HYPERMOBILITY Jean Oliver, MCSP, SRP Chartered Physiotherapist Achilles Physiotherapy Clinic, Cambridge October 2005 No 7
|
|
|
- Mitchell Hoover
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HYPERMOBILITY Jean Oliver, MCSP, SRP Chartered Physiotherapist Achilles Physiotherapy Clinic, Cambridge October 2005 No 7 Introduction Hypermobility (HM) excessive mobility can occur in a single joint, or it can be more widespread throughout the body. Usually HM joints cause no problems and are even an asset in sports such as gymnastics and artistic professions such as ballet and music. However, in a significant percentage of people HM joints do cause symptoms ranging from minor sprains to more persistent arthralgia and chronic pain to such an extent that their quality of life may be jeopardised. Since there are often no demonstrable signs HM is underdiagnosed as a cause of symptomatology. 1 In the main, HM is genetically determined, those affected having loose connective tissue in particular, ligaments and articular capsules. This connective tissue is fragile and is more easily injured, 2 taking longer to heal than the norm. There is now evidence that proprioception in some HM joints is also impaired. 3 Women are affected more than men. HM patients fall into two groups: 1. Overuse/malalignment These patients have one or several HM joints that suffer the consequences of overuse or malalignment caused by e.g. leg-length inequality, asymmetrical hip rotation or flat feet. HM patients experience the ill-effects of malalignment far earlier than people without HM. 2. Hypermobility syndrome (HMS) This syndrome was defined by Kirk et al 4 as generalised joint laxity with associated musculoskeletal complaints in the absence of any systemic disease. Arthralgia is a common feature of this syndrome. The suffering of some of these patients is incalculable and their quality of life may be jeopardised by the syndrome. Diagnosing hypermobility Questions to ask The diagnosis is often arrived at by the patient s affirmative answers to the following questions regarding their childhood and teenage years. 5 Were you supple in your teens? Did you have any knee problems in your teens? Were you ever able to get your hands flat on the floor when your knees were straight? Did you go over on your ankles a lot? Did you have growing pains in your legs? Did your joints click a lot? Did you fidget a lot as a child? Did you bump into things/fall over a lot as a child? Symptoms Pain and stiffness related to soft tissue damage and proprioceptive impairment/lack of warning signs. The patient is often alarmed at the rate at which pain in one joint appears to spread to other areas of the body, e.g. the patient may sprain an ankle and shortly afterwards his/her knee, hip and back feel the strain as his/her body attempts to compensate for the original injury. Statements such as I feel as if I m falling to bits and I feel as if I can t hold up my head express the patient s anxiety but often sound bizarre. Arthralgia, the severity of which is often influenced by the phases of the menstrual cycle and by changes in the weather. 6 Signs Testing for HM should be a routine part of the examination of patients with musculoskeletal problems. Range of movement The patient may exhibit what appears to be a normal range of movement, e.g. touching the toes. However, this may be very limited for an HM
2 patient, who previously may have been able to get the palms of his/her hands on the floor. The patient will nonetheless complain of feeling stiff. Many scales have been devised to screen for the hypermobility syndrome (see Further reading ), the Beighton score, which is a 9-point scale, being the most well known. Although this score includes the spinal hyperflexion and thumb abduction with wrist hyperflexion tests two high indicators for HM many HM patients would in fact score 0 in this test because too few joints are included. This is why the BSR Special Interest Group on Hypermobility proposed the use of the Brighton score to help in diagnosis (Table 1). Importantly this scoring system reminds us that organs may be involved. Joint effusions sometimes, but not always, in the acute stage. Easy bruising Striae atrophicae TABLE Brighton revised diagnostic criteria for benign joint hypermobility syndrome. (Reprinted from Grahame R et al, J Rheumatol 2000;27(7):1777-9, with permission.) Major criteria 1. A Beighton score of 4/9 or greater (either currently or historically) 2. Arthralgia for longer than 3 months in 4 or more joints Minor criteria 1. A Beighton score of 1, 2 or 3/9 (0, 1, 2, or 3 if aged 50+) 2. Arthralgia ( 3 months) in 1 3 joints, or back pain ( 3 months), spondylosis, spondylolysis/spondylolisthesis 3. Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint, or in one joint on more than one occasion 4. Soft tissue rheumatism 3 lesions (e.g. epicondylitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis) 5. Marfanoid habitus: tall, slim, span:height ratio >1.03, upper:lower segment ratio <0.89, arachnodactyly (+ Steinberg/wrist signs) 6. Abnormal skin: striae, hyperextensibility, thin skin, papyraceous scarring 7. Eye signs: drooping eyelids or myopia or antimongoloid slant 8. Varicose veins or hernia or uterine/rectal prolapse Benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS) is diagnosed in the presence of two major criteria, or one major and two minor criteria, or four minor criteria. Two minor criteria will suffice where there is an unequivocally affected first-degree relative. BJHS is excluded by the presence of Marfan s or Ehlers Danlos syndrome (EDS) [other than the EDS Hypermobility type (formerly EDS III) as defined by the Ghent 1996 and the Villefranche 1998 criteria, respectively]. Criteria Major 1 and Minor 1 are mutually exclusive, as are Major 2 and Minor 2. Varicose veins Hernias Risk factors Unaccustomed physical exercise A change of occupation/studying, e.g. to an office job involving a lot of sitting, or pre-exam time Premenstrual Pregnancy (effect of the hormone relaxin) Sudden gain in weight Repetitive movements Malalignment Cold weather (usually) Unsupportive sandals or flat deck shoes Sleeping prone (neck) Hypermobility in children and adolescents Symptoms usually start during the adolescent growth spurt in the knees or spine but they can occur much earlier. At first they come on after activity sport, or walking or after a protracted period of sitting. HM children may be thought to be lazy, or be trying to avoid going to a gym lesson. They often fidget and sit in distorted postures to try to gain stability. Problems with writing are common; when children move on from using thicker pencils they experience difficulties in gripping a thinner pen. Some children have associated dyspraxia. Hypermobility in adults HM in men is less easily recognised because their increased muscle bulk reduces joint range of movement. The conventional explanation for the observed clinical differences between men and women is the effect of the female hormones on the collagen (and muscles). HM people working with computers or performing repetitive movements are at a higher risk from work-related upper limb syndrome (WRULS) formerly known as repetitive strain injury (RSI) in their hands, wrists and forearms, which can strike suddenly and without any warning signs. Although range of movement decreases with age, some elderly HM people still maintain impressive flexibility, that is unless pathology has stiffened their joints. Differential diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 7,8 Pathology Although not unique to them, the following pathology occurs more frequently in HM patients: 2
3 FEET : excessive calcaneal eversion (Figure 1.1) and flat feet Ankle sprains Hallux abductovalgus or osteoarthritis (OA) of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint Heel pain: plantar fasciitis 1. Excessive calcaneal eversion KNEES : hyperextension (Figure 1.2) Medial knee pain Anterior pain (chondromalacia patellae) Anterior cruciate ligament ruptures Joint effusions HIPS : anteversion (Figure 1.3) ( squinting patellae when standing) Clicking hip Trochanteric bursitis Associated with low back/pelvic pain and inability to stand for long periods LOW BACK : increased lumbar lordosis/sway back in teens, able to get hands flat in forward flexion (Figure 1.4) and/or do the crab (hyperextension) (Figure 1.5) Lower two lumbar levels show disc narrowing and facet joint arthrosis Pars defects/spondylolisthesis 10 Spinal stenosis PELVIS Sacroiliac joint instability or hypomobility, especially during pregnancy Symphysis pubis diastasis Weakness of pelvic floor muscles/uterine prolapse 2. Hyperextension of the knees 3. Anteversion of the hip 4. Spinal hyperflexion THORACIC SPINE : stiffness/scoliosis The thoracic spine is often the first area to stiffen up NECK : forward head posture Acute wryneck episodes Susceptible to whiplash injuries Headaches, often associated with tight ligamentum flavum on neck flexion Low cervical disc with nerve root entrapment 5. Spinal hyperextension TEMPEROMANDIBULAR JOINT Clicking and subluxation/dislocation HANDS : excessive thumb abduction and wrist flexion (Figure 1.6) OA of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb Repetitive strain 6. Thumb abduction with wrist hyperflexion ELBOWS : hyperextension Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) Golfer s elbow (medial epicondylitis) SHOULDERS: hyperextension (Figure 1.7), excessive external rotation Rotator cuff tendinitis Subluxation/dislocation of glenohumeral joint Crepitus on scapulae movement 7. Shoulder hyperextension FIGURE 1. Hypermobile joints 9 frequently associated with pathology. 3
