Summary of Observation Policy for NHSP Staff
|
|
|
- Gavin Marsh
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summary of Observation Policy for NHSP Staff For full version see CMFT Intranet Contact Sister Donna Egan Critical Care Outreach Coordinator Bleep 8742 Tel Introduction Purpose This policy should be read in conjunction with the Early Warning Score (EWS) see trust intranet policy as this will highlight the frequency of clinical observations for specific patient groups based on clinical presentation to staff involved in the recording of clinical observations and subsequent patient management. This policy covers Central Manchester University Hospitals Foundation NHS Trust adult in-patient areas, including theatre areas and all day case areas for adult patients. Nurses, midwives and doctors have a pivotal role in the early identification of patients at risk of deterioration through the monitoring of patient observations and assessment. The importance of accurate observations is clearly documented and essential according to the NPSA (NPSA, 2007). The NICE clinical guidance 50 Caring for the Acutely ill Patient and linked competency document also ensure that standards are set for the assessment and treatment of patients within hospitals. This observation policy sets the standard for the accurate monitoring of observations, utilising research and best practice and by referring to the NICE competency document to ensure that the national standard is met and maintained. General Points Outpatient areas are not to be included within this policy; however the lead clinician and lead nurse of the outpatient clinics will determine the frequency of observations and the type of observations required following a risk assessment of patients as a general principle to be treated in each area. If the patient deteriorates the local policy should be followed. All patients being cared for in in-patient clinical areas, should have their observations performed, with the frequency as stated below. When observations are taken, a full set of observations should always be recorded, to include Pulse Rate, Respiratory Rate, Blood Pressure, Temperature and Neurological Status and oxygen saturation (see EWS policy), the exception is St Mary s Obstetric areas (see Maternity EWS policy). If an observation is unrecordable or undetectable e.g. SaO2 or blood pressure, escalate to the nurse in charge to assess the patient, refer to medical team if required A full set of observations including the EWS, must be undertaken on admission to all clinical areas (except theatre when they will be undertaken on discharge). Thereafter the frequency of subsequent observations will depend on the specialty and clinical condition of the patient. The only exception to this is St Mary s Obstetric areas where a robust assessment criteria is in place, designed to assess appropriateness for individual patients to determine who is eligible for the maternity EWS (see Maternity EWS policy) When patients are transferred from one ward/ department to another, a full
2 set of observations must be completed by the receiving practitioner within 10 minutes of arrival, with the exceptions as above. Patient observations should be measured by an appropriately trained and competent member of staff (see EWS policy) The frequency of observations should be determined by the nurses in charge of the shift / registrar or consultant managing the patient care and should be clearly documented on the observation chart or inputted into BORAS; unless a patient has a EWS of 3 when it is expected observations will be recorded hourly as a minimum (see EWS policy) and point 3. All observations should be documented on the Trust Temperature, Pulse and Respiration Chart (TPR) or agreed local documentation that has been reviewed by the critical care delivery group for use. Observations should then be initialed or inputted into the bedside observation recognition and alerting system. (BORAS) Only the Trust TPR chart should be used; if specific local documentation is required this must be agreed by the Critical Care delivery group. This local documentation must have EWS, frequency and space for initialing observations. A list of the alternative TPR charts is to be kept by the Outreach team. The outreach team will keep a live list of all Trust TPR charts in use. The frequency should be documented on the TPR chart or patient documentation by the medical team or nurse in charge of the patient or inputted into the BORAS system All chart entries should be clear, legible, written in black pen and the time and date of the observations clearly documented (see EWS policy). Ensure appropriate infection control measures have been taken between patients and isolation policy utilized when appropriate as per Trust policy. It is important to remember that all medical devices require pre use and post use checks in accordance with training guidance. All staff must aware of the indications and contraindications for use and the device is used for its intended purpose. Medical device users must be aware of the battery functionality of devices they use and how to identify, troubleshoot any user issues and report faulty devices to MEAM and via the Incident reporting system. To ensure that observations taken and recorded are as accurate as possible, it is important to remember that equipment can fail and provide false readings if the user is unfamiliar with all of the above. Review the patient using clinical skills and question and check any spurious readings.
3 s for clinical observations Why measured? A. Respiratory monitoring The Respiration rate is taken to: Determine baseline respiratory status Identifies respiratory disease. Identifies other complications (e.g. such as infection, shock, Acute Renal Failure, etc.) Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Observe pattern and character of breathing. Explain procedure to patient and gain consent. Ensure you have a clear view of the patients ribcage. Inspiration and expiration counts as one cycle. Count the patient s respiratory rate for one full minute.(ensure a clock or watch with a second hand is visible). During o r a f t e r c o u n t i n g t h e rate, assess the character of breathing. Note: Remember normal breathing is smooth and quiet; signs of difficulty breathing are shallow breathing, noisy breathing, wheezing, and the inability to speak clearly. Lifting the shoulders and use of accessory muscles on inspiration are signs of increased respiratory effort. Document the respiratory rate as a number on the TPR chart, agreed documentation or patientrack system and other respiratory observations in the nursing notes. Report any deterioration or other o b v i o u s c h a n g e s t o a senior member of staff. Respond to any EWS triggers as per policy
4 B. Pulse Rate Monitoring Why measured? The pulse or heart rate is taken to: Determine baseline cardiovascular status. Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Assess cardiovascular function. Explain procedure to patient and gain consent. Place one or two fingers over the pulse site (radial pulse is area of choice, use the third finger and fourth finger- not thumb or index finger), applying gentle pressure prior to taking the blood pressure. Identify the pulse. Count the beats felt for one full minute (ensure a clock or watch with a second hand is visible) During counting the rate; assess the rhythm and strength of the pulse. Remember a normal rhythm is regular; missing beats, irregularities and weak thready or bounding pulses may need further investigation and should be reported to a senior member of staff. If the patient has an irregular heart rate, a radial and apex pulse can be measured simultaneously by two practitioners to assess variance Document heart rate on the TPR chart, agreed local documentation or patientrack system and other pulse observations in the nursing notes. Report any deterioration or other obvious changes to a senior member of staff. Respond to any EWS triggers as per policy.
