Obesity is a growing problem worldwide; more than onethird
|
|
|
- Virgil Snow
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Do Physicians Underrecognize Obesity? Rachana Thapa, MD, Jennifer Friderici, MS, Reva Kleppel, MSW, MPH, Jan Fitzgerald, MS, RN, and Michael B. Rothberg, MD, MPH Objectives: A physician s advice is among the strongest predictors of efforts toward weight management made by obese patients, yet only a minority receives such advice. One contributor could be the physician s failure to recognize true obesity. The objectives of this study were to assess physicians ability to recognize obesity and to identify factors associated with recognition and documentation of obesity. Methods: Internal medicine residents and attending physicians at three academic urban primary care clinics and their adult patients participated in a study using recognition and documentation of patient obesity as the main measures. Results: A total of physicians completed weight assessments for 400 patients. The mean patient age was years, 56% were women, 77% were Hispanic, and 67% had one or more obesity-related comorbidity. There were 192 (48%) patients, of whom 66% were correctly identified by physicians as being obese, 86% of those with a body mass index (BMI) Q35, but only 49% of those with a BMI of 30 to 34.9 (P G ). Fewer obese Hispanic patients were identified than were non-hispanic patients (62% vs 76%; P = 0.03). No physician characteristics were significantly associated with recognition of obesity. Physicians documented obesity as a problem for % of patients. Attending physicians documented obesity more frequently than did residents (64% vs 43%, odds ratio 2.5, 95% confidence interval 1.3Y4.6) and normal-weight physicians documented obesity more frequently than overweight physicians (58% vs 41%, odds ratio From the Departments of Internal Medicine and Academic Affairs Administration, Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Massachusetts, and Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Reprint requests to Dr Michael B. Rothberg, Department of Medicine, Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic, 9500 Euclid Ave, Cleveland, OH [email protected] This article has been developed as a Journal CME Activity by the Southern Medical Association. Visit to view instructions, documentation, and the complete necessary steps to receive CME credit for reading this article. Fees may apply. CME credit will be available for 2 years after date of publication. This study was presented in poster form at the 2013 Society for General Internal Medicine National Meeting, Denver, Colorado. The authors have no financial relationships to disclose and no conflicts of interest to report. Accepted October 7, Copyright * 2014 by The Southern Medical Association /0Y2000/ DOI: /01.SMJ c , 95% confidence interval 1.0Y4.0). Documentation was more common for patients with a BMI Q35 and for non-hispanics. Documentation was not more common for patients with obesity-related comorbidities. Conclusions: Physicians have difficulty recognizing obesity unless patients BMI is Q35. Training physicians to recognize true obesity may increase rates of documentation, a first step toward treatment. Key Words: cross-sectional study, healthcare disparity, obesity, quality of care, survey Obesity is a growing problem worldwide; more than onethird of the US adult population is obese. 1 Obesity is known to be associated with numerous adverse health outcomes and an increase in mortality. 2,3 Physicians play a vital role in recognizing obesity and creating awareness of its implications for human health. A physician s advice is among the strongest predictors of efforts toward weight management made by patients. 4 Surprisingly, fewer than two-thirds of selfidentified obese patients reported having received weight loss advice from their healthcare providers, 5,6 and previous studies demonstrate that physicians fail to adequately document obesity. 7Y11 Some possible reasons for both phenomena include lack of time, busy physician schedules, lack of training/ knowledge, or failure to recognize obesity because of its ubiquitous nature. As the population has become increasingly obese, obese individuals, particularly those with a BMI between 30 and 35, do not appear out of the norm. Studies demonstrate that as many as 26% of obese patients do not recognize their own obesity, and minority populations, which have higher rates of obesity, are even less likely to perceive Key Points Physicians correctly identified 68% of patients as obese, but identified less than half of those with a body mass index between 30 and 35 as being obese. Physicians documented obesity in only half of the patients, but were more likely to document obesity for patients whom they recognized as obese. Physicians were less likely to identify Hispanic patients as obese.
