Patient Information Tethered Spinal Cord
|
|
|
- Moses Bryan
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Walton Centre for Neurology and Neurosurgery NHS Trust Author : Keren Smallwood and Amanda Deaves Date : August 2008 Review Date : August 2010 Patient Information Tethered Spinal Cord The Walton Centre for Neurology & Neurosurgery NHS Trust. All rights reserved. No reproduction by or for commercial organizations is allowed without the express written permission of the Walton Centre. You will need to bring this booklet into hospital with you
2 Patient Information Tethered Spinal Cord Appointment Record Date Day Clinic Comments Admission to hospital can be a daunting experience for most people, the following information is designed to give you information about your stay in hospital and what to expect during your stay. This information is intended as a guide only and may vary slightly depending upon your individual requirements. The Walton Centre is a Regional unit that admits patients 24 hours a day depending upon the urgency of their condition. It is because of this that you need to ring the hospital the morning of your admission to check that there is a bed available for you. Ring and ask the switchboard to bleep the bed manager on bleep We appreciate that you need to make arrangements for your hospital admission and discharge and we will make every effort to accommodate you, however, occasionally it is not possible and we do not want you to travel a long journey to be disappointed. The procedure you are being admitted for is UNTETHERING OF SPINAL CORD This booklet contains information about your hospital admission, procedure and care. It also has a glossary of terms (page ) you may find mentioned in this booklet or hear your surgeon use. From page 16 onward is physiotherapy information, giving you some guidance and describing the exercises you will need to do. Should you have any questions after reading this please do not hesitate to contact the Spinal Nurse Specialist on
3 Notes What does the spine compose of? The spinal column is a tower of bones (vertebra) that all sit on top of each other to form your vertebral column (back bone), from the base of your skull (cervical vertebra) to your tail bone (coccyx) just above your buttocks. These bones form a protective tube in which your spinal cord can run, with the bony column circling all around the spinal cord to protect it. Your spinal cord runs down the middle of this cylindrical tower of bones, and at the level of each bone (vertebra) it sends out 2 nerves, one on the left side and one on the right side. These nerves contain millions of nerve fibres and work almost like a telephone exchange. They carry messages from all parts of the body, inside and outside, back to our spinal cord and from there up the spinal cord to the brain. They also take messages from the brain to the body, for example, to tell our muscles to move our legs, or tell the bladder to open the valves that allow us to pass urine. These nerves contain a mixture of movement (motor) nerves and sensation (sensory) nerves. They also have their own areas of responsibility. The nerves in the neck part of the spine (cervical) are mostly responsible for the arms, hands, fingers and the area of the body from the neck to approx just above nipple line. The nerves in the Trunk (Thoracic) part of the spine, are mostly responsible for the chest and trunk area of the body. 2
4 The nerves in the lower back (lumbar and sacral) carry the messages for everything below the waist, including legs, feet and also bladder bowel and sexual function. Questions to ask my doctor or nurse Tethered Cord Syndrome Tethered cord syndrome is a complex condition that starts before we are born, as we are constructed, and grow in the womb. Soon after conception, as a baby develops in the womb, cells form together to build the spinal column. If this develops in a disorganised way the spinal column does not form fully and the spinal cord and/ or filum terminale can get trapped amidst this area of quickly developing structures. The spinal cord is then said to be tethered, which means it is abnormally attached within the bony spine. 80% of these abnormal developments are in the lower section of the spine (lumbar and sacral) Normally the spinal cord can move freely as you bend, stretch and grow. When these abnormal tissue attachments are present it limits the movement of the spinal cord within the bony spinal column. This is closely linked to a condition known as spina bifida occulta, which is a term used to describe an abnormality of the bone structure of the spine. This only causes a problem when there is an additional abnormality like a Tethered Cord. On page 14 and 15 you will find a list of terms and conditions some of which you may have heard your Doctor use. There may not be any or there may be a few that are relevant to you and your condition. Spinal cord tethering can also occur following an injury, infection or surgery to the spine when development of scar tissue can attach/tether the cord abnormally. As we have already mentioned the nerves at the bottom of the spine, carry the messages important for movement and sensation to the legs, feet and toes and they are also very important for bladder bowel and sexual function. 3
