Working Paper Series. RatSWD. Working Paper No Experiments, Surveys and the Use of Representative Samples as Reference Data
|
|
|
- Prudence Harmon
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 German Data Forum (RatSWD) RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 146 Experiments, Surveys and the Use of Representative Samples as Reference Data Thomas Siedler and Bettina Sonnenberg May 2010
2 Working Paper Series of the German Data Forum (RatSWD) The RatSWD Working Papers series was launched at the end of Since 2009, the series has been publishing exclusively conceptual and historical works dealing with the organization of the German statistical infrastructure and research infrastructure in the social, behavioral, and economic sciences. Papers that have appeared in the series deal primarily with the organization of Germany s official statistical system, government agency research, and academic research infrastructure, as well as directly with the work of the RatSWD. Papers addressing the aforementioned topics in other countries as well as supranational aspects are particularly welcome. RatSWD Working Papers are non-exclusive, which means that there is nothing to prevent you from publishing your work in another venue as well: all papers can and should also appear in professionally, institutionally, and locally specialized journals. The RatSWD Working Papers are not available in bookstores but can be ordered online through the RatSWD. In order to make the series more accessible to readers not fluent in German, the English section of the RatSWD Working Papers website presents only those papers published in English, while the the German section lists the complete contents of all issues in the series in chronological order. Starting in 2009, some of the empirical research papers that originally appeared in the RatSWD Working Papers series will be published in the series RatSWD Research Notes. The views expressed in the RatSWD Working Papers are exclusively the opinions of their authors and not those of the RatSWD. The RatSWD Working Paper Series is edited by: Chair of the RatSWD (2007/2008 Heike Solga; since 2009 Gert G. Wagner) Managing Director of the RatSWD (Denis Huschka) Contact: German Data Forum (RatSWD) Mohrenstraße Berlin office@ratswd.de
3 Experiments, Surveys and the Use of Representative Samples as Reference Data Thomas Siedler and Bettina Sonnenberg DIW Berlin (tsiedler[at]diw.de, bsonnenberg[at]diw.de) Abstract During the last two decades, laboratory experiments have come into increasing prominence and constitute a popular method of research to examine behavioral outcomes and social preferences. However, it has been debated whether results from these experiments can be extrapolated to the real world and whether, for example, sample selection into the experiment might constitute a major shortcoming of this methodology. This note discusses potential benefits of combining experimental methods and representative datasets as a means to overcome some of the limitations of lab experiments. We also outline how large representative surveys can serve as reference data for researchers collecting their own datasets in order to explore potential sample selection biases. Keywords: experiments, survey, representativity JEL-Classification: C01, C52, C8, C9, D0, D6, D81, D84 1
4 1. Introduction During the last two decades, laboratory experiments have come into increasing prominence and now constitute a popular method of research to examine behavioral outcomes and social preferences. There are obvious advantages of laboratory experiments. First, researchers can control the environment under which individuals make their decisions and allow causal inferences by exogenously varying one parameter while holding all others constant. Second, the simplicity of many such experiments makes it easy to explain the findings to nonacademics and policy makers. However, major limitations of most experiments are that they are administered to students, who usually self-select themselves into the study and are therefore not representative of the entire adult population. In fact, due to self-selection, experimental studies with student subjects might not even be representative of the entire student population. For example, Eckel and Grossman (2000) investigate the impact of recruitment methods on behavior in a series of dictator experiments with a charitable organisation as a recipient in laboratory sessions. The authors compare altruistic behavior among student subjects recruited voluntarily through announcements in graduate and undergraduate courses ( voluntary sample ) with students in which the experiment was conducted during class time ( pseudo-voluntary sample ). They find that pseudo-volunteers are significantly more generous on average than their volunteer counterparts, and that socioeconomic characteristics such as religion or survey measures of altruistic preferences have a larger effect on giving behavior among students recruited pseudo-voluntarily. Similarly, Harrison et al. (2007) examine potential self-selection bias in both a field experiment and a laboratory experiment with student subjects. The authors start with the observation that samples observed in the experiment might suffer from randomization bias (Heckman and Smith 1995). Being interested in individuals risk attitudes, the authors note that the likelihood to participate in the experiment might be higher for individuals with on average higher risk attitudes than among the general population. On the other hand, the researchers offer participants a fixed show-up fee that might encourage individuals that are more riskaverse to participate in the experiment, potentially outweighing sample selection into the experiment in their study due to randomization bias. The authors report significant selfselection into both the field experiment and the laboratory experiment with adult subjects drawn from the general Dutch population, arguing that their sample is on average more riskaverse than the general population (see also Roe et al. 2009). In addition, most laboratory experiments are conducted on very homogenous samples (typically students studying the same subject at the same university) and often information on potentially important socio- 2
5 economic background characteristics is missing or lacks sufficient variation. Another shortcoming of laboratory experiments is the lack of anonymity. In most laboratory studies, students play against each other and know that the other player is a student. Hence, the degree of anonymity is rather low. Both the degree of homogeneity and anonymity in the subject pool might influence revealed social preferences (Sapienza et al. 2007). The question has also been raised whether laboratory experiments are externally valid and to what extent laboratory findings can be extrapolated to the general population (Levitt and List 2007). A branch of the recent literature examines the external validity of laboratory experiments by comparing behavior in laboratory sessions with experimental outcomes in more heterogeneous and representative samples (Bosch-Domenech et al. 2002; Haigh and List 2005; Benz and Meier 2006). The majority of these studies report that the behavior in the lab differs from that observed in other contexts. For a detailed discussion of potential limitations of laboratory experiments measuring social preferences, see Levitt and List (2007). For a recent discussion regarding potential improvements and future challenges in the field of experimental economics, see Gächter (2009). Another strand of research in economics and the social sciences makes use of survey questions from large representative cross-sectional or household panel datasets. One criticism of using attitudinal questions from these surveys concerns the lack of behavioral underpinnings and the absence of meaningful survey questions in certain contexts. For example, Glaeser et al. (2000) and Ermisch et al. (2009) discuss the difficulties of measuring respondents trustworthiness by means of survey questions. Combining attitudinal survey questions with behavioral experiments that include monetary rewards can potentially provide a fuller understanding of economic behavior and help to overcome some of these shortcomings. This note briefly discusses potential benefits of combining experimental methods and representative datasets when studying economic outcomes and social behavior. We also provide a short overview about the recent literature combining the experimental approach with survey methods. Finally, we discuss potential benefits of using large representative surveys as reference data for researchers collecting their own datasets. An overview of recent selected studies combining behavioral experiments with survey questions or using representative surveys as reference datasets is provided in table 1. 3
6 2. Combining behavioral experiments and survey methods 2.1 Trust and trustworthiness A new research strand combines behavioral experiments and survey methods. Fehr et al. (2002) incorporate the standard trust-game experiment (Berg et al. 1995) into a representative survey of the German population and asked respondents several survey measures of trust. Fehr et al. (2002) find a positive association between attitudinal survey measures of trust and sender s behavior, but no significant correlation between survey-based measures of trust and trustworthiness in the experiment. In addition, the authors report that individuals aged 65 and above, highly skilled workers, and those living in larger households exhibit less trusting behavior in the experiment. Using nationally representative data for Germany, Naef and Schupp (2009) compare survey and behavioral measures of trust. The authors create a new survey measure of trust and find that it is significantly correlated with the experimental trust measure. Moreover, they report that their experimental measure of trust is not subject to a social desirability bias and is robust to variations in stakes and the use of strategy method. This study demonstrates how survey measures can be tested by combining the experimental approach with survey methods. In a representative sample of the Dutch population, Bellemare and Kröger (2007) measure levels of trust and trustworthiness elicited through an experiment similar to those presented by Berg et al. (1995) in a representative sample of the Dutch population. The authors also compare their representative trust experiment with a sample of college students in an equivalent laboratory experiment. They find that college students have considerably lower levels of trust and trustworthiness than individuals in the representative sample and that these differences can be explained mainly by differences in socio-economic and background characteristics, in particular age, gender, and education. For example, the authors find that women have higher levels of trust than men, but display lower levels of trustworthiness. In line with Fehr et al. (2002), Bellemare and Kröger (2007) find a positive, inverted U-shaped association between age and trust. The authors do not find evidence of a participation bias in their trust experiment with student subjects, and therefore argue that trust and trustworthiness as measured in the laboratory are informative about the behavior in the general population. Ermisch et al. (2009) integrate a new experimental trust design into a sample of the British population. The authors rationale for using an alternative trust design is based on observations that the sender s behavior in the standard trust-game experiment (Berg et al. 1995) is not only influenced by trust but also depends on other motivations such as sender s reciprocity, risk aversion, altruism, or inequality aversion (Cox 2004; Karlan 2005; Ermisch 4
