Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostatitis
|
|
|
- Jonah Jeremy Page
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostatic Diseases Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostatitis JMAJ 47(12): , 2004 Takashi DEGUCHI Professor, Department of Urology, Gifu University School of Medicine Abstract: Among various prostatic diseases, those presenting diverse symptoms including increased urinary frequency, feeling of incomplete emptying, difficulty in urination, perineal pain or discomfort, low back pain, and lower abdominal pain are categorized as prostatitis syndrome. Prostatitis syndrome is broadly divided into acute bacterial infection and chronic prostatitis, and the latter includes various forms of disease ranging from those involving bacterial infection to those accompanying no inflammatory reaction. Each of the disease groups classified in chronic prostatitis has been poorly understood with respect to etiology, pathology, diagnosis, and treatment. To tackle these diseases, new attempts are being made, including new classification, scoring of symptoms and their severity, the application of molecular biological techniques for diagnosis, and the development of treatment methods. Future developments are expected to lead to the elucidation of the etiology of chronic prostatitis through the accumulation of data, as well as the establishment of new evidence-based methods for diagnosis and treatment. Key words: Acute bacterial prostatitis; Chronic bacterial prostatitis; Non-bacterial prostatitis; Prostatodynia Introduction Among the independent prostatic diseases that do not have any underlying disease in the genitourinary system, a group of disorders presenting diverse symptoms including increased urinary frequency, feeling of incomplete emptying, difficulty in urination, perineal pain or discomfort, low back pain, and lower abdominal pain are categorized as prostatitis syndrome. Drach et al. 1) classify prostatitis syndrome into acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, non-bacterial prostatitis, and prostatodynia (Table 1). In 1995, the National Institute of Health (NIH) in the U.S. proposed a new disease classification 2) (Table 1). The NIH classification defines acute bacterial prostatitis as type I and chronic bacterial prostatitis as type II, while non-bacterial prostatitis and prostatodynia are combined in type III, chronic abacterial prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Type III This article is a revised English version of a paper originally published in the Journal of the Japan Medical Association (Vol. 130, No. 2, 2003, pages ). The Japanese text is a transcript of a lecture originally aired on April 28, 2003, by the Nihon Shortwave Broadcasting Co., Ltd., in its regular program Special Course in Medicine. JMAJ, December 2004 Vol. 47, No
2 T. DEGUCHI Table 1 Classification of Prostatitis Syndrome Classification by Drach et al. 1) NIH classification 2) Acute bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis Non-bacterial prostatitis Prostatodynia Type I : Acute bacterial prostatitis Type II : Chronic bacterial prostatitis Type III: Chronic abacterial prostatitis (Chronic pelvic pain syndrome) A: Inflammatory B: Noninflammatory Type IV: Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis was further subdivided into inflammatory (type IIIA) and noninflammatory (type IIIB). The NIH classification created a new category of asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis (type IV) to include cases lacking clinical symptoms and showing histopathological findings of inflammation or the presence of leukocytes in prostatic secretion tested for other diseases. Usually, the term acute prostatitis refers to acute bacterial prostatitis, i.e., NIH type I, and the term chronic prostatitis refers to a group of diseases including chronic bacterial prostatitis, non-bacterial prostatitis, and prostatodynia, which correspond to NIH type II, type IIIA, and type IIIB, respectively. Even with this new classification, the etiology and pathology of diseases constituting chronic prostatitis have not been fully elucidated, and clinical severity determination and systematic treatment methods have not yet been established. Under these circumstances, the NIH published the NIH Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index. 3) This index, designed to evaluate pain, discomfort, urination symptoms, and the effects of symptoms on daily life in scores, is expected to be used to determine severity and evaluate various treatment methods. A Japanese version of this index has been developed, and studies to examine its validity and usefulness have commenced. However, data based on these new approaches have not been accumulated sufficiently so far. This article outlines the clinical characteristics and treatment of various diseases in prostatitis syndrome according to conventional classification. Acute Prostatitis Acute bacterial prostatitis with rapid onset and development corresponds to type I in the NIH classification. This disease is caused by retrograde infection of bacteria from the urinary tract into the prostate. It starts abruptly with fever accompanying chills and shivering and bladder