Gastrointestinal problems in children with metabolic disorders
|
|
|
- Denis Hamilton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gastrointestinal problems in children with metabolic disorders Alexander Asamoah, MD, PhD Senior Staff Physician and Pediatric Clinical Geneticist Department of Medical Genetics Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit
2 Learning Objectives Review common GI problems in children with metabolic disorders Understand pathophysiology of some of the problems Understand symptoms of GER and GERD Recognize precipitating factors of GER and GERD Understand medical and surgical management of some of the GI problems
3 GI Problems of children with Metabolic disorders Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) Recurrent Vomiting Anorexia Nausea Chronic swallowing difficulties Chronic constipation Oral aversion Hyperactive gag reflex
4 Factors contributing to GI Problems in children with Metabolic disorders Hypotonia Developmental delay Dependence of G-tube Oral aversion Hyperactive gag reflex High osmotic loads of elemental formulas and dumping Medication side effects Bad taste and smell of metabolic formulas
5 Selected metabolic disorders Organic acid disorders Propionic acidemia Methylmalonic acidemia Isovaleryl acidemia Amino acid disorders Urea cycle defects Fatty acid oxidation disorders MADD (Glutaric aciduria II) Mitochondrial disorders with GI manifestions Pearson syndrome MNGIE (Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy)
6 Common presentation of Metabolic disorders Biochemical disturbances Metabolic acidosis/alkalosis Hypoglycemia Hyperammonemia Poor growth (failure to thrive) Developmental delay/hypotonia Seizures
7 Common presentation of Metabolic disorders Liver function abnormalities Muscle and heart disease Intolerance to fasting Increased susceptibility to infection Bone marrow suppression leading to anemia
8 Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting
9 Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting Anorexia loss of desire to eat, that is a true loss of appetite Nausea the unpleasant sensation of the imminent need to vomit usually referred to the throat or epigastrum Sensation may or may not ultimately lead to the act of vomiting
10 Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting Vomiting Forceful oral expulsion of gastric contents associated with contraction of the abdominal and chest wall musculature
11 Why is anorexia, nausea and vomiting common in children with metabolic problems? High ammonia from Organic acid disorders FAOD Urea cycle defects Metabolites from underlying disorder Gastric motility problems Fear of food Emotional issues
12 Pathophysiology Anorexia, nausea and vomiting
13
14 Pathophysiology Brain stem Chemoreceptor trigger zone Blood-borne toxins such as ammonia, etc Vomiting center Cerebral cortex Stomach and other viscera Vagal and sympathetic afferents
15 Proposed mechanism to explain how high ammonia cause anorexia Ammonia is a normal constituent of all body fluids (normal level is < 35 µmol/l) Excess ammonia excreted as urea by the liver through the urea cycle Metabolic disorders that result in build-up of ammonia will lead to problems such as (lethargy, coma, seizures, anorexia encephalopathy, etc.)
16 Proposed mechanism to explain how high ammonia cause anorexia Ammonia increases transport of aromatic amino acids (e.g. tryptophan) across the blood-brain barrier. This leads to increase in the level of serotonin Results in anorexia Preventing hyperammonemia may, in part, minimize anorexia
17 Vomiting and Gastroesophageal Dysmotility in Children with CNS Disorders Ravelli and Milla J of Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26: children with CNS disorders were studied 50 had retching and/or vomiting (18 cases of fundoplication) 24-hour ph probe and endoscopy Gastric electrical activity by electrogastrography (EGG) Gastric half-emptying time (T1/2) of a milk meal by electrical impedance tomography
18 Vomiting and gastroesophageal dysmotility 50 vomiting patients 29 had GER 31 had gastric dysrhythmias 12 Tachyarrhythmia 4 Bradyarrhythmia 15 unstable electrical activity 16 patients had GER and gastric dysrhythmia 11/18 patients with fundoplication had gastric dysrhythmia Gastric T1/2 was delayed in 12/13 with gastric dysrhythmia
19 Vomiting and gastroesophageal dysmotility Conclusions Children with CNS disorders who vomit have abnormal gastric motility as often as GER Many patients continue to vomit after fundoplication possibly due to gastric dysrhythmia Foregut dysmotility may be related to abnormal modulation of the enteric nervous system by the CNS or to involvement of the enteric nervous system by the same process affecting the brain