5 Why measured? C. Automated Blood pressure monitoring The blood pressure recordings are taken to: Determine a baseline. Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Assess response to treatments and / or medications. Explain procedure to patient and gain consent. Remove restrictive clothing from patients arm. Ensure t h e p a t i e n t s a r m i s supported, with the cuff sitting around the arm at heart level. (The inflatable part of the cuff should cover at least 80% of the upper arm). For automated machines press start and wait until the device indicates the reading is complete Note: Remember; a very low BP is dangerous as this reflects a lack of blood and oxygen to the brain, kidneys, gut and skin. Just as a very high BP is dangerous as this may cause stroke, heart failure or renal failure. Either of these may require further investigation. Automated machines can be inaccurate; recheck manually if in any doubt of reading or blood pressure alters significantly; Systolic by 30 or is <90 or > 160 mmhg Diastolic by 20 or is <50 or > 90 mmhg or the pulse rate is irregular Document the reading on the TPR chart, agreed documentation or patientrack system report any significant rise or fall in BP recordings to a senior member of staff. Respond to any EWS triggers as per policy 5
6 D. Manual blood pressure monitoring Qualified practitioners and HealthCare support workers who routinely use manual blood pressure monitoring, are only to undertake this type of clinical observation, once successful completion of competence and assessment are demonstrated, as per section 5. If the patients automated blood pressure in any doubt, has significantly dropped from normal limit or has an irregular pulse a manual blood pressure must be checked (see point d). Why measured? The blood pressure recordings are taken to: Determine a baseline. Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Assess response to treatments and or medications. Explain procedure to patient and gain consent. Remove r e s t r i c t i v e c l o t h i n g f r o m patients arm. Ensure the patient s arm is supported, with the cuff sitting around the arm at heart level. (The inflatable part of the cuff should cover at least 80% of upper arm.) Check equipment, ensure: the level is at zero, all tubing is into with no leaks and that the column is upright and visible. Apply appropriately sized cuff. Inflate the cuff until the radial pulse can no longer be felt manually, observe the reading and fully deflate the cuff. This provides an estimation of systolic pressure. Apply the stethoscope over the brachial pulse point and inflate the cuff to 30mmhg greater than the estimated systolic pressure. Deflate the cuff at a rate of 2mmhg per second. On hearing the first pulse sound, note the level in the column. This is the systolic pressure The disappearance of the pulse sound indicates the diastolic pressure. Document the reading on the TPR chart, agreed local documentation or patientrack system; report any significant rise or fall in BP recordings to a senior member of staff. Respond to any EWS triggers as per policy. 6
7 E. Pulse Oximetry Why measured? The pulse Oximetry reading are undertaken to: Determine a baseline. Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Assess response to treatments Limitations Poor peripheral blood flow Cardiac arrhythmias Bright overhead lights Carboxyhaemoglobin Nail varnish It gives information regarding saturations not patient ventilation or levels of CO2- consider patient status Explain procedure to patient and gain consent Apply probe to finger Look at wave form or signal indicator Document saturation indicated on TPR chart, agreed local Documentation or patientrack system 7
8 F. Temperature monitoring Why measured? The temperature is taken to: Assess for deviation from the normal range which may indicate; Disease, deterioration in condition, infection or reaction to treatment. Explain procedure to patient and gain consent Preferably tympanic temperature should be measured Place a clean plastic protector over the tympanic probe. Carefully insert the probe into the ear canal ensuring a snug fit, for genius 1 thermometer without causing patient discomfort (you will need to pull the ear gently upwards and slightly out to do this. This is not required for the smaller genius 2 thermometer Press the start button and wait until the device indicates the reading is complete. Remove the probe and dispose of the plastic probe protector. When using axillary, use specific devise for under the arm Place the thermometer in the centre of the armpit with the arm firmly against the chest Leave in place as per devise instructions For oral measurement, use specifically for under the tongue Place under the tongue in the sublingual pocket Leave in place for 3-5 minutes Note: Remember that there may be other factors to consider regarding the patient s temperature including environmental factors, circadian rhythms, ear wax and so on. Document the reading on the TPR chart agreed local documentation or BORAS system. Other observations such as shivering, or sweating in the nursing notes. Respond to any EWS triggers as per policy. 8
9 G. Alert, Voice, Pain or Unconscious (AVPU) Why measured? The AVPU assessments are undertaken to: Determine a baseline for the patient. Monitor fluctuations and potential deterioration. Assess response to treatments To complete the full EWS assessment for a patient Note; If the patient has a new alteration to their mental state, further assessment and treatment will be required. The patient s ability to manage their airway should be a priority Following an AVPU assessment, further assessment may be required see point 2 Assess patient s mental state by speaking to the patient and assessing whether they are alert and orientated, if so mark as alert If the patient s conscious level is slightly altered and they are newly confused or are not alert but responding only when spoken too, they should be marked as responding to voice/ new confusion If a patient is not responding to voice, administer painful stimuli such as periorbital push (if no facial fractures) or the trapezius pinch, to assess response, if responds should be marked as responding to pain If a patient is not responding to painful stimuli then the patient should be marked as unresponsive, - seek assistance Document AVPU indicated on TPR chart, agreed local Documentation or patientrack system Neurological Observations Indications: Patients with; Drugs overdose, head injury, falls with suspected head trauma, patients with new confusion or altered level of consciousness, unstable epileptic, any other patient defined by medical team. Registered Practitioners only to undertake neurological observations using the Glasgow Coma Score. The entire observations set should be undertaken by the same RN including vital signs to ensure consistency in the assessment process is maintained. The same RN should endeavour to perform neurological observation of the patient for their entire shift to ensure consistency in observation taking is maintained. The frequency of neurological observations should be defined by the medical team on a patient specific basis and documented clearly in the patient s medical records. 9