4 Psychological aspects A higher incidence of panic attacks and anxiety states has been found in people with HM. 11 Many HM patients are thought, erroneously, to be neurotic or at best to be exaggerating their symptoms. Investigations X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are usually negative in the acute stage, but may show premature OA in patients in early middle age. Treatment Reassurance is extremely important and the patient will be relieved that a diagnosis has at last been made to explain his/her symptoms and that the condition is not lifethreatening. From the outset, the importance of self-management should be stressed, but the patient (and sometimes his/her family) will need guidance and some initial monitoring. Periodic treatment for acute episodes may also be necessary. An increasing number of physiotherapists are gaining expertise in treating hypermobility, but it is easy to exacerbate the patient s symptoms if the therapist is not familiar with HM. Rest In the short term for acute episodes of soft tissue lesions. Alignment check with podiatrist or physiotherapist Correction with a heel raise and orthotics if necessary. Physiotherapy To teach self-management and back care. Exercise forms the basis of treatment, in particular reeducating the deep stabilising muscles of the affected joints and pelvic floor muscles. Some patients may be able to progress to joining a Pilates exercise class, while others fare better with swimming/hydrotherapy or gym ball exercises. Aerobics are often contraindicated. Pacing of activities is essential because HM patients often do not get warning signs of overuse and suffer a delayed reaction to overactivity. Stretching after warm-up, gentle stretching of the superficial muscles to the end of the patient s hypermobile range is pain-relieving. Overstretching is to be avoided. Hatha (gentle) yoga helps patients with minor problems. Stretching before going to bed will help relieve morning stiffness when getting dressed. Balance training, including t ai chi. Passive mobilisation for symptomatic relief, especially to areas that are difficult for the patient to reach, such as the thoracic spine. Repeated manipulation is harmful and creates dependency on the therapist. Ergonomic advice, especially apropos working with computers. The Alexander Technique Posture correction through sensory feedback. The technique suits the more reflective type of patient and is best taught when the patient is pain-free. Medication The usefulness of drugs in controlling pain in HM patients is limited. Analgesics Paracetamol with or without codeine are the first choices. NSAIDs/COX-2s should be reserved for situations where inflammation is suspected, especially in view of the recent European Medicines Agency (EMEA) 12 review of COX-2s and ongoing NSAIDs review. Opioid matrix patches are an alternative to simple or compound analgesics. Local steroid injections These may be useful, especially for trochanteric pain in patients with hypermobile hips. Inject knees as little as possible to decrease the risk of dependency and theoretical risks of weakening collagen, but removing large effusions is usually worthwhile. Pain management and self-management Most primary care organisations employ or will soon appoint pain management nurses. HM patients may well benefit from a consultation. Support group The Hypermobility Syndrome Association can be recommended for the more severely affected patients. ( Prognosis The earlier the diagnosis of HM is made, the more effective are treatment outcomes. Many symptoms from HM joints (especially if there is associated malalignment) can be successfully managed if the patient complies with weight reduction, alignment correction, exercise, and life-style modifications. However, after injury the rate of healing is slower than average; this is particularly noticeable after road traffic accidents and WRULS. It is likely that HM predisposes to premature osteoarthrosis. A minority of patients will have severe arthrosis in many joints. Further reading Keer R, Grahame R (ed). Hypermobility syndrome: recognition and management for physiotherapists. Edinburgh/ London/New York: Butterworth Heinemann; Bird HA. Heritable collagen disorders. Reports on the Rheumatic Diseases (Series 5), Topical Reviews 5. Arthritis Research Campaign; 2005 Feb. Bird HA. Joint hypermobility in children. Rheumatology 2005;44(6): Joint hypermobility. Information Booklet (for patients). Arthritis Research Campaign;
