About ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 2. Epithelial ovarian cancer. Diagnosis. What are the different types of ovarian cancer?
|
|
|
- Rosaline Jones
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fact sheet 2 About ovarian cancer We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected by ovarian cancer in the UK. We provide information and support, raise awareness and put you in touch with others who are suffering from ovarian cancer. Diagnosis There is a glossary with this fact sheet, to explain words you may not be familiar with. There are about 6800 new cases of ovarian cancer each year in the UK. The ovaries are tucked deep in the pelvis which is why this cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Symptoms can be similar to other conditions, which can delay diagnosis. At the moment, researchers are looking for the best way of finding or screening for ovarian cancer at an early stage. It will be some years before the results of these trials are known. At the moment ovarian cancer can be found with an ultrasound scan or CT scan. These scans are painless tests that create pictures of the inside of your body. Sometimes the cancer is found during an operation. The result of a blood test called CA125 can also suggest that you may have cancer. What are the different types of ovarian cancer? There are many types of ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer can be divided into three main groups epithelial, germ cell or sex-cord stromal tumours depending on the type of ovarian cells they are made up of. Epithelial ovarian cancer This is the most common type of ovarian cancer, making up 90% of cases. Epithelial ovarian cancer develops from cells that cover or line the ovaries. All epithelial ovarian cancers are grouped by how they look under a microscope. Although they may act slightly different, they are usually treated in the same way. This type of ovarian cancer can be subdivided into serous, mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell and borderline. Serous tumours make up 70% of cases. Mucinous tumours make up 10% of cases. Endometrioid tumours make up 5% of cases. They are more likely to be associated with disease in the uterus (womb). Sometimes an ovary is found to be affected when a woman is diagnosed with endometrial cancer. Clear cell tumours make up 3 to 5% of epithelial ovarian cancers and are nearly always malignant. This means they can spread to other parts of the body. Clear cell tumours tend to appear in women between 40 and 80 years old. sheet Clear cell tumours. Borderline tumours are also epithelial tumours, but behave differently. They make up 10 to 15% of cases, tend to grow slowly and have less chance of spreading. Often surgery is the only treatment needed. They grow on the outside of the ovary and do not tend to spread inside it. About ovarian cancer page 1 of 5 Ovacome 2009
2 This means that borderline tumours often have a better result than other ovarian tumours. time it is diagnosed. This is decided at the first operation or during scans. sheet Borderline ovarian tumours. Germ cell tumours Germ cell tumours make up 3% of ovarian cancers. They are made up of the cells that produce the eggs in the ovaries and are more common in young women. They can include dysgerminomas and non-dysgerminomas tumours. Not all germ cell tumours are malignant (cancer). Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 The cancer is on or in one or both ovaries and has not spread. The cancer has spread outside the ovary to the lining of the pelvis and can involve the uterus, fallopian tubes, bladder and rectum. The cancer has spread to the lining of the abdomen, the surface of the bowel, the omentum and the lymph glands in the pelvis or around the aorta. Sex-cord stromal tumours Sex-cord tumours are made up of the cells that produce hormones and support cells in the ovary. They make up 5% of ovarian cancers. The most common type is granulosa cell tumour and others include sertoli leydig. sheet Rare ovarian tumours. What is staging? Stage 4 The cancer has spread beyond the abdomen to the liver and lungs. The stages are then classified further with a, b and c. These letters show the state of the cancer at the time it is diagnosed. sheet The stages of ovarian cancer. You may also find that your doctor mentions grade or differentiation when talking about your cancer. The grade and differentiation of a tumour is decided by how the cancer cells look under the microscope. Grading is divided into three groups: one (low), two (intermediate) and three (high). It is a prediction of how your tumour may behave. Treatments Diagram of the female reproductive system The treatment and prognosis (how the disease will progress) depends on the type and stage of the cancer. The stage describes how the cancer has spread at the There are two main treatments for ovarian cancer surgery and chemotherapy. If your cancer has been found using a scan, a surgeon will look at the results with the multidisciplinary team (MDT). They will discuss which option is best for you. You may be offered one of these treatments or a combination of both. About ovarian cancer page 2 of 5 Ovacome 2009
