How To Read An Mri Of Nkle Ligaments
|
|
|
- Erika Wright
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Perrich et al. MRI of nkle Ligaments Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay FOUS ON: nkle Ligaments on MRI: ppearance of Normal and Injured Ligaments Kiley D. Perrich 1 Douglas W. Goodwin 1 Paul J. Hecht 2 Yvonne heung 1 OJETIVE. The objective of our study was to provide a pictorial survey of MR images of ankle ligaments in various conditions from intact to disrupted. ONLUSION. MR images of ankle ligaments from a sample of patients with ankle pain or injury are presented and reviewed. Perrich KD, Goodwin DW, Hecht PJ, heung Y Keywords: ankle, ligaments, MRI DOI: /JR Received December 21, 2008; accepted after revision February 12, Department of Radiology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical enter, One Medical enter Dr., Lebanon, NH ddress correspondence to Y. heung (yvonne.cheung@ hitchcock.org). 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical enter, Lebanon, NH. ME This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. JR 2009; 193: X/09/ merican Roentgen Ray Society E very day in the United States, roughly 10,000 people will suffer an ankle injury, with most of these being sprains [1]. MRI can depict ligament injuries and has been used to differentiate ligament tears from other causes of ankle pain, such as fracture, osteochondral injury, or tendon injury. ppropriate treatment planning for ankle injury requires differentiation between the various types of ligament injury. This article provides an overview of the MRI features of normal and abnormal ligaments of the ankle (ppendix 1). Injured ligaments on MRI may appear disrupted, thickened, heterogeneous, or attenuated in signal intensity, and may be abnormal in contour. Fluid-sensitive sequences are often helpful in detecting injury. Imaging was performed at our institution using our standard protocol (Table 1) on a 1.5-T scanner (Signa Horizon LX, GE Healthcare) with an extremity coil. Images used here were collected from patients referred for ankle MRI for ankle pain or for evaluation of injury from December 29, 2003 through ugust 10, Lateral omplex The lateral collateral ligament complex (Figs. 1 4) is the most commonly injured group of ankle ligaments and is often associated with ligament injury elsewhere in the ankle. The lateral complex, comprising the anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular ligaments, is adequately imaged with routine axial and coronal images [2 6]. Hyalinization of tissue in the an terolateral recess, a meniscoid lesion, may result from injury of the anterior talofibular ligament and can contribute to anterolateral impingement [7]. Medial omplex and Deltoid Ligaments Isolated medial collateral or deltoid ligament injuries (Figs. 1 and 5 9) are infrequent and are commonly associated with injury to other ligaments or malleolar fractures. The medial collateral ligament complex is further divided into superficial and deep layers. The deep ligaments have talar attachments and cross one joint, whereas the superficial ligaments have variable attachments and cross two joints. The three components that are most often visualized on MRI include the tibiospring and tibionavicular ligaments in the superficial layer and the posterior tibiotalar ligament of the deep layer [8]. Syndesmosis The syndesmotic ligaments include the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, the inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament, and the inferior interosseous ligament or membrane [9] (Figs. 1 and 10 12). syndesmotic ligament injury or high ankle sprain can be isolated or may occur in conjunction with injury of other ligament groups. It may also be associated with Weber or ankle fractures [9 12]. We have not included an image of the inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament because no such ligament injuries were encountered during the period of this study. JR:193, September
2 Perrich et al. TLE 1: Routine MRI Protocol to Evaluate for Ligament Injury Sequence Plane Frequency- Selective Fat Saturation TR TE Inversion Time (ms) Section Thickness / Interval (mm) Echo Train Length Matrix Spin-echo T1-weighted Sagittal No / STIR Sagittal No 4, / Fast spin-echo proton density weighted Oblique axial a Varies 2,000 3, / Fast spin-echo proton density and T2-weighted xial Yes 3,500 6, / Fast spin-echo proton density weighted oronal Yes 2,000 3, / a 45 degrees between coronal and sagittal planes. Spring alcaneonavicular Ligament omplex The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is also known as the spring ligament complex (Figs. 1 and 13 15). The complex extends from the calcaneus to the tarsal navicular. fibrocartilaginous portion of the ligament lies superficial to the talar head. The spring ligament consists of three components: the superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament, the medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament, and the inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament [13, 14]. Of these, the superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most often involved in acute traumatic injury. Published studies of isolated spring ligament injuries are rare [15, 