5 Scoring systems for hypermobility: Beighton score: Beighton P, Solomon L, Soskolne CL. Articular mobility in an African population. Ann Rheum Dis 1973; 32(5): Brighton criteria: Grahame R, Bird HA, Child A, Dolan AL, Edwards-Fowler A, Ferrell W et al. The revised (Brighton 1998) criteria for the diagnosis of benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS). J Rheumatol 2000;27(7): References 1. Beighton P, Grahame R, Bird H. Hypermobility of joints. 3rd edn. London: Springer Verlag; Grahame R, Jenkins JM. Joint hypermobility asset or liability? A study of joint mobility in ballet dancers. Ann Rheum Dis 1972; 31(2): Hall MG, Ferrell WR, Sturrock RD, Hamblen DL, Baxendale RH. The effect of the hypermobility syndrome on knee joint proprioception. Br J Rheumatol 1995;34(2): Kirk JA, Ansell BM, Bywaters EG. The hypermobility syndrome: musculoskeletal complaints associated with generalized joint hypermobility. Ann Rheum Dis 1967;26(5): Oliver J. Hypermobility: recognition and management. In Touch (The Journal of the Organisation of Chartered Physiotherapists in Private Practice) 2000;94(2): Grahame R. Hypermobility syndrome. Reports on the Rheumatic Diseases (Series 2), Topical Reviews 25. Arthritis & Rheumatism Council; 1993 Sept. 7. Bird HA, Wright V. Joint hypermobility mimicking pauciarticular juvenile polyarthritis. Br Med J 1978;2(6134): Bird HA. Joint hypermobility in children. Rheumatology 2005;44(6): Oliver J. Back in line. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann; Morgan AW, Gibbon W, Bird HA. A controlled study of spinal laxity in subjects with joint hyperlaxity and Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Br J Rheumatol 1997;36 Suppl 1:59(S136). 11. Bulbena A, Duro JC, Porta M et al. Anxiety disorders in the joint hypermobility syndrome. Psychiatry Res 1993;46(1): European Medicines Agency (EMEA) website: COMMENT Howard Bird Professor of Pharmacological Rheumatology University of Leeds This article provides comprehensive practical advice from the physiotherapy perspective. Intriguingly, consideration is given to some joints (e.g. the ankle) that are indeed important, though which have lapsed from conventional scoring systems. It should be remembered that adjacent hypermobile joints often complement each other. The illustration denotes spinal hyperflexion and spinal hyperextension, i.e. reflecting laxity of the hip almost as much as the spine. It should also be recalled that extreme hyperlaxity localised to a single joint, perhaps as a result of bony abnormality or neuropathy, may give just as much trouble as a more generalised syndrome. The physician is often more aware than the physiotherapist of the implications of collagen-linked laxity at organs other than the joints. These patients may have cardiac murmur, severe Raynaud s phenomenon and asthma in addition to features mentioned in the article. It is for this reason that the Brighton scoring system has recently been proposed, which although it incorporates the Beighton system also allows in patients on the basis of their organ involvement or extreme localised hyperlaxity at a small number of sites. Although the spectrum of benign familial hypermobility syndrome undoubtedly accounts for the majority of patients described in this issue, the physician may also encounter one of a very small number of patients in whom the hypermobility is a feature of a more serious inherited abnormality of connective tissue such as Ehlers Danlos syndrome, Marfan s syndrome or osteogenesis imperfecta. These appear to have their various additional problems, specific for each condition, which require specialist advice. Extreme examples can be associated with maternal and foetal mortality in pregnancy or at childbirth and then from vascular accident at a relatively young age. Patients also ask about analgesics to control pain. The self-management activity described should always be tried before resorting to drugs but a large proportion of these patients will still need background analgesics to control their symptoms and allow them a reasonable quality of life. NSAIDs are rationally restricted to shortterm use to quieten episodes of inflammation that sometimes follow traumatic dislocation. I would be less happy with the regular use of local steroid injections since this has the side-effect of reducing collagen content in the joint capsule and may therefore aggravate the hypermobility. The article makes the important point that repetitive movement can aggravate hypermobility. I see many overuse syndromes in my hypermobility clinic, presumably because extra muscular work is needed to stabilise the hypermobile joint before it can be used. 5
