To t a l K n e e R e p l a c e m e n t
|
|
|
- Duane Harrington
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
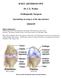
1 To t a l K n e e R e p l a c e m e n t Each year nearly 300,000 knee replacement surgeries are performed in the United States. Total knee replacement surgery involves removing and replacing the diseased parts of the knee joint with new, artificial parts. The muscles, tendons and ligaments are left in place around the knee to provide stability for the new joint. An artificial joint is usually made of metal (usually cobalt-chrome or titanium) and/or plastic polyethylene. A new joint may be fixed to existing bone either using a special cement or by press fitting which allows existing bone to grow into the new surface, locking it into place. The patient s surgeon will discuss the best options of knee replacement devices and whether it should be cemented or press fit into place, based on several different factors, including the patient s age, weight, activity level and bone quality. Normally, a knee bends smoothly and painlessly because the ends are covered in cartilage, which acts like a cushion, absorbing energy in the joint. If this cartilage wears away, bone surfaces can become damaged, which can result in pain and reduced use of the joint. Damage can result from normal wear and tear on the joint or from injury, infection or some diseases. If the bone beneath the cartilage becomes damaged, as well, this is called osteoarthritis. Ar tificial Knee Joint
2 Generally, a total knee replacement is indicated if the patient is suffering from severe knee pain during activity and/or severe interference with daily activities and work and if treatments such as pain medication, weight loss or use of a cane have already been tried. Osteoar thritic Knee Joint Nor mal Knee Joint
3 P r e p a r i n g f o r To t a l K n e e R e p l a c e m e n t Sur ger y Before surgery, a patient is generally asked to see their primary care physician for a general physical exam. The anesthesiologist will also evaluate the patient the day of surgery to discuss they type of anesthetics that will be used. One week prior to surgery routine tests will be run to help assess a patient s fitness for the procedure. These tests might include: Blood and urine tests Chest X-ray EKG X-rays of both knees Patients in good health may also be able to donate one or two units of their own blood to receive during or after surgery. In many cases this may not be necessary. Patients must remember to inform their doctor of the following: All current medications Any allergies to drugs, iodine or latex Previous instances of thrombosis of the legs or elsewhere Any recent infections Any past illnesses Before surgery, there are several important things to know: A spirin, medications containing aspirin or certain anti-inflammatories should not be taken one to two weeks before surgery, to minimize bleeding B lood thinners, such as Coumadin should be discontinued at least several days prior to surgery, after consulting with the prescribing physician V itamins and iron supplements should continue to be taken before and after surgery, especially if the patient has donated his or her own blood for the procedure O verweight patients should try to lose weight to decrease the pressure on the new knee Patients should not smoke K nee replacement surgery may not take place if infections are present elsewhere in the body, such as the bladder or skin
4 The Sur ger y Patients are generally admitted on the day of the operation, unless an underlying condition such as diabetes or cardiac or pulmonary disease requires an additional day of pre-operative hospitalization. Patients should bring sleepwear, slippers or shoes and personal hygiene supplies with them to the hospital. PAT I E N T S S H O U L D N O T E AT O R D R I N K A F T E R M I D N I G H T B E F O R E S U R G E R Y. Patients who take medication regularly ever y day should discuss this with their anesthesiologist and/or sur geon. It may be recommended by the physicians that the dose be postponed or taken as usual with a small s i p o f w a t e r. Total knee replacement is performed either under a general anesthetic, with the patient asleep during the procedure, or a spinal anesthetic, in which the patient is conscious but drowsy and unable to feel anything at the surgical site. Also, for postoperative pain management, your surgeon and anesthesiologist may recommend a regional nerve block. The surgery itself generally includes the following steps: A tourniquet is applied around the thigh to keep blood from the surgical site An incision is made over the kneecap or along its inner side Th e diseased bone-ends are precisely removed to allow for the replacement knee N ew artificial surfaces are fitted to the bone-ends, either with or without cement The wound is closed with sutures or staples A drain may be left in the wound for one to two days Th e knee may be wrapped in a splint or strong bandage, depending on the surgeon s preference D epending on its complexity, the operation usually takes from one to three hours At St. Luke s Hospital, there is a Specialty Hospital approach to orthopedics, such that in the operating room there are nurse assistants, scrubs and circulators who do only orthopedic procedures, including all total joint replacements.