5 Exercise 6 Start Position Lying on your back with one leg straight and the other leg bent. (You can vary the exercise by having your foot pointing either upwards, inwards or outwards). Action Exercise your straight leg by pulling the toes up, straightening the knee and lifting the leg 20cm off the bed. Hold for approximately 5 seconds, then slowly relax. Repeat 10 times with both legs Tethered cord Syndrome The abnormal stretching puts tension on the spinal cord and nerves, this causes problems with the messages, getting to and from the legs, feet, toes, bladder, bowel and can cause some problems with sexual function. Tethered cord syndrome tends to be a progressive disorder, and can remain undiagnosed until adulthood. This is because the spinal cord and nerves are stretched slowly over time, and general physical wear and tear of daily movement adds to the situation. It is sometimes only recognised after subtle symptoms become more obvious. People can experience some problems passing urine, unusual patches of sensation in the feet or legs. These symptoms are all due to the abnormal stretching of the nerves that have the responsibility for these areas. Because the symptoms often develop very slowly over time, it may have been a while before you have realised there is a problem. Slight changes can often be attributed to other more common conditions or reasons. Symptoms of a Tethered Cord can include :- 1. Persistent back pain. 2. Changes in sensation in the legs or feet. 3. Difficulty in walking. 4. Changes in control of bowel movements. 5. Not being able to empty the bladder fully. 6. Frequent urine infections. 7. An unequal appearance in the size of a persons legs or feet, so one side will appear smaller than the other As you can see these symptoms can easily be associated with other more common conditions. 4
6 Treatment Conservative Management This is an option if tethered cord has been recognised early and there are minimal symptoms. If your condition remains unchanged then it may be a possible to monitor your condition, and act only if there are any changes. Treatment It is more likely that you are reading this because you are considering an operation. The operation is performed to release the spinal cord from where it is attached, in order for it to hang freely within the spinal canal, and prevent any further stretching of the nerve roots or spinal cord. This is performed to prevent any further deterioration. It is very unlikely to improve any symptoms that you have already developed. Exercise 4 Start Position Lying on your back. Bend one leg and put your foot on the bed and put a cushion under the other knee. Action Exercise your straight leg by pulling your foot and toes up, tightening your thigh muscle and straightening the knee (keep knee on the cushion), Hold for approximately 5 seconds and then slowly relax. Repeat 10 times Reason for surgery The goal of an operation is to prevent any further deterioration in the function of the spinal cord and nerves. As has already been mentioned it is unlikely that surgery will make any improvement to any symptoms that you already have. This is due to some nerves already being damaged from the abnormal stretching that has already happened. If it is not treated, and you already have developed symptoms, then it is likely that you will continue to get more problems and deterioration as the nerves continue to be stretched and become more damaged, preventing messages from travelling through them. Exercise 5 Start Position Lying on your back with legs straight. Action Bend your ankles and push your knees down firmly against the bed. Hold for 5 seconds and then relax Repeat 10 times 5
7 Risks of Surgery Exercise 1 Start Position Lying on your back Action Bend your leg and bring your knee towards your chest and your heel towards your bottom. Repeat 10 times With any type of surgery there are risks, and although it is not common for them to happen, it is important that you understand that there is a potential for them to occur. The risks of surgery will be discussed in detail with you by your doctor, before your surgery. The risks with untethering of the spinal cord include :- 1. Risk from having a general anaesthetic 2. The risk of a leak of the spinal fluid (CSF), that flows around your brain and spinal cord. 3. Infection either in your wound and/or in the spinal fluid Exercise 2 Start Position Lying on your back or sitting Action Bend and Straighten your ankles briskly. If you keep your knees straight during the exercise you will stretch your calf muscles. Repeat 10 times 4. Haematoma (blood clot) 5. Increase in pain 6. Transient weakness, A temporary weakness that occurs due to a malfunction of the nerves, as a consequence of the surgical procedure. This is a common complication that resolves over time. 7. The risk of damage to the nerves, causing your symptoms to become worse, leading to problems with your legs, bladder, bowel and sexual function. In extreme cases this could also mean paralysis, unable to move from the waist down, but this is an exceptionally rare complication. 6