20 Clinical features of 50 vomiting patients with CNS disorder Failure to thrive Respiratory problems Constipation Non-ambulatory Oropharyngeal incoordination Spasticity Scoliosis Symptom Retching and/or vomiting Number Percent
21 Management of Nausea and Vomiting Recognize and correct complications of vomiting Fluid and electrolyte replacement Correct acid-base and metabolic disturbances Find underlying cause of vomiting Therapeutic strategies to suppress or eliminate symptoms Mild symptoms oral antiemetics Severe symptoms phenothiazines, butyrophenones, metoclopramide
22 Anti-emetic drugs Anti-cholinergics agents Scopolamine usually for motion sickness Side-effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, vision disturbance Antihistamines Benadryl Dramamine Phenergan Side effects include sedation
23 Anti-emetic drugs Dopamine receptor antagonists Phenothiazines Compazine Thorazine Butyrophenones Major tranquilizer Haldol Benzamide Reglan (Metoclopramide)
24 Anti-emetic drugs Serotonin antagonists Used in chemotherapy-induced nausea 3 currently approved in the US Ondansetron Granisetron Dolasetron Favorable toxicity profile Mild headache, constipation, dizziness
25 Anti-emetic drugs Neurokinin receptor antagonists Corticosteroids Cannabinoids Limited clinical use Modest antiemetic activity Unfavorable side effects Vertigo, xerostomia, hypotension, dysphoria Benzodiazepines
26 Anti-emetic drugs Most of these medications are for postoperative and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting Has been used in cyclical vomiting Few control trials have compared various therapeutic strategies or available pharmacologic agents in the symptomatic therapy of nausea and vomiting
27 What does this mean for children with metabolic disorders? Treat underlying cause Side effects of some of these medications may mask symptoms of the disorder we are treating There is the need to have trials using some of these medications
28 Constipation in metabolic disorders Definition - A decrease in the frequency of bowel movements or the painful passage of bowel movement Very common in all ages 3 % of pediatric clinic visits; 25% of pediatric gastroenterology visits Constipation seen in 46% of children with neurodevelopmental delay
29 Constipation Several factors lead to constipation Hypotonia Intestinal dysmotility Decreased bulk in diet Retained stool fills the large intestine (the colon) and cause it to stretch An over-stretched colon cannot work properly and therefore more stool is retained
30 Treatment of Constipation Stool softeners these are not habit-forming and may be taken for a long time without unusual side effects Some patients may require clean-out to help empty the colon of the large amount of stool Laxatives by mouth, suppositories or enemas for short period of time Work with your gastroenterologist
31 Dumping syndrome Hertz in 1913 made the association between postprandial symptoms and gastroenterostomy Mix first used the term dumping in 1922 after observing radiographically the presence of rapid stomach emptying in patients with vasomotor and GI symptoms Symptom complex due large amounts of food passing quickly into the small intestine
32 Dumping syndrome Functions of the stomach Reservoir Initiate digestion Release contents downstream into the duodenum in a controlled fashion Alterations in gastric anatomy after surgery or interference in its extrinsic innervation (vagotomy) may have profound effects on gastric emptying
33 Symptoms of dumping Early dumping Occurs 30 to 60 minutes after eating Accelerated gastric emptying of hyperosmolar contents into the small bowel This leads to fluid shift from the blood vessels into the bowel lumen Rapid bowel distention Late dumping Occurs 1 to 3 hours after a meal Initial hyperglycemia followed by hypoglycemia (hormone mediated)
34 Symptoms of dumping Early dumping systemic symptoms Desire to lie down Palpitation Fatigue Faintness Syncope Sweating Headche Flushing
35 Symptoms of dumping Early dumping abdominal symptoms Epigastric fullness Abdominal cramps Borborygmi Nausea diarrhea
36 Symptoms of dumping Late dumping Perspiration Shakiness Difficulty in concentration Decreased consciousness Hunger
37 When do we see dumping in children? After fundoplication Generalized autonomic dysfunction Malplacement of feeding gastrostomy tube After surgery for peptic ulcer
38 Dumping in FAOD Dumping has been used to describe hyperglycemic episodes seen in patients with fatty acid oxidation defects during intercurrent illnesses Hyperglycemia may be due to stress of hypoglycemia Probably mediated through Epinephrine and Cortisol release Should we call this phenomenon dumping or not?
