Path Planning of Automated Optical Inspection Machines for PCB Assembly Systems
|
|
|
- Asher Peters
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 96 International Journal Tae-Hyoung of Control, Park, Automation, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Systems, and Nam vol. Kim 4, no., pp , February 2006 Path Planning of Automated Optial Inspetion Mahines for PCB Assembly Systems Tae-Hyoung Park, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Nam Kim Abstrat: We propose a path planning method to improve the produtivity of AOI (automated optial inspetion) mahines in PCB (printed iruit board) assembly lines. The path-planning problem is the optimization problem of finding inspetion lusters and the visiting sequene of ameras to minimize the overall working time. A unified method is newly proposed to determine the inspetion lusters and visiting sequene simultaneously. We apply a hybrid geneti algorithm to solve the highly ompliated optimization problem. Comparative simulation results are presented to verify the usefulness of the proposed method. Keywords: AOI mahine, geneti algorithm, path planning, optimization, PCB assembly.. INTRODUCTION One important proess in eletroni manufaturing today is PCB (printed iruit board) assembly using SMT (surfae mount tehnology). SMT has replaed the older through-hole-tehnology beause it an dramatially inrease the densities of omponent per board. Fig. shows a SMT in-line system for PCB assembly. The AOI (automated optial inspetion) mahine is employed in the SMT in-line systems to perform a sequene of optial inspetions on omponent plaement and soldering. Due to the growth of image proessing tehnology, they have beome very popular in PCB assembly lines. Effiient operation of the AOI mahine is essential for reduing produt ost and therefore inreasing ompetitiveness. In this paper, we propose a method to redue the overall working time of the AOI mahine. The path-planning problem of the AOI mahine is to find the optimal path of a amera suh that the overall working time is minimized. Sine the image aquisition area of the amera is limited by its FO (field-of-view), all omponents and soldering pads in the PCB should be divided into many lusters. The size of eah luster should be within the size of the Manusript reeived February 23, 2005; revised August 2, 2005; aepted Deember 6, Reommended by Editorial Board member Sangdeok Park under the diretion of Editor Keum-Shik Hong. This work was supported by the Regional Researh Centers Program of the Ministry of Eduation & Human Resoure Development in Korea. Tae-Hyoung Park and Nam Kim are with the Shool of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Chungbuk , Korea ( s: {taehpark, namkim}@hungbuk.a.kr). Hwa-Jung Kim is with the R&D Center, KEC Mehatronis Co., LTD, Kumi, Kyungbook , Korea ( jjakji@korea.om). FO. The amera visits every luster and aquires an image to perform the PCB inspetion. The number of lusters and the moving path of amera have great influene on the total working time. Hene the pathplanning problem is to determine the lusters and visiting sequene minimizing the total working time. This problem is under the ategory of the NP-hard optimization problem, so it is very diffiult to find the optimal solution in a reasonable time. In this paper, we propose a method to find the near-optimal solution of the path-planning problem. Most researhes on AOI mahines have been foused on image proessing [-3]. It is very diffiult to diretly apply the typial lustering algorithms [4,5] to our problem beause our problem is different from the typial lustering problem in the viewpoint of deision variables and optimization riteria. The optimization method for the TSP (traveling salesman problem) [6] an be partly applied to our problem, but it is neessary to develop a new method to solve the whole path-planning problem. We an solve the path-planning problem by dividing the whole problem into two sub-problems: lustering problem and sequening problem. The lustering algorithms are applied to solve the upper stage problem, and then the TSP algorithms are applied to solve the lower stage problem. This hierarhial approah an generate a good solution in a short time, but may generate an ineffiient solution sine the lustering and sequening are not independent. To improve the effiieny of the solution, we newly propose the unified method that solves the lustering problem and sequening problem simultaneously. The hybrid geneti algorithm is applied to solve the optimization problem. We verify the effiieny and usefulness of the proposed method through the
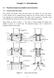