8 Pre operative assessment You will be brought into the hospital for your pre operative assessment. This includes being assessed by the anaesthetist he/ she will have a chat with you, discuss any relevant medical history and explain what having an anaesthetic will involve. You may have some blood tests performed, a member of the nursing and medical team will discuss your medical history with you and you will be examined. If any X-rays or a heart trace (ECG) are required these will also be done. It would be helpful if you could bring with you any medication that you are taking or a list of your medication and doses so the doctor can prescribe them This may all be done at the pre-operative assessment clinic and an appointment will be organised for you and sent to you if you are required to attend for this. If you are admitted straight to the ward, without attending the pre-operative clinic, do not worry, all your investigations will be performed the day you are admitted. In all cases your surgery will normally be the day following your admission, you will not go home overnight. There may be periods of waiting on your admission day, everything, will be done as quickly as possible but I am sure you will appreciate that the medical staff also have many other patients to care for, so please be patient. It is advisable not to bring any valuables with you into hospital, as the hospital does not accept any responsibility for their safety. Physiotherapy following Untethering of Spinal Cord If you have been advised a period of bed rest following your operation it is important to maintain your circulation and your muscle tone to assist in the recovery process. The following exercises should be carried out several times a day until you are able to get up out of bed. Once you are allowed to get up out of bed the physiotherapist will review your mobility if you experience any difficulties. Breathing Exercises Take a deep breath in, hold, and breathe out slowly, repeat 3 times. Return to breathing normally for a minute. Repeat the deep breathing for 3 more cycles. Lower limb Exercises These exercises should be performed slowly and carefully to ensure no discomfort is felt. Exercise 1 Start Position Lying on your back with knees together and bent You will be able to eat and drink up to midnight on the evening before your surgery and in some cases up to 6am on the morning of your surgery. This varies depending on what time you are due to have your operation. The ward staff will be able to clarify this for you. 7 Action Slowly roll your knees towards your chest and your heel towards your bottom. Repeat 10 times 16
9 Diastematomyelia (Split spinal cord) The spinal cord is separated into two by a bony abnormality. The bony abnormality sits like an island in the middle with the spinal cord separating to run either side of it and then sometimes the spinal cord comes back together after it goes past it. Laminectomy Removal of the lamina, which is part of the bony structure of the spinal bones, usually done to reduce pressure from bone on the spinal cord and nerves or to allow good access for surgery. Dermal Sinus A tract lined by skin cells that goes down from the skin to anywhere along the back of the spine or spinal cord. Spinal Dyspraphism This term encompasses all defects associated with malformations of the back of the spine. Meningocele A cystic filled cavity that comes through a bony deformity of the spine and is lined on the inside with the same coverings as the spinal cord, but does not contain any nerves. Myelomeningocele This is the same as a Meningocele (see above) except there are elements of the spinal cord and nerves within the cystic filled cavity. 15 The Day of your Operation You will be kept fasted (nothing to eat or drink) and need to wear a theatre gown following your morning bath or shower. Your details will be checked with you on the ward, before you go to theatre. You will be wearing a wrist band with your details on and have to answer a list of questions, for example, your name, date of birth and confirm that you have removed all jewellery, underwear and make up etc. You will be collected for theatre and taken to the theatre reception area where the nurse will check your details again, whilst this can appear repetitive it is all done to ensure your safety. From theatre reception you will be taken to the anaesthetic room, a small room within the theatre complex. Here the anaesthetist will give you your anaesthetic medication, and once you are asleep you will be taken into theatre and surgery performed. What is done during surgery varies with each individual and the structure of your spine. Remember the surgeon is dealing with structures that are different to normal, and although he/she is very experienced, they need to work with what they find inside you. This makes every case individual, and even though scans are very advanced, they still cannot show all the detail of the microscopic structures. The surgeon will see all the finer detail during your operation this makes you and your surgery unique. There are still general themes to the recovery of everyone, which are discussed in the next few pages and this should help you understand what to expect. 8
