization statements" are executed only once, at the beginning of a for loop. Note 2: There are 3 statements given to a for loop as shown. One for initialization purpose, other for condition testing and last one for iterating the loop. Each of these 3 statements are separated by semicolons. Example program to demo working of "for loop" int num,count; for(count=0;count<=num;count++)// count is initialized to zero inside for statement. The condition is checked and statements are executed. printf("%d",count); // Values from 0 are printed.
Lecture 2 Notes: Flow of Control
 6.096 Introduction to C++ January, 2011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology John Marrero Lecture 2 Notes: Flow of Control 1 Motivation Normally, a program executes statements from first to last. The
6.096 Introduction to C++ January, 2011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology John Marrero Lecture 2 Notes: Flow of Control 1 Motivation Normally, a program executes statements from first to last. The
Two-way selection. Branching and Looping
 Control Structures: are those statements that decide the order in which individual statements or instructions of a program are executed or evaluated. Control Structures are broadly classified into: 1.
Control Structures: are those statements that decide the order in which individual statements or instructions of a program are executed or evaluated. Control Structures are broadly classified into: 1.
9 Control Statements. 9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Objectives. 9.3 Statements
 9 Control Statements 9.1 Introduction The normal flow of execution in a high level language is sequential, i.e., each statement is executed in the order of its appearance in the program. However, depending
9 Control Statements 9.1 Introduction The normal flow of execution in a high level language is sequential, i.e., each statement is executed in the order of its appearance in the program. However, depending
QUIZ-II QUIZ-II. Chapter 5: Control Structures II (Repetition) Objectives. Objectives (cont d.) 20/11/2015. EEE 117 Computer Programming Fall-2015 1
 QUIZ-II Write a program that mimics a calculator. The program should take as input two integers and the operation to be performed. It should then output the numbers, the operator, and the result. (For
QUIZ-II Write a program that mimics a calculator. The program should take as input two integers and the operation to be performed. It should then output the numbers, the operator, and the result. (For
6. Control Structures
 - 35 - Control Structures: 6. Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose,
- 35 - Control Structures: 6. Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose,
Keywords are identifiers having predefined meanings in C programming language. The list of keywords used in standard C are : unsigned void
 1. Explain C tokens Tokens are basic building blocks of a C program. A token is the smallest element of a C program that is meaningful to the compiler. The C compiler recognizes the following kinds of
1. Explain C tokens Tokens are basic building blocks of a C program. A token is the smallest element of a C program that is meaningful to the compiler. The C compiler recognizes the following kinds of
Boolean Expressions, Conditions, Loops, and Enumerations. Precedence Rules (from highest to lowest priority)
 Boolean Expressions, Conditions, Loops, and Enumerations Relational Operators == // true if two values are equivalent!= // true if two values are not equivalent < // true if left value is less than the
Boolean Expressions, Conditions, Loops, and Enumerations Relational Operators == // true if two values are equivalent!= // true if two values are not equivalent < // true if left value is less than the
Moving from CS 61A Scheme to CS 61B Java
 Moving from CS 61A Scheme to CS 61B Java Introduction Java is an object-oriented language. This document describes some of the differences between object-oriented programming in Scheme (which we hope you
Moving from CS 61A Scheme to CS 61B Java Introduction Java is an object-oriented language. This document describes some of the differences between object-oriented programming in Scheme (which we hope you
Statements and Control Flow
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Types and Variables 3. Statements and Control Flow 4. Reading Input 5. Classes and Objects 6. Arrays 7. Methods 8. Scope and Lifetime 9. Utility classes 10. Introduction to
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Types and Variables 3. Statements and Control Flow 4. Reading Input 5. Classes and Objects 6. Arrays 7. Methods 8. Scope and Lifetime 9. Utility classes 10. Introduction to
This loop prints out the numbers from 1 through 10 on separate lines. How does it work? Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
 Java Loops & Methods The while loop Syntax: while ( condition is true ) { do these statements Just as it says, the statements execute while the condition is true. Once the condition becomes false, execution
Java Loops & Methods The while loop Syntax: while ( condition is true ) { do these statements Just as it says, the statements execute while the condition is true. Once the condition becomes false, execution
13 Classes & Objects with Constructors/Destructors
 13 Classes & Objects with Constructors/Destructors 13.1 Introduction In object oriented programming, the emphasis is on data rather than function. Class is a way that binds the data & function together.
13 Classes & Objects with Constructors/Destructors 13.1 Introduction In object oriented programming, the emphasis is on data rather than function. Class is a way that binds the data & function together.