16]. ecause of the proximity of the spring ligament to the posterior tibial tendon and its integral function in stabilizing the plantar arch, spring ligament injuries are often associated with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction [17]. Summary MRI provides a means of depicting ligament injuries and can be used to differentiate ligament tears from other causes of ankle pain and injury. In this article we have provided guidelines for the MRI differentiation of the various types of ligament injury. cknowledgment We thank Daniel Deneen for his assistance in preparing and editing this manuscript. References 1. Holmer P, Sondergaard L, Konradsen L, Nielsen PT, Jorgensen LN. Epidemiology of sprains in the lateral ankle and foot. Foot nkle Int 1994; 15: Erickson SJ, Smith JW, Ruiz ME, et al. MR imaging of the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle. JR 1991; 156: Farooki S, Sokoloff RM, Theodorou DJ, et al. Visualization of ankle tendons and ligaments with MR imaging: influence of passive positioning. Foot nkle Int 2002; 23: Kreitner KF, Ferber, Grebe P, Runkel M, erger S, Thelen M. Injuries of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle: assessment with MR imaging. Eur Radiol 1999; 9: Labovitz JM, Schweitzer ME, Larka U, Solomon MG. Magnetic resonance imaging of ankle ligament injuries correlated with time. J m Podiatr Med ssoc 1998; 88: Lee SH, Jacobson J, Trudell D, Resnick D. Ligaments of the ankle: normal anatomy with MR arthrography. J omput ssist Tomogr 1998; 22: Robinson P, White LM, Salonen D, Daniels TR, Ogilvie-Harris D. nterolateral ankle impingement: MR arthrographic assessment of the anterolateral recess. Radiology 2001; 221: Mengiardi, Pfirrmann W, Vienne P, Hodler J, Zanetti M. Medial collateral ligament complex of the ankle: MR appearance in asymptomatic subjects. Radiology 2007; 242: artonicek J. natomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis and its clinical relevance. Surg Radiol nat 2003; 25: rown KW, Morrison W, Schweitzer ME, Parellada J, Nothnagel H. MRI findings associated with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. JR 2004; 182: Ebraheim N, Lu J, Yang H, Mekhail O, Yeasting R. Radiographic and T evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot nkle Int 1997; 18: Morris JR, Lee J, Thordarson D, Terk MR, rustein M. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute Maisonneuve fractures. Foot nkle Int 1996; 17: Mengiardi, Zanetti M, Schottle P, et al. Spring ligament complex: MR imaging anatomic correlation and findings in asymptomatic subjects. Radiology 2005; 237: Taniguchi, Tanaka Y, Takakura Y, Kadono K, Maeda M, Yamamoto H. natomy of the spring ligament. J one Joint Surg m 2003; 85-: hen JP, llen M. MR diagnosis of traumatic tear of the spring ligament in a pole vaulter. Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26: Pathria MN, Rosenstein, jorkengren G, Gershuni D, Resnick D. Isolated dislocation of the tarsal navicular: a case report. Foot nkle 1988; 9: nderson MW, Kaplan P, Dussault RG, Hurwitz S. ssociation of posterior tibial tendon abnormalities with abnormal signal intensity in the sinus tarsi on MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29: JR:193, September 2009
3 MRI of nkle Ligaments PPENDIX 1: nkle Ligaments Lateral complex nterior talofibular ligament Posterior talofibular ligament alcaneofibular ligament Medial complex (deltoid) Tibionavicular ligament Tibiospring ligament Tibiocalcaneal ligament nterior tibiotalar ligament Posterior tibiotalar ligament nkle syndesmosis nterior inferior tibiofibular ligament Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament Inferior transverse ligament Distal interosseous ligament or membrane Spring ligament complex (calcaneonavicular ligament) Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament Medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament Inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament Fig. 1 nkle ligaments. (See ppendix 1 for full ligament names.), Ligaments visible laterally: anterior talofibular (L1), calcaneofibular (L2), anterior inferior tibiofibular (S) ligaments., Ligaments visible posteriorly: interosseous ligament or membrane (S1), posterior inferior tibiofibular (S2), inferior transverse tibiofibular (S3), posterior talofibular (L3), tibiocalcaneal (M4), and posterior tibiotalar (M5) ligaments., Ligaments visible medially: anterior tibiotalar (M1), tibionavicular (M2), tibiospring (M3), tibiocalcaneal (M4), posterior tibiotalar (M5), and superomedial calcaneonavicular (Sp1) ligaments. D, Ligaments composing calcaneonavicular and spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular (Sp1), medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular (Sp2), and inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular (Sp3) ligaments. Tibiospring ligament (M3) belongs to superficial layer of medial complex and is included here to show its insertion to superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. D JR:193, September
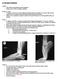