10 For a patient who has had a fall with suspected injury to the head; either witnessed or anecdotal, or obvious sign of injury to the head, neurological observations should be undertaken; ½ hourly for 2 hours Hourly for 4 hours 2 hourly for 6 hours 4 hourly for 12 hours -then until medical review dictates otherwise. The designated Trust neurological examination chart should be used In relation to a patient with a significant head injury, refer to the inpatient adult head injury guidelines for frequency of observations and management plan. Frequency of observations The frequency of observations should be as per EWS policy and determined by; a Registered Nurse in charge of the shift, Senior Doctor (Registrar or Consultant) and should be clearly documented on the observation chart; unless a patient has a EWS of 3 when observations will be recorded hourly as a minimum. All patients should have a minimum of 12 hourly observations, with the exceptions as per below. All acute (non elective) admissions should have a minimum of 4 hourly observations for 48hrs from the last trigger 3 or for 48hrs from admission/ transfer if not triggering on the EWS. Within the Emergency Department frequency is a minimum of hourly as per Trust EWS policy ( latest version available on the intranet) All Post operative patients should have frequency as below unless medical staff document alternative request; 30 minutes for 2 hours Hourly for 2 hours As patient need dictates minimum 4 hourly for 48hrs from the last trigger 3 or for 48hrs post surgery if not triggering on the EWS. All transfers from a higher level of care, for example Critical care or the coronary care unit to a ward must have a minimum of 4 hourly observations for 48hrs from the last trigger 3 or for 48hrs from transfer if not triggering on the EWS. When a patient is on the Liverpool care pathway the observations may be stopped according to the End of Life Policy. If a patient is a delayed discharge home and medically fit, it must be recorded in medical notes that their observations may reduce to daily and observations must be recorded on the day of discharge home. 10
11 Observation frequency can be reduced by a senior team member; Consultant, registrar or Registered Nurse in charge of shift (Trust member only) and should be documented on the TPR chart or / and in the patient case notes with a clear reason for reason for change. If a patient is on more frequent than hourly observations, then Temperature can be recorded hourly, unless other clinical symptoms suggest a change in Temperature. The previous recording can be used to calculate the EWS. If a patient is to be absent from the ward for investigations when observations are due then the observations should be taken prior to transfer (exception when transferred to theatre). If a patient is absent from the ward when clinical observations are due they must be completed with in 10 minutes of return to the ward. Communication Ensure concise and effective communication when referring patients to senior members of the team or other team members Use the SBAR tool as a guide for communication to maintain standards and effective Communication Patients refusing to consent to have observations completed or confused patients who lack capacity (see consent policy available on the intranet) Give full explanations regarding the importance of clinical observations. With continued refusal, inform the nurse in charge and document in the nursing notes and refer to appropriate member of parent medical team for review within an hour for full assessment. Measurement of acute pain / pain scores Accurate pain assessment is essential for effective pain management and g i v e s the patient a n a c t i v e r o l e i n t h e i r c a r e. Good p a i n management improves quality of care, aids recovery and reduces the risk of chronic pain developing. There are a number of tools available to assess pain intensity and gauge the effectiveness of a particular treatment. It is important to choose the most appropriate tool for your patient. The preferred scale in the trust is the 0 10 numerical rating scale.0 = No pain & 10 = the worst pain possible If this scale is not appropriate, details of other scales can be found in the acute pain guidelines (on the Trust intranet) or by contacting the acute pain team. Please see appendix 9 for details of the behavioural pain scale for use with ventilated and sedated patients in critical care. 11
12 Assessing pain intensity-the patient is asked: What number would you give to your pain right now, if 0 is no pain and 10 is the worst pain possible. The patient s verbal report should be obtained at rest and also during activity such as coughing, deep breathing or moving. Pain scores should be clearly documented at rest and movement, as well as actions taken to relieve pain. All pain scores of 5 or more should result in an intervention being made. If a pain score of 5 or more is given, further information about the pain can be obtained to aid management. This includes assessment of: -Location -Duration: e.g. is it constant or does it come and go? How long does it last? -Quality: can the patient describe what it feels like e.g. burning, aching, sharp. Frequency of pain assessment The frequency of pain assessment should be based on patient s pain intensity. At the very minimum pain should be assessed: -On admission -Along with routine recording of other vital signs - Within 1 