Name: Class: Date: 9. The compiler ignores all comments they are there strictly for the convenience of anyone reading the program.
 Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Supplemental Worksheet Problems To Accompany: The Pre-Algebra Tutor: Volume 1 Section 9 Order of Operations
 Supplemental Worksheet Problems To Accompany: The Pre-Algebra Tutor: Volume 1 Please watch Section 9 of this DVD before working these problems. The DVD is located at: http://www.mathtutordvd.com/products/item66.cfm
Supplemental Worksheet Problems To Accompany: The Pre-Algebra Tutor: Volume 1 Please watch Section 9 of this DVD before working these problems. The DVD is located at: http://www.mathtutordvd.com/products/item66.cfm
Sources: On the Web: Slides will be available on:
 C programming Introduction The basics of algorithms Structure of a C code, compilation step Constant, variable type, variable scope Expression and operators: assignment, arithmetic operators, comparison,
C programming Introduction The basics of algorithms Structure of a C code, compilation step Constant, variable type, variable scope Expression and operators: assignment, arithmetic operators, comparison,
Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition
 Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Representing algorithms Examples of algorithmic problem
Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Representing algorithms Examples of algorithmic problem
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Examination. CSC467 Compilers and Interpreters Fall Semester, 2005
 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination CSC467 Compilers and Interpreters Fall Semester, 2005 Time and date: TBA Location: TBA Print your name and ID
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination CSC467 Compilers and Interpreters Fall Semester, 2005 Time and date: TBA Location: TBA Print your name and ID
EVALUATION. WA1844 WebSphere Process Server 7.0 Programming Using WebSphere Integration COPY. Developer
 WA1844 WebSphere Process Server 7.0 Programming Using WebSphere Integration Developer Web Age Solutions Inc. USA: 1-877-517-6540 Canada: 1-866-206-4644 Web: http://www.webagesolutions.com Chapter 6 - Introduction
WA1844 WebSphere Process Server 7.0 Programming Using WebSphere Integration Developer Web Age Solutions Inc. USA: 1-877-517-6540 Canada: 1-866-206-4644 Web: http://www.webagesolutions.com Chapter 6 - Introduction
Embedded Systems. Review of ANSI C Topics. A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming. Basic features of C
 Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
Embedded Systems A Review of ANSI C and Considerations for Embedded C Programming Dr. Jeff Jackson Lecture 2-1 Review of ANSI C Topics Basic features of C C fundamentals Basic data types Expressions Selection
Object Oriented Software Design
 Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 28, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 28, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
What is a Loop? Pretest Loops in C++ Types of Loop Testing. Count-controlled loops. Loops can be...
 What is a Loop? CSC Intermediate Programming Looping A loop is a repetition control structure It causes a single statement or a group of statements to be executed repeatedly It uses a condition to control
What is a Loop? CSC Intermediate Programming Looping A loop is a repetition control structure It causes a single statement or a group of statements to be executed repeatedly It uses a condition to control
Perl in a nutshell. First CGI Script and Perl. Creating a Link to a Script. print Function. Parsing Data 4/27/2009. First CGI Script and Perl
 First CGI Script and Perl Perl in a nutshell Prof. Rasley shebang line tells the operating system where the Perl interpreter is located necessary on UNIX comment line ignored by the Perl interpreter End
First CGI Script and Perl Perl in a nutshell Prof. Rasley shebang line tells the operating system where the Perl interpreter is located necessary on UNIX comment line ignored by the Perl interpreter End
Object Oriented Software Design
 Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa September 14, 2011 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa September 14, 2011 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
Exercise 1: Python Language Basics
 Exercise 1: Python Language Basics In this exercise we will cover the basic principles of the Python language. All languages have a standard set of functionality including the ability to comment code,
Exercise 1: Python Language Basics In this exercise we will cover the basic principles of the Python language. All languages have a standard set of functionality including the ability to comment code,
Writing Control Structures
 Writing Control Structures Copyright 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved. Oracle Database 10g: PL/SQL Fundamentals 5-1 Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Identify
Writing Control Structures Copyright 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved. Oracle Database 10g: PL/SQL Fundamentals 5-1 Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Identify
Unix Shell Scripts. Contents. 1 Introduction. Norman Matloff. July 30, 2008. 1 Introduction 1. 2 Invoking Shell Scripts 2
 Unix Shell Scripts Norman Matloff July 30, 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Invoking Shell Scripts 2 2.1 Direct Interpretation....................................... 2 2.2 Indirect Interpretation......................................