4 Perrich et al. Fig. 2 Lateral complex: anterior talofibular ligament. nterior talofibular ligament is weakest of lateral ligaments. It extends from anterolateral malleolar tip to talar neck, stabilizing talus., 44-year-old woman with chronic ankle pain. nterior talofibular ligament is well visualized on fluid-sensitive sequences such as this axial T2-weighted image. Uninjured ligament is of uniform thickness and low T1 and T2 signal intensity (arrow)., 17-year-old boy with pain and swelling and history of remote ankle injury. Partial tear of anterior talofibular ligament on axial T2-weighted image shows thickened ligament with increased internal signal (arrowhead)., 17-year-old boy with ankle pain after injury. omplete tear of anterior talofibular ligament on axial T2- weighted image shows discontinuous ligament surrounded by extensive fluid signal (arrow). D, 19-year-old woman with continued ankle pain after sprain. xial T2-weighted image shows nodular soft tissue occupying anterolateral gutter (arrow). Torn anterior talofibular ligament, seen in more distal image, is not included. D Fig. 3 Lateral complex: calcaneofibular ligament. alcaneofibular ligament lies deep in relation to peroneal tendons and extends from lateral malleolar tip to trochlear eminence, stabilizing subtalar joint. alcaneofibular is often partially imaged in coronal or axial planes; multiple images are often needed to visualize its entire course., 31-year-old woman with suspected anterior tibial tendon tear. Oblique axial proton density weighted image of intact calcaneofibular ligament (arrow) shows regular contour and homogeneously low signal. (Fig. 3 continues on next page) 690 JR:193, September 2009
5 MRI of nkle Ligaments Fig. 3 (continued) Lateral complex: calcaneofibular ligament. alcaneofibular ligament lies deep in relation to peroneal tendons and extends from lateral malleolar tip to trochlear eminence, stabilizing subtalar joint. alcaneofibular is often partially imaged in coronal or axial planes; multiple images are often needed to visualize its entire course., 24-year-old man with Weber type fracture of fibula. Oblique axial T2-weighted image of partial tear of calcaneofibular ligament shows fluid signal in ligament and mildly irregular contour (arrowhead)., 41-year-old woman with ankle trauma. Oblique axial T2-weighted image of complete tear of calcaneofibular ligament shows discontinuous ligament with adjacent fluid signal (arrow). Ligament at its calcaneal insertion (asterisk) is not disrupted. Fig. 4 Lateral complex: posterior talofibular ligament. Posterior talofibular is least frequently injured of three lateral complex ligaments, extending from posterior talus (lateral tubercle) to fibular malleolar fossa. Posterior talofibular often appears striated on MRI because of its fibrofatty composition [7]., 37-year-old man with medial ankle pain. Normal posterior talofibular ligament (arrow) has linear striations on this axial proton density weighted image., 17-year-old boy with ankle pain after injury. omplete tear of posterior talofibular ligament is seen as ligament defect on axial T2-weighted image. Torn ends of discontinuous ligament are surrounded by fluid signal (arrow). Fig. 5 Medial complex and deltoid: tibionavicular ligament. Tibionavicular ligament inserts onto navicular and is visible on only 55% of MR images of asymptomatic subjects. ecause of its variable visualization, it is unreliable in assessing ligament injury. oronal T2-weighted image in 73-year-old woman with tarsal tunnel syndrome and foot pain shows intact tibionavicular ligament (arrow). JR:193, September
6 Perrich et al. Fig. 6 Medial complex and deltoid: tibiospring ligament. Tibiospring ligament connects medial malleolar colliculus to superomedial spring ligament., 44-year-old woman with ankle pain. oronal proton density weighted image of intact tibiospring ligament shows its attachment to spring ligament (arrow)., 20-year-old woman with Weber type fracture. omplete tear of tibiospring ligament on coronal T2-weighted image shows discontinuous, irregular fibers (arrow). Fig. 7 Medial complex and deltoid: tibiocalcaneal ligament. Tibiocalcaneal connects medial malleolus to sustentaculum tali (asterisk). This ligament is visualized in 88% of asymptomatic subjects on MR images [13]. oronal T2-weighted image in 29-yearold man with ankle pain shows complete tear and distal disruption of tibiocalcaneal ligament (arrow). Fig. 8 Medial complex and deltoid: anterior tibiotalar ligament. nterior tibiotalar ligament is thin and of uniformly low signal intensity on proton density weighted images. It is inconsistently visualized on routine MRI studies. Its absence is not reliable indicator of injury. oronal proton density weighted image in 56-year-old woman with ankle and foot pain shows intact anterior tibiotalar ligament (arrow). 692 JR:193, September 2009