39 Gastroesophageal reflux
40 Definitions GER - passage of gastric contents into the esophagus GERD symptoms or complications that may occur when gastric contents reflux into the esophagus or oropharynx Regurgitation passage of refluxed gastric content into the oropharynx
41 Gastro-esophageal reflux 40% of healthy infants spit up >1X /day Onset is first few weeks of life Peaks at 4 months and resolves by 8 to 12 months 1 in 300 infants have significant and associated complications
42 >=1X a day >=4 X aday mos 4-6 mos 7-9 mos mos
43 Gastro-esophageal reflux Non-pathogenic reflux No weight loss No irritability or behavior problems to suggest esophagitis No respiratory disease or apnea
44 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Symptom complex due to reflux of gastric contents through the lower esophageal sphincter into the esophagus May cause inflammation and scarring if acid is not cleared quickly
45 Gastroesophageal reflux disease Etiology (GERD) Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter Abdominal position of sphincter Angle of insertion of esophagus into the stomach Low sphincter pressure Higher pressure in stomach than in esophagus Placement of gastrostomy tube encourages reflux Large hiatus hernia in a neurologically impaired children
46 Risk factors for Gastroesophageal reflux disease Neurological disorder Cerebral palsy Congenital malformations Esophageal atresia TE fistula Severe chronic pulmonary disorders Cystic fibrosis Reactive airway disease
47 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Signs and symptoms Usually due to esophagitis Chest pain Irritability Refusing feeds Hyperactive gag reflex Swallowing difficulties Anemia, blood in vomit
48 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Signs and symptoms Aspiration Pneumonia Wheezing or coughing Apnea, cyanotic episodes (turning blue) Miscellaneous: stridor, hoarseness, hiccups Failure to thrive Vomiting Weight loss
49 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Neurobehavioral symptoms Infant spells (including seizure-like events) Sandifer syndrome Abnormal behavior posturing with tilting of head to one side Bizarre contortions of trunk
50 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Clinical evaluation Referral to Gastroenterologist Upper GI studies ph probe Endoscopy and esophageal biopsy
51 Upper GI radiography Advantage Useful for detecting anatomic abnormalities. Pyloric stenosis, malrotation, esophageal stricture, hiatal hernia, etc Limitation Cannot discriminate between physiologic and non-physiologic GER episodes
52 Esophageal ph monitoring Advantages Detects episodes of reflux Determines temporal association between acid GER and symptoms Determines effectiveness of esophageal clearance mechanisms Assesses adequacy of H2RA or PPI dosage in unresponsive patients
53 Esophageal ph monitoring Limitations Does not detect non-acid reflux Does not detect GER complications associated with normal range of GER Not useful in detecting association between GER and apnea unless combined with other testing techniques
54 Endoscopy and esophageal biopsy Advantages Enables visualization and biopsy of esophageal lining Determines presence of esophagitis, Barrett s esophagus and other complications Discriminates between reflux and non-reflux esophagitis
55 Endoscopy and esophageal biopsy Limitations Need for sedation or anesthesia Correlation between appearance on endoscopy and histopathology findings is poor Not useful for extraesophageal GERD
56 Treatment of Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Goals Control symptoms Alleviate pain or symptoms Diminish frequency of reflux Promote healing and growth Improve health-related quality of life Avoid complications Prevent recurrence Avoid adverse effects of treatment
57 Treatment of Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Lifestyle changes Pharmacotherapy (drug therapy) Surgical therapy Combination of above
58 Lifestyle changes Thicken feedings (1 Tbsp rice cereal to 1 oz formula) Small, frequent feeding Avoid foods and medications that lower the LES tone or increase gastric acidity Fatty foods, citrus, tomato, carbonated drinks, acidic beverages, tobacco smoke Place infant in a head-elevated prone position if at all necessary (remember SIDS and lying in prone position) Loose fitting clothes Avoid obesity
59 Drug treatment of GERD Antacids Histamine-2 receptor antagonists Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine Proton pump inhibitors Nexium, Prevacid, Protonix, Prilosec Prokinetic agents Reglan
60 Drug treatment of GERD Prokinetic drugs Increases LES tone and helps increase stomach emptying Example: Reglan (causes abdominal cramps, diarrhea, CNS depression, extrapyramidal signs) Propulsid withdrawn from the market because of heart rhythm problems and deaths. Not effective in treatment of GERD
61 Drug treatment of Gastroesophageal Antacids reflux disease (GERD) Used to neutralize stomach acids Provides symptomatic relief Does not promote healing of esophagitis Examples: Maalox, Mylanta, Carafate
62 Drug Treatment of GERD H2 receptor antagonists Partial suppression of stomach acid secretion Examples: Cimetidine, Famotidine, Ranitidine Proton Pump inhibitors Inhibits acid secretion Examples: Nexium, Prevacid, Protonix, Prilosec