10 Recovery Room When your operation is over you will be taken to the recovery area, it is here that you will wake up from your anaesthetic, and the recovery staff will monitor you till you are awake enough to return to the ward. You will be in your own bed as you wake up and you will stay in this whilst in recovery and be transferred back to the ward in it., you will not need to be moved from or onto any bed or trolley No visitors are allowed in the recovery area, and you will usually only need to spend approximately one hour here before you will be transferred back to the ward. You will have your blood pressure and pulse checked at regular intervals and the staff will check your leg movements and your wound. This can seem a bit repetitive but it is all done to ensure your safe recovery. Back on the ward Once the recovery staff are happy with your progress, and you have recovered enough from your anaesthetic, you will be transferred back to the ward. You will wake up in recovery with most of the things mentioned below, as you improve we will reduce the number of things you have. Until you are fully awake from the anaesthetic you will be given oxygen through a mask that goes over your nose and mouth. You will continue to have your blood pressure and pulse checked at regular intervals and your leg movements and wound. This is done less frequently after the first few hours once you return to the ward and as you get better it reduces to a few times a day. 9 Tethered cord can be complicated and can be present together with other abnormalities. The list that follows gives an explanation of some common associated abnormalities and terms that you may hear. Spina bifida occulta An abnormality present in the bones of the lower part of the spine present in 5-10% of the population. This only causes problems when there is an additional underlying abnormality as well. Filum Terminale This is a piece of tissue that works a bit like an elastic anchor for the spinal cord. It stretches as we move and bend, and brings the spinal cord back into the correct position when we straighten up again. Thickened Filum This is when the filum (see above) is thickened due to fatty or fibrous tissue. This makes it less like elastic and unable to give, so as the person moves it is the spinal cord and nerve roots that get stretched instead of the Filum terminale. Dermoid or Epidermoid cyst A benign tumour of skin cells Lipoma or lipomyelomeningocele Malformations in which a fatty lump under the skin develops in an abnormality of the lower spinal bones. The nerve roots, and filum terminale become embedded in the fatty lump, and therefore catch (tether) the spinal cord. 14
11 increase your tolerance to everyday activities, pace yourself and build it up slowly. Remember you have had surgery and this will make you feel tired causing sometimes the simplest of activities to be an effort, but this will improve as your recovery progresses. You can undertake all the usual activities of daily life as you feel comfortable this includes walking, shopping, driving, sexual activity. You can return to work as soon as you feel you can cope. Heavy lifting should only be performed in the correct way and should be avoided for the first three months. You will be sent an outpatient appointment by post, to come to clinic so we can check you are recovering well, this is usually about 3 months after you have been discharged home. If you have any queries at any time, before or after your surgery please do not hesitate to contact us or speak to your GP :- Spinal Nurse Specialist - Keren Smallwood Physiotherapist Secretary to your Consultant You will have a drip in your hand so that you can be given fluids through this until you are awake and well enough to drink and eat. This drip tube can also be used, to give you pain killing medication (analgesia) to ensure that you are comfortable. Some patients will have a PCA (patient controlled analgesia) this is a button that you control and you can press this when you want some pain killing medication. With each push of the button you give yourself a dose of painkiller (analgesia) through a small tube in your hand. This does have a safety override so that you cannot give yourself more than a set dose already programmed into the machine, regardless of how many times you press the button. It is not unusual for you to need to stay lying flat in bed for approx 3-5 days after this type of surgery. This is to put less pressure on the internal repair of the linings the brain and spinal cord sit inside, and help to reduce the risk of a fluid leak from the wound in your back. It is usual after this procedure to have a urinary catheter in place for a few days, it is inserted whilst you are asleep in the theatre. This is to drain all your urine into an external catheter bag for you. It also means that if you are unable to get out of bed for a few days you will not need to worry about using bedpans or bottles, but more importantly it allows the staff to monitor your fluid output. Whilst you remain on bed rest the nursing staff will give you the help that you will need with washing and changing. When you are drinking and eating well, your drip will be removed, and you will be encouraged to move around the bed. It is important that you do the physiotherapy exercises described in the Physiotherapy section of this booklet, to help prevent any problems occurring 13 10