2 Path Planning of Automated Optial Inspetion Mahines for PCB Assembly Systems 97 omparative simulation using a ommerial mahine. 2. PATH PLANNING PROBLEM Fig.. PCB assembly system and AOI mahine. Fig. 2 shows a typial AOI mahine that onsists of a gantry and a amera. The gantry moves in the y- diretion, and the amera moves along the gantry in the x-diretion. These x and y-diretion movements an our onurrently. Sine the FO (field-of-view) of the amera is bounded by its limit, the amera travels over the entire board area to aquire overall images. Fig. 3 depits inspetion windows, FO and amera path of the AOI mahine. The inspetion window is a retangular area to be inspeted by the amera, whih inludes omponent and soldering pad. Several hundreds or thousands of windows are usually loated in one PCB. The FO is the maximum image area that an be aquired by one shot of the amera. The size of the FO is a onstant parameter of the amera, whih is usually about several tens of millimeters. The inspetion luster is a group of inspetion windows that an be aptured by one shot of the amera. So the size of the FO limits that of the inspetion luster. The amera starts from a given initial position, and visits every luster to aquire image data for all inspetion windows. The amera path is the sequene of lusters visited by the amera. The number of inspetion lusters is equal to the number of shots by the amera. Hene if we redue the number of lusters, we an redue the total image aquisition time of the AOI mahine. The overall working time also inludes the amera moving time between lusters. The total moving time is deided by the visiting sequene of the amera. Therefore, inspetion lusters and visiting sequene should be determined to redue the overall working time. The path-planning problem of the AOI mahine is to determine the inspetion lusters and visiting sequene of the amera. Now we formulate the path-planning problem mathematially. Let W be a set of window indexes and C be a set of luster indexes as: W = {, L, m}, () C = {, L, n}, (2) Fig. 2. Struture of AOI mahine. Fig. 3. Inspetion windows, FO and amera path. where n is the number of lusters, whih is a variable to be determined. Define the luster variable {0,} m n as: z w z w =, if window w is a member of luster. 0, otherwise and define the sequene variable x ij = 0, otherwise. x ij {0,} n n as:, if luster j is visited diretly from luster i. Then the path-planning problem is formulated as the following integer- programming problem:
3 98 Tae-Hyoung Park, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Nam Kim s.t. min { nt aq + tij xij } (3) i C j C zw =, w W, (4) C zw, C, (5) ww max min FO, max min FO, X X X C, (6) Y Y Y C, (7) xij =, j C, (8) i C xij =, i C, (9) j C xij S, S C. (0) i S j S In (3), n is the number of lusters related with the luster variable z w. T aq is the image aquisition time for one luster, whih is assumed to be a onstant value. And t ij is the amera moving time between luster i and luster j, whih depends on the luster variable z w. Hene the objetive funtion in (3) is the overall working time, whih is the sum of total image aquisition time and total moving time. Constraint (4) means that every inspetion window should be inluded in an inspetion luster, and onstraint (5) means that every inspetion luster should inlude at least one inspetion window. X min max and X denote the maximum and the minimum x- oordinates of luster, respetively. Also Y max and Y min denote the maximum and the minimum y- oordinates of luster, respetively. Therefore onstraints (6)-(7) mean that the size of luster should be smaller than the size of the FO. Constraints (8)- (9) mean that every luster should be visited exatly one, and onstraint (0) prohibits split yles from the amera path. Hene the amera path should be the Hamiltonian tour for the traveling salesman problem. The path-planning problem is to find the luster variable and the sequene variable suh that the objetive funtion (3) is minimized subjet to the onstraints in (4)-(0). The formulated problem is a nonlinear integer-programming problem with oupled variables. It is known to be very hard to obtain the global solution for the ategory of these problems. Hene we approah the problem by the loal or heuristi method to obtain the near-optimal solution in a reasonable time. 3. HIERARCHICAL METHOD To overome the diffiulties of the path-planning problem, we divide the overall problem into two subproblems hierarhially: lustering problem and sequening problem. The lustering problem is to reate the minimum number of inspetion lusters, and the sequening problem is to find the visiting sequene minimizing the total moving time. The sequening problem an be modeled as a standard traveling salesman problem (TSP). Therefore we an diretly apply the well-known TSP algorithms [6,7] to the sequening problem. The start node and end node are pre-determined at the wait loation of a amera. The ost is the moving time, whih an be alulated by profiles of the x and y gantries. The typial lustering problem [4] is to reate lusters to minimize the sum of distanes between windows and the enter of lusters. The problem does not limit the maximum size of lusters. Also, the number of lusters is usually fixed as a given ondition. However, in our lustering problem, the maximum size of lusters should be bounded by the size of the FO. Furthermore, the number of lusters is not given a ondition but a variable to be minimized. Therefore it is neessary to modify the typial lustering algorithms for our lustering problem. 