Unix Shell Scripts Norman Matloff July 30, 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Invoking Shell Scripts 2 2.1 Direct Interpretation....................................... 2 2.2 Indirect Interpretation......................................
arrays C Programming Language - Arrays
 arrays So far, we have been using only scalar variables scalar meaning a variable with a single value But many things require a set of related values coordinates or vectors require 3 (or 2, or 4, or more)
arrays So far, we have been using only scalar variables scalar meaning a variable with a single value But many things require a set of related values coordinates or vectors require 3 (or 2, or 4, or more)
TIP: To access the WinRunner help system at any time, press the F1 key.
 CHAPTER 11 TEST SCRIPT LANGUAGE We will now look at the TSL language. You have already been exposed to this language at various points of this book. All the recorded scripts that WinRunner creates when
CHAPTER 11 TEST SCRIPT LANGUAGE We will now look at the TSL language. You have already been exposed to this language at various points of this book. All the recorded scripts that WinRunner creates when
The While Loop. Objectives. Textbook. WHILE Loops
 Objectives The While Loop 1E3 Topic 6 To recognise when a WHILE loop is needed. To be able to predict what a given WHILE loop will do. To be able to write a correct WHILE loop. To be able to use a WHILE
Objectives The While Loop 1E3 Topic 6 To recognise when a WHILE loop is needed. To be able to predict what a given WHILE loop will do. To be able to write a correct WHILE loop. To be able to use a WHILE
PROBLEM SOLVING SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON
 PROBLEM SOLVING WITH SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London
PROBLEM SOLVING WITH SEVENTH EDITION WALTER SAVITCH UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO CONTRIBUTOR KENRICK MOCK UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA, ANCHORAGE PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London
- User input includes typing on the keyboard, clicking of a mouse, tapping or swiping a touch screen device, etc.
 Java User Input WHAT IS USER INPUT? - Collecting and acting on user input is important in many types of programs or applications. - User input includes typing on the keyboard, clicking of a mouse, tapping
Java User Input WHAT IS USER INPUT? - Collecting and acting on user input is important in many types of programs or applications. - User input includes typing on the keyboard, clicking of a mouse, tapping
J a v a Quiz (Unit 3, Test 0 Practice)
 Computer Science S-111a: Intensive Introduction to Computer Science Using Java Handout #11 Your Name Teaching Fellow J a v a Quiz (Unit 3, Test 0 Practice) Multiple-choice questions are worth 2 points
Computer Science S-111a: Intensive Introduction to Computer Science Using Java Handout #11 Your Name Teaching Fellow J a v a Quiz (Unit 3, Test 0 Practice) Multiple-choice questions are worth 2 points
Translating to Java. Translation. Input. Many Level Translations. read, get, input, ask, request. Requirements Design Algorithm Java Machine Language
 Translation Translating to Java Introduction to Computer Programming The job of a programmer is to translate a problem description into a computer language. You need to be able to convert a problem description
Translation Translating to Java Introduction to Computer Programming The job of a programmer is to translate a problem description into a computer language. You need to be able to convert a problem description
COMS 4115 Programming Languages and Translators Fall 2013 Professor Edwards. Lullabyte
 COMS 4115 Programming Languages and Translators Fall 2013 Professor Edwards Lullabyte Stanley Chang (cc3527), Louis Croce (ljc2154), Nathan Hayes-Roth (nbh2113), Andrew Langdon (arl2178), Ben Nappier (ben2113),
COMS 4115 Programming Languages and Translators Fall 2013 Professor Edwards Lullabyte Stanley Chang (cc3527), Louis Croce (ljc2154), Nathan Hayes-Roth (nbh2113), Andrew Langdon (arl2178), Ben Nappier (ben2113),
Debugging. Common Semantic Errors ESE112. Java Library. It is highly unlikely that you will write code that will work on the first go
 Debugging ESE112 Java Programming: API, Psuedo-Code, Scope It is highly unlikely that you will write code that will work on the first go Bugs or errors Syntax Fixable if you learn to read compiler error
Debugging ESE112 Java Programming: API, Psuedo-Code, Scope It is highly unlikely that you will write code that will work on the first go Bugs or errors Syntax Fixable if you learn to read compiler error
Introduction to Java
 Introduction to Java The HelloWorld program Primitive data types Assignment and arithmetic operations User input Conditional statements Looping Arrays CSA0011 Matthew Xuereb 2008 1 Java Overview A high
Introduction to Java The HelloWorld program Primitive data types Assignment and arithmetic operations User input Conditional statements Looping Arrays CSA0011 Matthew Xuereb 2008 1 Java Overview A high
MATLAB Programming. Problem 1: Sequential
 Division of Engineering Fundamentals, Copyright 1999 by J.C. Malzahn Kampe 1 / 21 MATLAB Programming When we use the phrase computer solution, it should be understood that a computer will only follow directions;
Division of Engineering Fundamentals, Copyright 1999 by J.C. Malzahn Kampe 1 / 21 MATLAB Programming When we use the phrase computer solution, it should be understood that a computer will only follow directions;
PL/SQL Overview. Basic Structure and Syntax of PL/SQL
 PL/SQL Overview PL/SQL is Procedural Language extension to SQL. It is loosely based on Ada (a variant of Pascal developed for the US Dept of Defense). PL/SQL was first released in ١٩٩٢ as an optional extension
PL/SQL Overview PL/SQL is Procedural Language extension to SQL. It is loosely based on Ada (a variant of Pascal developed for the US Dept of Defense). PL/SQL was first released in ١٩٩٢ as an optional extension
We will learn the Python programming language. Why? Because it is easy to learn and many people write programs in Python so we can share.