2 themselves as obese. 5 We hypothesized that physicians, too, may fail to recognize obesity in their patients, and that this failure may contribute to their not offering weight loss advice. The objective of this study was to determine how well physicians recognize obesity and whether such recognition was associated with documentation of obesity or provision of weight loss advice. We also sought to identify patient- and physician-related factors associated with physicians ability to recognize and document obesity. Methods The subjects included in this cross-sectional study with chart review were internal medicine residents and attending physicians at three academic primary care clinics affiliated with Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, MA). For each physician, we included all of the adult patients he or she saw during the study session. Patients who were younger than 21 years old were excluded. We also excluded physicians who had no obese patients during any of the sessions they were surveyed because it was not possible to calculate either obesity recognition or documentation. The institutional review board at Baystate Medical Center approved the study. Participation in the survey was voluntary. Physicians provided personal demographics (physician s height, weight, year in training, and number of years he or she has lived in the United States) and answered seven questions that measured attitudes about obesity and its treatment. At the end of their clinic session, physicians were provided with a list of the patients seen during that session. Survey sessions were selected at random and the participating physicians were not aware of the study until the time of survey, when the patient visits were complete. Only a small portion of each physician s sessions were surveyed. Physicians were asked to indicate whether each patient was of a normal weight (body mass index [BMI] G25 kg/m 2 ), overweight (BMI 25Y29.9), or obese (BMI Q30) based on recall. Information regarding the patient s BMI was available to the physician before and during the patient s visit via the electronic health record (EHR), but not at the time the questionnaire was completed. For each patient seen and categorized, a research nurse reviewed the corresponding chart and recorded the following information: demographics, anthropometrics, and obesity-related comorbidities (diabetes, osteoarthritis, hyperlipidemia, coronary disease, and sleep apnea). The nurse also noted whether the physician had documented obesity as a problem or had addressed it within three visits before the index visit. Statistical Analysis Descriptive statistics (mean/standard deviation; n[%]) were used to characterize physicians and patients included in the study. For each outcome (obesity recognition, obesity documentation/counseling), fixed effects logistic regression models were fitted to derive adjusted odds ratios (AORs) and proportions as a function of patient- and physician-level predictors and covariates. For outcomes related to one putative exposure (eg, obesity recognition and patient s ethnicity), covariates were considered for inclusion in the model if their univariable (Fisher exact, unpaired t test) associations were significant at P e 0.20 (two-sided) with both exposure and outcome. Candidate covariates remained in the model if their removal changed the principal exposure coefficient by 910%. For research questions requiring predictive models, characteristics were considered for inclusion if their likelihood ratio test (intercept-only model vs single-predictor model) was significant at P e 0.2. Two-sided P values of e0.05 were considered significant for all hypothesis tests. Stata/MP 12.1 for Windows (StataCorp, College Station, TX) was used for all of the analyses. Results All of the 67 physicians who were invited to participate completed weight assessments. Sixty-two (92%) answered all of the questions on the demographic questionnaires and five submitted incomplete demographic questionnaires. After excluding physicians with no obese patients, those with incomplete demographic information, and those who did not answer any of the perception questions, there were respondents for analyses on physician attitude and identifying patients as obese. Physician characteristics appear in Table 1. Table 1. Proportion of obese patients recognized by physicians: characteristics Characteristic N (%) Univariable Identified, % P Multivariable a Identified, % P Position Resident 36 (69) V V Attending 16 (31) 75 V V Sex Female 27 () Male 25 (48) Location of medical school US 29 (56) Foreign 23 (44) Physician s BMI Normal (G25) 34 (65) Overweight 18 (35) 57 (25YG30) Obese (Q30) 0 (0) V V Obese patients, % G50 22 (42) V V Q50 30 (58) 75 V V a Mutually adjusted proportions, model includes only sex, US vs foreign medical school, and physician s weight class. BMI, body mass index. Southern Medical Journal Volume 107, Number 6, June
3 Thapa et al Do Physicians Underrecognize Obesity? Table 2. Patient characteristics Characteristic Mean/SD, n (%) n = 400 Obese, n (%) n = 192 Recognized as obese, n (%) n = 127 Age, y /16 50/15 48/14 Female sex 223 (56) 117 (61) 84 (66) Race Hispanic 263 (66) 123 (64) 77 (61) Black 72 (18) 36 (19) 28 (22) White 59 (15) 31 (16) 22 (17) Other 6 (1) 2 (1) V Comorbidities CAD 39 (10) 24 (13) 17 (13) DM 166 (42) 103 (54) 65 () Hyperlipidemia 167 (42) 86 (45) 54 (43) Obstructive sleep apnea 58 (15) 48 (25) 32 (25) Osteoarthritis 59 (15) 37 (19) 27 (21) Asthma 69 (17) 39 (20) 26 (20) At least (67) 147 (77) 95 (75) Actual BMI G (23) V Q25.0Y (30) V 30.0Y (23) 90 (47) 42 (33) Q (26) 102 (53) 85 (67) BMI, body mass index; CAD, coronary artery disease; DM, diabetes mellitus. Physician-level predictors of obesity recognition are shown in Table 2. In both unadjusted and adjusted models, the correct recognition of obesity was nonsignificantly associated with female sex, US versus foreign medical school training, and normal BMI versus overweight. Physicians documented obesity as a medical problem (Table 3) for % of obese patients (95% CI 42Y60). They were much more likely to document obesity for patients