6 RECENT PUBLICATIONS Clinical Assessment of the Musculoskeletal System A Handbook for Medical Students (Code 6321) Resulting from arc-funded research, this fully revised and updated Handbook covers 50 core skills appropriate for medical students at the point of qualification. Incorporating the widely used GALS screening examination and the detailed Regional Examination of the Musculoskeletal System ( REMS ), as well as historytaking skills and an introduction to the investigations available to assist in diagnosis, the Handbook and its accompanying DVD will be invaluable as an aid to study and revision. Doctors and allied health professionals may also find this publication of interest. Drugs for Arthritis Two new information sheets in the arc Drugs for Arthritis series have now been published: Pamidronate (Code 6265) Mycophenolate (Code 6266) As part of arc s educational work these resources are provided free of charge within the UK. To obtain copies, please order on-line at arc@bradshawsdirect.co.uk, or write to: arc Trading Ltd, James Nicolson Link, Clifton Moor, York YO30 4XX, quoting quantities and code numbers. This issue of Hands On can be downloaded as html or a PDF file from the Arthritis Research Campaign website ( and follow the links). Hard copies of this and all other arc publications are obtainable via the on-line ordering system ( by (arc@bradshawsdirect.co.uk), or from: arc Trading Ltd, James Nicolson Link, Clifton Moor, York YO30 4XX. Hands On welcomes comments about the new format and any specific comments on the content of these articles (please supply brief details of your position, institution/surgery and postal address). or handsonresponses@arc.org.uk 6
Biomechanical Pain and Hypermobility Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. Verna Cuthbert May 2014
 Biomechanical Pain and Hypermobility Syndrome in Children and Adolescents Verna Cuthbert May 2014 Differential Diagnosis. BIOMECHANICAL ARTHRITIS/ INFLAMMATION JOINT PAIN MISC NON ORGANIC Prince et al
Biomechanical Pain and Hypermobility Syndrome in Children and Adolescents Verna Cuthbert May 2014 Differential Diagnosis. BIOMECHANICAL ARTHRITIS/ INFLAMMATION JOINT PAIN MISC NON ORGANIC Prince et al
WHAT 350 HEDS PATIENTS TAUGHT ME IN 2013! Professor Rodney Grahame University College London The Hypermobility Unit, London UK
 WHAT 350 HEDS PATIENTS TAUGHT ME IN 2013! Professor Rodney Grahame University College London The Hypermobility Unit, London UK 1967 1970 1980 1990 2000 MUSCULOSKELETAL PAIN/JOINT INSTABILITY OVERLAP WITH
WHAT 350 HEDS PATIENTS TAUGHT ME IN 2013! Professor Rodney Grahame University College London The Hypermobility Unit, London UK 1967 1970 1980 1990 2000 MUSCULOSKELETAL PAIN/JOINT INSTABILITY OVERLAP WITH
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Introduction: Anatomy of the spine and lower back:
 Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
Castleknock GAA club member and Chartered Physiotherapist, James Sherry MISCP, has prepared an informative article on the common causes of back pain and how best it can be treated. To book a physiotherapy
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Cervical Spondylosis. Understanding the neck
 Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
 BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
BACK PAIN: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Diane Metzer LOWER BACK PAIN Nearly everyone at some point has back pain that interferes with work, recreation and routine daily activities. Four out of five adults experience
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck
 Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck www.csmr.org We have created this brochure to provide you with information regarding: Common Causes of Back and Neck Injuries and Pain Tips for Avoiding Neck and
Injury Prevention for the Back and Neck www.csmr.org We have created this brochure to provide you with information regarding: Common Causes of Back and Neck Injuries and Pain Tips for Avoiding Neck and
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario
 Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
Page 1 Closed Automobile Insurance Third Party Liability Bodily Injury Claim Study in Ontario Injury Descriptions Developed from Newfoundland claim study injury definitions No injury Death Psychological
What is a Sports Physician?