7 and Gambetta 2006 and Sapienza et al. 2007). In their one-shot trust experiment, the sender faces the decision as to whether or not to pass on a fixed amount of money (e.g., whether or not to send 10. If 10 are sent, the experimenter increases it by 30 so that the second person receives 40) and the receiver must decide whether or not to pay back a fixed amount of money (e.g., the sender has the choice of either paying back 22 or keeping all 40). Thus, the players cannot choose whether or not to transfer a certain amount of money between, say, 1-10; rather they face the decision whether to transfer the entire amount or nothing. The authors argue that this binary trust game is more likely to measure revealed trust and trustworthiness than the standard trust game experiment, in which the possibility of sending any amount favours the intrusion of other motives such as gift giving, let s risk part of it, I like to gamble. Ermisch et al. (2009) find that the experiment is more likely to reveal trust if people are older, if they are homeowners, if their financial situation is comfortable, or if they are divorced or separated. Trustworthiness is lower if a person s financial situation is perceived by them as difficult or as just getting by. 2.2 Risk attitudes Another recent example demonstrating the benefits of combining incentive-compatible experimental measures with survey methods is the study by Dohmen et al. (2009). In a previous related study, Dohmen et al. (2007) examine the relationship between individual s risk aversion, impatience, and cognitive abilities. They find that lower cognitive abilities are significantly associated with greater risk aversion and more pronounced impatience. These relationships are found to be robust to controlling for a broad set of socio-economic characteristics, such as age, gender, education, and income, which are measured through standard survey questions. In their study, both risk aversion and impatience are measured by choice experiments that involve real monetary choices and relatively large stakes. Respondents were told in advance that the experiment was about financial decisions, that they would have the chance to win money, and that the earned amount would depend on their choices in the experiment. Subjects were also informed that every seventh participant would win. For instance, in the lottery experiment, a financial decision is represented by the choice between a certain payoff (Option A) and a risky lottery (Option B). Participants were also informed that, for each paired lottery, Option B always implies a 50 percent chance of winning 300 and a 50 percent chance of winning nothing. The experiment starts with the following lottery choice: respondents can choose between a certain payoff of 0 (Option A) and Option B. If participants choose Option B, the amount of Option A is increased by 10 in 5
8 the next decision round. Thus, the second lottery choice is between the safe payoff of 10 and Option B. Similarly, conditional on prior decisions, a third lottery choice is between a certain payoff of 20 and Option B. The experiment ends when subjects choose Option A for the first time, or when the maximum amount of 190 for Option A is reached. This study is another example demonstrating the potential benefits of combining experimental and survey measures in a representative sample of the population. 3. Using representative surveys as reference data In this section, we briefly discuss potential benefits of using large representative surveys as reference datasets for researchers collecting their own data. Household panels might offer a useful reference point for experimental studies, thanks to their longitudinal character and the sampling of all household members for example, the British Household Panel Study (BHPS), the new household panel Understanding Society in the United Kingdom, and the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP, Sozio-oekonomisches Panel). Register data can constitute another fruitful source of reference data (Harrison et al. 2007). The basic idea here is that large representative surveys can serve as reference data for researchers collecting datasets that do not represent the full universe of the population of interest (e.g., through clinical trials, intervention studies, laboratory and behavioral experiments, and cohort studies). An important issue when investigators collect their own data is whether the sample represents the general population, or conversely, whether it is selective (for example, by design or through choice-based sampling). This approach might offer several benefits. First, by asking participants similar questions to those in representative surveys, researchers can compare their sample with either a sub-sample or the whole representative survey. Second, in contrast to many of the scales and questionnaire instruments developed by psychologists, for instance, questions in household panel surveys like the SOEP or BHPS are not copyrighted and can be used by other researchers free of charge. Thus, these datasets can be a valuable point of reference for designing new questionnaires. Combining experimental sessions with a questionnaire collecting basic individuals socio-demographic characteristics used in representative surveys gives researchers valid information as to the representativeness of their sample with respect to the individual characteristics surveyed. Two recent studies exemplify the potential for using questions from a panel survey when researchers collect their own data. In Germany, Geyer et al. (2009) examine whether individuals aged with operated congenital heart disease have adverse employment 6
9 chances compared to people without heart problems. The authors compare their sample of patients (N=314; treatment group) with a sample drawn from the SOEP, which serves as a comparison group. The treatment group consisted of women and men who had a congenital heart disease and were operated on at the University Hospital of Göttingen. The authors conducted a face-to-face interview with patients using several SOEP questions. Comparing their hospital sample with the SOEP as reference data they found considerable differences between the two samples with respect to gender, age, and employment status. Two recent projects that also follow the idea of using a representative household panel study (SOEP) as reference data are the Berlin Aging Study II and the Brain Gene Behavior Project. The Berlin Aging Study II, collecting data on objective socio-economic and biological characteristics like objective health, functional capacity, subjective health, and well-being, draws on SOEP questions with regard to health and life satisfaction to enable comparisons with the SOEP data (Max Planck Institute for Human Development 2009). Likewise, the Brain Gene Behavior Project, a large-scale study on the molecular genetic basis for personality, cognitive, and individual behavioral differences, makes use of the SOEP questionnaire to exploit comparable reference data (Neuroeconomics Lab Bonn and Socio- Economic Panel 2009). In the United Kingdom the study by Ermisch et al. (2009) demonstrates how a panel survey can help in determining the extent to which a particular sample is representative of the general population. The authors integrate a new experimental trust design into a former sample of the British population and compare their trust sample with a sample from the BHPS. By using a questionnaire similar to the BHPS, the authors are able to determine that their trust sample over-represents women, people who are retired, older, divorced, or separated. Together, these two studies show that household panel studies can serve as useful reference data for researchers collecting their own samples and can help to reveal the representativeness of their own collected data. 4. Conclusion The studies reviewed demonstrate that enormous academic benefits can be derived from combining experimental studies with representative surveys. 1 First, experiments based on representative samples help to assess potential biases of studies based on student subjects who self-select themselves into the sample. This advances our knowledge on whether and to what 1 See also Falk et al. (2009). 7
10 extent experimental studies on student samples can be generalized. Second, research measuring both revealed preferences and stated preferences allows researchers to validate their measures. For example, Fehr et al. (2002), Ermisch et al. (2009), and Naef and Schupp (2009) report that answers to attitudinal questions on trust toward strangers do predict real trusting behavior in the experiment. The recent studies by Eckel and Grossman (2000) and Roe et al. (2009) demonstrate the importance of self-selection into experimental studies, and their studies suggest that results from laboratory experiments might not be generalized to the entire population. In this note, we briefly discussed potential benefits of using large representative survey as reference data for researchers who are collecting their own datasets and point readers to two recent examples in the literature. 8