irritation symptoms, such as increased urinary frequency and miction pain, and eventually causes ejaculation pain, urinary disturbance, and sometimes urinary retention. Digital rectal examination reveals a swollen soft prostate presenting heat sensation and tenderness. Urine tests show pyuria and bacteriuria. Prostate massage is contraindicated during the acute phase because of the risk of inducing sepsis. First-voided urine or midstream urine is submitted to bacterial culture test for identification of causative bacteria. Most of the bacteria causing acute bacterial prostatitis are Gram-negative bacilli, including Escherichia coli responsible for 60% of cases. Antibacterial chemotherapy with second and third generation cephems and carbapenems, which have potent antibacterial activity against E. coli and other potential causative bacteria, is effective, although penetration into the prostate is not always beneficial. New oral quinolones are considered useful in treating acute bacterial prostatitis because they have wide antibacterial spectra covering almost all caus- 562 JMAJ, December 2004 Vol. 47, No. 12
3 PROSTATITIS Table 2 Diagnosis of Prostatitis Syndrome Classification by Expressed prostatic secretion or VB3 4,5) NIH classification 2) Drach et al. 1) Leukocytes Bacteria Acute bacterial prostatitis* Type I * Chronic bacterial prostatitis Type II Non-bacterial prostatitis Type IIIA Prostatodynia Type IIIB *Because prostate massage is contraindicated, diagnosis of acute prostatitis is made based on the results of urine tests and bacterial culture tests on first voided urine or midstream urine, combined with the palpitation findings of a swollen prostate with heat sensation and tenderness. ative bacteria and exert potent antibacterial activity. The selection and switching of antibacterial agents are made based on the drug sensitivity of causative bacteria indicated by the bacteriological tests of urine. Generally, severe cases are first treated with a parenteral cephem or carbapenem, and switched to oral fluoroquinolones after the resolution of acute symptoms. Treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis should basically be in-patient care with infusion and intravenous antibacterial agents although mild cases may be treated on an outpatient basis using oral fluoroquinolones. The use of antibacterial agents should be continued for 4 to 6 weeks. Chronic Prostatitis Chronic prostatitis with gradual clinical progression is a group of conditions including chronic bacterial prostatitis, non-bacterial prostatitis, and prostatodynia. The diagnosis of each condition is made based on leukocyte counts and bacterial culture results in the urine and expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) collected by the Meares and Stamey method 4) (Fig. 1) (Table 2). In this sampling method, 10 ml of first voided urine is taken as VB1, and midstream urine after voiding 200 ml is taken as VB2. Prostatic massage is performed thereafter, and expressed prostatic secretion is collected. The patient is VB1 VB2 EPS VB3 First voided urine 10ml After voiding 200ml Midstream urine Prostate massage Expressed prostatic secretion instructed to void again after massage, and 10 ml of first-voided urine is taken as VB3. However, because the sampling using the Meares and Stamey method is tedious and impractical in the clinical setting, a pre- and post-massage test using the urine taken before and after prostate massage has been proposed. 5) In this method, midstream urine before prostate massage and 10 ml of first-voided urine after massage are collected. The post-massage urine corresponds to VB3 in the Meares and Stamey method. Whichever sampling method is used, urine samples are subjected to quantitative bacterial culture tests and microscopic examination of urinary sediment. EPS is also subjected to culture tests and microscopy. 1. Chronic bacterial prostatitis Voiding First-voided urine 10ml after massage Fig. 1 Meares and stamey method (Meares, E.M. and Stamey, T.A.: Invest Urol 1968; 5: ) JMAJ, December 2004 Vol. 47, No
4 T. DEGUCHI Chronic bacterial prostatitis corresponds to type II in the NIH classification. According to the UTI Efficacy Evaluation Criteria in Japan, 6) diagnosis as having this disease is made when microscopic examination of EPS or VB3 urinary sediment shows an increased leukocyte count of 10 or more per field, and bacterial culture results in the isolation of at least 10 3 CFU/ml Gram-negative bacilli or 10 4 CFU/ml Gram-positive cocci. The most frequently isolated bacteria are E. coli among Gram-negative bacilli and Enterococcus and Staphylococcus species among Gram-negative cocci. However, bacteria are isolated only at a frequency of 5 to 10% from patients with diseases showing symptoms of chronic prostatitis. Digital rectal examination of the prostate does not show characteristic findings in most cases although it may reveal mild tenderness. Fluoroquinolones are the first choice of antibacterial agents for chronic bacterial prostatitis because of their wide antibacterial spectrum, good penetration into prostatic tissues, and suitability for outpatient treatment. An antibacterial agent is administered first for 4 weeks. If a response is obtained, the regimen is continued for an additional 4 weeks. If no response is seen, the regimen is changed based on the type and drug resistance of bacteria cultured from VB3 or EPS. Because treatment usually requires a long time, the development of any side effects must be monitored carefully. 