3.. Single-link lustering The single-link algorithm [4,8] is one of the typial lustering algorithms. It initiates from numerous initial lusters, and merges them together iteratively until the number of lusters reahes a fixed value. This algorithm is very simple to be implemented, and requires low omputational omplexity. However, the performane of the solution highly depends on the distribution of windows beause of loal improvement. To apply the single-link algorithm to our problem, the size of the FO should be onsidered. The modified single-link algorithm is as follows: S. Generate initial lusters by setting eah window as a luster. S2. For eah luster, find the nearest luster that an be merged together. If the size of the new luster is within the FO, merge the two lusters. S3. Repeat S2 until there is no more merging ISODATA lustering The ISODATA (iterative self-organizing data analysis) algorithm [4] is the most popular algorithm for the typial lustering problem. This algorithm was updated from the K-means algorithm [9], whih improves the lustering by moving the enter (mean) of k-lusters. The ISODATA algorithm improves them more effiiently through iterative merging or splitting. Basially this algorithm is also under the ategory of loal improvement method, so the solution depends on the initial lusters. The modified ISODATA algorithm for our lustering problem is as follows: S. Generate initial lusters by dividing the board into retangular grids. The size of eah grid is
4 Path Planning of Automated Optial Inspetion Mahines for PCB Assembly Systems 99 idential with the FO. S2. Delete the luster in whih there is no window. S3. For eah luster, move the enter to inlude more windows. S4. If some windows are not inluded in any lusters, add new lusters for those windows. S5. For eah luster, find the nearest luster that an be merged together. If the size of the new luster is within the FO, merge the two lusters. S6. Repeat S3-S5 until there is no more hange on lusters. 4. UNIFIED METHOD The hierarhial methods find the luster variables and the sequene variables at two different stages. However, it is desirable to find the solution simultaneously beause both variables are oupled to eah other. The proposed method is for the purpose of finding the luster variables and the sequene variables simultaneously. The geneti algorithms have been widely used for omplex optimization problems. These algorithms an allow the solution to get out of the loal problems and approah the global problem [0]. However, onvergene of the solution may take a lot of time, whih depends on the problem size and parameters. Several researhes have been announed for the typial lustering problems [,2] and TSP [3,4]. Fig. 4 shows the flow of the hybrid geneti algorithm proposed to solve our path-planning problem. To apply the geneti algorithm into our problem, we have to newly define the hromosome, fitness funtion, and operators. We define the hromosome of the lustering problem as: w w a * w 2 w 2 b * * w n Initialization Fitness Evaluation Stop? Stop? n Initialization Seletion Fitness Crossover Evaluation Initialization Mutation Fitness Sequening Evaluation Path Initialization Generation Fig. 4. Flow of hybrid geneti algorithm. w nx * (Cluster ) (Cluster2) (Cluster n) y The gene, the element of the hromosome, has the value of window index w W or mark *, where ij w ij denotes the j -th window of the i -th luster and * denotes the end of the luster. The order of lusters in the hromosome is equivalent to the visiting sequene of the amera. Therefore, one hromosome an represent both the lustering and sequening results. 4.. Initialization Eah generation onsists of N hromosomes, where N is the population size. The initial population is generated by random number generation. For eah gene of a hromosome, window index r W is seleted at random. If the size of the luster inluding the seleted window is within the size of the FO, the window index is set to the gene. Otherwise, another window index is seleted randomly until the feasible ondition is satisfied. If a feasible window index is not found, then set mark * to the gene. This initialization step starts from the first bit and moves toward the last bit of the hromosome Fitness evaluation and seletion Let t k be the working time for the k-th hromosome k ( k =, L, N), and t max be the maximum value for all hromosomes in a generation. We define the fitness funtion f k for the k-th hromosome as: f = ( t t ) k max k N i= N. () ( t t ) max The fitness will be 0 for the ase of a maximumtime hromosome, and for the ase of an averagetime hromosome. The value inreases as the working time dereases. The above fitness funtion is used at the seletion stage to perform reprodution of good hromosomes. We adopt the remainder stohasti sampling method [4] to prevent the stohasti sampling error Crossover operator At the rossover stage, two hromosomes (, 2 ) are seleted randomly with rossover probability. Then, the rossover operator hanges the seleted hromosomes to new hromosomes ( ', 2 ' ) by ombining the genes of eah hromosome as: S. Selet a luster from randomly. S2. Searh 2 until all windows of the seleted luster of are disovered. Then, selet the lusters of 2 if they inlude any of the disovered windows. S3. Searh until all windows of the seleted luster of 2 are disovered. Then, selet the lusters of if they inlude any of the disovered windows. S4. Repeat S2-S3 until the seleted windows of both i