whom they subsequently recalled as being obese (61% if recalled vs 31% if not; P = 0.001). In the multivariable model, physicians were more likely to document obesityinpatientswhosebmiswereq35 versus 30 to 34.9 (AOR 3.5, 95% CI 1.7Y7.3) and non-hispanic versus Hispanic (AOR 2.1, 95% CI 1.0Y4.3). Patient age was inversely associated with documentation (AOR 0.98, 95% CI 0.95Y1.00). There was no significant difference in documentation of obesity for patients with at least one obesity-related comorbidity versus without (% vs 49%; P = 0.84). Attending physicians documented obesity in a patient s record more frequently than did residents (64% vs 43%, AOR 2.5, 95% CI 1.3Y4.6) and normal-weight physicians documented a patient s obesity more frequently than did overweight physicians (58% vs 41%; AOR 2.0, 95% CI 1.0Y4.0). With regard to physicians attitudes toward obesity (Table 4), 56% agreed that obesity can be treated effectively by a primary care physician and 27% reported success. Most of the physicians (82%) reported feeling comfortable discussing obesity with patients; however, only 67% were confident offering A total of 400 patients were rated by participating physicians. Each physician saw an average of six (standard deviation 4) patients per session. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 2. The average patient was T 16 years old, 56% were women, and 66% were Hispanic. Among all of the patients, 192 (48%) were obese. Of these, 102 (53.1%) had class II obesity (BMI 935; classes as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 12 ) and 77% had at least one obesity-related comorbidity. Of the 192 obese patients, physicians correctly identified 127 (66%) as obese, (27%) as overweight, and 13 (7%) as normal weight. Physicians identified 85.9% of patients as obese (95% confidence interval [CI] 77.4Y94.4) of those with BMI 935 (class II obesity), but only 48.9% (95% CI 34.6Y63.3) of those with BMI30to34.9(AOR6.4,95%CI2.9Y14.1). The proportion of obese patients correctly classified by physicians was lower among Hispanic patients (63.8%, 95% CI 50.2Y77.3) than white patients (75.6%, 95% CI 55.9Y95.4) or black patients (82.7%, 95% CI 67.4Y97.9). Adjusting for sex, a possible confounder, reduced the difference between white and black patients (79.8%, 95% CI 62.2Y97.4 vs 81.6%, 95% CI 65.3Y97.9), but did not affect the estimate for Hispanic patients (63.3%, 95% CI 49.5Y77.1). Compared with white and black patients, Hispanic patients were 39% as likely to be correctly classified as obese (sex-adjusted proportions 63% vs 81%; AOR 0.39, 95% CI 0.16Y0.98). Table 3. Proportion of obese patients documented/ counseled for obesity by physician: characteristics Univariable Multivariable a Characteristic % P % P Position Resident Attending Sex Female Male 47 Location of medical school US Foreign Physician s BMI Normal (G25) Overweight (Q25) Obese patients, % G V V Q50 53 BMI, body mass index. a Mutually adjusted proportions; model includes only position and physician s weight class. Physician sex and location of medical school were tested in the model but removed when P value for likelihood ratio test was
4 Table 4. Attitudes toward obesity among physicians with complete questionnaires Question N (%) endorsing Av proportion of patients Av proportion of patients identified as obese P a with documentation in EHR P a Obesity is a major health problem for my patients Disagree 1 (2) Neutral 0 (0) V Agree (98) Obesity can be effectively treated by primary care physician Disagree 5 (10) Neutral 18 (35) Agree 29 (56) I feel comfortable discussing obesity with my patients Disagree 2 (4) Neutral 7 (14) Agree 42 (82) I feel confident in my ability to offer dietary advice to patients Disagree 7 (14) 41 Neutral 10 (20) Agree 34 (67) I feel comfortable prescribing weight loss medications Disagree 37 (72) Neutral 11 (22) 45 Agree 3 (6) I feel comfortable referring my patients for bariatric surgery Disagree 7 (13) Neutral 10 (19) 57 Agree 35 (67) I have had success getting 48 patients to lose weight Disagree 14 (29) Neutral 21 (44) Agree 13 (27) EHR, electronic health record. P value for Pearson correlation coefficient. dietary advice, and few (6%) were comfortable prescribing weight-loss medication. There was no significant association between physicians attitudes and the recognition of obesity. Discussion In this study of 67 physicians at three academic ambulatory clinics, we found that physicians had difficulty recognizing patients obesity. Although this difficulty was more evident for patients with a BMI between 30 and 35, and among patients with class II obesity (BMI 935), only 86% were correctly identified as being obese. We also found that documentation of obesity was poor, and that attending physicians as well as physicians who were of normal weight were more likely to document obesity in their patients. In addition, patients whom physicians were able to recall as being obese were more likely to have obesity documented in their EHR. The widespread failure of physicians to document obesity has been well studied. 7Y11 Lemay and colleagues determined that obesity was underdiagnosed based on documentation of obesity by physicians in a cross-sectional chart review. 13 Their study, also conducted at an academic health center in Massachusetts, found that patient height and weight were recorded for only 63% of patients. Of these, 41% were obese and 39% of them had their obesity documented. At the time of our study, the height and weight of nearly 100% of patients had been recorded, obesity was more prevalent (48%), and Southern Medical Journal Volume 107, Number 6, June