2. Non-bacterial prostatitis In the NIH classification, non-bacterial prostatitis is classified as inflammatory type-iiia disease in the category of chronic abacterial prostatitis without proof of infection. Diagnosis of this disease is made when the presence of inflammation is suggested by an increased leukocyte count of 10 or more per field in microscopic examination of EPS or VB3 urinary sediment, but when bacterial culture does not detect inflammation-causing bacteria. The presumed causes of this disease include chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, and other bacteria that do not grow in general bacterial cultures, as well as an inflammation reaction due to the intraprostatic reflux of urine, but the pathology of this disease has not been clarified. However, recent examination of bacterial genes in prostatic tissues using molecular biological methods for bacteria detection suggests that this disease may involve some forms of bacterial infection. 7) For this reason, antibacterial chemotherapy is attempted in treatment for non-bacterial prostatitis, similarly to treatment for chronic bacterial prostatitis. Fluoroquinolones are preferred as they have wide antibacterial spectra; exert antibacterial activity against chlamydia, mycoplasma, and ureaplasma, and show good penetration into prostatic tissues. Considering the possible involvement of chlamydia and other bacteria, the use of tetracyclines that are effective against these bacteria may also be an option. An antibacterial agent is administered first for 4 weeks. If a response is obtained, the regimen is continued for additional 4 weeks. If the patient complains of difficulty in urination, the regimen is combined with an 1-blocker as used for prostatic hyperplasia or an antiinflammatory plant extract. If he has symptoms of an unstable bladder, such as increased urinary frequency and urgency, anticholinergic drugs and smooth muscle relaxants are added to the regimen. In refractory cases, treatment for prostatodynia as discussed in the next section is incorporated. 3. Prostatodynia In the NIH classification, prostatodynia corresponds to noninflammatory type-iiib disease in the category of chronic abacterial prostatitis. Diagnosis of this disease is made when no leukocytes are observed on microscopic examination of EPS or VB3 urinary sediment, and no signs of inflammation are recognized. Similarly to non-bacterial prostatitis, the etiology of this disease is unknown. Presumed 564 JMAJ, December 2004 Vol. 47, No. 12
5 PROSTATITIS causes include psychogenic factors, pelvic vein congestion, and hypertonic pelvic floor muscles. When the involvement of psychogenic factors is strongly suspected, the use of minor tranquilizers and counseling are effective in some cases. When the involvement of pelvic vein congestion is suspected because MRI or transrectal ultrasound tomography indicates the dilation of veins on the anterior surface of the prostate, in particular Santorini s plexus, and when the condition is accompanied by hemorrhoids, such patients may benefit from a Chinese herbal medicine for resolving blood congestion ( oketsu ), such as keishi-bukuryo-gan (Cinnamon & Hoelen Formula). When hypertonicity of pelvic floor muscles is strong, lowfrequency electrical acupuncture and moxibustion are attempted. In addition, thermotherapy as used for prostatic hyperplasia has been reported to be effective in non-bacterial prostatitis and prostatodynia. The symptoms of chronic prostatitis often repeat improvements and exacerbations, and they resist treatment in many cases. Factors leading to the exacerbation of symptoms include drinking, driving, prolonged sitting for deskwork, fatigue, stress, and coldness. Some patients who feel discomfort or mild pain during ejaculation refrain from ejaculation for fear that ejaculation might aggravate the symptoms. However, ejaculation actually improves symptoms in many cases. In view of the present situation in which treatment for chronic prostatitis has not been established, it is important for us to instruct patients to avoid or curtail factors that aggravate symptoms in daily life, as well as to encourage practices that ameliorate symptoms. Conclusion Among various disease groups categorized in prostatitis syndrome, those classified in chronic prostatitis have been poorly understood with respect to etiology, pathology, diagnosis, and treatment. To tackle these diseases, new attempts are being made, including new classification, scoring of symptoms and their severity, the application of molecular biological techniques for diagnosis, and the development of treatment methods. Future developments are expected to lead to the elucidation of the etiology of chronic prostatitis through the accumulation of data, as well as the establishment of new evidence-based methods for diagnosis and treatment. REFERENCES 1) Drach, G.W., Fair, W.R., Meares, E.M. et al.: Classification of benign diseases