hour of an analgesic intervention to ascertain its effect. For patients who have a PCA or epidural in place, pain scores should be assessed according to local guidelines. For further information on pain assessment please see the Acute Pain Manual available on every ward and the intranet. Competency for Registered Bank Staff For Bank only Registered Nurses working in the trust; they will be ed by NHSP administrators, with a link to the Observations and EWS Trust Policy with instructions that they must read and sign they have read the Policy. On the orientation sheet when they first work in a ward there will be a check to sign by the nurse in charge and themselves, that they have gone through the policies and understand the processes that occur in CMFT with respect to undertaking and appropriate action relating to observation recording and results. Competency for CSW Bank Staff For Bank CSW they will be sent a copy of the observation and EWS supportive reading booklet supplied by the NVQ team and will be sent a copy of the assessment document. The questions should be completed before attendance to the ward and once completed they should call the NVQ assessors to observe them undertaking observations in practice. Once 5 sets have been 12
13 completed and assessed as competent they will receive a sticker for their badges that indicates they a r e competent to undertake observations, if this assessment is not complete they should not undertake observations in clinical wards unless observed and counter signed. From 1 st April 2011 all CSW bank staff must display the sticker on their name badge or will not be able to undertake observations.( see below) Observation competency for NHSP CSW. NHSP CSW staff currently employed by the Trust NHSP CSW new to the Trust The observation assessment documentation previously completed is to be taken to the NVQ assessors office in order to obtain a competency sticker for the back of the name badge to enable observation recording in the clinical area. Attend NHSP office to obtain the clinical observation and assessment manual Contact the NVQ assessors to complete assessments in order to obtain a competency sticker for the back of the name badge to enable observation recording in the clinical area. The sticker looks like this In the absence of the observation competency sticker CSW staff must not perform observations. 13
DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE
 DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE Title Supersedes Originator or modifier Ratification Title: Observation Policy Version: 3 Reference Number: CG003 Supersedes: Observation Policy V3 Description of Amendment(s): Addition
DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE Title Supersedes Originator or modifier Ratification Title: Observation Policy Version: 3 Reference Number: CG003 Supersedes: Observation Policy V3 Description of Amendment(s): Addition
Summary of EWS Policy for NHSP Staff
 Summary of EWS Policy for NHSP Staff For full version see CMFT Intranet Contact Sister Donna Egan outreach coordinator bleep 8742 Tel: 0161 276 8742 Introduction The close monitoring of patients physiological
Summary of EWS Policy for NHSP Staff For full version see CMFT Intranet Contact Sister Donna Egan outreach coordinator bleep 8742 Tel: 0161 276 8742 Introduction The close monitoring of patients physiological
Trust Guideline for the use of the Modified Early Obstetric Warning Score (MEOWS) in detecting the seriously ill and deteriorating woman.
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Maternity Services. Obstetricians, Midwives and Midwifery Care Assistants. All women receiving care from maternity
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Maternity Services. Obstetricians, Midwives and Midwifery Care Assistants. All women receiving care from maternity
Intro Who should read this document 2 Key Messages 2 Background 2
 Classification: Policy Lead Author: Nathan Griffiths, Consultant Nurse Paediatric Emergency Medicine Additional author(s): N/A Authors Division: Salford Healthcare Unique ID: DDCPan04(14) Issue number:
Classification: Policy Lead Author: Nathan Griffiths, Consultant Nurse Paediatric Emergency Medicine Additional author(s): N/A Authors Division: Salford Healthcare Unique ID: DDCPan04(14) Issue number:
MEASURING VITAL SIGNS TRAINING CHECKLIST
 Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
CROSS HEALTH CARE BOUNDARIES MATERNITY CLINICAL GUIDELINE Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Obstetric Early Warning Score Guideline Implementation
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy Version.: 1.0 Effective From: 3 December 2014 Expiry Date: 3 December 2016 Date Ratified: 1 September 2014
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust National Early Warning Score (NEWS) Policy Version.: 1.0 Effective From: 3 December 2014 Expiry Date: 3 December 2016 Date Ratified: 1 September 2014
Document Details Title. Early Warning Score Protocol for Community Hospitals and Prisons to detect the Deteriorating Patient
 Document Details Title Early warning Score Protocol for community Hospitals and Prisons to Detect the Deteriorating Patient Trust Ref No 1558-29748 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document This protocol
Document Details Title Early warning Score Protocol for community Hospitals and Prisons to Detect the Deteriorating Patient Trust Ref No 1558-29748 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document This protocol
DISCHARGE CRITERIA FOR PHASE I & II- POST ANESTHESIA CARE
 REFERENCES: The Joint Commission Accreditation Manual for Hospitals American Society of Post Anesthesia Nurses: Standards of Post Anesthesia Nursing Practice (1991, 2002). RELATED DOCUMENTS: SHC Administrative
REFERENCES: The Joint Commission Accreditation Manual for Hospitals American Society of Post Anesthesia Nurses: Standards of Post Anesthesia Nursing Practice (1991, 2002). RELATED DOCUMENTS: SHC Administrative
Health Technician skills checklist Health Services Department Lincoln Public Schools TEMPERATURE
 Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
Rev. 2/07 Health Technician skills checklist TEMPERATURE 1. Explain to student what you are going to do. 2. Wait for Welch-Allyn thermometer to beep, then apply probe cover. Make sure probe cover is secure.