63 Surgical treatment of GERD Nissen fundoplication Wrap upper part of stomach around the lower esophagus (like hotdog in a bun) Complete versus loose wrap ± gastrostomy ± pyloroplasty Gastrojejunostomy feedings (also usually requires pharmacotherapy)
64 Treatment of GERD in neurologically impaired children These patients are often resistant to standard medical therapy Surgical options Nissen fundoplication Gastrostomy or gastro-jejunostomy Surgery associated with high risk of complications and revisions
65 Summary Gastrointestinal problems are common in children with metabolic problems They could be a major source of morbidity Early recognition of problems are very important in management in hopes of minimizing complications and ensure growth Multi-disciplinary team approach Metabolic specialists Gastroenterologists Metabolic nutritionists Speech, Occupational and physical therapists Behavioral therapists
66 References cited North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition website Nelson et al. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1997, 151:569 Ravelli and Milla. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998,26:56-63 Gustafsson and Tibbling. Acta Pediatr 1994,83:1081 Sondheimer and Morris, J Pediatr 1979, 94:710 Pediatric in Review
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a clinical scenario where the gastric or duodenal contents reflux back up into the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, however, is a
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Gastroesophageal Reflux
 Gastroesophageal Reflux What is Gastroesophageal Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is involuntary regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus. Reflux causes a number of problems: 1. Chemical
Gastroesophageal Reflux What is Gastroesophageal Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is involuntary regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus. Reflux causes a number of problems: 1. Chemical
G E R D. (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
 G E R D (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a disorder caused by gastric acid flowing from the stomach into the esophagus. What are the symptoms of
G E R D (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a disorder caused by gastric acid flowing from the stomach into the esophagus. What are the symptoms of
Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal A surprisingly large number of children with motility disorders experience the same progression of events
www.complexchild.com Motility Disorders that are Commonly Mistaken for Reflux by Susan Agrawal A surprisingly large number of children with motility disorders experience the same progression of events
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center
 Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
Nash Heartburn Treatment Center a division of Nash Health Care NHCS Mission Statement: To provide superior quality health care services and to help improve the health of the community in a caring, efficient
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Scleroderma Education Program. Chapter 4. Gastrointestinal Tract
 Scleroderma Education Program Chapter 4 Gastrointestinal Tract Chapter 4-1 Chapter Highlights 1. Learn about how the GI tract works. 2. What happens when things go wrong? -Appetite loss -Difficulty chewing
Scleroderma Education Program Chapter 4 Gastrointestinal Tract Chapter 4-1 Chapter Highlights 1. Learn about how the GI tract works. 2. What happens when things go wrong? -Appetite loss -Difficulty chewing
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Surgery for "Heartburn" If you suffer from moderate to severe "heartburn" your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Antireflux
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
3702 Timberline Rd 2555 East 13th St Suite 220 Ft.Collins, CO 80525 Loveland, CO 80537 82001 7251 W. 20th St Greeley, CO 80634 4108 Laramie Cheyenne, WY Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Author(s): Peter
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
1-800-HRT-BURN. understanding gerd. Is it just a little HEARTBURN. or something more serious? NEW
 Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
Do you have GERD? Measure Yourself on the Richter Scale/Acid Test How significant is your heartburn? What are the chances that it is something more serious? If you need a yardstick, here s a simple self-test
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE)
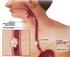 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Barrett s Esophagus (BE) Hashem El-Serag, M.D., M.P.H. Dan L. Duncan Professor of Medicine Chief, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children. David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians
 It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO. Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology
 DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO DIFFICULT PROBLEMS DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology Diabetic Enteropathy: What is it? Motility Disorders Esophageal
DIABETIC ENTEROPATHY: TWO DIFFICULT PROBLEMS DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT Gary L. Cornette, D.O., F.A.C.O.I Medical Director Gastroenterology Diabetic Enteropathy: What is it? Motility Disorders Esophageal
