A Patient s Guide to the Non-surgical Closure of an Atrial Septal Defect
|
|
|
- Walter Ray
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform A Patient s Guide to the Non-surgical Closure of an Atrial Septal Defect
2 This brochure is intended to provide you with general information about the non-surgical closure of an atrial septal defect (ASD). It is not intended to provide medical care or treatment recommendations. You should talk with a doctor about the diagnosis or treatment of your medical condition. Atrial Septal Defect Overview An atrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening (hole) in the wall between the two upper chambers (atria) of the heart. This opening allows abnormal flow of blood between the atria chambers and usually results in too much blood flow to the lungs. n ASDs are one of the most common congenital heart defects seen in pediatric cardiology and often occur in conjunction with other cardiac defects. 1-3 n In older patients with ASDs, stroke is also more common. n n There are four types of ASDs and their location in the heart determines their type. 1 Ostium secundum is the most common type of ASD, and are located in the center of the atrial septum. About 80% of ASDs are in the ostium secundum. 1 Non-surgical closure (using a transcatheter device) of ASDs only benefits patients with centrally located ostium secundum ASDs. 1,4 If left untreated, the ASD may be debilitating and could be fatal. 1,3 1
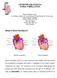
3 Aorta Pulmonary Artery Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle Right Ventricle Figure 1 Diagram of a healthy heart How does an ASD affect blood flow? To best understand how an ASD affects blood flow, it is helpful to first understand how a normal heart works (Figure 1). The heart is a pump with four chambers: two small upper chambers called the atria (you have a right and a left atrium) and two larger, more powerful pumping chambers called ventricles (again you have a right and a left ventricle). A healthy heart pumps blood through the body and is controlled by a unique electrical system within the heart itself. Typically, oxygen-poor blood flows from the body into the heart through the right atrium and then flows into the right ventricle. When the heart pumps, the blood in the right ventricle is pumped out through the pulmonary artery to the lungs where it is filtered and receives oxygen. From the lungs, the now oxygen-rich blood enters the heart through the left atrium. It then flows to the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta into the body to provide oxygen to all of the organs and cells. As it circulates through the body, it becomes oxygen-poor and returns to the heart and the cycle begins again. An ASD is an abnormal opening (a hole) in the tissue wall between the atria. Typically, there is lower resistance to flow on the right side of the heart, which causes the oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to flow through the opening and into the 2
4 Figure 2 Heart with atrial septal defect Figure 3 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder implanted during a catheter-based procedure 3
5 right atrium. This results in too much blood flow to the lungs and can cause heart failure (Figure 2). What are the symptoms of an ASD? Severity of symptoms often depends on the size of the hole. Large ASDs may cause fatigue, shortness of breath, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmia and/or an enlarged heart. How is an ASD treated? There are a number of treatment options for an ASD, and there is no single option that is right for every patient. You should discuss your options with your doctor; however, there are a few standard approaches that you may want to consider. The first option is medication that may be used in treating symptoms associated with the ASD. Other treatment options include open-heart surgery and catheter-based procedures to close the opening (Figure 3). How do I know which treatment option is right for me? Every person is unique. Your doctor is your best resource for learning about the treatment options available to you and the best course for your condition. Talk to your doctor and follow his or her advice for your care. Keep in mind an ASD can result in unpleasant and sometimes debilitating symptoms and early death if left untreated. With proper care, however, it can generally be managed with either surgery or catheter-based closure. There are different advantages and complications for each approach, and you should discuss these with your doctors. What is involved with a catheter-based procedure? A catheter-based procedure is a minimally invasive treatment option available to some patients. The procedure involves making a small incision, typically in the groin, and inserting a small tube, called a catheter or sheath, to navigate through the blood vessels to the procedure site within the heart (Figure 4). 4
6 Catheter entry site Figure 4 Catheter pathway in a transcatheter ASD closure procedure In patients with an ASD, the doctor guides the device through the catheter or sheath and deploys it in the ASD to seal the hole. Once the device is successfully placed in the defect, the doctor will carefully study its position using cardiac imaging systems. Once the physician is satisfied with the position, the device is released to remain permanently in the defect (Figure 3). The catheter or sheath is removed and the procedure is completed. The procedure itself lasts about one to two hours and takes place in a heart catheterization laboratory, where many minimally invasive, non-surgical procedures are performed. Your doctor may give you an anesthetic, and you should not feel any significant discomfort. 5