5 Thapa et al Do Physicians Underrecognize Obesity? documentation had improved to %. Similar to our study, Lemay et al found that physicians were more likely to document obesity among patients with a higher BMI and that attending physicians documented obesity more often than did residents. Other studies have found documentation rates ranging from 16% 7 to 31% 8 and most found that documentation rates were higher for the most obese patients. The use of an EHR to automatically compute BMI and display it as part of patients vital signs can improve documentation. In a study by Bordowitz et al, documentation after implantation of the EHR reached 71%. 9 The authors assessed documentation at any time, whereas we included documentation only in the previous three visits, which may account for our somewhat lower numbers. Our study differs from previous studies in that we obtained physicians direct impressions of individual patients BMI, in addition to noting documentation in the EHR. There could be many reasons that clinicians fail to document obesity, including lack of time or a belief that such documentation is not important. Indeed, we found that the rate of documentation was much lower than the rate of recognition of obesity. We hypothesized that one reason for not documenting obesity could be a failure to recognize it. Although the BMI is noted in the vital signs section, physicians may fail to look at it or take action. To the extent that recall represents a physician s working memory, it is likely representative of his or her overall impression of a patient. The fact that attending physicians had both better recall and better documentation implies that they paid more attention to obesity. This highlights the need for better resident training in obesity recognition and weight loss counseling. The underrecognition among physicians of obesity in Hispanic patients appears to be a novel finding. The reason for this is not entirely clear because all three clinics served a predominantly Hispanic population and 64% of the patients were obese. We hypothesized that the high prevalence of obesity in this population may cause physicians to consider obesity the norm and therefore fail to identify patients as obese. A previous study of patients in the same clinics demonstrated ethnic differences in patients abilities to identify themselves as obese, with whites more likely to self-report obesity than Hispanics and African Americans. 5 We did not find that physicians had difficulty identifying African Americans as obese. Further research on the correlation between ethnicity and obesity recognition seems warranted. Our study has several limitations. First, we relied upon physicians ability to recall their patients to complete the survey. If they actually looked at the patient at the time, they may have had a different response. By calling attention to the need to make an assessment, we also could have caused physicians to move away from their usual practice. Our goal was to obtain the impression a physician may develop during a busy clinical session while addressing competing problems. Another limitation was that we did not differentiate between documentation of obesity as a problem in the patient chart and actual weight loss counseling, which is arguably more important but poorly documented. Finally, our power to assess physician factors related to recognizing obesity was limited as a result of having fewer than expected physicians with at least one obese patient and having a higher-than-anticipated intraclass correlation, especially for recognition of obesity. Conclusions Physicians, especially residents in training, had difficulty recognizing true obesity unless patients had class II or greater obesity. Physicians had a low likelihood of identifying obesity among Hispanic patients. Even in a setting in which the BMI was automatically calculated by the EHR, we believe that physicians should be trained in the recognition of obesity, especially in Hispanic patients. References 1. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, et al. Prevalence of obesity in the United States, NCHS Data Brief 2012;82:1Y8. 2. Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, et al. Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N Engl J Med 2010;363: 2211Y Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, et al. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2013;309:71Y Rutledge T, Groesz LM, Linke SE, et al. Behavioural weight management for the primary careprovider. Obes Rev 2011;12:e290Ye Sivalingam SK, Ashraf J, Vallurupalli N, et al. Ethnic differences in the self-recognition of obesity and obesity-related comorbidities: a crosssectional analysis. J Gen Intern Med 2011;26:616Y Thande NK, Hurstak EE, Sciacca RE, et al. Management of obesity: a challenge for medical training and practice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009;17:107Y Schriefer SP, Landis SE, Turbow DJ, et al. Effect of a computerized body mass index prompt on diagnosis and treatment of adult obesity. Fam Med 2009;41:502Y Ruser CB, Sanders L, Brescia GR, et al. Identification and management of overweight and obesity by internal medicine residents. J Gen Intern Med 2005;20:1139Y Bordowitz R, Morland K, Reich D. The use of an electronic medical record to improve documentation and treatment of obesity. Fam Med 2007;39: 274Y Bardia A, Holtan SG, Slezak JM, et al. Diagnosis of obesity by primary care physicians and impact on obesity management. Mayo Clin Proc 2007;82:927Y Melamed OC, Nakar S, Vinker S. Suboptimal identification of obesity by family physicians. Am J Manag Care 2009;15:619Y Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. QuickStats: prevalence of obesity (class I, II, and III)* among adults aged Q20 years, by age group and sexvnational Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, United States, 2007Y2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2010;59: Lemay CA, Cashman S, Savageau J, et al. Underdiagnosis of obesity at a community health center. J Am Board Fam Pract 2003;16:14Y
The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity
 274 April 2007 Family Medicine Practice Management The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity Richard Bordowitz, MD, MPH; Kimberly Morland, PhD; Douglas Reich,
274 April 2007 Family Medicine Practice Management The Use of an Electronic Medical Record to Improve Documentation and Treatment of Obesity Richard Bordowitz, MD, MPH; Kimberly Morland, PhD; Douglas Reich,
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014
 Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014 Executive Summary The Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Appraisal is a 22-question anonymous self-assessment of many of the most
Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Assessment, 1 January 31 December, 2014 Executive Summary The Fleet and Marine Corps Health Risk Appraisal is a 22-question anonymous self-assessment of many of the most
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated black women in the United States
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 237 241 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated
Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 237 241 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Obesity and hypertension among collegeeducated
Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008
 Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008 Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D.; Molly M. Lamb, Ph.D.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Katherine M. Flegal, Ph.D. Key findings
Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Children and Adolescents: United States, 2005 2008 Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D.; Molly M. Lamb, Ph.D.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Katherine M. Flegal, Ph.D. Key findings
Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH
 Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH Brigid Jackson, MA Samantha Smith, MA Elizabeth Antognoli, PhD Sue Krejci, MBA Peter J. Lawson, MA MPH MBA Practice-based Research Network
Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH Brigid Jackson, MA Samantha Smith, MA Elizabeth Antognoli, PhD Sue Krejci, MBA Peter J. Lawson, MA MPH MBA Practice-based Research Network
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION STUDY DESCRIPTION
 ABSTRACT Paper 1675-2014 Validating Self-Reported Survey Measures Using SAS Sarah A. Lyons MS, Kimberly A. Kaphingst ScD, Melody S. Goodman PhD Washington University School of Medicine Researchers often
ABSTRACT Paper 1675-2014 Validating Self-Reported Survey Measures Using SAS Sarah A. Lyons MS, Kimberly A. Kaphingst ScD, Melody S. Goodman PhD Washington University School of Medicine Researchers often
2015 Bariatric Surgery Analysis Gender-Related Differences in Obesity, Complications and Risks
 2015 Bariatric Surgery Analysis Gender-Related Differences in Obesity, Complications and Risks Including Performance Outcomes for Bariatric Surgery Excellence Award Recipients Healthgrades 999 18 th Street
2015 Bariatric Surgery Analysis Gender-Related Differences in Obesity, Complications and Risks Including Performance Outcomes for Bariatric Surgery Excellence Award Recipients Healthgrades 999 18 th Street
Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care
 Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care Michelle A. Albert MD MPH Treacy S. Silbaugh B.S, John Z. Ayanian MD MPP, Ann Lovett RN
Impact of Massachusetts Health Care Reform on Racial, Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Care Michelle A. Albert MD MPH Treacy S. Silbaugh B.S, John Z. Ayanian MD MPP, Ann Lovett RN
Administration of Emergency Medicine
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY. Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010
 WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY Pre-Clinic Conference Jennifer Kinley, MD 12/15/2010 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES: Discuss the available pharmaceutical options for weight loss and risks of these medications Explain the
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity. in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
A secondary analysis of primary care survey data to explore differences in response by ethnicity.
 A secondary analysis of primary care survey data to explore differences in response by ethnicity. A report commissioned by the National Association for Patient Participation Autumn 2006 1.1 Introduction
A secondary analysis of primary care survey data to explore differences in response by ethnicity. A report commissioned by the National Association for Patient Participation Autumn 2006 1.1 Introduction
Diet, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behaviors as Risk Factors for Childhood Obesity: An Urban and Rural Comparison
 Diet, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behaviors as Risk Factors for Childhood Obesity: An Urban and Rural Comparison Jihong Liu, Sc.D. Sonya J. Jones, Ph.D. Han Sun, M.S. Janice C. Probst, Ph.D. Philip
Diet, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Behaviors as Risk Factors for Childhood Obesity: An Urban and Rural Comparison Jihong Liu, Sc.D. Sonya J. Jones, Ph.D. Han Sun, M.S. Janice C. Probst, Ph.D. Philip
The Cross-Sectional Study:
 The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
The Cross-Sectional Study: Investigating Prevalence and Association Ronald A. Thisted Departments of Health Studies and Statistics The University of Chicago CRTP Track I Seminar, Autumn, 2006 Lecture Objectives
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
 FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Dov B. Millstone, Anthony V. Perruccio, Elizabeth M. Badley, Y. Raja Rampersaud Dalla Lana School
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ADVERSE EVENTS IN MAJOR ELECTIVE SPINE, KNEE, AND HIP INPATIENT ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Dov B. Millstone, Anthony V. Perruccio, Elizabeth M. Badley, Y. Raja Rampersaud Dalla Lana School
Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico
 Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico Ruth Ríos-Motta, PhD, José A. Capriles-Quirós, MD, MPH, MHSA, Mario
Disparities in Realized Access: Patterns of Health Services Utilization by Insurance Status among Children with Asthma in Puerto Rico Ruth Ríos-Motta, PhD, José A. Capriles-Quirós, MD, MPH, MHSA, Mario
Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for
 Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for 1 CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVES & RESEARCH APPROACH 2. FINDINGS a. Visits to Museums and Archaeological Sites b. Interest in Archaeology c.