7 MRI of nkle Ligaments Fig. 9 Medial complex and deltoid: posterior tibiotalar ligament. Posterior tibiotalar is thickest of medial ligaments with intervening fat separating its fascicles, often resulting in striated appearance in normal ligament. Fascicular disruption, irregularity, and loss of striation are indicators of injury., 49-year-old man with chilles tendinopathy. oronal T2-weighted image of intact posterior tibiotalar ligament shows continuous fibers and intervening fat between fascicles (arrow)., 29-year-old man with ankle pain. oronal T2-weighted image of partial tear of posterior tibiotalar ligament shows irregular contour and disrupted fibers with fluid signal near its talar attachment (arrow)., 20-year-old man with persistent ankle pain after eversion injury. oronal T2-weighted image shows complete disruption of posterior tibiotalar ligament and irregular contour of visible fibers, none of which appears attached at its talar insertion (arrowhead). Fig. 10 Syndesmosis: anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. nterior inferior tibiofibular ligament extends from anterior tibial tubercle to fibular tubercle and is best visualized on axial images. Normal anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament may show fascicular appearance, which should not be confused with injury or tear., 43-year-old woman with ruptured plantar fascia. Intact anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament is low in signal intensity on axial proton density weighted image (arrow)., 19-year-old man with right-ankle pain after injury. xial T2-weighted image of partial tear of anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament shows fluid signal in thickened, irregular ligament (arrowhead)., 44-year-old man with high fibular fracture. xial proton density weighted image of complete tear of anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament shows discontinuous ligament (arrow). JR:193, September
8 Perrich et al. Fig. 11 Syndesmosis: posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament extends from posterior tibial tubercle to posterior fibula. Most inferior fascicles (not shown) comprise inferior transverse ligament., 17-year-old boy with avascular necrosis and steroid therapy. Intact posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (arrow) is seen on axial proton density weighted image., 44-year-old man with high fibular fracture. omplete tear of posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament on axial T2-weighted image is seen as discontinuous ligament (arrow). Fig. 12 Syndesmosis: distal interosseous ligament or membrane. Interosseous ligament is inferiormost portion of interosseous membrane. It connects medial fibula to lateral tibia. Its inferior margin lies adjacent to tibiofibular recess and is lined with synovium [11]. Recess extends superiorly 5 mm from joint line on MR images of healthy subjects [12]. When fluid signal extends more than 12 mm into tibiofibular recess, syndesmotic injury should be considered [12]., 14-year-old girl with ankle pain. Intact interosseous ligament or membrane is seen on coronal T2-weighted image. Note absence of fluid in tibiofibular recess (arrows)., 44-year-old woman with ankle pain. Torn interosseous ligament or membrane is seen on coronal T2-weighted image. Fluid signal extends into tibiotalar recess 13 mm superior to joint line (arrow), indicating high likelihood of interosseous ligament or membrane tear. Fig. 13 Spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament originates from sustentaculum tali of calcaneus and inserts onto superomedial tarsal navicular. It lies deep in relation to posterior tibial tendon (PTT). Superficial surface of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is composed of fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. Of three components of spring ligament complex, superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most likely to be injured. PTT dysfunction is often associated with spring ligament injury., 69-year-old man with high fibular fracture and pain. oronal T2-weighted image shows intact superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (straight arrow) and adjacent PTT (curved arrow). Normal tibiospring ligament is also visible (arrowhead). sterisk indicates fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. (Fig. 13 continues on next page) 694 JR:193, September 2009
9 MRI of nkle Ligaments Fig. 13 (continued) Spring ligament complex: superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament originates from sustentaculum tali of calcaneus and inserts onto superomedial tarsal navicular. It lies deep in relation to posterior tibial tendon (PTT). Superficial surface of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is composed of fibrocartilaginous gliding zone. Of three components of spring ligament complex, superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament is most likely to be injured. PTT dysfunction is often associated with spring ligament injury., 69-year-old man with ankle pain and talar osteochondral injury. xial T2-weighted image shows normal contour and homogeneously low signal in superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (arrowhead)., 50-year-old man with foot and ankle pain. Oblique axial T2-weighted image shows partial tear of superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament (arrow). bnormally thickened, irregular superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament contains bright fluid signal. Fig. 14 Spring ligament complex: medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament. Medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament extends from medial portion of navicular bone to calcaneal coronoid fossa and is best visualized in axial plane., 21-year-old man with chronic foot pain. Normal striated appearance