7 Figure 5 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder (top) and AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform (bottom) What happens after the procedure? Because the procedure is minimally invasive, your recovery will likely be quick and easy. Many patients are discharged from the hospital within 24 hours. Your doctor can provide guidelines for activities and medications. He or she may prescribe drugs that you should take at home to continue your treatment and recovery. The decision to prescribe these is up to your doctor. Many doctors require follow-up appointments over the next year to ensure the patient s recovery is going well. What to expect during and after the procedure will vary. Discuss all questions and concerns you have with your doctor. 6
8 What exactly are an AMPLATZER Septal Occluder and an AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform? The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder is a device specifically designed to close an ASD (Figure 5). The AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform is a device specifically designed to close a multi-fenestrated ASD, a type of ASD consisting of many small holes rather than just one (Figure 5). Your doctor will choose the appropriate device for your specific ASD. The selected device is implanted during a catheter-based procedure and remains permanently implanted. Both devices are made from a braided Nitinol, a metal with shape memory characteristics. This means the device will go back to its original shape even after it is stretched to pass through a catheter. The shapes of the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder and AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform were specifically designed to seal ASDs and multifenestrated ASDs respectively. Who should not receive the device? If you have any of the following conditions you may not be a good candidate to receive the device. n If you need to have surgery to fix other defects in your heart. n If you have an infection anywhere in your body. You may receive the device only after the infection is gone. n If you have a bleeding disorder, untreated ulcer, or if you are unable to take aspirin. n If you are unable to take antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy (i.e., blood thinning medications). n If you have blood clots in your heart. n If you have a patent foramen ovale. n If you, your heart, or your veins are very small or if there is any reason you cannot undergo the procedure. n If the device would interfere with or come in contact with other structures in your heart. 7
9 How long will it take me to recover? What activities should be avoided after my procedure? When can they resume? Every person recovers differently, and your doctor can help determine when activities can be resumed. In general, all strenuous activity should be avoided for one month after the procedure. Will I be able to feel the device? No, you will not be able to feel the device once it s implanted. What is a patient identification card? Will I need to carry it with me? As a patient with an implanted medical device it is important to carry a patient identification card with you to identify yourself as having an implanted device. The patient ID card includes your name, implant date, your doctor s contact information, and information about your device. You will be provided with this card after the procedure. 8
10 Can I travel with an implanted device? Will my device trigger airport security systems? Your doctor is your best resource for the answer to this question. Many patients find that with some extra planning and care they can enjoy traveling. It is always wise to carry your patient ID card just in case you encounter difficulties while traveling. Though some patients worry about airport security systems, there is really no need for concern. The metal parts in AMPLATZER occlusion devices are very small and usually do not trigger metal detector alarms. However, the sensitivity setting of the metal detector and other factors may affect how the metal detector responds to your device. Simply show your patient identification card to security personnel. Will medical equipment interfere with my device? Although most medical equipment will have no effect on your device it is best to tell hospital personnel that you have an implanted device before you undergo any medical procedure. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are generally acceptable, and your AMPLATZER occlusion device has no known hazards when using a 3-tesla MRI. If an MRI is needed, simply tell the MRI staff about your implant and show them your patient ID card. Can I have this procedure if I am pregnant? What if I am a nursing mother? The risk of increased x-ray exposure must be weighed against the potential benefits of this device. Your doctor will ensure that care will be taken to minimize the radiation exposure to the fetus and mother. It is unknown if the device affects breast milk. You should discuss this issue with your doctor. 9