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome
 Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome Paul E. Moore, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology Director, Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonary Medicine Vanderbilt University
Respiratory Concerns in Children with Down Syndrome Paul E. Moore, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Pharmacology Director, Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonary Medicine Vanderbilt University
Chronic abdominal pain of childhood
 Chronic abdominal pain of childhood Sandra I. Escalera, M.D. ProHealth Physicians Associate Clinical Professor Department of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine Objectives Brief overview of approach
Chronic abdominal pain of childhood Sandra I. Escalera, M.D. ProHealth Physicians Associate Clinical Professor Department of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine Objectives Brief overview of approach
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Impairment
 Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal This chapter consists of 2 parts: Part 6.1 Diseases of the digestive system Part 6.2 Abdominal wall hernias and obesity PART 6.1: DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Diseases of
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin
 Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Figure 2: Recurrent chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 1 patient with chest pain of suspected esophageal origin 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of n-esophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and
 understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and Heartburn Basics Heartburn is the most common symptom of a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also
understanding HEARTBURN and reflux diseases A patient s guide from your doctor and Heartburn Basics Heartburn is the most common symptom of a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also
NAUSEA AND VOMITING. Ryan F. Porter, M.D. and C. Prakash Gyawali, M.D., MRCP Division of Gastroenterology Washington University St.
 NAUSEA AND VOMITING Ryan F. Porter, M.D. and C. Prakash Gyawali, M.D., MRCP Division of Gastroenterology Washington University St. Louis, MO What is nausea and vomiting? Nausea is the unpleasant urge to
NAUSEA AND VOMITING Ryan F. Porter, M.D. and C. Prakash Gyawali, M.D., MRCP Division of Gastroenterology Washington University St. Louis, MO What is nausea and vomiting? Nausea is the unpleasant urge to
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Upper Endoscopy (EGD)
 Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Upper Endoscopy (EGD) Appointment Information: Patient Name: MRN: Physician Name: Location: _ For information on Directions, please visit: http://www.brighamandwomens.org/general/directions/directions.aspx
Figure 3: Dysphagia. 14 meets. esophageal. esophageal manometry +/- +/- impedance measurement. structural lesion? no. 19 yes
 Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
Figure 3: Dysphagia 1 patient with dysphagia 2 history and physical exam. suggestive of nesophageal etiology? 3 evaluate and treat as as indicated 4 upper GI GI endoscopy with biopsies 15 achalasia, absent
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM Codes for MNT
 / Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
/ Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function
 Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Causes, symptoms, and treatments Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects 18 million to 20 million people in the U.S. It is caused by stomach acid backing up into
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Causes, symptoms, and treatments Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects 18 million to 20 million people in the U.S. It is caused by stomach acid backing up into
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass. Patient Name
 Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Too Hot, Too Cold, Too High, Too Low - Blame it on Dysautonomia!
 Too Hot, Too Cold, Too High, Too Low - Blame it on Dysautonomia! MitoAction Webcast 6-May, 2011 Richard G. Boles, M.D. Medical Genetics Childrens Hospital Los Angeles Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Too Hot, Too Cold, Too High, Too Low - Blame it on Dysautonomia! MitoAction Webcast 6-May, 2011 Richard G. Boles, M.D. Medical Genetics Childrens Hospital Los Angeles Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders
 Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
Treatment Guide Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders Esophageal disorders especially those involving swallowing problems affect more than 15 million Americans of all ages. For many, they re temporary issues
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Introduction. What is syncope?
 Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
Syncope Introduction What is syncope? Syncope (SING-kuh-pee) is a medical term for fainting. When you faint, your brain is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, so you lose consciousness temporarily.
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Nausea and Vomiting. Understanding nausea and vomiting. What causes nausea and vomiting in people with cancer?