of uninjured medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament is shown on axial T2-weighted image (arrow)., 50-year-old man with foot and ankle pain. omplete tear of medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament is shown on axial T2-weighted image. Note irregular, wavy contour of ligament and interruption at its calcaneal attachment (arrow). Fig. 15 Spring ligament complex: inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament. Inferoplantar calcaneonavicular ligament lies anterior to medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament, extending from inferior navicular bone to calcaneal coronoid fossa. It is usually thickest of three components of spring ligaments and is seen in 91% of asymptomatic subjects [13]. Sagittal T1-weighted image shows intact inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament (arrow) in 20-year-old man with ankle pain and suspected osteochondral injury. FOR YOUR INFORMTION This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. JR:193, September
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
MR Imaging of the Anatomy of and Injuries to the Lateral and Posterolateral Aspects of the Knee
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.158 on 07/15/16 from IP address 37.44.192.158. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.158 on 07/15/16 from IP address 37.44.192.158. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better. By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the
 The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Syndesmosis Injuries
 Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
Syndesmosis Injuries Dr. Alex Rabinovich Outline Anatomy Injury types and classification Treatment options Nonoperative vs. Operative Indications for operative Operative technique Postoperative management
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás
 Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Semmelweis University Department of Traumatology Dr. Gál Tamás Anatomy Ankle injuries DIRECT INDIRECT Vertical Compression (Tibia plafond Pilon) AO 43-A,B,C Suppination (adduction + inversion) AO 44-A
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer
 Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning
Malleolar fractures Anna Ekman, Lena Brauer How to use this handout? The left column is the information as given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes. Learning
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY. Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery. Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch
 CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
Ankle Sports injuries. Ben Yates
 Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2013;21(3):391-5 Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases Rajesh Botchu, 1 Patricia Allen, 2 Winston J Rennie 1 1 Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2013;21(3):391-5 Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases Rajesh Botchu, 1 Patricia Allen, 2 Winston J Rennie 1 1 Department of Musculoskeletal Radiology,
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears. Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
8 Ankle sprain. 8.1 Introduction. 8.2 Anatomy. OrthopaedicsOne Articles. Contents
 8 Ankle sprain Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Classification (Staging) Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Postoperative Care Outcome Complications Controversy
8 Ankle sprain Contents Introduction Anatomy Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Classification (Staging) Imaging Conservative Treatment Operative Treatment Postoperative Care Outcome Complications Controversy
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
PROTOCOLS FOR INJURIES TO THE FOOT AND ANKLE I. DIGITAL FRACTURES A. Background Digital fractures commonly occur in the workplace and are usually the result of a crush injury from a falling object, or
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO
 AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
AOBP with thanks to: Dawn Dillinger, DO Kyle Bodley, DO Common maneuvers in some sports that can increase risk for injury Jumping Pivoting while running Sudden stopping while running Maneuvering a ball
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC. Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program
 J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
J. M. Skamai, ATC R. L. Trenney, M.Ed., ATC Department of Kinesiology, Health, and Sport Science Athletic Training Education Program Evidence Category A Recommendation based on consistent and upper quality
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings
 Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Deficiencies of MRI in the diagnosis of chronic symptomatic lateral ankle ligament injuries
 Foot and Ankle Surgery 13 (2007) 171 176 www.elsevier.com/locate/fas Deficiencies of MRI in the diagnosis of chronic symptomatic lateral ankle ligament injuries V. Kumar MRCS (Glasg), BTEC (sports)*, I.
Foot and Ankle Surgery 13 (2007) 171 176 www.elsevier.com/locate/fas Deficiencies of MRI in the diagnosis of chronic symptomatic lateral ankle ligament injuries V. Kumar MRCS (Glasg), BTEC (sports)*, I.