associated with prostatic pain: prostatitis or prostatodynia? J Urol 1978; 120: ) Executive summary: NIH workshop on chronic prostatitis. Bethesda, Maryland, ) Litwin, M.S., McNaughton-Collins, M., Fowler, F.J. Jr. et al.: The National Institutes of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index: development and validation of a new outcome measure. Chronic Prostatitis Collaborative Research Network. J Urol 1999; 162: ) Meares, E.M. and Stamey, T.A.: Bacteriologic localization patterns in bacterial prostatitis and urethritis. Invest Urol 1968; 5: ) Nickel, J.C.: The Pre and Post Massage Test (PPMT): a simple screen for prostatitis. Tech Urol 1997; 3: ) UTI Efficacy Evaluation Criteria (3rd. Ed.) Appendix. Chemotherapy 1991; 39: ) Krieger, J.N., Riley, D.E., Roberts, M.C. et al.: Prokaryotic DNA sequences in patients with chronic idiopathic prostatitis. J Clin Microbiol 1996; 34: JMAJ, December 2004 Vol. 47, No
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men
 Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
Prostatic Diseases Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men JMAJ 47(12): 543 548, 2004 Tomonori YAMANISHI Associate Professor, Department of Urology, Dokkyo University School
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection
 Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
Prostatic Diseases Therapies for Prostate Cancer and Treatment Selection JMAJ 47(12): 555 560, 2004 Yoichi ARAI Professor and Chairman, Department of Urology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
in association with 1 ST JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston, Jamaica October 4 th 2014 VOIDING DISORDERS IN CHILDREN Dr. Colin Abel Paediatric Urologist Bustamante
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
 Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
Urinary Tract Infections in Children National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Urinary
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS
 Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Fecal incontinence (Encopresis) It is the fecal incontinence condition observed in children with chronic constipation over 1-2 years.
 WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
WHAT IS DYSFUNCTIONAL URINATION (URINATION FUNCTION DISORDER)? It stands for the urination phase disorders, which appear due to wrongly acquired urination habits during the toilet training of some neurologically
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH
 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management
 Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management Nursing Education Material Mohamad Fakih, MD, MPH 1 This presentation This presentation targets all nurses with patient care responsibilities including the
Appropriate Urinary Catheter Use and Management Nursing Education Material Mohamad Fakih, MD, MPH 1 This presentation This presentation targets all nurses with patient care responsibilities including the
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS
 Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy (DMT) means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy (DMT) means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE
 PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
PATIENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER VII-E-5 PAGE 1 OF 7 APPROVED BY: CATEGORY: Tri-site Nursing Policy and Procedures Review Committee Body Systems; Genitourinary 1.0 GOALS To influence patient care providers
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Empower Physical Therapy
 PAYMENT AND COLLECTION POLICY Payment is expected at the time of service. Unpaid balances left by your insurance companies will be your responsibility. In the event you are unable to pay the balance in
PAYMENT AND COLLECTION POLICY Payment is expected at the time of service. Unpaid balances left by your insurance companies will be your responsibility. In the event you are unable to pay the balance in
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence
 Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2014) M. Grabe (chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
 Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It is important to investigate the cause of hematuria because rarely, it is caused by a serious condition, such as
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package. Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula
 Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
Prevention and Recognition of Obstetric Fistula Training Package Module 8: Pre-repair Care and Referral for Women with Obstetric Fistula Early detection and treatment If a woman has recently survived a
How prostate cancer is diagnosed
 How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
How prostate cancer is diagnosed This information is an extract from the booklet Having tests for prostate cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
QS114. NICE quality standard for irritable bowel syndrome in adults (QS114)
 NICE quality standard for irritable bowel syndrome in adults (QS114) QS114 NICE approved the reproduction of its content for this booklet. The production of this booklet is sponsored by Thermo Fisher Scientific,