5 Diseased Bone Removal Ar tificial Joint Placement
6 The result of the surgery is that the knee joint has been completely resurfaced by the new, artificial joint. The patient s existing muscles and ligaments surrounding the new joint help maintain its stability. Most surgeons prescribe antibiotics for a brief period before and after the operation. Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) Some surgeons recommend that patients start gentle continuous knee movement immediately or a few days following surgery. A special Continuous Passive Motion device, called a CPM Machine, is used. The leg rests on the machine, which is set to allow the knee to bend continually a certain amount each day, with the amount increasing each day. The Role of Physical and Occupational Therapy P atients who undergo knee replacement surgery receive a great deal of help from a physical therapist in order to regain muscle strength and increase their knee motion after surgery. P hysical therapists work with patients to help them advance from using a walker to crutches to a cane over a period of 10 to 14 days to weeks (longer for non-cemented knees). A fter surgery, patients should work not only with their physical therapist, but also on their own, with the aim of achieving and maintaining as much motion as possible in the knee. Greater range of motion may be achieved over time. As in the operating room, at St. Luke s, there is a dedicated team of orthopedic nurses and techs, as well as orthopedic physical therapists, whose sole job is taking care of patients on the orthopedic division.
7 Post Sur ger y Day of Sur ger y Most of the day will be spent in bed The diet will be advanced as tolerated Fluids will be delivered via an intravenous line as necessary Pain medications will be given either as pills or injections Blood transfusions may be necessary to replace blood lost during surgery If a patient has difficulty urinating, a bladder catheter may be necessary B reathing exercises begin immediately after surgery and additional oxygen may be delivered through a small nasal tube A n inflatable device delivering intermittent pressure may be placed around the feet to aid in circulation and prevent blood clots Post-Operative D a y s O n e a n d T w o P atients are encouraged to stand and walk with the help of a physical therapist, depending on their medical condition, after the acute pain has cleared Th e physical therapist will begin the exercise programs that will be done both in bed and in the therapy department S itting may be allowed, including using the bathroom D aily blood tests help the surgeon determine if a transfusion is necessary I f a drain has been placed in the knee, it is usually removed by the second day D rink more fluids to prevent urinary tract infections, fever and constipation, and eat a well-balanced diet to help aid the healing process
8 Post-Operative Days Three and Four Most patients will be ready for discharge on post-operative day three or four By these days, the patient should be able to get around using a walker P hysical therapists and other clinical workers will provide instruction about how to get out of bed, use the bathroom and dress and develop a home exercise program in anticiaption of discharge from the hospital Wa l k i n g A f t e r S u r g e r y With the aid of a physical therapist, patients are encouraged to begin walking the day after surgery. The length of time during which crutches or a walker are required varies from patient to patient. Goals to Achieve Before Leaving the Hospital W alk independently on a flat surface using a support (walker, crutches or cane) Climb stairs Bend the knee 90 degrees (not always easy to do soon after surgery) Straighten leg as far as possible Raise straightened leg off the bed Move safely and independently from bed to chair
9 Returning Home Patients are usually discharged three to four days after surgery, depending on physical ability and other factors. A patient must be able to function at a certain level before he or she will be allowed to return home; social workers can help with details during this intermediate period. Some patients may go directly to an in-patient rehabilitation or skilled nursing facility before returning home. A patient should contact his or her physician if: Pain in the knee increases The wound becomes red or warm There is an opening in the wound There is drainage from the wound The knee becomes increasingly swollen Either calf becomes painful, swollen or tender The patient feels hot or ill Sudden coughing or chest pain develops
10 To t a l H i p R e p l a c e m e n t S u r g e r y After decades of unreliable treatments for hip pain and disability, the metal ball and plastic socket were pioneered in Since that time improvements have been made to these artificial components, many of which no longer need cement to bind the bone and joint. In a normal hip, the bone is covered by a smooth lining of cartilage. This surface, with a small amount of joint fluid, allows the joint to move smoothly. Various diseases, such as osteoarthritis, can cause the smooth cartilage lining to break down. These conditions can lead to pain and stiffness in the joint. In a hip that has been affected by osteoarthritis, cartilage has been destroyed, the joint space is narrow and the bone has been eroded. Outgrowths of new bone, called spurs, develop at the margins of the joint. Initial treatment includes losing weight, moderate exercise, restriction of activity and pain medication. Reducing the amount that a person walks and use of a cane may also help.