11 What if I experience one or more of the following symptoms after the procedure: chest pain, numbness, sudden weakness, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath or rapid heartbeat? If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, seek emergency medical help. An echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) should be performed. What risks are associated with the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder and AMPLATZER Multi- Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform? There are certain potential risks associated with catheter-based procedures as well as additional risks that may be associated with the device. Your doctor is the best source of information about the risks of having an implanted device. Be sure to talk about all your questions and concerns. Potential risks include but are not limited to those listed in the following tables. Adverse Events associated with the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder n Air embolus (an air bubble that blocks blood flow in a vessel) n Allergic dye reaction n Anesthesia reaction n Apnea (temporary absence of breathing) n Arrhythmia (loss of regular heart rhythm) n Arteriovenous fistulae (abnormal connection between an artery and a vein) n Bleeding n Brachial plexus injury (injury to the nerves in the arm or lower neck) n Cardiac perforation (piercing of the heart) n Cardiac tamponade (compression of the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle and the outer covering sac of the heart) n Death n Device embolization/migration (dislodging of the device) n Dissection (separation of the layers of the heart tissue) n Fever n Foreign material embolic event (when a mass, such as an air bubble or blood clot, gets stuck in a small blood vessel and blocks or decreases blood flow) n Headache/Migraines Continued 10
12 Continued n Heart block (an interruption in the normal rhythm of the heart beat) n Hematoma/Pseudoaneurysm (collection of blood outside of a vessel) including blood loss requiring transfusion n Hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells) n Hyper/Hypotension (abnormally high/low blood pressure) n Infection including endocarditis (redness and swelling of the lining of the heart and its valves) n Myocardial infarction (heart attack) n Perforation (piercing of a vessel or the heart) n Pericardial effusion (excess fluid that may cause pressure on the heart) n Peripheral embolism (when a small clot or piece of debris passes through the peripheral system causing decreased or blocked blood flow in an artery or vein) n Peripheral pulse loss (loss of pulse in extremities) n Phrenic nerve injury n Pleural effusion (excess fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity) n Residual shunt (blood flow through the defect due to incomplete closure) n Stroke/Transient ischemic attack (temporary lack of oxygen to the brain) n Thromboembolic event (when a blood clot breaks loose and plugs a vessel) n Thrombus formation/ embolization (blood clot formation and breaking loose) n Tissue erosion (abrasion of the device through the heart tissue) n Tissue trauma or damage n Valve damage n Valvular insufficiency n Vascular access site complications n Vessel trauma or damage n Valvular regurgitation (abnormal backward flow of blood through a valve) Adverse Events associated with the AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform n Air embolus (an air bubble that blocks blood flow in a vessel) n Allergic dye reaction n Anesthesia reaction n Apnea (temporary absence of breathing) n Arrhythmia (loss of regular heart rhythm) n Brachial plexus injury (injury to the nerves in the arm or lower neck) n Cardiac perforation (piercing of the heart) n Death n Device collapse due to structural failure n Device embolization/migration (dislodging of the device) Continued 11
13 Continued n Device removal (due to embolization or misplacement) n Fever n Headache/Migraines n Hematoma/Pseudoaneurysm (collection of blood outside of a vessel) including blood loss requiring transfusion n Hyper/Hypotension (abnormally high/low blood pressure) n Infection including endocarditis (swelling of the lining of the heart and its valves) n Infectious endocarditis n Perforation (piercing of a vessel or the heart) n Pericardial effusion (excess fluid that may cause pressure on the heart) n Phrenic nerve injury n Stroke/Transient ischemic attack (temporary lack of oxygen to the brain) n Thrombus (blood clot) formation on the device surface with the risk of breaking loose n Tissue erosion (abrasion of the device through the heart tissue) n Valvular regurgitation (abnormal backward flow of blood through a valve) n Vascular access site complications You should also be aware that: n People who are allergic to nickel may have an allergic reaction to this device. n Some patients have experienced tissue erosion, a very serious or life-threatening condition caused by the device rubbing against the wall of the heart and creating a hole. This may cause blood to build up in the sac that surrounds the heart. If too much blood builds up in this sac the heart will not be able 12
14 to work properly. Symptoms of this may be shortness of breath and/or chest pain, fainting, and irregular heartbeat. If you have any of these symptoms, immediately call your doctor or go to the emergency room for an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart). Your doctor will be able to tell if you have this complication by doing this examination. As of May 2012, it is estimated that world-wide, erosion may occur in 1 to 3 of every 1000 patients. 5 This means that the risk of you experiencing an erosion is estimated to be somewhere between 0.1% and 0.3%. 5 The majority, almost 90%, of erosions occur within 1 year of being implanted, but some erosions have happened several years after implant. 5 My follow-up questions:
15 For additional information, please contact your doctor.
16 References 1. Moake L, Ramaciotti C. Atrial Septal Defect Treatment Options. AACN Clin Issues. 2005;16(2): McMahon CJ, Feltes TF, Fraley JK, et al. Natural history of growth of secundum atrial septal defects and implications for transcatheter closure. Heart. 2002;87: Omeish A, Hijazi AM. Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in Children & Adults Using the Amplatzer Septal Occluder. J Interv Cardiol. 2001;14(1): Balzer D. Transcatheter closure of intracardiac shunts. Cardiac Science. 2004;6: Crawford GB, Brindis RG, Krucoff MW, et al. Percutaneous atrial Septal Occluder devices and cardiac erosion: A review of the literature. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent. 2012(80)2: Global Headquarters One St. Jude Medical Drive St. Paul, Minnesota USA Fax Cardiovascular Division 177 East County Road B St. Paul, Minnesota USA Fax Amplatzer Products 5050 Nathan Lane North Plymouth, Minnesota USA Fax US Division 6300 Bee Cave Road Building Two, Suite 100 Austin, Texas USA Fax SJMhealth.com SJM Coordination Center BVBA The Corporate Village Da Vincilaan 11 Box F Zaventem, Belgium Fax Rx Only Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale and use by or on the order of a physician. (MM00310EN) Indications: The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder is a percutaneous, transcatheter, atrial septal defect closure device intended for the occlusion of atrial septal defects (ASD) in secundum position or patients who have undergone a fenestrated Fontan procedure and who now require closure of the fenestration. Patients indicated for ASD closure have echocardiographic evidence of ostium secundum atrial septal defect and clinical evidence of right ventricular volume overload (such as, 1.5: degree of left-to-right shunt or RV enlargement). The AMPLATZER Multi-Fenestrated Septal Occluder - Cribriform is a percutaneous, transcatheter, atrial septal defect closure device intended for the closure of multi-fenestrated (cribriform) atrial septal defects (ASD). Patients indicated for ASD closure have echocardiographic evidence of fenestrated ostium secundum atrial septal defect and clinical evidence of right ventricular volume overload (ie, 1.5: degree of left-to-right shunt or RV enlargement). Brief Summary: Please review the Instructions for Use prior to using these devices for a complete listing of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, potential adverse events and directions for use. Products referenced are approved for CE Mark. AMPLATZER, ST. JUDE MEDICAL, and the nine-squares symbol are trademarks and service marks of St. Jude Medical, Inc. and its related companies St. Jude Medical. All rights reserved. MM00310 (05.2) EN Global 01/13 IPN
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device
 WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Patient Information Guide WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease
 Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Listen to Your Heart. What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke. The S-ICD System. The protection you need
 Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Wingspan Stent System with Gateway PTA Balloon Catheter TABLE OF CONTENTS Definitions... 2 What is the Purpose of This Booklet?... 3 What is an Intracranial Lesion?... 3 Who
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
Living with. Atrial Fibrillation
 Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects
 Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm
 Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Treatments to Restore Normal Rhythm In many instances when AF causes significant symptoms or is negatively impacting a patient's health, the major goal of treatment is to restore normal rhythm and prevent
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Patient Information
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation
 Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation A Patient s Guide to Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation
A Patient's Guide to Transcatheter Closure of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus Using the AMPLAIZER Duct Occiuder System
 A Patient's Guide to Transcatheter Closure of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus Using the AMPLAIZER Duct Occiuder System AGA Medical Corporation 682 Mendelssohn Avenue * Golden Valley MN 55427 lisa [Tell 763P513-9227
A Patient's Guide to Transcatheter Closure of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus Using the AMPLAIZER Duct Occiuder System AGA Medical Corporation 682 Mendelssohn Avenue * Golden Valley MN 55427 lisa [Tell 763P513-9227
Cardiac Catheterization
 Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation
 A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
A Patient Guide to Atrial Fibrillation and Catheter Ablation Al-Sabah Arrhythmia Institute 1111 Amsterdam Avenue New York, NY 10025 Phone: 212-523-2400 Fax: 212-523-2571 www.stlukescardiology.org Printed
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) A patient s guide
 Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) A patient s guide Valvular heart disease The heart is a muscle which pumps blood to your lungs and around the body. There are four valves within the heart.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) A patient s guide Valvular heart disease The heart is a muscle which pumps blood to your lungs and around the body. There are four valves within the heart.