 Nausea and Vomiting Understanding nausea and vomiting Nausea is a subjective unpleasant feeling in the back of your throat and stomach that may lead to vomiting. There are many words that describe nausea
Nausea and Vomiting Understanding nausea and vomiting Nausea is a subjective unpleasant feeling in the back of your throat and stomach that may lead to vomiting. There are many words that describe nausea
Dogs and cats with pancreatitis can have a wide variety of signs, which include, but are not limited to the following:
 Pancreatitis is defined as inflammation of the pancreas and can be caused by a number of inciting factors. The pancreas is responsible for tasks such as glucose regulation and aids in the digestion of
Pancreatitis is defined as inflammation of the pancreas and can be caused by a number of inciting factors. The pancreas is responsible for tasks such as glucose regulation and aids in the digestion of
Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure
 Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure Please review this information before your procedure. Please talk to your doctor if you have any questions or do not understand any of this information.
Patient Information Guide for the ReShape Procedure Please review this information before your procedure. Please talk to your doctor if you have any questions or do not understand any of this information.
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
Pediatric Gastroenterology Fellowship Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year
 Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year Goal 1: Gain experience and competency in managing common and rare gastrointestinal, liver and nutritional problems. (Competencies: patient
Pediatric Nutrition Rotation Goals and Objectives - 1 st Year Goal 1: Gain experience and competency in managing common and rare gastrointestinal, liver and nutritional problems. (Competencies: patient
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy. Patient Name
 Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
Informed Consent for Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Patient Name Please read this form carefully and ask about anything you may not understand. I consent to have a laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve
What can I eat? Peptic ulcers. What are peptic ulcers? What tests are needed? Will the ulcer come back? What causes a peptic ulcer?
 In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
In association with: INFORMATION ABOUT Peptic ulcers www.corecharity.org.uk What are peptic ulcers? What causes a peptic ulcer? How are NSAIDs and aspirin involved? How do I know if I ve got an ulcer?
Nausea and vomiting. Definition. Causes. Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/nausea/my00572. By Mayo Clinic staff
 Nausea and vomiting By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/nausea/my00572 Definition Nausea and vomiting are very common symptoms that can be caused by a wide variety of
Nausea and vomiting By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/nausea/my00572 Definition Nausea and vomiting are very common symptoms that can be caused by a wide variety of
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System
 Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
Normal Gastrointestinal Motility and Function
 Normal Gastrointestinal Motility and Function "Motility" is an unfamiliar word to many people; it is used primarily to describe the contraction of the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. Because the
Normal Gastrointestinal Motility and Function "Motility" is an unfamiliar word to many people; it is used primarily to describe the contraction of the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. Because the
Section 2. Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery
 Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS
 FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
FUNCTIONAL BOWEL DISORDERS Contributed by the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) and edited by the Patient Care Committee of the ACG. INTRODUCTION Doctors use the
Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome
 Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome These cards highlight routine care for people with CdLS needed by specific age groups, including infancy, early and late childhood, adolescence
Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome These cards highlight routine care for people with CdLS needed by specific age groups, including infancy, early and late childhood, adolescence
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room
 Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History
 Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
Dallas Neurosurgical and Spine Associates, P.A Patient Health History DOB: Date: Reason for your visit (Chief complaint): Past Medical History Please check corresponding box if you have ever had any of
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
NHRMC General Surgery Specialists. Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303
 Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
What on Earth is the Autonomic Nervous System? Dysautonomia and Autonomic Dysfunction
 www.complexchild.com What on Earth is the Autonomic Nervous System? Dysautonomia and Autonomic Dysfunction Most people have never heard of the Autonomic Nervous System, even though it controls most of
www.complexchild.com What on Earth is the Autonomic Nervous System? Dysautonomia and Autonomic Dysfunction Most people have never heard of the Autonomic Nervous System, even though it controls most of
11/10/2014. I have nothing to Disclose. Covered Stents discussed are NOT FDA approved for the indications covered in my presentation
 I have nothing to Disclose Ramsey Dallal, MD, FACS Vice Chair Department of Surgery Chief Bariatric i and Minimally i Invasive Surgery Einstein Healthcare Network Nemacolin, PA 2014 Covered Stents discussed
I have nothing to Disclose Ramsey Dallal, MD, FACS Vice Chair Department of Surgery Chief Bariatric i and Minimally i Invasive Surgery Einstein Healthcare Network Nemacolin, PA 2014 Covered Stents discussed
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
University of California, Berkeley 2222 Bancroft Way Berkeley, CA 94720 Appointments 510/642-2000 Online Appointment www.uhs.berkeley.