11 Table 1: Studies Combining an Experimental Design with Survey Methods Author(s) Topic Method Data Finding Measure levels of trust and Trust and trustworthiness Representative sample of the trustworthiness elicited measured by an invest- andreward Dutch population and a through an experiment similar experiment. laboratory sample with college to those presented by Berg et students. al. (1995) in a representative sample of the Dutch population. Bellemare and Kröger 2007 Benz and Meier 2006 Dohmen et al Eckel and Grossman 2000 Explore the correlation between individual behavior in laboratory experiments and in a similar situation in the field. Investigate the relevance of survey questions on risktaking behavior in field experiments and actual behavior in the real world. Compare the effect of recruitment method in dictator experiments with student subjects. Donation lab experiments with college students. Risk-taking measured by a lottery game in a field experiment and SOEP survey questions with a representative sample of 450 participants. Altruism measured by means of dictator games. Secret use of the real donation spending behavior of the students. Comparison with representative data of the whole SOEP sample on seven different survey questions with regard to risk attitudes. Laboratory experiment with selfrecruited students (voluntary sample) and in classroom recruited college students during the class period (pseudovoluntary sample). The smaller amount of students investments predominantly demonstrates differences in socio-economic and background characteristics. While these characteristics can explain different revealed behavior, they have almost no impact on stated trust. Return ratios are significantly lower in the lab sample as well. The authors find a rather moderate or weak relationship between lab and field behavior. The general risk attitude survey questions is significantly correlated with behavior in the lottery game as well as with actual behavior in the real world, e.g., with regard to financial, sports, and healthrelated behavior. Simultaneously, specific behavior is best predicted by contextspecific risk survey measures in the respective domain. Volunteers are less generous in distributing endowments and are more motivated by incentives than classroomrecruited students. Respondents characteristics such as sex, religion, and altruism influence the behavior of pseudo-volunteers more than that of volunteers. The authors conclude that self- selection into the sample matters. 9
12 Author(s) Topic Method Data Finding Measure trust and One-shot trust experiment trustworthiness in Britain with former respondents of using an experimental and the BHPS in combination with survey design. survey questionnaires. Ermisch et al Fehr et al Investigate trust and trustworthiness by comparing behavioral experimental outcomes and representative survey data. Implementation of a trust experiment in a representative survey of the German population in Comparison with representative BHPS sample allows the authors to examine whether their experimental sample is representative of the general population For example, the authors report that their experimental sample over-represents women, people who are retired, divorced, or separated. Individual behavior in experiments is found to be a reliable and superior measure compared to standard common trust survey questions. Trust in strangers and past trusting behavior correlate with trust behavior in the experiment, but no survey measure predicts trustworthiness. Gächter et al Geyer et al Glaeser et al The authors present survey and experimental evidence on trust and voluntary cooperation in Russia using both a student and a nonstudent sample. Examine the effect of congenital heart disease on employment status. Examine the validity of trust survey questions with a behavioral trust experiment. One-shot public goods experiment. Sample of 628 patients surveyed in clinic combined with medical check-up (treatment group). Laboratory experiment with Harvard undergraduates. Not fully representative survey data of Russian non-students and a student subject pool. Their comparison group is 10 percent sample drawn from the German SOEP Survey measures on trust (selfreported attitudes and behavior) of 258 Harvard undergraduates. Non-students display higher levels of trust than students, and also contribute more to the public good as long as socioeconomic background is not controlled for. Individuals who believe that most other people are fair contribute significantly more to the public good game than those without such beliefs. Likewise, optimists make higher contributions than pessimists. The authors find significant differences between male patients and male control subjects. Those with congenital heart disease are less likely to be employed full-time, more likely to be employed parttime, and in marginal employment. The differences between treatment and control group depend on the severity of the disease. Ten out of 12 GSS trust questions do not predict trust, but are related to trustworthiness as measured in the experiment. Trust in the experiment is associated with past trusting behavior. 10
13 Author(s) Topic Method Data Finding Trust and trustworthiness rise with closer social distance. Harrison et al Investigate whether experiment samples are biased because of the risk of randomization. The authors undertake both a laboratory experiment and a field experiment to examine whether selection into the experiment influences measures of risk attitudes. Eliciting individual risk attitudes through an experimental lottery game in both a field experiment and a laboratory experiment. First, the authors collect information on subjects socioeconomic characteristics by means of questionnaires and use this information to correct for potential self-selection into the field experiment. Second, in their laboratory experiment, they investigate the impact of variation in recruitment information on individual risk attitudes. The authors find that the use of show-up fees generates a more risk-averse sample. Participants in both the field and laboratory experiment are found to be more risk-averse than the general population once they control for selection into the experiment. Levitt and List 2007 Naef and Schupp 2009 Discuss whether estimates on pro-social behavior from laboratory experiments can be extrapolated to the real world. Test the correlation and validity of trust survey questions with experimental measures of trust. Literature review. The authors argue that pro-social behavior in experiments depends on a number of experimental situation and design factors, e.g., stakes, sample recruitment, anonymity, as well as unobserved respondents characteristics. They caution against generalizing results from laboratory to real-world situations. Trust experiment with survey respondents, representative for Germany. Self-reported trust and trustworthiness by different measurements with an representative survey sample GSS Survey question do not measure trust in the experiment. However, the authors find a significant correlation between self-reported SOEP trust measures and experimental measures of trust. Students are found to be slightly more trustful than non-students. 11
14 References: Bosch-Domenech, A./Montalvo, J.G./Nagel, R. and Satorra, A. (2002): One, two, (three), infinity,...: Newspaper and lab beauty-contest experiments. American Economic Review 92 (5), Bellemare, C. and Kroeger, S. (2007): On representative social capital. European Economic Review 51, Benz, M. and Meier, S. (2006): Do people behave in experiments as in the field? Evidence from donations. Working Paper No. 248, Institute for Empirical Research in Economics, University of Zurich. Berg, J./Dickhaut, J. and McCabe, K. (1995): Trust, reciprocity, and social history. Games and Economic Behavior 10, Cox, J.C. (2004): How to identify trust and reciprocity. Games and Economic Behavior 46, Dhami, M.K./Hertwig, R. and Hoffrage, U. (2004): The Role of Representative Design in an Ecological Approach to Cognition. Psychological Bulletin 130 (6), Dohmen, T./Falk, A./Huffman, D. and Sunde, U. (2007): Are risk aversion and impatience related to cognitive ability? IZA discussion paper No [Forthcoming in the American Economic Review]. Dohmen, T./Falk, A./Huffman, D./Sunde, U./Schupp, J. and Wagner, G.G. (2009): Individual Risk Attitudes: New Evidence from a Large, Representative, Experimentally-Validated Survey. [Forthcoming in Journal of the European Economic Association]. Eckel, C.E. and Grossman, P.J. (2000): Volunteers and pseudo-volunteers: The effect of recruitment method in dictator experiments. Experimental Economics 3, Ermisch, J. and Gambetta, D. (2006): People s trust: the design of a survey-based experiment. ISER Working Paper 34/2006. Ermisch, J./Gambetta, D./Laurie, H./Siedler, T. and Uhrig, N. (2009): Measuring people s trust. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) 172 (4), Falk, A./Dohmen, T. and Sunde, U. (2009): Kontrolliert und repräsentativ: Beispiele zur Komplementarität von Labor- und Felddaten. Perspektiven der Wirtschaftspolitik 10 (1), Fehr, E./Fischerbach, U./von Rosenbladt, B./Schupp, J. and Wagner, G.G. (2002): A Nation-Wide Laboratory. Schmollers Jahrbuch 122 (4), Gächter, S./Herrmann, B. and Thöni, C. (2004): Trust, voluntary cooperation, and socio-economic background: survey and experimental evidence. Journal of Behavior & Organisation 55, Gächter, S. (2009): Experimental Economics. [In this volume]. Geyer, S./Norozi, K./Buchhorn, R. and Wessel, A. (2009): Chances of employment in a population of women and men after surgery of congenital heart disease: Gender-specific comparisons between patients and the general population. Congenital Heart Disease 4 (1), Glaeser E.L./Laibson, D.I./Scheinkman, J.A. and Soutter, C.L. (2000): Measuring trust. Quarterly Journal of Economics 115,
Schmollers Jahrbuch 129 (2009), 367 374 Duncker & Humblot, Berlin. European Data Watch. The German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP) as Reference Data Set
 Schmollers Jahrbuch 129 (2009), 367 374 Duncker & Humblot, Berlin European Data Watch This section offers descriptions as well as discussions of data sources that are of interest to social scientists engaged
Schmollers Jahrbuch 129 (2009), 367 374 Duncker & Humblot, Berlin European Data Watch This section offers descriptions as well as discussions of data sources that are of interest to social scientists engaged
Egalitarianism and Competitiveness
 Institute for Empirical Research in Economics University of Zurich Working Paper Series ISSN 1424-0459 Working Paper No. 415 Egalitarianism and Competitiveness Björn Bartling, Ernst Fehr, Michel André
Institute for Empirical Research in Economics University of Zurich Working Paper Series ISSN 1424-0459 Working Paper No. 415 Egalitarianism and Competitiveness Björn Bartling, Ernst Fehr, Michel André
Working Paper Series. RatSWD. Working Paper No. 163. DataCite: The International Data Citation Initiative. Datasets Programme.