NICE quality standard for irritable bowel syndrome in adults (QS114) QS114 NICE approved the reproduction of its content for this booklet. The production of this booklet is sponsored by Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Use of antibiotics in chronic prostatitis syndromes
 Daniel A. Shoskes, MD Cleveland Clinic Florida, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA SHOSKES DA. Use of antibiotics in chronic prostatitis syndromes. The Canadian Journal of Urology. 2001;8(Supp 1):24-28. Chronic
Daniel A. Shoskes, MD Cleveland Clinic Florida, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA SHOSKES DA. Use of antibiotics in chronic prostatitis syndromes. The Canadian Journal of Urology. 2001;8(Supp 1):24-28. Chronic
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Text update April 2010) M. Grabe (chairman), T.E. Bjerklund-Johansen, H. Botto, M. Çek, K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke, F. Wagenlehner, B. Wullt Introduction Infections
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations. J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D.
 Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D. Department of Urology University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Official Recommendations for
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Transrectal Prostate Biopsy: Organizational Recommendations J. Stuart Wolf, Jr., M.D. Department of Urology University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Official Recommendations for
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women
 Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Understanding and Preventing Bladder Infections in Women Recurrent bladder or urinary tract infections (UTI s) are a very common diagnosis. In fact,
LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014
 LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014 GUIDE Acknowledgements Acknowledgements The WSIB would like to acknowledge the significant contributions of the following regulated Health
LOW BACK INJURIES PROGRAM OF CARE PROGRAM OF CARE 4TH EDITION 2014 GUIDE Acknowledgements Acknowledgements The WSIB would like to acknowledge the significant contributions of the following regulated Health
Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients
 Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients Damon Dyche and Jay Hollander William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Michigan As our population ages, the number of patients presenting to
Chapter 31: Lower Urinary Tract Conditions in Elderly Patients Damon Dyche and Jay Hollander William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, Michigan As our population ages, the number of patients presenting to
Other Noninfectious Diseases. Chapter 31 Lesson 3
 Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Other Noninfectious Diseases Chapter 31 Lesson 3 Diabetes Diabetes- a chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert food into energy. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death by disease
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
 LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Applicable CPT Code(s): 84152 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Complexed (Direct Measurement) 84153 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Total 84154 Prostate Specific
LCD for Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Applicable CPT Code(s): 84152 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Complexed (Direct Measurement) 84153 Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA); Total 84154 Prostate Specific
Prostatitis A guide to infection or inflammation of the prostate
 Prostatitis A guide to infection or inflammation of the prostate 2 Prostatitis A guide to infection or inflammation of the prostate About this booklet This booklet is for men who want to know more about
Prostatitis A guide to infection or inflammation of the prostate 2 Prostatitis A guide to infection or inflammation of the prostate About this booklet This booklet is for men who want to know more about
COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP)
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 18 December 2002 COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS (CPMP) NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON THE
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Concentrated Oral Aloe Vera for Alleviating IC Symptoms A White Paper
 Concentrated Oral Aloe Vera for Alleviating IC Symptoms A White Paper A survey was sent to approximately 20,000 individuals who have taken Aloe Vera, primarily for interstitial cystitis (IC). A total of
Concentrated Oral Aloe Vera for Alleviating IC Symptoms A White Paper A survey was sent to approximately 20,000 individuals who have taken Aloe Vera, primarily for interstitial cystitis (IC). A total of
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Internal Pelvic Floor Self-Massage Guide
 1 110 East 42nd Street, Suite 1504 New York, NY 10017 www.beyondbasicsphysicaltherapy.com Internal Pelvic Floor Self-Massage Guide By: Amy Stein, DPT, BCB-PMD Author of Heal Pelvic Pain Illustration from