5 00 Tae-Hyoung Park, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Nam Kim hromosomes are exatly the same. S5. Exhange the seleted lusters between and 2, and make new hromosomes ' and 2 '. For example, assume that two hromosomes are seleted as: = 2 = In S, we randomly selet an initial luster from as: = 3 * * 3 * * * In S2, lusters are seleted from 2 as: 2 = In S3, lusters are seleted from again as: = Sine the seleted windows of both hromosomes are exatly the same, we go to S5. In S5, the new hromosomes are generated as: ' = 2 ' = 4.4. Mutation operator In the mutation stage, one hromosome is seleted randomly with mutation probability. Then, the mutation operator hanges the seleted hromosome to new hromosome ' by random alteration of genes. The proposed mutation operator is as follows: S. Selet a luster from randomly. S2. Chek whether the windows of the seleted luster an be moved to other lusters. If possible, move them to the feasible lusters and make a new hromosome '. In S2, the size of the luster is heked before moving the window sine the size of the luster should be bounded by the FO. For example, assume that a hromosome is seleted as: = In S, we randomly selet a luster from as: = In S2, all seleted windows 3, 9, 6, 2 are heked to move. If only two windows 6, 2 an be moved, we move them to the feasible lusters as: ' = 3 * * 3 * * * * 8 7 *8 2 4 * 9 * 3 6 * * * *9 * 3 6 * * 3 * * 3 * * * 3 * * 8 7 * * 3 6 * * * 3 * * 9 * * 3 * * * * 0 2 * 3 * * * * 0 2 * 3 6 * * 3 9 * * 0 2 2* 4.5. Sequene operator The sequene operator generates new luster sequenes of the hromosomes whose genes are hanged by rossover operator or mutation operator. This operator is also an unary operator for the hromosome. In the sequene operator, a sequene array is used as auxiliary data. The element of the sequene array is the luster, and the index of the sequene array denotes the visiting sequene of the luster. The proposed sequene operator is as follows: S. Set the first luster of as a urrent luster, and add it to a sequene array. S2. Find the nearest luster from the urrent luster, where the luster should not be an element of the sequene queue. Set the nearest luster as a urrent luster, and add it to the sequene array. S3. Repeat S2-S3 until all lusters are inluded in the sequene array. S4. Selet a pair of lusters from the sequene array, and exhange the sequene if the total moving time is redued. S5. Repeat S4 until all pairs of lusters are seleted from the sequene array. S6. Make a new hromosome ' by reassignment of lusters aording to the order of the sequene array. Assume that rossover operator or mutation operator has hanged the following hromosome. = 3 6 * * 3 9 * * * (Cluster) (Cluster2) (Cluster3) (Cluster4) (Cluster5) The sequene array is generated by S-S3 as: (Cluster ) (Cluster 4) (Cluster 2) (Cluster 5) (Cluster 3) And the sequene array is modified by S4-S5 as: (Cluster 5) (Cluster 3) (Cluster 4) (Cluster ) (Cluster 2) By S6, a new hromosome is generated from the sequene array as: ' = 02 2 * 3 9 * * 3 6 * * While the rossover operator and mutation operator hange both lusters and sequene, the sequene operator hanges sequene only. An initial sequene is generated by the nearest neighbour searh at S-S3, and the sequene is improved by 2-opt heuristis [7] at S4-S5. This method is one of the typial loal searh methods for TSP. The other TSP methods suh as 3-opt heuristis or Lin-Kernighan heuristi an also be applied to the sequene operator, but whih may result in the lower onvergene speed. The rossover operator and mutation operator guarantee the diversity of searh, but the sequene operator helps the fast onvergene by loal improvement. The hybrid geneti algorithm is the