11 A patient is a candidate for hip replacement sur ger y if he or she has: Severe pain in the hip associated with activity Severe hip pain at night Severe interference with daily activities and work To t a l h i p r e p l a c e m e n t i n v o l v e s : R emoving of the head of the femur and the surface layer of its socket in the pelvis Replacing the head of the femur with a metallic ball and stem, which fits into the canal of the femur Replacing the socket with a combination of plastic, metal or ceramic in one of many shapes, sizes and designs; custom-made components may also be used Hip components are fixed to the bone either with or without cement. Cement fills the space between the new hip and the bone and locks it in place. This is the standard choice for many surgeons, particularly for patients over age 70. Press fit surgeries do not use bone cement and have a surface that allows bone to grow into the implant. A g e L i m i t s f o r To t a l H i p R e p l a c e m e n t s There is no upper age limit for total hip replacement, as long as the general health of the patient allows for such an operation. For younger patients, age limits depend upon the severity of the pain and loss of function. Younger patients have to understand the long-term impact of the procedure and know that revision surgery in 15 to 20 years may be required, although on a less comprehensive basis.
12 P r e p a r i n g f o r To t a l H i p R e p l a c e m e n t Sur ger y Before surgery, a patient is generally asked to see their primary care physician for a general physical exam. The anesthesiologist will also evaluate the patient before the surgery to discuss the type of anesthetics that will be used. Prior to surgery, routine tests will be run to help assess a patient s fitness for the procedure. These tests might include: Blood and urine tests Chest X-ray EKG Patients in good health may also be able to donate one or two units of their own blood to receive during or after surgery. In many cases, this may not be necessary. Patients must remember to inform their doctor of the following: All current medications Any allergies to drugs, iodine or latex Previous instances of thrombosis of the legs or elsewhere Any recent infections Any past illnesses Before surgery, there are several important things to know: A spirin, medications containing aspirin or anti-inflammatories should not be taken one to two weeks before surgery, to minimize bleeding B lood thinners, such as Coumadin, should be discontinued at least several days prior to surgery, after consulting with your physician V itamins and iron supplements should continue to be taken before and after surgery, especially if the patient has donated his or her own blood for the procedure O verweight patients should try to lose weight to decrease the pressure on the new hip Patients should not smoke H ip replacement surgery will not take place if infections are present elsewhere in the body, such as the bladder or skin
13 Hospital Admission Patients are generally admitted on the day of the operation, unless an underlying condition such as diabetes or cardiac or pulmonary disease requires an additional day of pre-operative hospitalization. Patients should bring sleepwear, slippers or shoes and personal hygiene supplies with them to the hospital. PAT I E N T S S H O U L D N O T E AT O R D R I N K A F T E R M I D N I G H T B E F O R E S U R G E R Y. Patients who take medication regularly ever y day should discuss this with their anesthesiologist and/or sur geon. It may be recommended by the physicians that the dose be postponed or taken as usual with a small s i p o f w a t e r. A physical therapist may explain hip exercises and walker training before surgery or several days before admission to help patients become familiar with postsurgical expectations. The Sur ger y Hip replacement surgery is usually performed under a general anesthetic, but regional anesthesia is another good option. The procedure itself generally lasts two hours. The steps of the operation include: Making an incision along the side of the hip Dislocating the head of the femur and removing it using a power saw Preparing the socket and femur to accept the artificial hip I nserting the artificial joint and fixing it to the bone, either with or without cement A dding a femoral prosthesis to equalize leg length, with the modular ball on the stem Placing new the hip into the new socket M aintaining stability of the new joint through the tension of hip and thigh muscles Closing the wound with staples or sutures Installing a drain to minimize the post-operative hematoma