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the ATP in the JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: Part Three consists of ankle injury evaluation and taping. Part Two
CHAPTER 58 Ankle and Foot
 CHAPTER 58 Ankle and Foot Riyad B. Abu-Laban and Nicholas G.W. Rose To him whose feet hurt, everything hurts. Socrates The ankle and foot are highly evolved structures designed to support the body s weight
CHAPTER 58 Ankle and Foot Riyad B. Abu-Laban and Nicholas G.W. Rose To him whose feet hurt, everything hurts. Socrates The ankle and foot are highly evolved structures designed to support the body s weight
DELTOID LIGAMENT INJURY. Raymond Tsukuda, D.P.M., F.A.C.F.A.S. Department of Podiatry Kaiser Baldwin Park Medical Center
 DELTOID LIGAMENT INJURY Raymond Tsukuda, D.P.M., F.A.C.F.A.S. Department of Podiatry Kaiser Baldwin Park Medical Center Objectives 1) Historical and recent perspective on deltoid injuries 2) Update review
DELTOID LIGAMENT INJURY Raymond Tsukuda, D.P.M., F.A.C.F.A.S. Department of Podiatry Kaiser Baldwin Park Medical Center Objectives 1) Historical and recent perspective on deltoid injuries 2) Update review
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY.
 QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
QUESTION I HAVE BEEN ASKED TO REHAB GRADE II AND III MCL INJURIES DIFFERENTLY BY DIFFERENT SURGEONS IN THE FIRST 6WEEKS FOLLOWING INJURY. SOME ARE HINGE BRACED 0-90 DEGREES AND ASKED TO REHAB INCLUDING
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013
 Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Ankle Injury/Sprains in Youth Soccer Players Elite Soccer Community Organization (ESCO) November 14, 2013 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, FACFAS Weil Foot and Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Ankle Injury/Sprains
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine
 Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
Head Position and Impact Direction in Whiplash Injuries: Associations with MRI-Verified Lesions of Ligaments and Membranes in the Upper Cervical Spine 1 Journal of Neurotrauma Volume 22, Number 11, November
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine
 Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Family Medicine / Emergency Medicine / Orthopedic: Ankle sprain Author: Joe Lau OMS-IV, Theodore Flaum, DO Introduction: Ankle sprain, a.k.a. sprained
Clinical Integration of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Family Medicine / Emergency Medicine / Orthopedic: Ankle sprain Author: Joe Lau OMS-IV, Theodore Flaum, DO Introduction: Ankle sprain, a.k.a. sprained
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete
 Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Foot and Ankle Injuries in the Adolescent Athlete Kevin Latz, MD Children s Mercy Hospital Center for Sports Medicine Foot and Ankle Injuries Very common Influenced by the unique properties of growth plates
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
Evaluation and Treatment of Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries
 55 Evaluation and Treatment of Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries David A. Porter, MD, PhD Abstract Athletes sustain ankle syndesmosis injuries far less frequently than they do lateral ankle sprains; however,
55 Evaluation and Treatment of Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries David A. Porter, MD, PhD Abstract Athletes sustain ankle syndesmosis injuries far less frequently than they do lateral ankle sprains; however,
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL)
 Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
Anatomic Percutaneous Ankle Reconstruction of Lateral Ligaments (A Percutaneous Anti ROLL) Mark Glazebrook James Stone Masato Takao Stephane Guillo Introduction Ankle stabilization is required when a patient
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains
 Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
The multitude of symptoms following a whiplash injury has given rise to much discussion because of the lack of objective radiological findings.
 HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
HELPFUL PERSONAL INJURY INFORMATION COURTESY OF RIVERVIEW CHIROPRACTIC FROM ABSTRACT: Dynamic kine magnetic resonance imaging in whiplash patients Pain Research and Management 2009 Nov-Dec 2009;Vol. 14,
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella
 Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
Ligamentous and Tendon Injuries About the Ankle
 Ligamentous and Tendon Injuries About the Ankle Dec. 8, 2004 Brecht & Watnik 2004, OTA Presentations Krause 2003, Miller s Review Course Mizel et al 2004, ICL 53 OKU Foot & Ankle 3 Outline Anatomy Sprains
Ligamentous and Tendon Injuries About the Ankle Dec. 8, 2004 Brecht & Watnik 2004, OTA Presentations Krause 2003, Miller s Review Course Mizel et al 2004, ICL 53 OKU Foot & Ankle 3 Outline Anatomy Sprains
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants.
 Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation
 167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis
 C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
C H A P T E R 1 5 FORGET ME NOT: The Triple Arthrodesis Andrea D. Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION The triple arthrodesis is a procedure that is performed much less commonly for the same conditions as it was 20
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lower Leg and Ankle Injuries. Ankle Injuries. Ankle Anatomy. Jon DeBord, PT, MS, ATC, SCS. Rehab Summit 2008. Most common injury in sports.