6 Path Planning of Automated Optial Inspetion Mahines for PCB Assembly Systems 0 geneti algorithm that adopts the loal searh to overome the problem of onvergene speed. 5. SIMULATION We used a ommerial AOI mahine (AI-400, Samsung Tehwin Co. LTD) [5] for simulation. The size of the FO was 6(mm) 2(mm), and the image aquisition time for one FO was 0.25 (se). The maximum speed and aeleration of the X and Y gantries were 700 (mm/se) and 0.2 (mm/se 2 ), respetively. All PCBs used in the simulation were ommerial boards with different number of windows. Table shows the number of windows and size of test PCBs used in our simulation. We implemented the proposed algorithms using C++ programming language under MS-Windows XP, and installed them to the off-line programming software of the ommerial mahine. The population size for the geneti algorithm was set at 00. The rossover probability and mutation probability were set at 0.3 and 0.2, respetively. These parameters were determined by experimental ase study. As inreasing the population size, the alulation time was inreased but the optimization performane was improved. Fig. 5 presents onvergene graphs of the proposed geneti algorithm. Aording to variations of rossover probability and mutation probability, the best working time in eah generation was hanged as in Fig. 5(a) and Fig. 5(b). The parameters of the geneti algorithm were seleted suh that the best working time onverged to its minimum value in a short generation. Fig. 6 indiates the results of path planning obtained from different methods. Fig. 6(a) shows a test PCB with 44 inspetion widows. Fig. 6(b)-(d) show inspetion lusters and amera paths generated by different path-planning methods. Fig. 6(b) was obtained from the hierarhial method with single-link lustering (method ). Fig. 6() was obtained from the hierarhial method with the ISODATA lustering (method 2). Fig. 6(d) was obtained from the unified method using the hybrid geneti algorithm (method 3). Method 2 is the ommerial path-planning version of Table. Test PCBs. No. of PCB Id windows PCB size X(mm) x Y(mm) x x x x x x x x 245 working time (se) working time (se) generation (a) Crossover probability (P ) generation (b) Mutation probability (P m ). Fig. 5. Convergene graphs for GA parameters. AI-400. Both the number of lusters and distane of the amera path were redued by method 3, whih resulted in the redution of the overall working time of the AOI mahine. Fig. 7 shows the results of path planning for two PCBs with different distribution of inspetion windows. Both PCBs have the same number of inspetion windows and the same board size while they have different distributions of inspetion windows. Fig. 7(a) and Fig. 7(b) indiate the lusters and sequenes generated for PCBs with sattered inspetion windows and onentrated inspetion windows, respetively. As the inspetion windows are sattered, the number of lusters is inreased to over all inspetion windows and the overall working time of the AOI is also inreased. This simulation shows that the overall working time of the AOI depends on the distribution of inspetion windows as well as on the number of inspetion windows. Table 2 presents omparative results of path planning results for the test PCBs in Table. The working time is the sum of total image aquisition time and total moving time of the amera. This table shows that the working time stritly depends on the number of lusters, so that lustering is more
7 02 Tae-Hyoung Park, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Nam Kim (a) Inspetion windows. (a) PCB with sattered inspetion windows. (lusters: 87, working time: 30. se ) (b) Hierarhial method using single-link lustering. () Hierarhial method using ISOSATA lustering. (b) PCB with onentrated inspetion windows. (lusters: 39, working time: 9.6 se) Fig. 7. Example of path planning for PCBs with different window distributions(pcb size: 244(mm) x 26(mm), inspetion windows: 000). Table 2. Path-planning results: working time. (d) Unified method. Fig. 6. Examples of path planning by different methods. important than sequening in the sense of time optimization. The performane of method 3 is the best among all methods. Table 3 indiates the improvement ratio of method 3 with respet to the other methods. It verifies that the proposed method 3 an improve the performane by about 6 ~ 0%. Table 4 ompares the omputational time of eah method. The algorithms were run at the Pentium-I 3GHz omputer. The omputational time of method 3 is relatively longer than that of other methods. Sine the path planning is performed at an offline omputer, long alulation time an be allowed if it generates better performane. PCB Id. Method Method 2 Method 3 Working No. of lusters time (se) No. of lusters Working time (se) Working No. of time lusters (se) Method : Hierarhial method using single-link lustering Method 2: Hierarhial method using ISODATA lustering Method 3: Unified method