14 Post Sur ger y Day of Sur ger y The patient will be in bed or upright in a chair The diet will be advanced as tolerated Fluids will be delivered via an intravenous line in the arm for 24 to 48 hours Blood transfusions may be necessary to replace blood lost during surgery If a patient has difficulty urinating, a bladder catheter may be necessary B reathing exercises begin immediately after surgery and additional oxygen may be delivered through a small nasal tube Elastic stockings may be worn to improve circulation in the legs A n inflatable device delivering intermittent pressure may be placed around legs to aid in circulation and prevent blood clots Post-Operative Days One and Two P atients are encouraged to stand and walk with the help of a physical therapist, depending on their medical condition and strength W eight bearing on the operated side will depend upon the type of fixation used, and the bone quality. If cement was used the patient is usually allowed to walk on the operated leg with a walker; if cement was not used the patient will be instructed in weight-bearing restrictions, if any Th e physical therapist will begin the exercise programs that will be done both in bed and in the therapy department Sitting may be allowed, including using the bathroom Daily blood tests help the surgeon determine if a transfusion is necessary If a drain has been placed in the hip, it is usually removed by the second day D rink more fluids to prevent urinary tract infections, fever and constipation, and eat a well-balanced diet to help aid the healing process Pain medications will be given either as pills or injections By the second day, a regular diet may be started
15 Post-Operative Day Three By this day, the patient should be able to get around more easily P hysical therapists and other clinical workers will provide instruction about how to get out of bed, use the bathroom and dress Stair climbing is the last goal before discharge Returning Home Patients are usually discharged two to four days after surgery, depending on physical ability and other factors. Some patients may go directly to an in-patient rehabilitation or skilled nursing facility before returning home. A patient should contact his or her physician if: The wound becomes red or warm There is drainage from the wound Pain increases from the hip or thigh Either calf becomes painful, swollen or tender The patient develops an elevated temperature Sudden coughing or chest pain develops When can a patient begin to walk normally again? This depends on many factors, including the patient s pre-operative walking ability, the patient s size and physical condition, and the nature and quality of the implant fixation in the patient s bone. After surgery, your physician will know better how quickly you ll be able to advance to full weight-bearing.
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY
 HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
HEADER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY FROM PREPARATION TO RECOVERY ABOUT THE HIP JOINT The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the body to the legs. The leg bone is called the femur. The
Before Surgery You will likely be asked to see your family physician or an internal medicine doctor for a thorough medical evaluation.
 Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Anterior Hip Replacement - Before and After Surgery Your Hip Evaluation An orthopaedic surgeon specializes in problems affecting bones and joints. The surgeon will ask you many questions about your hip
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
Total Knee Replacement Contents Introduction Total Knee Replacement Preparing for surgery Pre-op visit Day of surgery After surgery (In Hospital) After surgery (In Rehab) Exercise Program and Physical
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Hip Replacement. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107
 Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
Information for Patients Hip Replacement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tel: 01473 702107 DMI ref: 0134-08.indd(RP) Issue 3: February 2008 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2005-2008. All rights reserved.
 Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Total Hip Replacement Hip replacement surgery, or arthroplasty, uses implants to resurface and replace the bones in the joint, re-creating the smooth gliding surfaces that were once intact. Hip replacement
Anterior Approach. to Hip Replacement Surgery
 Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org
 OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
OS01 Total Hip Replacement Further information You can get more information and share your experience at www.aboutmyhealth.org Local information You can get information locally from: Taunton and Somerset
PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY
 1 PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY It is important to us that all of our patients know what to expect before surgery, during their hospitalization and after surgery. Office Visits Planning begins with
1 PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY SURGERY It is important to us that all of our patients know what to expect before surgery, during their hospitalization and after surgery. Office Visits Planning begins with
YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
A Partnership for Better Healthcare A Partnership for Better Healthcare YOUR GUIDE TO TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PEI Limited M50 Business Park Ballymount Road Upper Ballymount Dublin 12 Tel: 01-419 6900 Fax:
PALM BEACH ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE, P.A. FAQ: OUT-PATIENT SURGERY
 DISCLAIMER This information is a general guideline for most out-patient surgeries. Since every case is unique, your surgeon may give you further or differing instructions. Please follow his or her guidelines.
DISCLAIMER This information is a general guideline for most out-patient surgeries. Since every case is unique, your surgeon may give you further or differing instructions. Please follow his or her guidelines.
Total Hip Replacement
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Total Hip Replacement The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Procedure Information Guide Total hip replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every effort to ensure that the
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
 Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total Knee Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview Reasons for Surgery Evaluation Preparing for Surgery Your Surgery Risks Expectations after Surgery Convalescence Also: Partial Knee Replacement Overview
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Total Hip Replacement Surgery Home Care Instructions Surgery: Date: Doctor: This handout will review the care you need to follow once you are home. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask your
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments. For Knee Replacement Surgery
 No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments For Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Here s how it works....2 Why does my knee
No two knees are alike. That s why we personalize your surgery just for you. Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments For Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Here s how it works....2 Why does my knee
MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty MAKOplasty
 Pre-op Patient Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Your Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Page I 1 Partial Knee Resurfacing...2 Benefits Possible with the Procedure...4 Your Guide to Surgery...5 Frequently
Pre-op Patient Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Your Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Page I 1 Partial Knee Resurfacing...2 Benefits Possible with the Procedure...4 Your Guide to Surgery...5 Frequently
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
Anterior Hip Replacement
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of hip replacement and arthritis management must be made in
Fine jewelry is rarely reactive, but cheaper watches, bracelets, rings, earrings and necklaces often contain nickel.
 BEFORE SURGERY What should I do to prepare for my surgery? Arrange for a family member or friend to accompany you to the hospital on the day of your surgery. Cancel any dental appointments that fall within
BEFORE SURGERY What should I do to prepare for my surgery? Arrange for a family member or friend to accompany you to the hospital on the day of your surgery. Cancel any dental appointments that fall within
it s time for rubber to meet the road
 your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
your total knee replacement surgery Steps to returning to a Lifestyle You Deserve it s time for rubber to meet the road AGAIN The knee is the largest joint in the body. The knee is made up of the lower
.org. Shoulder Joint Replacement. Anatomy
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
Y O U R S U R G E O N S. choice of. implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y
 Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Y O U R S U R G E O N S choice of implants F O R Y O U R S U R G E R Y Your Surgeon Has Chosen the C 2 a-taper Acetabular System The
One REVISION TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Ted W. Parcel, DO Larry Martin, MD Scott Sherrill, MD
 One REVISION TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Ted W. Parcel, DO Larry Martin, MD Scott Sherrill, MD 84484 RTKR New Cover.indd 1 10/30/13 10:53 AM CMC-Lincoln has earned the Joint Commission s Gold Seal of Approval
One REVISION TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Ted W. Parcel, DO Larry Martin, MD Scott Sherrill, MD 84484 RTKR New Cover.indd 1 10/30/13 10:53 AM CMC-Lincoln has earned the Joint Commission s Gold Seal of Approval
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks
 Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Hip Replacement Surgery Understanding the Risks Understanding the Risks of Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction This booklet is designed to help your doctor talk to you about the most common risks you
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
 HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT Information for Patients WHAT IS HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT? The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head) and a part of the pelvis
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement The Knee Joint A total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgery performed to remove and replace your knee joint. The knee joint, comprised of the femur
Total Knee Replacement The Knee Joint A total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgery performed to remove and replace your knee joint. The knee joint, comprised of the femur
Arthritis of the hip. Normal hip In an x-ray of a normal hip, the articular cartilage (the area labeled normal joint space ) is clearly visible.
 Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Arthritis of the hip Arthritis of the hip is a condition in which the smooth gliding surfaces of your hip joint (articular cartilage) have become damaged. This usually results in pain, stiffness, and reduced
Delivering Excellence. Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust. Information for Patients. Hip and Knee service. Total Knee Replacement NHS
 www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
www.noc.nhs.uk/hipandknee/default.aspx Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre NHS Trust www.noc.nhs.uk NHS Total Knee Replacement Information for Patients Hip and Knee service Delivering Excellence Contents Page
Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Total knee replacement: The enhanced recovery programme Aim This leaflet aims to explain the enhanced recovery programme after total knee replacement surgery, and outline what
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
A PATIENT S GUIDE: UNDERSTANDING ROBOTIC KNEE SURGERY UNDERSTANDING MAKOPLASTY GARY WEXLER MD PALM BEACH ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE
 UNDERSTANDING MAKOPLASTY A PATIENT S GUIDE: UNDERSTANDING ROBOTIC KNEE SURGERY GARY WEXLER MD PALM BEACH ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Robotic Knee Replacement: A Joint Adventure INTRODUCTION 3 ANATOMY AND COMMON
UNDERSTANDING MAKOPLASTY A PATIENT S GUIDE: UNDERSTANDING ROBOTIC KNEE SURGERY GARY WEXLER MD PALM BEACH ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Robotic Knee Replacement: A Joint Adventure INTRODUCTION 3 ANATOMY AND COMMON
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery
 Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery You are scheduled for an admission to Cooper University Hospital for Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm surgery (EVAR). Please read this handout,
Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Surgery You are scheduled for an admission to Cooper University Hospital for Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm surgery (EVAR). Please read this handout,
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement
 Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with sciatic and lumbar plexus
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Replacement What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with sciatic and lumbar plexus
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Total Knee Replacement
 Dr C.S. Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities
Dr C.S. Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Total Joint Replacement
 Total Joint Replacement Brinceton M. Phipps MD Animas Orthopedic Associates 575 Rivergate Lane, Suite 105 Durango Colorado 970-259-3020 www.brincetonphippsmd.com www.animasorthopedics.com Frequently Asked
Total Joint Replacement Brinceton M. Phipps MD Animas Orthopedic Associates 575 Rivergate Lane, Suite 105 Durango Colorado 970-259-3020 www.brincetonphippsmd.com www.animasorthopedics.com Frequently Asked
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery
 Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with an additional nerve
Dr. Anseth s Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery What hospital do you use? Abbott Northwestern Hospital What type of anesthesia do you use? General anesthesia with an additional nerve
Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program
 Patient Education: Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program Thank you for choosing Johns Hopkins for your hip replacement surgery. We use a team-based approach, and you are
Patient Education: Hip Replacement Surgery Johns Hopkins Hip and Knee Replacement Program Thank you for choosing Johns Hopkins for your hip replacement surgery. We use a team-based approach, and you are
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Welcome to the Joint Replacement Center at DMOS. With over forty years of total joint experience, DMOS was the first group of surgeons in Iowa to perform the total joint procedures.
Total Knee Replacement Welcome to the Joint Replacement Center at DMOS. With over forty years of total joint experience, DMOS was the first group of surgeons in Iowa to perform the total joint procedures.