 Lower Leg and Ankle Injuries Jon DeBord, PT, MS, ATC, SCS Rehab Summit 2008 Ankle Injuries Most common injury in sports 38-45% of all sportsrelated injuries 86% are sprains Mechanism Forceful inversion
Lower Leg and Ankle Injuries Jon DeBord, PT, MS, ATC, SCS Rehab Summit 2008 Ankle Injuries Most common injury in sports 38-45% of all sportsrelated injuries 86% are sprains Mechanism Forceful inversion
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Ankle ligament injuries
 ARTIGO DE REVISÃO Ankle ligament injuries Per A.F.H. Renström, M.D., Ph.D. 1 and Scott A. Lynch, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT Acute ankle ligament sprains are common injuries. The majority of these occur during athletic
ARTIGO DE REVISÃO Ankle ligament injuries Per A.F.H. Renström, M.D., Ph.D. 1 and Scott A. Lynch, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT Acute ankle ligament sprains are common injuries. The majority of these occur during athletic
Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries
 Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 35 50 Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Fernando A. Peña, MDT, J. Chris Coetzee, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot and Ankle Service, University of Minnesota 2450 Riverside
Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 35 50 Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Fernando A. Peña, MDT, J. Chris Coetzee, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot and Ankle Service, University of Minnesota 2450 Riverside
Imaging of Sports Injuries
 Imaging of Sports Injuries Capable of tremendous mobility Paradox Must be loose enough to function but stable enough to prevent symptoms Shoulder injuries occur when the balance between stability & mobility
Imaging of Sports Injuries Capable of tremendous mobility Paradox Must be loose enough to function but stable enough to prevent symptoms Shoulder injuries occur when the balance between stability & mobility
Lateral Ankle Instability Repair using TWINFIX Ti 3.5 mm Suture Anchors
 *smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Lateral Ankle Instability Repair using TWINFIX Ti 3.5 mm Suture Anchors Prepared in Consultation with: James Calder, MD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Lateral Ankle Instability
*smith&nephew ANKLE TECHNIQUE GUIDE Lateral Ankle Instability Repair using TWINFIX Ti 3.5 mm Suture Anchors Prepared in Consultation with: James Calder, MD KNEE HIP SHOULDER EXTREMITIES Lateral Ankle Instability
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Plantar fasciitis - suspected
 Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Syndesmotic Injuries in Athletes
 23 Syndesmotic Injuries in Athletes Jeffrey R. Thormeyer, James P. Leonard and Mark Hutchinson Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Illinois, Chicago, USA 1. Introduction Ankle injuries are
23 Syndesmotic Injuries in Athletes Jeffrey R. Thormeyer, James P. Leonard and Mark Hutchinson Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Illinois, Chicago, USA 1. Introduction Ankle injuries are
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation
 Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation Poster No.: C-0809 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. A. Z. Khodair, R. L. Younes; Qwuesna/EG Extremities, Musculoskeletal
Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation Poster No.: C-0809 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. A. Z. Khodair, R. L. Younes; Qwuesna/EG Extremities, Musculoskeletal
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 16 (2005) 779 799 Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners Karen P. Barr, MD a, *, Mark A. Harrast, MD a,b a Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Box
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 16 (2005) 779 799 Evidence-Based Treatment of Foot and Ankle Injuries in Runners Karen P. Barr, MD a, *, Mark A. Harrast, MD a,b a Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Box
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. II. Elbow
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Ankle injuries are commonly
 Foot Fractures Frequently Misdiagnosed as Ankle Sprains DANIEL B JUDD, MD and DAVID H KIM, MD Tripler Army Medical Center, Honolulu, Hawaii Most ankle injuries are straightforward ligamentous injuries
Foot Fractures Frequently Misdiagnosed as Ankle Sprains DANIEL B JUDD, MD and DAVID H KIM, MD Tripler Army Medical Center, Honolulu, Hawaii Most ankle injuries are straightforward ligamentous injuries
The ankle is one of the most
 COVER ARTICLE Management of Ankle Sprains MICHAEL W WOLFE, MD, Lewis-Gale Clinic, Salem, Virginia TIM L UHL, PHD, AT-C, PT, and CARL G MATTACOLA, PHD, AT-C University of Kentucky College of Allied Health