12 After a Few Days Your surgeon will decide when he/she is happy for you to get out of bed, depending on your individual procedure and your recovery. When you are allowed to get up out of bed, then it is always better to have the head of your bed slowly lifted so that you do not feel dizzy. When you have been lying in bed for a few days your body needs to adjust to the changes required for you to be upright again, so if you get straight up you are likely to feel very dizzy and sick. However if you sit up gradually then your body can gently adjust itself to being upright again. There is a physiotherapy team working on all the wards, and a physiotherapist will see you if you have any difficulties, once you are able to get out of bed. If needed they will check your walking and movement and give you advice on exercises. It is important that once you are out of bed that you gradually return to doing as much for yourself as you can. This is all part of your expected recovery and although it is difficult at first you will find that the more you are able to do the easier you are able to move and you will become more comfortable. Once you are up and walking around we will be able to remove your catheter, this is easily done on the ward and is not painful. You will then be able to use the toilet. After removal of your catheter initially you will be expected to pass urine into a bedpan or urine bottle, which you can take to the toilet with you. This is so that the nursing staff can make sure that your bladder is working properly without the catheter. Some patients will need to have a scan of their bladder. This involves using a small ultra sound machine, by your bed. We hold a small probe on the surface of your abdomen just below your belly button, and it can tell us how much urine you have in your bladder. If we do this after you have been to the toilet then we can tell if you have emptied your bladder properly and that it is working well. 11 Going Home. Once you are walking around the ward, are feeling better and the medical staff are happy with your wound healing you will be allowed to go home. Medication will be organised for you to take home, however this can sometimes mean you need to wait till the evening on your discharge day. If you can arrange with your GP to have some already at home this will prevent you needing to wait. It is possible to arrange a district nurse to check your wound and remove your stitches approximately a week after your surgery. This can mean waiting in your house all day so some patients prefer to go to their local GP surgery for the practice nurse to do this. If you would prefer to do this please let the ward staff know. If you feel you will be unable to go to your surgery then a date for the district nurse visit will be given to you before you leave the ward. Please make sure that if you are not going home to your usual address and you are going to stay with someone else you inform the staff, to ensure that the district nurse comes to the correct address. If you need transport home it is advisable to let the staff know when you are admitted, so this can be arranged in advance. If you are travelling home by car, sit in the front passenger seat and recline the seat back to make you more comfortable whilst travelling. The evidence shows that patients who return to a normal routine as quickly as possible make the best recovery. You should progressively return to your normal daily routine as quickly as possible. It is important that you do not go home and spend a lot of time lying down, as this can cause problems. It is better to spend time moving around your house, doing things in short sessions, then resting. Gradually 12
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Contents. Overview. Removing the womb (hysterectomy) Overview
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding womb (endometrial) cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Overview Contents Overview Removing
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion. What is a lumbar spinal fusion? Page 1 of 5
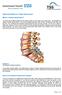 Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Patient Information for Lumbar Spinal Fusion What is a lumbar spinal fusion? You have been offered surgery to the lumbar region of your spine, your lower back. The operation is called a lumbar spinal fusion.
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery
 Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
Enhanced recovery programme (ERP) for patients undergoing bowel surgery Information for patients, relatives and carers An enhanced recovery programme (ERP) has been established at Imperial College Healthcare
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy
 Laparoscopic Nephrectomy Information for Patients This leaflet explains: What is a Nephrectomy?... 2 Why do I need a nephrectomy?... 3 What are the risks and side effects of laparoscopic nephrectomy?...
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy Information for Patients This leaflet explains: What is a Nephrectomy?... 2 Why do I need a nephrectomy?... 3 What are the risks and side effects of laparoscopic nephrectomy?...