Research into Issues Surrounding Human Bones in Museums Prepared for 1 CONTENTS 1. OBJECTIVES & RESEARCH APPROACH 2. FINDINGS a. Visits to Museums and Archaeological Sites b. Interest in Archaeology c.
T obacco use is rising among young adults (aged 18 24
 ii20 Tobacco use by Massachusetts public college students: long term effect of the Massachusetts Tobacco Control Program N A Rigotti, S Regan, N E Majchrzak, J R Knight, H Wechsler... Tobacco Control 2002;11(Suppl
ii20 Tobacco use by Massachusetts public college students: long term effect of the Massachusetts Tobacco Control Program N A Rigotti, S Regan, N E Majchrzak, J R Knight, H Wechsler... Tobacco Control 2002;11(Suppl
Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students
 Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students ABSTRACT Joseph Adwere-Boamah Alliant International University A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to predict
Multiple logistic regression analysis of cigarette use among high school students ABSTRACT Joseph Adwere-Boamah Alliant International University A binary logistic regression analysis was performed to predict
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA
 EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI)
 Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Texas Diabetes Fact Sheet
 I. Adult Prediabetes Prevalence, 2009 According to the 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) survey, 984,142 persons aged eighteen years and older in Texas (5.4% of this age group) have
I. Adult Prediabetes Prevalence, 2009 According to the 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) survey, 984,142 persons aged eighteen years and older in Texas (5.4% of this age group) have
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts
 Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
Racial Disparities in US Healthcare
 Racial Disparities in US Healthcare Paul H. Johnson, Jr. Ph.D. Candidate University of Wisconsin Madison School of Business Research partially funded by the National Institute of Mental Health: Ruth L.
Racial Disparities in US Healthcare Paul H. Johnson, Jr. Ph.D. Candidate University of Wisconsin Madison School of Business Research partially funded by the National Institute of Mental Health: Ruth L.
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
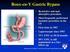 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005. Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007
 Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Impact of Diabetes on Treatment Outcomes among Maryland Tuberculosis Cases, 2004-2005 Tania Tang PHASE Symposium May 12, 2007 Presentation Outline Background Research Questions Methods Results Discussion
Spam e-mail on health and pharmaceutical topics are received. Weight Problems and Spam E-mail for Weight Loss Products.
 Original Article Weight Problems and Spam E-mail for Weight Loss Products Joshua Fogel, PhD, and Sam Shlivko, BS Background: This study focuses on young adult behaviors with regard to spam e-mails that
Original Article Weight Problems and Spam E-mail for Weight Loss Products Joshua Fogel, PhD, and Sam Shlivko, BS Background: This study focuses on young adult behaviors with regard to spam e-mails that
Smoking in the United States Workforce
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Smoking in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002, the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) 2006, and
P F I Z E R F A C T S Smoking in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002, the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) 2006, and
BACKGROUND. ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes
 BACKGROUND More than 25% of people with diabetes take insulin ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes Insulin identified as the most effective
BACKGROUND More than 25% of people with diabetes take insulin ADA and the European Association recently issued a consensus algorithm for management of type 2 diabetes Insulin identified as the most effective
The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session
 Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part Two From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part Two From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE
 FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
Using Health Information Technology to Drive Health Care Quality, Safety and Healthier Patient Outcomes
 Using Health Information Technology to Drive Health Care Quality, Safety and Healthier Patient Outcomes 2 Using Health Information Technology to Drive Health Care Quality, Safety and Healthier Patient
Using Health Information Technology to Drive Health Care Quality, Safety and Healthier Patient Outcomes 2 Using Health Information Technology to Drive Health Care Quality, Safety and Healthier Patient
LONG-TERM CARE: The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research. Perceptions, Experiences, and Attitudes among Americans 40 or Older
 The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research Research Highlights LONG-TERM CARE: Perceptions, Experiences, and Attitudes among Americans 40 or Older T. Tompson, J. Benz, J. Agiesta, D.
The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research Research Highlights LONG-TERM CARE: Perceptions, Experiences, and Attitudes among Americans 40 or Older T. Tompson, J. Benz, J. Agiesta, D.