 German Data Forum (RatSWD) www.germandataforum.de RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 163 DataCite: The International Data Citation Initiative Datasets Programme Max Wilkinson November 2010 Working
German Data Forum (RatSWD) www.germandataforum.de RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 163 DataCite: The International Data Citation Initiative Datasets Programme Max Wilkinson November 2010 Working
Strategic and Non-Strategic Pro-Social Behavior in Financial Markets
 Strategic and Non-Strategic Pro-Social Behavior in Financial Markets Arno Riedl Maastricht University Paul Smeets Maastricht University October 2011 Preliminary Version: Please do not cite or distribute
Strategic and Non-Strategic Pro-Social Behavior in Financial Markets Arno Riedl Maastricht University Paul Smeets Maastricht University October 2011 Preliminary Version: Please do not cite or distribute
Gender Stereotypes Associated with Altruistic Acts
 Gender Stereotypes Associated 1 Gender Stereotypes Associated with Altruistic Acts Lacey D. Seefeldt Undergraduate Student, Psychology Keywords: Altruism, Gender Stereotypes, Vignette Abstract Possible
Gender Stereotypes Associated 1 Gender Stereotypes Associated with Altruistic Acts Lacey D. Seefeldt Undergraduate Student, Psychology Keywords: Altruism, Gender Stereotypes, Vignette Abstract Possible
Financial capability and saving: Evidence from the British Household Panel Survey
 CRS02 NOVEMBER 2010 Financial capability and saving: Evidence from the British Household Panel Survey About the Consumer Financial Education Body The Consumer Financial Education Body (CFEB) is an independent
CRS02 NOVEMBER 2010 Financial capability and saving: Evidence from the British Household Panel Survey About the Consumer Financial Education Body The Consumer Financial Education Body (CFEB) is an independent
The Relationship Between Economic Preferences and Psychological Personality Measures
 D I S C U S S I O N P A P E R S E R I E S IZA DP No. 6470 The Relationship Between Economic Preferences and Psychological Personality Measures Anke Becker Thomas Deckers Thomas Dohmen March 2012 Armin
D I S C U S S I O N P A P E R S E R I E S IZA DP No. 6470 The Relationship Between Economic Preferences and Psychological Personality Measures Anke Becker Thomas Deckers Thomas Dohmen March 2012 Armin
Working Paper Series. RatSWD. Working Paper No. 47. Virtual Worlds as Petri Dishes for the Social and Behavioral Sciences
 RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 47 Virtual Worlds as Petri Dishes for the Social and Behavioral Sciences Edward Castronova, Matthew Falk December 2008 Working Paper Series of the Council
RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 47 Virtual Worlds as Petri Dishes for the Social and Behavioral Sciences Edward Castronova, Matthew Falk December 2008 Working Paper Series of the Council
Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for
 Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for 1 CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVES & RESEARCH APPROACH 2. FINDINGS a. Visits to Museums and Archaeological Sites b. Interest in Archaeology c.
Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for 1 CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVES & RESEARCH APPROACH 2. FINDINGS a. Visits to Museums and Archaeological Sites b. Interest in Archaeology c.
Working Paper Series des Rates für Sozial- und Wirtschaftsdaten, No. 163
 econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Wilkinson,
econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Wilkinson,
Seemingly Irrelevant Events Affect Economic Perceptions and Expectations: The FIFA World Cup 2006 as a Natural Experiment
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2275 Seemingly Irrelevant Events Affect Economic Perceptions and Expectations: The FIFA World Cup 2006 as a Natural Experiment Thomas Dohmen Armin Falk David Huffman
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2275 Seemingly Irrelevant Events Affect Economic Perceptions and Expectations: The FIFA World Cup 2006 as a Natural Experiment Thomas Dohmen Armin Falk David Huffman
GENDER BASED PRESCRIPTIONS Evidence for altruism
 0507 Documentos de Trabajo GENDER BASED PRESCRIPTIONS Evidence for altruism FERNANDO AGUIAR (IESA-CSIC, Córdoba) PABLO BRAÑAS-GARZA RAMÓN COBO-REYES (Universidad de Granada) NATALIA JIMÉNEZ (Universidad
0507 Documentos de Trabajo GENDER BASED PRESCRIPTIONS Evidence for altruism FERNANDO AGUIAR (IESA-CSIC, Córdoba) PABLO BRAÑAS-GARZA RAMÓN COBO-REYES (Universidad de Granada) NATALIA JIMÉNEZ (Universidad
Further professional education and training in Germany
 European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions Further professional education and training in Germany Introduction Reasons for participating in further training or education Rates
European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions Further professional education and training in Germany Introduction Reasons for participating in further training or education Rates
Charity as a Signal of Trustworthiness
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 5299 Charity as a Signal of Trustworthiness Sebastian Fehrler November 2010 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor Charity as a Signal
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 5299 Charity as a Signal of Trustworthiness Sebastian Fehrler November 2010 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor Charity as a Signal
Individual Risk Attitudes: Measurement, Determinants and Behavioral Consequences
 1 Individual Risk Attitudes: Measurement, Determinants and Behavioral Consequences Thomas Dohmen 1, Armin Falk 2, David Huffman 1, Uwe Sunde 3 Forthcoming in the Journal of The European Economic Association
1 Individual Risk Attitudes: Measurement, Determinants and Behavioral Consequences Thomas Dohmen 1, Armin Falk 2, David Huffman 1, Uwe Sunde 3 Forthcoming in the Journal of The European Economic Association
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
 NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES PRESENTED BY Name: WINNIE MUGERA Reg No: L50/62004/2013 RESEARCH METHODS LDP 603 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Date: APRIL 2013 SAMPLING Sampling is the use of a subset of the
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING TECHNIQUES PRESENTED BY Name: WINNIE MUGERA Reg No: L50/62004/2013 RESEARCH METHODS LDP 603 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Date: APRIL 2013 SAMPLING Sampling is the use of a subset of the
Life Satisfaction and Relative Income: Perceptions and Evidence
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4390 Life Satisfaction and Relative Income: Perceptions and Evidence Guy Mayraz Gert G. Wagner Jürgen Schupp September 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4390 Life Satisfaction and Relative Income: Perceptions and Evidence Guy Mayraz Gert G. Wagner Jürgen Schupp September 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
Working Paper Series. RatSWD. Working Paper No. 127. Potential and availability of market research data for empirical social and economic research
 RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 127 Potential and availability of market research data for empirical social and economic research Erich Wiegand August 2009 Working Paper Series of the Council
RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 127 Potential and availability of market research data for empirical social and economic research Erich Wiegand August 2009 Working Paper Series of the Council
Discrimination and In-Group Favoritism in a Citywide Trust Experiment
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2765 Discrimination and In-Group Favoritism in a Citywide Trust Experiment Armin Falk Christian Zehnder April 2007 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2765 Discrimination and In-Group Favoritism in a Citywide Trust Experiment Armin Falk Christian Zehnder April 2007 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
IPDET Module 6: Descriptive, Normative, and Impact Evaluation Designs
 IPDET Module 6: Descriptive, Normative, and Impact Evaluation Designs Intervention or Policy Evaluation Questions Design Questions Elements Types Key Points Introduction What Is Evaluation Design? Connecting
IPDET Module 6: Descriptive, Normative, and Impact Evaluation Designs Intervention or Policy Evaluation Questions Design Questions Elements Types Key Points Introduction What Is Evaluation Design? Connecting