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder)
 Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients
 Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
Elbow Joint Replacement A guide for patients GATESHEAD UPPER LIMB UNIT Mr Andreas Hinsche Mr John Harrison Mr Jagannath Chakravarthy Page 1 of 7 The elbow joint The elbow consists of three bones; the humerus
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
General Surgery Elective Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy This information aims to explain what will happen before, during and after your surgery to remove your gallbladder. It includes information about the
Spina Bifida Occulta. Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60. Occulta Means Hidden
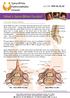 Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Varicose Veins Operation. Patient information Leaflet
 Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Varicose Veins Operation Patient information Leaflet 22 nd August 2014 WHAT IS VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY (HIGH LIGATION AND MULTIPLE AVULSIONS) The operation varies from case to case, depending on where the
Inguinal Hernia (Female)
 Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy)
 Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
Patient Information and Daily Programme for Patients Having Whipple s Surgery (Pancreatico duodenectomy) Date of admission Date of surgery Expected Length of Stay in hospital We will aim to discharge you
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 5: August 2014 Review date: July 2017 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis
 Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Posterior Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Issue 6: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon you have been diagnosed with
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery (ERALS) programme: patient information and advice 2
 This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
This booklet is funded by, and developed in collaboration between University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and Pfizer Limited. NPKAM0198 March 2014 Enhanced recovery after laparoscopic surgery
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients
 Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
Recovery plan: radical cystectomy Information for patients Help for you following a bereavement 5 This leaflet will help you know what to expect during your time with us. Please take some time to read
We ve got your back. Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery
 We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
We ve got your back Physical Therapy After Lumbar Fusion Surgery Physical therapy is an extremely important part of you recovery after spinal surgery. This booklet, prepared by the therapists who specialize
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis
 Patient information Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis Ear, Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 230 V6 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery
Patient information Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis Ear, Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 230 V6 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION
 SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
SPINE SURGERY - LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Introduction This booklet has been compiled by the physiotherapy department to help you understand lumbar
Low Back Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. Table of contents Page Why do I need low back surgery?... 1 What kinds of low back surgeries are there?... 2 Before your surgery... 3 After your
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet
 Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
Vesico-Vaginal Fistula
 Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
Saint Mary s Hospital The Warrell Unit Vesico-Vaginal Fistula Information For Patients Contents Page What is a vesico-vaginal fistula? 3 How does a fistula develop? 3 What tests will I need? 3 How can
Coccydynia. (Coccyx Pain) Information for patients. Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312
 Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion.
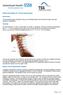 Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
Patient information for cervical spinal fusion. Introduction This booklet has been compiled to help you understand spinal cervical fusion surgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Anatomy The cervical
What is a mastoidectomy and why do I need this operation? What is the benefit of having a mastoidectomy?
 Mastoidectomy What is a mastoidectomy and why do I need this operation? A mastoidectomy is performed to remove infected mastoid air cells situated behind the middle ear and the removal of infected structures
Mastoidectomy What is a mastoidectomy and why do I need this operation? A mastoidectomy is performed to remove infected mastoid air cells situated behind the middle ear and the removal of infected structures
Removal of the Submandibular Salivary Gland
 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Removal of the Submandibular Salivary Gland Information for patients This leaflet will help you understand your treatment and should answer many of the questions
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Removal of the Submandibular Salivary Gland Information for patients This leaflet will help you understand your treatment and should answer many of the questions
Laminectomy for Tethered Cord
 Laminectomy for Tethered Cord A tethered spinal cord is characterized by an abnormal attachment of the spinal cord to the surrounding tissues. The lower end of a normal spinal cord is found in the upper
Laminectomy for Tethered Cord A tethered spinal cord is characterized by an abnormal attachment of the spinal cord to the surrounding tissues. The lower end of a normal spinal cord is found in the upper
Total Hip Replacement
 NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
NOTES Total Hip Replacement QUESTIONS DATES PHONE NOS. Compiled by Mr John F Nolan FRCS for The British Hip Society 2009. A patient s information booklet 16 1 Introduction This booklet has been produced
Primary and revision lumbar discectomy. (nerve root decompression)
 Primary and revision lumbar discectomy (nerve root decompression) The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a lumbar discectomy. It explains the benefits,
Primary and revision lumbar discectomy (nerve root decompression) The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a lumbar discectomy. It explains the benefits,
Surgery for Disc Prolapse
 Contact Details Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Surgery for Disc Prolapse Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Surgery for disc
Contact Details Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Surgery for Disc Prolapse Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Surgery for disc
ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION. Under the Care of Mr M Paterson - 11 -
 ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION Under the Care of Mr M Paterson Acknowledgement: Drawings by Jean Paterson Perth Australia 2006 Brochure: R. Grubb Amended:
ADVICE TO PATIENT DUE TO HAVE MICRODISCECTOMY / SPINAL STENOSIS DECOMPRESSION Under the Care of Mr M Paterson Acknowledgement: Drawings by Jean Paterson Perth Australia 2006 Brochure: R. Grubb Amended:
Your spinal Anaesthetic
 Your spinal Anaesthetic Information for patients Your spinal anaesthetic This information leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation with a spinal anaesthetic. It has been written by patients,
Your spinal Anaesthetic Information for patients Your spinal anaesthetic This information leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation with a spinal anaesthetic. It has been written by patients,