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
Vital and Diagnostic Signs
 GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
GENERAL The four vital signs and the five diagnostic signs evaluated during patient assessment provide valuable information to the care provider, and when recorded properly, to the receiving facility/personnel.
Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi
 Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi What is EWS? After qualifying, junior doctors are expected to distinguish between the moderately sick patients who can be managed in the
Early Warning Scores (EWS) Clinical Sessions 2011 By Bhavin Doshi What is EWS? After qualifying, junior doctors are expected to distinguish between the moderately sick patients who can be managed in the
Unless this copy has been taken directly from the Trust intranet site (Pandora) there is no assurance that this is the most up to date version
 Policy No: RM64 Version: 4.0 Name of Policy: Use of the National Early Warning Score System in Adult Patients Policy Effective From: 30/07/2015 Date Ratified 27/07/2015 Ratified Resuscitation and Deterioration
Policy No: RM64 Version: 4.0 Name of Policy: Use of the National Early Warning Score System in Adult Patients Policy Effective From: 30/07/2015 Date Ratified 27/07/2015 Ratified Resuscitation and Deterioration
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Leeds Teaching Hospital Ward Healthcheck Metrics Programme
 Ward Healthcheck paper - Appendix 2 Appen Leeds Teaching Hospital Ward Healthcheck Metrics Programme Metrics Information Introduction The nursing care Metrics were initially developed in the north west
Ward Healthcheck paper - Appendix 2 Appen Leeds Teaching Hospital Ward Healthcheck Metrics Programme Metrics Information Introduction The nursing care Metrics were initially developed in the north west
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
1 Early Warning Score (EWS) Management Protocol
 1 1.1 Education of staff... 3 1.2 Clinical staff responsibilities... 3 1.3 Communication/handover requirements... 5 1.4 Evaluation... 5 1.5 Appendix One: Adult... 6 1.6 Appendix Two: Modified Early Obstetric
1 1.1 Education of staff... 3 1.2 Clinical staff responsibilities... 3 1.3 Communication/handover requirements... 5 1.4 Evaluation... 5 1.5 Appendix One: Adult... 6 1.6 Appendix Two: Modified Early Obstetric
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement
 Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
1.4.4 Oxyhemoglobin desaturation
 Critical Care Therapy and Respiratory Care Section Category: Clinical Section: Clinical Monitoring Title: Monitoring of Patients Undergoing Conscious Sedation Policy #: 09 Revised: 05/00 1.0 DESCRIPTION
Critical Care Therapy and Respiratory Care Section Category: Clinical Section: Clinical Monitoring Title: Monitoring of Patients Undergoing Conscious Sedation Policy #: 09 Revised: 05/00 1.0 DESCRIPTION
National Clinical Programmes
 National Clinical Programmes Section 3 Background information on the National Clinical Programmes Mission, Vision and Objectives July 2011 V0. 6_ 4 th July, 2011 1 National Clinical Programmes: Mission
National Clinical Programmes Section 3 Background information on the National Clinical Programmes Mission, Vision and Objectives July 2011 V0. 6_ 4 th July, 2011 1 National Clinical Programmes: Mission
Acutely ill patients in hospital
 Acutely ill patients in hospital Recognition of and response to acute illness in adults in hospital Issued: July 2007 NICE clinical guideline 50 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg50 NICE 2007 Contents Introduction...
Acutely ill patients in hospital Recognition of and response to acute illness in adults in hospital Issued: July 2007 NICE clinical guideline 50 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg50 NICE 2007 Contents Introduction...
PARAMEDIC TRAINING CLINICAL OBJECTIVES
 Page 1 of 21 GENERAL PATIENT UNIT When assigned to the General Patient unit paramedic student should gain knowledge and experience in the following: 1. Appropriate communication with patients and members
Page 1 of 21 GENERAL PATIENT UNIT When assigned to the General Patient unit paramedic student should gain knowledge and experience in the following: 1. Appropriate communication with patients and members
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group)
 Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010.
 ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
ACLS Study Guide The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. Please read the below information carefully This letter is to confirm your
MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Adult Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) Policy and Escalation Pathway Version 3.0
 Policy Statement: The purpose of this policy is to provide clear guidance and instruction to staff with regard to the Trust s approach to the use of the adult Modified Early Warning Score & Escalation
Policy Statement: The purpose of this policy is to provide clear guidance and instruction to staff with regard to the Trust s approach to the use of the adult Modified Early Warning Score & Escalation
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course
 Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes to Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Written by: Jay Snaric, MS And Kimberly Hickman, RN CPR St. Louis 44 Meramec Valley Plaza St. Louis MO 63088 www.stlcpr.com
Board of Directors. 28 January 2015
 Executive Summary Purpose: Board of Directors 28 January 2015 Briefing on the requirements for the Trust to comply with Hard Truths Commitments Regarding the Publishing of Staffing Data Director of Nursing
Executive Summary Purpose: Board of Directors 28 January 2015 Briefing on the requirements for the Trust to comply with Hard Truths Commitments Regarding the Publishing of Staffing Data Director of Nursing
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors
 How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND
 RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND Monitor patient on the ward to detect trends in vital signs and to manage accordingly To recognise deteriorating trends and request relevant medical/out
RGN JOY LAUDE WATFORD GENERAL HOSPITAL, ENGLAND Monitor patient on the ward to detect trends in vital signs and to manage accordingly To recognise deteriorating trends and request relevant medical/out
INSTRUCTOR NOTES: Introduction slide. The program may be taught in a group setting or self taught.
 Introduction slide. The program may be taught in a group setting or self taught. 1 Enabling objectives define the specific knowledge, skills, and/or abilities to be demonstrated, compared, listed, described,
Introduction slide. The program may be taught in a group setting or self taught. 1 Enabling objectives define the specific knowledge, skills, and/or abilities to be demonstrated, compared, listed, described,
Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice
 Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice Copyright 2013 222 South Prospect Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 www.aana.com Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice The AANA Scope and Standards
Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice Copyright 2013 222 South Prospect Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 www.aana.com Scope and Standards for Nurse Anesthesia Practice The AANA Scope and Standards
Objectives. Burn Assessment and Management. Questions Regarding the Case Study. Case Study. Patient Assessment. Patient Assessment
 Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
National Early Warning Score. National Clinical Guideline No. 1
 National Early Warning Score National Clinical Guideline No. 1 February 2013 The National Early Warning Score and COMPASS Education programme project is a work stream of the National Acute Medicine Programme,
National Early Warning Score National Clinical Guideline No. 1 February 2013 The National Early Warning Score and COMPASS Education programme project is a work stream of the National Acute Medicine Programme,
CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION
 Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
Summary: CH CONSCIOUS SEDATION It is the policy of Carondelet Health that moderate conscious sedation of patients will be undertaken with appropriate evaluation and monitoring. Effective Date: 9/4/04 Revision
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
EVIDENCING CARE: IMPROVING RECORD KEEPING PRACTICE A GUIDE ON CARE PLANNING SECTION 2
 EVIDENCING CARE: IMPROVING RECORD KEEPING PRACTICE A GUIDE ON CARE PLANNING SECTION 2 Acknowledgements Northern Ireland Practice and Education Council (NIPEC) would like to thank all the nursing and midwifery
EVIDENCING CARE: IMPROVING RECORD KEEPING PRACTICE A GUIDE ON CARE PLANNING SECTION 2 Acknowledgements Northern Ireland Practice and Education Council (NIPEC) would like to thank all the nursing and midwifery
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]
![SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D]](/thumbs/27/9667060.jpg) SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER SOCIAL DETOXIFICATION SERVICES [ASAM LEVEL III.2-D] I. Definitions: Detoxification is the process of interrupting the momentum of compulsive drug and/or alcohol use in an individual
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT
 BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
BVM VENTILATION OF AN APNEIC ADULT PATIENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Points Checks responsiveness NOTE: After checking responsiveness and breathing for at least 5 but no 1 Checks breathing
The Implementation of a Paediatric Early Warning Tool for use within the Emergency Department and on Acute Paediatric wards
 Stockport NHS Foundation Trust NHS Every patient The Implementation of a Paediatric Early Warning Tool for use within the Emergency Department and on Acute Paediatric wards SN Nicola Adshead SN Raynie
Stockport NHS Foundation Trust NHS Every patient The Implementation of a Paediatric Early Warning Tool for use within the Emergency Department and on Acute Paediatric wards SN Nicola Adshead SN Raynie
Oxygen Therapy. Oxygen therapy quick guide V3 July 2012.
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in a compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in a liquid form. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the patient by means of plastic tubing
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
 Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
Overview Estimated scenario time: 10 15 minutes Estimated debriefing time: 10 minutes Target groups: Paramedics, nurses, respiratory therapists, physicians, and others who manage respiratory emergencies.
Policy & Procedure Manual Administration - Role and Expectations of the Most Responsible Physician (MRP)
 The Scarborough Hospital Policy & Procedure Manual Administration - Role and Expectations of the Most Responsible Purpose To clarify and standardize the role of the Most Responsible at The Scarborough
The Scarborough Hospital Policy & Procedure Manual Administration - Role and Expectations of the Most Responsible Purpose To clarify and standardize the role of the Most Responsible at The Scarborough
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) removal
 Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Interscalene Block. Nancy A. Brown, MD
 Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
Interscalene Block Nancy A. Brown, MD What is an Interscalene Block? An Interscalene block is a form of regional anesthesia used in conjunction with general anesthesia for surgeries of the shoulder and
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Responder Psychomotor Examination PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA
 PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
PATIENT ASSESSMENT/MANAGEMENT TRAUMA Scenario # Note: Areas denoted by ** may be integrated within sequence of Primary Survey/Resuscitation SCENE SIZE-UP Determines the mechanism of injury/nature of illness
Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients
 Physio for VATS patients Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients July 2008 (Review date: July 2011) Physiotherapy Department...01392 402438
Physio for VATS patients Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Physiotherapy for Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery Patients July 2008 (Review date: July 2011) Physiotherapy Department...01392 402438
Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with
 Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information
 Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Keeping your lungs healthy
 Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
Keeping your lungs healthy A guide for you after spinal cord injury and other neurological conditions Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide
National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians Emergency Medical Technician Psychomotor Examination BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT
 BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
BLEEDING CONTROL/SHOCK MANAGEMENT Candidate: Examiner: Date: Signature: Possible Applies direct pressure to the wound 1 NOTE: The examiner must now inform the candidate that the wound continues to bleed.