The German Data Forum (RatSWD) and its Mission for the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences
 The German Data Forum (RatSWD) and its Mission for the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences Claudia Oellers (RatSWD) Dr. Ingrid Tucci (DIW Berlin) Le German Data Forum (RatSWD) et sa mission pour
The German Data Forum (RatSWD) and its Mission for the Social, Behavioral, and Economic Sciences Claudia Oellers (RatSWD) Dr. Ingrid Tucci (DIW Berlin) Le German Data Forum (RatSWD) et sa mission pour
June 2013. Financial literacy and inclusion
 June 2013 Financial literacy and inclusion Results of oecd/infe survey across CouNtRIes and by gender FINANCIAL LITERACY AND INCLUSION: RESULTS OF OECD/INFE SURVEY ACROSS COUNTRIES AND BY GENDER FOREWORD
June 2013 Financial literacy and inclusion Results of oecd/infe survey across CouNtRIes and by gender FINANCIAL LITERACY AND INCLUSION: RESULTS OF OECD/INFE SURVEY ACROSS COUNTRIES AND BY GENDER FOREWORD
Trust and Control at the Workplace: Evidence from Representative Samples of Employees in Europe
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4297 Trust and Control at the Workplace: Evidence from Representative Samples of Employees in Europe Christian Grund Christine Harbring July 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4297 Trust and Control at the Workplace: Evidence from Representative Samples of Employees in Europe Christian Grund Christine Harbring July 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur
Risk Aversion and Sorting into Public Sector Employment
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 3503 Risk Aversion and Sorting into Public Sector Employment Christian Pfeifer May 2008 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor Risk
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 3503 Risk Aversion and Sorting into Public Sector Employment Christian Pfeifer May 2008 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor Risk
Who Chooses Annuities? An Experimental Investigation of the Role of Gender, Framing and Defaults
 Who Chooses Annuities? An Experimental Investigation of the Role of Gender, Framing and Defaults Julie R. Agnew, Lisa R. Anderson, Jeffrey R. Gerlach and Lisa R. Szykman December 18, 2007 Julie R. Agnew
Who Chooses Annuities? An Experimental Investigation of the Role of Gender, Framing and Defaults Julie R. Agnew, Lisa R. Anderson, Jeffrey R. Gerlach and Lisa R. Szykman December 18, 2007 Julie R. Agnew
Working Paper Series. RatSWD. Working Paper No. 2. A Modern Statistical Infrastructure for Excellent Research an Policy Advice
 RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 2 A Modern Statistical Infrastructure for Excellent Research an Policy Advice Report on the German Council for Social and Economic Data during its First Period
RatSWD Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 2 A Modern Statistical Infrastructure for Excellent Research an Policy Advice Report on the German Council for Social and Economic Data during its First Period
Good decision vs. good results: Outcome bias in the evaluation of financial agents
 Good decision vs. good results: Outcome bias in the evaluation of financial agents Christian König-Kersting 1, Monique Pollmann 2, Jan Potters 2, and Stefan T. Trautmann 1* 1 University of Heidelberg;
Good decision vs. good results: Outcome bias in the evaluation of financial agents Christian König-Kersting 1, Monique Pollmann 2, Jan Potters 2, and Stefan T. Trautmann 1* 1 University of Heidelberg;
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF WORKFORCE DIVERSITY IN SERVICE AND MANUFACTURING SECTORS IN INDIA
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Business Management (IMPACT: IJRBM) ISSN(E): 2321-886X; ISSN(P): 2347-4572 Vol. 2, Issue 3, Mar 2014, 1-8 Impact Journals A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF WORKFORCE DIVERSITY
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Business Management (IMPACT: IJRBM) ISSN(E): 2321-886X; ISSN(P): 2347-4572 Vol. 2, Issue 3, Mar 2014, 1-8 Impact Journals A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF WORKFORCE DIVERSITY
Working Paper Series of the German Data Forum (RatSWD)
 Working Paper Series of the German Data Forum (RatSWD) The RatSWD Working Papers series was launched at the end of 2007. Since 2009, the series has been publishing exclusively conceptual and historical
Working Paper Series of the German Data Forum (RatSWD) The RatSWD Working Papers series was launched at the end of 2007. Since 2009, the series has been publishing exclusively conceptual and historical
Gambling participation: activities and mode of access
 Gambling participation: activities and mode of access January 2015 1 Key findings 1.1 The following findings are based on a set of questions commissioned by the Gambling Commission in omnibus surveys conducted
Gambling participation: activities and mode of access January 2015 1 Key findings 1.1 The following findings are based on a set of questions commissioned by the Gambling Commission in omnibus surveys conducted
Long-term impact of childhood bereavement
 Long-term impact of childhood bereavement Preliminary analysis of the 1970 British Cohort Study (BCS70) Samantha Parsons CWRC WORKING PAPER September 2011 Long-Term Impact of Childhood Bereavement Preliminary
Long-term impact of childhood bereavement Preliminary analysis of the 1970 British Cohort Study (BCS70) Samantha Parsons CWRC WORKING PAPER September 2011 Long-Term Impact of Childhood Bereavement Preliminary
Do testosterone levels in females have influence on the distrust game, the beauty contest game, and risk-aversion?
 Do testosterone levels in females have influence on the distrust game, the beauty contest game, and risk-aversion? Takafumi MATSUBA, Jun SATO and Kenya KURA Abstract One of the famous neuroscientific studies
Do testosterone levels in females have influence on the distrust game, the beauty contest game, and risk-aversion? Takafumi MATSUBA, Jun SATO and Kenya KURA Abstract One of the famous neuroscientific studies
Summary. Accessibility and utilisation of health services in Ghana 245
 Summary The thesis examines the factors that impact on access and utilisation of health services in Ghana. The utilisation behaviour of residents of a typical urban and a typical rural district are used
Summary The thesis examines the factors that impact on access and utilisation of health services in Ghana. The utilisation behaviour of residents of a typical urban and a typical rural district are used
Disability Living Allowance Reform. Equality Impact Assessment May 2012
 Disability Living Allowance Reform Equality Impact Assessment May 2012 Reform of Disability Living Allowance Brief outline of the policy 1. Disability Living Allowance is a benefit that provides a cash
Disability Living Allowance Reform Equality Impact Assessment May 2012 Reform of Disability Living Allowance Brief outline of the policy 1. Disability Living Allowance is a benefit that provides a cash
Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the
 Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the field Andrea Leuermann Benjamin Roth March 29, 2012 Work in progress Abstract We investigate how individuals assess
Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the field Andrea Leuermann Benjamin Roth March 29, 2012 Work in progress Abstract We investigate how individuals assess
Does Charity Begin at Home or Overseas?
 ISSN 1178-2293 (Online) University of Otago Economics Discussion Papers No. 1504 JUNE 2015 Does Charity Begin at Home or Overseas? Stephen Knowles 1 and Trudy Sullivan 2 Address for correspondence: Stephen
ISSN 1178-2293 (Online) University of Otago Economics Discussion Papers No. 1504 JUNE 2015 Does Charity Begin at Home or Overseas? Stephen Knowles 1 and Trudy Sullivan 2 Address for correspondence: Stephen
9.916 Altruism and Cooperation
 9.916 Altruism and Cooperation Today s Lecture I give everyone $10 Anonymous pairs Chance to send $0-$10 Anything you send, x3 How much do you send Puzzle of altruism: How could it evolve free-riders should
9.916 Altruism and Cooperation Today s Lecture I give everyone $10 Anonymous pairs Chance to send $0-$10 Anything you send, x3 How much do you send Puzzle of altruism: How could it evolve free-riders should
Leadership at School: Does the Gender of Siblings Matter?