 LING115 Lecture Note Session #4 Python (1) 1. Introduction As we have seen in previous sessions, we can use Linux shell commands to do simple text processing. We now know, for example, how to count words.
LING115 Lecture Note Session #4 Python (1) 1. Introduction As we have seen in previous sessions, we can use Linux shell commands to do simple text processing. We now know, for example, how to count words.
How To Understand Bg
 Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
PYTHON Basics http://hetland.org/writing/instant-hacking.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2009 PYTHON Basics http://hetland.org/writing/instant-hacking.html Python is an easy to learn, modern, interpreted, object-oriented programming language. It was designed to be as simple
CWCS Workshop May 2009 PYTHON Basics http://hetland.org/writing/instant-hacking.html Python is an easy to learn, modern, interpreted, object-oriented programming language. It was designed to be as simple
ESCI 386 IDL Programming for Advanced Earth Science Applications Lesson 6 Program Control
 ESCI 386 IDL Programming for Advanced Earth Science Applications Lesson 6 Program Control Reading: Bowman, Chapters 16 CODE BLOCKS A code block consists of several lines of code contained between a BEGIN
ESCI 386 IDL Programming for Advanced Earth Science Applications Lesson 6 Program Control Reading: Bowman, Chapters 16 CODE BLOCKS A code block consists of several lines of code contained between a BEGIN
Classes and Objects in Java Constructors. In creating objects of the type Fraction, we have used statements similar to the following:
 In creating objects of the type, we have used statements similar to the following: f = new (); The parentheses in the expression () makes it look like a method, yet we never created such a method in our
In creating objects of the type, we have used statements similar to the following: f = new (); The parentheses in the expression () makes it look like a method, yet we never created such a method in our
PA2: Word Cloud (100 Points)
 PA2: Word Cloud (100 Points) Due: 11:59pm, Thursday, April 16th Overview You will create a program to read in a text file and output the most frequent and unique words by using an ArrayList. Setup In all
PA2: Word Cloud (100 Points) Due: 11:59pm, Thursday, April 16th Overview You will create a program to read in a text file and output the most frequent and unique words by using an ArrayList. Setup In all
1 Description of The Simpletron
 Simulating The Simpletron Computer 50 points 1 Description of The Simpletron In this assignment you will write a program to simulate a fictional computer that we will call the Simpletron. As its name implies
Simulating The Simpletron Computer 50 points 1 Description of The Simpletron In this assignment you will write a program to simulate a fictional computer that we will call the Simpletron. As its name implies
Selection Statements
 Chapter 5 Selection Statements 1 Statements So far, we ve used return statements and expression ess statements. e ts. Most of C s remaining statements fall into three categories: Selection statements:
Chapter 5 Selection Statements 1 Statements So far, we ve used return statements and expression ess statements. e ts. Most of C s remaining statements fall into three categories: Selection statements:
Visual Logic Instructions and Assignments
 Visual Logic Instructions and Assignments Visual Logic can be installed from the CD that accompanies our textbook. It is a nifty tool for creating program flowcharts, but that is only half of the story.
Visual Logic Instructions and Assignments Visual Logic can be installed from the CD that accompanies our textbook. It is a nifty tool for creating program flowcharts, but that is only half of the story.