Oxygen - update April 2009 OXG
 PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
PRESENTATION Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas provided in compressed form in a cylinder. It is also available in liquid form, in a system adapted for ambulance use. It is fed via a regulator and flow meter to the
Obstetric Emergencies
 Obstetric Emergencies Dr. Si Lay Khaing Senior Lecturer/ O&G Specialist Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya 15 th March 2014 Abstract Life Saving, The obstetric patient is unique in medicine as two
Obstetric Emergencies Dr. Si Lay Khaing Senior Lecturer/ O&G Specialist Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya 15 th March 2014 Abstract Life Saving, The obstetric patient is unique in medicine as two
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
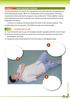 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Before and After Your Cardioversion
 2013 Before and After Your Cardioversion Before and After Your Cardioversion Preparing for your cardioversion Your doctor has recommended cardioversion to treat your heart rhythm problem. This booklet
2013 Before and After Your Cardioversion Before and After Your Cardioversion Preparing for your cardioversion Your doctor has recommended cardioversion to treat your heart rhythm problem. This booklet
Document Ratification Group Approved on 25 th June 2009 Trust Executive Board Date July 2009 Next Review Date June 2011
 Verification of Adult Death by Registered Nurses Document Type: Policy Register Number: 07016 Status Public Developed in response to: Contributes to CQC Core Standard Hospital at night and Reduction in
Verification of Adult Death by Registered Nurses Document Type: Policy Register Number: 07016 Status Public Developed in response to: Contributes to CQC Core Standard Hospital at night and Reduction in
Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P
 Patient Monitoring Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P Patient monitoring during surgery is an extremely important task that is commonly the responsibility
Patient Monitoring Reading Assignment: Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant, pages 467-473, Appendix L, O and P Patient monitoring during surgery is an extremely important task that is commonly the responsibility
Adoption of the National Early Warning Score: a survey of hospital trusts in England, Northern Ireland and Wales
 The UK s European university Adoption of the National Early Warning Score: a survey of hospital trusts in England, Northern Ireland and Wales Ugochi Nwulu, University of Kent Professor Jamie Coleman, University
The UK s European university Adoption of the National Early Warning Score: a survey of hospital trusts in England, Northern Ireland and Wales Ugochi Nwulu, University of Kent Professor Jamie Coleman, University
HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment
 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Release: 1 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit addresses
HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Release: 1 HLTEN609B Practise in the respiratory nursing environment Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor Descriptor This unit addresses
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
Cardiac Catheterisation. Cardiology
 Cardiac Catheterisation Cardiology Name: Cardiac catheterisation Version: 1 Page 1 of 7 Contents Page Number(s) 1. Introduction 3 2. Management pre operative 3 3. Management post operative 5 4. Discharge
Cardiac Catheterisation Cardiology Name: Cardiac catheterisation Version: 1 Page 1 of 7 Contents Page Number(s) 1. Introduction 3 2. Management pre operative 3 3. Management post operative 5 4. Discharge
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
S9 Administer thrombolytic treatment in acute ischaemic stroke
 S9 Administer thrombolytic treatment in acute ischaemic Screening and initiating treatment, overseeing competency of treatment About this workforce competence This competence is about the emergency administration
S9 Administer thrombolytic treatment in acute ischaemic Screening and initiating treatment, overseeing competency of treatment About this workforce competence This competence is about the emergency administration
Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients
 LEVELS OF CARE 1 Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES LEVELS OF CARE 2 Intensive Care Society 2009 All rights reserved. No reproduction, copy or transmission of this publication
LEVELS OF CARE 1 Levels of Critical Care for Adult Patients STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES LEVELS OF CARE 2 Intensive Care Society 2009 All rights reserved. No reproduction, copy or transmission of this publication
Making the components of inpatient care fit
 Making the components of inpatient care fit Named nurse roles and responsibillities booklet RDaSH Adult Mental Health Services Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Admission 3 3 Risk Assessment / Risk Management
Making the components of inpatient care fit Named nurse roles and responsibillities booklet RDaSH Adult Mental Health Services Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Admission 3 3 Risk Assessment / Risk Management
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
 Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) What is ECT? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a physical therapy in which a patient under general anesthetic will have an electrical current passed through his or her
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) What is ECT? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a physical therapy in which a patient under general anesthetic will have an electrical current passed through his or her
Epidural Management. Policy/Purpose. Scope
 Fluid & Medications Management Policy/Purpose... 1 Scope... 1 Associated documents... 2 General... 2 Epidural Indications... 2 Contra-indications:... 2 Educational requirements... 3 Procedural Considerations...