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Caring for your body. Antenatal exercises
 Caring for your body Antenatal exercises Antenatal Exercises FROM EARLY PREGNANCY TO DELIVERY INTRODUCTION.................................................3 DEEP BREATHING & FOOT AND ANKLE EXERCISES..................4
Caring for your body Antenatal exercises Antenatal Exercises FROM EARLY PREGNANCY TO DELIVERY INTRODUCTION.................................................3 DEEP BREATHING & FOOT AND ANKLE EXERCISES..................4
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
An operation for prolapse Colpocleisis
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit An operation for prolapse Colpocleisis Information for Patients What is a prolapse? A prolapse is a bulge or lump in the vagina caused by sagging
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit An operation for prolapse Colpocleisis Information for Patients What is a prolapse? A prolapse is a bulge or lump in the vagina caused by sagging
Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition
 Department of Neurosurgery Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition What happens when you are in hospital page 2 Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition This leaflet explains what to expect when you are
Department of Neurosurgery Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition What happens when you are in hospital page 2 Ulnar Nerve Decompression/Transposition This leaflet explains what to expect when you are
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Trans Urethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Liver Resection. Patient Information Booklet. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Liver Resection Patient Information Booklet Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway. Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS)
 Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
Premier Orthopaedic Pathway Physiotherapy after dynamic hip screw (DHS) The surgery After a fractured hip a dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used to hold the bones in place while the fracture heals. It allows
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA
 SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA 21 Tillot St Dutton Park QLD 4102 PO Box 8022 Woolloongabba QLD 4102 Phone: 07 3844 4600 Fax: 07 3844 4601 Email: [email protected] www.spinabifida.org July 2010 DISCLAIMER
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA 21 Tillot St Dutton Park QLD 4102 PO Box 8022 Woolloongabba QLD 4102 Phone: 07 3844 4600 Fax: 07 3844 4601 Email: [email protected] www.spinabifida.org July 2010 DISCLAIMER
Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear
 Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear Most women, up to nine in ten (90%), tear to some extent during childbirth. Most tears occur in the perineum, the area between the
Caring for your perineum and pelvic floor after a 3rd or 4th degree tear Most women, up to nine in ten (90%), tear to some extent during childbirth. Most tears occur in the perineum, the area between the
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis)
 Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Ilioinguinal dissection (removal of lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis) This sheet answers common questions about ilio-inguinal dissection. If you would like further information, or have any particular
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
total hip replacement
 total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
total hip replacement EXCERCISE BOOKLET patient s name: date of surgery: physical therapist: www.jointpain.md Get Up and Go Joint Program Philosophy: With the development of newer and more sophisticated
Lumbar Nerve Root Block
 Lumbar Nerve Root Block Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Imaging techniques, such as an MRI scan, can reveal small disc bulges and / or wear and tear in the spine with possible
Lumbar Nerve Root Block Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Imaging techniques, such as an MRI scan, can reveal small disc bulges and / or wear and tear in the spine with possible
Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients We have recently seen you in clinic as you have had pain for a long period
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurosciences Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Stimulation Information for patients We have recently seen you in clinic as you have had pain for a long period
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained
 Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
Excision or Open Biopsy of a Breast Lump Your Operation Explained Patient Information Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedure known as excision or open biopsy of a breast lump. It explains
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Parathyroidectomy An operation to remove overactive parathyroid glands Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Parathyroidectomy An operation to remove overactive parathyroid glands Information for patients What are the parathyroid glands? There are four parathyroid glands
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Parathyroidectomy An operation to remove overactive parathyroid glands Information for patients What are the parathyroid glands? There are four parathyroid glands
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery. A Guide for Patients and Families
 Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Colon Cancer Surgery and Recovery A Guide for Patients and Families This Booklet You are receiving this booklet because you will be having surgery shortly. This booklet tells you what to do before, during,
Spigelian Hernia Repair
 Spigelian Hernia Repair WHAT IS A SPIGELIAN HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 2 SPIGELIAN HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT ARE
Spigelian Hernia Repair WHAT IS A SPIGELIAN HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 2 SPIGELIAN HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT ARE
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Patient Information. Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression. Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Epigastric Hernia Repair
 Epigastric Hernia Repair WHAT IS EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 3 EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT
Epigastric Hernia Repair WHAT IS EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES IT? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 2 WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF THE HERNIA WAS NOT TREATED? 3 EPIGASTRIC HERNIA REPAIR 3 WHAT
Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence
 Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence This leaflet explains more about tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) including the benefits, risks and any alternatives, and
Having a tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) operation for stress urinary incontinence This leaflet explains more about tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) including the benefits, risks and any alternatives, and
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Periurethral bulking agent for stress urinary incontinence (macroplastique)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet provides information about having an injection
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet provides information about having an injection
GreenLight laser prostatectomy
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Umbilical or Paraumbilical Hernia Adults
 Umbilical or Paraumbilical Hernia Adults WHAT IS AN UMBILICAL OR PARAUMBILICAL HERNIA? 2 THE OPERATION? 2 ANY ALTERNATIVES 3 BEFORE THE OPERATION 3 AFTER YOUR SURGERY - IN HOSPITAL 4 POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS?