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013
 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) March, 2013 This handout is meant to help with discussions about the condition, and it is not a complete discussion of AF. We hope it will complement your appointment with one
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM. UNLOCK the ANSWER. Your heart and long-term monitoring
 INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM UNLOCK the ANSWER Your heart and long-term monitoring UNLOCK the ANSWER Irregular heartbeats can be related to a variety of conditions, including unexplained fainting,
INSERTABLE CARDIAC MONITORING SYSTEM UNLOCK the ANSWER Your heart and long-term monitoring UNLOCK the ANSWER Irregular heartbeats can be related to a variety of conditions, including unexplained fainting,
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter
 Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Living With Your. Pacemaker
 Living With Your Pacemaker Your Pacemaker At a Glance n Your heart is a muscle about the size of your fist and has a complex electrical system. It generates its own electricity, which causes it to contract
Living With Your Pacemaker Your Pacemaker At a Glance n Your heart is a muscle about the size of your fist and has a complex electrical system. It generates its own electricity, which causes it to contract
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
VNS Therapy for Epilepsy
 VNS Therapy for Epilepsy This pamphlet provides general information for the public. It is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, interactions or adverse effects involving any
VNS Therapy for Epilepsy This pamphlet provides general information for the public. It is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, interactions or adverse effects involving any
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
CardiacAdvantage. Catheterization. Patient Guide. Cardiac
 Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide
 Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. A Guide for Adults
 Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
Radiofrequency Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation A Guide for Adults Fast Facts n There are different ways to treat atrial fibrillation (A-fib). One kind of treatment involves putting the heart back into
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options. A Guide for Patients
 Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Catheterization, and Treatment Options A Guide for Patients Coronary Artery Disease If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with coronary artery
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Page 1 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures. About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures
 Page 1 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures Page 2 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures Page 3 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter
Page 1 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures Page 2 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter Procedures Page 3 of 36 mc1311-01 About Your Heart-Catheter
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Atrial fibrillation. Treatment Guide
 Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Treatment Guide Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular or abnormal heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 3 million Americans today. Thankfully, more options
Visited 9/14/2011. What is Atrial Fibrillation? What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation. The Normal Heart Rhythm. 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM
 1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
1 of 7 9/14/2011 10:50 AM Current URL: What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation What is atrial fibrillation? What causes atrial fibrillation? How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed? What are the dangers
Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information. ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency
 Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency Do you suffer from heavy legs or visible veins? This makes diseases of the veins
Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency Do you suffer from heavy legs or visible veins? This makes diseases of the veins
IVC Filter Insertion PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN V4.00-03/2011 SW9264 Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified Interpreter present? Yes No A Cultural
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN V4.00-03/2011 SW9264 Facility: A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified Interpreter present? Yes No A Cultural
Cardiac Catheterization
 Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
BRYAN. Cervical Disc System. Patient Information
 BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
BRYAN Cervical Disc System Patient Information 3 BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION BRYAN Cervical Disc System PATIENT INFORMATION 1 BRYAN Cervical Disc System This patient information brochure
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Note to Teachers about The Virtual Stroke Lab Student Handout
 Note to Teachers about The Virtual Stroke Lab Student Handout This document contains a handout that can be distributed for students to fill out as they complete The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free online Virtual
Note to Teachers about The Virtual Stroke Lab Student Handout This document contains a handout that can be distributed for students to fill out as they complete The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free online Virtual
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