 What is a Sports Physician? Dr Mike Bundy MBBS MRCGP Dip Sports Med FFSEM Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Medical Director at Pure Sports Medicine Ex-England Rugby senior team Doctor www.puresportsmed.com
What is a Sports Physician? Dr Mike Bundy MBBS MRCGP Dip Sports Med FFSEM Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Medical Director at Pure Sports Medicine Ex-England Rugby senior team Doctor www.puresportsmed.com
Appointment Types First outpatient. Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle
 Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle Conditions Treated Ankle & foot pain & stiffness Back pain & stiffness Carpal Tunnel/ Nerve impingement/entrapment
Clinic Types CATS Spine CATS Hip and Knee CATS General Orthopaedic Injection Clinic Podiatry/Foot and Ankle Conditions Treated Ankle & foot pain & stiffness Back pain & stiffness Carpal Tunnel/ Nerve impingement/entrapment
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Pain HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management
 HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
How To Treat Heel Pain
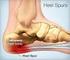 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis
 Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Pain Management Top Diagnosis Codes (Crosswalk)
 Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Pain Management Top s (Crosswalk) 274.00 Gout arthropathy, M1000 Idiopathic gout, unspecified site unspecified M10011 Idiopathic gout, right shoulder M10012 Idiopathic gout, left shoulder M10019 Idiopathic
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine
 www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine Are we speaking your language? If you would like information in another
www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine Are we speaking your language? If you would like information in another
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis
 Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
Stickler Syndrome and Arthritis Arthritis Foundation Pacific Region, Nevada Office Presented by: Crystal Schulz, MPH Community Development Manager Arthritis Foundation Improving lives through leadership
CAUTION: FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY. ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY IMPLIED.
 CAUTION: FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY. ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY IMPLIED. DIAGNOSIS CODE LIST: ICD-10's only, Report page# 1 CODE DESCRIPTION -------------------------------------------------------------------
CAUTION: FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY. ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY IMPLIED. DIAGNOSIS CODE LIST: ICD-10's only, Report page# 1 CODE DESCRIPTION -------------------------------------------------------------------
Thoracic and Chest Pain Anatomy Risk Factors and Prevention Posture: Increased thoracic curve
 Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Doctor of Science in Physical Therapy
 Doctor of Science in Physical Therapy The mission for the Doctor of Science (Sc.D.) Program in Physical Therapy is to provide advanced post-professional education to practicing physical therapists in Texas
Doctor of Science in Physical Therapy The mission for the Doctor of Science (Sc.D.) Program in Physical Therapy is to provide advanced post-professional education to practicing physical therapists in Texas
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury. Canadian Family Physician
 Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
COMMON ROWING INJURIES
 COMMON ROWING INJURIES Prevention and Treatment Jo A. Hannafin, MD, PhD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery, Cornell University Medical College Team Physician, US Rowing FISA
COMMON ROWING INJURIES Prevention and Treatment Jo A. Hannafin, MD, PhD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery, Cornell University Medical College Team Physician, US Rowing FISA
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
APPENDIX F INTERJURISDICTIONAL RESEARCH
 Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis
 Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
Spine University s Guide to Transient Osteoporosis 2 Introduction The word osteoporosis scares many people because they ve heard about brittle bone disease. They may know someone who has had it or seen
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation
 Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your shoulder dislocation. It is not a substitute
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT:
 UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
THE TMJ TREATMENT CENTER
 THE TMJ TREATMENT CENTER TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS, CRANIOFACIAL DISORDERS, CERVICOCRANIAL INSTABILITY & EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME ABOUT DR. MITAKIDES & THE TMJ TREATMENT CENTER Dedicated to the diagnosis