Flowchart Techniques
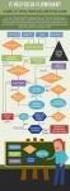 C H A P T E R 1 Flowchart Techniques 1.1 Programming Aids Programmers use different kinds of tools or aids which help them in developing programs faster and better. Such aids are studied in the following
C H A P T E R 1 Flowchart Techniques 1.1 Programming Aids Programmers use different kinds of tools or aids which help them in developing programs faster and better. Such aids are studied in the following
Collections and iterators
 Objects First With Java A Practical Introduction Using BlueJ Grouping objects Collections and iterators 2.0 Concepts covered so far Abstraction Modularization Classes define types Class and object diagrams
Objects First With Java A Practical Introduction Using BlueJ Grouping objects Collections and iterators 2.0 Concepts covered so far Abstraction Modularization Classes define types Class and object diagrams
5.2 Q2 The control variable of a counter-controlled loop should be declared as: a.int. b.float. c.double. d.any of the above. ANS: a. int.
 Java How to Program, 5/e Test Item File 1 of 5 Chapter 5 Section 5.2 5.2 Q1 Counter-controlled repetition requires a.a control variable and initial value. b.a control variable increment (or decrement).
Java How to Program, 5/e Test Item File 1 of 5 Chapter 5 Section 5.2 5.2 Q1 Counter-controlled repetition requires a.a control variable and initial value. b.a control variable increment (or decrement).
Syllabus OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING C++
 1 Syllabus OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING C++ 1. Introduction : What is object oriented programming? Why do we need objectoriented. Programming characteristics of object-oriented languages. C and C++. 2.
1 Syllabus OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING C++ 1. Introduction : What is object oriented programming? Why do we need objectoriented. Programming characteristics of object-oriented languages. C and C++. 2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The JDK command to compile a class in the file Test.java is A) java Test.java B) java
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The JDK command to compile a class in the file Test.java is A) java Test.java B) java
Chapter One Introduction to Programming
 Chapter One Introduction to Programming 1-1 Algorithm and Flowchart Algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculation. More precisely, algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of
Chapter One Introduction to Programming 1-1 Algorithm and Flowchart Algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculation. More precisely, algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of
JAVA - QUICK GUIDE. Java SE is freely available from the link Download Java. So you download a version based on your operating system.
 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_quick_guide.htm JAVA - QUICK GUIDE Copyright tutorialspoint.com What is Java? Java is: Object Oriented Platform independent: Simple Secure Architectural- neutral
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_quick_guide.htm JAVA - QUICK GUIDE Copyright tutorialspoint.com What is Java? Java is: Object Oriented Platform independent: Simple Secure Architectural- neutral
TETRIX Add-On Extensions. Encoder Programming Guide (ROBOTC )
 Introduction: In this extension, motor encoders will be added to the wheels of the Ranger Bot. The Ranger Bot with Encoders will be programmed to move forward until it detects an object, turn 90, and move
Introduction: In this extension, motor encoders will be added to the wheels of the Ranger Bot. The Ranger Bot with Encoders will be programmed to move forward until it detects an object, turn 90, and move
Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives
 Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives This course covers PL/SQL, a procedural language extension to SQL. Through an innovative project-based approach, students learn procedural logic constructs
Database Programming with PL/SQL: Learning Objectives This course covers PL/SQL, a procedural language extension to SQL. Through an innovative project-based approach, students learn procedural logic constructs
Introduction to Minitab Macros. Types of Minitab Macros. Objectives. Local Macros. Global Macros
 Minitab Macros 10.1 Introduction to Minitab Macros 10.2 Global Minitab Macros 10.3 Local Minitab Macros 10.4 Advanced Minitab Macro Programming 10.5 Hints on Debugging Macros Introduction to Minitab Macros
Minitab Macros 10.1 Introduction to Minitab Macros 10.2 Global Minitab Macros 10.3 Local Minitab Macros 10.4 Advanced Minitab Macro Programming 10.5 Hints on Debugging Macros Introduction to Minitab Macros
Computational Mathematics with Python
 Computational Mathematics with Python Basics Claus Führer, Jan Erik Solem, Olivier Verdier Spring 2010 Claus Führer, Jan Erik Solem, Olivier Verdier Computational Mathematics with Python Spring 2010 1
Computational Mathematics with Python Basics Claus Führer, Jan Erik Solem, Olivier Verdier Spring 2010 Claus Führer, Jan Erik Solem, Olivier Verdier Computational Mathematics with Python Spring 2010 1
Chapter 2: Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Elements of Java Basic components of a Java program Primitive data types Arithmetic expressions Type casting. The String type (introduction) Basic I/O statements Importing packages. 1 Introduction
Chapter 2: Elements of Java Basic components of a Java program Primitive data types Arithmetic expressions Type casting. The String type (introduction) Basic I/O statements Importing packages. 1 Introduction
Bash shell programming Part II Control statements
 Bash shell programming Part II Control statements Deniz Savas and Michael Griffiths 2005-2011 Corporate Information and Computing Services The University of Sheffield Email M.Griffiths@sheffield.ac.uk