PACEMAKER PATIENT INFORMATION
 PACEMAKER PATIENT INFORMATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 11 Contents What is a pacemaker? Why do I need a pacemaker? The heart and normal electrical conduction Complete or
PACEMAKER PATIENT INFORMATION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 11 Contents What is a pacemaker? Why do I need a pacemaker? The heart and normal electrical conduction Complete or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet
 What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
What is Heart Failure? CorCap Cardiac Support Device Patient Information Booklet Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body. To compensate
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Living with Your Pacemaker
 Brief Statement Additional Device Information An implantable pacemaker system relieves symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances. They do this by restoring normal heart rates. A normal heart rate provides
Brief Statement Additional Device Information An implantable pacemaker system relieves symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances. They do this by restoring normal heart rates. A normal heart rate provides
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
5 MILLION AMERICANS 1. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) AFib affects an estimated
 A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
A Patient s Guide To with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) CAUSES RISK FACTORS SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENTS INSIDE The Healthy Heart... 2 Your Heart In AFib... 4 How Do You Get It?... 6 How Do You Know If You
Patient Information. PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems
 Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY
 INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
INFORMED CONSENT INFORMATION ADDRESSOGRAPH DATA CERVICAL MEDIASTINOSCOPY WITH BIOPSY You have decided to have an important procedure and we appreciate your selection of UCLA Healthcare to meet your needs.
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. What you need to know
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION What you need to know Table of contents Atrial fibrillation overview... 1 What is a-fib?.... 2 Risk factors for a-fib... 3 Symptoms of a-fib.... 4 Complications from a-fib... 4 How
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION What you need to know Table of contents Atrial fibrillation overview... 1 What is a-fib?.... 2 Risk factors for a-fib... 3 Symptoms of a-fib.... 4 Complications from a-fib... 4 How
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Advances in the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation At VCU Medical Center
 Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Contact Us For additional information or to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists, please call: Ken Ellenbogen, M.D. Cardiology/Electrophysiology 804-828-7565 or 804-628-0147 You can also
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Atrial Fibrillation Centre
 About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
About this guide We have prepared this guide to help you to: learn about atrial fibrillation manage atrial fibrillation and reduce the risk of stroke find out about medicines and other treatment options
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Department of Surgery
 Thoracic Surgery After Your Lung Surgery Patient Education Discharge Information You have just had lung surgery. The following are definitions of terms you may hear in connection with your surgery: THORACOTOMY
Thoracic Surgery After Your Lung Surgery Patient Education Discharge Information You have just had lung surgery. The following are definitions of terms you may hear in connection with your surgery: THORACOTOMY
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation
 The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
The Patient s Guide to the Electrophysiologic Study (EPS) and Catheter Ablation 2 P a g e Table of Contents Introduction How the Heart Works 3 How the Heart s Electrical System Works 3 Commonly Used Heart
Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information
 Patient Information Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Page 1 of 8 Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information Emory University Hospital Midtown Cardiac Electrophysiology Service
Patient Information Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Page 1 of 8 Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patient Information Emory University Hospital Midtown Cardiac Electrophysiology Service
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
Ventricular Assist Device Program. Patient Education Brochure
 Ventricular Assist Device Program Patient Education Brochure TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. How the Heart Works 3. Heart Disease and VADs 4. Alternative Treatments 5. The Implantation Procedure 6.
Ventricular Assist Device Program Patient Education Brochure TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. How the Heart Works 3. Heart Disease and VADs 4. Alternative Treatments 5. The Implantation Procedure 6.
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Let s talk about: Stroke
 Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
Let s talk about: Stroke February 20 th 2013 Laura Wilson Christine Stables Questions 1. Why is knowing about stroke important? 2. What exactly is a stroke and what are the symptoms? 3. What should I do
Atrial Fibrillation. Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
Atrial Fibrillation Information for you, and your family, whänau and friends Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group CONTENTS Introduction 1 The heart 2 What is atrial fibrillation? 3 How common