THE TMJ TREATMENT CENTER TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS, CRANIOFACIAL DISORDERS, CERVICOCRANIAL INSTABILITY & EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME ABOUT DR. MITAKIDES & THE TMJ TREATMENT CENTER Dedicated to the diagnosis
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
DIVISION OF RHEUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO POSTGRADUATE EDUCTION ORTHOPAEDIC OFF-SERVICE GOALS & OBJECTIVES GOAL #1 develop the ability to order and understand interpretation
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Treatment of Joint Hypermobility Syndrome, Including Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, with Hackett-Hemwall Prolotherapy
 W O N D E R W H Y? Treatment of Joint Hypermobility Syndrome, Including Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, with Hackett-Hemwall Prolotherapy Ross A. Hauser, MD & Hilary J. Phillips A B S T R A C T Joint hypermobility
W O N D E R W H Y? Treatment of Joint Hypermobility Syndrome, Including Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, with Hackett-Hemwall Prolotherapy Ross A. Hauser, MD & Hilary J. Phillips A B S T R A C T Joint hypermobility
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain
 Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Information on the Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain
 Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
Chiropractic Care of Lower Back Pain Lower back pain is probably the most common condition seen the the Chiropractic office. Each month it is estimated that up to one third of persons experience some type
Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED
 Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED Physical Therapists in the ED PT consult icon available Debbie Fleming-McDonnell, PT, DPT flemingd@wusm.wustl.edu Pam Wendl, PT, DPT wendlp@wusm.wustl.edu
Orientation to Movement-Based Physical Therapy in the ED Physical Therapists in the ED PT consult icon available Debbie Fleming-McDonnell, PT, DPT flemingd@wusm.wustl.edu Pam Wendl, PT, DPT wendlp@wusm.wustl.edu
Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries
 Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries North American Spine Society Public Education Series Treatment of the Young Athlete Although not common, low back injuries can occur in young athletes who
Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries North American Spine Society Public Education Series Treatment of the Young Athlete Although not common, low back injuries can occur in young athletes who
COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES
 CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back. Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist
 How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist Lesson Objectives Statistics of Back Pain Anatomy of the Spine Causes of Back Pain Four Work Factors Core Muscles Connection
How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist Lesson Objectives Statistics of Back Pain Anatomy of the Spine Causes of Back Pain Four Work Factors Core Muscles Connection
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Overuse injuries. 1. Main types of injuries
 OVERUSE INJURIES Mr. Sansouci is an ardent runner and swimmer. To train for an upcoming 10-km race, he has decided to increase the intensity of his training. Lately, however, his shoulder and Achilles
OVERUSE INJURIES Mr. Sansouci is an ardent runner and swimmer. To train for an upcoming 10-km race, he has decided to increase the intensity of his training. Lately, however, his shoulder and Achilles
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace
 AbilityNet Factsheet September 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles,
AbilityNet Factsheet September 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles,
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Medical Report Prepared for The Court on
 Medical Report Prepared for The Court on Mr Sample Report Claimant's Address Claimant's Date of Birth Instructing Party Instructing Party Address Instructing Party Ref Solicitors Ref Corex Ref 1 The Lane
Medical Report Prepared for The Court on Mr Sample Report Claimant's Address Claimant's Date of Birth Instructing Party Instructing Party Address Instructing Party Ref Solicitors Ref Corex Ref 1 The Lane
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
CMS Imaging Efficiency Measures Included in Hospital Outpatient Quality Data Reporting Program (HOP QDRP) 2009
 CMS Imaging Efficiency Measures Included in Hospital Outpatient Quality Data Reporting Program (HOP QDRP) 2009 OP 8: MRI LUMBAR SPINE FOR LOW BACK PAIN Measure Description: This measure estimates the percentage
CMS Imaging Efficiency Measures Included in Hospital Outpatient Quality Data Reporting Program (HOP QDRP) 2009 OP 8: MRI LUMBAR SPINE FOR LOW BACK PAIN Measure Description: This measure estimates the percentage
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008. 1. Purpose of this document To standardise the treatment of whiplash associated disorder.