COVER ARTICLE Management of Ankle Sprains MICHAEL W WOLFE, MD, Lewis-Gale Clinic, Salem, Virginia TIM L UHL, PHD, AT-C, PT, and CARL G MATTACOLA, PHD, AT-C University of Kentucky College of Allied Health
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Case Log Guidelines for Foot and Ankle Orthopaedic Surgery Review Committee for Orthopaedic Surgery
 Case Log Guidelines for Foot and Ankle Orthopaedic Surgery Review Committee for Orthopaedic Surgery The ACGME Case Log System for Foot and Ankle Orthopaedic Surgery allows fellows to document their operative
Case Log Guidelines for Foot and Ankle Orthopaedic Surgery Review Committee for Orthopaedic Surgery The ACGME Case Log System for Foot and Ankle Orthopaedic Surgery allows fellows to document their operative
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Shoulder Pain and Weakness
 Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
5/13/2015. NATA Position Statements. Implementing the NATA Position Statement Recommendations for Ankle Sprain Rehab: An Evidence-Based Approach
 Implementing the NATA Position Statement Recommendations for Ankle Sprain Rehab: An Evidence-Based Approach Thomas W. Kaminski, PhD, ATC, FNATA, FACSM, RC Fellow Professor/Director of Athletic Training
Implementing the NATA Position Statement Recommendations for Ankle Sprain Rehab: An Evidence-Based Approach Thomas W. Kaminski, PhD, ATC, FNATA, FACSM, RC Fellow Professor/Director of Athletic Training
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Acute Ankle Trauma: Value of a Short Dedicated Extremity MR Imaging Examination in Prediction of Need for Treatment 1
 Jeroen J. Nikken, MD, PhD Edwin H. G. Oei, MD, MSc Abida Z. Ginai, MD, PhD Gabriel P. Krestin, MD, PhD Jan A. N. Verhaar, MD, PhD Arie B. van Vugt, MD, PhD M. G. Myriam Hunink, MD, PhD Published online
Jeroen J. Nikken, MD, PhD Edwin H. G. Oei, MD, MSc Abida Z. Ginai, MD, PhD Gabriel P. Krestin, MD, PhD Jan A. N. Verhaar, MD, PhD Arie B. van Vugt, MD, PhD M. G. Myriam Hunink, MD, PhD Published online
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME. Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4.
 OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which
 To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
Shoulder Dyslexia: The Alphabet Soup. Alison Nguyen 4/13/06
 Shoulder Dyslexia: The Alphabet Soup Alison Nguyen 4/13/06 Mystery Cases Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 Shoulder Dyslexia: The Alphabet Soup Shoulder dyslexia: addressing the endless alphabet soup Ant-inf
Shoulder Dyslexia: The Alphabet Soup Alison Nguyen 4/13/06 Mystery Cases Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 Shoulder Dyslexia: The Alphabet Soup Shoulder dyslexia: addressing the endless alphabet soup Ant-inf
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
REHABILITATION OF TENDON AND LIGAMENT INJURIES
 REHABILITATION OF TENDON AND LIGAMENT INJURIES Carol Gillis, DVM, PhD, DACVSMR Equine Ultrasound & Rehabilitation carolgillis@earthlink.net www.equineultrasound.com 803-522-1700 The first step to healing
REHABILITATION OF TENDON AND LIGAMENT INJURIES Carol Gillis, DVM, PhD, DACVSMR Equine Ultrasound & Rehabilitation carolgillis@earthlink.net www.equineultrasound.com 803-522-1700 The first step to healing
Isolated Syndesmosis Ankle Injury
 Isolated Syndesmosis Ankle Injury Kars P. Valkering, MD; Diederik A. Vergroesen, MD; Peter A. Nolte, MD, PhD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search: 20121120-13 Isolated
Isolated Syndesmosis Ankle Injury Kars P. Valkering, MD; Diederik A. Vergroesen, MD; Peter A. Nolte, MD, PhD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search: 20121120-13 Isolated
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash. Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199
 On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
On Cervical Zygapophysial Joint Pain After Whiplash 1 Spine December 1, 2011; Volume 36, Number 25S, pp S194 S199 Nikolai Bogduk, MD, PhD FROM ABSTRACT Objective To summarize the evidence that implicates
Common foot and ankle ballet injuries
 Common foot and ankle ballet injuries The instrument through which dance speaks is also the instrument through which life is lived... the human body Martha Graham, 1979 How Can We Help You? Physical therapy
Common foot and ankle ballet injuries The instrument through which dance speaks is also the instrument through which life is lived... the human body Martha Graham, 1979 How Can We Help You? Physical therapy
Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 549109, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/549109 Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 549109, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/549109 Case Report Reconstructive Osteotomy for Ankle Malunion Improves Patient Satisfaction and Function
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