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease
 Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Prognostic impact of uric acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Siegmund Braun, Martin Hadamitzky, Massimiliano Fusaro, Hans-Ullrich Haase, Kathrin A. Birkmeier, Albert Schomig,
Access Provided by your local institution at 02/06/13 5:22PM GMT
 Access Provided by your local institution at 02/06/13 5:22PM GMT brief communication Reducing Disparities in Access to Primary Care and Patient Satisfaction with Care: The Role of Health Centers Leiyu
Access Provided by your local institution at 02/06/13 5:22PM GMT brief communication Reducing Disparities in Access to Primary Care and Patient Satisfaction with Care: The Role of Health Centers Leiyu
Traditional View of Diabetes. Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? 8/9/2012. Change in Traditional View of Diabetes
 Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Are children with type 1 diabetes obese: What can we do? Traditional View of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes ( T1DM) Onset Juvenile Lean Type 2 Diabetes ( T2DM) Onset Adult Obese QI Project Indrajit Majumdar
Does referral from an emergency department to an. alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent. emergency room visits in patients with alcohol
 Does referral from an emergency department to an alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent emergency room visits in patients with alcohol intoxication? Robert Sapien, MD Department of Emergency Medicine
Does referral from an emergency department to an alcohol treatment center reduce subsequent emergency room visits in patients with alcohol intoxication? Robert Sapien, MD Department of Emergency Medicine
Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies
 Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies Current Population Reports By Brett O Hara and Kyle Caswell Issued July 2013 P70-133RV INTRODUCTION The
Health Status, Health Insurance, and Medical Services Utilization: 2010 Household Economic Studies Current Population Reports By Brett O Hara and Kyle Caswell Issued July 2013 P70-133RV INTRODUCTION The
The Importance and Impact of Nursing Informatics Competencies for Baccalaureate Nursing Students and Registered Nurses
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
Data Analysis, Research Study Design and the IRB
 Minding the p-values p and Quartiles: Data Analysis, Research Study Design and the IRB Don Allensworth-Davies, MSc Research Manager, Data Coordinating Center Boston University School of Public Health IRB
Minding the p-values p and Quartiles: Data Analysis, Research Study Design and the IRB Don Allensworth-Davies, MSc Research Manager, Data Coordinating Center Boston University School of Public Health IRB
Osteoporosis has been identified by the US Surgeon General
 New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
Multivariate Logistic Regression
 1 Multivariate Logistic Regression As in univariate logistic regression, let π(x) represent the probability of an event that depends on p covariates or independent variables. Then, using an inv.logit formulation
1 Multivariate Logistic Regression As in univariate logistic regression, let π(x) represent the probability of an event that depends on p covariates or independent variables. Then, using an inv.logit formulation
Atilla Soykan and Bedriye Oncu. Introduction
 Family Practice Vol. 20, No. 5 Oxford University Press 2003, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmg511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Which GP deals better
Family Practice Vol. 20, No. 5 Oxford University Press 2003, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmg511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Which GP deals better
2. Incidence, prevalence and duration of breastfeeding
 2. Incidence, prevalence and duration of breastfeeding Key Findings Mothers in the UK are breastfeeding their babies for longer with one in three mothers still breastfeeding at six months in 2010 compared
2. Incidence, prevalence and duration of breastfeeding Key Findings Mothers in the UK are breastfeeding their babies for longer with one in three mothers still breastfeeding at six months in 2010 compared
Effect of Anxiety or Depression on Cancer Screening among Hispanic Immigrants
 Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Keeping Current Seminar Series Mental Health, Acculturation and Cancer Screening among Hispanics Wednesday, June 2nd from 12:00 1:00 pm Trustees Conference Room (Bulfinch
Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Keeping Current Seminar Series Mental Health, Acculturation and Cancer Screening among Hispanics Wednesday, June 2nd from 12:00 1:00 pm Trustees Conference Room (Bulfinch
UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE
 UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE December 2015 Beginning in January 2014, the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) has
UNINSURED ADULTS IN MAINE, 2013 AND 2014: RATE STAYS STEADY AND BARRIERS TO HEALTH CARE CONTINUE December 2015 Beginning in January 2014, the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) has
Weight Loss Surgery Program
 Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
Weight loss surgery helped me lose 112 pounds. Jennifer Weaver Weight Loss Surgery Program baylor university medical center at dallas Follow us on: Facebook.com/BaylorHealth YouTube.com/BaylorHealth When
Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University
 Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University Outline Background Motivation Objectives Study design Results