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 6976 Leadership at School: Does the Gender of Siblings Matter? Giorgio Brunello Maria De Paola October 2012 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 6976 Leadership at School: Does the Gender of Siblings Matter? Giorgio Brunello Maria De Paola October 2012 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
Survey Research. Classifying surveys on the basis of their scope and their focus gives four categories:
 Survey Research Types of Surveys Surveys are classified according to their focus and scope (census and sample surveys) or according to the time frame for data collection (longitudinal and cross-sectional
Survey Research Types of Surveys Surveys are classified according to their focus and scope (census and sample surveys) or according to the time frame for data collection (longitudinal and cross-sectional
Incentives and response rates - first experiences from
 Incentives and response rates - first experiences from the SOEP-Innovation-Sample 2009 Jürgen Schupp - joint work with Martin Kroh, Elisabeth Liebau, Nico Siegel, Simon Huber, and Gert G. Wagner 2 nd Panel-Survey-Methodology-Workshop
Incentives and response rates - first experiences from the SOEP-Innovation-Sample 2009 Jürgen Schupp - joint work with Martin Kroh, Elisabeth Liebau, Nico Siegel, Simon Huber, and Gert G. Wagner 2 nd Panel-Survey-Methodology-Workshop
Descriptive Inferential. The First Measured Century. Statistics. Statistics. We will focus on two types of statistical applications
 Introduction: Statistics, Data and Statistical Thinking The First Measured Century FREC 408 Dr. Tom Ilvento 213 Townsend Hall ilvento@udel.edu http://www.udel.edu/frec/ilvento http://www.pbs.org/fmc/index.htm
Introduction: Statistics, Data and Statistical Thinking The First Measured Century FREC 408 Dr. Tom Ilvento 213 Townsend Hall ilvento@udel.edu http://www.udel.edu/frec/ilvento http://www.pbs.org/fmc/index.htm
4. Work and retirement
 4. Work and retirement James Banks Institute for Fiscal Studies and University College London María Casanova Institute for Fiscal Studies and University College London Amongst other things, the analysis
4. Work and retirement James Banks Institute for Fiscal Studies and University College London María Casanova Institute for Fiscal Studies and University College London Amongst other things, the analysis
Stigmatisation of people with mental illness
 Stigmatisation of people with mental illness Report of the research carried out in July 1998 and July 2003 by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) on behalf of the Royal College of Psychiatrists Changing
Stigmatisation of people with mental illness Report of the research carried out in July 1998 and July 2003 by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) on behalf of the Royal College of Psychiatrists Changing
Lab Experiments Are a Major Source of Knowledge in the Social Sciences
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4540 Lab Experiments Are a Major Source of Knowledge in the Social Sciences Armin Falk James J. Heckman October 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4540 Lab Experiments Are a Major Source of Knowledge in the Social Sciences Armin Falk James J. Heckman October 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009
 Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
BY Aaron Smith NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE MARCH 10, 2016 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES:
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE MARCH 10, 2016 BY Aaron Smith FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Aaron Smith, Associate Director, Research Dana Page, Senior Communications Manager 202.419.4372
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE MARCH 10, 2016 BY Aaron Smith FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Aaron Smith, Associate Director, Research Dana Page, Senior Communications Manager 202.419.4372
The Ariel Mutual Funds/Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. Black Investor Survey. Saving and Investing Among High Income African-American and White Americans
 The Ariel Mutual Funds/Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. Black Investor Survey: Saving and Investing Among High Income African-American and Americans April, 2000 0 Prepared for Ariel Mutual Funds and Charles
The Ariel Mutual Funds/Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. Black Investor Survey: Saving and Investing Among High Income African-American and Americans April, 2000 0 Prepared for Ariel Mutual Funds and Charles
Uni versi ty of Hei del berg. Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the field
 Uni versi ty of Hei del berg Department of Economics Discussion Paper Series No. 534 Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the field Andrea Leuermann and Benjamin
Uni versi ty of Hei del berg Department of Economics Discussion Paper Series No. 534 Does good advice come cheap? - On the assessment of risk preferences in the lab and the field Andrea Leuermann and Benjamin
The Wage Return to Education: What Hides Behind the Least Squares Bias?
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 8855 The Wage Return to Education: What Hides Behind the Least Squares Bias? Corrado Andini February 2015 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 8855 The Wage Return to Education: What Hides Behind the Least Squares Bias? Corrado Andini February 2015 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
Human Capital and Ethnic Self-Identification of Migrants
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2300 Human Capital and Ethnic Self-Identification of Migrants Laura Zimmermann Liliya Gataullina Amelie Constant Klaus F. Zimmermann September 2006 Forschungsinstitut
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2300 Human Capital and Ethnic Self-Identification of Migrants Laura Zimmermann Liliya Gataullina Amelie Constant Klaus F. Zimmermann September 2006 Forschungsinstitut
Who Buys Books in Canada?
 Who Buys Books in Canada? A Statistical Analysis Based on Household Spending Data http://www.hillstrategies.com info@hillstrategies.com Statistical insights on the arts, Vol. 3 No. 4 Hill Strategies Research
Who Buys Books in Canada? A Statistical Analysis Based on Household Spending Data http://www.hillstrategies.com info@hillstrategies.com Statistical insights on the arts, Vol. 3 No. 4 Hill Strategies Research
low first offers, exit early, and earn less profit. By A.Brooks and M.Schweitzer Paper found in a list cited on the webpage:
 110151467 1 #63 A Critique of: Can Nervous Nelly Negotiate? How anxiety causes negotiators to make low first offers, exit early, and earn less profit. By A.Brooks and M.Schweitzer Paper found in a list
110151467 1 #63 A Critique of: Can Nervous Nelly Negotiate? How anxiety causes negotiators to make low first offers, exit early, and earn less profit. By A.Brooks and M.Schweitzer Paper found in a list
Age and the development of trust and reciprocity *
 Age and the development of trust and reciprocity * Matthias Sutter,,# and Martin G. Kocher Max Planck Institute for Research into Economic Systems Jena University of Innsbruck This version: 15 December
Age and the development of trust and reciprocity * Matthias Sutter,,# and Martin G. Kocher Max Planck Institute for Research into Economic Systems Jena University of Innsbruck This version: 15 December
Attitudes to Mental Illness - 2011 survey report
 Attitudes to Mental Illness - 2011 survey report Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 Acknowledgements This document was published by the NHS Information
Attitudes to Mental Illness - 2011 survey report Copyright 2011, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All Rights Reserved. 1 Acknowledgements This document was published by the NHS Information
12/30/2012. Research Design. Quantitative Research: Types (Campbell & Stanley, 1963; Crowl, 1993)
 Quantitative Prepared by: Amanda J. Rockinson-Szapkiw Liberty University A research design is a plan that guides the decision as to: when and how often to collect data what data to gather and from whom
Quantitative Prepared by: Amanda J. Rockinson-Szapkiw Liberty University A research design is a plan that guides the decision as to: when and how often to collect data what data to gather and from whom
Chapter Seven. Multiple regression An introduction to multiple regression Performing a multiple regression on SPSS
 Chapter Seven Multiple regression An introduction to multiple regression Performing a multiple regression on SPSS Section : An introduction to multiple regression WHAT IS MULTIPLE REGRESSION? Multiple
Chapter Seven Multiple regression An introduction to multiple regression Performing a multiple regression on SPSS Section : An introduction to multiple regression WHAT IS MULTIPLE REGRESSION? Multiple
Socially Responsible Investments:
 Socially Responsible Investments: Return Expectations or Social Preferences? Arno Riedl Paul Smeets Maastricht University Abstract This paper explores why retail investors deviate from holding the market
Socially Responsible Investments: Return Expectations or Social Preferences? Arno Riedl Paul Smeets Maastricht University Abstract This paper explores why retail investors deviate from holding the market
Degree Outcomes for University of Reading Students
 Report 1 Degree Outcomes for University of Reading Students Summary report derived from Jewell, Sarah (2008) Human Capital Acquisition and Labour Market Outcomes in UK Higher Education University of Reading
Report 1 Degree Outcomes for University of Reading Students Summary report derived from Jewell, Sarah (2008) Human Capital Acquisition and Labour Market Outcomes in UK Higher Education University of Reading
EVALUATING POINT-OF-CARE TECHNOLOGY WITH THE IBM COMPUTER USABILITY SATISFACTION QUESTIONNAIRE
 EVALUATING POINT-OF-CARE TECHNOLOGY WITH THE IBM COMPUTER USABILITY SATISFACTION QUESTIONNAIRE Dr. Thomas W. Dillon, James Madison University, dillontw@jmu.edu M. Tony Ratcliffe, James Madison University,
EVALUATING POINT-OF-CARE TECHNOLOGY WITH THE IBM COMPUTER USABILITY SATISFACTION QUESTIONNAIRE Dr. Thomas W. Dillon, James Madison University, dillontw@jmu.edu M. Tony Ratcliffe, James Madison University,
Decision & Risk Analysis Lecture 6. Risk and Utility
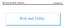 Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
Sample Size and Power in Clinical Trials
 Sample Size and Power in Clinical Trials Version 1.0 May 011 1. Power of a Test. Factors affecting Power 3. Required Sample Size RELATED ISSUES 1. Effect Size. Test Statistics 3. Variation 4. Significance
Sample Size and Power in Clinical Trials Version 1.0 May 011 1. Power of a Test. Factors affecting Power 3. Required Sample Size RELATED ISSUES 1. Effect Size. Test Statistics 3. Variation 4. Significance
Non-random/non-probability sampling designs in quantitative research
 206 RESEARCH MET HODOLOGY Non-random/non-probability sampling designs in quantitative research N on-probability sampling designs do not follow the theory of probability in the choice of elements from the
206 RESEARCH MET HODOLOGY Non-random/non-probability sampling designs in quantitative research N on-probability sampling designs do not follow the theory of probability in the choice of elements from the
Executive Summary. Viability of the Return of a Major League Baseball Franchise to Montreal (the Expos )
 Executive Summary Viability of the Return of a Major League Baseball Franchise to Montreal (the Expos ) November 2013 Table of Contents 1. CONTEXT AND OBJECTIVES... 3 2. RESEARCH METHODS... 5 3. KEY RESULTS...