3 Important questions to ask Will I be referred quickly to a medical team that specialises in diagnosing and treating gynaecological cancers? Will medical professionals discuss the surgery and chemotherapy with me before my treatment starts? Will the surgery be done by a gynaecologist trained in managing gynaecological cancers? Will my chemotherapy be carried out by staff with a special interest in gynaecological cancers? Can I see a specialist nurse or counsellor and a symptom-control (palliative care) team? Can I and my family get information on support services? Will I get information on any ongoing clinical trials? Surgery In most cases, surgery is needed. A specially qualified surgeon (a gynaeoncologist) should do this operation, which is called a staging laparotomy. Laparotomy means to operate on the abdomen. The surgeon will take samples from around your abdomen and send them to a laboratory to find out how far the cancer has spread. chemotherapy and operate later. You should discuss any advantages and disadvantages of this option with your surgeon. If you are a younger woman and the cancer is at an early stage, your surgeon may try to adapt the operation so that you may still be able to have a baby. After surgery you are likely to be in hospital for about a week and you will have to take it easy at home for several weeks. You should avoid lifting and driving for four to six weeks. Chemotherapy In most cases, you will be advised to have chemotherapy, either to prepare for surgery or to kill any cancer cells left after surgery. Chemotherapy is a type of drug that kills cancer cells. A doctor called an oncologist prescribes it. There are many different types of chemotherapy and your oncologist will discuss the various options. Most chemotherapies for ovarian cancer are given as an intravenous treatment (using a small tube into your vein) at hospital. The side effects of different chemotherapies vary. We can give you fact sheets to explain the different types of chemotherapy and the side effects. The aim of the operation is to remove as much of the tumour as possible, but cause as little damage as possible to your surrounding organs. Sometimes it is not possible to remove all the tumour. Where possible, the surgeon will do a hysterectomy (remove your womb) and a salpingo-oophorectomy (remove your ovaries and fallopian tubes). Your surgeon will discuss your operation and give you the chance to ask as many questions as you want to. You will be asked to sign a consent form to give your permission for the operation. Many surgeons prefer to do the operation first. However, in some cases it is better to try and reduce the size of the tumour with Remission and relapse About ovarian cancer page 3 of 5 Ovacome 2009 In most cases, chemotherapy is able to shrink the tumour until there is no sign of cancer left. This is called a complete remission. Sometimes a small amount of cancer is still left at the end of treatment. This is called a partial remission. In a small number of cases, the chemotherapy does not kill the cancer and the disease does not improve. If this happens, the oncologist will change the type of chemotherapy. After the treatment, you will be closely monitored and visit the hospital regularly to check that the cancer has not come back. Gradually the time between checks will get
4 longer. If you have any worries, you can see your oncologist in-between appointments. Although ovarian cancer is frequently controlled by chemotherapy (put into remission), very often it will come back. This is called a relapse or recurrence. It is difficult to predict how long the benefits of the chemotherapy will last. For some women it only lasts a few months, for others remission continues for over five years and they are considered cured. If your cancer comes back after the initial (first line) chemotherapy, your oncologist will suggest another course (second line). The aim is to achieve as long a remission as possible. Some women go on to have successful third- and fourth-line treatment, sometimes more. Your wishes will always be taken into account. how to use existing treatments more effectively. If you would like to take part in a trial, you should discuss this with your doctor. If you would like more information or you would like to discuss anything to do with ovarian cancer, phone our support line on , Monday to Friday from 9am to 4pm. Or, you can visit our website at Written by Louise Bayne, Chief Executive Officer, Ovacome. Reviewed July 2009 ovacome PO Box 6294, London W1A 7WJ Phone: Website: ovacome@ovacome.org.uk sheet Treatment for relapsed ovarian cancer. Many new ways of treating cancer are being investigated, as well as studies of About ovarian cancer page 4 of 5 Ovacome 2009
5 Glossary Aorta CA125 CT scan Laparatomy Lymph glands Malignant MDT Omentum Prognosis Remission Ultrasound scan The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdomen. An artery is a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart. This is a protein found in the blood. The amount of CA125 will be higher for some people with specific types of cancer. It is best known for ovarian cancer. A CT (computerised tomography) scan uses x-rays to produce images of the body. An operation to open the abdomen. A staging laparotomy is an abdominal operation to find if and how the cancer has spread. These are small pearl-like glands that are connected to the lymph system and act as filters to bacteria or cancer cells. Malignant tumours are ones that have the ability to invade and destroy surrounding tissues and can spread to other organs in the body. Multidisciplinary Team several members of different hospital departments who meet to discuss the treatment plan for individual patients. A sheet of fat in the abdomen that protects the intestines. An assessment of how the disease is expected to behave. Period of time when a cancer goes away. An ultrasound scan uses sound waves to build up a picture of the organs using a probe placed on the abdomen. A trans-vaginal scan does the same thing but is placed in the vagina. About ovarian cancer page 5 of 5 Ovacome 2009
Fact sheet 10. Borderline ovarian tumours. The difficult cases. What is borderline ovarian cancer (BOC)?