8 Path Planning of Automated Optial Inspetion Mahines for PCB Assembly Systems 03 Table 3. Path-planning results: improvement by Method 3. PCB Id. W.r.t. Method (%) W.r.t. Method 2 (%) Ave Table 4. Path-planning results: omputational time. PCB Id. Method Method 2 Method 3 (se) (se) (se) CONCLUSIONS In this paper, we proposed a path-planning method for AOI mahines. We defined the path-planning problem and formulated it mathematially. By mathematial formulation, we verified that the problem is a nonlinear integer-programming problem with two oupled variables. To obtain the better solution, we tried to find the two deision variables onurrently. The hybrid geneti algorithm was applied to overome the problem of loal improvement and onvergene speed. The hromosome, fitness funtion and operators were newly defined to solve our problem by geneti algorithm. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm an be implemented and installed suessfully to pratial mahines. Also, it an ontribute to improve the produtivity of the mahine by reduing the number of lusters and the amera moving time. The optimization performane of the proposed method was relatively higher than the other methods. The AOI mahines have beome more popular in the PCB assembly systems, so our results will be useful for inreasing the produtivity of eletroni manufaturing systems. REFERENCES [] T. S. Newman and A. K. Jain, A survey of automated visual inspetion, Computer ision and Image Understanding, vol. 6, no. 2, pp , 995. [2] Y. Hara, N. Akiyama, and K. Karasaki, Automati inspetion system for printed iruit boards, IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene, vol. PAMI-5, no. 6, pp , 983. [3] H. H. Loh and M. S. Lu, Printed iruit board inspetion using image analysis, IEEE Trans. on Industry Appliations, vol. 35, no. 2, pp , 999. [4] A. K. Jain, M. N. Murty, and P. J. Flynn, Data lustering: A review, ACM Computing Surveys, vol. 3, no. 3, pp , 999. [5] B. S. Everitt, S. Landau, and M. Leese, Cluster Analysis, Fourth Edition, Arnold, 200. [6] G. Reinelt, The Traveling Salesman: Computational Solutions for TSP Appliations, Springer-erlag, 994. [7] M. Bellmore and G. Nemhauser, The travelingsalesman problem: A survey, Operation Researh, vol. 6, pp , 968. [8] E. Dahlhaus, "Fast parallel algorithm for the single link heuristis of hierarhial lustering, IEEE Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Proessing, vol., no. 4, pp , 992. [9] T. Kanungo, D. M. Mount, N. S. Netanyahu, C. D. Piatko, R. Silverman, and A. Y. Wu, An effiient k-means lustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation, IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene, vol. 24, pp , [0] Z. Mihalewiz, Geneti Algorithms+Data Strutures=Evolution Programs, Springer-erlag, 996. [] L. Y. Tseng and S. B. Yang, A geneti approah to the automati lustering problem, Pattern Reognition, vol. 34, pp , 200. [2] H. S. Kim and S. B. Cho, An effiient geneti algorithm with less fitness evaluation by lustering, IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 2, pp , 200. [3] J. Gu, Effiient loal searh with searh spae smoothing: A ase study of the traveling salesman problem, IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man and Cybernetis, vol. 24, no. 5, pp , 994. [4] R. Baraglia, J. I. Hidalgo, and R. Perego, A hybrid heuristi for the traveling salesman problem, IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 5, no. 6, pp , 200. [5] Samsung Tehwin Co., LTD, SMT Inspetion equipment - AI400, om.
9 04 Tae-Hyoung Park, Hwa-Jung Kim, and Nam Kim Tae-Hyoung Park reeived the Ph.D. in Control and Instrumentation Engineering from Seoul National University, Korea in 994. From 994 to 997, he was a Senior Researh Engineer at Samsung Tehwin Co., where he developed the optimization software for PCB assembly systems. Sine 997 he has been a Professor of Control and Instrumentation Engineering at Chungbuk National University. From 2000 to 200, he was a isiting Professor at the University of Toronto, Canada. His researh interests inlude robotis, optimization algorithms, and eletroni manufaturing systems. Nam Kim reeived the Ph.D. degree in Eletronis Engineering from Yonsei University, Korea in 988. Sine 989, he has worked as a Professor in the Dept. of Computer and Communiation Engineering, Chungbuk National University. From 992 to 993, he was a isiting Professor at Stanford University. From 2000 to 200 he was a isiting Professor at Calteh. He is interested in the appliations of holography, diffrative optis, optial interonnetion, and the optial memory system. Hwa-Jung Kim reeived the M.S. degree in Control and Instrumentation Engineering from Chungbuk National University, Korea in He is urrently a Researh Engineer in the Mehatronis Laboratory at KEC Co. His researh interests inlude robotis, optimization algorithms, and mahine vision.
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Optimize Position and Path Planning of Automated Optical Inspection
 Journal of Computational Information Systems 8: 7 (2012) 2957 2963 Available at http://www.jofcis.com Optimize Position and Path Planning of Automated Optical Inspection Hao WU, Yongcong KUANG, Gaofei
Journal of Computational Information Systems 8: 7 (2012) 2957 2963 Available at http://www.jofcis.com Optimize Position and Path Planning of Automated Optical Inspection Hao WU, Yongcong KUANG, Gaofei
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA faramarz@sienes.sdsu.edu
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
In this chapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use directed graphs.
 Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
Chapter 19 State Diagrams In this hapter, we ll see state diagrams, an example of a different way to use direted graphs. 19.1 Introdution State diagrams are a type of direted graph, in whih the graph nodes
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
Solving the Game of Awari using Parallel Retrograde Analysis
 Solving the Game of Awari using Parallel Retrograde Analysis John W. Romein and Henri E. Bal Vrije Universiteit, Faulty of Sienes, Department of Mathematis and Computer Siene, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Solving the Game of Awari using Parallel Retrograde Analysis John W. Romein and Henri E. Bal Vrije Universiteit, Faulty of Sienes, Department of Mathematis and Computer Siene, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
Robust Classification and Tracking of Vehicles in Traffic Video Streams
 Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Discovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks
 Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
JEFFREY ALLAN ROBBINS. Bachelor of Science. Blacksburg, Virginia
 A PROGRAM FOR SOLUtiON OF LARGE SCALE VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEMS By JEFFREY ALLAN ROBBINS Bahelor of Siene Virginia Polytehni Institute and State University Blaksburg, Virginia 1974 II Submitted to the Faulty
A PROGRAM FOR SOLUtiON OF LARGE SCALE VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEMS By JEFFREY ALLAN ROBBINS Bahelor of Siene Virginia Polytehni Institute and State University Blaksburg, Virginia 1974 II Submitted to the Faulty
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
Agent-Based Grid Load Balancing Using Performance-Driven Task Scheduling
 Agent-Based Grid Load Balaning Using Performane-Driven Task Sheduling Junwei Cao *1, Daniel P. Spooner, Stephen A. Jarvis, Subhash Saini and Graham R. Nudd * C&C Researh Laboratories, NEC Europe Ltd.,
Agent-Based Grid Load Balaning Using Performane-Driven Task Sheduling Junwei Cao *1, Daniel P. Spooner, Stephen A. Jarvis, Subhash Saini and Graham R. Nudd * C&C Researh Laboratories, NEC Europe Ltd.,
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, kstef@s.uoi.gr Evaggelia
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS
 TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS ICSRiM - University of Leeds Shool of Computing & Shool of Musi Leeds LS2 9JT, UK +44-113-343-2583 kia@i-maestro.org www.i-maestro.org,
TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED LEARNING FOR MUSIC WITH I-MAESTRO FRAMEWORK AND TOOLS ICSRiM - University of Leeds Shool of Computing & Shool of Musi Leeds LS2 9JT, UK +44-113-343-2583 kia@i-maestro.org www.i-maestro.org,
Modeling and analyzing interference signal in a complex electromagnetic environment
 Liu et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communiations and Networking (016) 016:1 DOI 10.1186/s13638-015-0498-8 RESEARCH Modeling and analyzing interferene signal in a omplex eletromagneti environment Chun-tong
Liu et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communiations and Networking (016) 016:1 DOI 10.1186/s13638-015-0498-8 RESEARCH Modeling and analyzing interferene signal in a omplex eletromagneti environment Chun-tong
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Research Center. Abstract
 Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objective Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms
 Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Marker Tracking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferencing System
 Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
From a strategic view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise
 Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: prabal@mech.iitd.ac.in. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
Green Cloud Computing
 International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
A Game Theoretical Approach to Gateway Selections in Multi-domain Wireless Networks
 1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
Product Warranties and Double Adverse Selection
 rodut Warranties and Double Adverse eletion David A. oberman Assistant rofessor of Marketing INEAD Boulevard de Constane 77305 Fontainebleau Cede, Frane The author thanks rofessors Andy Mithell, Jak Mintz,
rodut Warranties and Double Adverse eletion David A. oberman Assistant rofessor of Marketing INEAD Boulevard de Constane 77305 Fontainebleau Cede, Frane The author thanks rofessors Andy Mithell, Jak Mintz,
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MONITORING AND SURVEILLANCE THROUGH A NETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UNITS
 AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Dataflow Features in Computer Networks
 Magyar Kutatók 1. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 1 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researhers on Computational Intelligene and Informatis Gyula Max Budapest University of Tehnology and Eonomis, Department
Magyar Kutatók 1. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 1 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researhers on Computational Intelligene and Informatis Gyula Max Budapest University of Tehnology and Eonomis, Department
Picture This: Molecular Maya Puts Life in Life Science Animations
 Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR. A Thesis by. Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu
 VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
Online Energy Generation Scheduling for Microgrids with Intermittent Energy Sources and Co-Generation