Executive Summary Viability of the Return of a Major League Baseball Franchise to Montreal (the Expos ) November 2013 Table of Contents 1. CONTEXT AND OBJECTIVES... 3 2. RESEARCH METHODS... 5 3. KEY RESULTS...
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley
 Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
Chapter 9 Overall Outline
 Chapter 9 - Prosocial Behavior Objectives 1) An exploration of the bases of prosocial behaviour 2) An examination of the effects of personality, gender, religion, culture, and other variables on prosocial
Chapter 9 - Prosocial Behavior Objectives 1) An exploration of the bases of prosocial behaviour 2) An examination of the effects of personality, gender, religion, culture, and other variables on prosocial
Types of Error in Surveys
 2 Types of Error in Surveys Surveys are designed to produce statistics about a target population. The process by which this is done rests on inferring the characteristics of the target population from
2 Types of Error in Surveys Surveys are designed to produce statistics about a target population. The process by which this is done rests on inferring the characteristics of the target population from
2014 New Brunswick Gambling Prevalence Study. Department of Health and Department of Finance
 Department of Health and Department of Finance Report May 27, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary...5 Study Background... 5 Methodology... 6 Summary of Key Findings... 7 Conclusions... 15 1.0 Introduction...
Department of Health and Department of Finance Report May 27, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary...5 Study Background... 5 Methodology... 6 Summary of Key Findings... 7 Conclusions... 15 1.0 Introduction...
Better Sexy than Flexy? A Lab Experiment Assessing the Impact of Perceived Attractiveness and Personality Traits on Hiring Decisions
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7847 Better Sexy than Flexy? A Lab Experiment Assessing the Impact of Perceived Attractiveness and Personality Traits on Hiring Decisions Stijn Baert Lynn Decuypere December
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7847 Better Sexy than Flexy? A Lab Experiment Assessing the Impact of Perceived Attractiveness and Personality Traits on Hiring Decisions Stijn Baert Lynn Decuypere December
Discussion Papers. Silke Anger. Working Time as an Investment? The Effects of Unpaid Overtime on Wages, Promotions, and Layoffs
 Discussion Papers Silke Anger Working Time as an Investment? The Effects of Unpaid Overtime on Wages, Promotions, and Layoffs Berlin, December 2005 Opinions expressed in this paper are those of the author
Discussion Papers Silke Anger Working Time as an Investment? The Effects of Unpaid Overtime on Wages, Promotions, and Layoffs Berlin, December 2005 Opinions expressed in this paper are those of the author
Individual Differences in Susceptibility to Investment Fraud! Brian Knutson Stanford University"
 Individual Differences in Susceptibility to Investment Fraud Brian Knutson Stanford University" Gregory Samanez-Larkin" Yale University" April 2014 RESEARCH ON FRAUD SUSCEPTIBILITY 04/2014 1 Overview"
Individual Differences in Susceptibility to Investment Fraud Brian Knutson Stanford University" Gregory Samanez-Larkin" Yale University" April 2014 RESEARCH ON FRAUD SUSCEPTIBILITY 04/2014 1 Overview"
Is Temporary Agency Employment a Stepping Stone for Immigrants?
 D I S C U S S I O N P A P E R S E R I E S IZA DP No. 6405 Is Temporary Agency Employment a Stepping Stone for Immigrants? Elke Jahn Michael Rosholm March 2012 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
D I S C U S S I O N P A P E R S E R I E S IZA DP No. 6405 Is Temporary Agency Employment a Stepping Stone for Immigrants? Elke Jahn Michael Rosholm March 2012 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
Time limiting contributory Employment and Support Allowance to one year for those in the work-related activity group
 Time limiting contributory Employment and Support Allowance to one year for those in the work-related activity group Equality impact assessment October 2011 Equality impact assessment for time limiting
Time limiting contributory Employment and Support Allowance to one year for those in the work-related activity group Equality impact assessment October 2011 Equality impact assessment for time limiting
Insights: Financial Capability. The Financial Welfare of Military Households. Background. November 2014 Author: What s Inside:
 Insights: Financial Capability November 2014 Author: William Skimmyhorn Department of Social Sciences United States Military Academy West Point, NY 10996 william.skimmyhorn@usma.edu (845) 938-4285 What
Insights: Financial Capability November 2014 Author: William Skimmyhorn Department of Social Sciences United States Military Academy West Point, NY 10996 william.skimmyhorn@usma.edu (845) 938-4285 What
Sports Coaching in the UK III. A statistical analysis of coaches and coaching in the UK
 Sports Coaching in the UK III A statistical analysis of coaches and coaching in the UK January 2011 Contents Executive Summary... 3 1. Introduction... 5 2. Participation in Sport... 6 3. Use of Coaching...
Sports Coaching in the UK III A statistical analysis of coaches and coaching in the UK January 2011 Contents Executive Summary... 3 1. Introduction... 5 2. Participation in Sport... 6 3. Use of Coaching...
Your Future by Design
 Retirement Research Series Your Future by Design Health, money, retirement: The different needs of men and women This research report is one of several reports in the Your Future by Design Retirement Research
Retirement Research Series Your Future by Design Health, money, retirement: The different needs of men and women This research report is one of several reports in the Your Future by Design Retirement Research
Does student performance reduce imprisonment? *
 Does student performance reduce imprisonment? * Kaja Høiseth Brugård Center for Economic Research at NTNU and Department of Economics, Norwegian University of Science and Technology Torberg Falch Department
Does student performance reduce imprisonment? * Kaja Høiseth Brugård Center for Economic Research at NTNU and Department of Economics, Norwegian University of Science and Technology Torberg Falch Department
THE NATIONAL PERSONAL BUDGET SURVEY
 THE NATIONAL PERSONAL BUDGET SURVEY June 2011 Chris Hatton and John Waters Contents Summary 1 The POET Surveys 1 Major Findings 2 Background 5 Development of POET survey tools 5 How this survey came about
THE NATIONAL PERSONAL BUDGET SURVEY June 2011 Chris Hatton and John Waters Contents Summary 1 The POET Surveys 1 Major Findings 2 Background 5 Development of POET survey tools 5 How this survey came about
In contrast to other age groups, more Canadians
 Youth volunteering on the rise Frank Jones In contrast to other age groups, more Canadians aged 15 to 24 are becoming volunteers. The volunteer participation rate of most of the population changed little
Youth volunteering on the rise Frank Jones In contrast to other age groups, more Canadians aged 15 to 24 are becoming volunteers. The volunteer participation rate of most of the population changed little
Patient Responsibility in Health Care: An AARP Bulletin Survey
 Patient Responsibility in Health Care: An AARP Bulletin Survey May 2011 Patient Responsibility in Health Care: An AARP Bulletin Survey Data Collected by SSRS Report Prepared by Teresa A. Keenan, Ph.D.
Patient Responsibility in Health Care: An AARP Bulletin Survey May 2011 Patient Responsibility in Health Care: An AARP Bulletin Survey Data Collected by SSRS Report Prepared by Teresa A. Keenan, Ph.D.