 For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Treatment of colon cancer
 Treatment of colon cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding colon cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents How treatment
Treatment of colon cancer This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding colon cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents How treatment
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT
 OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre National Cancer Plan May 2015 Contents About this booklet 1 The Ovaries
Fact sheet 9. Screening for ovarian cancer
 Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Screening for ovarian cancer Page 1 of 5 Ovacome
 Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Ovarian Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet
 U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Types of surgery for kidney cancer
 Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Useful information for cancer patients Contents This information is about the different operations that you may have for kidney cancer. Surgery can be used to treat almost any stage of kidney cancer. There
Ovarian cancer. Patient information from the BMJ Group. What is ovarian cancer? What are the symptoms?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
Patient information from the BMJ Group Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a serious disease. If it s diagnosed at an early stage, ovarian cancer can usually be cured. But even cancers that are more advanced
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Ovarian Cancer. in Georgia, 1999-2003. Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health
 Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Hysterectomy for womb cancer
 Gynaecology Oncology Service Hysterectomy for womb cancer April 2014 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to provide you with general information about your operation.
Gynaecology Oncology Service Hysterectomy for womb cancer April 2014 Great Staff Great Care Great Future INTRODUCTION This leaflet has been produced to provide you with general information about your operation.
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Ovarian cancer. A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment
 Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side of the womb.
 Surgery for Suspicious Ovarian Cysts Patient Information sheet The Ovaries The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side
Surgery for Suspicious Ovarian Cysts Patient Information sheet The Ovaries The ovaries are part of a woman s reproductive system. There are two ovaries, the size and shape of almonds, one on either side
The main surgical options for treating early stage cervical cancer are:
 INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
INFORMATION LEAFLET ON TOTAL LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY (TLRH) FOR EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER (TREATING EARLY STAGE CERVICAL CANCER BY RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY THROUGH KEYHOLE SURGERY) Aim of the leaflet
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org
 Understanding Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 Ovarian Cancer: An Overview...1 Risk Factors...2 Medical Evaluation...3 Working with your treatment
Understanding Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE foundationforwomenscancer.org Contents Introduction...1 Ovarian Cancer: An Overview...1 Risk Factors...2 Medical Evaluation...3 Working with your treatment
Treating Melanoma S kin Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Treating Melanoma Skin Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating melanoma skin cancer from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website.
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report
 Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families
 Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
How common is bowel cancer?
 information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
information Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology Bowel Cancer (1 of 6) How common is bowel cancer? Each year 35,000 people in Britain are diagnosed with cancer of the bowel, that is to say cancer
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Ovarian Cancer. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Ovarian Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Contents About This Booklet 1 The Ovaries 2 Understanding
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Ovarian Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Contents About This Booklet 1 The Ovaries 2 Understanding
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer Overview
 Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer Overview The information that follows is based on the more detailed information in our document Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer. You can get this document and other information
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer Overview The information that follows is based on the more detailed information in our document Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer. You can get this document and other information
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Uterine Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Uterine Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Your bladder cancer diary. WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network
 Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Your bladder cancer diary WA Cancer and Palliative Care Network Patient information and persons to contact Your Name Date of Birth URMN (Patient Hospital Unit Number) Address Phone Mobile GP Name Phone
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer
 Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
Quick Facts about Appendix Cancer What is the appendix? The appendix is a pouch-like tube attached to the first part of the large intestine (cecum). The appendix is about 10 centimetres long and has no
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Treatment options for recurrent ovarian cancer
 Treatment options for recurrent ovarian cancer There are a number of treatment options for women with recurrent ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy is the treatment most commonly offered and on occasion, surgery
Treatment options for recurrent ovarian cancer There are a number of treatment options for women with recurrent ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy is the treatment most commonly offered and on occasion, surgery
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis and treatment
 Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis and treatment Epithelial ovarian cancer Understanding your diagnosis and treatment Contents Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis and treatment Epithelial ovarian cancer Understanding your diagnosis and treatment Contents Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
How To Plan A Staging Investigation For Cancer Of The Oesophagus Or Stomach
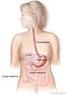 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Upper Gastrointestinal Centre Staging of cancers of the oesophagus and stomach Information for patients Introduction This leaflet gives you information about
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
Endometriosis. Information and advice. Page 12 Patient Information
 Endometriosis Information and advice Page 12 Patient Information Contents page What is Endometriosis?... page 3 Symptoms page 5 Treatments.. page 7 Further information and support.. page 9 Contact us page
Endometriosis Information and advice Page 12 Patient Information Contents page What is Endometriosis?... page 3 Symptoms page 5 Treatments.. page 7 Further information and support.. page 9 Contact us page
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
BOWEL CANCER. The doctor has explained that you have a growth or tumour, in your bowel or rectum and could be cancer.