Bash shell programming Part II Control statements Deniz Savas and Michael Griffiths 2005-2011 Corporate Information and Computing Services The University of Sheffield Email M.Griffiths@sheffield.ac.uk
PL / SQL Basics. Chapter 3
 PL / SQL Basics Chapter 3 PL / SQL Basics PL / SQL block Lexical units Variable declarations PL / SQL types Expressions and operators PL / SQL control structures PL / SQL style guide 2 PL / SQL Block Basic
PL / SQL Basics Chapter 3 PL / SQL Basics PL / SQL block Lexical units Variable declarations PL / SQL types Expressions and operators PL / SQL control structures PL / SQL style guide 2 PL / SQL Block Basic
Chapter 8 Selection 8-1
 Chapter 8 Selection 8-1 Selection (Decision) The second control logic structure is selection: Selection Choosing between two or more alternative actions. Selection statements alter the sequential flow
Chapter 8 Selection 8-1 Selection (Decision) The second control logic structure is selection: Selection Choosing between two or more alternative actions. Selection statements alter the sequential flow
Handling PL/SQL Errors
 Handling PL/SQL Errors In PL/SQL, a warning or error condition is called an exception. Exceptions can be internally defined (by the run-time system) or user defined. Examples of internally defined exceptions
Handling PL/SQL Errors In PL/SQL, a warning or error condition is called an exception. Exceptions can be internally defined (by the run-time system) or user defined. Examples of internally defined exceptions
Shell Scripts (1) For example: #!/bin/sh If they do not, the user's current shell will be used. Any Unix command can go in a shell script
 Shell Programming Shell Scripts (1) Basically, a shell script is a text file with Unix commands in it. Shell scripts usually begin with a #! and a shell name For example: #!/bin/sh If they do not, the
Shell Programming Shell Scripts (1) Basically, a shell script is a text file with Unix commands in it. Shell scripts usually begin with a #! and a shell name For example: #!/bin/sh If they do not, the
Outline. Conditional Statements. Logical Data in C. Logical Expressions. Relational Examples. Relational Operators
 Conditional Statements For computer to make decisions, must be able to test CONDITIONS IF it is raining THEN I will not go outside IF Count is not zero THEN the Average is Sum divided by Count Conditions
Conditional Statements For computer to make decisions, must be able to test CONDITIONS IF it is raining THEN I will not go outside IF Count is not zero THEN the Average is Sum divided by Count Conditions
1 Introduction. 2 Overview of the Tool. Program Visualization Tool for Educational Code Analysis
 Program Visualization Tool for Educational Code Analysis Natalie Beams University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK nataliebeams@gmail.com Program Visualization Tool for Educational Code Analysis 1 Introduction
Program Visualization Tool for Educational Code Analysis Natalie Beams University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK nataliebeams@gmail.com Program Visualization Tool for Educational Code Analysis 1 Introduction
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq
 qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq Introduction to Programming using Java wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq Introduction to Programming using Java wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui
Python Loops and String Manipulation
 WEEK TWO Python Loops and String Manipulation Last week, we showed you some basic Python programming and gave you some intriguing problems to solve. But it is hard to do anything really exciting until
WEEK TWO Python Loops and String Manipulation Last week, we showed you some basic Python programming and gave you some intriguing problems to solve. But it is hard to do anything really exciting until
Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version
 Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version Pseudo-code is an informal way to express the design of a computer program or an algorithm in 1.45. The aim is to get the idea quickly and also easy
Pseudo code Tutorial and Exercises Teacher s Version Pseudo-code is an informal way to express the design of a computer program or an algorithm in 1.45. The aim is to get the idea quickly and also easy
Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops. Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà, Fernando Orejas Dept. of Computer Science, UPC
 Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà, Fernando Orejas Dept. of Computer Science, UPC Example Assume the following specification: Input: read a number N > 0 Output:
Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà, Fernando Orejas Dept. of Computer Science, UPC Example Assume the following specification: Input: read a number N > 0 Output:
Example. Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops. The while statement. Write the numbers 1 N. Assume the following specification:
 Example Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops Assume the following specification: Input: read a number N > 0 Output: write the sequence 1 2 3 N (one number per line) Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà,
Example Introduction to Programming (in C++) Loops Assume the following specification: Input: read a number N > 0 Output: write the sequence 1 2 3 N (one number per line) Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà,
Excel & Visual Basic for Applications (VBA)
 Excel & Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) The VBA Programming Environment Recording Macros Working with the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) 1 Why get involved with this programming business? If you can't program,
Excel & Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) The VBA Programming Environment Recording Macros Working with the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) 1 Why get involved with this programming business? If you can't program,
Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale
 Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale Introduction to C programming Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 25, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna)
Informatica e Sistemi in Tempo Reale Introduction to C programming Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa October 25, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna)
Visual Basic Cheat Sheet
 thecodingguys 2013 Visual Basic Cheat Sheet 12/24/2013 A cheat sheet to the Visual Basic language, ideal for newcomers to the language for more visit http://www.thecodingguys.net KEEP IN TOUCH TABLE OF
thecodingguys 2013 Visual Basic Cheat Sheet 12/24/2013 A cheat sheet to the Visual Basic language, ideal for newcomers to the language for more visit http://www.thecodingguys.net KEEP IN TOUCH TABLE OF
Media Console Using Atlas Import Wizard
 Media Console Using Atlas Import Wizard Use the Atlas Import Wizard to create media plans when you have large campaigns or campaigns that use many different URLs and ads. This job aid covers the basic
Media Console Using Atlas Import Wizard Use the Atlas Import Wizard to create media plans when you have large campaigns or campaigns that use many different URLs and ads. This job aid covers the basic
Computational Mathematics with Python
 Boolean Arrays Classes Computational Mathematics with Python Basics Olivier Verdier and Claus Führer 2009-03-24 Olivier Verdier and Claus Führer Computational Mathematics with Python 2009-03-24 1 / 40
Boolean Arrays Classes Computational Mathematics with Python Basics Olivier Verdier and Claus Führer 2009-03-24 Olivier Verdier and Claus Führer Computational Mathematics with Python 2009-03-24 1 / 40
Conditionals (with solutions)
 Conditionals (with solutions) For exercises 1 to 27, indicate the output that will be produced. Assume the following declarations: final int MAX = 25, LIMIT = 100; int num1 = 12, num2 = 25, num3 = 87;
Conditionals (with solutions) For exercises 1 to 27, indicate the output that will be produced. Assume the following declarations: final int MAX = 25, LIMIT = 100; int num1 = 12, num2 = 25, num3 = 87;
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2014 Mid-term exam Solutions
 Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2014 Mid-term exam Solutions 1. Question: Consider the following module of Python code... def thing_one (x): y = 0 if x == 1: y = x x = 2 if x == 2: y = -x x =
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2014 Mid-term exam Solutions 1. Question: Consider the following module of Python code... def thing_one (x): y = 0 if x == 1: y = x x = 2 if x == 2: y = -x x =
Basics of I/O Streams and File I/O
 Basics of This is like a cheat sheet for file I/O in C++. It summarizes the steps you must take to do basic I/O to and from files, with only a tiny bit of explanation. It is not a replacement for reading
Basics of This is like a cheat sheet for file I/O in C++. It summarizes the steps you must take to do basic I/O to and from files, with only a tiny bit of explanation. It is not a replacement for reading
JavaScript: Control Statements I
 1 7 JavaScript: Control Statements I 7.1 Introduction 2 The techniques you will learn here are applicable to most high-level languages, including JavaScript 1 7.2 Algorithms 3 Any computable problem can
1 7 JavaScript: Control Statements I 7.1 Introduction 2 The techniques you will learn here are applicable to most high-level languages, including JavaScript 1 7.2 Algorithms 3 Any computable problem can
McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 20 1. 01 0
 1.1 McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 Objectives: To describe the evolution of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages. To understand how a program in a high-level
1.1 McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 Objectives: To describe the evolution of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages. To understand how a program in a high-level
Iteration CHAPTER 6. Topic Summary
 CHAPTER 6 Iteration TOPIC OUTLINE 6.1 while Loops 6.2 for Loops 6.3 Nested Loops 6.4 Off-by-1 Errors 6.5 Random Numbers and Simulations 6.6 Loop Invariants (AB only) Topic Summary 6.1 while Loops Many
CHAPTER 6 Iteration TOPIC OUTLINE 6.1 while Loops 6.2 for Loops 6.3 Nested Loops 6.4 Off-by-1 Errors 6.5 Random Numbers and Simulations 6.6 Loop Invariants (AB only) Topic Summary 6.1 while Loops Many
The different kinds of variables in a Java program
 The different kinds of variables in a Java program The different kinds of variables in a Java program Java has 4 different kinds of variables Class variables Instance variables Local variables Parameter
The different kinds of variables in a Java program The different kinds of variables in a Java program Java has 4 different kinds of variables Class variables Instance variables Local variables Parameter
C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
 C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these C++ Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
C++ INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these C++ Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
Performing Simple Calculations Using the Status Bar
 Excel Formulas Performing Simple Calculations Using the Status Bar If you need to see a simple calculation, such as a total, but do not need it to be a part of your spreadsheet, all you need is your Status
Excel Formulas Performing Simple Calculations Using the Status Bar If you need to see a simple calculation, such as a total, but do not need it to be a part of your spreadsheet, all you need is your Status
Lecture Notes on Linear Search
 Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 29, 2013 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 29, 2013 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Calling the Function. Two Function Declarations Here is a function declared as pass by value. Why use Pass By Reference?