 Guideline Title: WHIPLASH ASSOCIATED DISORDER Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008 Ratified by: Frances Hunt, Head of Physiotherapy Date: 16.09.15 Review date: 16.09.17 Links to policies: All
Guideline Title: WHIPLASH ASSOCIATED DISORDER Document Author: Frances Hunt Date 03/03/2008 Ratified by: Frances Hunt, Head of Physiotherapy Date: 16.09.15 Review date: 16.09.17 Links to policies: All
Colossus Important Diagnoses. Instructions for How to List Diagnoses
 1 Colossus Important Diagnoses Instructions for How to List Diagnoses 1. Only list diagnoses on HCFA-1500 or CMS-1500 billing forms 2. Use as many billing forms/pages as necessary (4 diagnoses per billing
1 Colossus Important Diagnoses Instructions for How to List Diagnoses 1. Only list diagnoses on HCFA-1500 or CMS-1500 billing forms 2. Use as many billing forms/pages as necessary (4 diagnoses per billing
Lower Back Pain HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management
 HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 Lumbar spine anatomy 2 What is lower back pain? 3 Conditions that may be causing your back pain 3 When should I see my doctor?
HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 Lumbar spine anatomy 2 What is lower back pain? 3 Conditions that may be causing your back pain 3 When should I see my doctor?
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
A compressive dressing that you apply around your ankle, and
 Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Ankle Injuries & Treatment The easiest way to remember this is: R.I.C.E. Each of these letters stands for: Rest. Rest your ankle. Do not place weight on it if it is very tender. Avoid walking long distances.
Care and Prevention of Sedentary Workplace Injuries. By: Colin Beattie, BKIN, mpt, cafci Registered physical therapist & medical acupuncturist
 Care and Prevention of Sedentary Workplace Injuries By: Colin Beattie, BKIN, mpt, cafci Registered physical therapist & medical acupuncturist Learning Objectives By the end of this presentation you should
Care and Prevention of Sedentary Workplace Injuries By: Colin Beattie, BKIN, mpt, cafci Registered physical therapist & medical acupuncturist Learning Objectives By the end of this presentation you should
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp.
 Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging 1 Bengt H Johansson, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 197-199 Whiplash trauma can
Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging 1 Bengt H Johansson, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 197-199 Whiplash trauma can
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace
 AbilityNet Factsheet March 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles, nerves
AbilityNet Factsheet March 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles, nerves
Manual Handling- The Whole Story!
 Manual Handling- The Whole Story! For Responsible Managers and Assessors Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager July 2005 Course Content 1 What is Manual Handling? 2 What s the Problem?
Manual Handling- The Whole Story! For Responsible Managers and Assessors Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager July 2005 Course Content 1 What is Manual Handling? 2 What s the Problem?
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns. Chapter 21
 Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
Good Golf For Bad Backs
 Good Golf For Bad Backs Golfer s Back! Playing golf is a challenge in itself, let alone with a bad back! Many golfers are however, injuring themselves unnecessarily on the course. The causes of injury
Good Golf For Bad Backs Golfer s Back! Playing golf is a challenge in itself, let alone with a bad back! Many golfers are however, injuring themselves unnecessarily on the course. The causes of injury