Fluid & Medications Management Policy/Purpose... 1 Scope... 1 Associated documents... 2 General... 2 Epidural Indications... 2 Contra-indications:... 2 Educational requirements... 3 Procedural Considerations...
MLFD Standard Operating Guidelines SOG# 12-22 Subject: Patient Transfer of Care Initiated 1/30/2013
 MLFD Standard Operating Guidelines SOG# 12-22 Subject: Patient Transfer of Care Initiated 1/30/2013 Approved: Revised PURPOSE It is the purpose of this SOG to provide and ensure the highest level of patient
MLFD Standard Operating Guidelines SOG# 12-22 Subject: Patient Transfer of Care Initiated 1/30/2013 Approved: Revised PURPOSE It is the purpose of this SOG to provide and ensure the highest level of patient
PG Certificate / PG Diploma / MSc in Clinical Pharmacy
 PG Certificate / PG Diploma / MSc in Clinical Pharmacy Programme Information September 2014 Entry School of Pharmacy Queen s University Belfast Queen s University Belfast - Clinical Pharmacy programme
PG Certificate / PG Diploma / MSc in Clinical Pharmacy Programme Information September 2014 Entry School of Pharmacy Queen s University Belfast Queen s University Belfast - Clinical Pharmacy programme
Chapter 26. Assisting With Oxygen Needs. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen It has no taste, odor, or color. It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Quality standard Published: 11 June 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/qs89
 Pressure ulcers Quality standard Published: 11 June 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/qs89 NICE 2015. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 6 Why this quality standard is needed... 6 How this quality standard
Pressure ulcers Quality standard Published: 11 June 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/qs89 NICE 2015. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction... 6 Why this quality standard is needed... 6 How this quality standard
You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an investigation known as a Gastroscopy.
 Gastroscopy (OGD) The Procedure Explained You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an investigation known as a Gastroscopy. This procedure requires your formal consent. If you are unable
Gastroscopy (OGD) The Procedure Explained You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an investigation known as a Gastroscopy. This procedure requires your formal consent. If you are unable
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair
 Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Guideline Health Service Directive
 Guideline Health Service Directive Guideline QH-HSDGDL-025-3:2014 Effective Date: 17 January 2014 Review Date: 17 January 2016 Supersedes: qh-hsdptl-025-3:2012 Patient Access and Flow Health Service Directive
Guideline Health Service Directive Guideline QH-HSDGDL-025-3:2014 Effective Date: 17 January 2014 Review Date: 17 January 2016 Supersedes: qh-hsdptl-025-3:2012 Patient Access and Flow Health Service Directive
Ruchika D. Husa, MD, MS Assistant t Professor of Medicine in the Division of Cardiology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
 Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) Ruchika D. Husa, MD, MS Assistant t Professor of Medicine i in the Division of Cardiology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center MEWS Simple physiological scoring
Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) Ruchika D. Husa, MD, MS Assistant t Professor of Medicine i in the Division of Cardiology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center MEWS Simple physiological scoring
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide. Second print August 2004
 Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide Second print August 2004 National Patient Safety Agency Seven steps to patient safety 113 Appendix Four F Examples of events according to severity
Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide Second print August 2004 National Patient Safety Agency Seven steps to patient safety 113 Appendix Four F Examples of events according to severity
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer )
 Departments of Haematology, Nephrology and Pharmacy Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer ) [Care Pathway Review Date] Guidance for use This Care Pathway is intended
Departments of Haematology, Nephrology and Pharmacy Care Pathway for the Administration of Intravenous Iron Sucrose (Venofer ) [Care Pathway Review Date] Guidance for use This Care Pathway is intended
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
A National Early Warning Score for the NHS
 A National Early Warning Score for the NHS Professor Gary B Smith FRCA FRCP Centre of Postgraduate Medical Research & Education, School of Health and Social Care, Bournemouth University - from local data
A National Early Warning Score for the NHS Professor Gary B Smith FRCA FRCP Centre of Postgraduate Medical Research & Education, School of Health and Social Care, Bournemouth University - from local data
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate
 Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Preoperative Education: CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY
 Preoperative Education: CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY 1 Dear Patient, In order to make your hospital stay as comfortable as possible, we have prepared this informational packet for you designed to outline and
Preoperative Education: CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY 1 Dear Patient, In order to make your hospital stay as comfortable as possible, we have prepared this informational packet for you designed to outline and
VA SAN DIEGO HEALTHCARE SYSTEM MEMORANDUM 118-28 SAN DIEGO, CA
 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA (PCA) AND PATIENT- CONTROLLED EPIDURAL ANALGESIA (PCEA) FOR ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT 1. PURPOSE: To assure the safe and effective use of patient controlled analgesia
GUIDELINES FOR PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA (PCA) AND PATIENT- CONTROLLED EPIDURAL ANALGESIA (PCEA) FOR ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT 1. PURPOSE: To assure the safe and effective use of patient controlled analgesia
Please Do Not Call 911
 The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
OEM MAXNIBP Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Name of procedure: Laparoscopic (key-hole) ovarian surgery. Left/ Right unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy* (removal of one fallopian tube and ovary)
 For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