BY Maeve Duggan NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE AUGUST 19, 2015 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT:
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE AUGUST 19, 2015 BY Maeve Duggan FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Maeve Duggan, Research Associate Dana Page, Senior Communications Manager
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE AUGUST 19, 2015 BY Maeve Duggan FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Maeve Duggan, Research Associate Dana Page, Senior Communications Manager
Financial incentives, personal information and dropout rate in online studies
 Financial incentives, personal information and dropout rate in online studies A. Frick 1, M. T. Bächtiger & U.-D. Reips Whereas in a classical laboratory setting participants often feel compelled to stay
Financial incentives, personal information and dropout rate in online studies A. Frick 1, M. T. Bächtiger & U.-D. Reips Whereas in a classical laboratory setting participants often feel compelled to stay
VIRTUAL VOLUNTEERING: Current Status and Future Prospects. Vic Murray University of Victoria Yvonne Harrison University of Victoria
 VIRTUAL VOLUNTEERING: Current Status and Future Prospects Vic Murray University of Victoria Yvonne Harrison University of Victoria VIRTUAL VOLUNTEERING: Current Status and Future Prospects Vic Murray University
VIRTUAL VOLUNTEERING: Current Status and Future Prospects Vic Murray University of Victoria Yvonne Harrison University of Victoria VIRTUAL VOLUNTEERING: Current Status and Future Prospects Vic Murray University
Motivations For Social Responsible investments: Return Expectations or Social Preferences? Abstract
 Motivations For Social Responsible investments: Return Expectations or Social Preferences? January 14, 2013 Abstract This paper explores why investors deviate from holding the market portfolio by investigating
Motivations For Social Responsible investments: Return Expectations or Social Preferences? January 14, 2013 Abstract This paper explores why investors deviate from holding the market portfolio by investigating
The German Taxpayer-Panel
 Schmollers Jahrbuch 127 (2007), 497 ± 509 Duncker & Humblot, Berlin The German Taxpayer-Panel By Susan Kriete-Dodds and Daniel Vorgrimler The use of panel data has become increasingly popular in socioeconomic
Schmollers Jahrbuch 127 (2007), 497 ± 509 Duncker & Humblot, Berlin The German Taxpayer-Panel By Susan Kriete-Dodds and Daniel Vorgrimler The use of panel data has become increasingly popular in socioeconomic
Clinical Study Design and Methods Terminology
 Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Chapter 5 Conceptualization, Operationalization, and Measurement
 Chapter 5 Conceptualization, Operationalization, and Measurement Chapter Outline Measuring anything that exists Conceptions, concepts, and reality Conceptions as constructs Conceptualization Indicators
Chapter 5 Conceptualization, Operationalization, and Measurement Chapter Outline Measuring anything that exists Conceptions, concepts, and reality Conceptions as constructs Conceptualization Indicators
Association Between Variables
 Contents 11 Association Between Variables 767 11.1 Introduction............................ 767 11.1.1 Measure of Association................. 768 11.1.2 Chapter Summary.................... 769 11.2 Chi
Contents 11 Association Between Variables 767 11.1 Introduction............................ 767 11.1.1 Measure of Association................. 768 11.1.2 Chapter Summary.................... 769 11.2 Chi
Empirical Methods in Applied Economics
 Empirical Methods in Applied Economics Jörn-Ste en Pischke LSE October 2005 1 Observational Studies and Regression 1.1 Conditional Randomization Again When we discussed experiments, we discussed already
Empirical Methods in Applied Economics Jörn-Ste en Pischke LSE October 2005 1 Observational Studies and Regression 1.1 Conditional Randomization Again When we discussed experiments, we discussed already
The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people
 The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people An analysis using the third wave of Understanding Society January 2014 www.pfrc.bris.ac.uk www.ilcuk.org.uk A working
The relationship between mental wellbeing and financial management among older people An analysis using the third wave of Understanding Society January 2014 www.pfrc.bris.ac.uk www.ilcuk.org.uk A working
Attitudes towards Financial Planners. Factuality research
 Attitudes towards Financial Planners Factuality research October 2014 Main findings 2 Main findings v v v v v The image of financial planners remains problematic, with 27% expressing a positive opinion
Attitudes towards Financial Planners Factuality research October 2014 Main findings 2 Main findings v v v v v The image of financial planners remains problematic, with 27% expressing a positive opinion
HIGH-RISK STOCK TRADING: INVESTMENT OR GAMBLING?
 HIGH-RISK STOCK TRADING: INVESTMENT OR GAMBLING? Jennifer Arthur, M.Sc. PhD Candidate, University of Adelaide Co-Authors: Dr. Paul Delfabbro & Dr. Robert Williams 14 th Annual Alberta Research Gambling
HIGH-RISK STOCK TRADING: INVESTMENT OR GAMBLING? Jennifer Arthur, M.Sc. PhD Candidate, University of Adelaide Co-Authors: Dr. Paul Delfabbro & Dr. Robert Williams 14 th Annual Alberta Research Gambling
Community Life Survey Summary of web experiment findings November 2013
 Community Life Survey Summary of web experiment findings November 2013 BMRB Crown copyright 2013 Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. What did we want to find out from the experiment? 4 3. What response rate
Community Life Survey Summary of web experiment findings November 2013 BMRB Crown copyright 2013 Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. What did we want to find out from the experiment? 4 3. What response rate
Introducing Social Psychology
 Introducing Social Psychology Theories and Methods in Social Psychology 27 Feb 2012, Banu Cingöz Ulu What is social psychology? A field within psychology that strives to understand the social dynamics
Introducing Social Psychology Theories and Methods in Social Psychology 27 Feb 2012, Banu Cingöz Ulu What is social psychology? A field within psychology that strives to understand the social dynamics
Performance Pay, Sorting and Social Motivation
 WORKING PAPER 07-12 Tor Eriksson and Marie-Claire Villeval Performance Pay, Sorting and Social Motivation Department of Economics ISBN 9788778822451 (print) ISBN 9788778822468 (online) Performance Pay,
WORKING PAPER 07-12 Tor Eriksson and Marie-Claire Villeval Performance Pay, Sorting and Social Motivation Department of Economics ISBN 9788778822451 (print) ISBN 9788778822468 (online) Performance Pay,
RESEARCH METHODS IN I/O PSYCHOLOGY
 RESEARCH METHODS IN I/O PSYCHOLOGY Objectives Understand Empirical Research Cycle Knowledge of Research Methods Conceptual Understanding of Basic Statistics PSYC 353 11A rsch methods 01/17/11 [Arthur]
RESEARCH METHODS IN I/O PSYCHOLOGY Objectives Understand Empirical Research Cycle Knowledge of Research Methods Conceptual Understanding of Basic Statistics PSYC 353 11A rsch methods 01/17/11 [Arthur]
Abstract. The finding of this thesis should contribute to the charity organizations to modify the fundraising strategy to promote the donors to give.
 Charity donor attitudes and preference - An analysis of a questionnaire survey in Norway Alima UMB School of Economics and Business Master Thesis 30 credits 2013 Abstract Since private donations take a
Charity donor attitudes and preference - An analysis of a questionnaire survey in Norway Alima UMB School of Economics and Business Master Thesis 30 credits 2013 Abstract Since private donations take a
Is Economics a Good Major for Future Lawyers? Evidence from Earnings Data
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 9416 Is Economics a Good Major for Future Lawyers? Evidence from Earnings Data John V. Winters October 2015 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 9416 Is Economics a Good Major for Future Lawyers? Evidence from Earnings Data John V. Winters October 2015 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the
Fidelity Charitable Gift Fund Gender Differences in Charitable Giving 2009 Executive Summary
 Fidelity Charitable Gift Fund Gender Differences in Charitable Giving 2009 Executive Summary Introduction To explore gender differences in charitable giving, the Fidelity Charitable Gift Fund fielded an
Fidelity Charitable Gift Fund Gender Differences in Charitable Giving 2009 Executive Summary Introduction To explore gender differences in charitable giving, the Fidelity Charitable Gift Fund fielded an
Paid and Unpaid Labor in Developing Countries: an inequalities in time use approach
 Paid and Unpaid Work inequalities 1 Paid and Unpaid Labor in Developing Countries: an inequalities in time use approach Paid and Unpaid Labor in Developing Countries: an inequalities in time use approach
Paid and Unpaid Work inequalities 1 Paid and Unpaid Labor in Developing Countries: an inequalities in time use approach Paid and Unpaid Labor in Developing Countries: an inequalities in time use approach