1 110 East 42nd Street, Suite 1504 New York, NY 10017 www.beyondbasicsphysicaltherapy.com Internal Pelvic Floor Self-Massage Guide By: Amy Stein, DPT, BCB-PMD Author of Heal Pelvic Pain Illustration from
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
es of Urinary Incontinence:
 Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Daily Habits and Urinary Incontinence
 Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION
 PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
PROCEDURE FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN WITH BLADDER OR BOWEL DYSFUNCTION First Issued Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date Procedure for the effective
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
GUIDELINES ON UROLOGICAL INFECTIONS (Limited text update March 2015) M. Grabe (Chair), R. Bartoletti, T.E. Bjerklund Johansen, M. Çek, B. Köves (Guidelines Associate), K.G. Naber, R.S. Pickard, P. Tenke,
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
June 2010 Case Study: 33-year-old Male with Pudendal Pain Tuesday, 01 June 2010 13:44
 Welcome to the June 2010 Neurography Institute Case Study. In this issue, we learn how MR Neurography (MRN) and Interventional MR (IMR) helped a thirtysomething male regain his active lifestyle without
Welcome to the June 2010 Neurography Institute Case Study. In this issue, we learn how MR Neurography (MRN) and Interventional MR (IMR) helped a thirtysomething male regain his active lifestyle without
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Prevention of CAUTI is discussed in the CDC/HICPAC document, Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection 4.
 Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function
 Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557
 FIGHTING PAIN. TOUCHING LIVES. JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557 Personal Information Emergency Contact Today s Date: Name: Patient: Realtionship: Birth Date: Age: Sex:
FIGHTING PAIN. TOUCHING LIVES. JAMES PETROS, M.D., INC. PHONE: (408) 528-8833 FAX: (408) 528-8557 Personal Information Emergency Contact Today s Date: Name: Patient: Realtionship: Birth Date: Age: Sex:
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Age in years Females (% prevalence) Males (% prevalence) 6-15 Vesicoureteral reflux (4.4%) Vesicoureteral reflux (0.5%)
 Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
Magdalena E. Sobieszczyk Urinary Tract Infections AIMS: 1. Understand epidemiology and microbiology of urinary tract infections 2. Understand pathogenesis of lower and upper urinary tract infections 3.
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Self Catheterization Guide
 Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
www.complexchild.com Recognizing and Treating Fevers in Children with Complex Medical Issues by Susan Agrawal Fevers can be some of the scariest symptoms we see in our children, but they are also some
CHOC CHILDREN SUROLOGY CENTER. Constipation
 Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions and Reporting
 AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education. Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis
 Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Reactive Arthritis (ReA) / Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Arthritis Introduction: For as long as scientists have studied rheumatic disease,
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Painful Bladder Syndrome and Interstitial Cystitis
 Painful Bladder Syndrome and Interstitial Cystitis PAINFUL BLADDER AND INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS OVERVIEW Painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC) is a disorder with symptoms of mild to severe
Painful Bladder Syndrome and Interstitial Cystitis PAINFUL BLADDER AND INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS OVERVIEW Painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC) is a disorder with symptoms of mild to severe
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis
 Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
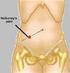 Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
Appendicitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The appendix is a small, tube-like structure
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS
 FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
Clinical Effectiveness Group (Association for Genitourinary Medicine and the Medical Society for the Study of Venereal Diseases)
 2001 National guideline for the management of prostatitis Clinical Effectiveness Group (Association for Genitourinary Medicine and the Medical Society for the Study of Venereal Diseases) Acute Prostatitis
2001 National guideline for the management of prostatitis Clinical Effectiveness Group (Association for Genitourinary Medicine and the Medical Society for the Study of Venereal Diseases) Acute Prostatitis
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate)
 Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Treating your enlarged prostate gland HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) This leaflet is designed to answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