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Revision Total Hip Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Revision Hip Replacement or arthritis management. All decisions
Your Practice Online
 P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
P R E S E N T S Your Practice Online Disclaimer This information is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Knee replacement or arthritis management. All decisions about
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Living with Your New Knee
 AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Living with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Movements that you once took for granted
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide
 Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Lumbar Decompression Surgery Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page 3: Page 5: Page 7: Page 8: Page 9: Page 10: Page 11: Page 12: The Lumbar Spine Lumbar Surgery Before Surgery Medications Day of Surgery Evening
Total elbow joint replacement for rheumatoid arthritis: A Patient s Guide
 www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
www.orthop.washington.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview 2 Review of the condition 3 Considering surgery 5 Preparing for surgery 6 About the procedure 8 Recovering from surgery 9 Convalescence and Rehabilitation
Excision of Vaginal Mesh
 What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
[PREPARING FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT: IMPORTANT INSIGHT FOR PATIENTS]
![[PREPARING FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT: IMPORTANT INSIGHT FOR PATIENTS] [PREPARING FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT: IMPORTANT INSIGHT FOR PATIENTS]](/thumbs/26/7449249.jpg) 2012 US CENTER FOR SPORTS MEDICINE DR. COREY G. SOLMAN, JR. [PREPARING FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT: IMPORTANT INSIGHT FOR PATIENTS] Information regarding the expectations before, during and after surgery
2012 US CENTER FOR SPORTS MEDICINE DR. COREY G. SOLMAN, JR. [PREPARING FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT: IMPORTANT INSIGHT FOR PATIENTS] Information regarding the expectations before, during and after surgery
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
Total Hip Arthroplasty (Hip Replacement) PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Condition and treatment
 The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
The State of Queensland (Queensland Health), 2011 Permission to reproduce should be sought from [email protected] DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v4.00-04/2011 SW9336 Facility: Total Hip
One REVISION TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT. Ted W. Parcel, DO Scott Sherrill, MD
 One REVISION TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Ted W. Parcel, DO Scott Sherrill, MD 84484 RTHR New Cover.indd 1 10/30/13 10:53 AM CMC-Lincoln has earned the Joint Commission s Gold Seal of Approval for Disease-Specific
One REVISION TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Ted W. Parcel, DO Scott Sherrill, MD 84484 RTHR New Cover.indd 1 10/30/13 10:53 AM CMC-Lincoln has earned the Joint Commission s Gold Seal of Approval for Disease-Specific
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY. Dr C.S. Waller. Orthopaedic Surgeon
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Dr C.S. Waller Orthopaedic Surgeon Specializing in surgery of the hip and knee 83826199 What is Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy involves the inspection of the inside of the knee joint with a
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Anterior Cruciate Ligament
 Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Anterior Cruciate Ligament The anterior cruciate ligament or ACL is one of the major ligaments located in the knee joint. This ligament
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Anterior Cruciate Ligament The anterior cruciate ligament or ACL is one of the major ligaments located in the knee joint. This ligament
Low Back Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 Knee Microfracture Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Table of Contents 1. Introduction
Rehabilitation After Your Total Knee Replacement
 1809 E. 13 th Street Suite 200 Tulsa, OK 74104-4243 (918) 582-6800 www.toctulsa.com Rehabilitation After Your Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard
1809 E. 13 th Street Suite 200 Tulsa, OK 74104-4243 (918) 582-6800 www.toctulsa.com Rehabilitation After Your Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
Total Hip or Knee Joint Replacement
 Preparing for your Total Hip or Knee Joint Replacement Pre-operative education for patients St. Clair Hospital Center for Orthopedics Copyright 2011 by St. Clair Hospital The Orthopedic Team Physicians
Preparing for your Total Hip or Knee Joint Replacement Pre-operative education for patients St. Clair Hospital Center for Orthopedics Copyright 2011 by St. Clair Hospital The Orthopedic Team Physicians
Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Welcome to Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Welcome to the Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital.
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS Total Hip Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Welcome to Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Welcome to the Orthopaedic Department at Warwick Hospital.
Total Hip Replacement. University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center
 Total Hip Replacement University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center Total Hip Replacement Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided to undergo hip replacement surgery,
Total Hip Replacement University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center Total Hip Replacement Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided to undergo hip replacement surgery,
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Labeling Information System Description
 Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
Patient Labeling Information System Description The Trident Ceramic Acetabular System is an artificial hip replacement device that features a new, state-of-the-art ceramic-on-ceramic bearing couple. The
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