Umbilical or Paraumbilical Hernia Adults WHAT IS AN UMBILICAL OR PARAUMBILICAL HERNIA? 2 THE OPERATION? 2 ANY ALTERNATIVES 3 BEFORE THE OPERATION 3 AFTER YOUR SURGERY - IN HOSPITAL 4 POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS?
Elbow arthroscopy. Key points
 Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients
 Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients What are Haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids (piles) are enlarged blood vessels around the anus (back passage). There are two types of haemorrhoids:
Removal of Haemorrhoids (Haemorrhoidectomy) Information for patients What are Haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids (piles) are enlarged blood vessels around the anus (back passage). There are two types of haemorrhoids:
Returning to fitness after heart surgery
 Returning to fitness after heart surgery A patient s guide 1 Increasing activity After your operation, your heart function should be improved and so your ability to exercise will also be improved. However,
Returning to fitness after heart surgery A patient s guide 1 Increasing activity After your operation, your heart function should be improved and so your ability to exercise will also be improved. However,
Subtotal Colectomy. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Subtotal Colectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm This leaflet
Subtotal Colectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm This leaflet
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Laparoscopic Surgery for Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Laparoscopic Surgery for Inguinal Hernia Repair What is an Inguinal Hernia Repair? 2 What is a Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair? 2 Are there any alternatives to Laparoscopic Hernia Repair? 3 Am I a
Laparoscopic Surgery for Inguinal Hernia Repair What is an Inguinal Hernia Repair? 2 What is a Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair? 2 Are there any alternatives to Laparoscopic Hernia Repair? 3 Am I a
LASER TREATMENT FOR VARICOSE VEINS
 LASER TREATMENT FOR VARICOSE VEINS How can varicose veins be treated by laser? Laser treatment of varicose veins, Endovascular Laser Ablation (known as EVLA), is a minimally invasive procedure for treating
LASER TREATMENT FOR VARICOSE VEINS How can varicose veins be treated by laser? Laser treatment of varicose veins, Endovascular Laser Ablation (known as EVLA), is a minimally invasive procedure for treating
Name of procedure: Laparoscopic (key-hole) ovarian surgery. Left/ Right unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy* (removal of one fallopian tube and ovary)
 For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
For staff use only: Patient Details: Surname: First names: Date of birth: Hospital no: Female: (Use hospital identification label) Gynaecology Patient agreement to treatment Name of procedure: Laparoscopic
An operation for prolapse Sacrospinous Fixation Sacrospinous Hysteropexy
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit An operation for prolapse Sacrospinous Fixation Sacrospinous Hysteropexy Information For Patients 1 What is a prolapse? Prolapse is a bulge or lump
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit An operation for prolapse Sacrospinous Fixation Sacrospinous Hysteropexy Information For Patients 1 What is a prolapse? Prolapse is a bulge or lump
Surgery for Stress Incontinence
 Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre. Patient information guide
 Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty
 Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Having a kidney biopsy
 Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide. Second print August 2004
 Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide Second print August 2004 National Patient Safety Agency Seven steps to patient safety 113 Appendix Four F Examples of events according to severity
Seven steps to patient safety The full reference guide Second print August 2004 National Patient Safety Agency Seven steps to patient safety 113 Appendix Four F Examples of events according to severity
University College Hospital. Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 18 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please
University College Hospital Prostate high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 18 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