 Constipation Why Am I Constipated? Constipation is passage of small amounts of hard, dry bowel movements, usually fewer than three times a week. People who are constipated may find it difficult and painful
Constipation Why Am I Constipated? Constipation is passage of small amounts of hard, dry bowel movements, usually fewer than three times a week. People who are constipated may find it difficult and painful
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Millions of Americans suffer from abdominal pain, bloating, constipation and diarrhea. Now new treatments can relieve your pain and discomfort.
 3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
3888-IBS Consumer Bro 5/8/03 10:38 AM Page 1 TAKE THE IBS TEST Do you have recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort? YES NO UNDERSTANDING IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME A Consumer Education Brochure Do you often
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN
 NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN Constipation in Children Version: 1 Page 1 of 8 Background Constipation is a common complaint in infants and children. The aetiology
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Yorkhill Hospital CONSTIPATION IN CHILDREN Constipation in Children Version: 1 Page 1 of 8 Background Constipation is a common complaint in infants and children. The aetiology
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Obesity Affects Quality of Life
 Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
A guide for adults with. Intestinal. Dysmotility
 A guide for adults with Intestinal Dysmotility This leaflet contains information for patients with dysmotility of the gut and discusses symptoms and management. page 2 Contents Introduction 4 Symptoms
A guide for adults with Intestinal Dysmotility This leaflet contains information for patients with dysmotility of the gut and discusses symptoms and management. page 2 Contents Introduction 4 Symptoms
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Autonomic Dysfunction in Children with Cerebral Palsy, Static Encephalopathy, and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Autonomic Dysfunction in Children with Cerebral Palsy, Static Encephalopathy, and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Many children with cerebral palsy, static encephalopathy, and
www.complexchild.com Autonomic Dysfunction in Children with Cerebral Palsy, Static Encephalopathy, and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Many children with cerebral palsy, static encephalopathy, and
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE (C. DIFF)
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium, or bug, that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk
University College Hospital. Laparoscopic Fundoplication. Gastrointestinal Services Division
 University College Hospital Laparoscopic Fundoplication Gastrointestinal Services Division 2 3 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact us on 020 3447 9202. We
University College Hospital Laparoscopic Fundoplication Gastrointestinal Services Division 2 3 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of the document, please contact us on 020 3447 9202. We
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Over 660 Contact Hours of Online Continuing Nursing Education!
 Over 660 of Online Continuing Nursing Education! Choose from Four Great Series: Clinical Health Care Clinical & Continuing Education MedSenses AACN NetLearning is committed to providing you with the very
Over 660 of Online Continuing Nursing Education! Choose from Four Great Series: Clinical Health Care Clinical & Continuing Education MedSenses AACN NetLearning is committed to providing you with the very
understanding GI bleeding
 understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
understanding GI bleeding a consumer education brochure American College of Gastroenterology 4900B South 31st Street, Arlington, VA 22206 703-820-7400 www.acg.gi.org American College of Gastroenterology
Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome
 Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome by Dr Liz Marder This article was written for parents for the Down s Syndrome Association newsletter and is reproduced here with the permission
Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome by Dr Liz Marder This article was written for parents for the Down s Syndrome Association newsletter and is reproduced here with the permission
Hospice and Palliative Medicine
 Hospice and Palliative Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills
Hospice and Palliative Medicine Maintenance of Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills
INFORMED CONSENT FOR LAPAROSCOPIC GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 INFORMED CONSENT FOR LAPAROSCOPIC GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGICAL PROCEDURE It is very important to [insert physician, practice name] that you understand and consent to the treatment your doctor is rendering and
INFORMED CONSENT FOR LAPAROSCOPIC GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGICAL PROCEDURE It is very important to [insert physician, practice name] that you understand and consent to the treatment your doctor is rendering and
Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC
 Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC Please feel free to talk with any member of the Obesity Treatment Center team at Catholic Medical Center regarding any questions, concerns or comments
Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC Please feel free to talk with any member of the Obesity Treatment Center team at Catholic Medical Center regarding any questions, concerns or comments
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM
 MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
MEDICAL HISTORY AND SCREENING FORM The purpose of preventive exams is to screen for potential health problems and provide education to promote optimal health. It is best practice for chronic health problems
Overview. Geriatric Overview. Chapter 26. Geriatrics 9/11/2012
 Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
Chapter 26 Geriatrics Slide 1 Overview Trauma Common Medical Emergencies Special Considerations in the Elderly Medication Considerations Abuse and Neglect Expanding the Role of EMS Slide 2 Geriatric Overview
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
Nutritional Challenges After Surgery
 Nutritional Challenges After Surgery L I N D A P A T A K I M S R D C S O L D C N S C M D A N D E R S O N C A N C E R C E N T E R H O U S T O N, T E X A S Objectives Identify the reasons that GIST and its
Nutritional Challenges After Surgery L I N D A P A T A K I M S R D C S O L D C N S C M D A N D E R S O N C A N C E R C E N T E R H O U S T O N, T E X A S Objectives Identify the reasons that GIST and its
Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More
 Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More By: Jeremie Pederson D.C., C.S.C.S. Many people are concerned about the FDA news release dated May 25, 2010
Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More By: Jeremie Pederson D.C., C.S.C.S. Many people are concerned about the FDA news release dated May 25, 2010
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Borland-Groover Clinic PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #:
 PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Referring: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #: Place Sticker Here Directions: Please circle any of the following you have personally
PATIENT GENERATED MEDICAL HISTORY Name: DOB: Email: Primary Care Physician: Referring: Pharmacy: Pharmacy Phone #: Place Sticker Here Directions: Please circle any of the following you have personally
Denver Spine Surgeons David Wong, MD, Sanjay Jatana, MD, Gary Ghiselli, MD
 Cervical and Lumbar Spine Health History Name: Today s Date: Referring Provider: How did you find us: (Please circle) Primary care physician, Google search, Facebook, Friend or Family member, Website (JatanaSpine
Cervical and Lumbar Spine Health History Name: Today s Date: Referring Provider: How did you find us: (Please circle) Primary care physician, Google search, Facebook, Friend or Family member, Website (JatanaSpine
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet
 Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet What is Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery? Antireflux surgery (also known as fundoplication) is the standard surgical method of treating gastro-oesophageal
Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Information Sheet What is Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery? Antireflux surgery (also known as fundoplication) is the standard surgical method of treating gastro-oesophageal
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE. Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION
 NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
NEW PATIENT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Physician Initials Date PATIENT INFORMATION JHH# DOB# AGE HOME PH CELL PH DAY PH EMAIL Who is your REFERRING PHYSICIAN? (The doctor who referred you to Johns Hopkins Neurology.)
Appendix A. Rome III Diagnostic Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Appendix A Rome III Diagnostic Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders 885 886 Appendix A: Rome III Diagnostic Criteria for FGIDs A. Functional Esophageal Disorders A1. Functional Heartburn
Appendix A Rome III Diagnostic Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders 885 886 Appendix A: Rome III Diagnostic Criteria for FGIDs A. Functional Esophageal Disorders A1. Functional Heartburn
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security
 Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR
 ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
The Management of Gastro-oesophageal Reflux in Infants
 TSMJ Volume : Cases The Management of Gastro-oesophageal Reflux in Infants Yousef El-Gohary, Andrew Karwowski, Gracia Chong, Melissa Kern, Sara Molloy, Boitumelo Pule, th Year Medicine ABSTRACT Objective:
TSMJ Volume : Cases The Management of Gastro-oesophageal Reflux in Infants Yousef El-Gohary, Andrew Karwowski, Gracia Chong, Melissa Kern, Sara Molloy, Boitumelo Pule, th Year Medicine ABSTRACT Objective:
Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care
 Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care Sleeve Gastrectomy Restrictive surgical weight loss procedure Able to eat a smaller amount of food to feel satiety, less than 6 ounces at a meal Surgery The
Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery & Follow Up Care Sleeve Gastrectomy Restrictive surgical weight loss procedure Able to eat a smaller amount of food to feel satiety, less than 6 ounces at a meal Surgery The