 Patient and Carer Information BOWEL CANCER Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are not
Patient and Carer Information BOWEL CANCER Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are not
Understanding your pathology report
 Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Understanding your pathology report 2 Contents Contents Introduction 3 What is a pathology report? 3 Waiting for your results 4 What s in a pathology report? 4 Information about your breast cancer 5 What
Ovarian Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer
 Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Lymph Node Dissection for Penile Cancer Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Removal of Lymph Nodes Why are the Lymph Nodes so important when I have penile cancer? Lymph nodes are small bean shaped
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS
 INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
INTRAPERITONEAL HYPERTHERMIC CHEMOTHERAPY (IPHC) FOR PERITONEAL CARCINOMATOSIS AND MALIGNANT ASCITES. INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILY MEMBERS Description of Treatment A major difficulty in treating
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
The causes of kidney cancer are unknown. However, there are several factors that may increase your risk including:
 Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Kidney cancer Summary Kidney cancer is more common in people over the age of 55 years. Most kidney cancers are found when the doctor is checking for something else. A person is usually able to live quite
Follow-Up Care for Endometrial (Uterus) Cancer after Discharge from the Cancer Center
 Follow-Up Care for Endometrial (Uterus) Cancer after Discharge from the Cancer Center Disclaimer This is general information developed by The Ottawa Hospital. It is not intended to replace the advice of
Follow-Up Care for Endometrial (Uterus) Cancer after Discharge from the Cancer Center Disclaimer This is general information developed by The Ottawa Hospital. It is not intended to replace the advice of
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet
 Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Secondary liver cancer Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
I will be having surgery and radiation treatment for breast cancer. Do I need drug treatment too?
 What is node-positive breast cancer? Node-positive breast cancer means that cancer cells from the tumour in the breast have been found in the lymph nodes (sometimes called glands ) in the armpit area.
What is node-positive breast cancer? Node-positive breast cancer means that cancer cells from the tumour in the breast have been found in the lymph nodes (sometimes called glands ) in the armpit area.
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
How treatment is planned Giving your consent The benefits and disadvantages of treatment Second opinion
 Treatment overview for lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents How
Treatment overview for lung cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. Contents How
The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the chest wall and lymph nodes Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have had surgery for
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Tubular breast cancer
 Tubular breast cancer This booklet is for people who would like more information about tubular breast cancer. It describes what tubular breast cancer is, its symptoms, how a diagnosis is made and the possible
Tubular breast cancer This booklet is for people who would like more information about tubular breast cancer. It describes what tubular breast cancer is, its symptoms, how a diagnosis is made and the possible
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy
 Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy We dedicate this book to all of the women who have entrusted their care to us. By allowing us to take part in their surgery and after care,
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy bilateral salpingooophorectomy We dedicate this book to all of the women who have entrusted their care to us. By allowing us to take part in their surgery and after care,
About the kidneys and kidney cancer
 About the kidneys and kidney cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding kidney cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. The kidneys
About the kidneys and kidney cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding kidney cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 5. The kidneys
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection
 Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Radical Hysterectomy and Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's
Inflammatory breast cancer
 april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Patient information leaflet
 BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Cancer of the Thyroid Explained
 Cancer of the Thyroid Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the condition known as thyroid cancer. We hope it will answer some of the questions that you or those who care
Cancer of the Thyroid Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the condition known as thyroid cancer. We hope it will answer some of the questions that you or those who care
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Radiotherapy: English. Radiotherapy
 Radiotherapy: English Radiotherapy This fact sheet is about radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is used to treat some cancers. It can also be used to control the symptoms of cancer. Many people with cancer will
Radiotherapy: English Radiotherapy This fact sheet is about radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is used to treat some cancers. It can also be used to control the symptoms of cancer. Many people with cancer will
Kidney Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Kidney Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount
Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours
 Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours What is this cancer? Pancreatic Endocrine Tumours are also called Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. This cancer is rare and it starts
Chemoembolization for Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours What is this cancer? Pancreatic Endocrine Tumours are also called Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours. This cancer is rare and it starts
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health
 Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health Information for you Published in February 2005, minor amendments in June 2005 Revised 2009 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? Polycystic
Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health Information for you Published in February 2005, minor amendments in June 2005 Revised 2009 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? Polycystic
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER. How Will I Know If My Prostate Cancer Returns?
 WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide
 Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information there
Treating Oesophageal Cancer A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating from our website. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information there