 Online Energy Generation Sheduling for Mirogrids with Intermittent Energy Soures and Co-Generation Lian Lu Information Engineering Dept. he Chinese Univ. of Hong Kong Jinlong u Information Engineering
Online Energy Generation Sheduling for Mirogrids with Intermittent Energy Soures and Co-Generation Lian Lu Information Engineering Dept. he Chinese Univ. of Hong Kong Jinlong u Information Engineering
Paid Placement Strategies for Internet Search Engines
 Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
A Reputation Management Approach for Resource Constrained Trustee Agents
 A Reputation Management Approah for Resoure Constrained rustee Agents Han Yu, Chunyan Miao, Bo An 2, Cyril Leung 3, and Vitor R. Lesser 4 Nanyang ehnologial University, Singapore 2 he Key Lab of Intelligent
A Reputation Management Approah for Resoure Constrained rustee Agents Han Yu, Chunyan Miao, Bo An 2, Cyril Leung 3, and Vitor R. Lesser 4 Nanyang ehnologial University, Singapore 2 he Key Lab of Intelligent
A Design Environment for Migrating Relational to Object Oriented Database Systems
 To appear in: 1996 International Conferene on Software Maintenane (ICSM 96); IEEE Computer Soiety, 1996 A Design Environment for Migrating Relational to Objet Oriented Database Systems Jens Jahnke, Wilhelm
To appear in: 1996 International Conferene on Software Maintenane (ICSM 96); IEEE Computer Soiety, 1996 A Design Environment for Migrating Relational to Objet Oriented Database Systems Jens Jahnke, Wilhelm
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Expanding Operations in Fast-Food Industry under Uncertain Market Conditions
 International Journal of Trade, Eonomis and Finane, Vol., No., June, 200 200-023X Expanding Operations in Fast-Food Industry under Unertain Market Conditions Seyhan Sipahi, Senior Member, IACSIT Abstrat
International Journal of Trade, Eonomis and Finane, Vol., No., June, 200 200-023X Expanding Operations in Fast-Food Industry under Unertain Market Conditions Seyhan Sipahi, Senior Member, IACSIT Abstrat
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
5.2 The Master Theorem
 170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
Method for characterizing single photon detectors in saturation regime by cw laser
 Method for haraterizing single oton detetors in saturation regime by w laser Jungmi Oh, Cristian Antonelli, 2 Moshe Tur, 3 and Misha Brodsky,* AT&T Labs, 2 S. Laurel Ave., Middletown, New Jersey 7748,
Method for haraterizing single oton detetors in saturation regime by w laser Jungmi Oh, Cristian Antonelli, 2 Moshe Tur, 3 and Misha Brodsky,* AT&T Labs, 2 S. Laurel Ave., Middletown, New Jersey 7748,
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Microcontroller Based PWM Controlled Four Switch Three Phase Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 7, No., November 00, 95-04 UDK: 004.466 Miroontroller Based PWM Controlled Four Swith Three Phase Inverter Fed Indution Motor Drive Nalin Kant Mohanty, Ranganath
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 7, No., November 00, 95-04 UDK: 004.466 Miroontroller Based PWM Controlled Four Swith Three Phase Inverter Fed Indution Motor Drive Nalin Kant Mohanty, Ranganath
ECONOMICS OF SECURITY PATCH MANAGEMENT
 ECONOMCS OF SECURTY PATCH MANAGEMENT Huseyin Cavusoglu * Hasan Cavusoglu Jun Zhang AB Freeman Shool o Business, Tulane University 7 MAlister Drive, New Orleans, LA 70118, USA Sauder Shool o Business, The
ECONOMCS OF SECURTY PATCH MANAGEMENT Huseyin Cavusoglu * Hasan Cavusoglu Jun Zhang AB Freeman Shool o Business, Tulane University 7 MAlister Drive, New Orleans, LA 70118, USA Sauder Shool o Business, The
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
F220 Series. Installation Instructions. Photoelectric Smoke/Heat Detectors
 F0 Series EN Installation Instrutions Photoeletri Smoke/Heat Detetors F0 Series Installation Instrutions.0 General Information EN.0 General Information. F0-B6 Series Bases Use with the F0 Series Heat and
F0 Series EN Installation Instrutions Photoeletri Smoke/Heat Detetors F0 Series Installation Instrutions.0 General Information EN.0 General Information. F0-B6 Series Bases Use with the F0 Series Heat and
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Scalable Hierarchical Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising
 Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google amra@google.om Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh abhidas@mirosoft.om Alexander J. Smola
Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google amra@google.om Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh abhidas@mirosoft.om Alexander J. Smola
STRATEGIC DESIGN FOR THE SUPPLY NETWORK OF MULTI-SITE ENTERPRISES: A MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SOLVING APPROACHES
 STRATEGIC DESIGN FOR THE SUPPLY NETWORK OF MULTI-SITE ENTERPRISES: A MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SOLVING APPROACHES Florene Pirard 1, Fouad Riane 2, Serguei Iassinovski 2, Valérie Botta-Genoulaz 1 1 Laboratoire
STRATEGIC DESIGN FOR THE SUPPLY NETWORK OF MULTI-SITE ENTERPRISES: A MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SOLVING APPROACHES Florene Pirard 1, Fouad Riane 2, Serguei Iassinovski 2, Valérie Botta-Genoulaz 1 1 Laboratoire
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Recommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model
 WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Optimal Online Buffer Scheduling for Block Devices *
 Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK A.M.Adamaszek@warwik.a.uk
Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK A.M.Adamaszek@warwik.a.uk