Racial Disparities and Barrier to Statin Utilization in Patients with Diabetes in the U.S. School of Pharmacy Virginia Commonwealth University Outline Background Motivation Objectives Study design Results
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075
 Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Strategies for Identifying Students at Risk for USMLE Step 1 Failure
 Vol. 42, No. 2 105 Medical Student Education Strategies for Identifying Students at Risk for USMLE Step 1 Failure Jira Coumarbatch, MD; Leah Robinson, EdS; Ronald Thomas, PhD; Patrick D. Bridge, PhD Background
Vol. 42, No. 2 105 Medical Student Education Strategies for Identifying Students at Risk for USMLE Step 1 Failure Jira Coumarbatch, MD; Leah Robinson, EdS; Ronald Thomas, PhD; Patrick D. Bridge, PhD Background
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report
 2015 State of Michigan Department of Health and Human Services 2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report September 2015 Draft Draft 3133 East Camelback
2015 State of Michigan Department of Health and Human Services 2015 Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Adult Medicaid Health Plan CAHPS Report September 2015 Draft Draft 3133 East Camelback
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
SAMPLE DESIGN RESEARCH FOR THE NATIONAL NURSING HOME SURVEY
 SAMPLE DESIGN RESEARCH FOR THE NATIONAL NURSING HOME SURVEY Karen E. Davis National Center for Health Statistics, 6525 Belcrest Road, Room 915, Hyattsville, MD 20782 KEY WORDS: Sample survey, cost model
SAMPLE DESIGN RESEARCH FOR THE NATIONAL NURSING HOME SURVEY Karen E. Davis National Center for Health Statistics, 6525 Belcrest Road, Room 915, Hyattsville, MD 20782 KEY WORDS: Sample survey, cost model
Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control
 Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control Kerri L. Cavanaugh, MD MHS, Kenneth A. Wallston, PhD, Tebeb Gebretsadik, MPH, Ayumi Shintani, PhD, MPH, Darren DeWalt, MD MPH, Michael Pignone, MD
Low diabetes numeracy predicts worse glycemic control Kerri L. Cavanaugh, MD MHS, Kenneth A. Wallston, PhD, Tebeb Gebretsadik, MPH, Ayumi Shintani, PhD, MPH, Darren DeWalt, MD MPH, Michael Pignone, MD
Chi Squared and Fisher's Exact Tests. Observed vs Expected Distributions
 BMS 617 Statistical Techniques for the Biomedical Sciences Lecture 11: Chi-Squared and Fisher's Exact Tests Chi Squared and Fisher's Exact Tests This lecture presents two similarly structured tests, Chi-squared
BMS 617 Statistical Techniques for the Biomedical Sciences Lecture 11: Chi-Squared and Fisher's Exact Tests Chi Squared and Fisher's Exact Tests This lecture presents two similarly structured tests, Chi-squared
Summary. Accessibility and utilisation of health services in Ghana 245
 Summary The thesis examines the factors that impact on access and utilisation of health services in Ghana. The utilisation behaviour of residents of a typical urban and a typical rural district are used
Summary The thesis examines the factors that impact on access and utilisation of health services in Ghana. The utilisation behaviour of residents of a typical urban and a typical rural district are used
New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine
 New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Disclosures & Relevant Relationships I have nothing to disclose No financial conflicts Editor,
New Cholesterol Guidelines: Carte Blanche for Statin Overuse Rita F. Redberg, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Disclosures & Relevant Relationships I have nothing to disclose No financial conflicts Editor,
The Youth Vote in 2012 CIRCLE Staff May 10, 2013
 The Youth Vote in 2012 CIRCLE Staff May 10, 2013 In the 2012 elections, young voters (under age 30) chose Barack Obama over Mitt Romney by 60%- 37%, a 23-point margin, according to the National Exit Polls.
The Youth Vote in 2012 CIRCLE Staff May 10, 2013 In the 2012 elections, young voters (under age 30) chose Barack Obama over Mitt Romney by 60%- 37%, a 23-point margin, according to the National Exit Polls.
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity
 Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity June 2009 Executive summary Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person s weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in metres. It is one of the most commonly
Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity June 2009 Executive summary Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person s weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in metres. It is one of the most commonly
Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital. Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow
 Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow Presentation Overview Obesity Health Related Risks Who Qualifies for Weight Loss Surgery? Gastric-bypass
Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow Presentation Overview Obesity Health Related Risks Who Qualifies for Weight Loss Surgery? Gastric-bypass
UNC Leadership Survey 2012: Women in Business
 UNC Leadership Survey 2012: Women in Business Quantitative Report UNC Kenan-Flagler Business School Executive Development 2013 Table of Contents Introduction 3 How to Read This Report 4 Key Findings 5
UNC Leadership Survey 2012: Women in Business Quantitative Report UNC Kenan-Flagler Business School Executive Development 2013 Table of Contents Introduction 3 How to Read This Report 4 Key Findings 5
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009
 Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
Living a happy, healthy and satisfying life Tineke de Jonge, Christianne Hupkens, Jan-Willem Bruggink, Statistics Netherlands, 15-09-2009 1 Introduction Subjective well-being (SWB) refers to how people