 Functions in C++ Let s take a look at an example declaration: Lecture 2 long factorial(int n) Functions The declaration above has the following meaning: The return type is long That means the function
Functions in C++ Let s take a look at an example declaration: Lecture 2 long factorial(int n) Functions The declaration above has the following meaning: The return type is long That means the function
In this Chapter you ll learn:
 Now go, write it before them in a table, and note it in a book. Isaiah 30:8 To go beyond is as wrong as to fall short. Confucius Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. Lewis
Now go, write it before them in a table, and note it in a book. Isaiah 30:8 To go beyond is as wrong as to fall short. Confucius Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. Lewis
Tutorial on C Language Programming
 Tutorial on C Language Programming Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science Introduction to System Software p.1/64 Tutorial on C programming C program structure:
Tutorial on C Language Programming Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science Introduction to System Software p.1/64 Tutorial on C programming C program structure:
Keil C51 Cross Compiler
 Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
LOOPS CHAPTER CHAPTER GOALS
 jfe_ch04_7.fm Page 139 Friday, May 8, 2009 2:45 PM LOOPS CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER GOALS To learn about while, for, and do loops To become familiar with common loop algorithms To understand nested loops To implement
jfe_ch04_7.fm Page 139 Friday, May 8, 2009 2:45 PM LOOPS CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER GOALS To learn about while, for, and do loops To become familiar with common loop algorithms To understand nested loops To implement
Test case design techniques I: Whitebox testing CISS
 Test case design techniques I: Whitebox testing Overview What is a test case Sources for test case derivation Test case execution White box testing Flowgraphs Test criteria/coverage Statement / branch
Test case design techniques I: Whitebox testing Overview What is a test case Sources for test case derivation Test case execution White box testing Flowgraphs Test criteria/coverage Statement / branch
Introduction to Python
 WEEK ONE Introduction to Python Python is such a simple language to learn that we can throw away the manual and start with an example. Traditionally, the first program to write in any programming language
WEEK ONE Introduction to Python Python is such a simple language to learn that we can throw away the manual and start with an example. Traditionally, the first program to write in any programming language
Chapter 5. Selection 5-1
 Chapter 5 Selection 5-1 Selection (Decision) The second control logic structure is selection: Selection Choosing between two or more alternative actions. Selection statements alter the sequential flow
Chapter 5 Selection 5-1 Selection (Decision) The second control logic structure is selection: Selection Choosing between two or more alternative actions. Selection statements alter the sequential flow
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 4 CSU 370 Fall 2007 (Pucella) Tuesday, Sep 18, 2007
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 4 CSU 370 Fall 2007 (Pucella) Tuesday, Sep 18, 2007 The Java Type System By now, you have seen a fair amount of Java. Time to study in more depth the foundations of the language,
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 4 CSU 370 Fall 2007 (Pucella) Tuesday, Sep 18, 2007 The Java Type System By now, you have seen a fair amount of Java. Time to study in more depth the foundations of the language,
Chapter 5 Programming Statements. Chapter Table of Contents
 Chapter 5 Programming Statements Chapter Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 57 IF-THEN/ELSE STATEMENTS... 57 DO GROUPS... 58 IterativeExecution... 59 JUMPING... 61 MODULES... 62 Defining and Executing a Module....
Chapter 5 Programming Statements Chapter Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 57 IF-THEN/ELSE STATEMENTS... 57 DO GROUPS... 58 IterativeExecution... 59 JUMPING... 61 MODULES... 62 Defining and Executing a Module....
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java programming
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java programming 1 Keywords boolean if interface class true char else package volatile false byte final switch while throws float private case return native void protected break
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java programming 1 Keywords boolean if interface class true char else package volatile false byte final switch while throws float private case return native void protected break
Conditional Statements. 15-110 Summer 2010 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Conditional Statements 15-110 Summer 2010 Margaret Reid-Miller Conditional statements Within a method, we can alter the flow of control (the order in which statements are executed) using either conditionals
Conditional Statements 15-110 Summer 2010 Margaret Reid-Miller Conditional statements Within a method, we can alter the flow of control (the order in which statements are executed) using either conditionals
